• •
陈培强1,2( ), 郑群1, 姜玉廷1, 陈今茂2, 王旭东2, 黄龙2, 苏醒2, 阮曼2(
), 郑群1, 姜玉廷1, 陈今茂2, 王旭东2, 黄龙2, 苏醒2, 阮曼2( ), 徐万里2(
), 徐万里2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-10-01
修回日期:2025-11-13
出版日期:2025-11-17
通讯作者:
阮曼,徐万里
作者简介:陈培强 (1994-),男,博士研究生,E-mail: chenpeiqiang@hrbeu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Peiqiang CHEN1,2( ), Qun ZHENG1, Yuting JIANG1, Jinmao CHEN2, Xudong WANG2, Long HUANG2, Xing SU2, Man RUAN2(
), Qun ZHENG1, Yuting JIANG1, Jinmao CHEN2, Xudong WANG2, Long HUANG2, Xing SU2, Man RUAN2( ), Wanli XU2(
), Wanli XU2( )
)
Received:2025-10-01
Revised:2025-11-13
Online:2025-11-17
Contact:
Man RUAN, Wanli XU
摘要:
流道结构对确保电解液均匀分布和降低泵送功耗具有关键作用,直接影响海水激活电池的整体性能。本文在传统直通型流道结构的基础上,提出了三种带有突扩比特征的新型流道结构,搭建了适用于海水激活电池系统模拟的电化学-流多物理场耦合模型,并开展了相应的电池放电实验,以验证仿真结果的可靠性。进一步地,探究了电池在高电密运行条件下的电解液流动特性和电化学性能。研究结果表明:在电液流量为300 mL/min、电流密度600 mA/cm2的运行条件下,带有进出口非对称突扩型流道结构的海水激活电池表现出最优的综合性能:较高的电解液均匀因子(0.866)、最低的泵送功耗(19.92 mW)以及最长的有效放电时间(714s)。该新型流道结构在海水激活电池的工程应用中潜力显著。
中图分类号:
陈培强, 郑群, 姜玉廷, 陈今茂, 王旭东, 黄龙, 苏醒, 阮曼, 徐万里. 带有突扩比的新型流道结构对海水激活电池性能影响研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251123.
Peiqiang CHEN, Qun ZHENG, Yuting JIANG, Jinmao CHEN, Xudong WANG, Long HUANG, Xing SU, Man RUAN, Wanli XU. Study on the Impact of Novel Flow Channel Structure with Sudden-Expansion Ratio on Aqueous AgO-Al Battery[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251123.
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 阳极长度/ mm | 100 |
| 阳极宽度/ mm | 100 |
| 阳极厚度/ mm | 0.25 |
| 阴极长度/ mm | 100 |
| 阴极宽度/ mm | 100 |
| 阴极厚度/ mm | 1 |
| 阴阳极间隔/ mm | 0.5 |
| 进口直径/ mm | 12 |
| 出口直径/ mm | 12 |
表1 模型几何参数
Table 1 Geometric parameters of the model
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 阳极长度/ mm | 100 |
| 阳极宽度/ mm | 100 |
| 阳极厚度/ mm | 0.25 |
| 阴极长度/ mm | 100 |
| 阴极宽度/ mm | 100 |
| 阴极厚度/ mm | 1 |
| 阴阳极间隔/ mm | 0.5 |
| 进口直径/ mm | 12 |
| 出口直径/ mm | 12 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 开路电压 | 2.06 V |
| OH-浓度 | 4.5 mol/L |
| 阴极孔隙率 | 0.56 |
| 电解液密度 | 1250 kg/m3 |
| 电解液比热容 | 4182 J/kg·K |
| 电解液动力粘性系数 | 0.0025 kg/m·s |
| 压力 | 101325 Pa |
| 运行温度 | 80 ℃ |
表2 电化学及动力学参数
Table 2 Electrochemical and kinetic parameters
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 开路电压 | 2.06 V |
| OH-浓度 | 4.5 mol/L |
| 阴极孔隙率 | 0.56 |
| 电解液密度 | 1250 kg/m3 |
| 电解液比热容 | 4182 J/kg·K |
| 电解液动力粘性系数 | 0.0025 kg/m·s |
| 压力 | 101325 Pa |
| 运行温度 | 80 ℃ |
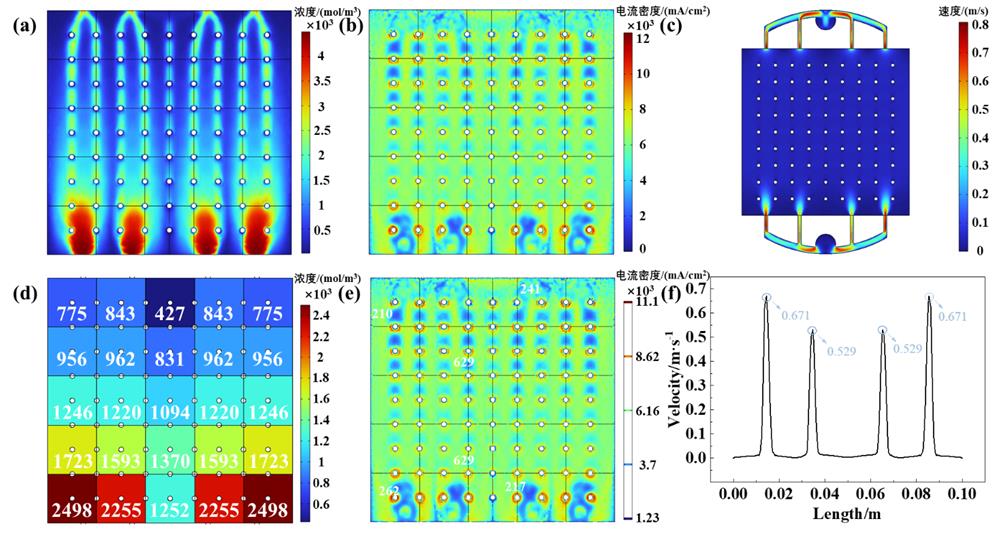
图5 直通型流道的性能 (a) OH-离子浓度云图, (b) 电流密度云图, (c)速度云图, (d) 区域浓度分布, (e) 电流密度等高线图, (f) 近进口2mm处速度分布.
Fig.5 Performance of straight through type flow channel. (a) concentration distribution, (b) current density distribution, (c) velocity distribution, (d) regional concentration distribution, (e) current density contour distribution, (f) Velocity distribution at the inlet 2mm.
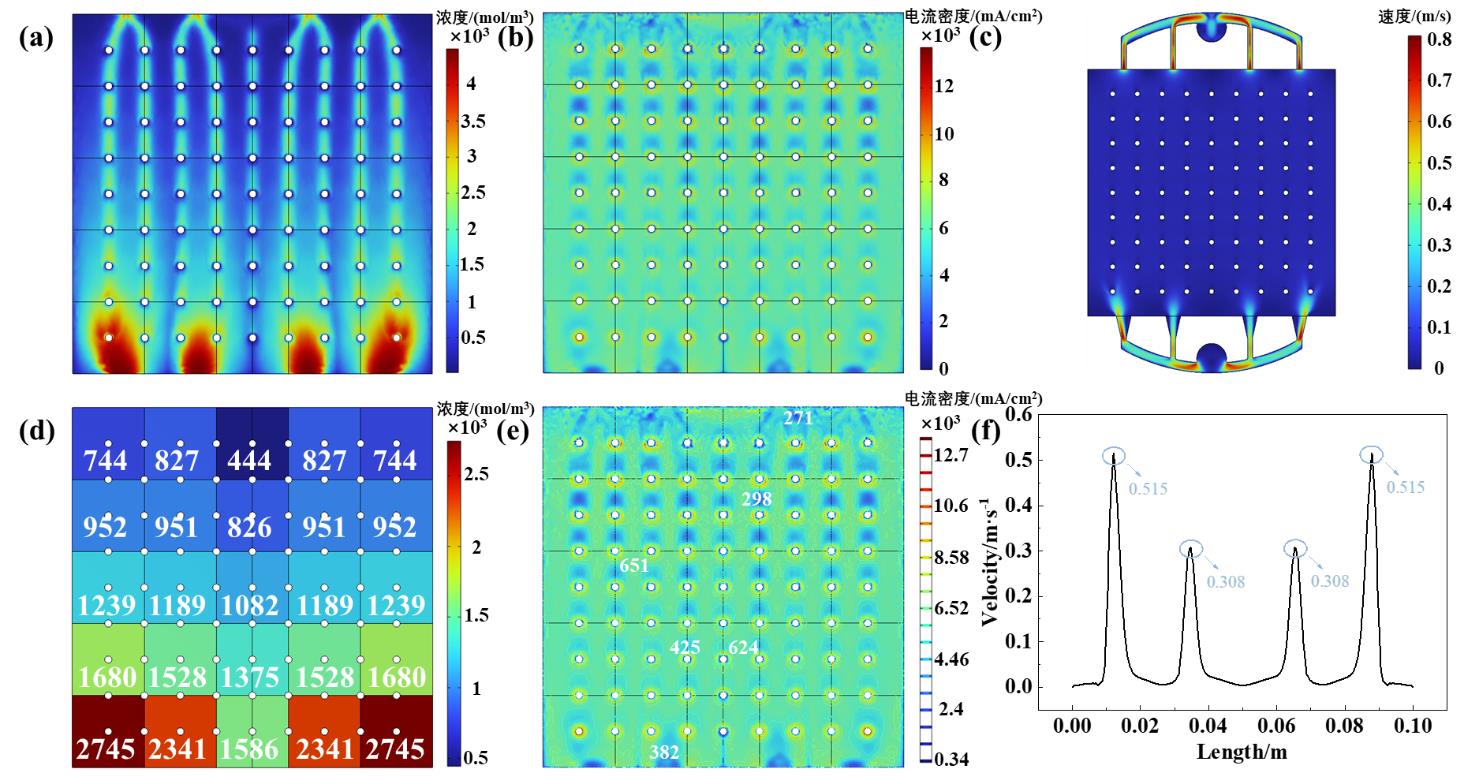
图6 进口突扩型流道的性能 (a) OH-离子浓度云图, (b) 电流密度云图, (c)速度云图, (d) 区域浓度分布, (e) 电流密度等高线图, (f) 近进口2mm处速度分布.
Fig.6 Performance of inlet sudden expansion type flow channel. (a) concentration distribution, (b) current density distribution, (c) velocity distribution, (d) regional concentration distribution, (e) current density contour distribution, (f) Velocity distribution at the inlet 2mm.
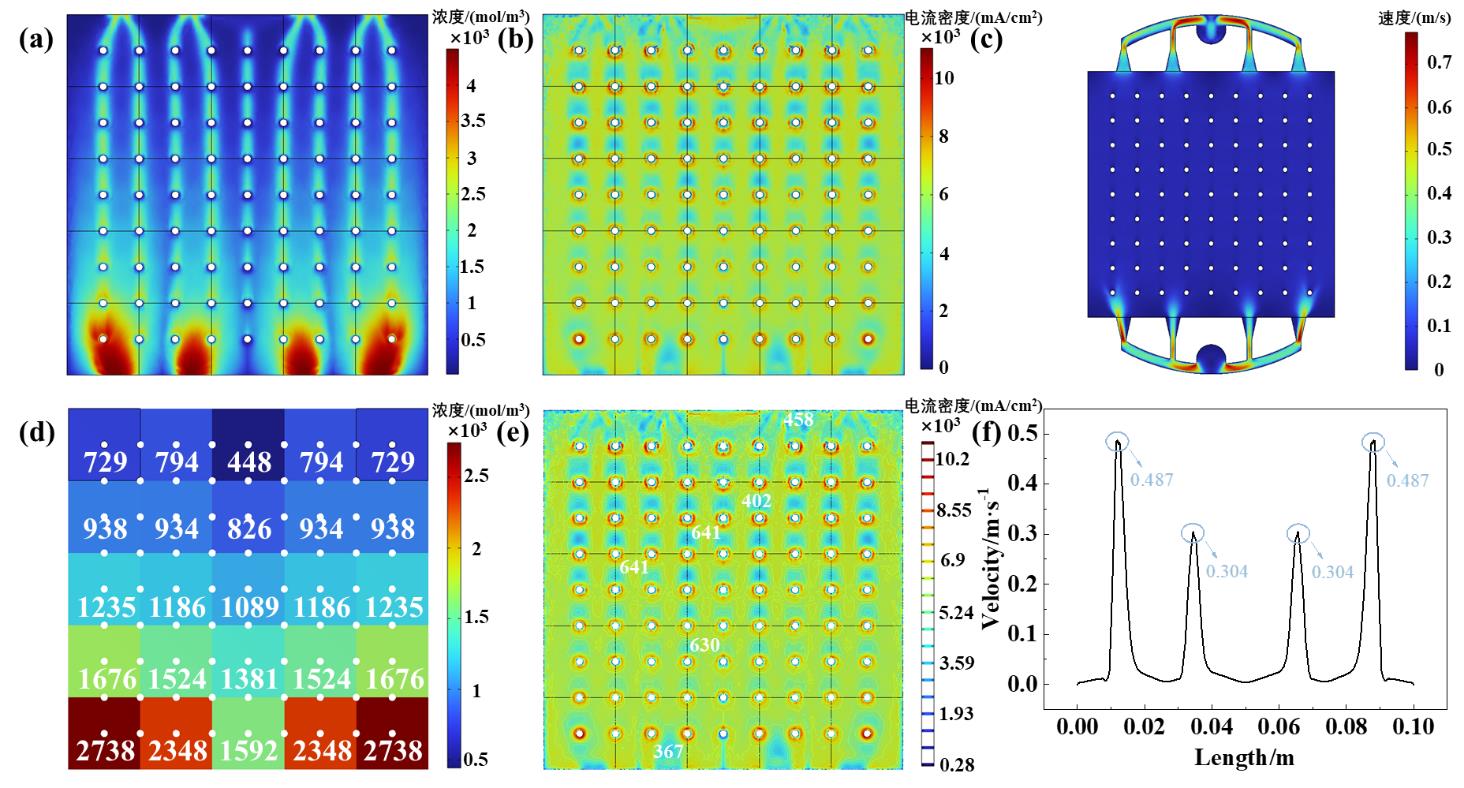
图7 进出口对称突扩型流道的性能 (a) OH-离子浓度云图, (b) 电流密度云图, (c)速度云图, (d) 区域浓度分布, (e) 电流密度等高线图, (f) 近进口2mm处速度分布.
Fig.7 Performance of inlet/outlet symmetric sudden expansion type flow channel. (a) concentration distribution, (b) current density distribution, (c) velocity distribution, (d) regional concentration distribution, (e) current density contour distribution, (f) Velocity distribution at the inlet 2mm.
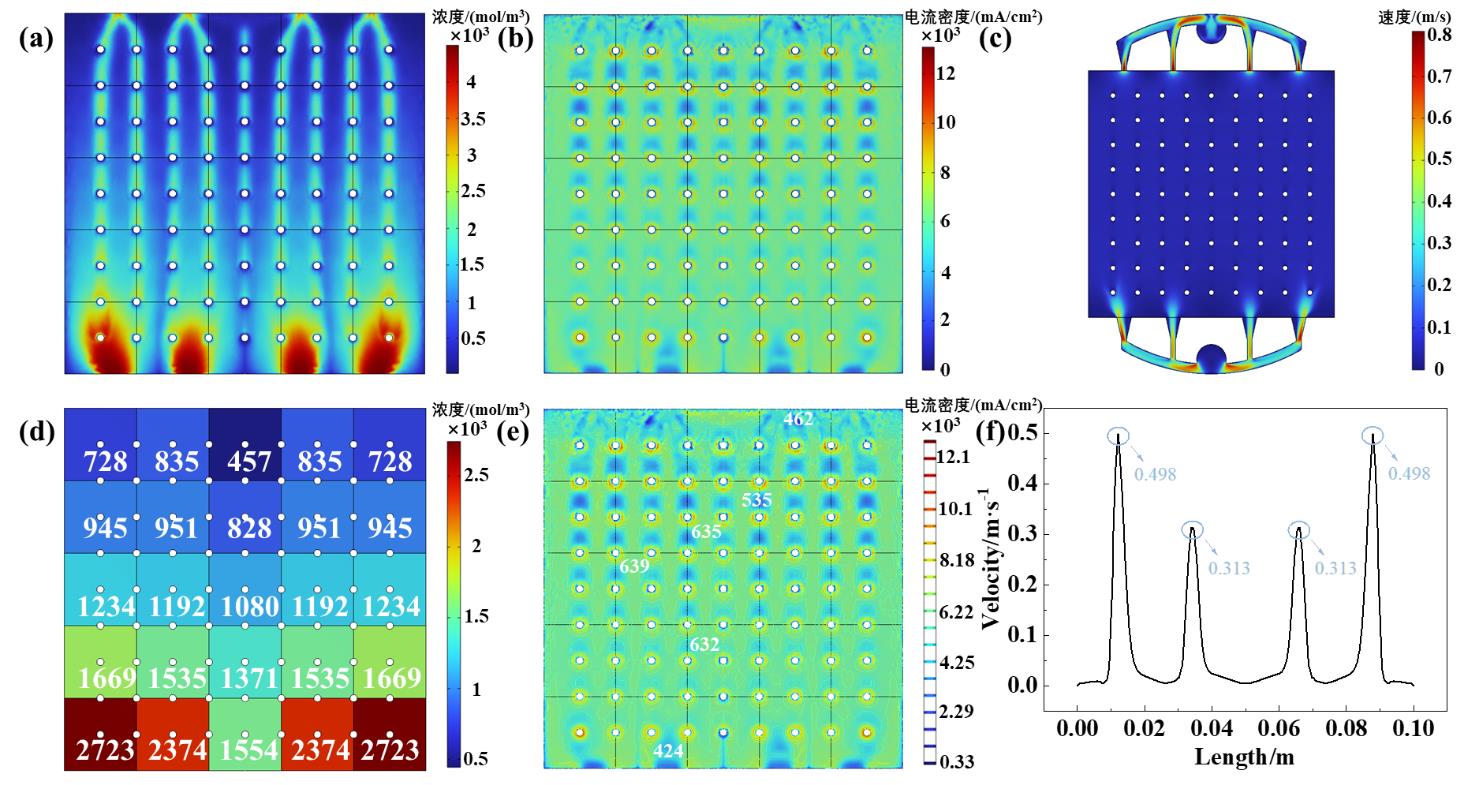
图8 进出口非对称突扩型流道的性能 (a) OH-离子浓度云图, (b) 电流密度云图, (c)速度云图, (d) 区域浓度分布, (e) 电流密度等高线图, (f) 近进口2mm处速度分布.
Fig.8 Performance of inlet/outlet asymmetric sudden expansion type flow channel. (a) concentration distribution, (b) current density distribution, (c) velocity distribution, (d) regional concentration distribution, (e) current density contour distribution, (f) Velocity distribution at the inlet 2mm.
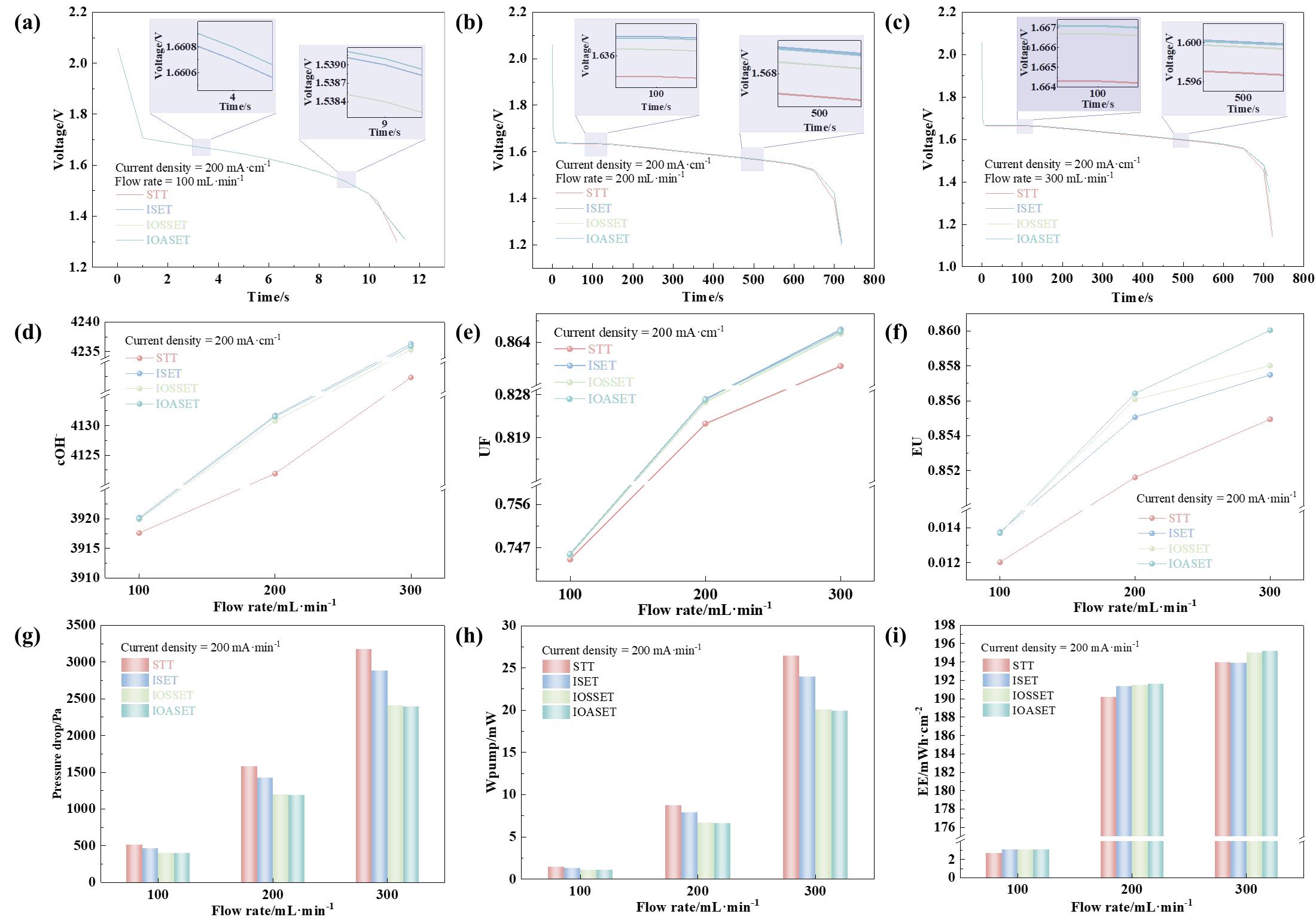
图9 不同流道结构的整体性能对比 (a) 放电电压-100 mL/min, (b) 放电电压-200 mL/min, (c) 放电电压-300 mL/min, (d) OH- 离子浓度, (e) 均匀因子, (f) 电解液利用率, (g) 压降, (h) 泵送功耗, (i) 能量密度.
Fig.9 The overall performance comparison of the different flow channel. (a) discharge voltage-100 mL/min, (b), discharge voltage-200 mL/min (c) discharge voltage-300 mL/min, (d) average concentration of OH-, (e) uniformity factor of OH-, (f) electrolyte utilization, (g) pressure drop, (h) pumping loss, (i) discharge energy density.
| [8] | Zheng Q, Xing F, Li X F, et al. Flow field design and optimization based on the mass transport polarization regulation in a flow-through type vanadium flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 324: 402-411. |
| [9] | Messaggi M, Canzi P, Mereu R, et al. Analysis of flow field design on vanadium redox flow battery performance: Development of 3D computational fluid dynamic model and experimental validation[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 228: 1057-1070. |
| [10] | Ali E, Kwon H, Choi J, et al. A numerical study of electrode thickness and porosity effects in all vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2020, 28: 101208. |
| [11] | Bhattarai A, Wai N, Schweiss R, et al. Advanced porous electrodes with flow channels for vanadium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 341: 83-90. |
| [12] | 陈森洋, 靳蒲航, 谭志明, 等. 质子交换膜燃料电池中蛇形流道液滴运动数值仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 183-194. |
| Chen S Y, Jin P H, Tan Z M, et al. Numerical simulation of droplet movement in serpentine channel in proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 183-194. | |
| [13] | Cai G C, Liang Y M, Liu Z C, et al. Design and optimization of bio-inspired wave-like channel for a PEM fuel cell applying genetic algorithm[J]. Energy, 2020, 192: 116670. |
| [14] | Li N, Wang W T, Xu R Y, et al. Design of a novel nautilus bionic flow field for proton exchange membrane fuel cell by analyzing performance[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2023, 200: 123517. |
| [15] | Liu Y L, Huang Z B, Xie X, et al. Redox flow battery: Flow field design based on bionic mechanism with different obstructions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 498: 155663. |
| [16] | Sun Y, Lin Y X, Wang Q L, et al. Novel design and numerical investigation of a windward bend flow field for proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Energy, 2024, 290: 130142. |
| [17] | Su R H, Wang Z M, Cai Y H, et al. Scaling up flow fields from lab-scale to stack-scale for redox flow batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 486: 149946. |
| [18] | Iranzo A, Arredondo C H, Kannan A M, et al. Biomimetic flow fields for proton exchange membrane fuel cells: a review of design trends[J]. Energy, 2020, 190: 116435. |
| [19] | Zhang S Y, Liu S, Xu H T, et al. Performance of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with honeycomb-like flow channel design[J]. Energy, 2022, 239: 122102. |
| [20] | Liu X, Du H L, Gao J Y, et al. Design of a cobweb bionic flow field for organic redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 591: 233848. |
| [21] | Xie X, Yin B F, Xu S, et al. Effects of microstructure shape parameters on water removal in a PEMFC lotus-like flow channel[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(5): 3473-3483. |
| [22] | Trainham J A, Newman J. A comparison between flow-through and flow-by porous electrodes for redox energy storage[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 1981, 26(4): 455-469. |
| [23] | Xu Q, Zhao T S, Zhang C. Performance of a vanadium redox flow battery with and without flow fields[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 142: 61-67. |
| [24] | Aaron D, Tang Z J, Papandrew A B, et al. Polarization curve analysis of all-vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2011, 41(10): 1175-1182. |
| [25] | Wei L, Zhao T S, Zhao G, et al. A high-performance carbon nanoparticle-decorated graphite felt electrode for vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 176: 74-79. |
| [26] | Zeng Y K, Zhou X L, An L, et al. A high-performance flow-field structured iron-chromium redox flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 324: 738-744. |
| [27] | Ye Q, Hu J, Cheng P, et al. Design trade-offs among shunt current, pumping loss and compactness in the piping system of a multi-stack vanadium flow battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 296: 352-364. |
| [28] | Sun J, Liu B C, Zheng M L, et al. Serpentine flow field with changing rib width for enhancing electrolyte penetration uniformity in redox flow batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 49: 104135. |
| [29] | Pan L M, Xie J Y, Guo J C, et al. In-plane gradient design of flow fields enables enhanced convections for redox flow batteries[J]. Energy Advances, 2023, 2(12): 2006-2017. |
| [30] | Yin Y, Wang X F, Shangguan X, et al. Numerical investigation on the characteristics of mass transport and performance of PEMFC with baffle plates installed in the flow channel[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(16): 8048-8062. |
| [31] | Limjeerajarus N, Santiprasertkul T. Novel hybrid serpentine-interdigitated flow field with multi-inlets and outlets of gas flow channels for PEFC applications[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(25): 13601-13611. |
| [32] | Sun J, Jiang H R, Zhang B W, et al. Towards uniform distributions of reactants via the aligned electrode design for vanadium redox flow batteries[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 259: 114198. |
| [33] | Chen P Q, Xiong C H, Zheng Q, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental investigation on the optimization of flow-guided structures for high-performance aqueous AgO-Al batteries[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 235: 126167. |
| [1] | 陈培强, 郑群, 姜玉廷, 等. 电液流量及电流密度对海水激活电池输出特性的影响研究[J/OL]. 化工学报, 2025: 1-27. (2025-07-04). . |
| Chen P Q, Zheng Q, Jiang Y T, et al. Effects of electrolyte flow rate and current density on the output performance of seawater-activated batteries: a numerical and experimental study[J/OL]. CIESC Journal, 2025: 1-27. (2025-07-04). . | |
| [2] | Li S Y, Tian X. Progress of seawater batteries: From mechanisms, materials to applications[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 617: 235161. |
| [3] | Chen J L, Sun L, Wang K, et al. Research and applications of rechargeable seawater battery[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 76: 109659. |
| [4] | Khatir F A, Barzegari M M, Talebi-Ghadikolaee H, et al. Integration of design of experiment and finite element method for the study of geometrical parameters in metallic bipolar plates for PEMFCs[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(79): 39469-39482. |
| [5] | Xiong K N, Wu W, Wang S F, et al. Modeling, design, materials and fabrication of bipolar plates for proton exchange membrane fuel cell: a review[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 301: 117443. |
| [6] | Huang P Y, Chen Z W, Zhang J, et al. Stainless steel bipolar plate fuel cell with different flow field structures prepared by laser additive manufacturing[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 183: 122186. |
| [7] | Jang J, Shin M, Kwon Y, et al. Carbon cloth modified by direct growth of nitrogen-doped carbon nanofibers and its utilization as electrode for zero gap flow batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 481: 148644. |
| [1] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [2] | 任现超, 谷雅秀, 段少斌, 贾文竹, 李汉林. 翅片式椭圆套管蒸发式冷凝器传热传质性能实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 75-83. |
| [3] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [4] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [5] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [6] | 黄博, 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. 薄膜型LNG船液货舱温度场计算分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 195-204. |
| [7] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [8] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [9] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [10] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [11] | 孙浩然, 吴成云, 王艳蒙, 孙静楠, 胡仞与, 段钟弟. 热对流影响下液滴蒸发特性模型与实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 123-132. |
| [12] | 苏伟, 赵大海, 金旭, 刘忠彦, 李静, 张小松. 吸湿液滴与混合润湿性表面协同抑霜特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 140-151. |
| [13] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [14] | 黄正宗, 刘科成, 李泽方, 曾平生, 刘永富, 闫红杰, 刘柳. 锌精馏炉砖砌式换热室数值模拟与场协同优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4425-4439. |
| [15] | 王一飞, 李玉星, 欧阳欣, 赵雪峰, 孟岚, 胡其会, 殷布泽, 郭雅琦. 基于裂尖减压特性的CO2管道断裂扩展数值计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4683-4693. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号