• •
收稿日期:2025-10-23
修回日期:2026-01-04
出版日期:2026-01-05
通讯作者:
程文婷
作者简介:程文婷(1983—),女,博士,副教授,wtcheng@sxu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Wenting CHENG1,2( ), Enqi WANG1,2, Fangqin CHENG1,2
), Enqi WANG1,2, Fangqin CHENG1,2
Received:2025-10-23
Revised:2026-01-04
Online:2026-01-05
Contact:
Wenting CHENG
摘要:
将NaCl和Na2SO4为主的煤化工废盐作为研究对象,通过浓度和频次排序筛选了当中的9种典型无机杂质K+、NH4+、NO3-、HCO3-、CO32-、Ca2+、Mg2+、Al3+、Fe3+及6种典型有机杂质戊烷、苯酚、苯乙烯、油酰胺、十二烷、氯苯,并采用COSMOtherm软件绘制了它们的电荷密度分布谱图(σ-profile分布图)。随后在273.15 ~ 323.15 K温度范围内,研究了温度、杂质类型、杂质浓度等因素对NaCl和Na2SO4溶剂化的影响。结果发现无机杂质中Al3+、Fe3+、Mg2+和CO32-等高价离子的σ值偏离阈值程度大且σ-profile极性峰值高,它们因具有较大的离子半径和较高的电荷密度而具有更强的水分子争夺能力,与低价离子相比它们能显著减弱NaCl和Na2SO4溶剂化;有机杂质中油酰胺、十二烷的σ-profile非极性峰值较高,疏水效应强且空间位阻大,能够使得NaCl和Na2SO4的溶剂化明显减弱;与NaCl相比,Na2SO4的溶剂化自由能对周围理化环境的变化更敏感,即更易通过改变理化条件的方法来调控Na2SO4的溶解结晶行为。
中图分类号:
程文婷, 王恩琪, 程芳琴. 煤化工废盐中杂质对NaCl和Na2SO4溶剂化影响研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251182.
Wenting CHENG, Enqi WANG, Fangqin CHENG. Study on impact of impurities in coal chemical waste salt on solvation of NaCl and Na2SO4[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251182.
| 物质名称 | 浓度范围mg·L-1 | 物质名称 | 浓度范围mg·L-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | 0.20932 ~ 6452 | Al3+ | 0.1276 ~ 71 |
| NH4+ | 21.54 ~ 43.3 | 戊烷 | 0.51 ~ 0.55 |
| NO3- | 0.25 ~ 2500 | 苯酚 | 5 ~ 75 |
| HCO3- | 0.12 ~ 10990 | 苯乙烯 | 0.9 ~ 64.63 |
| CO32- | 0 ~ 119.69 | 油酰胺 | 2.18 ~ 37 |
| Ca2+ | 0.06 ~ 1960 | 十二烷 | 0.6 ~ 17 |
| Mg2+ | 0.2 ~ 1176 | 氯苯 | 0.17 ~ 0.5 |
| Fe3+ | 0.06 ~ 9.87 |
表1 典型杂质名称及浓度
Table 1 Typical impurity names and concentrations
| 物质名称 | 浓度范围mg·L-1 | 物质名称 | 浓度范围mg·L-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| K+ | 0.20932 ~ 6452 | Al3+ | 0.1276 ~ 71 |
| NH4+ | 21.54 ~ 43.3 | 戊烷 | 0.51 ~ 0.55 |
| NO3- | 0.25 ~ 2500 | 苯酚 | 5 ~ 75 |
| HCO3- | 0.12 ~ 10990 | 苯乙烯 | 0.9 ~ 64.63 |
| CO32- | 0 ~ 119.69 | 油酰胺 | 2.18 ~ 37 |
| Ca2+ | 0.06 ~ 1960 | 十二烷 | 0.6 ~ 17 |
| Mg2+ | 0.2 ~ 1176 | 氯苯 | 0.17 ~ 0.5 |
| Fe3+ | 0.06 ~ 9.87 |
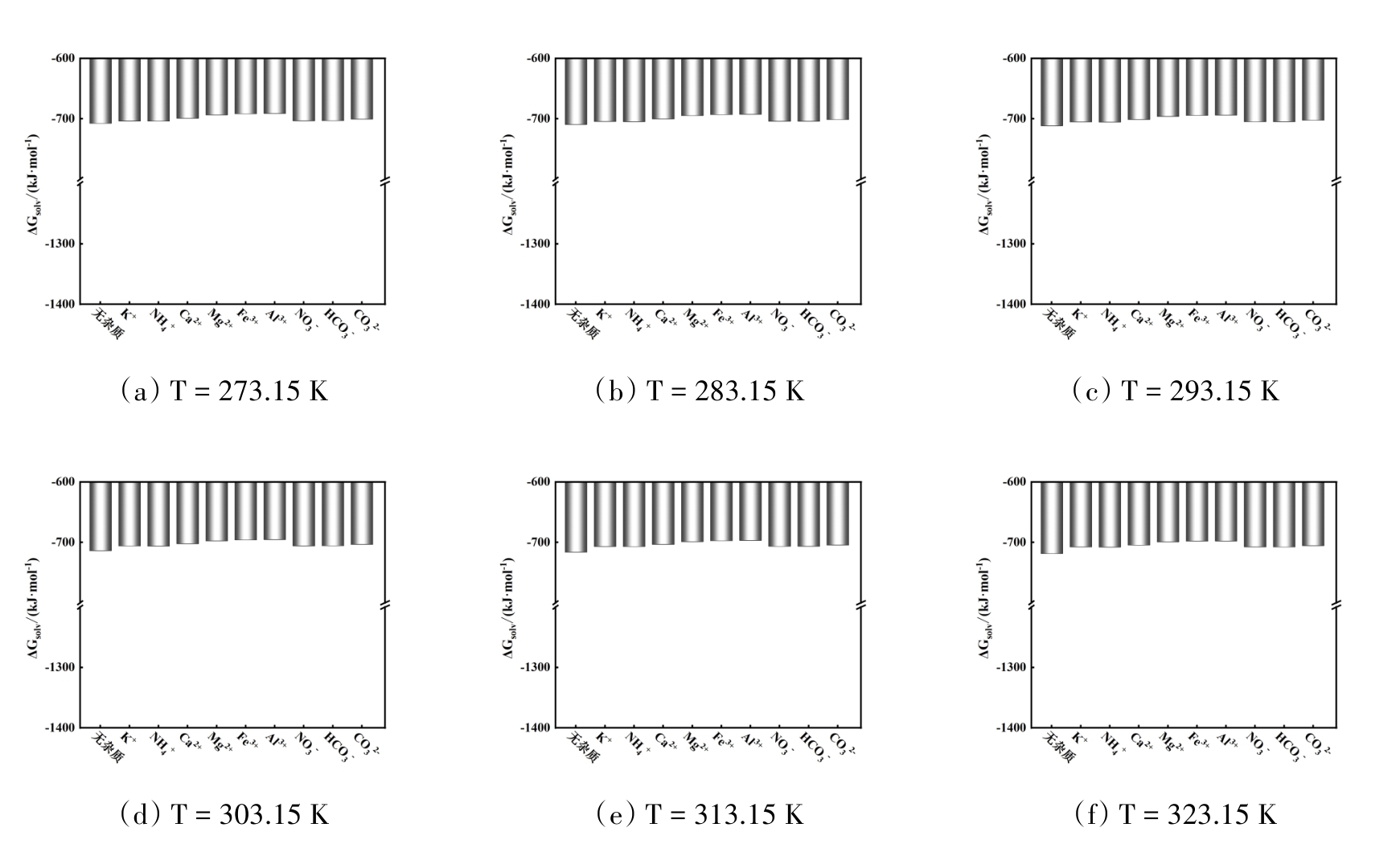
图5 温度在273.15 ~ 323.15 K范围内不同无机杂质存在时NaCl的溶剂化自由能
Fig. 5 Solvation free energy of NaCl with different inorganic impurities in the temperature range of 273.15 ~ 323.15 K
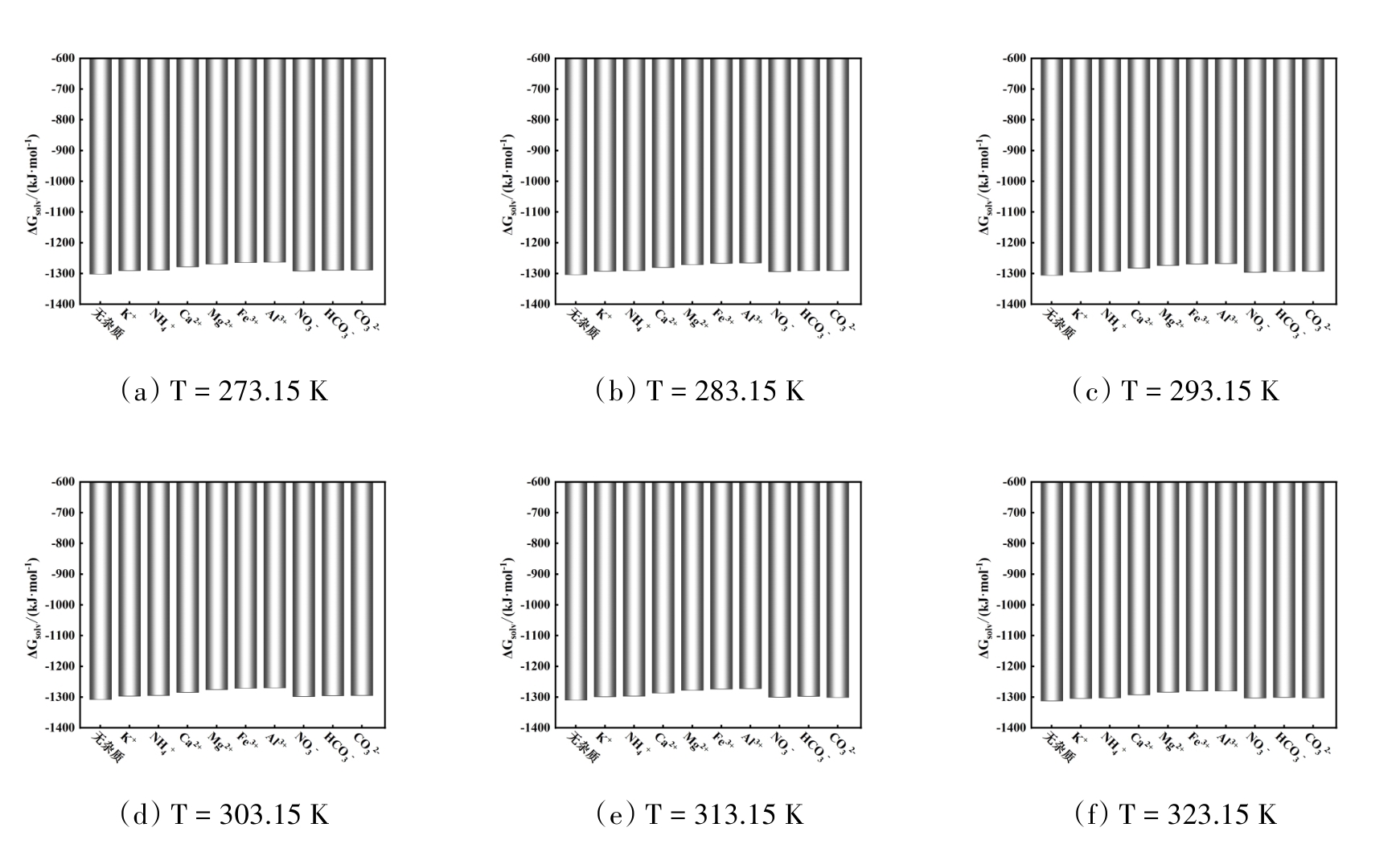
图7 温度在273.15 ~ 323.15 K范围内不同无机杂质存在时Na2SO4的溶剂化自由能
Fig. 7 Solvation free energy of Na2SO4 with different inorganic impurities in the temperature range of 273.15 ~ 323.15 K
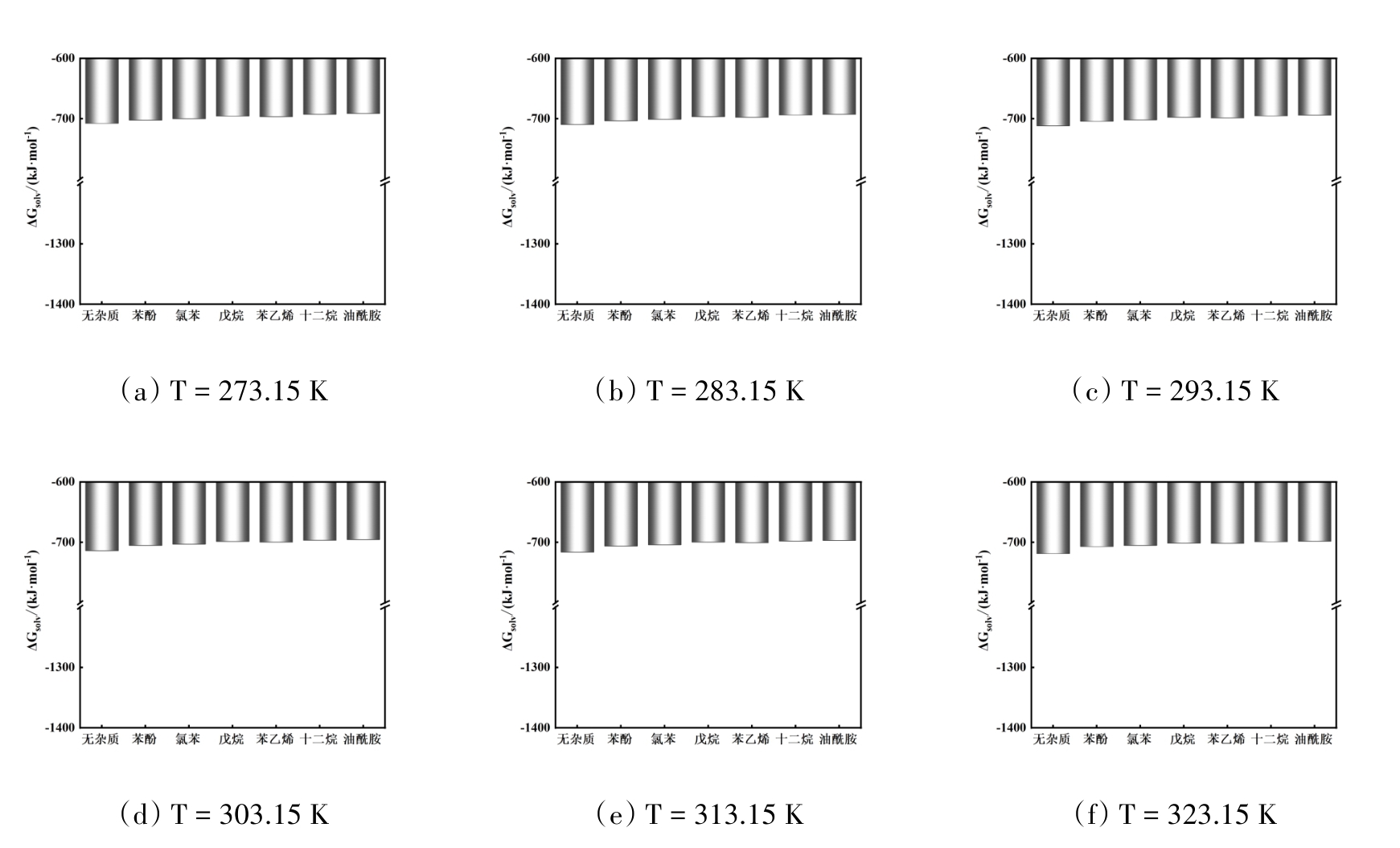
图9 温度在273.15 ~ 323.15 K范围内不同有机杂质存在时NaCl的溶剂化自由能
Fig. 9 Solvation free energy of NaCl with different organic impurities in the temperature range of 273.15 ~ 323.15 K
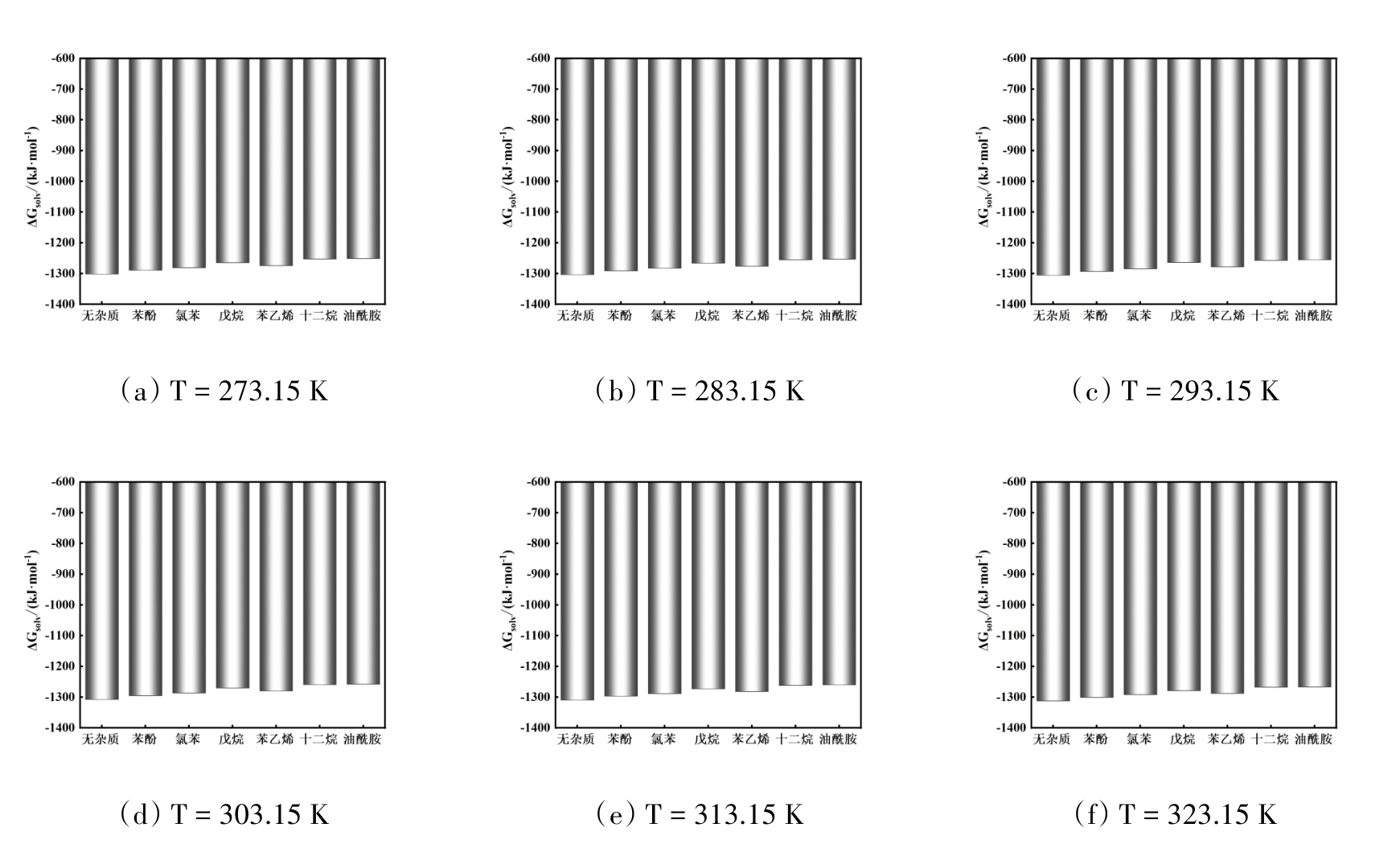
图11 温度在273.15 ~ 323.15 K范围内不同有机杂质存在时Na2SO4的溶剂化自由能
Fig. 11 Solvation free energy of Na2SO4 with different organic impurities in the temperature range of 273.15 ~ 323.15 K
| [1] | 朱彬彬. "十五五" 我国煤化工产业发展趋势[J]. 石油石化绿色低碳, 2025, 10(4): 1-6. |
| Zhu B B. "Development Trends of China's Coal Chemical Industry in the 15th Five-Year Plan Period."[J]. Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction in Petroleum and Petrochemical Industry, 2025, 10(4): 1-6. | |
| [2] | 张朋朋, 陈涛, 陈虎, 等. 煤化工行业固体废物资源化利用现状及展望[J]. 煤化工, 2024, 52(3): 1-5, 10. |
| Zhang P P, Chen T, Chen H, et al. Current status and prospect of resource utilization of solid waste in coal chemical industry[J]. Coal Chemical Industry, 2024, 52(3): 1-5, 10. | |
| [3] | 程文婷, 李杰, 徐丽, 等. AlCl3·6H2O在FeCl3、CaCl2、KCl及KCl–FeCl3溶液中溶解度的实验及预测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 642-652. |
| Cheng W T, Li J, Xu L, et al. Experimental and Predictive Studies on the Solubility of AlCl3·6H2O in FeCl3, CaCl2, KCl, and KCl–FeCl3 Solutions[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 642-652. | |
| [4] | Shen B, Zhao B, Du H, et al. Influence of organic impurities on fractional crystallization of NaCl and Na2SO4 from high-salinity coal chemical wastewater: thermodynamics and nucleation kinetics analysis[J]. Molecules, 2024, 29(9), 1928. |
| [5] | 樊锐, 刘玉坤. 工业废盐资源化处置现状及分析[J]. 环境与发展, 2020,32(8): 52-53. |
| Fan R, Liu Y K. Current status and analysis of industrial waste salt resource disposal[J]. Environment & Development, 2020, 32(8): 52-53. | |
| [6] | 王年禧, 霍慧敏, 何艺, 等. 化工废盐产生和处理技术研究进展及启示[J]. 环境工程学报, 2024, 18(11): 3149-3156. |
| Wang N X, Huo H M, He Y, et al. Research progress and inspiration on the generation and treatment technology of chemical waste salt[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2024, 18(11): 3149-3156. | |
| [7] | Burrows C J, Harper J B, Sander W, et al. Solvation effects in organic chemistry[J]. The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2022, 87(3): 1599-1601. |
| [8] | 黄欣, 陈业钢, 苏楠楠, 等. 高盐废水分质结晶及资源化利用研究进展[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2019, 36(1): 10-23. |
| Huang X, Chen Y G, Su N N, et al. Research on fractional crysallization technologies for recovering salts from high salinity wastewater[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2019, 36(1): 10-23. | |
| [9] | Su N N, Wang Y L, Xiao Y, et al. Mechanism of influence of organic impurity on crystallization of sodium sulfate[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(5): 1705-1713. |
| [10] | Sheng K, Wang Z, Li L, et al. Solvent-mediated separation and reversible transformation of 1D supramolecular polymorphs built from [W10O32]4– templated 48-nuclei silver(I) cluster[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(19): 10595-10603. |
| [11] | Al-Otaibi J S, Mary Y S, Mary Y S, et al. Theoretical and experimental investigation of a pyrazole derivative- solvation effects, reactivity analysis and MD simulations[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2022, 793: 139469. |
| [12] | 杨超. 胆碱类低共熔溶剂的分子设计及其性能研究[D]. 唐山:华北理工大学, 2021. |
| Yang C. Molecular design and properties of choline deepEutectic solvents[D]. Tangshan: North China University of Science and Technology, 2021. | |
| [13] | Qin Z X, Cheng H Y, Song Z, et al. Selection of deep eutectic solvents for extractive deterpenation of lemon essential oil[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2022, 350: 118524. |
| [14] | Zhou T, Chen L, Ye Y M, et al. An overview of mutual solubility of ionic liquids and water predicted by COSMO-RS[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(17): 6256-6264. |
| [15] | 杨同, 王欢, 邓春. 六氟化铀及氟化物汽液相平衡数据预测及精馏过程模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 463-474. |
| Yang T, Wang H, Deng C. Prediction of vapor-liquid equilibrium data of uranium hexatluoride and fluoride and simulation of distillation process[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 463-474. | |
| [16] | 周绍明. 酮类溶剂萃取煤化工高浓含酚废水液液相平衡研究及COSMO-SAC模型预测[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2018. |
| Zhou S M. Study on liquid-liquid equilibrium of high concentration phenol containing wastewater extracted from coal chemical industry using ketone solvents and prediction of COSMO-SAC model[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018. | |
| [17] | 黄赛金, 禹新良. 基于N-P关联式计算溶剂化吉布斯自由能[J]. 湖南工程学院学报(自然科学版), 2024, 34(2): 53-57. |
| Huang S J, Yu X L. Calculation of solvation gibbs energy based on the N-P scheme[J]. Journal of Hunan Institute of Engineering(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 34(2): 53-57. | |
| [18] | 张旭东, 刘彦花, 申峻, 等. COSMO-RS模型在离子液体/低共熔溶剂筛选中的应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(11): 4383-4396. |
| Zhang X D, Liu Y H, Shen J, et al. Recent progres on application of COSMO-RS model in screening of ionic liquids/deep eutectic solvents[J]. ClESC Journal, 2023, 74(11): 4383-4396. | |
| [19] | 李成, 肖杰, 贺飞, 等. 某煤化工副产杂盐资源化及无害化应用研究[J]. 山东化工, 2023, 52(10): 251-253, 256. |
| Li C, Xiao J, He F, et al. Study on resource utilization and harmless application of siscellaneous salt from a coal chemical by-Product[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2023, 52(10):251-253, 256. | |
| [20] | 李鑫达, 王正江, 王璟, 等. 有机物杂质对高盐废水中无机盐结晶回收的影响研究进展[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2025, 42(3): 47-56. |
| Li X D, Wang Z J, Wang J, et al. Research progress on the influence of organics impurities on inorganic salt recovery crystallization process for high salinity wastewater[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2025, 42(3): 47-56. | |
| [21] | 张钟,赵迪,许高洁,等.煤化工含盐废液中杂质对硫酸钠溶解行为影响研究[J].环境工程,2024, 42(9):156-166. |
| Zhang Z, Zhao D, Xu G J, et al. Study on the influence of impurities in salt containing wastewater from coal chemical industry on the dissolution behavior of sodium sulfate[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2024, 42(9): 156-166. | |
| [22] | 高腾飞, 李国选, 雷志刚. 从催化裂化柴油中分离联苯的溶剂筛选:实验和计算热力学[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5314-5323. |
| Gao T F, Li G X, Lei Z G. Solvents selection for separation of biphenyl from FCC diesel: experimental and computational thermodynamics[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(12): 5314-5323. | |
| [23] | Qi C X, Zhang Z X, Chen L F, et al. Systematic screening ionic liquid as extractant for benzene-cyclohexane separation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 345: 127168. |
| [24] | Cheng H Y, Li J S, Wang J W, et al. Enhanced vitamin E extraction selectivity from deodorizer distillate by a biphasic system: a COSMO-RS and experimental study[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(4): 5547-5554. |
| [25] | 黄立果. 低转变温度混合物(LTTMs)用于苯-正庚烷萃取分离的研究[D]. 东营:中国石油大学(华东), 2019. |
| Huang L G. Study on extraction and separation of benzene-heptane by low transition temperature mixtures (LTTMs)[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum (Huadong), 2019. | |
| [26] | 赵迪. 用于蒽和咔唑分离的离子液体合成与应用研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京), 2022. |
| Zhao D. Synthesis and application of ionic liquids for separation of anthracene and carbazole[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology (Beijing), 2022. | |
| [27] | Euldji I, Benmouloud W, Paduszyński K, et al. Hybrid improved grey wolf support vector regression algorithm for modeling solubilities of APIs in pure ionic liquids: σ-profile descriptors[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2024, 64(4): 1361-1376. |
| [28] | Laakso J P, Gorji A E, Uusi-Kyyny P, et al. Machine learning modeling of the CO2 solubility in ionic liquids by using σ-profile descriptors[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2025, 307: 121226. |
| [29] | Zhang J, Wang Q, Shen W F. Message-passing neural network based multi-task deep-learning framework for COSMO-SAC based σ-profile and Vcosmo prediction[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 254: 117624. |
| [30] | 柳士开. 苯-环己烷体系LTTMs萃取剂筛选和相平衡研究[D]. 东营:中国石油大学(华东)化学工程与技术, 2018. |
| Liu S K. Extractant screening of LTTMs and phase equilibrium study for benzene-cyclohexane system[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum (Huadong), 2018. | |
| [31] | Jiang J Y, Guo L, Tang L P, et al. The manner and extent to which the hydration shell impacts interactions between hydrated species[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2021, 23(36): 20496-20508. |
| [32] | Yuan L, Wen J W, Ning P G, et al. Inhibition role of solvation on the selective extraction of co(II): toward eco-friendly separation of Ni and co[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2022, 10(3): 1160-1171. |
| [33] | Chen J, Zheng L L, Ji X H, et al. Aqueous self-assembly of hydrophobic molecules influenced by the molecular geometry[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2022, 126(6): 1334-1340. |
| [1] | 密晓光, 孙国刚, 程昊, 张晓慧. 印刷电路板式天然气冷却器性能仿真模型和验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| [2] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [3] | 张文锋, 郭玮, 张新玉, 曹昊敏, 丁国良. 铝管铝翅片换热器模型开发及软件实现[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 84-92. |
| [4] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [5] | 臧子晴, 李修真, 谈莹莹, 刘晓庆. 分凝器对两级分离自复叠制冷循环特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [6] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [7] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [8] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [9] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [10] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [11] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [12] | 卓森庆, 陈华, 陈伟, 尚彬, 刘恒恒, 古汤汤, 白韡, 王龙炎, 曹昊敏, 丁国良. 多联式空调系统APF性能仿真的模型开发与软件实现[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 370-376. |
| [13] | 王一飞, 李玉星, 欧阳欣, 赵雪峰, 孟岚, 胡其会, 殷布泽, 郭雅琦. 基于裂尖减压特性的CO2管道断裂扩展数值计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4683-4693. |
| [14] | 田鹏, 张忠林, 任超, 孟国超, 郝晓刚, 刘叶刚, 侯起旺, ABUDULA Abuliti, 官国清. 基于自热再生的一种低温甲醇洗工艺建模与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4601-4612. |
| [15] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号