化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2505-2523.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241243
郭乃胜1( ), 朱小波1, 王双2,3(
), 朱小波1, 王双2,3( ), 陈平3, 褚召阳1, 王志臣2,3
), 陈平3, 褚召阳1, 王志臣2,3
收稿日期:2024-11-02
修回日期:2024-12-10
出版日期:2025-06-25
发布日期:2025-07-09
通讯作者:
王双
作者简介:郭乃胜(1978—),男,博士,教授,naishengguo@126.com
基金资助:
Naisheng GUO1( ), Xiaobo ZHU1, Shuang WANG2,3(
), Xiaobo ZHU1, Shuang WANG2,3( ), Ping CHEN3, Zhaoyang CHU1, Zhichen WANG2,3
), Ping CHEN3, Zhaoyang CHU1, Zhichen WANG2,3
Received:2024-11-02
Revised:2024-12-10
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-07-09
Contact:
Shuang WANG
摘要:
聚氨酯(PU)因其性能调整自由度高而受到广泛关注。然而,其多样的性质导致学者在PU改性沥青的高低温流变性能改性效果上存在分歧。因此深入了解不同PU原料特性、合成工艺、成品结构与改性沥青高低温性能间的联系至关重要。基于PU的化学改性机理,结合分子形成过程与聚合物改性沥青的性能评价标准,系统探讨了不同种类软硬段的性质以及不同合成方法制备的PU改性剂的结构对于改性沥青的影响。研究表明,PU分子在沥青内部的物理交联与化学交联程度是性能改善的关键因素:软硬段性质及分子结构主要影响物理交联的微观结构稳定性,而异氰酸酯基团的含量直接决定了化学交联的强度和复杂性。进一步分析了PU与聚合物及其他改性剂的复合体系在沥青中的作用机理。外加改性剂通过改变沥青的内部组分与PU的结构分布来提升性能。然而,目前研究尚难通过微观结构精准量化PU的交联程度,这限制了合成参数与工艺的精确调控,进而导致改性效果的可预测性较低。此外,复合体系结构不稳定、改性剂间化学作用微弱等问题往往引发储存稳定性下降或某些性能劣化。最后,提出了PU及其复合改性沥青研究的发展趋势与展望。
中图分类号:
郭乃胜, 朱小波, 王双, 陈平, 褚召阳, 王志臣. 聚氨酯改性沥青高低温性能及影响因素的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2505-2523.
Naisheng GUO, Xiaobo ZHU, Shuang WANG, Ping CHEN, Zhaoyang CHU, Zhichen WANG. Research progress on high and low temperature performance and influencing factors of polyurethane modified asphalt[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2505-2523.
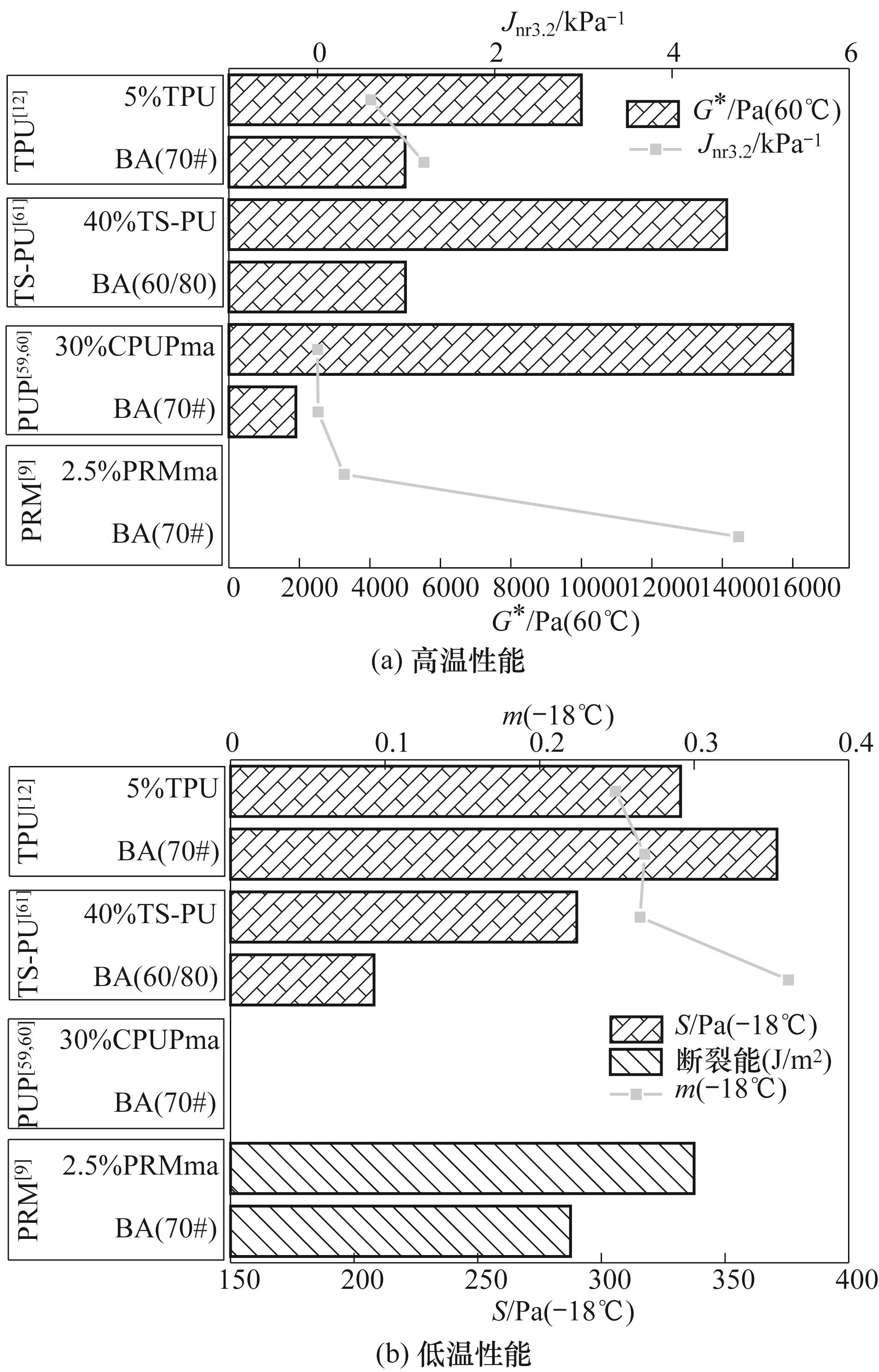
图13 不同分子结构下PU改性沥青的高低温性能的改性效果对比
Fig.13 Comparison of modification effects on high and low temperature properties of PU-modified asphalt with different molecular structures
| 复合改性剂 | 基质沥青 | 制备条件 | 参考样本 | 沥青改性效果 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高温流变性能 | 低温流变性能 | 抗永久变形能力 | 储存稳定性 | ||||
| EP+TSPU[ | 70# | 60℃搅拌3 min;60℃固化4 d | SBSMA | + | - | + | + |
| EP+TSPU[ | 70# | 150℃、500 r/min搅拌30 min;150℃、500 r/min搅拌3 min;150℃固化3 h;60℃养护4 d | SBSMA | + | + | + | + |
| EP+PUP[ | 80/100pen grade | 3000 r/min、(130±10)℃剪切2 h;同温度剪切40、5 min;120℃固化4 h | EPMA/PUMA | * | * | * | + |
| SBS+PUP[ | 60/80pen grade | 160℃、1500 r/min剪切10 min+15 min;5000 r/min剪切30 min,180℃养护2 h;120℃、1000 r/min剪切60 min+5 min+5 min;3000 r/min剪切20 min,固化2 h | SBSMA | * | * | + | + |
| CRM+TPU[ | PG64-22 | 177℃、700 r/min剪切30 min+60 min | CRMA/TPUMA | + | + | + | * |
| SBS+WTPU[ | 60/80pen grade | 175℃、3000 r/min剪切1 h;180℃、3000 r/min剪切1 h | SBSMA | - | + | + | - |
| APAO+WTPU[ | 60/80pen grade | 190℃、2000 r/min剪切30 min+20 min | BA/TPUMA | + | + | + | + |
| RET+PUP[ | 70# | 170~180℃、5000 r/min剪切2 h+1 h | RETMA | + | + | + | * |
表1 聚氨酯的聚合物复合体系及其改性效果
Table 1 Polymer composite modifiers and their modification effects
| 复合改性剂 | 基质沥青 | 制备条件 | 参考样本 | 沥青改性效果 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高温流变性能 | 低温流变性能 | 抗永久变形能力 | 储存稳定性 | ||||
| EP+TSPU[ | 70# | 60℃搅拌3 min;60℃固化4 d | SBSMA | + | - | + | + |
| EP+TSPU[ | 70# | 150℃、500 r/min搅拌30 min;150℃、500 r/min搅拌3 min;150℃固化3 h;60℃养护4 d | SBSMA | + | + | + | + |
| EP+PUP[ | 80/100pen grade | 3000 r/min、(130±10)℃剪切2 h;同温度剪切40、5 min;120℃固化4 h | EPMA/PUMA | * | * | * | + |
| SBS+PUP[ | 60/80pen grade | 160℃、1500 r/min剪切10 min+15 min;5000 r/min剪切30 min,180℃养护2 h;120℃、1000 r/min剪切60 min+5 min+5 min;3000 r/min剪切20 min,固化2 h | SBSMA | * | * | + | + |
| CRM+TPU[ | PG64-22 | 177℃、700 r/min剪切30 min+60 min | CRMA/TPUMA | + | + | + | * |
| SBS+WTPU[ | 60/80pen grade | 175℃、3000 r/min剪切1 h;180℃、3000 r/min剪切1 h | SBSMA | - | + | + | - |
| APAO+WTPU[ | 60/80pen grade | 190℃、2000 r/min剪切30 min+20 min | BA/TPUMA | + | + | + | + |
| RET+PUP[ | 70# | 170~180℃、5000 r/min剪切2 h+1 h | RETMA | + | + | + | * |
| 复合改性剂 | 基质沥青 | 制备条件 | 参考样本 | 沥青改性效果 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高温流变性能 | 低温流变性能 | 抗永久变形能力 | 储存稳定性 | ||||
| VO+COPU[ | 70# | 130~140℃、3000 r/min剪切30 min+45 min | VA | + | + | + | * |
| WO+MDI(Liquefied)[ | PG 64-22 | 140℃、3500 r/min剪切20 min+30 min;140℃、800 r/min剪切5 min+5 min;90℃固化1 h | WBBA | + | + | + | * |
| IS+COPU[ | 60/70pen grade | 125℃、2000 r/min剪切10 min | BA | + | + | + | + |
| GO+SBS+TPU[ | 90# | 160℃、300 r/min搅拌30 min;160℃、3000 r/min剪切45 min | TPU-SBSMA | + | + | * | * |
| Nano TiO2+TPU[ | 90# | 160℃、5000 r/min剪切0.5 h;130℃搅拌0.5 h;170℃、5000 r/min剪切0.5 h | BA | + | + | * | * |
| OMMT+TPU[ | 90# | (135±5)℃、2000 r/min剪切0.5 h+0.5 h;135℃固化1 h | BA | + | + | * | + |
| OATT+PUP[ | 60/80pen grade | 135℃、3000 r/min剪切15 min+30 min+1 h;125℃固化2 h | BA | + | + | * | - |
| BG+TPU[ | 70# | 135℃搅拌10 min;145℃、3000 r/min剪切40 min | BA/SBSMA | * | - | + | * |
| RA+TPU[ | 90# | 150℃、3000 r/min剪切0.5 h;150℃、5000 r/min剪切0.5 h | BA/PUMA/RAMA | + | + | + | * |
表2 聚氨酯的其他复合体系及其改性效果
Table 2 Other composite modifiers and their modification effects
| 复合改性剂 | 基质沥青 | 制备条件 | 参考样本 | 沥青改性效果 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高温流变性能 | 低温流变性能 | 抗永久变形能力 | 储存稳定性 | ||||
| VO+COPU[ | 70# | 130~140℃、3000 r/min剪切30 min+45 min | VA | + | + | + | * |
| WO+MDI(Liquefied)[ | PG 64-22 | 140℃、3500 r/min剪切20 min+30 min;140℃、800 r/min剪切5 min+5 min;90℃固化1 h | WBBA | + | + | + | * |
| IS+COPU[ | 60/70pen grade | 125℃、2000 r/min剪切10 min | BA | + | + | + | + |
| GO+SBS+TPU[ | 90# | 160℃、300 r/min搅拌30 min;160℃、3000 r/min剪切45 min | TPU-SBSMA | + | + | * | * |
| Nano TiO2+TPU[ | 90# | 160℃、5000 r/min剪切0.5 h;130℃搅拌0.5 h;170℃、5000 r/min剪切0.5 h | BA | + | + | * | * |
| OMMT+TPU[ | 90# | (135±5)℃、2000 r/min剪切0.5 h+0.5 h;135℃固化1 h | BA | + | + | * | + |
| OATT+PUP[ | 60/80pen grade | 135℃、3000 r/min剪切15 min+30 min+1 h;125℃固化2 h | BA | + | + | * | - |
| BG+TPU[ | 70# | 135℃搅拌10 min;145℃、3000 r/min剪切40 min | BA/SBSMA | * | - | + | * |
| RA+TPU[ | 90# | 150℃、3000 r/min剪切0.5 h;150℃、5000 r/min剪切0.5 h | BA/PUMA/RAMA | + | + | + | * |
| [1] | Cornille A, Auvergne R, Figovsky O, et al. A perspective approach to sustainable routes for non-isocyanate polyurethanes[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2017, 87: 535-552. |
| [2] | 洪斌, 陆国阳, 高峻凌, 等. 路用聚氨酯胶结料的抗紫外老化性能[J]. 中国公路学报, 2020, 33(10): 240-253. |
| Hong B, Lu G Y, Gao J L, et al. Anti-ultraviolet aging performance of polyurethane binders used in roads[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2020, 33(10): 240-253. | |
| [3] | 余苗, 龙承梁, 刘曲平. 聚氨酯超薄磨耗层抗滑性能衰变研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 42(7): 29-36, 68. |
| Yu M, Long C L, Liu Q P. Decay of slip resistance of polyurethane ultra-thin wear layer[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2023, 42(7): 29-36, 68. | |
| [4] | 徐世法, 张业兴, 郭昱涛, 等. 基于贯入阻力测试系统的聚氨酯混凝土压实时机确定方法[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(7): 226-235. |
| Xu S F, Zhang Y X, Guo Y T, et al. Determination of polyurethane concrete compaction timing based on penetration resistance test system[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(7): 226-235. | |
| [5] | Li X R, Li J, Wang J Y, et al. Recent applications and developments of polyurethane materials in pavement engineering[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 304: 124639. |
| [6] | Martín-Alfonso M J, Partal P, Navarro F J, et al. Role of water in the development of new isocyanate-based bituminous products[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(18): 6933-6940. |
| [7] | Huang G, Yang T H, He Z Y, et al. Polyurethane as a modifier for road asphalt: a literature review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 356: 129058. |
| [8] | Zhang L, Li P F, Hu G F, et al. Study on the aging resistance of polyurethane precursor modified bitumen and its mechanism[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(17): 9520. |
| [9] | 李添帅, 陆国阳, 梁栋, 等. 聚氨酯前驱体基化学改性沥青及其改性机理[J]. 中国公路学报, 2021, 34(10): 45-59. |
| Li T S, Lu G Y, Liang D, et al. Polyurethane-precursor-based chemically modified asphalt and its modification mechanism[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2021, 34(10): 45-59. | |
| [10] | Li Z L, Yang F, Yuan J J, et al. Study on preparation and pavement performance of polyurethane modified asphalt based on in situ synthesis method[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 309: 125196. |
| [11] | Wang M, Liu J H, Yan K Z. Research on the performance and mechanism of asphalt modified by thermoplastic polyurethane with different chemical structures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 409: 133814. |
| [12] | 金鑫. TPU改性沥青及胶浆的流变特性与内在机制研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学, 2021. |
| Jin X. Study on rheological properties and inherent mechanism of TPU modified asphalt and mastic[D]. Dalian: Dalian Maritime University, 2021. | |
| [13] | Zhang Z P, Wei Y M, Liu X S, et al. Combined modification of asphalt with organic attapulgite (OATT) and polyurethane (PU): preparation, properties and modification mechanisms[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 406: 133435. |
| [14] | Li S, Xu W Y, Zhang F F, et al. Effect of graphene oxide on the low-temperature crack resistance of polyurethane-SBS-modified asphalt and asphalt mixtures[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(3): 453. |
| [15] | Wu S H, Montalvo L. Repurposing waste plastics into cleaner asphalt pavement materials: a critical literature review[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 280: 124355. |
| [16] | Cong L, Yang F, Guo G H, et al. The use of polyurethane for asphalt pavement engineering applications: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 225: 1012-1025. |
| [17] | 金鑫, 郭乃胜, 尤占平, 等. 聚氨酯改性沥青研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(21): 3686-3694. |
| Jin X, Guo N S, You Z P, et al. Research and development trends of polyurethane modified asphalt[J]. Materials Reports, 2019, 33(21): 3686-3694. | |
| [18] | 赵孝彬, 杜磊, 张小平, 等. 聚氨酯弹性体及其微相分离[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2002, 18(2): 16-20. |
| Zhao X B, Du L, Zhang X P, et al. Polyurethane elastomers and microphase separation[J]. Polymeric Materials Science & Cngineering, 2002, 18(2): 16-20. | |
| [19] | Liu J, Lv S T, Peng X H, et al. Improvements on performance of bio-asphalt modified by castor oil-based polyurethane: an efficient approach for bio-oil utilization[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 305: 124784. |
| [20] | 区洁, 田立颖, 王新灵. 软硬段对聚氨酯弹性体结构性能的影响[J]. 功能高分子学报, 2010, 23(2): 160-165. |
| Ou J, Tian L Y, Wang X L. Effect of hard and soft segment on structure-property of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer[J]. Journal of Functional Polymers, 2010, 23(2): 160-165. | |
| [21] | Gallu R, Méchin F, Gérard J F, et al. Influence of the chain extender of a segmented polyurethane on the properties of polyurethane-modified asphalt blends[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 328: 127061. |
| [22] | Joshi M, Adak B, Butola B S. Polyurethane nanocomposite based gas barrier films, membranes and coatings: a review on synthesis, characterization and potential applications[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2018, 97: 230-282. |
| [23] | Yang T H, He Z Y, Huang G, et al. Study on materials composition and process parameters of polyurethane-modified asphalt synthesized in-situ by the one-shot process[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 374: 130661. |
| [24] | 王道珵. 聚合物改性沥青高温与低温性能评价指标研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2019. |
| Wang D C. Study on high and low temperature performance index of polymer modified asphalt[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2019. | |
| [25] | 袁迎捷, 张争奇, 胡长顺. Superpave沥青规范对改性沥青的适用性[J]. 长安大学学报(自然科学版), 2004, 24(1): 9-11. |
| Yuan Y J, Zhang Z Q, Hu C S. Applicability of superpave specification to modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Chang'an University(Natural Science Edition), 2004, 24(1): 9-11. | |
| [26] | Lin P, Huang W D, Li Y, et al. Investigation of influence factors on low temperature properties of SBS modified asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 154: 609-622. |
| [27] | Gong X, Liu Q T, Liu X F, et al. Green synthesis of end-capped polyurethane prepolymer with high storage stability and its effects on bitumen properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 401: 132860. |
| [28] | Xue Y H, Liu C C, Lv S T, et al. Research on rheological properties of CNT-SBR modified asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 361: 129587. |
| [29] | Wang H, Jing Y F, Zhang J P, et al. Preparation and performance evaluation of swine manure bio-oil modified rubber asphalt binder[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 294: 123584. |
| [30] | Zhao Z G, Wu S P, Liu Q T, et al. Recycling waste disposable medical masks in improving the performance of asphalt and asphalt mixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 337: 127621. |
| [31] | Zhang H L, Su M M, Zhao S F, et al. High and low temperature properties of nano-particles/polymer modified asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 114: 323-332. |
| [32] | Kong L, Wang Z L, Su S N, et al. Exploring the interplay between thermo-oxidative degradation and asphalt aging in thermoplastic polyurethane-modified asphalt: mechanisms, properties, and performance evolution[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2024, 412: 134694. |
| [33] | Dong Z J, Zhou T, Luan H, et al. Composite modification mechanism of blended bio-asphalt combining styrene-butadiene-styrene with crumb rubber: a sustainable and environmental-friendly solution for wastes[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 214: 593-605. |
| [34] | 郭乃胜, 褚召阳, 房辰泽, 等. 沥青及沥青混合料氯盐侵蚀损伤的多尺度研究进展[J]. 中国公路学报, 2023, 36(12): 77-106 |
| Guo N S, Chu Z Y, Fang C Z, et al. Progress of multi-scale research on chloride salt erosion damage of asphalt and asphalt mixture [J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2023, 36(12): 77-106. | |
| [35] | 贺传兰, 邓建国, 张银生. 聚氨酯材料的老化降解[J]. 聚氨酯工业, 2002, 17(3): 1-5. |
| He C L, Deng J G, Zhang Y S. The aging and degradation of polyurethane materials[J]. Polyurethane Industry, 2002, 17(3): 1-5. | |
| [36] | 刘厚钧. 聚氨酯弹性体手册[M]. 2版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2012. |
| Liu H J. Handbook of Polyurethane Elastomers[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2012. | |
| [37] | Gallu R, Méchin F, Dalmas F, et al. Rheology-morphology relationships of new polymer-modified bitumen based on thermoplastic polyurethanes (TPU)[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 259: 120404. |
| [38] | 刘瑾, 李真, 罗筱烈. 聚氨酯弹性体的热降解行为研究[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 1998, 14(1): 128-129, 132. |
| Liu J, Li Z, Luo Y L. Study on thermal degradation of polyurethane elastomers[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 1998, 14(1): 128-129, 132. | |
| [39] | Liu H, Zhang Z P, Zhu Y X, et al. Modification of asphalt using polyurethanes synthesized with different isocyanates[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 327: 126959. |
| [40] | Zhang Z P, Sun J, Jia M, et al. Effects of polyurethane thermoplastic elastomer on properties of asphalt binder and asphalt mixture[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2021, 33(3): 04020477. |
| [41] | 韩继成. 聚氨酯(PU)改性乳化沥青制备及性能研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2017. |
| Han J C. Manufacturing and study on properties of polyurethane (PU) modified bitumen emulsions[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2017. | |
| [42] | Li T S, Carreño Gómez N H, Lu G Y, et al. Use of polyurethane precursor-based modifier as an eco-friendly approach to improve performance of asphalt[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part B: Pavements, 2021, 147(3): 04021031. |
| [43] | Yang F, Cong L, Li Z L, et al. Study on preparation and performance of a thermosetting polyurethane modified asphalt binder for bridge deck pavements[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 326: 126784. |
| [44] | Cuadri A A, García-Morales M, Navarro F J, et al. Processing of bitumens modified by a bio-oil-derived polyurethane[J]. Fuel, 2014, 118: 83-90. |
| [45] | Li T S, Guo Z X, Liang D, et al. Chemical and physical effects of polyurethane-precursor-based reactive modifier on the low-temperature performance of bitumen[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 328: 127055. |
| [46] | 赵孝彬, 杜磊, 张小平. 聚氨酯的结构与微相分离[J]. 聚氨酯工业, 2001, 16(1): 4-8. |
| Zhao X B, Du L, Zhang X P. Brief review of relations of structure and microphase separation of polyurethane[J]. Polyurethane Industry, 2001, 16(1): 4-8. | |
| [47] | Gong X, Liu Q T, Wang H, et al. Synthesis of environmental-curable CO2-based polyurethane and its enhancement on properties of asphalt binder[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2023, 384: 135576. |
| [48] | Zuliani A, Rapisarda M, Chelazzi D, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and soil burial degradation of biobased polyurethanes[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(22): 4948. |
| [49] | Stirna U, Lazdina B, Vilsone D, et al. Structure and properties of the polyurethane and polyurethane foam synthesized from castor oil polyols[J]. Journal of Cellular Plastics, 2012, 48(6): 476-488. |
| [50] | Ban X Y, Zhang Z P, Chang P T, et al. The performance and distribution of polyurethane-modified asphalt that exhibits different molecular weights[J]. Sustainability, 2023, 15(8): 6627. |
| [51] | Gallu R, Méchin F, Dalmas F, et al. Investigating compatibility between TPU and bitumen SARA fractions by means of Hansen solubility parameters and interfacial tension measurements[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 289: 123151. |
| [52] | Gong X, Liu Q T, Wan P, et al. A comparative study of the properties CO2-based polyurethane modified asphalts prepared by prepolymer and in-situ polymerization methods[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 364: 129958. |
| [53] | Madbouly S A. Waterborne polyurethane dispersions and thin films: biodegradation and antimicrobial behaviors[J]. Molecules, 2021, 26(4): 961. |
| [54] | Wang X Q, Ma B, Wei K, et al. Thermal storage properties of polyurethane solid-solid phase-change material with low phase-change temperature and its effects on performance of asphalt binders[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 55: 105686. |
| [55] | Zhao Y C, Gong X, Liu Q T. Research on rheological properties and modification mechanism of waterborne polyurethane modified bitumen[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 371: 130775. |
| [56] | Zuliani A, Bandelli D, Chelazzi D, et al. Environmentally friendly ZnO/castor oil polyurethane composites for the gas-phase adsorption of acetic acid[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 614: 451-459. |
| [57] | Cuadri A A, García-Morales M, Navarro F J, et al. Effect of transesterification degree and post-treatment on the in-service performance of NCO-functionalized vegetable oil bituminous products[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 111: 126-134. |
| [58] | Sun M, Zheng M L, Qu G Z, et al. Performance of polyurethane modified asphalt and its mixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 191: 386-397. |
| [59] | Xia L, Cao D W, Zhang H Y, et al. Study on the classical and rheological properties of castor oil-polyurethane pre polymer (C-PU) modified asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2016, 112: 949-955. |
| [60] | Xia L, Cao D W, Zhang H L. Rheological and aging properties of vegetable oil-based polyurethane (V-PU) modified asphalt[J]. Polymers, 2023, 15(9): 2158. |
| [61] | Zhang Z P, Sun J, Jia M, et al. Study on a thermosetting polyurethane modified asphalt suitable for bridge deck pavements: formula and properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 241: 118122. |
| [62] | Cuadri A A, García-Morales M, Navarro F J, et al. Isocyanate-functionalized castor oil as a novel bitumen modifier[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 97: 320-327. |
| [63] | 刘帅, 马兴元. 封闭型无溶剂聚氨酯的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(23): 3892-3899. |
| Liu S, Ma X Y. Research progress of blocked solvent-free polyurethane[J]. Materials Reports, 2019, 33(23): 3892-3899. | |
| [64] | Kazemi M, Faisal Kabir S, Fini E H. State of the art in recycling waste thermoplastics and thermosets and their applications in construction[J]. Resources, Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2021, 174: 105776. |
| [65] | Jin X, Sun S W, Guo N S, et al. Influence on polyurethane synthesis parameters upon the performance of base asphalt[J]. Frontiers in Materials, 2021, 8: 656261. |
| [66] | Ginzburg V V, Bicerano J, Christenson C P, et al. Theoretical modeling of the relationship between Young's modulus and formulation variables for segmented polyurethanes[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics, 2007, 45(16): 2123-2135. |
| [67] | Lesueur D. The colloidal structure of bitumen: consequences on the rheology and on the mechanisms of bitumen modification[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2009, 145(1/2): 42-82. |
| [68] | He Q S, Zhang H L, Li J, et al. Performance evaluation of polyurethane/epoxy resin modified asphalt as adhesive layer material for steel-UHPC composite bridge deck pavements[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 291: 123364. |
| [69] | 万宁, 贺求生, 张烁, 等. 桥面铺装用聚氨酯/环氧树脂改性沥青的性能研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2022, 39(6): 73-81. |
| Wan N, He Q S, Zhang S, et al. Study on performance of polyurethane/epoxy resin modified asphalt for bridge deck pavement[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2022, 39(6): 73-81. | |
| [70] | Zhang Z P, Sun J, Huang Z G, et al. A laboratory study of epoxy/polyurethane modified asphalt binders and mixtures suitable for flexible bridge deck pavement[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 274: 122084. |
| [71] | Xia W J, Chen X, Xu T. Development of shape memory polyurethane/SBS compositely modified asphalt and synergistic modification mechanism[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 364: 129936. |
| [72] | Yun J, Mazumder M, Na I H, et al. Evaluation of effect of thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) on crumb rubber modified (CRM) asphalt binder[J]. Materials, 2022, 15(11): 3824. |
| [73] | Chen B, Dong F Q, Yu X, et al. Evaluation of properties and micro-characteristics of waste polyurethane/styrene-butadiene-styrene composite modified asphalt[J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(14): 2249. |
| [74] | Yan K Z, Yuan J, Wang M, et al. Preparation process and performance of thermoplastic polyurethane/amorphous poly alpha olefin compound modified bitumen[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 352: 131562. |
| [75] | Xu C, Zhang Z Q, Zhao F Q, et al. Improving the performance of RET modified asphalt with the addition of polyurethane prepolymer (PUP)[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 206: 560-575. |
| [76] | 王结良, 梁国正, 赵雯, 等. 聚氨酯基互穿网络聚合物[J]. 绝缘材料, 2003, 36(4): 33-37. |
| Wang J L, Liang G Z, Zhao W, et al. Interpenetrating polymer networks based on polyurethane[J]. Insulating Materials, 2003, 36(4): 33-37. | |
| [77] | Vila-Cortavitarte M, Lastra-González P, Calzada-Pérez M Á, et al. Analysis of the influence of using recycled polystyrene as a substitute for bitumen in the behaviour of asphalt concrete mixtures[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 170: 1279-1287. |
| [78] | Bratasyuk N A, Zuev V V. The study of the curing mechanism, kinetic and mechanical performance of polyurethane/epoxy composites using aliphatic and aromatic amines as curing agents[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2020, 687: 178598. |
| [79] | Geckil T, Seloglu M. Performance properties of asphalt modified with reactive terpolymer[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 173: 262-271. |
| [80] | Zheng W H, Wang H N, You Z P, et al. Mechanism and rheological characterization of MDI modified wood-based bio-oil asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 309: 125113. |
| [81] | Meng Y Y, Zhan L, Hu C C, et al. Research on modification mechanism and performance of an innovative bio-based polyurethane modified asphalt: a sustainable way to reducing dependence on petroleum asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 350: 128830. |
| [82] | Li S, Xu W Y, Zhang F F, et al. A study on the rheological properties and modification mechanism of graphene oxide/polyurethane/SBS-modified asphalt[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(3): e0262467. |
| [83] | Li S, Xu W Y, Zhang F F, et al. Effect of graphene oxide on aging properties of polyurethane-SBS modified asphalt and asphalt mixture[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(17): 3496. |
| [84] | Ji H D, He D P, Li B, et al. Evaluation of rheological and anti-aging properties of TPU/nano-TiO2 composite-modified asphalt binder[J]. Materials, 2022, 15(9): 3000. |
| [85] | Jia M, Zhang Z P, Liu H T, et al. The synergistic effect of organic montmorillonite and thermoplastic polyurethane on properties of asphalt binder[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 229: 116867. |
| [86] | Yan W, Ou Y J, Xie J, et al. Study on properties of bone glue/polyurethane composite modified asphalt and its mixture[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(14): 3769. |
| [87] | Jin X, Guo N S, You Z P, et al. Rheological properties and micro-characteristics of polyurethane composite modified asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 234: 117395. |
| [88] | Yang X, Mills-Beale J, You Z P. Chemical characterization and oxidative aging of bio-asphalt and its compatibility with petroleum asphalt[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 142: 1837-1847. |
| [89] | Kazemi M, Goli A, Mohammadi A. Efficacy of biobased polyurethane on bitumen self-healing[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering Materials, 2022, 11(1): 221-234. |
| [90] | 凃成, 何敏, 曹东伟, 等. 生物质热解油重组分对石油沥青高温性能影响研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2015, 15(35): 76-80. |
| Tu C, He M, Cao D W, et al. Influence study of biomass pyrolysis oil heavy fractions on petroleum asphalt high-temperature performance [J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2015, 15(35): 76-80. | |
| [91] | Fang Y, Zhang Z Q, Yang J H, et al. Comprehensive review on the application of bio-rejuvenator in the regeneration of waste asphalt materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 295: 123631. |
| [92] | 李宁利, 朱壮壮, 栗培龙. 生物质油替代路用石油沥青的适用性研究[J]. 可再生能源, 2022, 40(4): 448-454. |
| Li N L, Zhu Z Z, Li P L. Research on the applicability of biomass oils to substitute road petroleum pitch[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2022, 40(4): 448-454. | |
| [93] | Su N Y, Xiao F P, Wang J G, et al. Productions and applications of bio-asphalts—A review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 183: 578-591. |
| [94] | Sun D Q, Sun G Q, Du Y C, et al. Evaluation of optimized bio-asphalt containing high content waste cooking oil residues[J]. Fuel, 2017, 202: 529-540. |
| [95] | Yang X L, Liu G Y, Rong H L, et al. Investigation on mechanism and rheological properties of bio-asphalt/PPA/SBS modified asphalt[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 347: 128599. |
| [96] | Yeganeh H, Shamekhi M A. Novel polyurethane insulating coatings based on polyhydroxyl compounds, derived from glycolysed PET and castor oil[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2006, 99(3): 1222-1233. |
| [97] | Kaynak C, Meyva Y. Use of maleic anhydride compatibilization to improve toughness and other properties of polylactide blended with thermoplastic elastomers[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2014, 25(12): 1622-1632. |
| [1] | 梁碧麟, 余倩, 贾思琦, 李芳, 李其明. Ni-MOF-74金属有机框架膜的结构调变及气体分离性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2714-2721. |
| [2] | 陆艳秋, 狄扬, 石文博, 殷聪聪, 汪勇. 基于新型有机多孔聚合物的智能响应膜研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2101-2118. |
| [3] | 赵浩帆, 任豪杰, 刘宗凯, 董冠英, 张亚涛. MOFs玻璃膜在气体分离领域的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2042-2054. |
| [4] | 李紫鹃, 谭晓艳, 吴永盛, 杨陈怡, 陈红, 毕小刚, 刘捷, 喻发全. 分子模拟研究三维扭曲催化芳烃-降冰片烯环化聚合物膜的CO2/N2分离机理[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2348-2357. |
| [5] | 张冰, 李建惠, 马欣蓉, 陈杨, 李晋平, 李立博. 蒸气相辅助法制备MOF基材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2026-2041. |
| [6] | 高冰冰, 许诺, 白云翔, 张春芳, 杨永强, 董亮亮. 氦气分离聚合物膜[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2119-2135. |
| [7] | 张耀辉, 班宇杰, 杨维慎. 以蒸气加工法制备和修饰金属-有机框架膜[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2070-2086. |
| [8] | 石孟琪, 王欢, 王守娟, 席跃宾, 孔凡功. 木质素基炭材料的制备及其在锂硫电池中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1463-1483. |
| [9] | 赵海钎, 陈方, 陈涛, 郭建维, 林文静, 杨楚芬. 叶酸修饰的pH响应共聚物混合胶束用于抗癌药物递送[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1702-1710. |
| [10] | 李远华, 凌思棋, 封科军, 冯颖, 郭于菁, 谢世桓. 基于cMOFs的固定化脂肪酶微反应器的构筑及其扁桃酸催化应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1170-1179. |
| [11] | 肖俊兵, 钟湘宇, 任建地, 钟芳芳, 刘昌会, 贾传坤. 基于生物碳材料强化的硬脂酸相变材料储热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1312-1322. |
| [12] | 刘彦贝, 王若名, 刘娟, Raza Taimoor, 陆玉正, Raza Rizwan, 朱斌, 李松波, 安胜利, 云斯宁. CeO2@La0.6Sr0.4Co0.2Fe0.8O3-δ 电解质的制备及半导体离子燃料电池性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1353-1362. |
| [13] | 肖俊兵, 邹博, 任建地, 刘昌会, 贾传坤. 基于相图分析的氯化物复合熔盐储热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 963-974. |
| [14] | 张静, 元跃, 刘艳梅, 王智文, 陈涛. 生物法制备衣康酸研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 909-921. |
| [15] | 贾晶宇, 孔德齐, 沈圆辉, 张东辉, 李文彬, 唐忠利. 合成氨反应器尾气变压吸附氨分离工艺的模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 718-730. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号