化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (7): 3258-3265.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20200022
收稿日期:2020-01-06
修回日期:2020-04-02
出版日期:2020-07-05
发布日期:2020-07-05
通讯作者:
孙奉仲
作者简介:魏伟(1988—),女,博士研究生,
Wei WEI1,2( ),Xiucai LI3,Fengzhong SUN1(
),Xiucai LI3,Fengzhong SUN1( )
)
Received:2020-01-06
Revised:2020-04-02
Online:2020-07-05
Published:2020-07-05
Contact:
Fengzhong SUN
摘要:
准确预测燃煤锅炉尾部烟气的酸露点和酸凝结对深度降低排烟温度、保障尾部换热设备的安全高效运行十分重要。尾部烟气中存在的飞灰颗粒对酸露点和酸凝结液滴的发生有很大影响,不可忽略。考虑烟气中超细飞灰颗粒对酸露点和酸凝结的影响,提出了飞灰粒径对考虑局部凝结质量传输效果的酸露点和酸凝结迭代计算方法,实现了酸露点和壁面温度下酸凝结的准确预测。当飞灰粒径低于中肯半径(rash<r0)时,飞灰粒径对凝结率有显著影响;随着飞灰粒径的降低,硫酸蒸气、水蒸气以及酸液凝结率明显增加,尤其是硫酸蒸气凝结率;飞灰粒径越小,凝结越易发生。然而,过冷度超过30℃时,烟气中超细飞灰颗粒对低温壁面酸凝结的影响可以忽略不计。烟气携带而不被低温壁面捕获的凝结酸液量较少,烟气中超细飞灰颗粒对烟气酸蒸气的降低作用可以忽略不计。理论计算方法为分析现场酸-灰作用积灰层提供理论依据,对于优化燃煤锅炉尾部烟道的安全高效运行有重大指导意义。
中图分类号:
魏伟, 李秀财, 孙奉仲. 超细飞灰对烟气酸露点与酸凝结的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(7): 3258-3265.
Wei WEI, Xiucai LI, Fengzhong SUN. Research on effect of ultrafine ash particles on acid dew point and acid condensation for coal-fired boilers[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(7): 3258-3265.
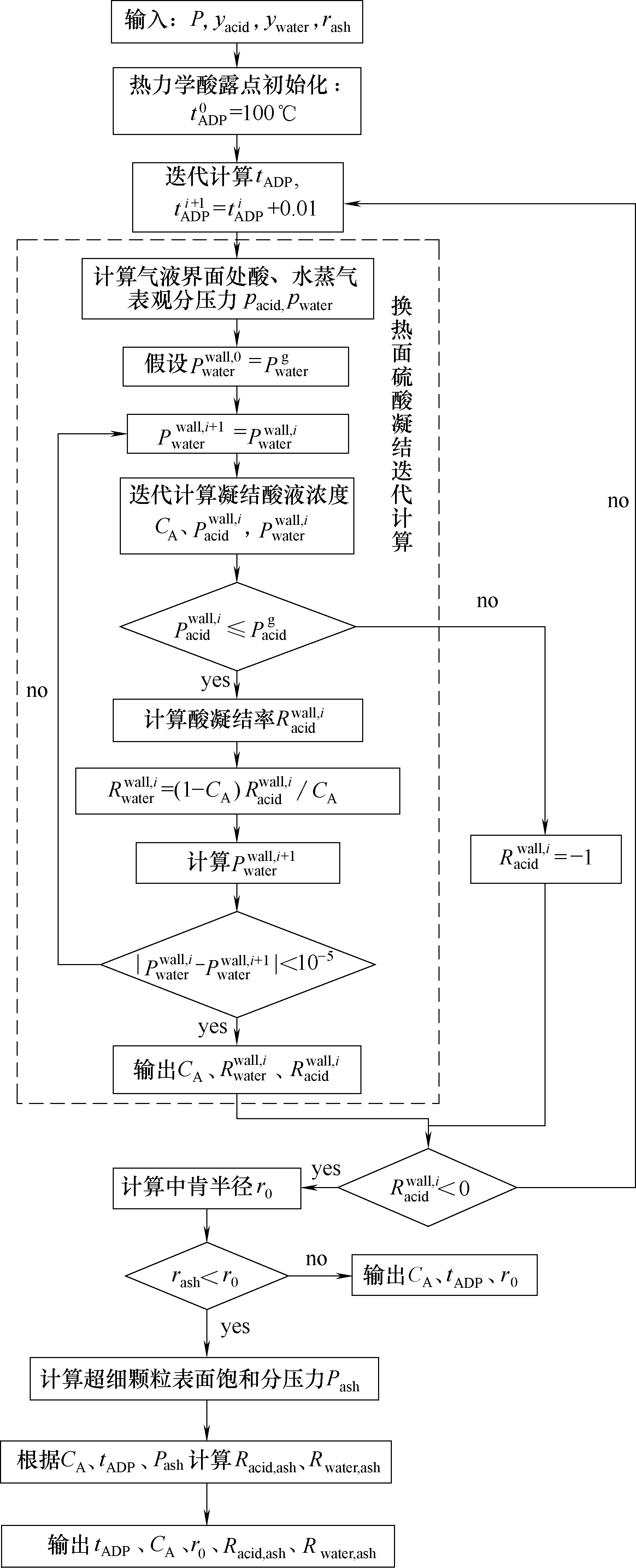
图1 考虑超细飞灰颗粒(rash<r0)的迭代计算模型图Pwaterwall,i、Pacidwall,i分别为气液平衡界面水蒸气和酸蒸气的饱和分压力;Pwaterg、Pacidg分别为烟气中的水蒸气和酸蒸气的饱和分压力
Fig.1 Flow chart of acid condensation calculation with account of fine ash particle (rash<r0)
| 过冷度/℃ | 酸液凝结率增加量/(g/(m2?s)) | 涨幅/% |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 357.18×10-6 | 124.57 |
| 10 | 221.77×10-6 | 46.87 |
| 15 | 134.68×10-6 | 22.78 |
| 20 | 79.75×10-6 | 12 |
| 25 | 45.98×10-6 | 6.49 |
| 30 | 25.68×10-6 | 3.5 |
| 35 | 13.83×10-6 | 1.84 |
| 40 | 7.11×10-6 | 0.94 |
表1 不同过冷度下酸液凝结率涨幅的汇总表
Table 1 Summary of acid condensation rate increment under different degree of supercooling
| 过冷度/℃ | 酸液凝结率增加量/(g/(m2?s)) | 涨幅/% |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 357.18×10-6 | 124.57 |
| 10 | 221.77×10-6 | 46.87 |
| 15 | 134.68×10-6 | 22.78 |
| 20 | 79.75×10-6 | 12 |
| 25 | 45.98×10-6 | 6.49 |
| 30 | 25.68×10-6 | 3.5 |
| 35 | 13.83×10-6 | 1.84 |
| 40 | 7.11×10-6 | 0.94 |
| 超细颗粒质量比/% | 反应后烟气含酸量/ (μl/L) | 反应后烟气含水量 /% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19.782 | 9.995 |
| 2 | 19.564 | 9.989 |
| 3 | 19.346 | 9.984 |
| 4 | 19.128 | 9.979 |
| 5 | 18.91 | 9.974 |
表2 超细颗粒质量比对降低烟气酸蒸气含量的汇总表
Table 2 Effect of fine ash particles mass ratio on reducing gas compositions
| 超细颗粒质量比/% | 反应后烟气含酸量/ (μl/L) | 反应后烟气含水量 /% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19.782 | 9.995 |
| 2 | 19.564 | 9.989 |
| 3 | 19.346 | 9.984 |
| 4 | 19.128 | 9.979 |
| 5 | 18.91 | 9.974 |
| 反应时间/s | 反应后烟气含酸量/(μl/L) | 反应后烟气含水量/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19.978 | 9.999 |
| 5 | 19.891 | 9.997 |
| 10 | 19.782 | 9.995 |
| 20 | 19.564 | 9.989 |
| 30 | 19.346 | 9.984 |
表3 反应时间对降低烟气酸蒸气含量的汇总表
Table 3 Effect of reaction time on reducing gas compositions
| 反应时间/s | 反应后烟气含酸量/(μl/L) | 反应后烟气含水量/% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 19.978 | 9.999 |
| 5 | 19.891 | 9.997 |
| 10 | 19.782 | 9.995 |
| 20 | 19.564 | 9.989 |
| 30 | 19.346 | 9.984 |
| 烟气温度/℃ | 反应后烟气含酸量/(μl/L) | 反应后烟气含水量/% |
|---|---|---|
| 120 | 19.778 | 9.996 |
| 110 | 19.776 | 9.995 |
| 100 | 19.782 | 9.995 |
| 90 | 19.791 | 9.994 |
| 80 | 19.801 | 9.993 |
表4 烟气温度对降低烟气酸蒸气含量的汇总表
Table 4 Effect of gas temperature on reducing gas compositions
| 烟气温度/℃ | 反应后烟气含酸量/(μl/L) | 反应后烟气含水量/% |
|---|---|---|
| 120 | 19.778 | 9.996 |
| 110 | 19.776 | 9.995 |
| 100 | 19.782 | 9.995 |
| 90 | 19.791 | 9.994 |
| 80 | 19.801 | 9.993 |
| 1 | 岑可法, 樊建人, 池作和, 等. 锅炉和热交换器的积灰、结渣、磨损和腐蚀的防止原理与计算[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994. |
| Qin K F, Fan J R, Chi Z H, et al. Boiler and Heat Exchanger Fouling, Slagging, Abrasion and Corrosion Prevention Principles and Calculation[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994. | |
| 2 | Li M, Tang S, Wang F, et al. Gas-side fouling, erosion and corrosion of heat exchangers for middle/low temperature waste heat utilization: a review on simulation and experiment[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 126: 737-761. |
| 3 | 冯俊凯, 沈幼庭, 杨瑞昌. 锅炉原理及计算 [M]. 3版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003. |
| Feng J K, Shen Y T, Yang R C. Principle and Calculation of the Boiler [M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Science Press, 2003. | |
| 4 | Noda N, Makino H. Influence of operating temperature on performance of electrostatic precipitator for pulverized coal combustion boiler[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2010, 21(4): 495-499. |
| 5 | ZareNezhad B, Aminian A. Accurate prediction of the dew points of acidic combustion gases by using an artificial neural network model[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2011, 52(2): 911-916. |
| 6 | Cox W, Huijbregts W, Leferink R. Components susceptible to dew-point corrosion[J]. ASM Handbook, Corrosion: Environments and Industries, 2006, (13): 491-496. |
| 7 | Huijbregts W M M, Leferink R. Latest advances in the understanding of acid dewpoint corrosion: corrosion and stress corrosion cracking in combustion gas condensates[J]. Anti-corrosion Methods and Materials, 2004, 51(3): 173-188. |
| 8 | 王晓芳, 佟会玲, 马千里, 等. 循环流化床烟气脱硫塔内烟气露点的测定[J]. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 28(5): 13-16. |
| Wang X F, Tong H L, Ma Q L, et al. Measurements of dew point temperature of flue gas in circulating fluidized bed reactor for flue gas desulfurization[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2003, 28(5): 13-16. | |
| 9 | 石丽国, 石立红, 王长权, 等. 燃煤锅炉烟气露点温度确定方法的分析[J]. 计量与测试技术, 2008, 35(9): 69-70. |
| Shi L G, Shi L H, Wang C Q, et al. The analysis of the measurement of flue gas dew point in the coal-fired boiler[J]. Metrology & Measurement Technique, 2008, 35(9): 69-70. | |
| 10 | Xiang B, Tang B, Wu Y, et al. Predicting acid dew point with a semi-empirical model[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 106: 992-1001. |
| 11 | 向柏祥, 赵从振, 丁艳军, 等. 烟气酸露点的测量和预测模型分析[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 55(10): 1117-1124. |
| Xiang B X, Zhao C Z, Ding Y J, et al. Measuring and analyzing the prediction model on the acid dew point in flue gas[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2015, 55(10): 1117-1124. | |
| 12 | Blanco J M, Peña F. Increase in the boiler’s performance in terms of the acid dew point temperature: environmental advantages of replacing fuels[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2008, 28(7): 777-784. |
| 13 | 张基标, 郝卫, 赵之军, 等. 锅炉烟气低温腐蚀的理论研究和工程实践[J]. 动力工程学报, 2011, 31(10): 730-733, 738. |
| Zhang J B, Hao W, Zhao Z J, et al. Theoretical and practical research on mechanism of low-temperature corrosion caused by boiler flue gas[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2011, 31(10): 730-733, 738. | |
| 14 | Wang Y C, Tang G H. Prediction of sulfuric acid dew point temperature on heat transfer fin surface[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 98: 492-501. |
| 15 | 王禹晨, 唐桂华. 新型换热表面硫酸腐蚀特性的数值预测[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(z1): 76-83. |
| Wang Y C, Tang G H. Numerical predictions of sulfuric acid corrosion on novel heat transfer surfaces[J]. CIESC Jorunal, 2016, 67(z1): 76-83. | |
| 16 | 王凤平, 李明, 陈华, 等. 混合烟气体系露点温度的热力学分析[J]. 石油化工腐蚀与防护, 2002, 19(1): 56-58. |
| Wang F P, Li M, Chen H, et al. Thermodynamic analysis of dew point temperature in mixed flue gas system [J]. Petrochemical Corrosion and Protection, 2002, 19(1): 56-58. | |
| 17 | 李志敏. 燃煤锅炉排烟的酸-灰耦合作用与露点的动态变化机制研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2016. |
| Li Z M. Research on acid-grey couping mechanism and dew point dynamic characteristics of coal-fired boiler[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2016. | |
| 18 | Wei W, Sun F, Shi Y, et al. Theoretical prediction of acid dew point and safe operating temperature of heat exchangers for coal-fired power plants[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 123: 782-790. |
| 19 | 金保升, 唐志永, 孙克勤, 等. 燃煤电站烟囱中硫酸冷凝沉积速度的数值预测[J].中国电机工程学报, 2006, 26(9): 40-44. |
| Jin B S, Tang Z Y, Sun K Q, et al. Numerical prediction of the deposit rate of condensed sulfuric acid from the flue gas of power plant chimney[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2006, 26(9): 40-44. | |
| 20 | 王花. 火电厂脱硫装置酸腐蚀现象的研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2010. |
| Wang H. Acid corrosion phenomenon reasearch of WFGD in power plant[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2010. | |
| 21 | Jeong K. Condensation of water vapor and sulfuric acid in boiler flue gas[D]. Bethlehem: Lehigh University, 2009. |
| 22 | Jeong K, Levy E K. Theoretical prediction of sulfuric acid condensation rates in boiler flue gas[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(25/26): 8010-8019. |
| 23 | He Y, Han H, Tang S, et al. Sulfuric acid deposition characteristics of H-type finned tube bank with 10 rows[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 81: 137-141. |
| 24 | Wang Y, Tang G. Acid condensation and heat transfer characteristics on H-type fin surface with bleeding dimples and longitudinal vortex generators[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(33): 4405-4417. |
| 25 | Han H, He Y L, Tao W Q. A numerical study of the deposition characteristics of sulfuric acid vapor on heat exchanger surfaces[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 101: 620-630. |
| 26 | Chen H, Pan P, Wang Y, et al. Field study on the corrosion and ash deposition of low-temperature heating surface in a large-scale coal-fired power plant[J]. Fuel, 2017, 208: 149-159. |
| 27 | Chen H, Pan P, Chen X, et al. Fouling of the flue gas cooler in a large-scale coal-fired power plant[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 117: 698-707. |
| 28 | 陈则韶. 高等工程热力学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2008. |
| Chen Z S. Advanced Engineering Thermodynamics[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2008. | |
| 29 | King M J, Davenport W G, Moats M S. Sulfuric Acid Manufacture Analysis, Control and Optimization [M]. 2nd ed. Burlington: Elsevier Publications, 2013. |
| 30 | Louie D K. Handbook of Sulphuric Acid Manufacturing[M]. DKL Engineering Inc., 2008. |
| 31 | Hodge F G, Silence W L. Predicting the corrosivity of an operating FGD system[J]. Power Engineering, 1994, (12): 30-33. |
| 32 | Dietz R, Marchal D. Attempt to predict quantitatively the acid deposits formed downstream of furnaces operating on heavy fuel oil[J]. International Chemical Engineering, 1977, 17(4): 583-591. |
| 33 | Cheney J L, Fortune C R. The present relationships of sulfuric acid concentration to acid dewpoint for flue gases[J]. Analytical Letters, 1977, 10(10): 797-816. |
| 34 | 张志刚. 新型低温省煤器潮湿积灰清除方法的理论研究[D]. 吉林: 东北电力大学, 2015. |
| Zhang Z G. The theoretical study of wet fouling removal method on the new low temperature economizer[D]. Jilin: Northeast Dianli University, 2015. | |
| 35 | 岳勇, 陈雷, 姚强, 等. 燃煤锅炉颗粒物粒径分布和痕量元素富集特性实验研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2005, 25(18): 74-79. |
| Yue Y, Chen L, Yao Q, et al. Experimental study on characteristics of particulate matter size distribution and trace elements enrichment in emissions from a pulverized coal-fired boiler[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2005, 25(18): 74-79. | |
| 36 | 刘娟娟, 乔晓磊, 冯翠英, 等. 循环流化床锅炉飞灰微观特性的研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2011, 36(11): 1922-1927. |
| Liu J J, Qiao X L, Feng C Y, et al. Research on microcosmic characteristics of fly-ash from circulating fluidized bed boilers[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2011, 36(11): 1922-1927. | |
| 37 | 齐立强, 阎维平, 原永涛. 燃煤锅炉电除尘器飞灰物化性质及逃逸机制[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2007, 27(5): 45-48. |
| Qi L Q, Yan W P, Yuan Y T, et al. Physicochemical characteristics and the mechanism of fly ash escaped from electrostatic precipitator of coal-fired boiler[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2007, 27(5): 45-48. |
| [1] | 苏伟, 马东旭, 金旭, 刘忠彦, 张小松. 表面润湿性对霜层传递特性影响可视化实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 122-131. |
| [2] | 曹跃, 余冲, 李智, 杨明磊. 工业数据驱动的加氢裂化装置多工况切换过渡状态检测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3841-3854. |
| [3] | 杨克, 贾岳, 纪虹, 邢志祥, 蒋军成. 垃圾焚烧飞灰对瓦斯爆炸压力及火焰传播的抑制作用及机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3597-3607. |
| [4] | 诸程瑛, 王振雷. 基于改进深度强化学习的乙烯裂解炉操作优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3429-3437. |
| [5] | 尹刚, 李伊惠, 何飞, 曹文琦, 王民, 颜非亚, 向禹, 卢剑, 罗斌, 卢润廷. 基于KPCA和SVM的铝电解槽漏槽事故预警方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3419-3428. |
| [6] | 周继鹏, 何文军, 李涛. 异形催化剂上乙烯催化氧化失活动力学反应工程计算[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2416-2426. |
| [7] | 高学金, 姚玉卓, 韩华云, 齐咏生. 基于注意力动态卷积自编码器的发酵过程故障监测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2503-2521. |
| [8] | 时国华, 何林珅, 赵玺灵, 张世钢. 余热回收喷淋塔的烟气颗粒物脱除特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1735-1745. |
| [9] | 郑书闽, 郭鹏程, 颜建国, 王帅, 李文博, 周淇. 微小通道内过冷流动沸腾阻力特性实验及预测研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1549-1560. |
| [10] | 王瑞恒, 何品晶, 吕凡, 章骅. 垃圾焚烧飞灰水洗后三种固液分离方法参数比较及优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1712-1723. |
| [11] | 顾学荣, 刘硕士, 杨思宇. 基于并行EGO和代理模型辅助的多参数优化方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1205-1215. |
| [12] | 张生安, 刘桂莲. 高效太阳能电解水制氢系统及其性能的多目标优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1260-1274. |
| [13] | 袁海鸥, 叶方俊, 张硕, 罗祎青, 袁希钢. 考虑中间换热器的能量集成精馏序列合成[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 796-806. |
| [14] | 陈家辉, 杨鑫泽, 陈顾中, 宋震, 漆志文. 以离子液体密度为例的分子性质预测模型建模方法探讨[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 630-641. |
| [15] | 王雅琳, 潘雨晴, 刘晨亮. 基于GSA-LSTM动态结构特征提取的间歇过程监测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3994-4002. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号