化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 5816-5827.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250679
• 综述与专论 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-06-22
修回日期:2025-07-16
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
王天平,叶春松
作者简介:王天平(1993—),男,博士,tpwang@suda.edu.cn
基金资助:
Tianping WANG1( ), Xuxiang JIA2, Yu WANG3, Chunsong YE4(
), Xuxiang JIA2, Yu WANG3, Chunsong YE4( )
)
Received:2025-06-22
Revised:2025-07-16
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
Tianping WANG, Chunsong YE
摘要:
水冷发电机在核电站、火电厂和水电站应用广泛,但其定子空心铜导线在内冷水中容易发生腐蚀堵塞,进而导致系统运行异常甚至生产安全事故。揭示腐蚀堵塞机理,并基于此发展腐蚀堵塞控制技术具有重要意义。介绍了定子内冷水系统的特点和腐蚀堵塞危害,系统总结了铜腐蚀产物“形成-脱落-局部沉积”的腐蚀堵塞形成机理,探讨了用于控制腐蚀堵塞的水化学调控技术,并结合理论和工程实践重新审视了铜导线在不同水化学条件下的腐蚀堵塞倾向,得出微碱性水化学条件能更有效地抑制腐蚀堵塞的结论。最后从机理研究和工程应用两方面进行了展望,提出进一步揭示腐蚀堵塞的动力学过程以及开发系统状态监测与故障诊断平台,从而更好地为水冷发电机的安全经济运行提供理论依据和技术支撑。
中图分类号:
王天平, 贾旭翔, 王宇, 叶春松. 发电机定子铜导线腐蚀堵塞机理及控制技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5816-5827.
Tianping WANG, Xuxiang JIA, Yu WANG, Chunsong YE. Research progress on mechanism and control strategies of corrosion and plugging in generator stator copper conductors[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5816-5827.
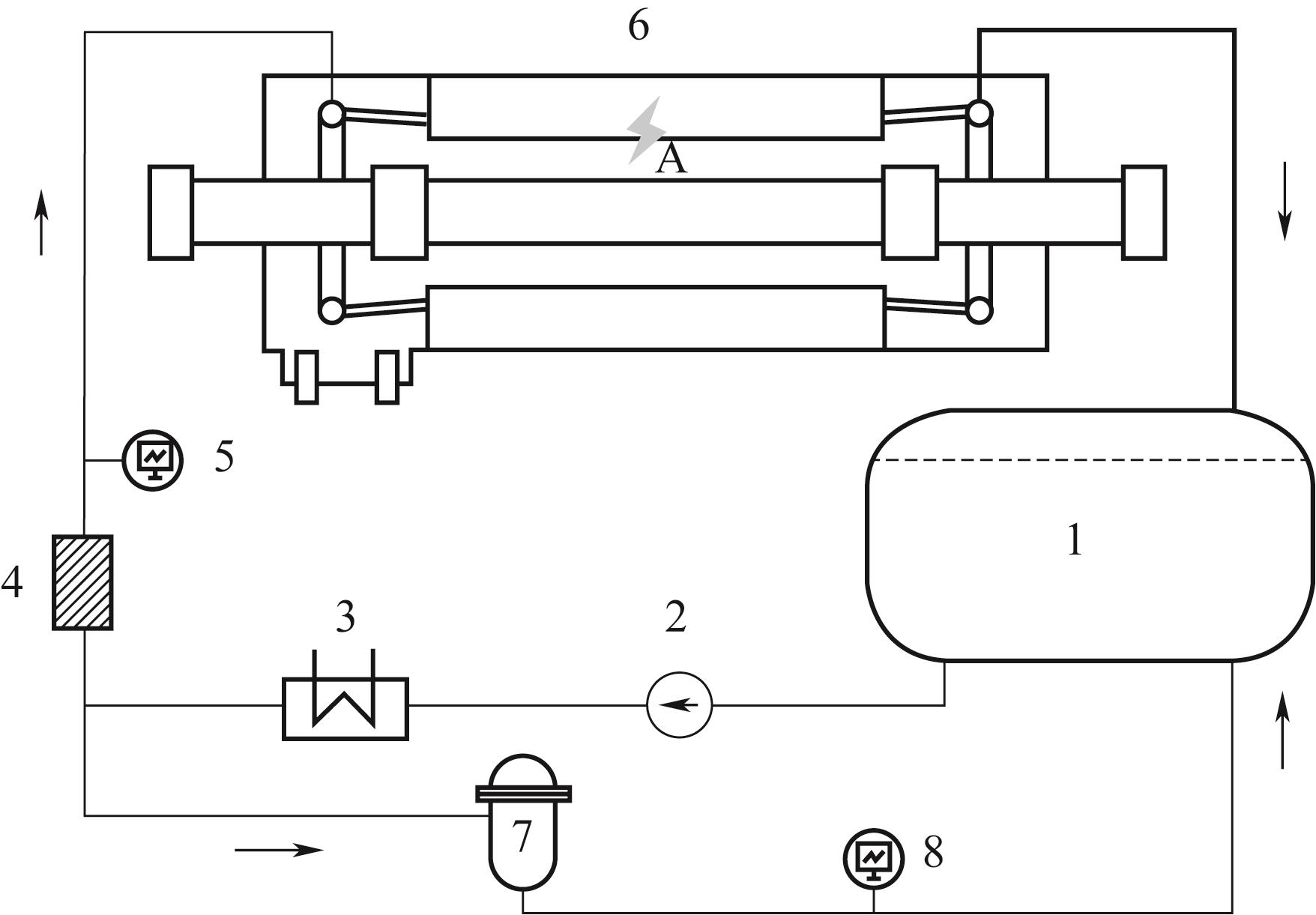
图2 发电机定子内冷水系统示意图1—冷却水水箱;2—循环水泵;3—冷却器;4—过滤器;5—主路水质监测系统;6—带强电流的发电机定子;7—旁路处理系统;8—旁路水质监测系统
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of the internal cooling water system of generator stators1—cooling water tank; 2—circulating water pump; 3—cooler; 4—filter; 5—water quality monitoring system of mainstream; 6—generator stator with strong current; 7—bypass treatment system; 8—water quality monitoring system of bypass
| 水化学条件 | pH25℃ | 电导率κ25℃/(μS/cm) | 铜含量/(μg/L) | 溶解氧含量/(μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高氧微碱性 | 8.0~9.0 | ≤2.0 | ≤20 | >2000 |
| 低氧中性 | 约7.0 | ≤0.2 | ≤20或30 | |
| 高氧中性 | 约7.0 | ≤0.2 | >2000 |
表1 定子内冷水系统不同水化学条件的调控要求[1, 10-13]
Table 1 Requirements of different water chemistry conditions in the stator internal cooling water system[1, 10-13]
| 水化学条件 | pH25℃ | 电导率κ25℃/(μS/cm) | 铜含量/(μg/L) | 溶解氧含量/(μg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高氧微碱性 | 8.0~9.0 | ≤2.0 | ≤20 | >2000 |
| 低氧中性 | 约7.0 | ≤0.2 | ≤20或30 | |
| 高氧中性 | 约7.0 | ≤0.2 | >2000 |
| [1] | The International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam. Technical guidance document: chemistry management in generator water cooling during operation and shutdown: IAP [S]. Banff: IAPWS, 2019. |
| [2] | 于华强, 孟新静, 葛红花. 定子铜线圈在内冷水中的腐蚀与控制[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2021, 42(10): 61-67, 85. |
| Yu H Q, Meng X J, Ge H H. Corrosion and protection of stator copper coil in internal cooling water[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2021, 42(10): 61-67, 85. | |
| [3] | Svoboda R. Corrosion and deposits in water-cooled generator stator windings(part 1): Behaviour of copper[J]. PowerPlant Chemistry, 2018, 20(5): 297-309. |
| [4] | Svoboda M, Bauer T. Corrosion and deposits in water-cooled generator stator windings(part 4): Operating experience with flow restrictions in stator cooling water systems[J]. Powerplant Chemistry, 2019, 21(2): 62-72. |
| [5] | Svoboda R, Blecken W. Corrosion and deposits in water-cooled generator stator windings: overview of water cooling of generators[J]. PowerPlant Chemistry, 2018, 20(5): 290-294. |
| [6] | Maughan C V, Svoboda M. Water-cooled stator windings copper oxide issues[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference (EIC). Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2016: 145-150. |
| [7] | 孟龙, 李俊菀, 王峻峰, 等. 发电机定冷水处理的要点与新技术的概述[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2019, 40(11): 821-825. |
| Meng L, Li J W, Wang J F, et al. Overview of the key points and new technologies of generator stator cooling water treatment[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2019, 40(11): 821-825. | |
| [8] | Fan S P, Zhang R Y, Cao S N, et al. Reviews of generator stator cooling water treatment technology[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2015, 737: 574-578. |
| [9] | 曹顺安, 封冰清, 张芮源. 发电机内冷水处理机理与技术综述[J]. 工业水处理, 2016, 36(5): 15-19. |
| Cao S A, Feng B Q, Zhang R Y. Review on the treatment mechanism and technology of inner cooling water of generators[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2016, 36(5): 15-19. | |
| [10] | International Council on Large Electric Systems. Guide on stator water chemistry management [S]. Paris: CIGRE, 2011. |
| [11] | Electric Power Research Institute. Stator water cooling system chemistry[R]. Palo Alto: EPRI, 2021. |
| [12] | 国家能源局. 发电机内冷水处理导则: [S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2016. |
| National Energy Administration of the P e o p l e ' s Republic of China. Guideline for generator internal cooling water treatment: [S]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2016. | |
| [13] | 国家能源局. 大型发电机内冷却水质及系统技术要求: [S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2024. |
| National Energy Administration of the P e o p l e ' s Republic of China. Requirements for internal cooling water quality and its system in large generators: [S]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2024. | |
| [14] | Svoboda R, Blecken W. Conductivity limits for direct water-cooled generators[J]. PowerPlant Chemistry, 2022, 24(2): 52-63. |
| [15] | Cavallini C, Dalla Palma M, Fellin F, et al. Investigation of corrosion-erosion phenomena in the primary cooling system of SPIDER[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design, 2021, 166: 112271. |
| [16] | Hall D S, Behazin M, Jeffrey Binns W, et al. An evaluation of corrosion processes affecting copper-coated nuclear waste containers in a deep geological repository[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2021, 118: 100766. |
| [17] | Cavallini C, Gasparrini C, Zaupa M, et al. Corrosion and metal release of copper and stainless steel exposed to ultrapure water[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2022, 50(11): 4491-4495. |
| [18] | Hultquist G. Why copper may be able to corrode in pure water[J]. Corrosion Science, 2015, 93: 327-329. |
| [19] | Guo X, Shi B X, Fu Z H, et al. Atom-scale insight into the adsorption behavior of imidazole corrosion inhibitors at defective copper/water interfaces[J]. Corrosion Science, 2025, 246: 112744. |
| [20] | She X M, Peng J, Qiang Y J, et al. Recent advances in protective technologies against copper corrosion[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2024, 201: 75-94. |
| [21] | 罗雪, 荆川, 黄海军, 等. 规整有机分子自聚集体对铜的高效缓蚀的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(10): 4733-4749. |
| Luo X, Jing C, Huang H J, et al. Study on highly efficient corrosion inhibition of copper by regular self-aggregates of organic molecule[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(10): 4733-4749. | |
| [22] | Khadom A A. Artificial neural network for predication of zinc consumption rate of cathodic protection of copper in saline water: a short communication[J]. Results in Chemistry, 2022, 4: 100370. |
| [23] | Knudsen O Ø, Vada E, Krieger W, et al. Cathodic protection of aluminium in seawater[J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2025, 76(6): 822-832. |
| [24] | Jha V K, Jana S, Pal S, et al. Thin-film coating of the hydrophobic lotus leaf on copper by the floating film transfer method and investigation on the corrosion behavior of coated copper in saline water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(1): 85-95. |
| [25] | 赵璐璐, 唐二军, 邢旭腾, 等. POSS改性氧化石墨烯对涂层防腐和疏水性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1977-1986. |
| Zhao L L, Tang E J, Xing X T, et al. Effects of POSS modified graphene oxide in anti-corrosion and hydrophobic properties of coatings[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 1977-1986. | |
| [26] | Bauer T, Svoboda M, Svoboda R. Corrosion and deposits in water-cooled generator stator windings(part 3): Removal of flow restrictions[J]. PowerPlant Chemistry, 2019, 21(1): 10-22. |
| [27] | 周洋, 伏文, 刘建军, 等. 660 MW水内冷发电机定子线棒堵塞的化学清洗[J]. 化工管理, 2024(6): 71-75. |
| Zhou Y, Fu W, Liu J J, et al. Chemical cleaning of stator wire rod blockage of 660 MW water-cooled generator[J]. Chemical Enterprise Management, 2024(6): 71-75. | |
| [28] | Electric Power Research Institute. Best practices for chemical cleaning of water-cooled generator stator bars[R]. Palo Alto: EPRI, 2022. |
| [29] | Svoboda M, Svoboda R. Operation and maintenance solutions for generator water cooling[C]//2012 20th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering and the ASME 2012 Power Conference. Anaheim, California, USA: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2013: 797-803. |
| [30] | 季刚. 双水内冷同步调相机定子绕组水路堵塞时温度特征研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2020. |
| Ji G. Research on the temperature characteristics of the stator with waterway blockage in dual water internal cooled synchronous condenser[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2020. | |
| [31] | Sun F C, Wang A D, Ji G, et al. Steady-state temperature field of stator bar of double water internal cooling synchronous condenser[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2019, 576(1): 012012. |
| [32] | Wang T P, Wang Y, Jia X X, et al. Corrosion failure analysis of hollow copper coil used in generator internal cooling water system operated at low-oxygen/neutral water chemistry[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2022, 141: 106642. |
| [33] | Wang T P, Jia X X, Wang Y, et al. Corrosion and plugging of the hollow copper conductor caused by CO2 inleakage: thermodynamic analysis and field evidence[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(37): 14891-14900. |
| [34] | Howell A G. Copper deposition in stator cooling water systems[C]//ASME 2014 Power Conference. Baltimore, Maryland, USA: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2014. |
| [35] | 张明, 詹佳佳, 瞿子涵, 等. 大型发电机内冷却水水质指标的验证研究[J]. 标准科学, 2024(S1): 240-244. |
| Zhang M, Zhan J J, Qu Z H, et al. Verification and research on water quality index of cooling water in large generator[J]. Standard Science, 2024(S1): 240-244. | |
| [36] | 叶春松. 纯水中微量铜腐蚀控制原理及应用技术研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2002. |
| Ye C S. Study on control principle and application technology of trace copper corrosion in pure water[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2002. | |
| [37] | Wang T P, Jia X X, Wang Y, et al. Influence of CO2 inleakage on the slight-alkalization of generator internal cooling water[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022, 48: 91-97. |
| [38] | Svoboda R. A practical view on the dissolution of air in demineralized water[J]. PowerPlant Chemistry, 2020, 22(4): 160-169. |
| [39] | Feng B, Zha F L, Li L, et al. The corrosion behavior of T2 brass in power plant generator stator cooling water[J]. Russian Journal of Electrochemistry, 2019, 55(10): 943-952. |
| [40] | 吴俊杰, 刘凯, 查方林, 等. 铜钝化膜在微碱性内冷水中演化过程研究[C]//电厂化学2016年学术年会, 苏州. 中国电机工程学会, 2016: 168-173. |
| Wu J J, Liu K, Zha F L, et al. Study on evolution process of passivation film on copper surface in alkalescent internal cooling water[C]//2016 Academic Annual Conference of Power Plant Chemistry, Suzhou. Chinese Society for Electrical Engineering, 2016: 168-173. | |
| [41] | 王欣宇. 发电机定冷水系统铜含量超标的处理与分析[J]. 工业水处理, 2018, 38(3): 103-106. |
| Wang X Y. Treatment and analysis of excessive copper ion content in generator stator cooling water system[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2018, 38(3): 103-106. | |
| [42] | 任武兵. 火电厂发电机定子冷却水回路堵塞的原因及处理措施[J]. 化学工程与装备, 2022(6): 207-208, 225. |
| Ren W B. Causes and treatment measures of stator cooling water circuit blockage in thermal power plant[J]. Chemical Engineering & Equipment, 2022(6): 207-208, 225. | |
| [43] | Park B G, Hwang I S, Rhee I H, et al. Effect of the electrochemical corrosion potential of copper on plugging of generator water-cooling circuits[J]. Corrosion, 2005, 61(6): 559-570. |
| [44] | Liang Y P, Wu L, Bian X, et al. Influence of void transposition structure on the leakage magnetic field and circulating current loss of stator bars in water-cooled turbo-generators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(6): 3389-3396. |
| [45] | 边旭, 孟雨鹏, 梁艳萍, 等. 计及复杂换位结构的百万千瓦级汽轮发电机定子流固耦合传热研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2024, 44(13): 5328-5338. |
| Bian X, Meng Y P, Liang Y P, et al. Study of fluid-solid coupled heat transfer in stator of million-kilowatt-class turbo-generator with complex transposition structure[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2024, 44(13): 5328-5338. | |
| [46] | Yang G Z, Pointeau V, Tevissen E, et al. A review on clogging of recirculating steam generators in pressurized-water reactors[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2017, 97: 182-196. |
| [47] | Wang T P, Lin P, Jiang T, et al. Feasibility evaluation on using the ORP to better monitor generator internal cooling water system[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2022, 85(7): 2027-2037. |
| [48] | Palmer D A. The solubility of crystalline cupric oxide in aqueous solution from 25℃ to 400℃[J]. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics, 2017, 114: 122-134. |
| [49] | Palmer D A. Solubility measurements of crystalline Cu2O in aqueous solution as a function of temperature and pH[J]. Journal of Solution Chemistry, 2011, 40(6): 1067-1093. |
| [50] | 王天平. 发电机空心铜导线腐蚀堵塞机理及防治工艺研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2023. |
| Wang T P. Mechanism of corrosion and plugging on hollow copper conductor of generator and its prevention and treatment[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2023. | |
| [51] | 李俊菀, 宋敬霞, 曹杰玉, 等. 某电厂3号机组发电机内冷水系统碱性富氧运行工况评价[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2014, 35(11): 1140-1143. |
| Li J W, Song J X, Cao J Y, et al. Evaluation of alkaline and enriched dissolved oxygen operating condition of generator inner cooling water system of unit 3 in a power plant[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2014, 35(11): 1140-1143. | |
| [52] | Svoboda R. Review of alkaline treatment for generator stator cooling water systems[J]. PowerPlant Chemistry, 2014, 16(6): 352-360. |
| [53] | 张芮源. 基于离子交换微碱化处理发电机内冷水的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2017. |
| Zhang R Y. Study on the generator stator cooling water treatment by ion exchange slight-basification[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2017. | |
| [54] | 吴婉荣. 发电机内冷水系统的防腐蚀及微碱性处理研究[D]. 吉林: 东北电力大学, 2022. |
| Wu W R. Anti-corrosion and alkaline treatment of cooling water system of generator[D]. Jilin: Northeast Electric Power University, 2022. | |
| [55] | 宋晶, 武继琳. 一种DCS控制方式下的电厂发电机定子冷却水自动配水及回收方式优化改进[J]. 电力系统装备, 2022(5): 104-106. |
| Song J, Wu J L. Optimization and improvement of automatic water distribution and recovery mode of generator stator cooling water in power plant under DCS control[J]. Electric Power System Equipment, 2022(5): 104-106. | |
| [56] | Chen X C, Li W, Gu X T, et al. An electrochemical method for alkalizing the rotor cooling water of a synchronous condenser[J]. Processes, 2025, 13(3): 742. |
| [57] | 王瑞升. 发电机内冷水电膜微碱化处理技术在330MW发电机组的应用[C]//2023年电力行业技术监督工作交流会暨专业技术论坛论文集(下册). 南宁: 中国电力技术市场协会, 2023: 807-811. |
| Wang R S. Application of electro-membrane technology for slight-alkalization of generator internal cooling water in a 330MW power unit[C]//2023 Electric Power Industry Technical Supervision Work Exchange Conference and Professional Technical Forum (Volume 2). Nanning: China Electricity Technology Market Association, 2023: 807-811. | |
| [58] | 程一杰, 冯礼奎, 于志勇, 等. 电容去离子技术用于模拟调相机转子冷却水处理的研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2024, 44(10): 174-182. |
| Cheng Y J, Feng L K, Yu Z Y, et al. Capacitive deionization technology for simulating the rotor cooling water treatment of synchronous condenser[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2024, 44(10): 174-182. | |
| [59] | 陈建亮, 郝洪铎, 柯波, 等. 溶有CO2的发电机内冷水的pH控制策略研究[J]. 工业水处理, 2024, 44(9): 193-198. |
| Chen J L, Hao H D, Ke B, et al. Research on pH control strategy for internal cooling water in generators with dissolved CO2 [J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2024, 44(9): 193-198. | |
| [60] | 国家能源局. 发电厂低电导率水pH在线测量方法: [S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2013. |
| National Energy Administration of the People's Republic of China. Test method for on-line pH measurement of water of low conductivity for power plant: [S]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2013. | |
| [61] | Bauer T, Svoboda M, Chetwynd R J. Stator cooling water system instrumentation[C]//Proceedings of ASME 2015 Power Conference. San Diego, California, USA: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2015: V001T13A001. |
| [62] | Svoboda R. Interpretation of stator cooling water chemistry data[J]. PowerPlant Chemistry, 2018, 20(3): 154-162. |
| [63] | Wang T P, Jia X X, Wang Y, et al. Effects of water chemistry on corrosion and plugging in the copper heat exchangers of water-cooled generators in power plants[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 257: 124218. |
| [64] | 唐郭. 核电站二期机组发电机定子冷却水系统运行优化分析[J]. 产业与科技论坛, 2021, 20(15): 40-41. |
| Tang G. Operation optimization analysis of stator cooling water system of generator in the second phase of nuclear power plant[J]. Industrial & Science Tribune, 2021, 20(15): 40-41. | |
| [65] | 王珂, 张贵泉, 张兆, 等. 盐雾环境下发电机定子停用防护技术[J]. 热力发电, 2022, 51(3): 148-152. |
| Wang K, Zhang G Q, Zhang Z, et al. Shutdown protection technology of generator stator in salt spray environment[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2022, 51(3): 148-152. | |
| [66] | 马飞. 一种发电机定子冷却水低溶氧控制方法探讨[J]. 大电机技术, 2017(3): 56-58, 74. |
| Ma F. Low dissolved oxygen control method for generator stator cooling water[J]. Large Electric Machine and Hydraulic Turbine, 2017(3): 56-58, 74. | |
| [67] | Wang Y B, Du C C, Yan Z F, et al. Fast deoxygenation in a miniaturized annular centrifugal device[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 297: 121546. |
| [68] | Wang Y B, Chang Y, Shang Q C, et al. Deep deoxidation of water in a miniaturized annular rotating device: experimental investigation and machine learning modeling[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 499: 156358. |
| [69] | Lee J, Baek S M, Boo C, et al. Water deoxygenation using a hollow fiber membrane contactor to prevent pipe corrosion for sustainable management of district heating systems: a pilot-scale study[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 277: 124049. |
| [70] | Zhang R Y, Cao S A, Pan H W. Evaluation of hollow copper strands corrosion behavior in stator cooling water using response surface methodology[J]. Materials and Corrosion, 2018, 69(6): 804-813. |
| [71] | Xie X J, Zhang Y L, Wang R, et al. Research on the effect of the pH value on corrosion and protection of copper in desalted water[J]. Anti-Corrosion Methods and Materials, 2018, 65(6): 528-537. |
| [72] | Electric Power Research Institute. Layup guide for the generator stator cooling water system[R]. Palo Alto: EPRI, 2019. |
| [73] | Svoboda M, Bauer T. Changing stator cooling water chemistry[J]. PowerPlant Chemistry, 2014, 16(6): 344-351. |
| [74] | Deen K M, Mehrjoo N, Asselin E. Thermo-kinetic diagrams: the Cu-H2O-acetate and the Cu-H2O systems[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2021, 895: 115467. |
| [75] | Ning Z Y, Wen D, Zhou Q L, et al. Theoretical explanation of passivation behavior in OFP-Cu and OF-Cu[J]. Acta Materialia, 2024, 271: 119882. |
| [76] | Svoboda R, Reinboth B A, Svoboda M. Monitoring generator cooling water system chemistry by the electrochemical potential[J]. PowerPlant Chemistry, 2011, 13(8): 496-502. |
| [77] | 明菊兰, 钱洲亥, 于志勇, 等. 换流阀内冷水系统腐蚀结垢的影响因素[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2021, 42(10): 97-103. |
| Ming J L, Qian Z H, Yu Z Y, et al. Influence factors of corrosion and scaling in inner cooling water system of converter valve[J]. Corrosion & Protection, 2021, 42(10): 97-103. | |
| [78] | Adak B. Copper corrosion & clogging in APS deionized water cooling system[D]. Chicago: Graduate College of the Illinois Institute of Technology, 2009. |
| [79] | Yang G Z. Investigations of the tube support plate (TSP) clogging phenomenon in PWR steam generators - understanding and prioritization of its formation mechanisms[D]. Paris: Université Pierre et Marie Curie, 2017. |
| [80] | 孙勇, 张春雷, 汪永威, 等. 发电机内冷水二氧化碳溶入量的评估及应用[J]. 工业水处理, 2018, 38(9): 110-112. |
| Sun Y, Zhang C L, Wang Y W, et al. Assessment and application of the quantity of carbon dioxide dissolved in inner cooling water of generators[J]. Industrial Water Treatment, 2018, 38(9): 110-112. | |
| [81] | Svoboda R, Chetwynd R. Corrosion and deposits in water-cooled generator stator windings(part 2): Detection of flow restrictions[J]. Powerplant Chemistry, 2018, 20(6): 326-336. |
| [82] | 翁超华. 汽轮发电机定子绕组水冷系统状态评估与主动预警研究[D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2023. |
| Weng C H. Condition assessment and active early warning research of turbogenerator stator windings water cooling system[D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2023. | |
| [83] | Wang B Q, Mu Y Q, Shen F M, et al. Identification of corrosion factors in blast furnace gas pipe network with corrosion big data online monitoring technology[J]. Corrosion Science, 2024, 230: 111906. |
| [1] | 丁宏鑫, 干文翔, 赵雍洋, 贾润泽, 康子祺, 赵玉隆, 向勇. X65钢焊接接头在超临界CO2相及富H2O相中的腐蚀机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3426-3435. |
| [2] | 康佳, 刘欢, 李海燕, 罗茂亮, 姚洪. 宽温区HCl/NaOH热介质中碳钢腐蚀行为及涂层性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2872-2885. |
| [3] | 李品贤, 郭峰, 骆政园, 温伯尧, 白博峰. 纳米颗粒吸附界面对微孔喉中液滴运移及堵塞的调控[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2929-2938. |
| [4] | 胡家玮, 王聪, 刘美婧. 一种抑制隧道排水管道中结晶体形成的双层阻垢疏水涂层[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3053-3072. |
| [5] | 李彦, 郭红利, 苏国庆, 张建文. 加氢装置空冷器气液两相流动与冲刷腐蚀问题[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 141-150. |
| [6] | 裴欣哲, 孙朱行, 林钰翔, 张朝阳, 钱勇, 吕兴才. 电催化分解液氨阳极材料的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1843-1854. |
| [7] | 赵璐璐, 唐二军, 邢旭腾, 刘少杰, 褚晓萌, 呼娜, 张泽. POSS改性氧化石墨烯对涂层防腐和疏水性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1977-1986. |
| [8] | 冯彬彬, 卢明佳, 黄志宏, 常译文, 崔志明. 碳载体在质子交换膜燃料电池中的应用及优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1469-1484. |
| [9] | 康飞, 吕伟光, 巨锋, 孙峙. 废锂离子电池放电路径与评价研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3903-3911. |
| [10] | 陈佳起, 赵万玉, 姚睿充, 侯道林, 董社英. 开心果壳基碳点的合成及其对Q235碳钢的缓蚀行为研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [11] | 李艳辉, 丁邵明, 白周央, 张一楠, 于智红, 邢利梅, 高鹏飞, 王永贞. 非常规服役超临界锅炉的微纳尺度腐蚀动力学模型建立及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2436-2446. |
| [12] | 姚翰林, 辛忠. 液相沉淀反应在管式微通道反应器中的流动行为研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3518-3528. |
| [13] | 魏小兰, 戚文杰, 丁静, 陆建峰, 王维龙, 刘书乐. 氯化物熔盐中铬的价态对镍基合金腐蚀性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3182-3192. |
| [14] | 陈泉, 郑泽希, 李然, 孙其诚, 杨晖. 散斑能见度光谱法测量筒仓内颗粒流的颗粒温度[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2603-2611. |
| [15] | 苏国庆, 张建文, 李彦. 蝶阀后管线腐蚀发生与发展机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5504-5516. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号