• •
收稿日期:2025-09-16
修回日期:2025-10-11
出版日期:2025-12-12
通讯作者:
高明
作者简介:苏泽世(2001--),男,硕士研究生, suzeshi123@163.com
基金资助:
Zeshi SU( ), Ming GAO(
), Ming GAO( ), Qirong ZUO, Wuhan DONG
), Qirong ZUO, Wuhan DONG
Received:2025-09-16
Revised:2025-10-11
Online:2025-12-12
Contact:
Ming GAO
摘要:
随着高功耗芯片热通量持续攀升,传统两相浸没式液冷因介电液体气膜易覆盖、补液易受阻而产生临界热通量(qCHF)低、过冲大等问题。本文提出一种易于通过阵列排布扩展至更大面积的自驱射流装置,利用导流管-射流孔板耦合结构在40 mm×40 mm光滑表面上实现气液分离与局部射流冲击,系统研究了导流管内径、长度、射流孔宽度及射流距离对池沸腾性能的影响。实验以低GWP介电工质Noah 2100A为工质,采用可视化与多参数同步测量,结果表明:此装置使qCHF与最大核态沸腾传热系数 hMNB 分别最高提升77.5%与68.3%;减小导流管内径、增大射流孔宽度、适度延长管长或选择最优射流距离均可显著强化换热,但各参数均存在边际效应;强化机理归因于重力压差驱动的气液分离、补液流量增加及射流冲击抑制气膜覆盖。本研究为数据中心等大尺寸芯片的两相浸没式冷却提供了高可靠、易扩展的自驱强化方案。
中图分类号:
苏泽世, 高明, 左启荣, 董无含. 基于自驱射流装置的强化池沸腾换热研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251043.
Zeshi SU, Ming GAO, Qirong ZUO, Wuhan DONG. Study on enhanced pool boiling heat transfer based on self-driven jet device[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251043.
| 液体密度/kg·m-3 | 热导率/W·m-1·K-1 | 动力黏度/Pa·s | 饱和压力/ kPa | 相变潜热/kJ·kg-1 | 表面张力系数/mN·m-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1601 | 0.0609 | 3.562 × 10⁻⁷ | 35.38 | 93.22 | 11.44 |
表1 工质Noah 2100A在常温常压下的热物理性质
Table 1 Thermophysical properties of working fluid Noah 2100A at room temperature and pressure
| 液体密度/kg·m-3 | 热导率/W·m-1·K-1 | 动力黏度/Pa·s | 饱和压力/ kPa | 相变潜热/kJ·kg-1 | 表面张力系数/mN·m-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1601 | 0.0609 | 3.562 × 10⁻⁷ | 35.38 | 93.22 | 11.44 |
| 导流管内径Dtube/mm | 导流管长度Ltube/mm | 射流孔宽度Wjet/mm | 射流距离Hjet/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 40 | 2 | 2 |
| 6 | 60 | 2 | 2 |
| 6 | 80 | 2 | 2 |
| 7 | 60 | 2 | 2 |
| 8 | 60 | 3 | 2 |
| 8 | 60 | 2 | 2 |
| 8 | 60 | 2 | 4 |
| 8 | 60 | 2 | 6 |
| 8 | 60 | 2 | 8 |
| 8 | 60 | 1 | 2 |
表2 自驱射流装置特征参数
Table 2 Characteristic parameters of self-propelled jet device
| 导流管内径Dtube/mm | 导流管长度Ltube/mm | 射流孔宽度Wjet/mm | 射流距离Hjet/mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 40 | 2 | 2 |
| 6 | 60 | 2 | 2 |
| 6 | 80 | 2 | 2 |
| 7 | 60 | 2 | 2 |
| 8 | 60 | 3 | 2 |
| 8 | 60 | 2 | 2 |
| 8 | 60 | 2 | 4 |
| 8 | 60 | 2 | 6 |
| 8 | 60 | 2 | 8 |
| 8 | 60 | 1 | 2 |
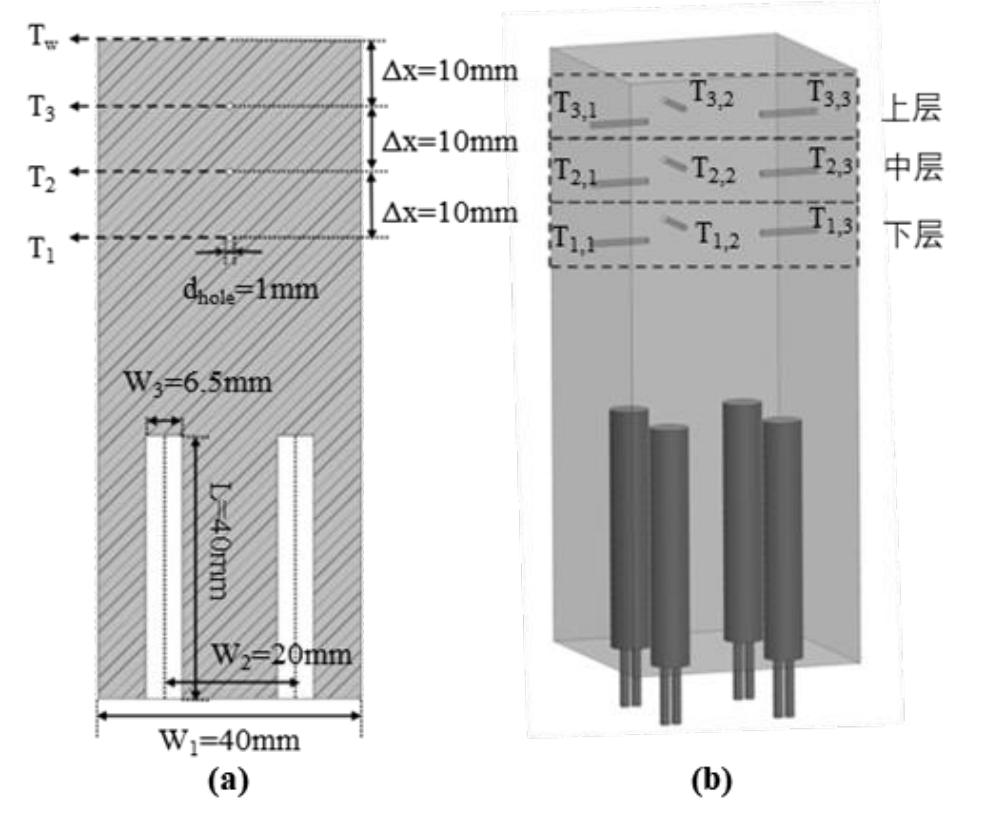
图4 导热铜块孔位示意图:(a) 二维尺寸示意图;(b) 三维示意图
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of hole positions in thermal conductive copper block: (a) Two dimensional diagram; (b) 3D schematic diagram
| 参数 | 数值 | 不确定度 |
|---|---|---|
| Tsat | 47℃ | ±0.05K |
| Ti,n | —— | ±0.02K |
| kCu,heating | 388W/(m·K) | ±3.88W/(m·K) |
| Δx1.3 | 20mm | ±0.025mm |
| ∆xwall | 10mm | ±0.025mm |
表3 数据处理中所涉及各参数的数值及不确定度汇总
Table 3 Summary of parameters and uncertainties
| 参数 | 数值 | 不确定度 |
|---|---|---|
| Tsat | 47℃ | ±0.05K |
| Ti,n | —— | ±0.02K |
| kCu,heating | 388W/(m·K) | ±3.88W/(m·K) |
| Δx1.3 | 20mm | ±0.025mm |
| ∆xwall | 10mm | ±0.025mm |
| [1] | Desai S B, Madhvapathy S R, Sachid A B, et al. MoS2transistors with 1-nanometer gate lengths[J]. Science, 2016, 354(6308): 99-102. |
| [2] | Ilager S, Ramamohanarao K, Buyya R. Thermal prediction for efficient energy management of clouds using machine learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2021, 32(5): 1044-1056. |
| [3] | Itoh S, Nakano K, Ishibashi A. Current status and future prospects of ZnSe-based light-emitting devices[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2000, 214/215: 1029-1034. |
| [4] | Wang Y B, Rao Z, Liu S C, et al. Evaluating the performance of liquid immersing preheating system for Lithium-ion battery pack[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2021, 190: 116811. |
| [5] | Liu J H, Fan Y N, Xie Q M. Feasibility study of a novel oil-immersed battery cooling system: Experiments and theoretical analysis[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2022, 208: 118251. |
| [6] | 郭豪文. 纯电动汽车浸没式液体冷却电池包的模拟与实验研究[D]. 杭州:崔立祺. 浙江大学, 2022. |
| Guo H. Simulation and experimental study of immersed liquid cooling battery pack for electric vehicle [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2022. | |
| [7] | Wang Y F, Wu J T. Thermal performance predictions for an HFE-7000 direct flow boiling cooled battery thermal management system for electric vehicles[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020, 207: 112569. |
| [8] | Anderson T M, Mudawar I. Microelectronic cooling by enhanced pool boiling of a dielectric fluorocarbon liquid[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 1989, 111(3): 752-759. |
| [9] | Mudawar I, Anderson T M. Parametric investigation into the effects of pressure, subcooling, surface augmentation and choice of coolant on pool boiling in the design of cooling systems for high-power-density electronic chips[J]. Journal of Electronic Packaging, 1990, 112(4): 375-382. |
| [10] | Mudawar I, Anderson T M. Optimization of enhanced surfaces for high flux chip cooling by pool boiling[J]. Journal of Electronic Packaging, 1993, 115(1): 89-100. |
| [11] | Liang G T, Mudawar I. Review of pool boiling enhancement by surface modification[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 128: 892-933. |
| [12] | Sajjad U, Sadeghianjahromi A, Ali H M, et al. Enhanced pool boiling of dielectric and highly wetting liquids - a review on enhancement mechanisms[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 119: 104950. |
| [13] | Jithin K V, Rajesh P K. Numerical analysis of single-phase liquid immersion cooling for lithium-ion battery thermal management using different dielectric fluids[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 188: 122608. |
| [14] | Huang C, Zhu H X, Ma Y J, et al. Evaluation of lithium battery immersion thermal management using a novel pentaerythritol ester coolant[J]. Energy, 2023, 284: 129250. |
| [15] | 吴曦蕾,杨佳亮,郭豪文,庄园,李晨阳,刘滢,韩晓红.数据中心浸没式液体冷却系统的发展历程及关键环节设计[J].制冷与空调,2022,22(11):61-74 |
| Wu X, Yang J, Guo H, et al. Development history and design of key links in immersion liquid cooling system for data center [J]. Refrigeration and Air-Conditioning, 2022, 22(11): 61-74. | |
| [16] | Hayes A, Raghupathi P A, Emery T S, et al. Regulating flow of vapor to enhance pool boiling[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 149: 1044-1051. |
| [17] | Yuan L L, Hong F J, Cheng P. Pool boiling enhancement through a guidance structure mounted above heating surface[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 139: 751-763. |
| [18] | Xu J Y, Hong F J, Zhang C Y. Experimental investigation on self-induced jet impingement boiling using R1336mzz(Z)[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 220: 124963. |
| [19] | Mody F, Chauhan A, Shukla M, et al. Evaluation of heater size and external enhancement techniques in pool boiling heat transfer with dielectric fluids[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 183: 122176. |
| [20] | 张欢, 王雪丽, 杜研, 等. 加热面尺寸对饱和池沸腾换热性能的影响[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 417-424. |
| Zhang H, Wang X L, Du Y, et al. Influence of heater size on saturated pool boiling heat transfer performance[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Science and Technology, 2021, 41(3): 417-424. | |
| [21] | 林祥伟, 林心怡, 黎芷均, 等. 表面材质对介电液体气泡成核及沸腾换热的微观影响机理[J]. 物理学报, 2025, 74(17): 308-317. |
| Lin X W, Lin X Y, Li Z J, et al. Microscopic influence mechanism of surface material on nucleation and boiling heat transfer of dielectric liquid bubbles[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2025, 74(17): 308-317. | |
| [22] | 陈真真, 陈洪强, 黄磊, 等. 超声波强化换热研究进展[J]. 工程科学学报, 2022, 44(12): 2164-2176. |
| Chen Z Z, Chen H Q, Huang L, et al. Research progress on the intensification of heat transfer by ultrasound[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2022, 44(12): 2164-2176. | |
| [23] | El-Genk M S, Ali A M, Al-Hajri E. Saturated pool boiling of PF-5060 from copper surfaces with sintered copper powder layers [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 138: 1224-1235. |
| [24] | Gupta S K, Misra R D. An experimental investigation on pool boiling heat transfer enhancement using Cu-Al₂O₃ nano-composite coating[J]. Experimental Heat Transfer, 2019, 32(2): 133–158. |
| [25] | Boziuk T R, Smith M K, Glezer A. Enhanced boiling heat transfer on plain and featured surfaces using acoustic actuation[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 108: 181-190. |
| [26] | Deng W, Ahmad S, Liu H Q, et al. Improving boiling heat transfer with hydrophilic/hydrophobic patterned flat surface: a molecular dynamics study[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 182: 121974. |
| [27] | Liang G T, Chen Y, Wang J J, et al. Experiments and modeling of boiling heat transfer on hybrid-wettability surfaces[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2021, 144: 103810. |
| [28] | Wang J J, Liang G T. Experimental investigation of pool boiling performance and bubble behavior on square micro-pillar structured surfaces[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2025, 239: 126556. |
| [29] | 何昌秋, 田加猛, 陈义齐, 等. 电场-宏观结构表面协同强化薄液膜沸腾传热特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2589-2602. |
| He C Q, Tian J M, Chen Y Q, et al. Synergistic heat transfer enhancement characteristics due to electric field and macro-structured surface during thin film boiling[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2589-2602. | |
| [30] | Može M, Zupančič M, Golobič I. Investigation of the scatter in reported pool boiling CHF measurements including analysis of heat flux and measurement uncertainty evaluation methodology[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 169: 114938. |
| [31] | 姜林林, 蒋金周, 张海滨. 水平微细圆管内R290流动沸腾流态可视化研究[J]. 制冷学报, 2023, 44(1): 129-135. |
| Jiang L L, Jiang J Z, Zhang H B. Visualization research on flow pattern of R290 flow boiling in horizontal micro-tubes[J]. Journal of Refrigeration, 2023, 44(1): 129-135. | |
| [32] | Huo X, Chen L, Tian Y S, et al. Flow boiling and flow regimes in small diameter tubes[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2004, 24(8–9): 1225–1239. |
| [33] | Lv X D, Zhang D L, Song G L, et al. Experimental study on flow patterns in narrow rectangular channels[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2023, 156: 104562. |
| [34] | Huo X, Chen L, Tian Y S, et al. Flow boiling and flow regimes in small diameter tubes[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2004, 24(8/9): 1225-1239. |
| [35] | Bhagwat S M, Ghajar A J. A flow pattern independent drift flux model based void fraction correlation for a wide range of gas–liquid two phase flow[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2014, 59: 186-205. |
| [36] | 郑晓倩, 刘道平, 陈永军, 等. 圆弧形导流式气泡泵的冷态试验研究[J]. 流体机械, 2015, 43(9): 58-62. |
| Zheng X Q, Liu D P, Chen Y J, et al. Experimental study of circular arc form guided bubble pump under cold state[J]. Fluid Machinery, 2015, 43(9): 58-62. |
| [1] | 张圣美, 李明, 张莹, 易茜, 杨依婷, 刘雅莉. 乳化剂和温度对相变微胶囊性能的影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 444-452. |
| [2] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [3] | 任现超, 谷雅秀, 段少斌, 贾文竹, 李汉林. 翅片式椭圆套管蒸发式冷凝器传热传质性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 75-83. |
| [4] | 袁琳慧, 王瑜. 单服务器浸没射流式液冷系统散热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 160-169. |
| [5] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [6] | 黄博, 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. 薄膜型LNG船液货舱温度场计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 195-204. |
| [7] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [8] | 孔俊龙, 毕扬, 赵耀, 代彦军. 储能电池直冷热管理系统的模拟实验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 289-296. |
| [9] | 胡金琦, 闵春华, 李小龙, 范元鸿, 王坤. 振动叶片耦合柔性板强化流体混沌混合与传热研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4824-4837. |
| [10] | 刘卓龙, 甘云华, 屈可扬, 陈宁光, 潘铭晖. 均匀电场对生物柴油小尺度射流扩散燃烧特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4800-4808. |
| [11] | 罗海梅, 王泓, 孙照明, 尹艳华. 同向双螺杆传热系数计算模型的分析与验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4809-4823. |
| [12] | 龚路远, 果正龙, 赵登辉, 郭亚丽, 周健, 韩倩倩, 沈胜强. 不同疏水性表面冷凝传热性能及动力学特征研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3932-3943. |
| [13] | 刘建海, 王磊, 鲁朝金, 白志山, 张平雨. 耦合电化学与多相流模型的电解槽性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3885-3893. |
| [14] | 陈科拯, 高蓬辉, 焉富春, 程博. 考虑液滴动态行为的亲-疏水复合结构表面冷凝特性影响因素分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3976-3989. |
| [15] | 常心泉, 张克学, 王军, 夏国栋. 自由分子区内不规则颗粒的热泳力计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3944-3953. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号