化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (9): 4539-4550.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250330
曾宁1,2( ), 郭振江2, 陈建华2, 张子轩3, 曾玉娇3, 肖炘3, 刘松林4, 薛绍秀4, 周智武4, 卢振明1(
), 郭振江2, 陈建华2, 张子轩3, 曾玉娇3, 肖炘3, 刘松林4, 薛绍秀4, 周智武4, 卢振明1( ), 王利民2,5(
), 王利民2,5( )
)
收稿日期:2025-03-31
修回日期:2025-06-06
出版日期:2025-09-25
发布日期:2025-10-23
通讯作者:
卢振明,王利民
作者简介:曾宁(2000—),女,硕士研究生,zengning@wust.edu.cn
基金资助:
Ning ZENG1,2( ), Zhenjiang GUO2, Jianhua CHEN2, Zixuan ZHANG3, Yujiao ZENG3, Xin XIAO3, Songlin LIU4, Shaoxiu XUE4, Zhiwu ZHOU4, Zhenming LU1(
), Zhenjiang GUO2, Jianhua CHEN2, Zixuan ZHANG3, Yujiao ZENG3, Xin XIAO3, Songlin LIU4, Shaoxiu XUE4, Zhiwu ZHOU4, Zhenming LU1( ), Limin WANG2,5(
), Limin WANG2,5( )
)
Received:2025-03-31
Revised:2025-06-06
Online:2025-09-25
Published:2025-10-23
Contact:
Zhenming LU, Limin WANG
摘要:
针对湿法磷酸工艺中非水溶磷损失高的问题,采用分子动力学研究方法,从微观角度观察湿法磷酸工艺中磷矿的分解过程。基于该工艺的实际反应,建立了两阶段的分子动力学模型,模拟结果表明,在磷矿的分解演化过程中,
中图分类号:
曾宁, 郭振江, 陈建华, 张子轩, 曾玉娇, 肖炘, 刘松林, 薛绍秀, 周智武, 卢振明, 王利民. 二水湿法磷酸工艺中非水溶磷的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4539-4550.
Ning ZENG, Zhenjiang GUO, Jianhua CHEN, Zixuan ZHANG, Yujiao ZENG, Xin XIAO, Songlin LIU, Shaoxiu XUE, Zhiwu ZHOU, Zhenming LU, Limin WANG. Molecular dynamics simulation of water-insoluble phosphorus in dihydrate wet-process phosphoric acid[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4539-4550.
| Molecule | ε/ meV | σ/ nm | Rc/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2O-H2O | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-H2SO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-Ca5F(PO4)3 | 5.15 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-CaSO4 | 3.09 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-共晶磷 | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O- | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-H3PO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-H2SO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-Ca5F(PO4)3 | 5.15 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-CaSO4 | 3.09 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-共晶磷 | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4- | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-H3PO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3-Ca5F(PO4)3 | 0.0 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3-CaSO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3-共晶磷 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3- | 10.30 | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3-H3PO4 | 5.15 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 5.15 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| CaSO4-CaSO4 | 7.21 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| CaSO4-共晶磷 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| CaSO4- | 6.18 | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| CaSO4-H3PO4 | 3.09 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| CaSO4-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 3.09 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| 共晶磷-共晶磷 | 7.21 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| 共晶磷- | 10.30 | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| 共晶磷-H3PO4 | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| 共晶磷-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| 7.21 | 0.34 | 1.10 | |
| 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 | |
| 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 | |
| H3PO4-H3PO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H3PO4-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca(H2PO4)2-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
表1 各分子LJ势参数
Table 1 LJ potential parameters of each molecule
| Molecule | ε/ meV | σ/ nm | Rc/ nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2O-H2O | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-H2SO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-Ca5F(PO4)3 | 5.15 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-CaSO4 | 3.09 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-共晶磷 | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O- | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-H3PO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2O-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-H2SO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-Ca5F(PO4)3 | 5.15 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-CaSO4 | 3.09 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-共晶磷 | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4- | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-H3PO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H2SO4-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3-Ca5F(PO4)3 | 0.0 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3-CaSO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3-共晶磷 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3- | 10.30 | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3-H3PO4 | 5.15 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca5F(PO4)3-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 5.15 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| CaSO4-CaSO4 | 7.21 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| CaSO4-共晶磷 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| CaSO4- | 6.18 | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| CaSO4-H3PO4 | 3.09 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| CaSO4-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 3.09 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| 共晶磷-共晶磷 | 7.21 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| 共晶磷- | 10.30 | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| 共晶磷-H3PO4 | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| 共晶磷-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| 7.21 | 0.34 | 1.10 | |
| 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 | |
| 6.18 | 0.34 | 1.10 | |
| H3PO4-H3PO4 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| H3PO4-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| Ca(H2PO4)2-Ca(H2PO4)2 | 10.30 | 0.34 | 1.10 |
| 转变前的分子 | 转变区域 | 转变后的分子 | 转变比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca5F(PO4)3 | 与H3PO4相接触(距离小于0.34 nm) | 删除Ca5F(PO4)3 | 1.0 |
| H3PO4 | 与被消耗的Ca5F(PO4)3相接触(距离小于0.34 nm) | Ca(H2PO4)2 | 0.7 |
表2 第一阶段分子转变
Table 2 Molecular transformation at the first stage
| 转变前的分子 | 转变区域 | 转变后的分子 | 转变比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca5F(PO4)3 | 与H3PO4相接触(距离小于0.34 nm) | 删除Ca5F(PO4)3 | 1.0 |
| H3PO4 | 与被消耗的Ca5F(PO4)3相接触(距离小于0.34 nm) | Ca(H2PO4)2 | 0.7 |
| 转变前的分子 | 转变区域 | 转变前的分子 | 转变比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | 与H2SO4相接触(距离小于1 nm) | 删除Ca(H2PO4)2 | 0.5 |
| H2SO4 | 与被消耗的Ca(H2PO4)2相接触(距离小于1 nm) | CaSO4 | 1.0 |
| H2O | 全区 | H3PO4 | 与H2SO4相接触的Ca(H2PO4)2分子数/水分子数 |
表3 第二阶段分子转变
Table 3 Molecular transformation at the second stage
| 转变前的分子 | 转变区域 | 转变前的分子 | 转变比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ca(H2PO4)2 | 与H2SO4相接触(距离小于1 nm) | 删除Ca(H2PO4)2 | 0.5 |
| H2SO4 | 与被消耗的Ca(H2PO4)2相接触(距离小于1 nm) | CaSO4 | 1.0 |
| H2O | 全区 | H3PO4 | 与H2SO4相接触的Ca(H2PO4)2分子数/水分子数 |
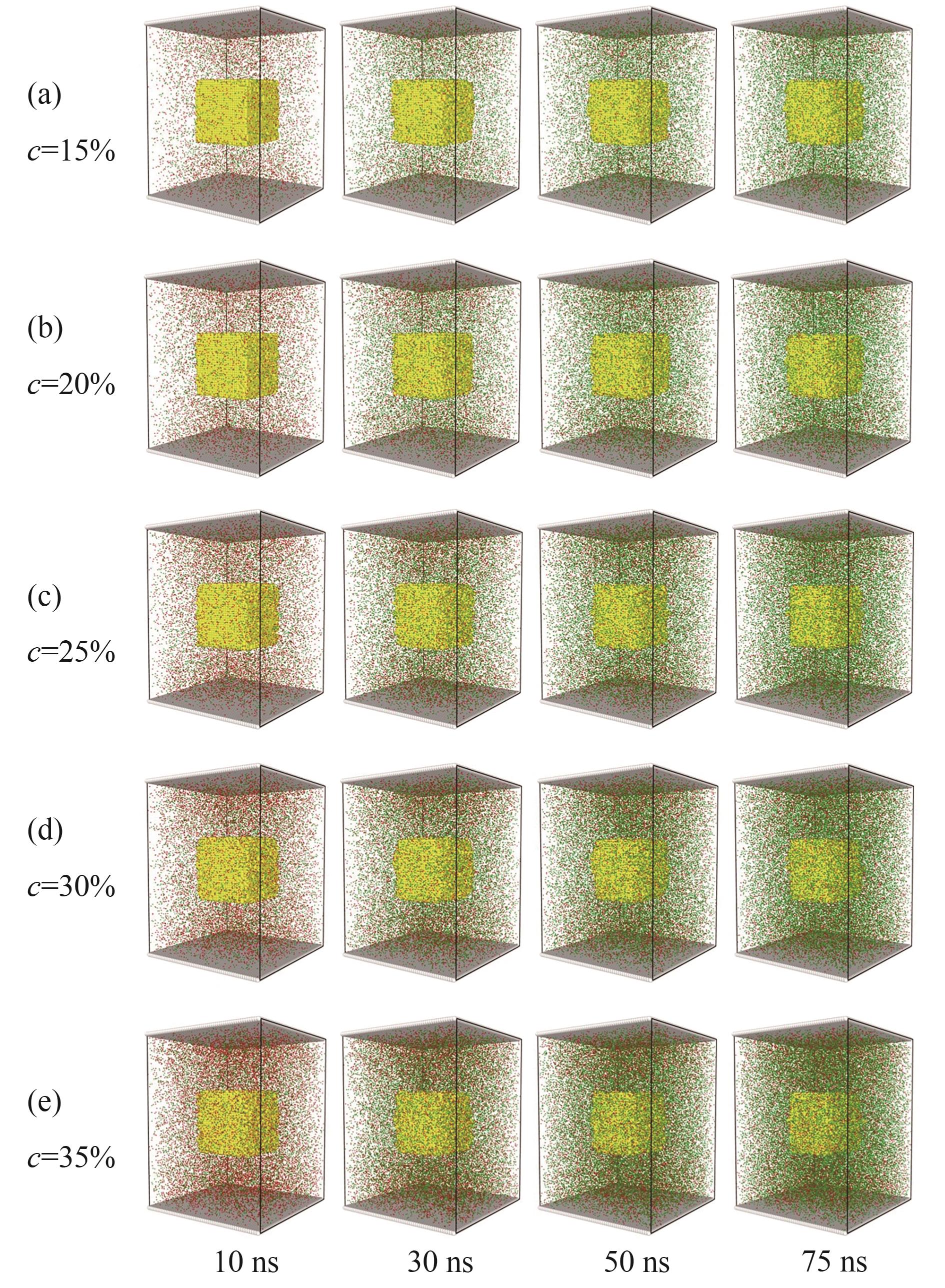
图3 第一阶段不同磷酸浓度下反应快照[中间黄色粒子为磷矿,红色粒子为磷酸,绿色粒子为Ca(H2PO4)2,为方便观察隐藏了水分子]
Fig.3 Snapshot of the reaction under different phosphoric acid concentrations in the first stage [the middle yellow particle is phosphate rock, the red particle is phosphoric acid, and the green particle is Ca(H2PO4)2, water molecules are hidden for convenient observation]
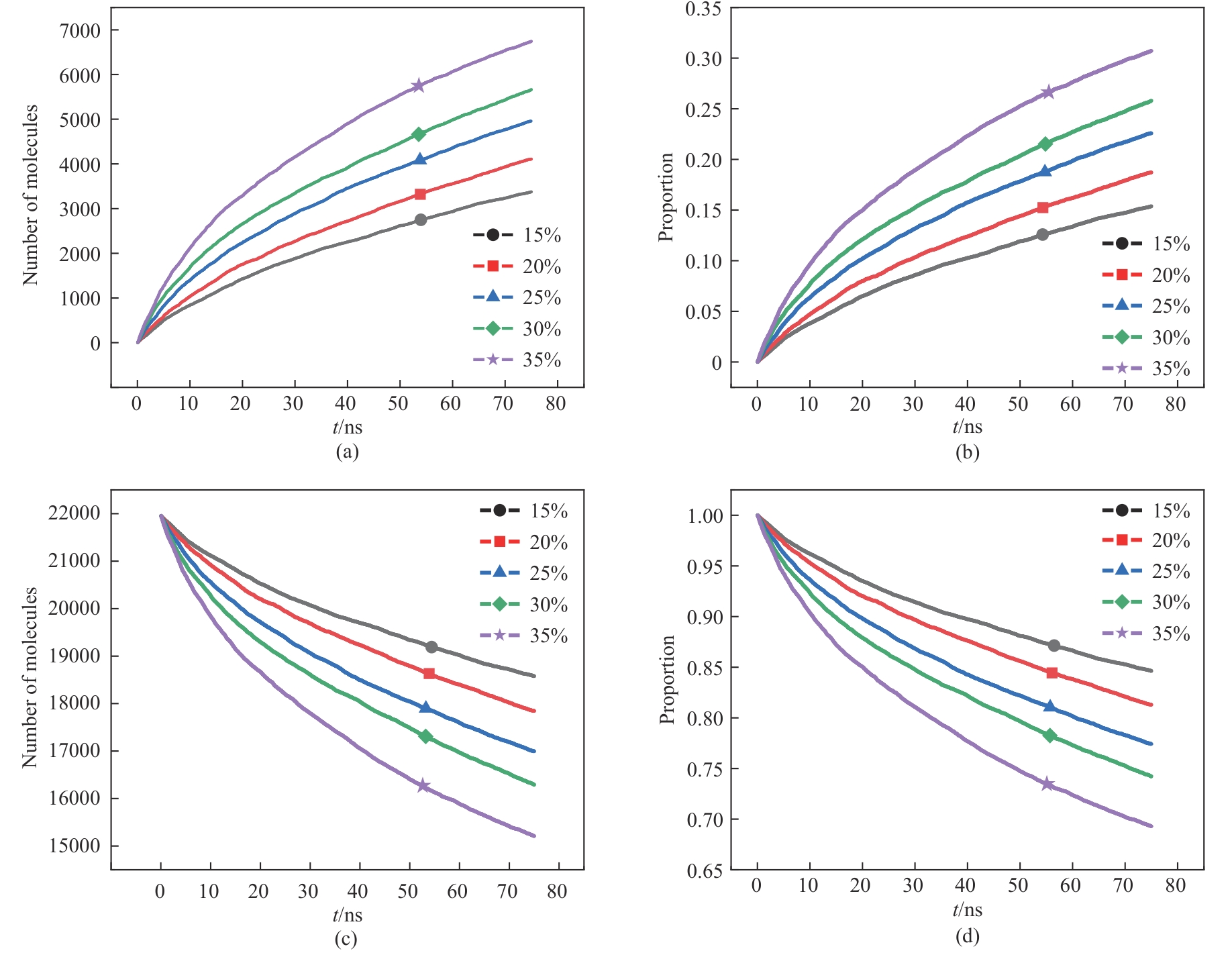
图5 不同磷酸浓度下分子数及比例随时间变化:(a)、(b)消耗磷矿分子;(c)、(d)未参与反应的磷矿分子
Fig.5 Change of molecular number and proportion with time under different phosphoric acid concentrations: (a), (b) consumption of phosphate rock molecules; (c), (d) phosphate rock molecules not involved in the reaction
| 磷酸质量分数/% | 反应物消耗分子数/个 | 产物分子数/个 | 比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 3375 | 16864 | 0.20013 |
| 20 | 4108 | 20544 | 0.19996 |
| 25 | 4957 | 24565 | 0.20179 |
| 30 | 5663 | 28266 | 0.20035 |
| 35 | 6743 | 33349 | 0.20220 |
表4 反应物消耗与产物比例关系
Table 4 Relation between reactant consumption and product proportion
| 磷酸质量分数/% | 反应物消耗分子数/个 | 产物分子数/个 | 比例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 3375 | 16864 | 0.20013 |
| 20 | 4108 | 20544 | 0.19996 |
| 25 | 4957 | 24565 | 0.20179 |
| 30 | 5663 | 28266 | 0.20035 |
| 35 | 6743 | 33349 | 0.20220 |

图7 第二阶段不同硫酸浓度下反应快照[白色的粒子为CaSO4,紫色的粒子为共晶磷,绿色粒子为Ca(H2PO4)2,深蓝色的粒子为硫酸,中间黄色的固体为磷矿,为方便观察隐藏了水和磷酸分子]
Fig.7 Snapshot of the reaction under different sulfuric acid concentrations in the second stage [the white particle is CaSO4, the purple particle is eutectic phosphorus, the green particle is Ca(H2PO4)2, the dark blue particle is sulfuric acid, and the yellow solid in the middle is phosphate rock, which hides water and phosphoric acid molecules for convenient observation]
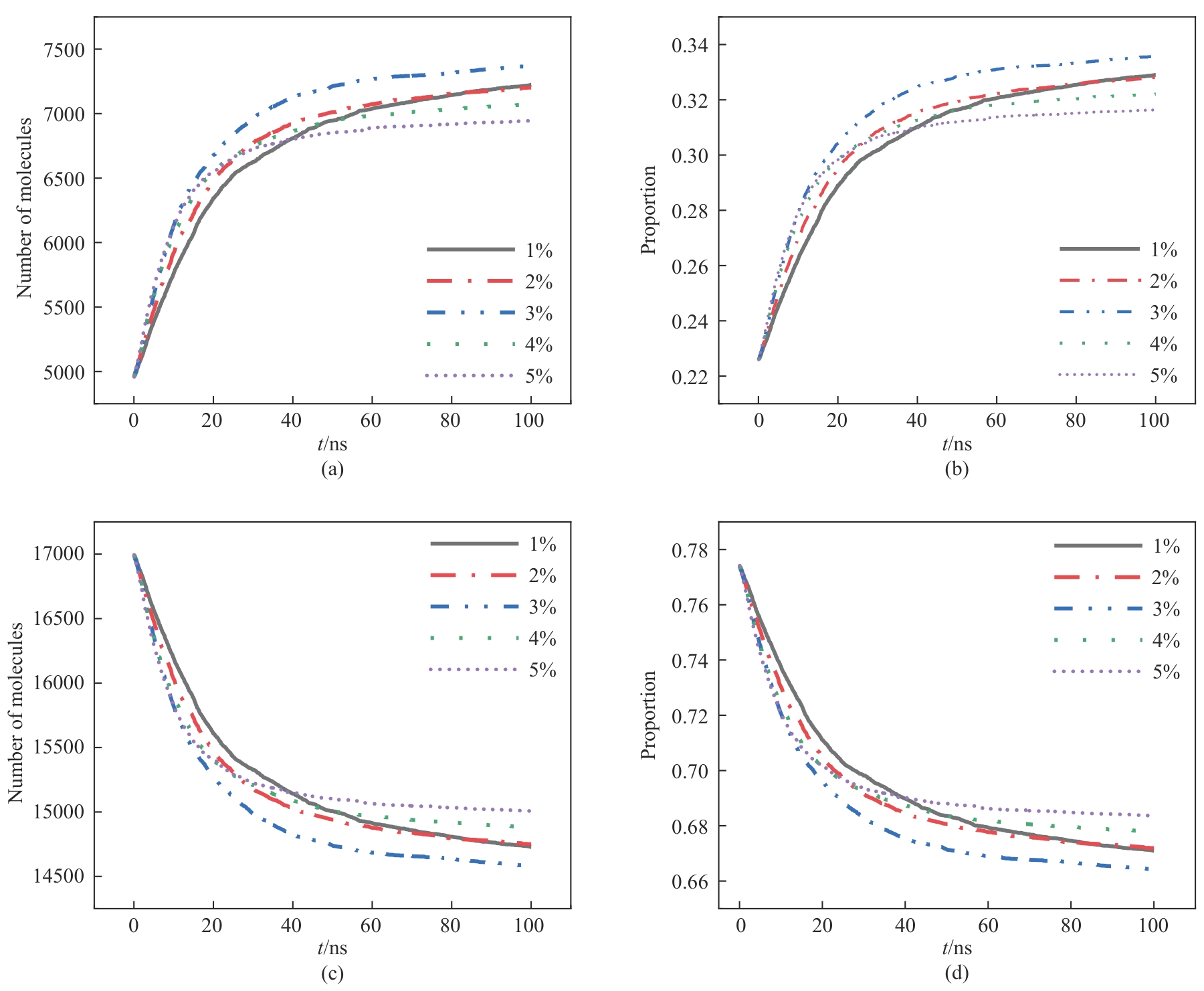
图9 不同硫酸浓度下分子数及比例随时间变化: (a)、(b)消耗磷矿分子; (c)、(d)未参与反应的磷矿分子
Fig.9 Molecular number and proportion change over time under different sulfuric acid concentrations: (a), (b) consumption of phosphate rock molecules; (c), (d) phosphate rock molecules not involved in the reaction
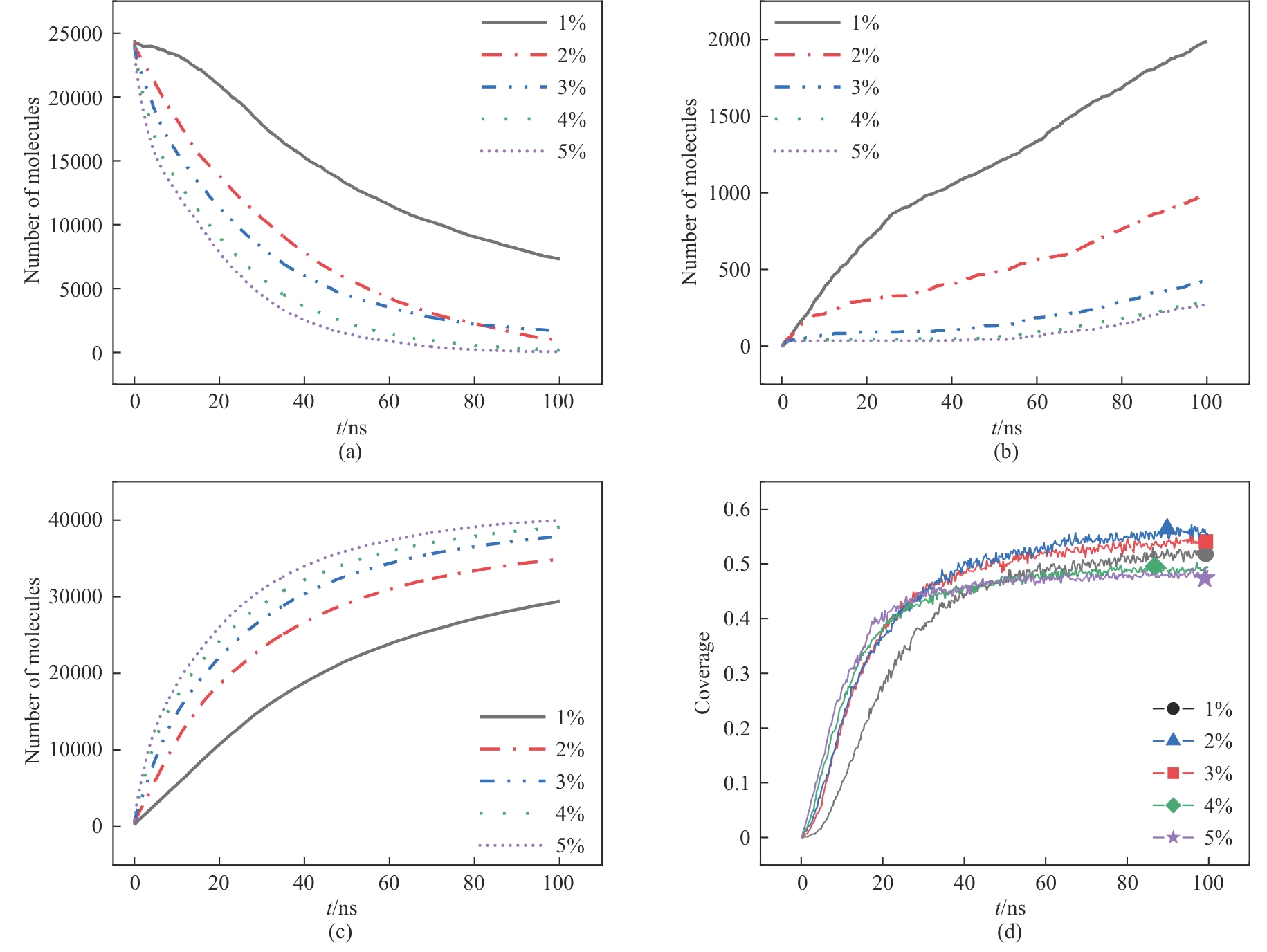
图10 不同硫酸浓度下各物质分子数随时间变化: (a)Ca(H2PO4)2;(b)共晶磷;(c)CaSO4;(d)磷矿表面覆盖率
Fig.10 Molecular number of each substance changes with time under different sulfuric acid concentrations: (a) Ca(H2PO4)2; (b) eutectic phosphorus; (c) CaSO4; (d) surface coverage of phosphate rock
| [1] | Li R H, Wang J J, Zhou B Y, et al. Recovery of phosphate from aqueous solution by magnesium oxide decorated magnetic biochar and its potential as phosphate-based fertilizer substitute[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 215: 209-214. |
| [2] | Geeson M B, Cummins C C. Phosphoric acid as a precursor to chemicals traditionally synthesized from white phosphorus[J]. Science, 2018, 359(6382): 1383-1385. |
| [3] | Lampila L E. Applications and functions of food-grade phosphates[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2013, 1301(1): 37-44. |
| [4] | 吴佩芝. 湿法磷酸[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 1987. |
| Wu P Z. Wet Phosphoric Acid[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 1987. | |
| [5] | 李枫. 磷酸生产工艺浅析及窑法磷酸工艺优化改进构想[J]. 中氮肥, 2022(6): 1-5. |
| Li F. Brief analysis of phosphoric acid production process and the idea of optimization and improvement of kiln phosphoric acid process[J]. M-Sized Nitrogenous Fertilizer Progress, 2022(6): 1-5. | |
| [6] | 王炳棋. 两步法湿法磷酸中石膏相转化过程及杂质的影响研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2021. |
| Wang B Q. Study on the phase transformation process of gypsum in two-step wet-process phosphoric acid and the influence of impurities[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2021. | |
| [7] | 崔继荣, 高永峰. 我国磷化工发展现状及措施建议[J]. 肥料与健康, 2020, 47(4): 1-4. |
| Cui J R, Gao Y F. Development status of phosphorus chemical industry in China and suggestions for development measures[J]. Fertilizer & Health, 2020, 47(4): 1-4. | |
| [8] | 张亚明, 李文超, 王海军. 我国磷矿资源开发利用现状[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2020, 49(6): 43-46. |
| Zhang Y M, Li W C, Wang H J. Status quo of development and utilization of phosphate resources in China[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2020, 49(6): 43-46. | |
| [9] | 李维, 高辉, 罗英杰, 等. 国内外磷矿资源利用现状、趋势分析及对策建议[J]. 中国矿业, 2015, 24(6): 6-10. |
| Li W, Gao H, Luo Y J, et al. Status,trends and suggestions of phosphorus ore resources at home and abroad[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2015, 24(6): 6-10. | |
| [10] | 樊蕾, 方晓峰. 我国中低品位磷矿利用技术现状及前景展望[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2015, 44(8): 42-46. |
| Fan L, Fang X F. Status and prospect of medium and low grade phosphate rock utilization technology in China[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2015, 44(8): 42-46. | |
| [11] | 朱干宇, 孟子衡, 李会泉, 等. 磷资源高效利用制备磷酸技术现状探讨[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2023, 38(7): 24-30, 35. |
| Zhu G Y, Meng Z H, Li H Q, et al. Current status of phosphoric acid preparation technology for efficient utilization of phosphorus resources[J]. Phosphate & Compound Fertilizer, 2023, 38(7): 24-30, 35. | |
| [12] | 贺雷, 朱干宇, 郑光明, 等. 湿法磷酸体系磷石膏结晶过程与机理研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2022, 54(7): 110-116. |
| He L, Zhu G Y, Zheng G M, et al. Study on crystallization process and mechanism of phosphogypsum in wet process phosphoric acid system[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(7): 110-116. | |
| [13] | 董泽, 翟延波, 任志威, 等. 磷石膏建材资源化利用研究进展[J]. 无机盐工业, 2022, 54(4): 5-9. |
| Dong Z, Zhai Y B, Ren Z W, et al. Research progress on phosphogypsum utilization in building materials[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2022, 54(4): 5-9. | |
| [14] | Tayibi H, Choura M, López F A, et al. Environmental impact and management of phosphogypsum[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2009, 90(8): 2377-2386. |
| [15] | 彭家惠, 彭志辉, 张建新, 等. 磷石膏中可溶磷形态、分布及其对性能影响机制的研究[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2000, 28(4): 309-313. |
| Peng J H, Peng Z H, Zhang J X, et al. Study on the form and distribution of water-soluble P2O5 in phosphogypsum and effective mechanism of properties[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2000, 28(4): 309-313. | |
| [16] | 彭家惠, 万体智, 汤玲, 等. 磷石膏中杂质组成、形态、分布及其对性能的影响[J]. 中国建材科技, 2000, 9(6): 31-35. |
| Peng J H, Wan T Z, Tang L, et al. Composition, morphology and distribution of impurities in phosphogypsum and their effects on properties[J]. China Building Materials Science & Technology, 2000, 9(6): 31-35. | |
| [17] | 朱明芳, 周凌翔. 降低二水法湿法磷酸磷石膏枸溶磷、提升磷矿分解率的技术与应用[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2013, 28(1): 33-35. |
| Zhu M F, Zhou L X. Technology and its application for decrease of citric-soluble phosphate content in phosphogypsum and improvement of decomposition rate of phosphate rock in dihydrate WPA production[J]. Phosphate & Compound Fertilizer, 2013, 28(1): 33-35. | |
| [18] | Bouchkira I, Latifi A M, Khamar L, et al. Modeling and multi-objective optimization of the digestion tank of an industrial process for manufacturing phosphoric acid by wet process[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2022, 156: 107536. |
| [19] | 宁廷建. 湿法磷酸工艺对磷石膏品质的影响[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2011. |
| Ning T J. Effect of wet-process phosphoric acid technology on phosphogypsum quality [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2011. | |
| [20] | 王良士, 龙志奇, 于瀛, 等. 湿法磷酸生产过程中控制硫酸钙结晶的研究[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2008, 37(4): 1-4. |
| Wang L S, Long Z Q, Yu Y, et al. Study on the crystallization of calcium sulfate during the course of phosphoric acid production by wet-process[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2008, 37(4): 1-4. | |
| [21] | Negrón C P, Suazo-Hernández J, de la Luz Mora M, et al. Lemon peel waste as a natural enhancer for increasing phosphorus solubilization in phosphate rocks[J]. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 2025, 25(2): 4796-4812. |
| [22] | Fang K N, Xu L, Yang M, et al. One-step wet-process phosphoric acid by-product CaSO4 and its purification[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 309: 123048. |
| [23] | 曾玉娇, 肖炘, 杨刚, 等. 基于机理与数据混合驱动的湿法磷酸生产过程代理建模与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 936-944. |
| Zeng Y J, Xiao X, Yang G, et al. Surrogate modeling and optimization of wet phosphoric acid production process based on mechanism and data hybrid driven[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 936-944. | |
| [24] | 王典. 基于Aspen Plus的二水法湿法磷酸工艺模拟[J]. 硫磷设计与粉体工程, 2020(1): 18-21. |
| Wang D. Aspen Plus-based simulation for dihydrate wet-process phosphoric acid process[J]. Sulphur Phosphorus & Bulk Materials Handling Related Engineering, 2020(1): 18-21. | |
| [25] | Mathias M P, Chen C C, Walters M. Modeling the complex chemical reactions and mass transfer in a phosphoric acid reactor[C]//Proceedings of Third Joint China/USA Chemical Engineering Conference(Volume Ⅰ). Beijing, 2000: 657-664. |
| [26] | Grema A S, Imam Y Y, Mohammed H I. Modeling and simulation of hemihydrate phosphoric acid plant[J]. Arid Zone Journal of Engineering, Technology and Environment, 2018, 14(2): 169-171. |
| [27] | Soboleva I V, Lyashenko S E. Mathematical simulation and optimization of continuous dihydrate-semihydrate production of wet process phosphoric acid from low-grade ores[J]. Theoretical Foundations of Chemical Engineering, 2024, 58(2): 463-468. |
| [28] | 张文惠, 王丽娜, 林佳玮, 等. 不同原子尺寸下二元Lennard-Jones液体微观结构的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 原子与分子物理学报, 2026, 43: 012002. |
| Zhang W H, Wang L N, Lin J W, et al. Microstructures of binary Lennard-Jones liquids with different atomic sizes studied by molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Journal of Atomic and Molecular Physics, 2026, 43: 012002. | |
| [29] | 张文惠, 王丽娜, 林佳玮, 等. 系列势阱深度下二元Lennard-Jones液体相分离程度的分子动力学研究[J]. 分子科学学报, 2023, 39(3): 253-263. |
| Zhang W H, Wang L N, Lin J W, et al. Phase separation of binary Lennard-Jones liquids with a series of potential well depths investigated by molecular dynamics method[J]. Journal of Molecular Science, 2023, 39(3): 253-263. | |
| [30] | Liu Y W, Zhang X R. A unified mechanism for the stability of surface nanobubbles: contact line pinning and supersaturation[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2014, 141(13): 134702. |
| [31] | 许小云, 刘瑾, 樊建明. 二水硫酸钙结晶过程研究进展[J]. 应用化工, 2005, 34(6): 325-327, 331. |
| Xu X Y, Liu J, Fan J M. Research progress on the crystallization course of dihydrate calcium sulphate[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2005, 34(6): 325-327, 331. | |
| [32] | Guo Z J, Feng Y T, Zhang H H, et al.The behaviors of interfacial nanobubbles on flat or rough electrode surfaces in electrochemistry[J]. Langmuir,2024, 40(50): 26661-26671. |
| [33] | 孙晨阳, 侯超峰, 葛蔚. LJ势氩系统分子动力学模拟中截断半径的选择[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(3): 259-264. |
| Sun C Y, Hou C F, Ge W. Application of cutoff distance selection in molecular dynamics simulation of LJ argon system[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2021, 21(3): 259-264. | |
| [34] | 张沂圭. 二水硫酸钙结晶条件与结晶技术[J]. 硫磷设计与粉体工程, 2003(3): 14-18. |
| Zhang Y G. Conditions and technologies for crystallization of CaSO4·2H2O[J]. Sulphur Phosphorus & Bulk Materials Handling Related Engineering, 2003(3): 14-18. | |
| [35] | 李美, 彭家惠, 张建新, 等. 湿法磷酸萃取工艺对磷石膏晶形的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2013, 16(1): 147-152. |
| Li M, Peng J H, Zhang J X, et al. Influence of extraction process on crystal morphology of phosphogypsum produced in wet-process phosphoric acid[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2013, 16(1): 147-152. | |
| [36] | 王松年, 石利棉, 黎绍忠. 如何降低湿法磷酸副产磷石膏的总磷损失[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2008, 23(1): 33. |
| Wang S N, Shi L M, Li S Z. How to reduce the total phosphorus loss of phosphogypsum by-product of wet-process phosphoric acid[J]. Phosphate & Compound Fertilizer, 2008, 23(1): 33. | |
| [37] | 薛雪, 曾彦, 张桂军. 使用中低品位磷矿生产湿法磷酸的技术改造[J]. 磷肥与复肥, 2010, 25(5): 36-38. |
| Xue X, Zeng Y, Zhang G J. Technical transformation of WPA production with low grade phosphate rock[J]. Phosphate & Compound Fertilizer, 2010, 25(5): 36-38. |
| [1] | 刘峰, 韩春硕, 张益, 刘彦成, 郁林军, 申家伟, 高晓泉, 杨凯. 高温高盐环境下单烃链和双烃链表面活性剂对油水界面性质影响的微观机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2939-2957. |
| [2] | 朱峰, 赵跃, 马凤翔, 刘伟. 改性UIO-66对SF6/N2混合气体及其分解产物的吸附特性[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1604-1616. |
| [3] | 徐芳, 张锐, 崔达, 王擎. ReaxFF-MD揭示木质素热解反应机制的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1253-1263. |
| [4] | 张奇, 张睿, 郑涛, 曹欣, 刘植昌, 刘海燕, 徐春明, 张荣, 孟祥海. 基于分子模拟的新型双阳离子质子型离子液体捕集CO2研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(2): 797-811. |
| [5] | 徐娜, 李子璇, 刘子璐, 吕耀东, 张释文. 溶液环境对液相纳米颗粒体系分散稳定性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3815-3824. |
| [6] | 贾海林, 曾锦祥, 潘荣锟, 潘仕利, 周凯旋. 无氟泡沫灭火剂真火实验与分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3825-3834. |
| [7] | 于宏鑫, 邵双全. 水结晶过程的分子动力学模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 250-258. |
| [8] | 毕丽森, 刘斌, 胡恒祥, 曾涛, 李卓睿, 宋健飞, 吴翰铭. 粗糙界面上纳米液滴蒸发模式的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 172-178. |
| [9] | 曾如宾, 沈中杰, 梁钦锋, 许建良, 代正华, 刘海峰. 基于分子动力学模拟的Fe2O3纳米颗粒烧结机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [10] | 张永泉, 玄伟伟. 碱金属/(FeO+CaO+MgO)对硅酸盐灰熔渣结构和黏度的影响机理[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1764-1771. |
| [11] | 袁妮妮, 郭拓, 白红存, 何育荣, 袁永宁, 马晶晶, 郭庆杰. 化学链燃烧过程Fe2O3/Al2O3载氧体表面CH4反应:ReaxFF-MD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4054-4061. |
| [12] | 刘洪超, 陈苏航, 段先力, 吴凡, 徐小飞, 宋先雨, 赵双良, 刘洪来. Janus石墨烯量子点在生物膜中的输运行为:分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2835-2843. |
| [13] | 于泽沛, 冯妍卉, 冯黛丽, 张欣欣. 三维石墨烯-碳纳米管复合结构热导率的分子动力学模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1822-1827. |
| [14] | 刘明, 徐哲. 甲烷水合物声子导热及量子修正[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(4): 1424-1431. |
| [15] | 刘万强,杨帆,袁华,张远达,易平贵,周虎. 醇类有机物热传导的分子动力学模拟及微观机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(11): 5159-5168. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号