• •
收稿日期:2025-09-18
修回日期:2025-11-21
出版日期:2025-11-24
通讯作者:
白凡
作者简介:汪淏(2001—),男,硕士研究生,202307703129@wust.edu.cn
基金资助:
Hao WANG1,2( ), Lujun CAI1,2, Fan BAI1,3(
), Lujun CAI1,2, Fan BAI1,3( ), Feng ZHANG4
), Feng ZHANG4
Received:2025-09-18
Revised:2025-11-21
Online:2025-11-24
Contact:
Fan BAI
摘要:
为解决印刷电路板式换热器(PCHE)整体热-力学耦合分析的跨尺度问题,提出了一种基于均匀化建模的多尺度方法,建立了用于预测PCHE整体流、固温度场和热变形的热-力耦合方程。该方法将含大量微流道的PCHE换热芯体简化为均匀介质,其等效热力学和力学参数由细观代表性体积胞元的流–固–热耦合有限元模型确定。针对含150个流道的平行流PCHE芯体,分别采用均匀化模型和经典模型开展热–力学耦合仿真计算。通过对比发现,均匀化模型预测的流体宏观温度与经典模型预测的流道截面平均温度的最大相对误差不超过7%;两种模型预测的固体域横截面平均温度的最大相对误差不超过4.1%,预测的热变形最大相对误差不超过3.4%。均匀化模型的优势在于计算效率的大幅提升。
中图分类号:
汪淏, 蔡路军, 白凡, 张峰. 平行流道PCHE芯体热-力耦合分析多尺度方法[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251051.
Hao WANG, Lujun CAI, Fan BAI, Feng ZHANG. A multiscale approach for the thermo-mechanical coupling analysis of parallel-flow PCHE core[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251051.
| 区域 | 材料 | 动力粘度 /Pa·s | 热传导系数 /(W/(m·K)) | 定压热容 /(J/(kg·K)) | /Pa·m6·mol-2 | /m3·mol-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冷流 | 空气 | 2.94×10-5 | 0.0441 | 1054.8 | 4.24×10-2 | 2.26×10-5 |
| 热流 | 氦气 | 4.55×10-5 | 0.351 | 5196.5 | 6.90×10-2 | 1.48×10-5 |
| 固体域 | 617合金 | \ | 20.87 | 537.6 | \ | \ |
表1 各材料的物性参数
Table 1 Thermophysical properties of the materials
| 区域 | 材料 | 动力粘度 /Pa·s | 热传导系数 /(W/(m·K)) | 定压热容 /(J/(kg·K)) | /Pa·m6·mol-2 | /m3·mol-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冷流 | 空气 | 2.94×10-5 | 0.0441 | 1054.8 | 4.24×10-2 | 2.26×10-5 |
| 热流 | 氦气 | 4.55×10-5 | 0.351 | 5196.5 | 6.90×10-2 | 1.48×10-5 |
| 固体域 | 617合金 | \ | 20.87 | 537.6 | \ | \ |
| 流道 | 流体介质 | 工作压力 /MPa | 入口温度 /°C | 入口流量 /(m³/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冷流道 | 空气 | 0.52 | 355 | 1.23×10⁻⁶ |
| 热流道 | 氦气 | 3.00 | 750 | 6.80×10⁻⁷ |
表2 PCHE设计工况参数
Table 2 Design condition of the PCHE
| 流道 | 流体介质 | 工作压力 /MPa | 入口温度 /°C | 入口流量 /(m³/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冷流道 | 空气 | 0.52 | 355 | 1.23×10⁻⁶ |
| 热流道 | 氦气 | 3.00 | 750 | 6.80×10⁻⁷ |
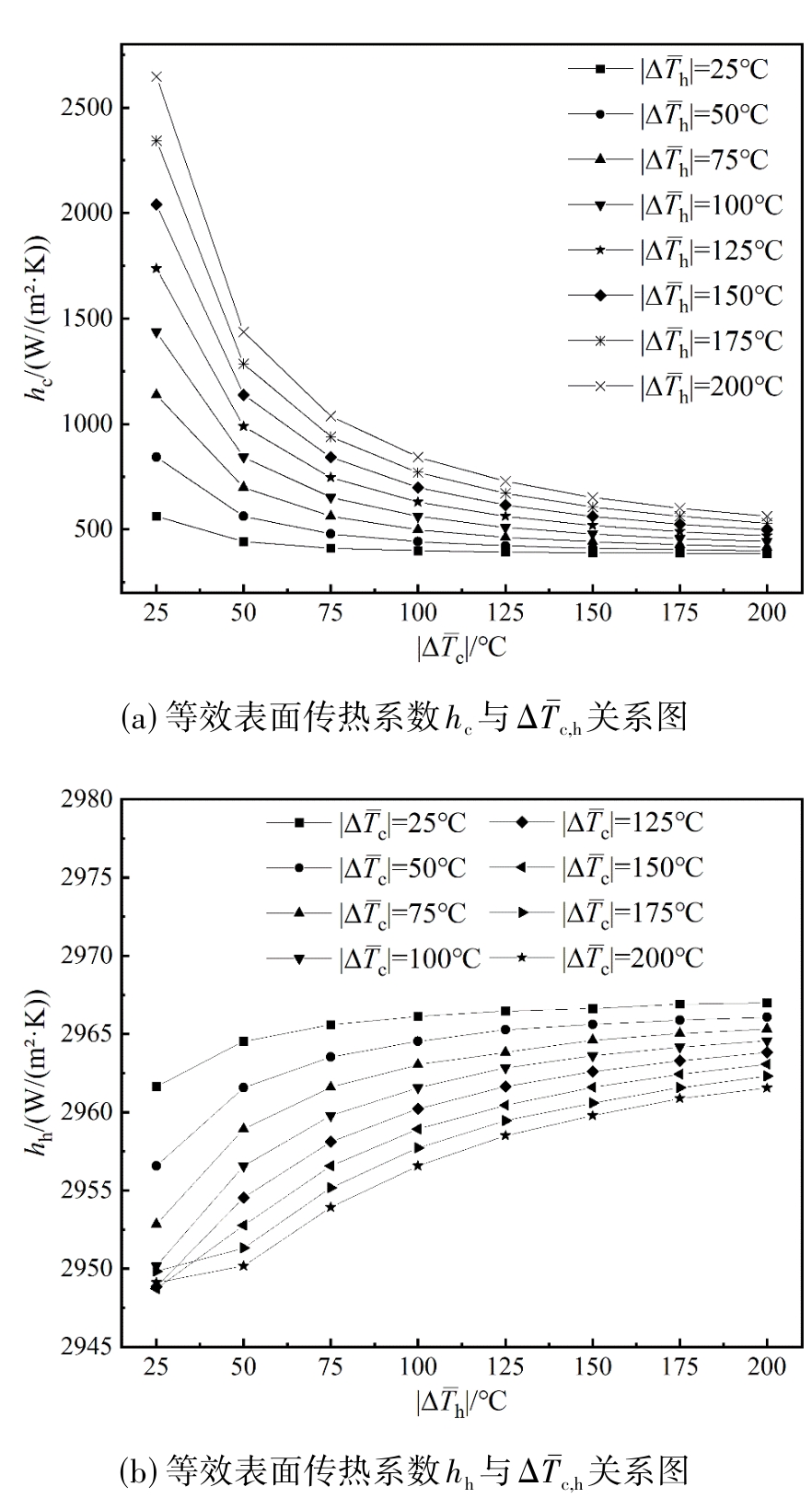
图4 等效表面传热系数hc,h与流、固平均温差ΔT¯c,h关系曲线
Fig.4 Variation of equivalent surface heat transfer coefficient hc,h with fluid-solid mean temperature difference ΔT¯c,h
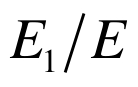 | 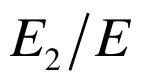 | 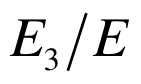 | 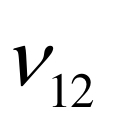 | 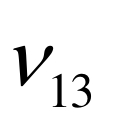 | 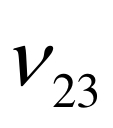 | 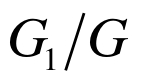 | 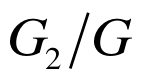 | 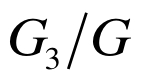 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.727 | 0.590 | 0.410 | 0.296 | 0.283 | 0.201 | 0.622 | 0.449 | 0.272 |
表3 等效弹性模量
Table 3 Equivalent elastic modulus
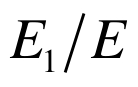 | 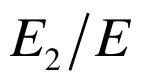 | 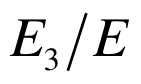 | 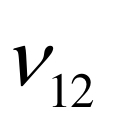 | 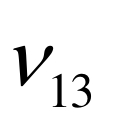 | 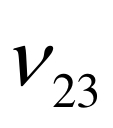 | 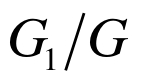 | 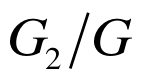 | 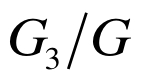 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.727 | 0.590 | 0.410 | 0.296 | 0.283 | 0.201 | 0.622 | 0.449 | 0.272 |
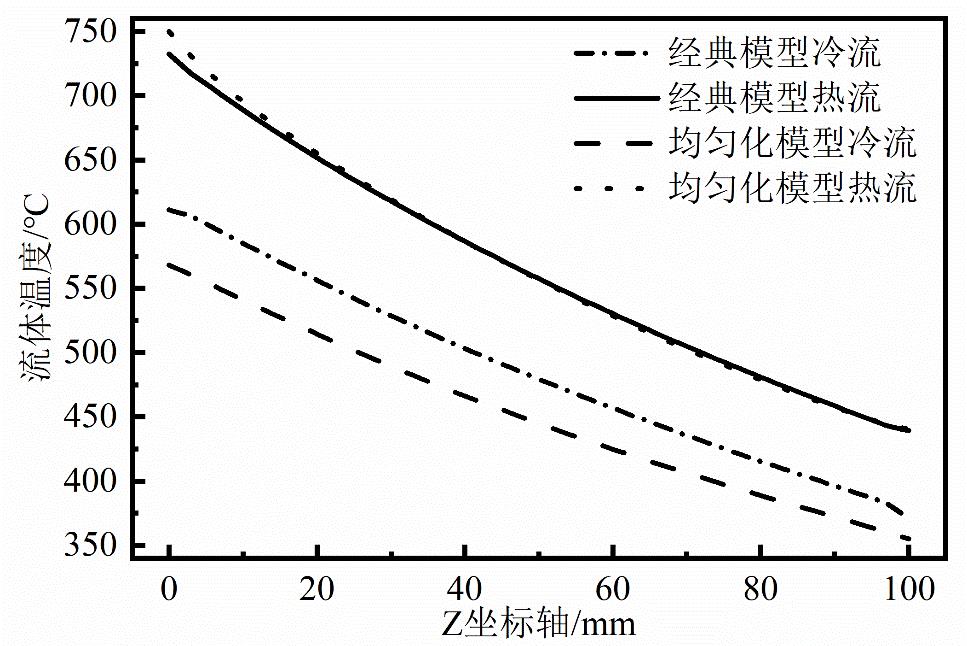
图9 经典模型流道截面平均温度与均匀化模型流体宏观温度的对比
Fig.9 Comparison of fluid temperatures: cross-sectionally averaged temperatures in classical model vs. macroscopic temperatures in homogenization model
| [1] | 梁迪, 李晓凤, 杨卓, 等. 微通道换热器研究与应用进展综述[J]. 制冷与空调, 2023, 37(2): 217-224. |
| Liang D, Li X F, Yang Z, et al. Review on research and application of microchannel heat exchanger[J]. Refrigeration and Air Conditioning, 2023, 37(2): 217-224. | |
| [2] | 张义飞, 刘舫辰, 张双星, 等. 超临界二氧化碳用印刷电路板式换热器性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. |
| Zhang Y F, Liu F C, Zhang S X, et al. Performance analysis of printed circuit heat exchanger for supercritical carbon dioxide[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 183-190. | |
| [3] | 任冠宇, 张义飞, 李新泽, 等. 翼型印刷电路板式换热器流动传热特性数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 108-117. |
| Ren G Y, Zhang Y F, Li X Z, et al. Numerical study on flow and heat transfer characteristics of airfoil printed circuit heat exchangers[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 108-117. | |
| [4] | Ma Y F, Liu D C, Wang J H, et al. Thermal-hydraulic performance and optimization of printed circuit heat exchangers for supercritical fluids: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2025, 208: 115051. |
| [5] | Haunstetter J, Dreißigacker V, Zunft S. Ceramic high temperature plate fin heat exchanger: Experimental investigation under high temperatures and pressures[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 151: 364-372. |
| [6] | Kim E S, Oh C H, Sherman S. Simplified optimum sizing and cost analysis for compact heat exchanger in VHTR[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2008, 238(10): 2635-2647. |
| [7] | 史新鑫, 李博, 李彦默, 等. 印刷电路板式换热器焊接质量影响因素分析[J]. 热加工工艺, 2023, 52(7): 113-116, 121. |
| Shi X X, Li B, Li Y M, et al. Analysis on influence factors of welding quality of printed circuit heat exchanger[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2023, 52(7): 113-116, 121. | |
| [8] | Chai L, Tassou S A. A review of printed circuit heat exchangers for helium and supercritical CO2 Brayton cycles[J]. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2020, 18: 100543. |
| [9] | He L, Oldfield M L G. Unsteady conjugate heat transfer modeling[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2011, 133(3): 031022. |
| [10] | Abdi M, Chaib K, Menouer A, et al. A natural convection conjugate heat transfer of Nano-Encapsulated Phase Change Materials (NEPCMs) in an inclined blocked square enclosure[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Applications, 2023, 84(6): 604-625. |
| [11] | Kılıç M. Evaluation of combined thermal–mechanical compression systems: a review for energy efficient sustainable cooling[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(21): 13724. |
| [12] | Zhao Z C, Zhang Y R, Chen X D, et al. A numerical study on condensation flow and heat transfer of refrigerant in minichannels of printed circuit heat exchanger[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2019, 102: 96-111. |
| [13] | 钟绍庚, 张宏, 张荣刚, 等. 新型矩形印刷电路板式换热器的数值研究[J/OL]. 化工学报, 2025: 1-17. (2025-07-14). . |
| Zhong S G, Zhang H, Zhang R G, et al. Numerical study on heat transfer characteristics of a novel rectangular printed circuit heat exchanger[J/OL]. CIESC Journal, 2025: 1-17. (2025-07-14). . | |
| [14] | de la Torre R, François J L, Lin C X. Assessment of the design effects on the structural performance of the Printed Circuit Heat Exchanger under very high temperature condition[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2020, 365: 110713. |
| [15] | 吴家荣, 李红智, 杨玉, 等. 超临界二氧化碳动力循环中印刷电路板换热器芯体机械应力和热应力耦合分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2022, 42(2): 640-649. |
| Wu J R, Li H Z, Yang Y, et al. Coupling analysis of mechanical stress and thermal stress of printed circuit heat exchanger core in supercritical carbon dioxide power cycle[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(2): 640-649. | |
| [16] | Gu X, Liu X, Sun H, et al. Analysis of flow and heat transfer performance of different types of flow channels in printed circuit heat exchangers for pre-coolers[J]. Thermal Science, 2024, 28(4 Part A): 2977-2988. |
| [17] | Song K N, Hong S D. Structural integrity evaluation of a lab-scale PCHE prototype under the test conditions of HELP[J]. Science and Technology of Nuclear Installations, 2013, 2013(1): 520145. |
| [18] | 沈观林, 胡更开, 刘彬. 复合材料力学[M]. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2013. |
| Shen G L, Hu G K, Liu B. Mechanics of composite materials[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2013. | |
| [19] | Xu Z R, Tan Y, Liu D C, et al. Equivalent mechanical property calculation method of mini-channels in printed circuit heat exchanger[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2023, 412: 112468. |
| [20] | Shaw A, Mahajan H P, Hassan T. Assessment of compact heat exchanger design following elastic perfectly plastic methodology[C]//ASME 2020 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference, 2020 |
| [21] | Chen W N, Ma Q Y, Liu X Y, et al. Adaptability analysis of flow and heat transfer multi-scale numerical method for printed circuit heat exchanger[J]. Energy, 2024, 311: 133349. |
| [22] | Whitaker S. The Method of Volume Averaging[M]. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 1999. |
| [23] | Alshehri S M, Said I A, Usman S. A review and safety aspects of modular high-temperature gas-cooled reactors[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(8): 11479-11492. |
| [24] | Song Z K, Xu J X, Chen X. Design and optimization of a high-density cryogenic supercritical hydrogen storage system based on helium expansion cycle[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 49: 1401-1418. |
| [25] | Nguyen V D, Béchet E, Geuzaine C, et al. Imposing periodic boundary condition on arbitrary meshes by polynomial interpolation[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2012, 55: 390-406. |
| [26] | Zhao Z S, Dong H X, Ying W J. An FFT-Based MAC scheme for Stokes equations with periodic boundary conditions and its application to elasticity problems[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2024, 439: 115624. |
| [27] | Yin S Z, Pindera M J. Homogenized moduli and local stress fields of random fiber composites under homogeneous and periodic boundary conditions[J]. European Journal of Mechanics - A/Solids, 2022, 93: 104504. |
| [28] | Omairey S L, Dunning P D, Sriramula S. Development of an ABAQUS plugin tool for periodic RVE homogenisation[J]. Engineering with Computers, 2019, 35(2): 567-577. |
| [29] | Kanit T, Forest S, Galliet I, et al. Determination of the size of the representative volume element for random composites: statistical and numerical approach[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2003, 40(13/14): 3647-3679. |
| [30] | Gitman I M, Askes H, Sluys L J. Representative volume: Existence and size determination[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2007, 74(16): 2518-2534. |
| [31] | dos Santos W F, Proença S P B. A 3D RVE-based computational homogenization approach for predicting the effective fourth-order elasticity tensor of periodic porous materials[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part L: Journal of Materials: Design and Applications, 2025, 239(9): 1636-1653. |
| [1] | 袁琳慧, 王瑜. 单服务器浸没射流式液冷系统散热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 160-169. |
| [2] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [3] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [4] | 黄博, 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. 薄膜型LNG船液货舱温度场计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 195-204. |
| [5] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [6] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [7] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [8] | 孔俊龙, 毕扬, 赵耀, 代彦军. 储能电池直冷热管理系统的模拟实验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 289-296. |
| [9] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [10] | 密晓光, 孙国刚, 程昊, 张晓慧. 印刷电路板式天然气冷却器性能仿真模型和验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| [11] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [12] | 任现超, 谷雅秀, 段少斌, 贾文竹, 李汉林. 翅片式椭圆套管蒸发式冷凝器传热传质性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 75-83. |
| [13] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [14] | 段炼, 周星睿, 袁文君, 陈飞. 连续相速度脉动对微通道内聚合物液滴生成和形貌的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4578-4585. |
| [15] | 陈昇, 李子争, 苗超, 白学刚, 李飞, 刘家璇, 李天天, 杨爽, 吕蓉蓉, 王江云. 大尺度密集场景高危氯气非均匀湍流扩散特性三维CFD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4630-4643. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号