CIESC Journal ›› 2019, Vol. 70 ›› Issue (7): 2766-2774.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20190078
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Rong XU( ),Xu CHENG,Song DENG,Lyu QI,Xiuxiu REN,Qi ZHANG,Jing ZHONG(
),Xu CHENG,Song DENG,Lyu QI,Xiuxiu REN,Qi ZHANG,Jing ZHONG( )
)
Received:2019-01-25
Revised:2019-04-10
Online:2019-07-05
Published:2019-07-05
Contact:
Jing ZHONG
通讯作者:
钟璟
作者简介:徐荣(1983—),男,博士,副教授,<email>xurong@cczu.edu.cn</email>
基金资助:CLC Number:
Rong XU, Xu CHENG, Song DENG, Lyu QI, Xiuxiu REN, Qi ZHANG, Jing ZHONG. Carboxyl functionalization and reverse osmosis performance of ethenylene-bridged organosilica membranes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(7): 2766-2774.
徐荣, 程旭, 邓松, 戚律, 任秀秀, 张琪, 钟璟. 乙烯基桥联有机硅膜的羧基化改性及反渗透性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(7): 2766-2774.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
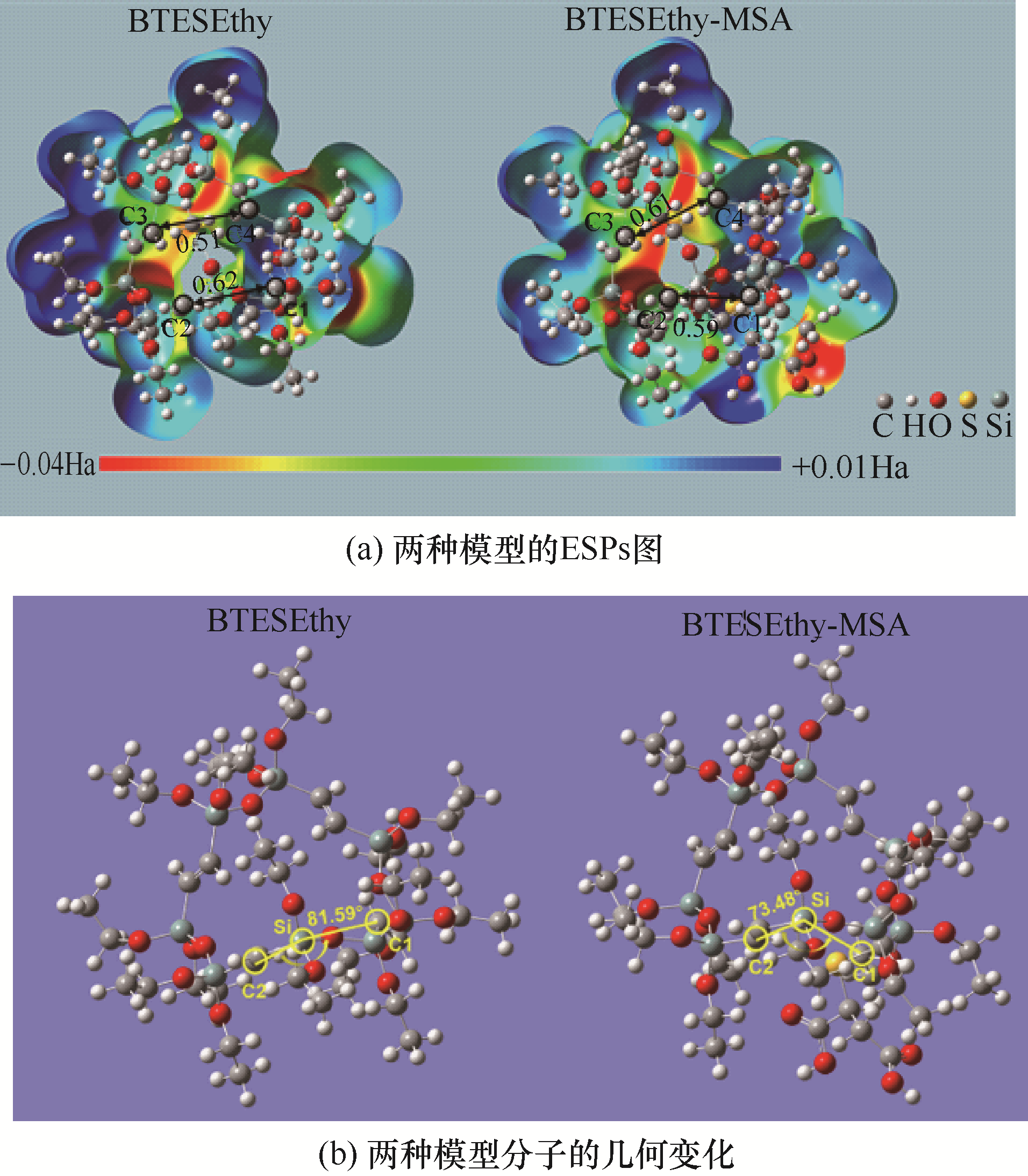
Fig.5 ESPs images of BTESEthy and BTESEthy-MSA calculated by density functional theory (DFT), and comparison of geometry changes in two model molecules
| 膜 | 测试条件 | 水渗透率/(m3/(m2·s·Pa)) | 截留率 /% | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SW30HR (FilmTec) | 21℃, 2.76 MPa, 2000 mg/L-NaCl | (2.2 ± 0.5) × 10-12 | 98.5 ± 0.7 | [ |
| ES10 (Nitto Denko) | 24℃, 1 MPa, 104 mg/L-NaCl | (1.2 ± 0.16) × 10-12 | 99.2 | [ |
| ZSM-5, Si/Al=5 | 25℃, 2.76 MPa, 5848 mg/L-NaCl | 1.4 × 10-13 | 92.9 | [ |
| silicalite | 25℃, 2.76 MPa, 5848 mg/L -NaCl | 1.4 × 10-13 | 90.6 | [ |
| BTESEthy | 25℃, 1.15 MPa, 2000 mg/L-NaCl | 2.1 ± 0.2 × 10-13 | 97 ± 0.8 | this work |
| BTESEthy-MSA | 25℃, 1.15 MPa, 2000 mg/L-NaCl | 3.5 ± 0.5 × 10-13 | 98 ± 0.5 | this work |
Table 1 Comparison of desalination performances of organosilica membranes and some typical RO membranes
| 膜 | 测试条件 | 水渗透率/(m3/(m2·s·Pa)) | 截留率 /% | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SW30HR (FilmTec) | 21℃, 2.76 MPa, 2000 mg/L-NaCl | (2.2 ± 0.5) × 10-12 | 98.5 ± 0.7 | [ |
| ES10 (Nitto Denko) | 24℃, 1 MPa, 104 mg/L-NaCl | (1.2 ± 0.16) × 10-12 | 99.2 | [ |
| ZSM-5, Si/Al=5 | 25℃, 2.76 MPa, 5848 mg/L-NaCl | 1.4 × 10-13 | 92.9 | [ |
| silicalite | 25℃, 2.76 MPa, 5848 mg/L -NaCl | 1.4 × 10-13 | 90.6 | [ |
| BTESEthy | 25℃, 1.15 MPa, 2000 mg/L-NaCl | 2.1 ± 0.2 × 10-13 | 97 ± 0.8 | this work |
| BTESEthy-MSA | 25℃, 1.15 MPa, 2000 mg/L-NaCl | 3.5 ± 0.5 × 10-13 | 98 ± 0.5 | this work |
| 1 | 张雪杰, 李亮, 蔡志强, 等. 改性化合物对聚酰胺膜材料亲水性及抗污染性能影响的分子力学计算与实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2012, 63(6): 1957-1966. |
| ZhangX J, LiL, CaiZ Q, et al. Effects of modification chemical on hydrophilic and antifouling properties of polyamide membranes:molecular mechanics calculation and experimental investigation[J]. CIESC Journal, 2012, 63(6): 1957-1966. | |
| 2 | 潘春佑, 徐国荣, 李露, 等. 聚酰胺反渗透复合膜改性技术研究进展[J]. 膜科学与技术, 2016, 36(6): 133-138. |
| PanC Y, XuG R, LiL, et al. Developments and perspectives on the polyamide-based reverse osmosis desalination membranes[J]. Membrane Science and Technology, 2016, 36(6): 133-138. | |
| 3 | GutmanJ, HerzbergM, WalkerS L. Biofouling of reverse osmosis membranes: positively contributing factors of sphingomonas[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(23): 13941-13950. |
| 4 | CastricumH L, SahA, KreiterR, et al. Hydrothermally stable molecular separation membranes from organically linked silica[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2008, 18(18): 2150-2158. |
| 5 | CastricumH L, SahA, KreiterR, et al. Hybrid ceramic nanosieves: stabilizing nanopores with organic links[J]. Chemical Communications, 2008, (9): 1103-1105. |
| 6 | KanezashiM, YadaK, YoshiokaT, et al. Design of silica networks for development of highly permeable hydrogen separation membranes with hydrothermal stability[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(2): 414-415. |
| 7 | KanezashiM, YadaK, YoshiokaT, et al. Organic-inorganic hybrid silica membranes with controlled silica network size: preparation and gas permeation characteristics[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 348 (1): 310-318. |
| 8 | 漆虹, 韩静, 江晓骆, 等. 有机-无机复合SiO2膜的制备及水蒸气稳定性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(7): 758-764. |
| QiH, HanJ, JiangX L, et al. Preparation and hydrothermal stability of organic-inorganic hybrid silica membrane[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(7): 758-764. | |
| 9 | QiH, HanJ, XuN, et al. Hybrid organic-inorganic microporous membranes with high hydrothermal stability for the separation of carbon dioxide[J]. ChemSusChem, 2010, 3(12): 1375-1378. |
| 10 | XuR, WangJ H, KanezashiM, et al. Development of robust organosilica membranes for reverse osmosis[J]. Langmuir, 2011, 27(23): 13996-13999. |
| 11 | XuR, KanezashiM, YoshiokaT, et al. Tailoring the affinity of organosilica membranes by introducing polarizable ethenylene bridges and aqueous ozone modification[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(13): 6147-6154. |
| 12 | XuR, IbrahimS M, KanezashiM, et al. New insights into the microstructure-separation properties of organosilica membranes with ethane, ethylene, and acetylene bridges[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(12): 9357-9364. |
| 13 | YamamotoK, OhshitaJ, MizumoT, et al. Preparation of hydroxyl group containing bridged organosilica membranes for water desalination[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2015, 156: 396-402. |
| 14 | 胡笛, 徐彩虹. 巯基-乙烯基加成反应合成含硅聚合物的研究进展[J]. 高分子通报, 2011, (10): 111-118. |
| HuD, XuC H. Research progress of silicon containing polymers by thiol-ene chemistry[J]. Polymer Bulletin, 2011, (10): 111-118. | |
| 15 | 吴建兵, 凌丽霞, 马国章, 等. 巯基-乙烯基点击反应在紫外光固化过程中的应用[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2013, 29(10): 169-174. |
| WuJ B, LingL X, MaG Z, et al. The application of thiol-ene click reaction in UV curing process[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 2013, 29(10): 169-174. | |
| 16 | AsaedaM, YangJ, SakouY. Porous silica-zirconia (50%) membranes for pervaporation of iso-propyl alcohol (IPA)/water mixtures[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 2002, 35(4): 365-371. |
| 17 | XuR, WangJ, KanezashiM, et al. Reverse osmosis performance of organosilica membranes and comparison with the pervaporation and gas permeation properties[J]. AIChE Journal, 2013, 59(4): 1298-1307. |
| 18 | HanY H, TaylorA, MantleM D, et al. Sol-gel-derived organic-inorganic hybrid materials[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2007, 353(3): 313-320. |
| 19 | EsquivelD, CanckE D, Jimenez-SanchidrianC, et al. Formation and functionalization of surface Diels-Alder adducts on ethenylene-bridged periodic mesoporous organosilica[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(29): 10990-10998. |
| 20 | SasidharanM, BhaumikA. Novel and mild synthetic strategy for the sulfonic acid functionalization in periodic mesoporous ethenylene-silica[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(7): 2618-2625. |
| 21 | YamamotoK, OhshitaJ, MizumoT, et al. Synthesis of organically bridged trialkoxysilanes bearing acetoxymethyl groups and applications to reverse osmosis membranes: acetoxymethyl-containing bridged silica membrane[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2016, 31(3): e3580. |
| 22 | ThommesM, MorellJ, CychoszK A, et al. Combining nitrogen, argon, and water adsorption for advanced characterization of ordered mesoporous carbons (CMKs) and periodic mesoporous organosilicas (PMOs)[J]. Langmuir, 2013, 29(48): 14893-14902. |
| 23 | FanC, NguyenV, ZengY, et al. Novel approach to the characterization of the pore structure and surface chemistry of porous carbon with Ar, N2, H2O and CH3OH adsorption[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2015, 209: 79-89. |
| 24 | IbrahimS M, NagasawaH, KanezashiM, et al. Organosilica bis(triethoxysilyl)ethane (BTESE) membranes for gas permeation (GS) and reverse osmosis (RO): the effect of preparation conditions on structure, and the correlation between gas and liquid permeation properties[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 526: 242-251. |
| 25 | GeiseG M, ParkH B, SagleA C, et al. Water permeability and water/salt selectivity trade off in polymers for desalination[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 369(1/2): 130-138. |
| 26 | XuR, LinP, ZhangQ, et al. Development of ethenylene-bridged organosilica membranes for desalination applications[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(7): 2183-2190. |
| 27 | ParkH, FreemanB, ZhangZ B, et al. Highly chlorine-tolerant polymers for desalination[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 47(32): 6019-6024. |
| 28 | HatakeyamaE S, GabrielC J, WiesenauerB R, et al. Water filtration performance of a lyotropic liquid crystal polymer membrane with uniform, sub-1-nm pores[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 366(1/2): 62-72. |
| 29 | KisoY, MuroshigeK, OguchiT, et al. Pore radius estimation based on organic solute molecular shape and effects of pressure on pore radius for a reverse osmosis membrane[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 369(1/2): 290-298. |
| 30 | LiL X, LiuN, McPhersonB, et al. Enhanced water permeation of reverse osmosis through MFI-type zeolite membranes with high aluminum contents[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2007, 46(5): 1584-1589. |
| 31 | AntonyA, FudiantoR, CoxS, et al. Assessing the oxidative degradation of polyamide reverse osmosis membrane-accelerated ageing with hypochlorite exposure[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 347(1/2): 159-164. |
| [1] | Yanpeng WU, Xiaoyu LI, Qiaoyang ZHONG. Experimental analysis on filtration performance of electrospun nanofibers with amphiphobic membrane of oily fine particles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 259-264. |
| [2] | Yitong LI, Hang GUO, Hao CHEN, Fang YE. Study on operating conditions of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform catalyst distributions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [3] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [4] | Jiayi ZHANG, Jiali HE, Jiangpeng XIE, Jian WANG, Yu ZHAO, Dongqiang ZHANG. Research progress of pervaporation technology for N-methylpyrrolidone recovery in lithium battery production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [5] | Kuikui HAN, Xianglong TAN, Jinzhi LI, Ting YANG, Chun ZHANG, Yongfen ZHANG, Hongquan LIU, Zhongwei YU, Xuehong GU. Four-channel hollow fiber MFI zeolite membrane for the separation of xylene isomers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2468-2476. |
| [6] | Zhaoguang CHEN, Yuxiang JIA, Meng WANG. Modeling neutralization dialysis desalination driven by low concentration waste acid and its validation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [7] | Lei WANG, Lei WANG, Yunlong BAI, Liuliu HE. Preparation of SA lithium ion sieve membrane and its adsorptive properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2046-2056. |
| [8] | Xiaoyu JIA, Jian YANG, Bo WANG, Mei LIN, Qiuwang WANG. Pore scale numerical simulations for wicking performance of metallic woven mesh [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1928-1938. |
| [9] | Hao GU, Fujian ZHANG, Zhen LIU, Wenxuan ZHOU, Peng ZHANG, Zhongqiang ZHANG. Desalination performance and mechanism of porous graphene membrane in temporal dimension under mechanical-electrical coupling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| [10] | Yongyao SUN, Qiuying GAO, Wenguang ZENG, Jiaming WANG, Yifei CHEN, Yongzhe ZHOU, Gaohong HE, Xuehua RUAN. Design and optimization of membrane-based integration process for advanced utilization of associated gases in N2-EOR oilfields [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2034-2045. |
| [11] | Chenxin LI, Yanqiu PAN, Liu HE, Yabin NIU, Lu YU. Carbon membrane model based on carbon microcrystal structure and its gas separation simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2057-2066. |
| [12] | Laiming LUO, Jin ZHANG, Zhibin GUO, Haining WANG, Shanfu LU, Yan XIANG. Simulation and experiment of high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells stack in the 1—5 kW range [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1724-1734. |
| [13] | Rong WANG, Yonghong WANG, Xinru ZHANG, Jinping LI. Construction of 6FDA-based polyimide carbon molecular sieve membranes for gas separation and its application [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1433-1445. |
| [14] | Yangguang LYU, Peipei ZUO, Zhengjin YANG, Tongwen XU. Triazine framework polymer membranes for methanol/n-hexane separation via organic solvent nanofiltration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1598-1606. |
| [15] | Xiaoxuan WANG, Xiaohong HU, Yunan LU, Shiyong WANG, Fengxian FAN. Numerical simulation of flow characteristics in a rotating membrane filter [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1489-1498. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||