• •
宋振超1,2,3( ), 韩嘉豪3, 张凌旋3, 武越3, 李聪明1,2(
), 韩嘉豪3, 张凌旋3, 武越3, 李聪明1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-10-10
修回日期:2025-11-16
出版日期:2025-12-15
通讯作者:
李聪明
作者简介:宋振超(1979—),男,硕士,13605211568@qq.com
基金资助:
Zhenchao SONG1,2,3( ), Jiahao HAN3, Lingxuan ZHANG3, Yue WU3, Congming LI1,2(
), Jiahao HAN3, Lingxuan ZHANG3, Yue WU3, Congming LI1,2( )
)
Received:2025-10-10
Revised:2025-11-16
Online:2025-12-15
Contact:
Congming LI
摘要:
该研究针对高毒性、难水解的氯化氰(CNCl)污染问题,系统探讨了尖晶石型双金属氧化物CuCr2O4表面催化CNCl水解的反应机理。基于密度泛函理论(DFT),通过构建(100)、(110)和(111)晶面的完美及氧空位缺陷模型,分析了表面稳定性、吸附特性与水解路径。研究表明,不同晶面结构与氧空位缺陷共同调控了水解路径与反应能垒,其中(110)氧空位表面展现出最优的催化协同性。研究构建了吸附能与反应能的预测模型,揭示了Cu与Cr之间的电子协同与位点互补机制是提升水解效率的关键。该工作为设计高效双金属水解催化剂提供了理论依据,该领域未来研究将侧重于实验验证及模型向其他尖晶石体系的拓展应用。
中图分类号:
宋振超, 韩嘉豪, 张凌旋, 武越, 李聪明. 复合金属CuCr2O4表面CNCl水解反应机理研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251122.
Zhenchao SONG, Jiahao HAN, Lingxuan ZHANG, Yue WU, Congming LI. Study on the hydrolysis reaction mechanism of CNCl on the surface of composite metal CuCr2O4[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251122.
| 表面 | 终端结构 | 表面终端原子 | 亚表面终端原子 | 表面能σ (eV·Å-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (100) | T1 | Cu*1 | Cr*2+O*4 | 0.14 |
| (100) | T2 | Cr*2+O*4 | Cu*1 | 0.03 |
| (100) | T3 | Cr*2+O*2 | Cu*1 | 0.10 |
| (100) | T4 | O*2 | Cu*1 | 0.28 |
| (110) | T1 | Cu*2+Cr*2+O*4 | Cr*2+O*4 | 0.15 |
| (110) | T2 | Cr*2+O*4 | Cu*2+Cr*2+O*4 | 0.07 |
| (110) | T3 | Cr*2+O*2 | Cu*2+Cr*2+O*4 | 0.09 |
| (110) | T4 | O*2 | Cu*2+Cr*2+O*4 | 0.17 |
| (111) | T1 | Cu*1+Cr*1 | Cu*1+O*4 | 0.22 |
| (111) | T2 | Cu*1+Cr*1 | O*4 | 0.06 |
| (111) | T3 | Cu*1 | O*4 | 0.11 |
| (111) | T4 | O*4 | Cr*3 | 0.03 |
| (111) | T5 | O*1 | Cr*3 | 0.03 |
| (111) | T6 | Cr*3 | O*4 | 0.07 |
| (111) | T7 | O*4 | Cu*1+Cr*1 | 0.36 |
| (111) | T8 | O*3 | Cu*1+Cr*1 | 0.22 |
表1 复合金属氧化物CuCr2O4不同终端结构的表面与亚表面原子的化学配比以及对应的表面能
Table 1 Chemical composition and surface energy of surface and sub-surface atoms of CuCr2O4 composite metal oxide with different terminal structures
| 表面 | 终端结构 | 表面终端原子 | 亚表面终端原子 | 表面能σ (eV·Å-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (100) | T1 | Cu*1 | Cr*2+O*4 | 0.14 |
| (100) | T2 | Cr*2+O*4 | Cu*1 | 0.03 |
| (100) | T3 | Cr*2+O*2 | Cu*1 | 0.10 |
| (100) | T4 | O*2 | Cu*1 | 0.28 |
| (110) | T1 | Cu*2+Cr*2+O*4 | Cr*2+O*4 | 0.15 |
| (110) | T2 | Cr*2+O*4 | Cu*2+Cr*2+O*4 | 0.07 |
| (110) | T3 | Cr*2+O*2 | Cu*2+Cr*2+O*4 | 0.09 |
| (110) | T4 | O*2 | Cu*2+Cr*2+O*4 | 0.17 |
| (111) | T1 | Cu*1+Cr*1 | Cu*1+O*4 | 0.22 |
| (111) | T2 | Cu*1+Cr*1 | O*4 | 0.06 |
| (111) | T3 | Cu*1 | O*4 | 0.11 |
| (111) | T4 | O*4 | Cr*3 | 0.03 |
| (111) | T5 | O*1 | Cr*3 | 0.03 |
| (111) | T6 | Cr*3 | O*4 | 0.07 |
| (111) | T7 | O*4 | Cu*1+Cr*1 | 0.36 |
| (111) | T8 | O*3 | Cu*1+Cr*1 | 0.22 |
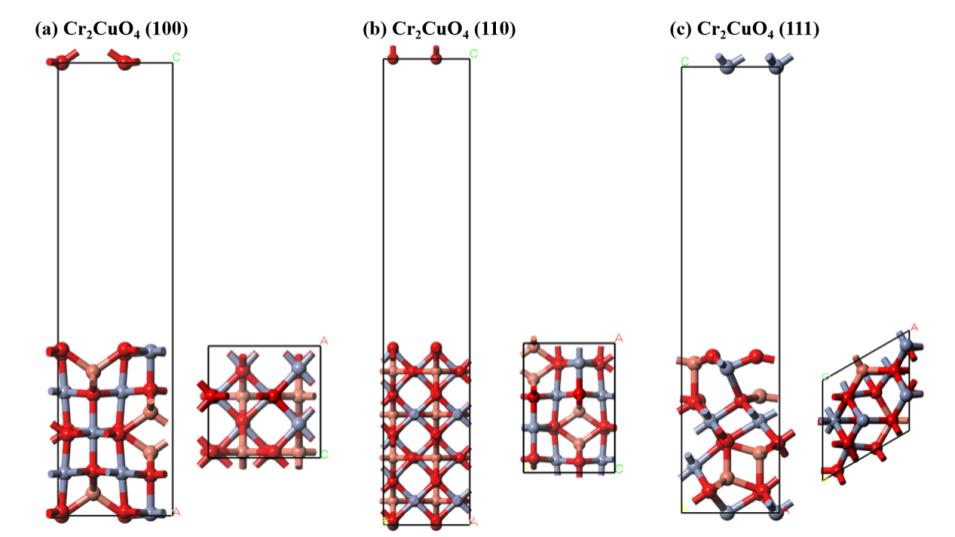
图1 复合金属氧化物CuCr2O4(100)、(110)和(111)表面的最稳定结构(正视图与俯视图)
Fig. 1 The most stable structures on the surfaces of CuCr2O4 (100), (110) and (111) composite metal oxides (front view and top view)
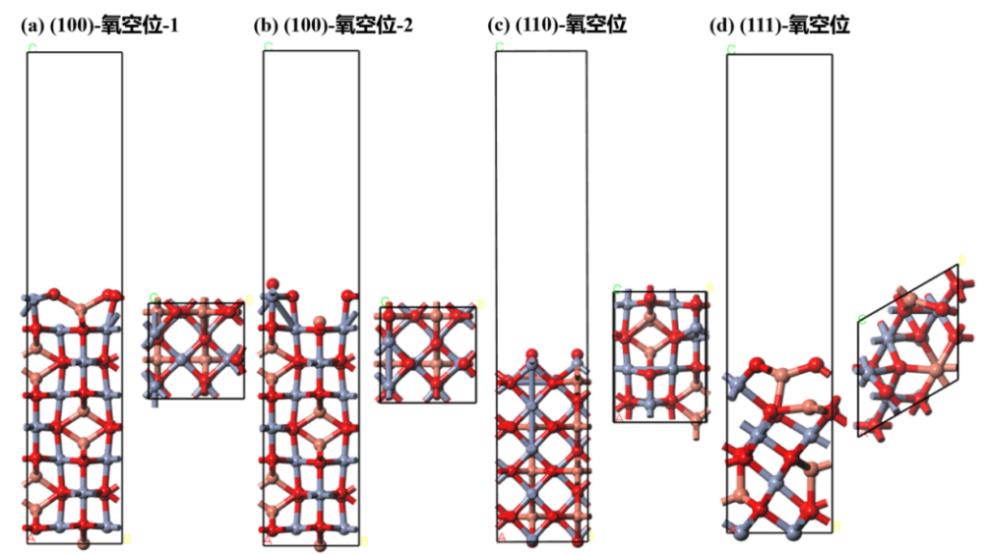
图4 几何优化后的复合金属氧化物CuCr2O4(100)、(110)和(111)氧空位缺陷表面结构
Fig. 4 Surface structure of geometrically optimized composite metal oxide CuCr2O4(100), (110) and (111) with oxygen vacancy defects
| 空位缺陷表面 | 氧空位形成能/eV |
|---|---|
| (100)-氧空位-1 | 3.65 |
| (100)-氧空位-2 | 3.20 |
| (110)-氧空位 | 3.73 |
| (111)-氧空位 | 2.02 |
表2 复合金属氧化物CuCr2O4(100)、(110)和(111)表面上的氧空位形成能
Table 2 Formation energy of oxygen vacancies on surfaces of CuCr2O4 (100), (110) and (111) composite metal oxides
| 空位缺陷表面 | 氧空位形成能/eV |
|---|---|
| (100)-氧空位-1 | 3.65 |
| (100)-氧空位-2 | 3.20 |
| (110)-氧空位 | 3.73 |
| (111)-氧空位 | 2.02 |
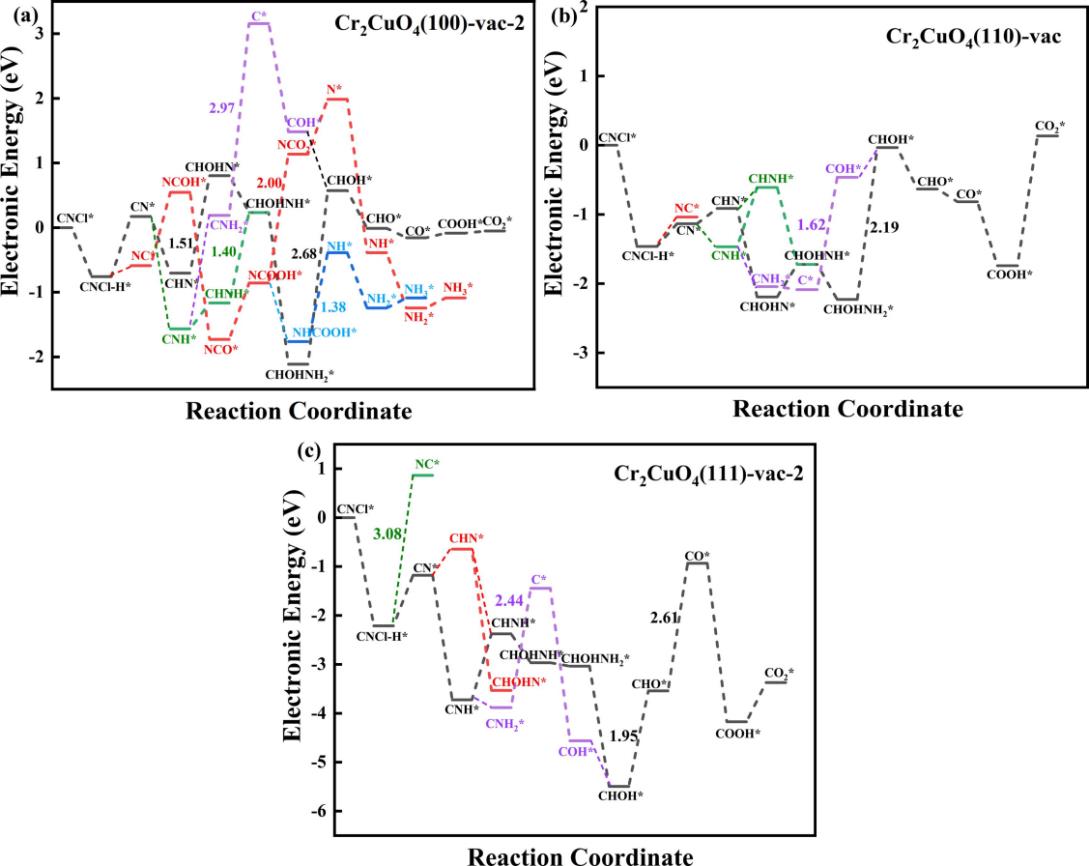
图5 CNCl在复合金属氧化物CuCr2O4(100)、(110)和(111)含氧空位缺陷表面的水解反应路径图
Fig. 5 Scheme of hydrolysis reaction path of CNCl on the surface of oxygen vacancy defects in CuCr2O4 (100), (110) and (111) composite metal oxides
| 表面类型 | 最优路径类型 | 决速步反应能 (eV) | 是否受氧空位促进 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (100)-完美 | CHOHNH2*→CHOH*+NH3 | 2.37 | 否 |
| (100)-氧空位 | NCOOH*→NCO2* | 2.00 | 是 |
| (110)-完美 | CNCl+H*→NC* | 1.41 | 否 |
| (110)-氧空位 | C*→COH* | 1.62 | 是 |
| (111)-完美 | CNCl*→ CNCl+H* | 2.11 | 否 |
| (111)-氧空位 | CHO*→CO* | 2.61 | 否 |
表3 CNCl在CuCr2O4各表面最优水解路径比较
Table 3 Comparison of the optimal hydrolysis paths of CNCl on various surfaces of CuCr2O4
| 表面类型 | 最优路径类型 | 决速步反应能 (eV) | 是否受氧空位促进 |
|---|---|---|---|
| (100)-完美 | CHOHNH2*→CHOH*+NH3 | 2.37 | 否 |
| (100)-氧空位 | NCOOH*→NCO2* | 2.00 | 是 |
| (110)-完美 | CNCl+H*→NC* | 1.41 | 否 |
| (110)-氧空位 | C*→COH* | 1.62 | 是 |
| (111)-完美 | CNCl*→ CNCl+H* | 2.11 | 否 |
| (111)-氧空位 | CHO*→CO* | 2.61 | 否 |
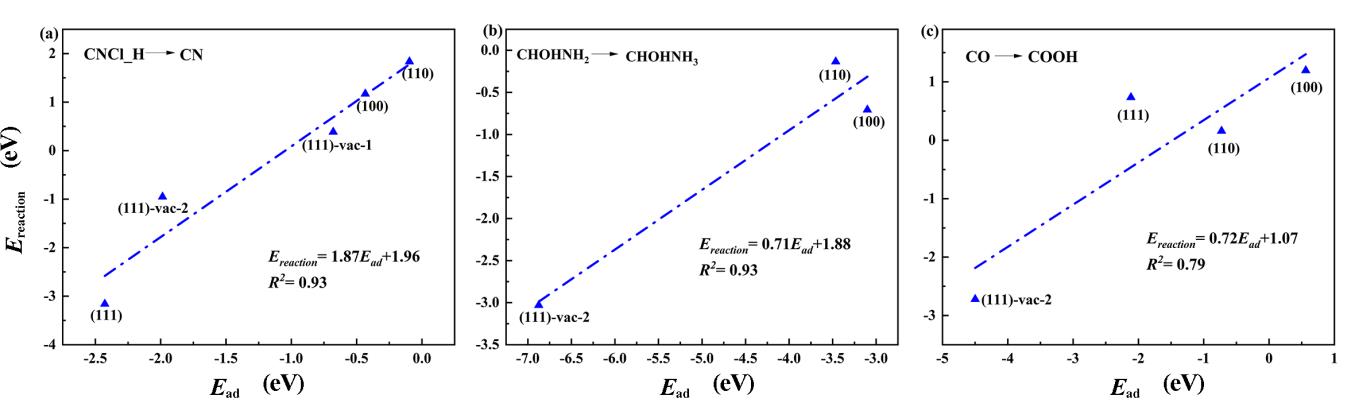
图7 CNCl水解中间体在CuCr2O4表面及其含氧空位缺陷表面的关键反应步骤的反应能和生成物中间体吸附能的关系
Fig. 7 The relationship between the reaction energy of the key reaction step of CNCl hydrolysis intermediate on the surface of CuCr2O4 and its oxygen vacancy defects and the adsorption energy of the generated intermediate
| [1] | 杨瑄琳. 基于聚丙烯酸酯改性的氯化氰防护材料研究[D]. 北京: 军事科学院, 2023. |
| [2] | Yu W Y, Li R X, Tian S N, et al. Adsorption behavior analysis of CNCl on transition metal-doped fluorinated diamanes: a first-principles study[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2025, 162(12): 124701. |
| [3] | Kanzariya A, Vadalkar S, Jana S K, et al. An ab-initio investigation of transition metal-doped graphene quantum dots for the adsorption of hazardous CO2, H2S, HCN, and CNCl molecules[J]. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2024, 186: 111799. |
| [4] | 蒋明, 宁平, 王重华, 等. 含氰化氢废气治理研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2012, 31(11): 2563-2569. |
| [5] | 张欣, 薛宇, 马懿星, 等. 电晕放电与介质阻挡放电净化氰化氢的机理[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 675-684. |
| [6] | Ganguly T, Chakraborty A B, Majumdar A. Transition metal mediated hydrolysis of C–S bonds: an overview of a new reaction strategy[J]. ACS Organic & Inorganic Au, 2023, 3(6): 332-349. |
| [7] | 盖星宇, 岳玉学, 杨春华, 等. 碳负载Cs和Cu基催化剂用于1, 1, 2-三氯乙烷的气相脱氯化氢[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 575-583. |
| [8] | Ehrburger P, Dentzer J, Dziedzinl P. Pyrolysis of impregnated carbon adsorbents after exposure to cyanide gases[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 1993, 24(3): 333-344. |
| [9] | Kong C, Han Y X, Hou L J, et al. The effect of metal matrix M (M = Co, Ni, Cu) on the water dissociation performance of oxophilic Cr from density functional theory[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2023, 47(34): 15894-15900. |
| [10] | Mu X M, Wang K, Lv K Y, et al. Doping of Cr to regulate the valence state of Cu and Co contributes to efficient water splitting[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(13): 16552-16561. |
| [11] | Movlarooy T, Fadradi M A. Adsorption of cyanogen chloride on the surface of boron nitride nanotubes for CNCl sensing[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2018, 700: 7-14. |
| [12] | Soltani A, Sousaraei A, Mirarab M, et al. Interaction of CNCl molecule and single-walled AlN nanotubes using DFT and TD-DFT calculations[J]. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 2017, 21(3): 270-276. |
| [13] | Yang Z, Li X, Zhang L X, et al. Understanding the hydrolysis mechanism of cyanogen chloride on copper and chromium surfaces[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2024, 9(5): e202304309. |
| [14] | Acharyya S S, Ghosh S, Siddiqui N, et al. Cetyl alcohol mediated synthesis of CuCr2O4 spinel nanoparticles: a green catalyst for selective oxidation of aromatic C–H bonds with hydrogen peroxide[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(7): 4838-4843. |
| [15] | Chen Z X, Tang B, Shen J, et al. Synthesis of CuCr2O4/reduced graphene oxide composite: a green catalyst for selective oxidation of cyclohexane to cyclohexanone with hydrogen peroxide[J]. ChemistrySelect, 2017, 2(33): 10941-10945. |
| [16] | Wołosiak-Hnat A, Milchert E, Lewandowski G. The influence of technological parameters on hydrogenolysis of glycerol in the presence of CuCr2O4 catalyst[J]. Journal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 2012, 15(2): 405-417. |
| [17] | Zhu P C, Tang F, Wang S F, et al. Adsorption performance of CNCl, NH3 and GB on modified graphene and the selectivity in O2 and N2 environment[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2022, 33: 104280. |
| [18] | Sun Z, Yu S F, Toan S, et al. Enabling low-temperature methanol activation via lattice oxygen induced Cu–O–Cr catalysis[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2023, 13(20): 13704-13716. |
| [19] | Zhu P C, Zhao J M, Yu W Y, et al. First-principles study of CH2O, CH4, Cl2, HCN, and CNCl gas adsorption behavior by h-BN boron site modification[J]. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2024, 1237: 114657. |
| [20] | Zhao J M, Zhang M C, Wang C Y, et al. First-principles study of CO, NH3, HCN, CNCl, and Cl2 gas adsorption behaviors of metal and cyclic C–metal B- and N-site-doped h-BNs[J]. Electronic Materials Letters, 2025, 21(2): 268-288. |
| [21] | Mohammadi M D, Abdullah H Y, Biskos G, et al. Adsorbing CNCl on pristine, C-, and Al-doped boron nitride nanotubes: a density functional theory study[J]. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2023, 1220: 113980. |
| [22] | Kresse G, Joubert D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method[J]. Physical Review B, 1999, 59(3): 1758-1775. |
| [23] | Freund H J, Roberts M W. Surface chemistry of carbon dioxide[J]. Surface Science Reports, 1996, 25(8): 225-273. |
| [24] | Tang C, Zhang L, Wijethunge D, et al. Controllable polarization and doping in ferroelectric In2Se3 monolayers and heterobilayers via intrinsic defect engineering[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2021, 125(44): 24648-24654. |
| [25] | Graves S, Meleson K, Wilking J, et al. Structure of concentrated nanoemulsions[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2005, 122(13): 134703. |
| [26] | Wegeberg C, Wenger O S. Luminescent first-row transition metal complexes[J]. JACS Au, 2021, 1(11): 1860-1876. |
| [27] | Pastor E, Sachs M, Selim S, et al. Electronic defects in metal oxide photocatalysts[J]. Nature Reviews Materials, 2022, 7(7): 503-521. |
| [28] | Asogwa F C, Igwe C C, Edet H O, et al. Computational insights into the electronic structure and adsorption properties of CN, CNCl, and NO2 on metal (Na, Zn, and Al,) doped fullerene surfaces[J]. Chemical Papers, 2024, 78(16): 8789-8801. |
| [29] | Nagarajan V, Chandiramouli R. Probing cyanogen chloride gas molecules using blue phosphorene nanosheets based on adsorption properties: a first-principles study[J]. Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2019, 1150: 63-70. |
| [30] | Baei M T, Taghartapeh M R, Soltani A, et al. Interaction of pure and metal atom substituted carbon nanocages with CNCl: a DFT study[J]. Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2017, 11(2): 354-360. |
| [31] | Yang X L, Lan L, Zheng C, et al. Fabrication of hierarchically porous CuBTC@PA-PEI composite for high-efficiency elimination of cyanogen chloride[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(6): 2440. |
| [32] | 于宁, 王秋月, 王志才, 等. 双位点协同调控增强钙钛矿氧化物的水氧化活性[J]. 化工进展, 2025, 44(7): 3976-3984. |
| [33] | Saadh M J, Salim K, Kumar A, et al. Highly enhanced cyanogen chloride and hydrogen cyanide sensing performance of BC4N monolayer with silicon-doped: A DFT approach[J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2025, 710: 417248. |
| [34] | Rood S C, Pastor-Algaba O, Tosca-Princep A, et al. Synergistic effect of simultaneous doping of ceria nanorods with Cu and Cr on CO oxidation and NO reduction[J]. Chemistry – A European Journal, 2021, 27(6): 2165-2174. |
| [35] | Houska J, Kozak T. Relationships between the distribution of O atoms on partially oxidized metal (Al, Ag, Cu, Ti, Zr, Hf) surfaces and the adsorption energy: A density-functional theory study[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2017, 121(22): 225303. |
| [36] | Maimaiti Y, Nolan M, Elliott S D. Reduction mechanisms of the CuO(111) surface through surface oxygen vacancy formation and hydrogen adsorption[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(7): 3036-3046. |
| [37] | Monika, Jogender, Kumar S, et al. Adsorption of hydrogen cyanide, cyanogen fluoride and cyanogen chloride on iron decorated graphene substrates: A DFT-D2 study[J]. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 2025, 35(5): 3560-3579. |
| [38] | Gao W, Chen Y, Li B, et al. Determining the adsorption energies of small molecules with the intrinsic properties of adsorbates and substrates[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 1196. |
| [39] | Xu L, Lin J, Bai Y H, et al. Atomic and molecular adsorption on Cu(111)[J]. Topics in Catalysis, 2018, 61(9): 736-750. |
| [40] | Qin H, Zhang H, Wu K M, et al. A systematic theoretical study of CO2 hydrogenation towards methanol on Cu-based bimetallic catalysts: role of the CHO&CH3OH descriptor in thermodynamic analysis[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2024, 26(28): 19088-19104. |
| [1] | 毛建拥, 葛纪军, 徐盼, 毕荣山. HDI制备过程中副产物水解氯生成机理实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 384-392. |
| [2] | 胡国祥, 朱忆魁, 龙华, 刘晓雯, 熊勤钢. 组分配比影响氯化胆碱-乳酸低共熔溶剂碱木质素溶解度的底层机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4449-4461. |
| [3] | 张茹, 朱传强, 张栋, 黄政, 肖雨果, 李明, 李长明. 采用高分子非催化还原脱硝的垃圾焚烧工艺伴生固废含氮污染物特征研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4944-4959. |
| [4] | 李相海, 赖德林, 孔纲, 周健. 双仿生表面水下疏油协同机制的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4551-4562. |
| [5] | 钱慧慧, 王文婕, 陈文尧, 周兴贵, 张晶, 段学志. 聚丙烯定向转化制芳烃:金属-分子筛协同催化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4838-4849. |
| [6] | 佟丽丽, 陈英, 艾敏华, 舒玉美, 张香文, 邹吉军, 潘伦. ZnO/WO3异质结光催化环烯烃[2+2]环加成制备高能量密度燃料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4882-4892. |
| [7] | 赵维, 邢文乐, 韩朝旭, 袁兴中, 蒋龙波. g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解水中有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769. |
| [8] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [9] | 杨宁, 李皓男, LIN Xiao, GEORGIADOU Stella, LIN Wen-Feng. 从塑料废弃物到能源催化剂:塑料衍生碳@CoMoO4复合材料在电解水析氢反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [10] | 常心泉, 张克学, 王军, 夏国栋. 自由分子区内不规则颗粒的热泳力计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3944-3953. |
| [11] | 高正, 汪辉, 屈治国. 数据驱动辅助高通量筛选阴离子柱撑金属有机框架储氢[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4259-4272. |
| [12] | 巢欣旖, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 甲醇和乙酸甲酯一步法制丙酸甲酯催化剂的可控制备与性能调控[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4030-4041. |
| [13] | 杨敏, 段新伟, 吴俊宏, 米杰, 王建成, 武蒙蒙. Sm2O3/γ-Al2O3催化剂的COS催化水解性能及失活机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4061-4070. |
| [14] | 周媚, 曾浩桀, 蒋火炎, 蒲婷, 曾星星, 刘宝玉. 二次晶化法改性合成MTW分子筛及其在苯和环己烯烷基化反应中的催化性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4071-4080. |
| [15] | 林嘉豪, 付芳忠, 叶昊辉, 胡金, 姚明灿, 范鹤林, 王旭, 王瑞祥, 徐志峰. NdF3含量对NdF3-LiF熔盐局域结构和输运性质的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3834-3841. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号