CIESC Journal ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (4): 2283-2292.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20201163
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
NA Tiancheng( ),LI Xiangcun(
),LI Xiangcun( ),GUO Jiao,LIU Siyuan,YANG Hongjie,JIANG Helong,JIANG Fulin,HE Gaohong(
),GUO Jiao,LIU Siyuan,YANG Hongjie,JIANG Helong,JIANG Fulin,HE Gaohong( )
)
Received:2020-08-17
Revised:2020-11-03
Online:2021-04-05
Published:2021-04-05
Contact:
LI Xiangcun,HE Gaohong
那天成( ),李祥村(
),李祥村( ),郭娇,刘思远,杨宏杰,姜贺龙,姜福林,贺高红(
),郭娇,刘思远,杨宏杰,姜贺龙,姜福林,贺高红( )
)
通讯作者:
李祥村,贺高红
作者简介:那天成(1988—),男,博士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
NA Tiancheng, LI Xiangcun, GUO Jiao, LIU Siyuan, YANG Hongjie, JIANG Helong, JIANG Fulin, HE Gaohong. Fe2C hybrid nitrogen-doped carbon membranes with regular pore structure for integrated Li-S battery cathodes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(4): 2283-2292.
那天成, 李祥村, 郭娇, 刘思远, 杨宏杰, 姜贺龙, 姜福林, 贺高红. Fe2C和氮共掺杂的具有有序孔道结构碳膜用于锂硫电池正极[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 2283-2292.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
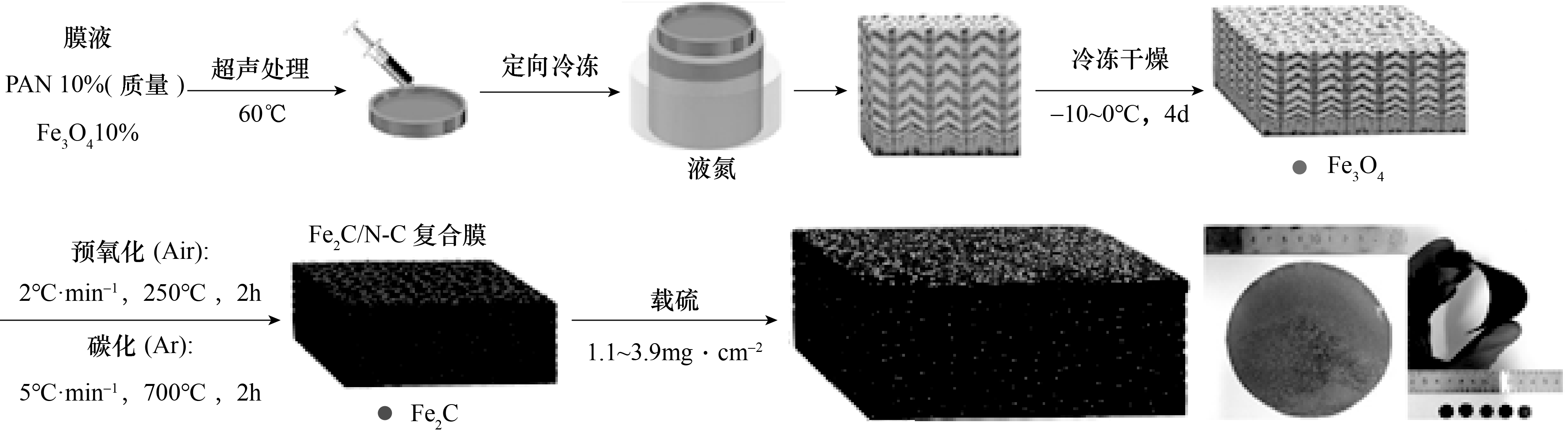
Fig.1 Schematic of the process of the membrane prepared by directional freezing method and the structure of membrane, the photographs of the Fe3O4/PAN directional porous composite membrane, and the membranes after pre-oxidation and carbonization
| 1 | Zhou G M, Li L, Ma C Q, et al. A graphene foam electrode with high sulfur loading for flexible and high energy Li-S batteries[J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 11: 356-365. |
| 2 | Peng H J, Huang J Q, Cheng X B, et al. Lithium-sulfur batteries: review on high-loading and high-energy lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(24): 1770141. |
| 3 | Pope M A, Aksay I A. Structural design of cathodes for Li-S batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2015, 5(16): 1500124. |
| 4 | Liu X, Huang J Q, Zhang Q, et al. Nanostructured metal oxides and sulfides for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(20): 1601759. |
| 5 | Qiu Y C, Li W F, Li G Z, et al. Polyaniline-modified cetyltrimethylammonium bromide-graphene oxide-sulfur nanocomposites with enhanced performance for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nano Research, 2014, 7(9): 1355-1363. |
| 6 | Peng H J, Xu W T, Zhu L, et al. Lithium-sulfur batteries: 3D carbonaceous current collectors: the origin of enhanced cycling stability for high-sulfur-loading lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(35): 6321-6358. |
| 7 | Singhal R, Chung S H, Manthiram A, et al. A free-standing carbon nanofiber interlayer for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(8): 4530-4538. |
| 8 | Luo Y Q, Guo L L, Xiao M, et al. Strategies for inhibiting anode dendrite growth in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020, 8(9): 4629-4646. |
| 9 | Liu H, Cheng X B, Xu R, et al. Plating/stripping behavior of actual lithium metal anode[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 9(44): 1902254. |
| 10 | Yu M P, Ma J S, Xie M, et al. Freestanding and sandwich-structured electrode material with high areal mass loading for long-life lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017, 7(11): 1602347. |
| 11 | Zeng L C, Yao Y, Shi J N, et al. A flexible S1-xSex@porous carbon nanofibers (x≤0.1) thin film with high performance for Li-S batteries and room-temperature Na-S batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 5: 50-57. |
| 12 | Zheng G Y, Yang Y, Cha J J, et al. Hollow carbon nanofiber-encapsulated sulfur cathodes for high specific capacity rechargeable lithium batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2011, 11(10): 4462-4467. |
| 13 | Wang H L, Yang Y, Liang Y Y, et al. Graphene-wrapped sulfur particles as a rechargeable lithium-sulfur battery cathode material with high capacity and cycling stability[J]. Nano Letters, 2011, 11(7): 2644-2647. |
| 14 | 杨蓉, 李兰, 王黎晴, 等. 微波法制备还原氧化石墨烯及其在锂硫电池中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(11): 4333-4340. |
| Yang R, Li L, Wang L Q, et al. Preparation of reduced graphene oxide by microwave method and its application in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(11): 4333-4340. | |
| 15 | Tang C, Li B Q, Zhang Q, et al. CaO-templated growth of hierarchical porous graphene for high-power lithium-sulfur battery applications[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(4): 577-585. |
| 16 | Xu F, Xu J, Xu H J, et al. Fabrication of novel powdery carbon aerogels with high surface areas for superior energy storage[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2017, 7: 8-16. |
| 17 | Roberts A D, Wang S X, Li X, et al. Hierarchical porous nitrogen-rich carbon monoliths via ice-templating: high capacity and high-rate performance as lithium-ion battery anode materials[J]. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(42): 17787-17796. |
| 18 | Lee J T, Zhao Y Y, Thieme S, et al. Sulfur-infiltrated micro- and mesoporous silicon carbide-derived carbon cathode for high-performance lithium sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(33): 4573-4579. |
| 19 | Yuan C Z, Zhu S Q, Cao H, et al. Hierarchical sulfur-impregnated hydrogenated TiO2 mesoporous spheres comprising anatase nanosheets with highly exposed (001) facets for advanced Li-S batteries[J]. Nanotechnology, 2016, 27(4): 045403. |
| 20 | Liang X, Kwok C Y, Lodi-Marzano F, et al. Tuning transition metal oxide-sulfur interactions for long life lithium sulfur batteries: the “goldilocks” principle[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(6): 1501636. |
| 21 | Yuan Z, Peng H J, Hou T Z, et al. Powering lithium-sulfur battery performance by propelling polysulfide redox at sulfiphilic hosts[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(1): 519-527. |
| 22 | Zhang S S, Tran D T. Pyrite FeS2as an efficient adsorbent of lithium polysulphide for improved lithium–sulphur batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(12): 4371-4374. |
| 23 | Li X L, Chu L B, Wang Y Y, et al. Anchoring function for polysulfide ions of ultrasmall SnS2 in hollow carbon nanospheres for high performance lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2016, 205: 46-54. |
| 24 | Liu Y, Li X C, Liu Y, et al. Promoting opposite diffusion and efficient conversion of polysulfides in “Trap” FexC-doped asymmetric porous membranes as integrated electrodes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 382: 122858. |
| 25 | Zhou F, Li Z, Luo X, et al. Low cost metal carbide nanocrystals as binding and electrocatalytic sites for high performance Li-S batteries[J]. Nano Letters, 2018, 18(2): 1035-1043. |
| 26 | Wang Y Z, Li M, Xu L C, et al. Polar and conductive iron carbide@N-doped porous carbon nanosheets as a sulfur host for high performance lithium sulfur batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 358: 962-968. |
| 27 | Zhang Y G, Li G R, Wang J Y, et al. Hierarchical defective Fe3-xC@C hollow microsphere enables fast and long-lasting lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(22): 2001165. |
| 28 | Gao B, Li X X, Ding K, et al. Recent progress in nanostructured transition metal nitrides for advanced electrochemical energy storage[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(1): 14-37. |
| 29 | Huang S Z, Lim Y V, Zhang X M, et al. Regulating the polysulfide redox conversion by iron phosphide nanocrystals for high-rate and ultrastable lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 51: 340-348. |
| 30 | Kou W, Chen G H, Liu Y, et al. Patterned macroporous Fe3C/C membrane-induced high ionic conductivity for integrated Li–sulfur battery cathodes[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(36): 20614-20623. |
| 31 | Zhang T, Zhang X F, Yan X J, et al. Synthesis of Fe3O4@ZIF-8 magnetic core-shell microspheres and their potential application in a capillary microreactor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 228: 398-404. |
| 32 | Pang Q, Tang J T, Huang H, et al. A nitrogen and sulfur dual-doped carbon derived from polyrhodanine@cellulose for advanced lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(39): 6021-6028. |
| 33 | Pang Q, Kundu D, Cuisinier M, et al. Surface-enhanced redox chemistry of polysulphides on a metallic and polar host for lithium-sulphur batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4759. |
| 34 | Diao Y, Xie K, Xiong S Z, et al. Shuttle phenomenon — the irreversible oxidation mechanism of sulfur active material in Li-S battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 235: 181-186. |
| 35 | Hu C, Chen H, Shen Y, et al. In situ wrapping of the cathode material in lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1): 479. |
| 36 | Liang X, Hart C, Pang Q, et al. A highly efficient polysulfide mediator for lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 5682. |
| [1] | Yuanchao LIU, Bin GUAN, Jianbin ZHONG, Yifan XU, Xuhao JIANG, Duan LI. Investigation of thermoelectric transport properties of single-layer XSe2 (X=Zr/Hf) [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3968-3978. |
| [2] | Jiaqi CHEN, Wanyu ZHAO, Ruichong YAO, Daolin HOU, Sheying DONG. Synthesis of pistachio shell-based carbon dots and their corrosion inhibition behavior on Q235 carbon steel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [3] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [4] | Meibo XING, Zhongtian ZHANG, Dongliang JING, Hongfa ZHANG. Enhanced phase change energy storage/release properties by combining porous materials and water-based carbon nanotube under magnetic regulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3093-3102. |
| [5] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| [6] | Kuikui HAN, Xianglong TAN, Jinzhi LI, Ting YANG, Chun ZHANG, Yongfen ZHANG, Hongquan LIU, Zhongwei YU, Xuehong GU. Four-channel hollow fiber MFI zeolite membrane for the separation of xylene isomers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2468-2476. |
| [7] | Zhaoguang CHEN, Yuxiang JIA, Meng WANG. Modeling neutralization dialysis desalination driven by low concentration waste acid and its validation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [8] | Qin YANG, Chuanjian QIN, Mingzi LI, Wenjing YANG, Weijie ZHAO, Hu LIU. Fabrication and properties of dual shape memory MXene based hydrogels for flexible sensor [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2699-2707. |
| [9] | Yuanchao LIU, Xuhao JIANG, Ke SHAO, Yifan XU, Jianbin ZHONG, Zhuan LI. Influence of geometrical dimensions and defects on the thermal transport properties of graphyne nanoribbons [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2708-2716. |
| [10] | Xiaoxuan WANG, Xiaohong HU, Yunan LU, Shiyong WANG, Fengxian FAN. Numerical simulation of flow characteristics in a rotating membrane filter [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1489-1498. |
| [11] | Rong WANG, Yonghong WANG, Xinru ZHANG, Jinping LI. Construction of 6FDA-based polyimide carbon molecular sieve membranes for gas separation and its application [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1433-1445. |
| [12] | Xiangshang CHEN, Zhenjie MA, Xihua REN, Yue JIA, Xiaolong LYU, Huayan CHEN. Preparation and mass transfer efficiency of three-dimensional network extraction membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1126-1133. |
| [13] | Min LI, Xueru YAN, Xinlei LIU. Advances in benzimidazole-linked polymer adsorbents and membranes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 599-616. |
| [14] | Guojuan QU, Tao JIANG, Tao LIU, Xiang MA. Modulating luminescent behaviors of Au nanoclusters via supramolecular strategies [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 397-407. |
| [15] | Houchuan YU, Teng REN, Ning ZHANG, Xiaobin JIANG, Yan DAI, Xiaopeng ZHANG, Junjiang BAO, Gaohong HE. Advances in two-dimensional graphene oxide membrane for ion selective transport [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 303-312. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||