• •
胡瑾秋1,2,3( ), 马铭骏1,2,3(
), 马铭骏1,2,3( ), 张来斌1,2,3, 董家延1,2,3
), 张来斌1,2,3, 董家延1,2,3
收稿日期:2025-10-27
修回日期:2025-12-22
出版日期:2026-01-05
通讯作者:
马铭骏
作者简介:胡瑾秋(1983—),女,博士,教授,hujq@cup.edu.cn
基金资助:
Jinqiu HU1,2,3( ), Mingjun MA1,2,3(
), Mingjun MA1,2,3( ), Laibin ZHANG1,2,3, Jiayan DONG1,2,3
), Laibin ZHANG1,2,3, Jiayan DONG1,2,3
Received:2025-10-27
Revised:2025-12-22
Online:2026-01-05
Contact:
Mingjun MA
摘要:
炼化装置进出料管道长期处于高温、高压与强腐蚀介质耦合作用下,冲刷腐蚀、化学腐蚀并存,传统基于阈值与规则库的健康分级在多源时变工况与类不均衡场景下存在应用局限性,依靠单一指标得到的管道腐蚀健康状态易失稳。为解决这一问题,本文以硫酸烷基化装置精制单元进出料管道为研究对象,提出了一种针对炼化装置管道的腐蚀健康状态评估方法。首先依据工程规范与企业管理规定设定四项指标阈值,将样本划分为健康/亚健康/退化/失效4个等级,接着提出基于门控线性单元增强自编码器(GLAE)和多层感知机(MLP)的健康状态评估分类模型,训练后对测试集样本进行健康状态评估。结果表明,基于GLAE-MLP健康状态评估模型在测试集中实现了97.2%的样本保持原判,仅2.7%发生相邻等级漂移,在与MLP、AE-MLP的对比中,GLAE-MLP模型分别在在准确率、精确率、召回率和F1分数4个指标上均表现更优,分别达到了97.24%、96.83%、95.51%、96.12%,能有效完成对管道腐蚀健康状态的评估。
中图分类号:
胡瑾秋, 马铭骏, 张来斌, 董家延. 基于GLAE-MLP的炼化装置管道腐蚀健康状态评估方法[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251192.
Jinqiu HU, Mingjun MA, Laibin ZHANG, Jiayan DONG. Corrosion health status assessment method for refining unit pipeline based on GLAE-MLP[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251192.
| 指标 | 定义和公式 | 工程依据 | 评估维度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 安全裕度 | ASME B31.3;API 579-1/FFS-1;API 570 | 绝对安全边界: | |
| 相对厚度比 | API 574 | 相对退化:跨管径和材质可比,便于可视化与横向比较。 | |
| 腐蚀速率 | API 570;API 574; API 581 | 腐蚀动力学 | |
| 年检维次数 | API 580;API 581 | 外部扰动:事件频度越高通常越不利;必要时用有效覆盖时长 |
表1 健康状态指标设置以及对应关系
Table 1 Health status indicator settings and corresponding relationships
| 指标 | 定义和公式 | 工程依据 | 评估维度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 安全裕度 | ASME B31.3;API 579-1/FFS-1;API 570 | 绝对安全边界: | |
| 相对厚度比 | API 574 | 相对退化:跨管径和材质可比,便于可视化与横向比较。 | |
| 腐蚀速率 | API 570;API 574; API 581 | 腐蚀动力学 | |
| 年检维次数 | API 580;API 581 | 外部扰动:事件频度越高通常越不利;必要时用有效覆盖时长 |
| 判别原则 | 健康 | 亚健康 | 退化 | 失效 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最不利原则 | 339 | 291 | 86 | 4 |
| 加权评分原则 | 364 | 302 | 52 | 2 |
| 中位数原则 | 379 | 313 | 27 | 1 |
表2 基于三个判定原则的划分结果
Table 2 Classification results based on three decision principles
| 判别原则 | 健康 | 亚健康 | 退化 | 失效 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最不利原则 | 339 | 291 | 86 | 4 |
| 加权评分原则 | 364 | 302 | 52 | 2 |
| 中位数原则 | 379 | 313 | 27 | 1 |
| 等级 | /mm | /(mm/a) | /(次/a) | 划分规则 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ健康 | [3,+∞) | [0.95,+∞) | [0,0.10) | [0,1) | 4个指标同时满足Ⅰ级 |
| Ⅱ亚健康 | [2,3) | [0.85,0.95) | [0.10,0.30) | [1,2) | 全部≥Ⅱ级,且至少一项在Ⅱ级 |
| Ⅲ退化 | [0,2) | [0.75,0.85) | [0.30,0.50) | [2,5) | 任何一项在Ⅲ级,则≥Ⅲ级 |
| Ⅳ失效 | (-∞,0] | (-∞,0.75) | [0.50,+∞) | [5,+∞) | 任何一项满足即为Ⅳ级 |
表3 基于最不利原则的P-4101-B21Y管段腐蚀健康状态划分规则
Table 3 Classification rules of corrosion health status of P-4101-B21Y pipe section based on the most unfavorable principle
| 等级 | /mm | /(mm/a) | /(次/a) | 划分规则 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ健康 | [3,+∞) | [0.95,+∞) | [0,0.10) | [0,1) | 4个指标同时满足Ⅰ级 |
| Ⅱ亚健康 | [2,3) | [0.85,0.95) | [0.10,0.30) | [1,2) | 全部≥Ⅱ级,且至少一项在Ⅱ级 |
| Ⅲ退化 | [0,2) | [0.75,0.85) | [0.30,0.50) | [2,5) | 任何一项在Ⅲ级,则≥Ⅲ级 |
| Ⅳ失效 | (-∞,0] | (-∞,0.75) | [0.50,+∞) | [5,+∞) | 任何一项满足即为Ⅳ级 |
| 等级 | /mm | /(mm/a) | /(次/a) | 说明 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ健康 | [4,+∞) | [0.96,+∞) | [0,0.05) | [0,1) | 4个指标同时满足Ⅰ级 |
| Ⅱ亚健康 | [3,4) | [0.88,0.96) | [0.10,0.20) | [1,2) | 全部≥Ⅱ级,且至少一项在Ⅱ级 |
| Ⅲ退化 | [1,3) | [0.78,0.88) | [0.30,0.40) | [2,5) | 任何一项在Ⅲ级,则≥Ⅲ级 |
| Ⅳ失效 | (-∞,1] | (-∞,0.78) | [0.40,+∞) | [5,+∞) | 任何一项满足即为Ⅳ级 |
表4 基于最不利原则的AL-4101-B41K管段腐蚀健康状态划分规则
Table 4 Classification rules of corrosion health status of AL-4101-B41K pipe section based on the most unfavorable principle
| 等级 | /mm | /(mm/a) | /(次/a) | 说明 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ健康 | [4,+∞) | [0.96,+∞) | [0,0.05) | [0,1) | 4个指标同时满足Ⅰ级 |
| Ⅱ亚健康 | [3,4) | [0.88,0.96) | [0.10,0.20) | [1,2) | 全部≥Ⅱ级,且至少一项在Ⅱ级 |
| Ⅲ退化 | [1,3) | [0.78,0.88) | [0.30,0.40) | [2,5) | 任何一项在Ⅲ级,则≥Ⅲ级 |
| Ⅳ失效 | (-∞,1] | (-∞,0.78) | [0.40,+∞) | [5,+∞) | 任何一项满足即为Ⅳ级 |
| T | X1/℃ | X2 | X3/ MPa | X4/(m³/h) | X5/(m/s) | X6/% | X7/ppm | X8/ppm | X9/ppm | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9.84 | 2.14 | 1.05 | 0.37 | 11.27 | 98.11 | 9.92 | 1.77 | 97.49 | 3.84 | 0.95 | 0.14 | 0 |
| 2 | 9.97 | 2.10 | 1.09 | 0.37 | 11.23 | 98.05 | 5.72 | 1.57 | 91.13 | 4.84 | 0.97 | 0.08 | 0 |
| 3 | 9.66 | 2.11 | 1.06 | 0.36 | 11.58 | 98.59 | 6.96 | 1.51 | 53.93 | 3.39 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 0 |
| 4 | 9.94 | 2.04 | 1.04 | 0.41 | 11.21 | 98.22 | 7.42 | 1.87 | 55.60 | 4.88 | 0.96 | 0.08 | 0 |
| 5 | 9.49 | 2.07 | 1.09 | 0.41 | 11.10 | 98.70 | 9.57 | 1.31 | 95.33 | 4.48 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 0 |
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| 1549 | 8.72 | 2.11 | 1.03 | 0.37 | 11.14 | 98.52 | 9.35 | 1.86 | 61.35 | 2.84 | 0.87 | 0.32 | 1 |
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| 3600 | 8.77 | 2.02 | 1.10 | 0.41 | 11.25 | 98.50 | 8.90 | 1.07 | 53.18 | 4.05 | 0.84 | 0.21 | 0 |
表5 硫酸烷基化精制单元进出料管道工况参数数据集
Table 5 Operating parameter dataset of inlet and outlet pipelines in the sulfuric acid alkylation refining unit
| T | X1/℃ | X2 | X3/ MPa | X4/(m³/h) | X5/(m/s) | X6/% | X7/ppm | X8/ppm | X9/ppm | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9.84 | 2.14 | 1.05 | 0.37 | 11.27 | 98.11 | 9.92 | 1.77 | 97.49 | 3.84 | 0.95 | 0.14 | 0 |
| 2 | 9.97 | 2.10 | 1.09 | 0.37 | 11.23 | 98.05 | 5.72 | 1.57 | 91.13 | 4.84 | 0.97 | 0.08 | 0 |
| 3 | 9.66 | 2.11 | 1.06 | 0.36 | 11.58 | 98.59 | 6.96 | 1.51 | 53.93 | 3.39 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 0 |
| 4 | 9.94 | 2.04 | 1.04 | 0.41 | 11.21 | 98.22 | 7.42 | 1.87 | 55.60 | 4.88 | 0.96 | 0.08 | 0 |
| 5 | 9.49 | 2.07 | 1.09 | 0.41 | 11.10 | 98.70 | 9.57 | 1.31 | 95.33 | 4.48 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 0 |
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| 1549 | 8.72 | 2.11 | 1.03 | 0.37 | 11.14 | 98.52 | 9.35 | 1.86 | 61.35 | 2.84 | 0.87 | 0.32 | 1 |
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| 3600 | 8.77 | 2.02 | 1.10 | 0.41 | 11.25 | 98.50 | 8.90 | 1.07 | 53.18 | 4.05 | 0.84 | 0.21 | 0 |
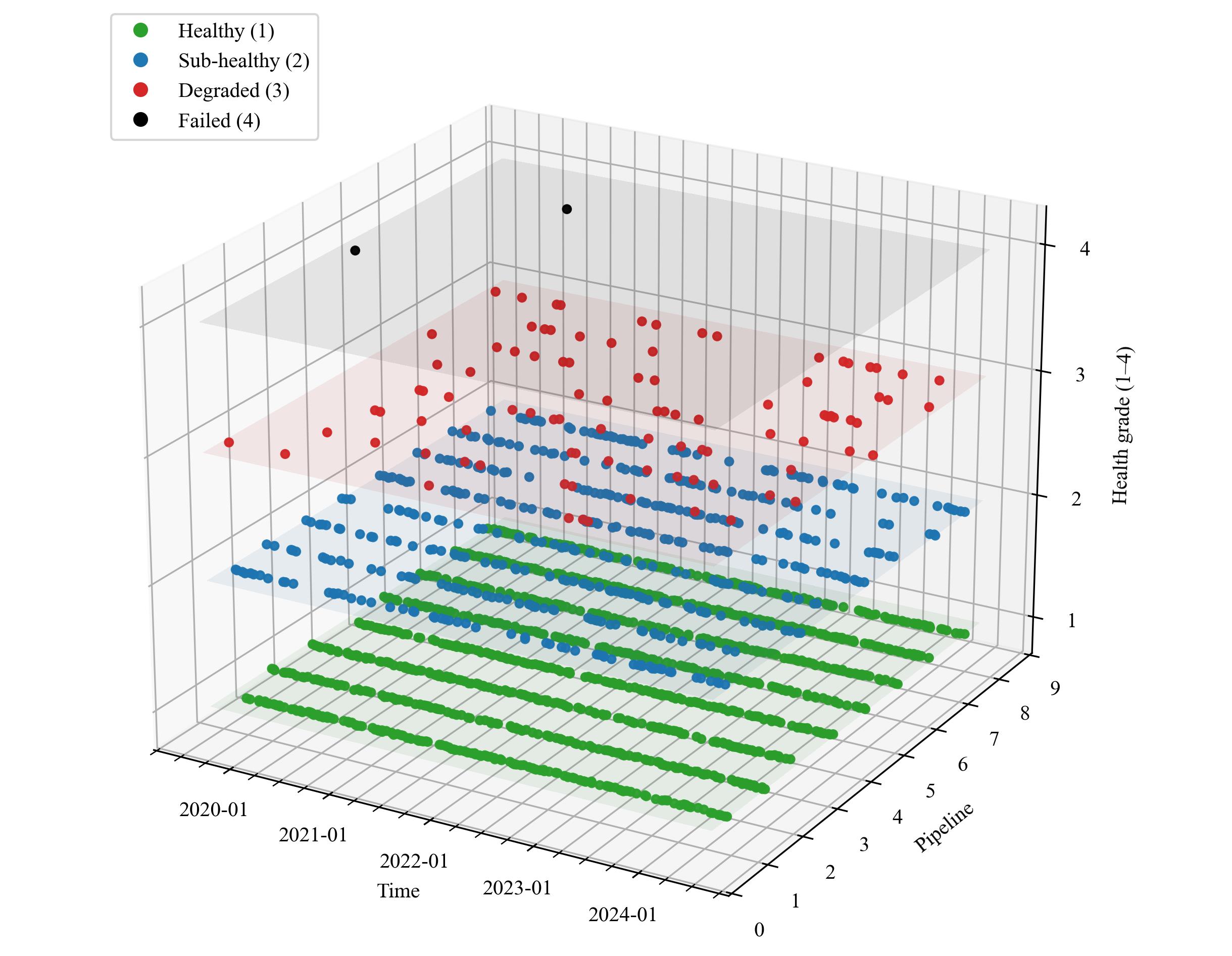
图6 数据集中不同健康状态对应的数据采集日期和采集管道分布
Fig.6 The distribution of data collection dates and collection pipelines corresponding to different health states in the dataset
| T | X1/℃ | X2 | X5/(m/s) | X6/% | X7/ppm | X8/ppm | X9/ppm | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9.84 | 2.14 | 11.27 | 98.11 | 9.92 | 1.77 | 97.49 | 3.84 | 0.95 | 0.14 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 9.97 | 2.10 | 11.23 | 98.05 | 5.72 | 1.57 | 91.13 | 4.84 | 0.97 | 0.08 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 9.66 | 2.11 | 11.58 | 98.59 | 6.96 | 1.51 | 53.93 | 3.39 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 9.94 | 2.04 | 11.21 | 98.22 | 7.42 | 1.87 | 55.60 | 4.88 | 0.96 | 0.08 | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | 9.49 | 2.07 | 11.10 | 98.70 | 9.57 | 1.31 | 95.33 | 4.48 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 0 | 1 |
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| 1549 | 8.72 | 2.11 | 11.14 | 98.52 | 9.35 | 1.86 | 61.35 | 2.84 | 0.87 | 0.32 | 1 | 2 |
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| 3600 | 8.77 | 2.02 | 11.25 | 98.50 | 8.90 | 1.07 | 53.18 | 4.05 | 0.84 | 0.21 | 0 | 1 |
表6 特征筛选后的硫酸烷基化精制单元进出料管道工况参数及状态标注
Table 6 Operating condition parameters and status annotation of inlet and outlet pipelines in the sulfuric acid alkylation refining unit after feature selection
| T | X1/℃ | X2 | X5/(m/s) | X6/% | X7/ppm | X8/ppm | X9/ppm | Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9.84 | 2.14 | 11.27 | 98.11 | 9.92 | 1.77 | 97.49 | 3.84 | 0.95 | 0.14 | 0 | 1 |
| 2 | 9.97 | 2.10 | 11.23 | 98.05 | 5.72 | 1.57 | 91.13 | 4.84 | 0.97 | 0.08 | 0 | 1 |
| 3 | 9.66 | 2.11 | 11.58 | 98.59 | 6.96 | 1.51 | 53.93 | 3.39 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 0 | 1 |
| 4 | 9.94 | 2.04 | 11.21 | 98.22 | 7.42 | 1.87 | 55.60 | 4.88 | 0.96 | 0.08 | 0 | 1 |
| 5 | 9.49 | 2.07 | 11.10 | 98.70 | 9.57 | 1.31 | 95.33 | 4.48 | 0.94 | 0.08 | 0 | 1 |
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| 1549 | 8.72 | 2.11 | 11.14 | 98.52 | 9.35 | 1.86 | 61.35 | 2.84 | 0.87 | 0.32 | 1 | 2 |
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| 3600 | 8.77 | 2.02 | 11.25 | 98.50 | 8.90 | 1.07 | 53.18 | 4.05 | 0.84 | 0.21 | 0 | 1 |
| 模型 | 准确率 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1分数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLP | 91.85% | 84.94% | 84.45% | 84.69% |
| AE-MLP | 92.82% | 86.46% | 89.52% | 87.60% |
| GLAE-MLP | 97.24% | 96.83% | 95.51% | 96.12% |
表7 3种评估模型的性能指标对比
Table 7 Comparison of performance metrics of 3 evaluation models
| 模型 | 准确率 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1分数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLP | 91.85% | 84.94% | 84.45% | 84.69% |
| AE-MLP | 92.82% | 86.46% | 89.52% | 87.60% |
| GLAE-MLP | 97.24% | 96.83% | 95.51% | 96.12% |
| [1] | Soomro A A, Mokhtar A A, Kurnia J C, et al. Integrity assessment of corroded oil and gas pipelines using machine learning: a systematic review[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2022, 131: 105810. |
| [2] | Yang J F, Li R, Chen L C, et al. Research on equipment corrosion diagnosis method and prediction model driven by data[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 158: 418-431. |
| [3] | 张洪华, 曾凌, 张小珍. 石油储油罐健康状态评估系统的建设分析[J]. 机电技术, 2022, 45(6): 87-90. |
| Zhang H H, Zeng L, Zhang X Z. Analysis on the construction of health assessment system for oil storage tanks[J]. Mechanical & Electrical Technology, 2022, 45(6): 87-90. | |
| [4] | 王宝轩, 沈功田, 闫河, 等. 大型石油储罐健康管理方法应用研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(16): 125-133. |
| Wang B X, Shen G T, Yan H, et al. Study on the application of health management methods for large oil storage tanks[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(16): 125-133. | |
| [5] | American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). Process Piping [S]. New York, NY: American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), 2022: 121-250. |
| [6] | American Petroleum Institute (API). Piping Inspection Code: In-Service Inspection, Rating, Repair, and Alteration of Piping Systems [S]. Washington, D.C.: American Petroleum Institute (API), 2023: 21-80 |
| [7] | American Petroleum Institute (API). Risk-Based Inspection [S]. Washington, D.C.: American Petroleum Institute (API), 2023: 31-70. |
| [8] | 练小晖. RBI技术在炼化装置中的应用[J]. 化工装备技术, 2012, 33(6): 37-40, 43. |
| Lian X H. Application of RBI technology in refining unit[J]. Chemical Equipment Technology, 2012, 33(6): 37-40, 43. | |
| [9] | Bhatia K, Khan F, Patel H, et al. Dynamic risk-based inspection methodology[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2019, 62: 103974. |
| [10] | Moore D A. Security Risk Assessment Methodology for the petroleum and petrochemical industries[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2013, 26(6): 1685-1689. |
| [11] | 杨旭东, 周艳丽, 刘志娟, 等. 基于RS-PSO-SVM算法的腐蚀管道剩余强度预测技术研究[J]. 石油工程建设, 2020, 46(3): 8-12. |
| Yang X D, Zhou Y L, Liu Z J, et al. Research on residual strength prediction technology of corroded pipeline based on RS-PSO-SVM algorithm[J]. Petroleum Engineering Construction, 2020, 46(3): 8-12. | |
| [12] | Lu Y J, Wang C W, Wang C H. A hybrid diagnostic system for corrosion mechanism identification in petrochemical equipment: Integrating Bayesian probabilities and association rule[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2025, 201: 107577. |
| [13] | 孙同敏. 基于DBN-SVM的航空发动机健康状态评估方法[J]. 控制工程, 2021, 28(6): 1163-1170. |
| Sun T M. Evaluation method of aero-engine health status based on DBN-SVM[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2021, 28(6): 1163-1170. | |
| [14] | 单增海, 李志远, 张旭, 等. 基于多传感器信息融合和多粒度级联森林模型的液压泵健康状态评估[J]. 中国机械工程, 2021, 32(19): 2374-2382. |
| Shan Z H, Li Z Y, Zhang X, et al. Health evaluation of hydraulic pump based on multi-sensor information fusion and multi-granularity cascade forest model[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 32(19): 2374-2382. | |
| [15] | 尹刚, 钱中友, 曹文琦, 等. 基于Adaboost-PSO-SVM的铝电解槽健康状态诊断方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(1): 354-365. |
| Yin G, Qian Z Y, Cao W Q, et al. Research on health diagnosis method of aluminum reduction cell based on Adaboost-PSO-SVM[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(1): 354-365. | |
| [16] | 陈雄姿, 于劲松, 唐荻音, 等. 基于贝叶斯LS-SVR的锂电池剩余寿命概率性预测[J]. 航空学报, 2013, 34(9): 2219-2229. |
| Chen X Z, Yu J S, Tang D Y, et al. Probabilistic prediction of lithium battery remaining life based on Bayesian LS-SVR[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2013, 34(9): 2219-2229. | |
| [17] | 李超然, 肖飞, 樊亚翔, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的锂离子电池SOH估算[J]. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(19): 4106-4119. |
| Li C R, Xiao F, Fan Y X, et al. SOH estimation of lithium-ion battery based on convolutional neural network[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2020, 35(19): 4106-4119. | |
| [18] | 陈丰, 徐欢. 基于MLP算法的电力企业数据健康度模型算法研究[J/OL]. 自动化技术与应用, 1-5[2025-10-12]. |
| Chen F, Xu H. Research on the algorithm of data health model for power enterprises based on MLP algorithm [J/OL]. Techniques of Automation and Applications, 1-5[2025-10-12]. | |
| [19] | 张驰, 郭媛, 黎明. 人工神经网络模型发展及应用综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(11): 57-69. |
| Zhang C, Guo Y, Li M. Review on the development and application of artificial neural network model[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(11): 57-69. | |
| [20] | 周敏. 中国石油炼化企业腐蚀与控制现状[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2012, 33(S2): 62-68. |
| Zhou M. Current situation of corrosion and control in PetroChina refining and chemical enterprises [J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2012, 33 (S2): 62-68. | |
| [21] | 匡正, 袁志波, 徐振磊. 基于HMM-MLP的泵站监测健康诊断系统研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2024(7): 255-261, 269. |
| Kuang Z, Yuan Z B, Xu Z L. Research on monitoring and health diagnosis system of pumping station based on HMM-MLP[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2024(7): 255-261, 269. | |
| [22] | Huang X H, Xiao H W, Liu X C, et al. Quantitative analysis of steel composition based on multivariate Genetic Algorithm-Optimized Multilayer Perceptron (GA-MLP) model combined with Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS)[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2025, 218: 114805. |
| [23] | 来杰, 王晓丹, 向前, 等. 自编码器及其应用综述[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(9): 218-230. |
| Lai J, Wang X D, Xiang Q, et al. Overview of self-encoder and its application[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(9): 218-230. | |
| [24] | 黄立威, 江碧涛, 吕守业, 等. 基于深度学习的推荐系统研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(7): 1619-1647. |
| Huang L W, Jiang B T, ( Lü/lv/lu/lyu) S Y, et al. Review of recommendation system based on deep learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(7): 1619-1647. | |
| [25] | Liu C, Zhen J T, Shan W. Time series classification based on convolutional network with a Gated Linear Units kernel[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 123: 106296. |
| [26] | Jahan I, Ahmed M F, Ali M O, et al. Self-gated rectified linear unit for performance improvement of deep neural networks[J]. ICT Express, 2023, 9(3): 320-325. |
| [27] | 裴洪, 胡昌华, 司小胜, 等. 基于机器学习的设备剩余寿命预测方法综述[J]. 机械工程学报, 2019, 55(8): 1-13. |
| Pei H, Hu C H, Si X S, et al. Overview of the prediction methods of equipment remaining life based on machine learning[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(8): 1-13. | |
| [28] | 贾科, 杨哲, 魏超, 等. 基于斯皮尔曼等级相关系数的新能源送出线路纵联保护[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44(15): 103-111. |
| Jia K, Yang Z, Wei C, et al. Pilot protection of new energy transmission line based on Spearman's rank correlation coefficient[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44(15): 103-111. | |
| [29] | Zhang L, Wang L. Optimization of site investigation program for reliability assessment of undrained slope using Spearman rank correlation coefficient[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2023, 155: 105208. |
| [30] | American Petroleum Institute (API), American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME). Fitness-For-Service [S]. Washington, D.C.: American Petroleum Institute (API); New York, NY: American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), 2021: 301-600. |
| [31] | Luo L Y, Fan X Q, Wang M, et al. Two-stage deep complex gated convolution attention network for multi-channel noise suppression[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2025, 19(7): 512. |
| [32] | Liu S H, Wang Y S, Sun J K, et al. An efficient Spatial–Temporal model based on gated linear units for trajectory prediction[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 492: 593-600. |
| [1] | 王三一, 黄文来. 电化学合成氨流程建模与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4474-4486. |
| [2] | 周轶磊, 李智, 彭鑫. 基于代理模型的连续重整反应过程自优化控制结构设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4499-4511. |
| [3] | 朱春梦, 李增, 柳楠, 赵云鹏, 石孝刚, 蓝兴英. 基于自编码器和多尺度符号转移熵的FCC沉降器跑剂故障检测[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4512-4523. |
| [4] | 王金江, 鲁振杰, 安维峥, 杨风允, 秦小刚. ORC发电系统工艺过程预警诊断技术研究与展望[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3137-3152. |
| [5] | 丁宏鑫, 干文翔, 赵雍洋, 贾润泽, 康子祺, 赵玉隆, 向勇. X65钢焊接接头在超临界CO2相及富H2O相中的腐蚀机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3426-3435. |
| [6] | 张涵川, 尚超, 吕文祥, 黄德先, 张亚宁. 基于无监督时序聚类的催化裂化装置工况划分识别与产率预测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2781-2790. |
| [7] | 康佳, 刘欢, 李海燕, 罗茂亮, 姚洪. 宽温区HCl/NaOH热介质中碳钢腐蚀行为及涂层性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2872-2885. |
| [8] | 熊敏, 刘冬妹, 王智超, 周利, 吉旭. 变负荷条件下绿氨生产操作参数的调控与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2791-2801. |
| [9] | 王法正, 隋璘, 熊伟丽. 面向多采样率数据的TTPA-LSTM软测量建模[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1635-1646. |
| [10] | 王宗廷, 王丽丽, 孙晓岩, 夏力, 陶少辉, 项曙光. 基于简化相平衡关联式的高效简捷精馏塔模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1133-1142. |
| [11] | 王大芬, 唐莉丽, 张鑫焱, 聂春雨, 李明珠, 吴菁. 基于时差的多输出tri-training异构软测量建模[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1143-1155. |
| [12] | 王天平, 贾旭翔, 王宇, 叶春松. 发电机定子铜导线腐蚀堵塞机理及控制技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5816-5827. |
| [13] | 赵斌, 廖静, 任延杰, 周俊臣, 李岩. 化学-电化学协同刻蚀制备超疏水铝合金及其性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 6008-6017. |
| [14] | 任超, 王凯, 韩洁, 阳春华. 事件-时间触发的慢时变工业过程动态调度方法[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 256-265. |
| [15] | 李彦, 郭红利, 苏国庆, 张建文. 加氢装置空冷器气液两相流动与冲刷腐蚀问题[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 141-150. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号