• •
邓爱明1,2,3( ), 何玉荣1,2,3(
), 何玉荣1,2,3( ), 唐天琪1,2,3
), 唐天琪1,2,3
收稿日期:2025-09-08
修回日期:2025-10-28
通讯作者:
何玉荣
作者简介:邓爱明(1997—),男,博士研究生,21b902012@stu.hit.edu.cn
基金资助:
Aiming DENG1,2,3( ), Yurong HE1,2,3(
), Yurong HE1,2,3( ), Tianqi TANG1,2,3
), Tianqi TANG1,2,3
Received:2025-09-08
Revised:2025-10-28
Contact:
Yurong HE
摘要:
喷雾流化床湿法造粒技术通过动态流化与雾化喷涂的协同作用,已成为制药、食品及化工领域颗粒功能化制造的核心技术之一。然而,颗粒包覆过程涉及到复杂的气液固三相耦合过程,进而难以实现造粒过程的精确控制。因此,以离散单元模型为基础,耦合液滴运动和蒸发模型、液滴与颗粒碰撞模型以及液桥力模型,发展了适用于描述喷雾流化床内颗粒包覆过程的“气体-液滴-颗粒”拟三相数学模型。在该模型基础上研究了不同导流板结构对颗粒流动、传热传质特性以及颗粒包覆机制的影响。研究发现,在本文工况内,合适的导流板间距、提高导流板长度和降低导流板高度,能够加快颗粒进入喷泉区,延长喷泉区的停留时间,进而改善床层颗粒流化状态,优化颗粒循环路径,有效提高颗粒包覆比例和颗粒生长均匀性,减少喷动区的过度包覆现象。
中图分类号:
邓爱明, 何玉荣, 唐天琪. 含导流板喷雾流化床内颗粒包覆过程热质传递特性模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251005.
Aiming DENG, Yurong HE, Tianqi TANG. Numerical study on heat and mass transfer characteristics of particle coating in a spray fluidized bed with draft plates[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251005.
| 判别准则 | 公式 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 聚合(I) | [ | |
| 反弹(Ⅱ) | [ | |
聚合(Ⅲ) (Wes < 2.5) | [ | |
| 反溅分离(Ⅳ) | [ | |
| 拉伸分离(Ⅴ) | [ |
表1 二元液滴不同碰撞结果的判定准则[35-36]
Table 1 Criteria for different outcomes of binary droplet collisions [35-36]
| 判别准则 | 公式 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 聚合(I) | [ | |
| 反弹(Ⅱ) | [ | |
聚合(Ⅲ) (Wes < 2.5) | [ | |
| 反溅分离(Ⅳ) | [ | |
| 拉伸分离(Ⅴ) | [ |
| 模拟参数 | 物理量 | 数值 | 单位 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 喷动床 | x、y、z方向尺寸 | 0.145×0.02×1 | m | |
| x、y、z方向网格数 | 29×3×100 | |||
| 导流板位置HB | 0.060/0.065/0.070/0.075/0.080/0.085/0.090 | m | ||
| 导流板长度LB | 0.060/0.065/0.070/0.075/0.080/0.085/0.090 | m | ||
| 导流板间距WB | 0.022/0.024/0.026/0.028 | m | ||
| 颗粒 | 颗粒直径,dp | 0.003 | m | |
| 颗粒密度,ρp | 2505 | kg/m3 | ||
| 颗粒数,Np | 12000 | |||
| 法向弹性恢复系数,en | 0.97 | |||
| 切向弹性恢复系数,et | 0.33 | |||
| 摩擦系数(颗粒-颗粒),μp-p | 0.10 | |||
| 摩擦系数(颗粒-壁面),μp-w | 0.30 | |||
| 滚动摩擦系数,μr | 0.125 | |||
| 初始颗粒温度,Tp | 288.15 | K | ||
| 液滴 | 液滴直径,dd | 0.0003 | m | |
| 液滴密度,ρd | 1000 | kg/m3 | ||
| 液体黏度,μd | 0.001 | Pa·s | ||
| 喷入液滴数目,Nd | 120000 | 个/s | ||
| 液体内溶质质量分数,w | 0.3 | |||
| 表面张力系数,σ | 0.0721 | N/m | ||
| 气体 | 喷口气速,usp | 43.5 | m/s | |
| 背景气速,ubg | 2.4 | m/s | ||
| 喷口气体温度,Tsp | 323.15/363.15 | K | ||
| 背景气体温度,Tbg | 363.15 | K | ||
| 气体剪切粘度,μg | 1.8×10-5 | Pa∙s |
表2 模型参数设置
Table 2 Parameters used in the simulation
| 模拟参数 | 物理量 | 数值 | 单位 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 喷动床 | x、y、z方向尺寸 | 0.145×0.02×1 | m | |
| x、y、z方向网格数 | 29×3×100 | |||
| 导流板位置HB | 0.060/0.065/0.070/0.075/0.080/0.085/0.090 | m | ||
| 导流板长度LB | 0.060/0.065/0.070/0.075/0.080/0.085/0.090 | m | ||
| 导流板间距WB | 0.022/0.024/0.026/0.028 | m | ||
| 颗粒 | 颗粒直径,dp | 0.003 | m | |
| 颗粒密度,ρp | 2505 | kg/m3 | ||
| 颗粒数,Np | 12000 | |||
| 法向弹性恢复系数,en | 0.97 | |||
| 切向弹性恢复系数,et | 0.33 | |||
| 摩擦系数(颗粒-颗粒),μp-p | 0.10 | |||
| 摩擦系数(颗粒-壁面),μp-w | 0.30 | |||
| 滚动摩擦系数,μr | 0.125 | |||
| 初始颗粒温度,Tp | 288.15 | K | ||
| 液滴 | 液滴直径,dd | 0.0003 | m | |
| 液滴密度,ρd | 1000 | kg/m3 | ||
| 液体黏度,μd | 0.001 | Pa·s | ||
| 喷入液滴数目,Nd | 120000 | 个/s | ||
| 液体内溶质质量分数,w | 0.3 | |||
| 表面张力系数,σ | 0.0721 | N/m | ||
| 气体 | 喷口气速,usp | 43.5 | m/s | |
| 背景气速,ubg | 2.4 | m/s | ||
| 喷口气体温度,Tsp | 323.15/363.15 | K | ||
| 背景气体温度,Tbg | 363.15 | K | ||
| 气体剪切粘度,μg | 1.8×10-5 | Pa∙s |
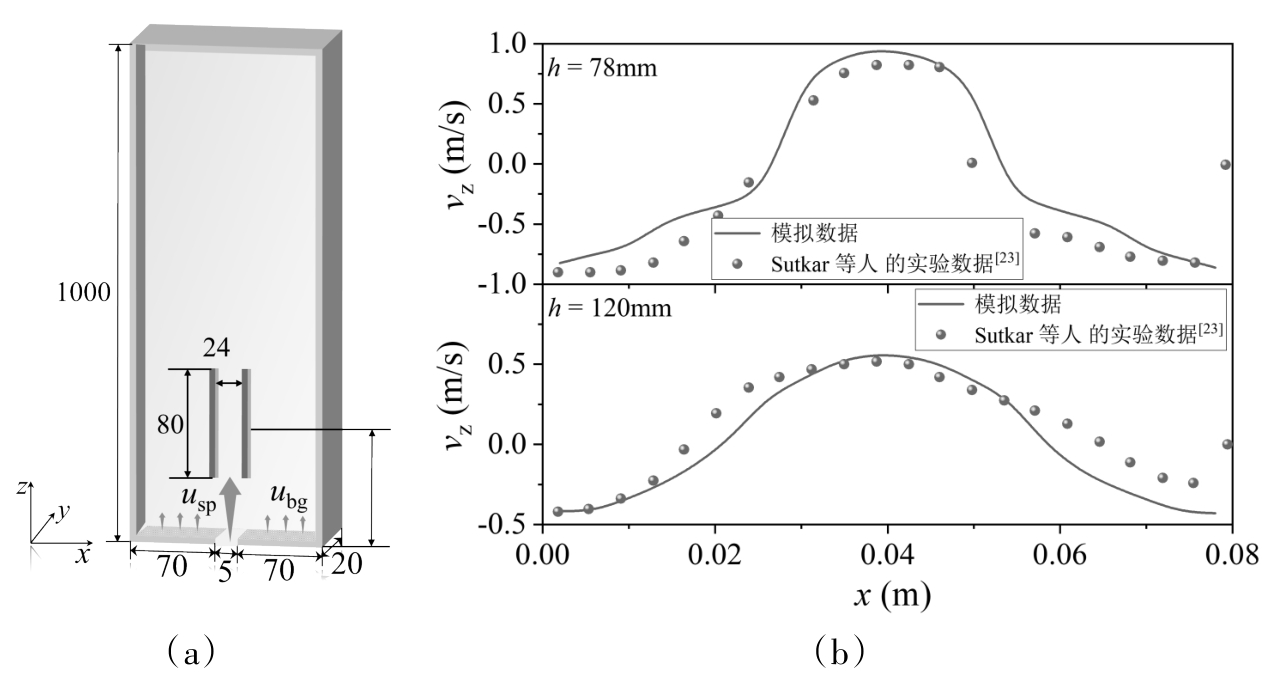
图2 喷动床的结构示意图(a)和模拟结果与实验结果[23]对比图(b)
Fig. 2 Structure diagram of spouted bed (a) and comparison of simulation results and experimental results [23] (b)

图3 无导流板与含导流板工况下颗粒直径标准差随时间的变化、颗粒生长和干燥区域分布(a)及颗粒循环轨迹图(b)
Fig. 3 Variation of particle diameter standard deviation over time, distribution of particle growth and drying regions (a), and particle circulation trajectories (b) under conditions without and with draft plates

图4 无导流板与添加导流板下的涂层颗粒分布及喷雾结束和干燥结束后的颗粒直径增长量分布
Fig. 4 Particle coating ratio and particle diameter growth distribution at the end of spraying and drying under conditions without and with draft plates
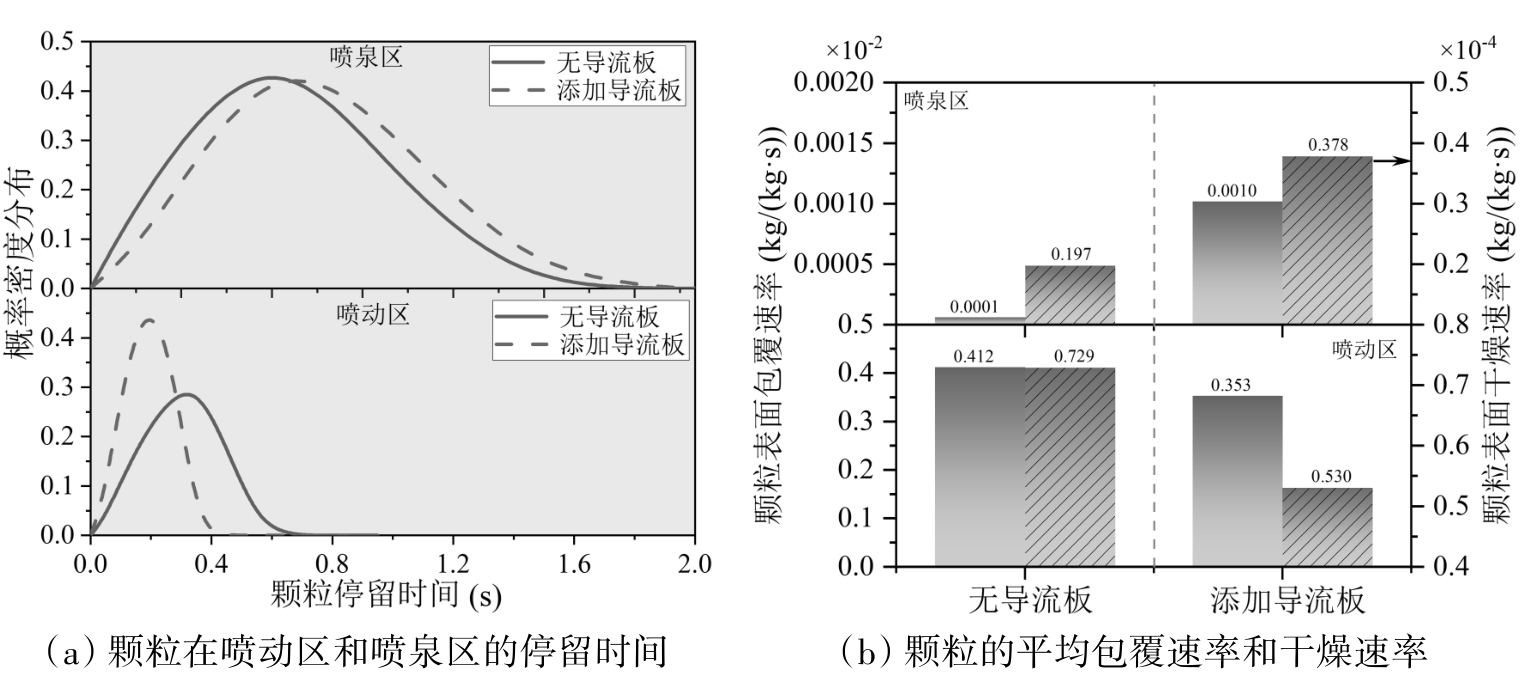
图5 喷雾阶段无导流板与添加导流板颗粒在喷动区和喷泉区的停留时间及其平均包覆速率和干燥速率
Fig. 5 Particle residence time in the spouting and fountain regions and their average coating and drying rates during the spraying stage under conditions without and with draft plates
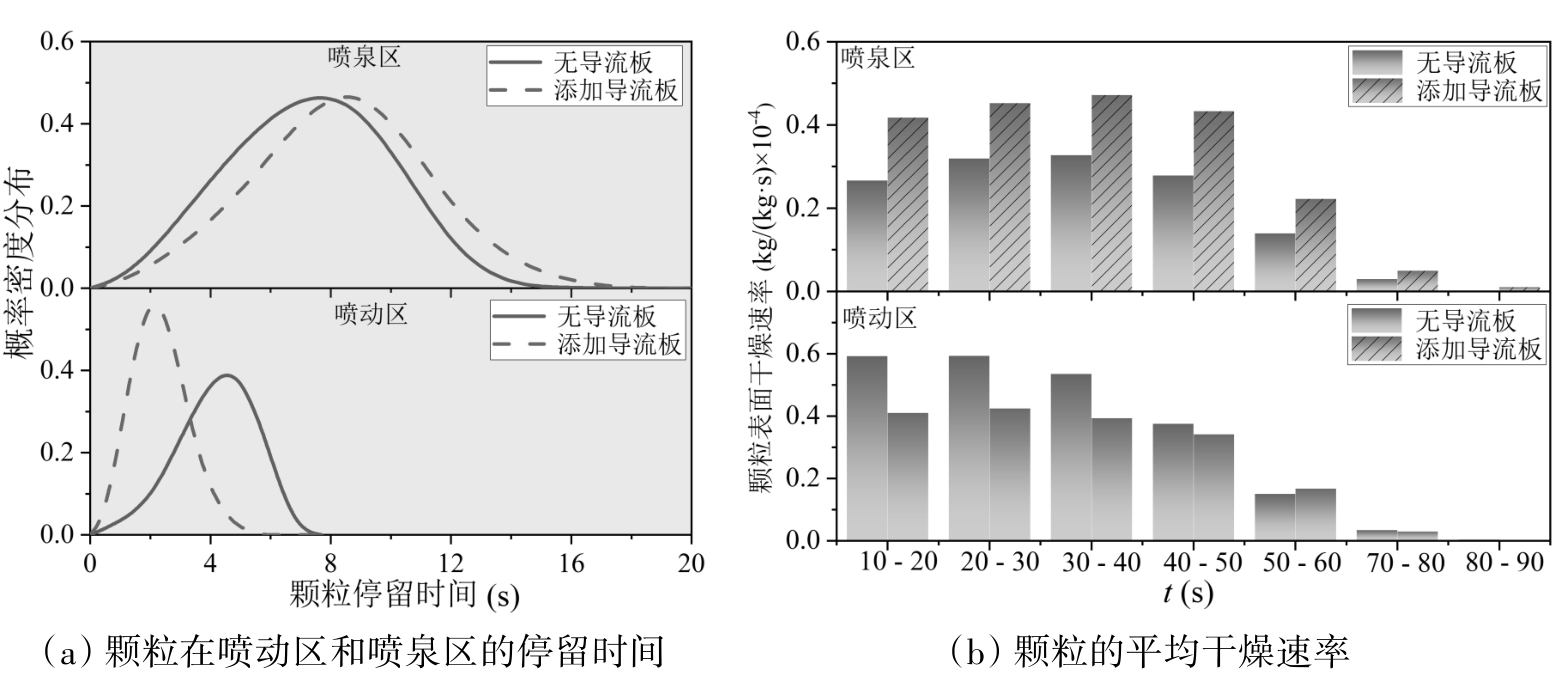
图6 干燥阶段无导流板与添加导流板颗粒在喷动区和喷泉区的停留时间及其平均干燥速率
Fig. 6 Particle residence time in the spouting and fountain regions and their average drying rates during the drying stage under conditions without and with draft plates
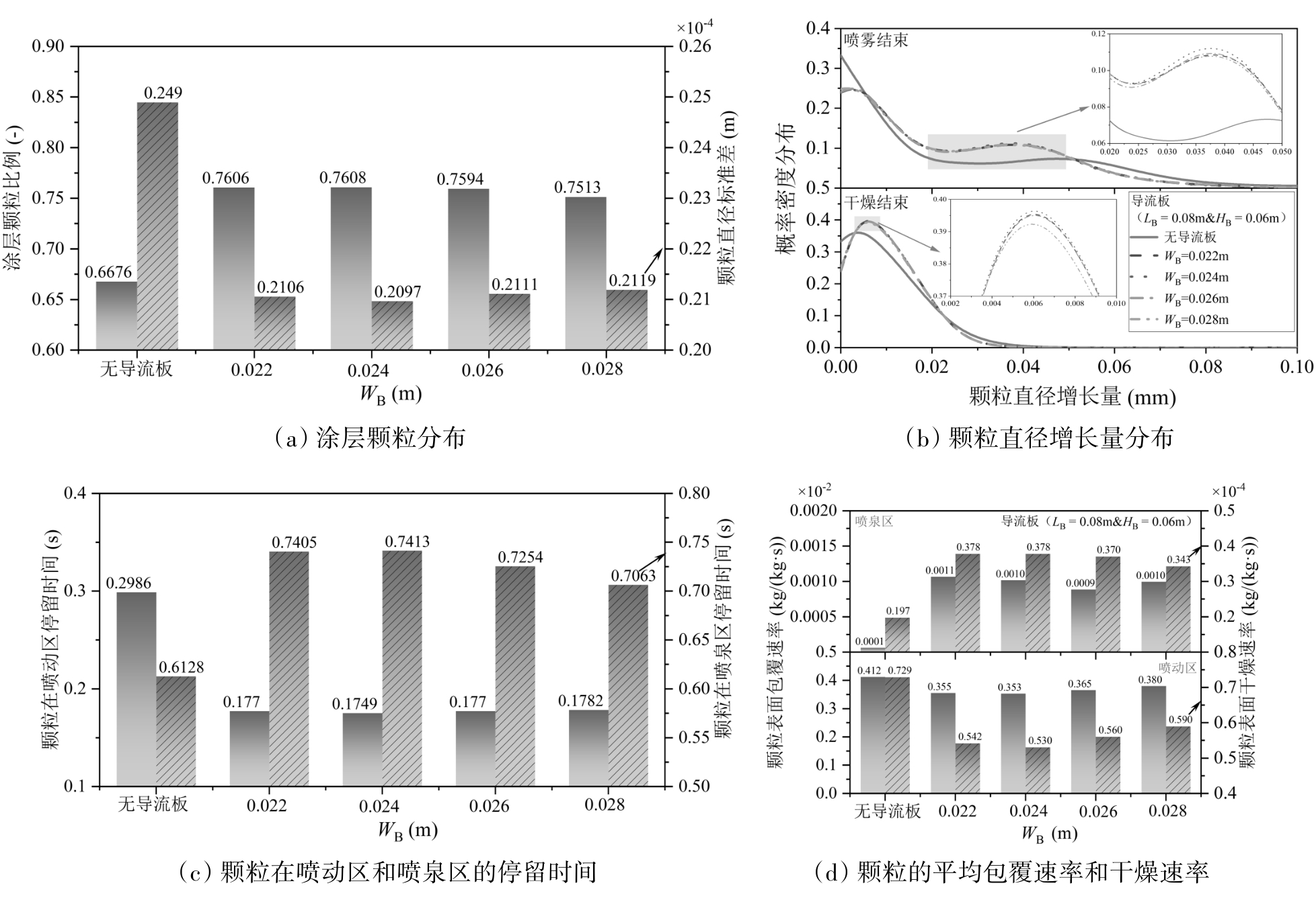
图7 不同导流板间距对涂层颗粒分布、粒径分布及喷雾阶段流化及热质传递特性的影响
Fig. 7 Effect of different draft plate spacings on particle coating distribution, particle size distribution, and fluidization and heat–mass transfer characteristics during the spraying stage

图8 不同导流板长度对涂层颗粒分布、粒径分布及喷雾阶段流化及热质传递特性的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of different draft plate lengths on particle coating distribution, particle size distribution, and fluidization and heat–mass transfer characteristics during the spraying stage

图9 不同导流板高度位置对涂层颗粒分布、粒径分布及喷雾阶段流化及热质传递特性的影响
Fig. 9 Effect of different draft plate heights on particle coating distribution, particle size distribution, and fluidization and heat–mass transfer characteristics during the spraying stage
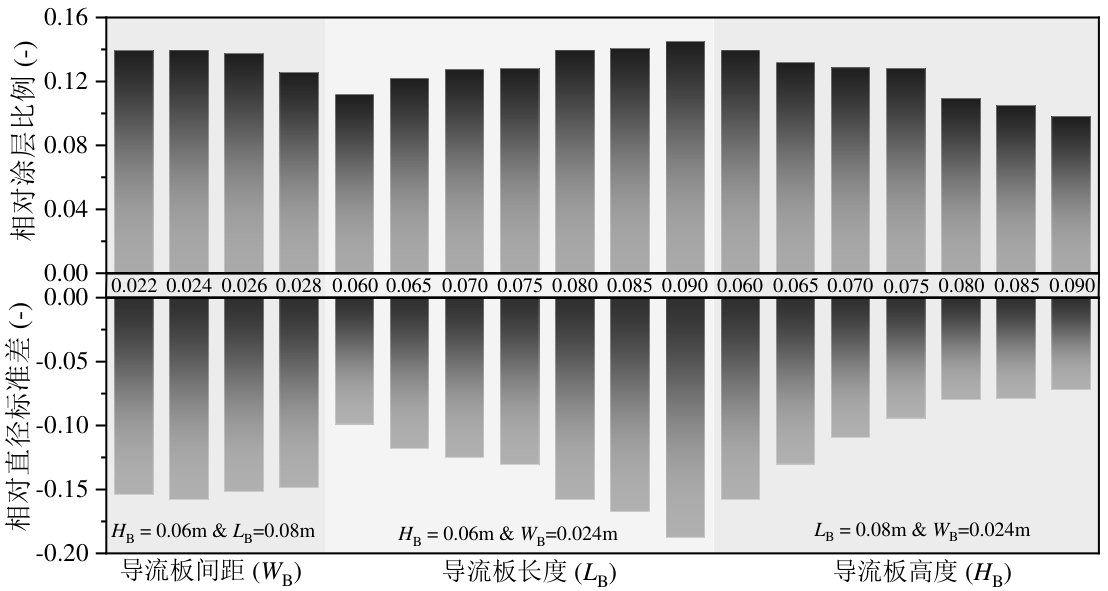
图10 不同导流板间距、长度和高度位置对颗粒相对涂层比例和相对直径标准差的影响
Fig. 10 Effect of different draft plate spacing, length, and height on particle relative coating ratio and relative diameter standard deviation
| [1] | Capece M, Dave R. Application of fluidized bed film coating for membrane encapsulation of catalysts[J]. Powder Technology, 2011, 211(2/3): 199-206. |
| [2] | Müller J, Abdollahifar M, Vinograd A, et al. Si-on-Graphite fabricated by fluidized bed process for high-capacity anodes of Li-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 407: 126603. |
| [3] | 周云龙, 卢志叶, 王猛. 基于递归分析的喷雾气固流化床团聚状态识别[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(9): 3835-3842. |
| Zhou Y L, Lu Z Y, Wang M. Recursive analysis and agglomerate state recognition of spray gas-solid fluidized bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(9): 3835-3842. | |
| [4] | 谢恒来, 吴曼, 赵军, 等. 导向管喷动流化床中废弃印刷线路板的非金属颗粒包覆改性[J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(3): 1185-1193. |
| Xie H L, Wu M, Zhao J, et al. Coating modification of non-metal particles of waste printed circuit boards in spout-fluid bed with draft tube[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(3): 1185-1193. | |
| [5] | Singh M, Shirazian S, Ranade V, et al. Challenges and opportunities in modelling wet granulation in pharmaceutical industry–A critical review[J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 403: 117380. |
| [6] | Trogrlić M, Madlmeir S, Forgber T, et al. Numerical and experimental validation of a detailed non-isothermal CFD-DEM model of a pilot-scale Wurster coater[J]. Powder Technology, 2021, 391: 97-113. |
| [7] | 罗琴, 赵银峰, 叶茂, 等. 电容层析成像在气固流化床测量中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(7): 2504-2512. |
| Luo Q, Zhao Y F, Ye M, et al. Application of electrical capacitance tomography for gas-solid fluidized bed measurement[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(7): 2504-2512. | |
| [8] | Pan S Y, Ma J L, Liu D Y, et al. Theoretical and experimental insight into the homogeneous expansion of wet particles in a fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2022, 397: 117016. |
| [9] | Milacic E, Nunez Manzano M, Madanikashani S, et al. Liquid injection in a fluidised bed: Temperature uniformity[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 256: 117622. |
| [10] | Kolkman T, van Sint Annaland M, Kuipers J A M. Whole-field imaging of temperature and hydrodynamics in a gas fluidized bed with liquid injection[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 168: 23-40. |
| [11] | Kolkman T, van Sint Annaland M, Kuipers J A M. Development of a non-invasive optical technique to study liquid evaporation in gas–solid fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 155: 277-293. |
| [12] | Šibanc R, Luštrik M, Dreu R. Analysis of pellet coating uniformity using a computer scanner[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2017, 533(2): 377-382. |
| [13] | Sondej F, Bück A, Koslowsky K, et al. Investigation of coating layer morphology by micro-computed X-ray tomography[J]. Powder Technology, 2015, 273: 165-175. |
| [14] | 任振华, 金辉, 刘石, 等. 煤炭超临界水流化床制氢反应器内颗粒流动及传热特性的数值分析[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2020, 41(1): 154-160. |
| Ren Z H, Jin H, Liu S, et al. Numerical analysis of particle flow and heat transfer characteristics in a coal-supercritical water fluidized bed reactor for hydrogen production[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2020, 41(1): 154-160. | |
| [15] | 李恒. 基于CFD-DEM模型的喷雾流化床颗粒流动、传热及包衣均匀性的模拟研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2022. |
| Li H. Simulation study of particle flow, heat transfer and coating uniformity in spray fluidized bed based on CFD-DEM model[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2022. | |
| [16] | Toschkoff G, Just S, Funke A, et al. Spray models for discrete element simulations of particle coating processes[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 101: 603-614. |
| [17] | Jiang Z C, Rieck C, Bück A, et al. Modeling of inter- and intra-particle coating uniformity in a Wurster fluidized bed by a coupled CFD-DEM-Monte Carlo approach[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 211: 115289. |
| [18] | Boehling P, Jacevic D, Detobel F, et al. Validating a numerical simulation of the ConsiGma(R) coater[J]. AAPS PharmSciTech, 2020, 22(1): 10. |
| [19] | Madlmeir S, Forgber T, Trogrlic M, et al. Quantifying the coating yield by modeling heat and mass transfer in a Wurster fluidized bed coater[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 252: 117505. |
| [20] | Singh S K D, Dietiker J F, Lu K. Polysiloxane coatings on microspheres based on multiphase flow with interface exchange-discrete element modelling[J]. Particuology, 2022, 69: 88-99. |
| [21] | Zhang W, Wang H M, You C F. Numerical simulation of fluidized bed coating process considering particle abrasion[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 445: 136632. |
| [22] | Zhou Y F, Shi Q, Huang Z L, et al. Effects of liquid action mechanisms on hydrodynamics in liquid-containing gas–solid fluidized bed reactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 285: 121-127. |
| [23] | Sutkar V S, Deen N G, Patil A V, et al. CFD–DEM model for coupled heat and mass transfer in a spout fluidized bed with liquid injection[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 288: 185-197. |
| [24] | Luan J Y, Feng D L, Han L C, et al. Quantitative correlation analysis of mixing and circulation characteristics in a liquid-containing gas–solid fluidized bed reactor under coupled effects of multiple parameters[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(32): 14430-14443. |
| [25] | Qian J, Law C K. Regimes of coalescence and separation in droplet collision[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1997, 331: 59-80. |
| [26] | 李铁男, 赵碧丹, 赵鹏, 等. 气固流化床启动阶段挡板内构件受力特性的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2649-2661. |
| Li T N, Zhao B D, Zhao P, et al. CFD-DEM simulation of the force acting on immersed baffles during the start-up stage of a gas-solid fluidized bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2649-2661. | |
| [27] | Tang T Q, He Y R, Ren A X, et al. Experimental study and DEM numerical simulation of dry/wet particle flow behaviors in a spouted bed[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(33): 15353-15367. |
| [28] | 李舒月, 王欢, 周少强, 等. 基于CPFD方法的U3O8氢还原流化床反应器数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3133-3151. |
| Li S Y, Wang H, Zhou S Q, et al. Numerical simulation of hydrogen reduction of U3O8 in fluidized bed reactors using CPFD method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3133-3151. | |
| [29] | Batchelor R W O G K. Thermal or electrical conduction through a granular material[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1977, 355(1682): 313-333. |
| [30] | Gunn D J. Transfer of heat or mass to particles in fixed and fluidised beds[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 1978, 21(4): 467-476. |
| [31] | Li H, Liu D Y, Ma J L, et al. Simulation of a Wurster fluidized bed by CFD–DEM with a cohesive contact model[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2022, 177: 157-166. |
| [32] | Hou Q F, Zhou Z Y, Yu A B. Computational study of the effects of material properties on heat transfer in gas fluidization[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(35): 11572-11586. |
| [33] | Hyun K, Sun R. Droplet collision processes in an inter-spray impingement system[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2005, 36(11): 1300-1321. |
| [34] | 张璜, 薄涵亮, 张帆. 基于二元液滴碰撞模型的喷雾计算研究[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2015, 49(S1): 220-226. |
| Zhang H, Bo H L, Zhang F. Study on spray calculation based on binary droplet collision model[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2015, 49(S1): 220-226. | |
| [35] | Post S L, Abraham J. Modeling the outcome of drop–drop collisions in Diesel sprays[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2002, 28(6): 997-1019. |
| [36] | Rabe C, Malet J, Feuillebois F. Experimental investigation of water droplet binary collisions and description of outcomes with a symmetric Weber number[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2010, 22(4): 047101. |
| [37] | Bach G A, Koch D L, Gopinath A. Coalescence and bouncing of small aerosol droplets[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2004, 518: 157-185. |
| [38] | van Buijtenen M S, van Dijk W J, Deen N G, et al. Numerical and experimental study on multiple-spout fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(11): 2368-2376. |
| [39] | Li H, Liu D Y, Ma J L, et al. Influence of cycle time distribution on coating uniformity of particles in a spray fluidized bed by using CFD-DEM simulations[J]. Particuology, 2023, 76: 151-164. |
| [40] | Zhou Y F, Shi Q, Huang Z L, et al. Realization and control of multiple temperature zones in liquid-containing gas–solid fluidized bed reactor[J]. AIChE Journal, 2016, 62(5): 1454-1466. |
| [1] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [2] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [3] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [4] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [5] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [6] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [7] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [8] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [9] | 段炼, 周星睿, 袁文君, 陈飞. 连续相速度脉动对微通道内聚合物液滴生成和形貌的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4578-4585. |
| [10] | 陈昇, 李子争, 苗超, 白学刚, 李飞, 刘家璇, 李天天, 杨爽, 吕蓉蓉, 王江云. 大尺度密集场景高危氯气非均匀湍流扩散特性三维CFD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4630-4643. |
| [11] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [12] | 黄正宗, 刘科成, 李泽方, 曾平生, 刘永富, 闫红杰, 刘柳. 锌精馏炉砖砌式换热室数值模拟与场协同优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4425-4439. |
| [13] | 王一飞, 李玉星, 欧阳欣, 赵雪峰, 孟岚, 胡其会, 殷布泽, 郭雅琦. 基于裂尖减压特性的CO2管道断裂扩展数值计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4683-4693. |
| [14] | 刘卓龙, 甘云华, 屈可扬, 陈宁光, 潘铭晖. 均匀电场对生物柴油小尺度射流扩散燃烧特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4800-4808. |
| [15] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号