化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (S1): 282-292.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190795
毛海涛1( ),王璐1,许志颖2,解万翠2,都健1,张磊1(
),王璐1,许志颖2,解万翠2,都健1,张磊1( )
)
收稿日期:2019-07-10
修回日期:2019-09-13
出版日期:2020-04-25
发布日期:2020-04-25
通讯作者:
张磊
作者简介:毛海涛(1994—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Haitao MAO1( ),Lu WANG1,Zhiying XU2,Wancui XIE2,Jian DU1,Lei ZHANG1(
),Lu WANG1,Zhiying XU2,Wancui XIE2,Jian DU1,Lei ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2019-07-10
Revised:2019-09-13
Online:2020-04-25
Published:2020-04-25
Contact:
Lei ZHANG
摘要:
由于混合物性能的可调控性,当前市场对其关注与日俱增。对于这类产品,基于模型的设计方法由于具有高效性以及普适性,相较于其他产品设计方法得到了更快的发展。但是对于很多性质,如气味、颜色等,准确且普适的模型尚不可得。因此,本文提出了一种基于分子表面电荷密度分布描述符(S描述符)和机器学习模型的混合物设计方法,采用描述符表征产品、再通过机器学习模型将其与性质关联,直接用于混合物产品设计。具体地,根据给定的产品性质需求,机器学习模型直接预测/设计混合物产品的S描述符;然后以欧几里德距离为指标,在给定的数据库中筛选出S描述符满足要求的候选混合物组成。最后,对候选混合物及其组分性质进行实验验证,完成设计。本文以香精的混合替代物设计作为算例,设计得到丙酸叶醇酯的两种混合香精替代物,通过实验对混合物进行了验证。结果表明,混合替代物的气味及其组分的各理化性质均与丙酸叶醇酯相近,证实本文所提出方法的有效性。
中图分类号:
毛海涛, 王璐, 许志颖, 解万翠, 都健, 张磊. 基于分子表面电荷密度分布与机器学习的混合物设计方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(S1): 282-292.
Haitao MAO, Lu WANG, Zhiying XU, Wancui XIE, Jian DU, Lei ZHANG. Mixture product design based on molecular surface charge density distribution and machine learning[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(S1): 282-292.
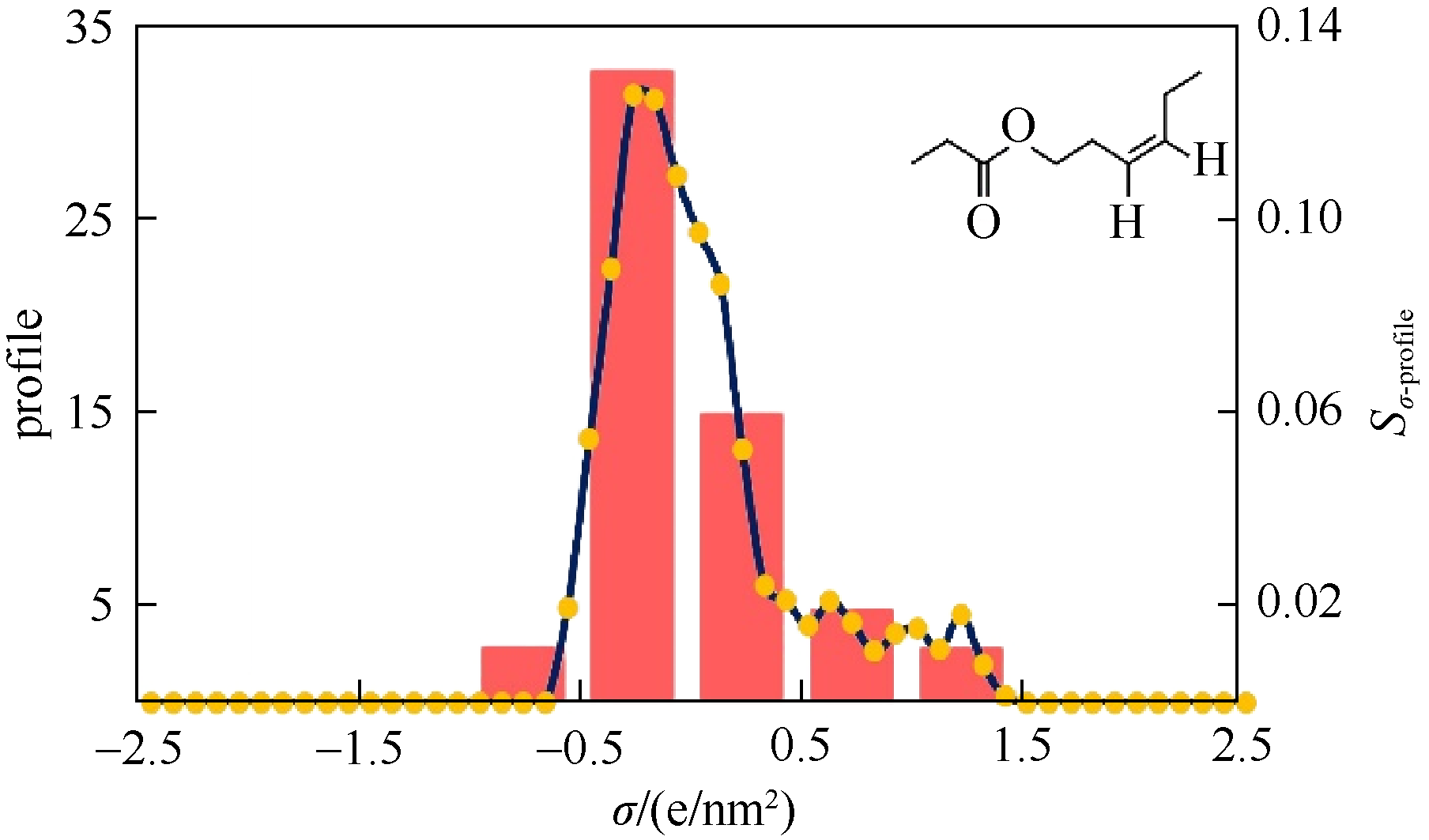
图1 分子表面电荷密度分布谱图以及对其极性区域积分得到的S描述符
Fig.1 Molecular surface charge density distribution spectrum and S descriptors integrated from the polar area of spectrum
| 组分性质 | 基团贡献法公式 | 阈值 |
|---|---|---|
表1 基团贡献法以及阈值
Table 1 Group contribution method and corresponding thresholds
| 组分性质 | 基团贡献法公式 | 阈值 |
|---|---|---|
| 传感器名称 | 检测气味类型 | 检出限/ (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| W1C | 有机化合物 | 10 |
| W5S | 氮氧化物 | 1 |
| W3C | 氨类 | 10 |
| W6S | 氢气 | 0.1 |
| W5C | 烷烃与非极性有机化合物 | 1 |
| W1S | 甲烷 | 100 |
| W1W | 含硫有机化合物 | 1 |
| W2S | 酒精 | 100 |
| W2W | 无机硫 | 1 |
| W3S | 有机化合物以及脂肪族有机化合物 | 10 |
表2 PEN3电子鼻的检测对象以及检出限
Table 2 Detected objections and detection limits of PEN3 E-nose
| 传感器名称 | 检测气味类型 | 检出限/ (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| W1C | 有机化合物 | 10 |
| W5S | 氮氧化物 | 1 |
| W3C | 氨类 | 10 |
| W6S | 氢气 | 0.1 |
| W5C | 烷烃与非极性有机化合物 | 1 |
| W1S | 甲烷 | 100 |
| W1W | 含硫有机化合物 | 1 |
| W2S | 酒精 | 100 |
| W2W | 无机硫 | 1 |
| W3S | 有机化合物以及脂肪族有机化合物 | 10 |
| 参数 | 数值 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 可食用 | 32.42 | 馊味 | 25.93 |
| 烘焙味 | 43.00 | 愉悦度 | 60.19 |
| 甜味 | 34.37 | 蒸气压/Pa | 53.86 |
| 水果味 | 31.54 | 扩散系数/(m2/h) | 0.16 |
| 花香味 | 29.95 |
表3 丙酸叶醇酯的物性需求
Table 3 First consumer needs of cis-3-hexenyl propionate
| 参数 | 数值 | 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 可食用 | 32.42 | 馊味 | 25.93 |
| 烘焙味 | 43.00 | 愉悦度 | 60.19 |
| 甜味 | 34.37 | 蒸气压/Pa | 53.86 |
| 水果味 | 31.54 | 扩散系数/(m2/h) | 0.16 |
| 花香味 | 29.95 |
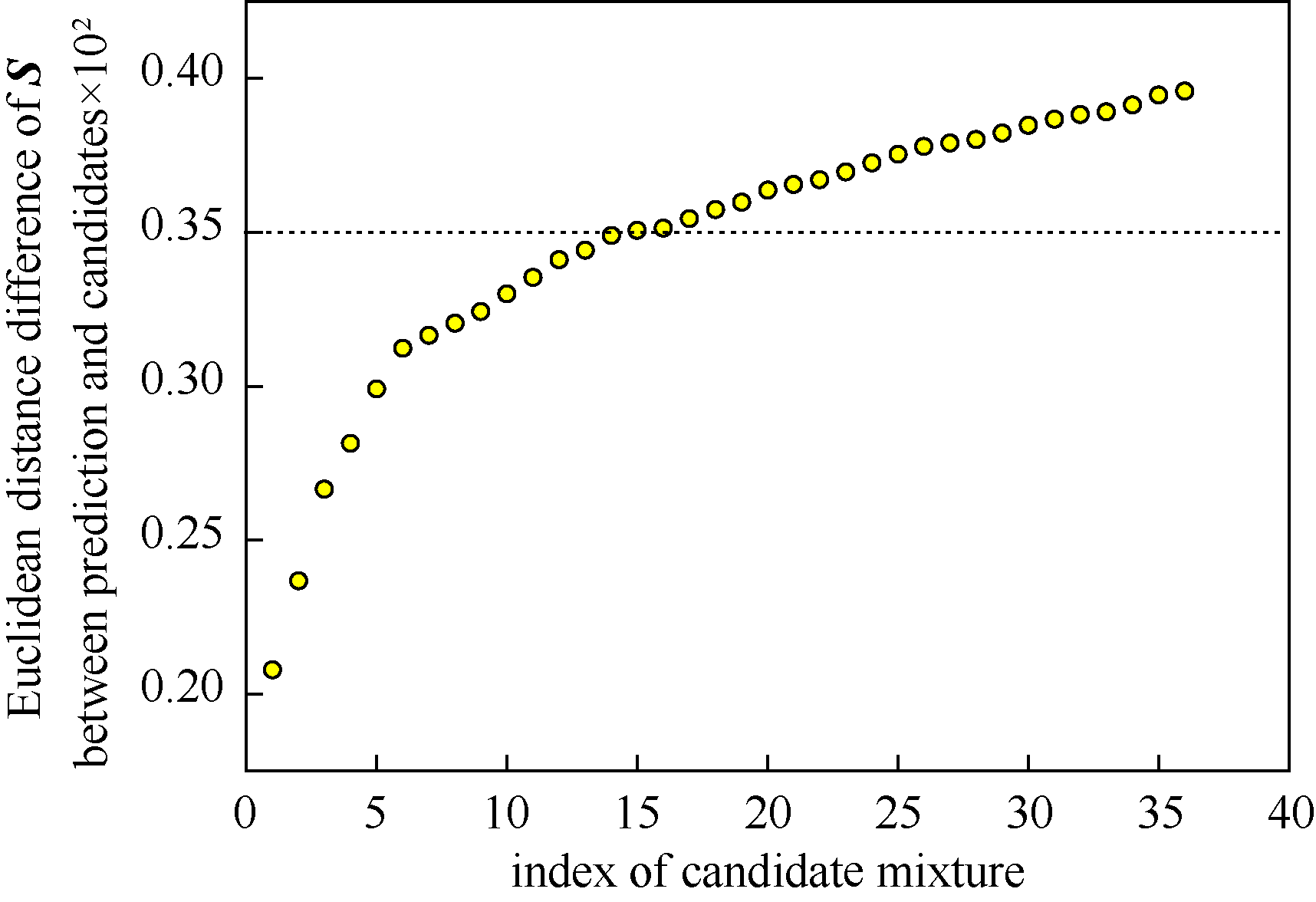
图6 IML模型预测结果与Keller数据库中组合的替代混合物之间的S描述符欧氏距离差
Fig.6 Euclidean distance differences between S descriptors predicted by IML models and screened ingredients from Keller database for cis-3-hexenyl propionate substitution
| 参数 | 丙酸叶醇酯 | 替代混合物1 | 替代混合物2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-异丙基苯甲醇 | 左旋香芹酮 | 混合物偏差 | 2-甲基戊酸 | 2-乙基丁酸烯丙酯 | 混合物偏差 | ||
| CAS No. | 33467-74-2 | 536-60-7 | 6485-40-1 | — | 97-61-0 | 7493-69-8 | — |
| 体积分数 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | — | 0.4 | 0.6 | — |
| 溶解度 | 158.9 | 1687 | 367.1 | 472.18 | 15000 | 157.3 | 5935.48 |
| 沸点Tb①(101.325 kPa) /K | 453-455 | 512.66 | 499.47 | 47.11-49.11 | 468.36 | 449.96 | 2.32-4.32 |
| 闪点Tf①/K | 333 | 498.15 | 465.15 | 138.75 | 364.26 | 327.59 | 9.258 |
| Ko/w① | 2.909 | 2.37 | 2.71 | -0.267 | 1.8 | 2.972 | -0.4058 |
| LC50②/(mol·L-1) | 3.36 | 3.25 | 3.39 | 0.002 | 2.45 | 4.03 | 0.038 |
表4 丙酸叶醇酯替代香精的设计结果
Table 4 Results for substitution design of cis-3-hexenyl propionate
| 参数 | 丙酸叶醇酯 | 替代混合物1 | 替代混合物2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-异丙基苯甲醇 | 左旋香芹酮 | 混合物偏差 | 2-甲基戊酸 | 2-乙基丁酸烯丙酯 | 混合物偏差 | ||
| CAS No. | 33467-74-2 | 536-60-7 | 6485-40-1 | — | 97-61-0 | 7493-69-8 | — |
| 体积分数 | 1 | 0.2 | 0.8 | — | 0.4 | 0.6 | — |
| 溶解度 | 158.9 | 1687 | 367.1 | 472.18 | 15000 | 157.3 | 5935.48 |
| 沸点Tb①(101.325 kPa) /K | 453-455 | 512.66 | 499.47 | 47.11-49.11 | 468.36 | 449.96 | 2.32-4.32 |
| 闪点Tf①/K | 333 | 498.15 | 465.15 | 138.75 | 364.26 | 327.59 | 9.258 |
| Ko/w① | 2.909 | 2.37 | 2.71 | -0.267 | 1.8 | 2.972 | -0.4058 |
| LC50②/(mol·L-1) | 3.36 | 3.25 | 3.39 | 0.002 | 2.45 | 4.03 | 0.038 |

图7 不同温度下丙酸叶醇酯及其替代混合物组分的蒸气压与扩散系数
Fig.7 Vapor pressure and diffusion coefficient for cis-3-hexenyl propionate and its substituted mixtures’ components of diverse temperatures
| 试剂 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 丙酸叶醇酯 | 北京迈瑞达科技有限公司,纯度>98% |
| 2-甲基戊酸 | 北京迈瑞达科技有限公司,纯度>98% |
| 2-乙基丁酸烯丙酯 | 北京迈瑞达科技有限公司,纯度>97% |
| 4-异丙基苯甲醇 | 河南郑州阿尔法化工有限公司,纯度>99% |
| 左旋香芹酮 | 河南郑州阿尔法化工有限公司,纯度>97% |
| 95%乙醇 | 天津市富宇化工有限公司 |
表5 丙酸叶醇酯替代混合物的测试实验设备以及试剂
Table 5 Equipment and materials for substitution of cis-3-hexenyl propionate
| 试剂 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 丙酸叶醇酯 | 北京迈瑞达科技有限公司,纯度>98% |
| 2-甲基戊酸 | 北京迈瑞达科技有限公司,纯度>98% |
| 2-乙基丁酸烯丙酯 | 北京迈瑞达科技有限公司,纯度>97% |
| 4-异丙基苯甲醇 | 河南郑州阿尔法化工有限公司,纯度>99% |
| 左旋香芹酮 | 河南郑州阿尔法化工有限公司,纯度>97% |
| 95%乙醇 | 天津市富宇化工有限公司 |
| 1 | Rodríguez O, Gomes P, Mata V, et al. Chapter 1 - A Product Engineering Approach in the Perfume Industry [M]//Teixeira M A. Perfume Engineering. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2019: 1-13. |
| 2 | Wibowo C, Ng K M. Product-oriented process synthesis and development: creams and pastes[J]. AIChE Journal, 2001, 47(12): 2746-2767. |
| 3 | Fung K Y, Ng K M. Product-centered processing: pharmaceutical tablets and capsules[J]. AIChE Journal, 2003, 49(5): 1193-1215. |
| 4 | Gani R, Brignole E A. Molecular design of solvents for liquid extraction based on UNIFAC[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 1983, 13(83): 331-340. |
| 5 | Joback K G. Designing molecules possessing desired physical property values[D]. Massachusetts: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1989 |
| 6 | Conte E, Gani R, Ng K M. Design of formulated products: a systematic methodology[J]. AIChE Journal, 2011, 57: 2431-2449. |
| 7 | Kontogeorgis G M, Michele M, Ng K M, et al. An integrated approach for the design of emulsified products[J]. AIChE Journal, 2019, 65: 75-86. |
| 8 | 张磊, 刘琳琳, 都健. 替代燃油的计算机辅助设计方法[J]. 化工进展, 2018, 37(6): 2438-2444. |
| Zhang L, Liu L L, Du J. A computer-aided design methodology for tailor-made surrogate fuels[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2018, 37(6): 2438-2444. | |
| 9 | Hornic K. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators[J]. Neural Networks, 1989, 2: 359-366. |
| 10 | Raccuglia P, Elbert K C, Adler P D, et al. Machine-learning-assisted materials discovery using failed experiments[J]. Nature, 2016, 533: 73-76. |
| 11 | 苏荣欣, 邹龙花, 齐崴, 等. 酪蛋白-胰酶水解历程分子量变化模拟与三维表征[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(1): 346-351. |
| Su R X, Zou L H, Qi W, et al. Simulation and 3D plot of molecular weight distribution of released peptides from pancreatic hydrolysis of casein[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(1): 346-351. | |
| 12 | 黄凯, 陈勇, 母志为, 等. 基于人工神经网络和遗传算法的甲烷制氢催化剂设计[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(8): 3481-3490. |
| Huang K, Chen Y, Mu Z W, et al. Catalyst design for production of hydrogen from methane based on artificial neural network and genetic algorithm[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(8): 3481-3490. | |
| 13 | 安爱民, 刘云利, 张浩琛, 等. 微生物燃料电池的动态性能分析及其神经网络预测控制[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(3): 1090-1098. |
| An A M, Liu Y L, Zhang H C, et al. Dynamic performance analysis and neural network predictive control of microbial fuel cell[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(3): 1090-1098. | |
| 14 | 林生岭, 徐绍芬, 王俊德, 等. 钙钛矿型LaxSr1-xNi1-yCoyO3光电催化活性研究[J]. 化学学报, 2005, 63(5): 385-390. |
| Lin S L, Xu S F, Wang J D, et al. Study on photo-electro catalytic activity of perovskite type oxides LaxSr1-xNi1-yCoyO3[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2005, 63(5): 385-390. | |
| 15 | Zhang L, Mao H, Liu L, et al. A machine learning based computer-aided molecular design/screening methodology for fragrance molecules[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2018, 115: 295-308. |
| 16 | Sanchez-Lengeling B, Aspuru-Guzik A. Inverse molecular design using machine learning: generative models for matter engineering[J]. Science, 2018, 361: 360-365. |
| 17 | Klamt A, Schueuermann G J. COSMO: a new approach to dielectric screening in solvents with explicit expressions for the screening energy and its gradient[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions II, 1993, 5: 799-805. |
| 18 | Rossiter K J. Structure-odor relationships[J]. Chemical Review, 1996, 96: 3201-3240. |
| 19 | Klamt A, Reinisch J, Eckert F, et al. Polarization charge densities provide a predictive quantification of hydrogen bond energies[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2011, 14(2): 955-963. |
| 20 | Lin S T, Sandler S I. A priori phase equilibrium prediction from a segment contribution solvation model[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2002, 41(5): 899-913. |
| 21 | Klamt A, Eckert F, Arlt W. COSMO-RS: an alternative to simulation for calculating thermodynamic properties of liquid mixtures[J]. Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, 2010, 1: 101-122. |
| 22 | Kang X, Liu X, Li J, et al. Heat capacity prediction of ionic liquids based on quantum chemistry descriptors[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(49): 16989-16994. |
| 23 | Kang X, Zhao Z, Qian J, et al. Predicting the viscosity of ionic liquids by the ELM intelligence algorithm[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2017, 56(39): 11344-11351. |
| 24 | Palomart J, Torrecilla J S, Ferro V R, et al. Development of an a priori ionic liquid design tool (Ⅱ): Ionic liquid selection through the prediction of COSMO-RS molecular descriptor by inverse neural network[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009, 48(4): 2257-2265. |
| 25 | Keller A, Vosshall L B. Olfactory perception of chemically diverse molecules[J]. BMC Neuroscience, 2016, 17: 55. |
| 26 | 周志华. 机器学习[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2016: 23-53. |
| Zhou Z H. Machine Learning[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2016: 23-53. | |
| 27 | 刘方, 徐龙, 马晓迅. BP神经网络的发展及其在化学化工中的应用[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(6): 2559-2573. |
| Liu F, Xu L, Ma X X. Development of BP neural network and its application in chemistry and chemical engineering[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(6): 2559-2573. | |
| 28 | de Bruyne M, Foster K, Carlson J R. Odor coding in the Drosophila antenna[J]. Neuron, 2001, 30(2): 537-552. |
| 29 | Tamir A. In Applications of Markov Chains in Chemical Engineering[M]. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier, 1998. |
| 30 | Marrero J, Gani R. Group-contribution based estimation of pure component properties[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2001, 183: 183-208. |
| 31 | Hukkerikar A S. Development of pure component property models for chemical product-process design and analysis[D]. Denmark: Technical University of Denmark, 2013. |
| 32 | 马琦, 伯继芳, 冯莉, 等. GC-MS结合电子鼻分析干燥方式对杏鲍菇挥发性风味成分的影响[J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(14): 276-282. |
| Ma Q, Bo J F, Feng L, et al. Effect of drying method on volatile components of pleurotus eryngii analyzed by combined use of GC-MS and electronic nose[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(14): 276-282. | |
| 33 | Reid R C, Prausnitz J M, Poling B E. The Properties of Gases & Liquids[M]. New York: McGrawHill, 1988. |
| 34 | Lee B I, Kesler M. A generalized thermodynamic correlation based on three-parameter corresponding states[J]. AIChE Journal, 1975, 21: 510-527. |
| [1] | 温凯杰, 郭力, 夏诏杰, 陈建华. 一种耦合CFD与深度学习的气固快速模拟方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3775-3785. |
| [2] | 尹刚, 李伊惠, 何飞, 曹文琦, 王民, 颜非亚, 向禹, 卢剑, 罗斌, 卢润廷. 基于KPCA和SVM的铝电解槽漏槽事故预警方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3419-3428. |
| [3] | 诸程瑛, 王振雷. 基于改进深度强化学习的乙烯裂解炉操作优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3429-3437. |
| [4] | 闫琳琦, 王振雷. 基于STA-BiLSTM-LightGBM组合模型的多步预测软测量建模[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3407-3418. |
| [5] | 徐野, 黄文君, 米俊芃, 申川川, 金建祥. 多源信息融合的离心式压缩机喘振诊断方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2979-2987. |
| [6] | 高学金, 姚玉卓, 韩华云, 齐咏生. 基于注意力动态卷积自编码器的发酵过程故障监测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2503-2521. |
| [7] | 黄磊, 孔令学, 白进, 李怀柱, 郭振兴, 白宗庆, 李平, 李文. 油页岩添加对准东高钠煤灰熔融行为影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2123-2135. |
| [8] | 贠程, 王倩琳, 陈锋, 张鑫, 窦站, 颜廷俊. 基于社团结构的化工过程风险演化路径深度挖掘[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1639-1650. |
| [9] | 吴心远, 刘奇磊, 曹博渊, 张磊, 都健. Group2vec:基于无监督机器学习的基团向量表示及其物性预测应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1187-1194. |
| [10] | 王子宗, 索寒生, 赵学良. 数字孪生智能乙烯工厂研究与构建[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1175-1186. |
| [11] | 张江淮, 赵众. 碳三加氢装置鲁棒最小协方差约束控制及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1216-1227. |
| [12] | 吴选军, 王超, 曹子健, 蔡卫权. 数据与物理信息混合驱动的固定床吸附穿透深度学习模型[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1145-1160. |
| [13] | 王雅琳, 潘雨晴, 刘晨亮. 基于GSA-LSTM动态结构特征提取的间歇过程监测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3994-4002. |
| [14] | 高学金, 程琨, 韩华云, 高慧慧, 齐咏生. 基于中心损失的条件生成式对抗网络的冷水机组故障诊断[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3950-3962. |
| [15] | 周乐, 沈程凯, 吴超, 侯北平, 宋执环. 深度融合特征提取网络及其在化工过程软测量中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3156-3165. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号