CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (5): 1914-1927.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230070
• Fluid dynamics and transport phenomena • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jialin DAI1,2( ), Weidong BI3, Yumei YONG1(
), Weidong BI3, Yumei YONG1( ), Wenqiang CHEN1,2, Hanyang MO1,4, Bing SUN5, Chao YANG1,2(
), Wenqiang CHEN1,2, Hanyang MO1,4, Bing SUN5, Chao YANG1,2( )
)
Received:2023-02-02
Revised:2023-04-19
Online:2023-06-29
Published:2023-05-05
Contact:
Yumei YONG, Chao YANG
代佳琳1,2( ), 毕唯东3, 雍玉梅1(
), 毕唯东3, 雍玉梅1( ), 陈文强1,2, 莫晗旸1,4, 孙兵5, 杨超1,2(
), 陈文强1,2, 莫晗旸1,4, 孙兵5, 杨超1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
雍玉梅,杨超
作者简介:代佳琳(1999—),女,硕士研究生,daijialin20@ipe.ac.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Jialin DAI, Weidong BI, Yumei YONG, Wenqiang CHEN, Hanyang MO, Bing SUN, Chao YANG. Effect of thermophysical properties on the heat transfer characteristics of solid-liquid phase change for composite PCMs[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1914-1927.
代佳琳, 毕唯东, 雍玉梅, 陈文强, 莫晗旸, 孙兵, 杨超. 热物性对混合型CPCMs固液相变特性影响模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1914-1927.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Ra | 本文Nuave结果 | 文献Nuave结果 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref.[ | 相对误差/% | Ref.[ | 相对误差/% | ||
| 1×103 | 1.423 | 1.432 | -0.628 | 1.424 | -0.070 |
| 1×104 | 1.757 | 1.768 | -0.626 | 1.771 | -0.791 |
| 1×105 | 4.234 | 4.308 | -1.718 | 4.324 | -2.081 |
| 1×106 | 8.362 | 8.605 | -2.824 | 8.597 | -2.734 |
Table 1 Verification results of fluid-solid coupling problems under natural covection
| Ra | 本文Nuave结果 | 文献Nuave结果 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref.[ | 相对误差/% | Ref.[ | 相对误差/% | ||
| 1×103 | 1.423 | 1.432 | -0.628 | 1.424 | -0.070 |
| 1×104 | 1.757 | 1.768 | -0.626 | 1.771 | -0.791 |
| 1×105 | 4.234 | 4.308 | -1.718 | 4.324 | -2.081 |
| 1×106 | 8.362 | 8.605 | -2.824 | 8.597 | -2.734 |
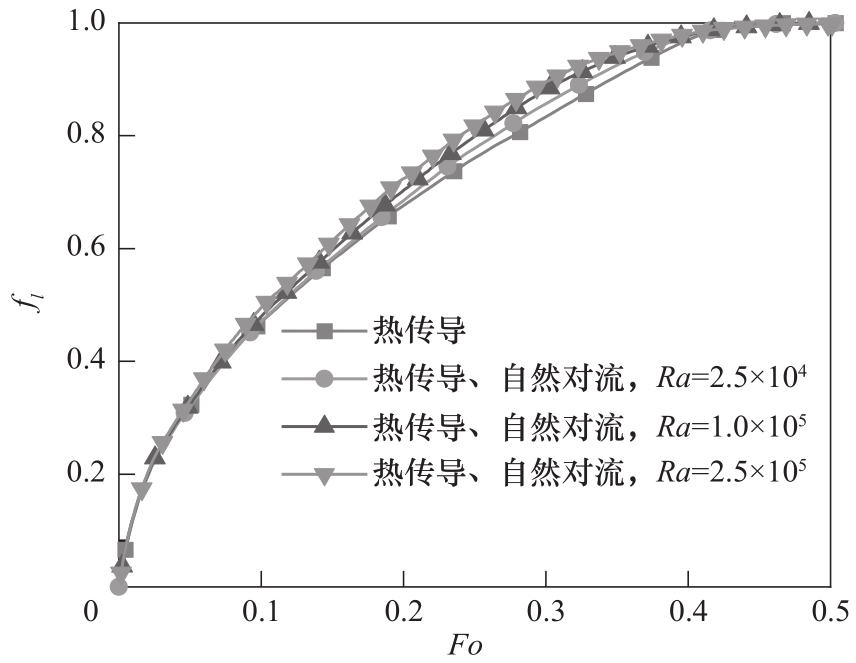
Fig. 5 Volume fraction of the liquid phase in the process of heat transfer by conduction versus phase change considering natural convection(Pr=0.1, St=1, Rcp=Rs=Rfcp=Rfs=1)
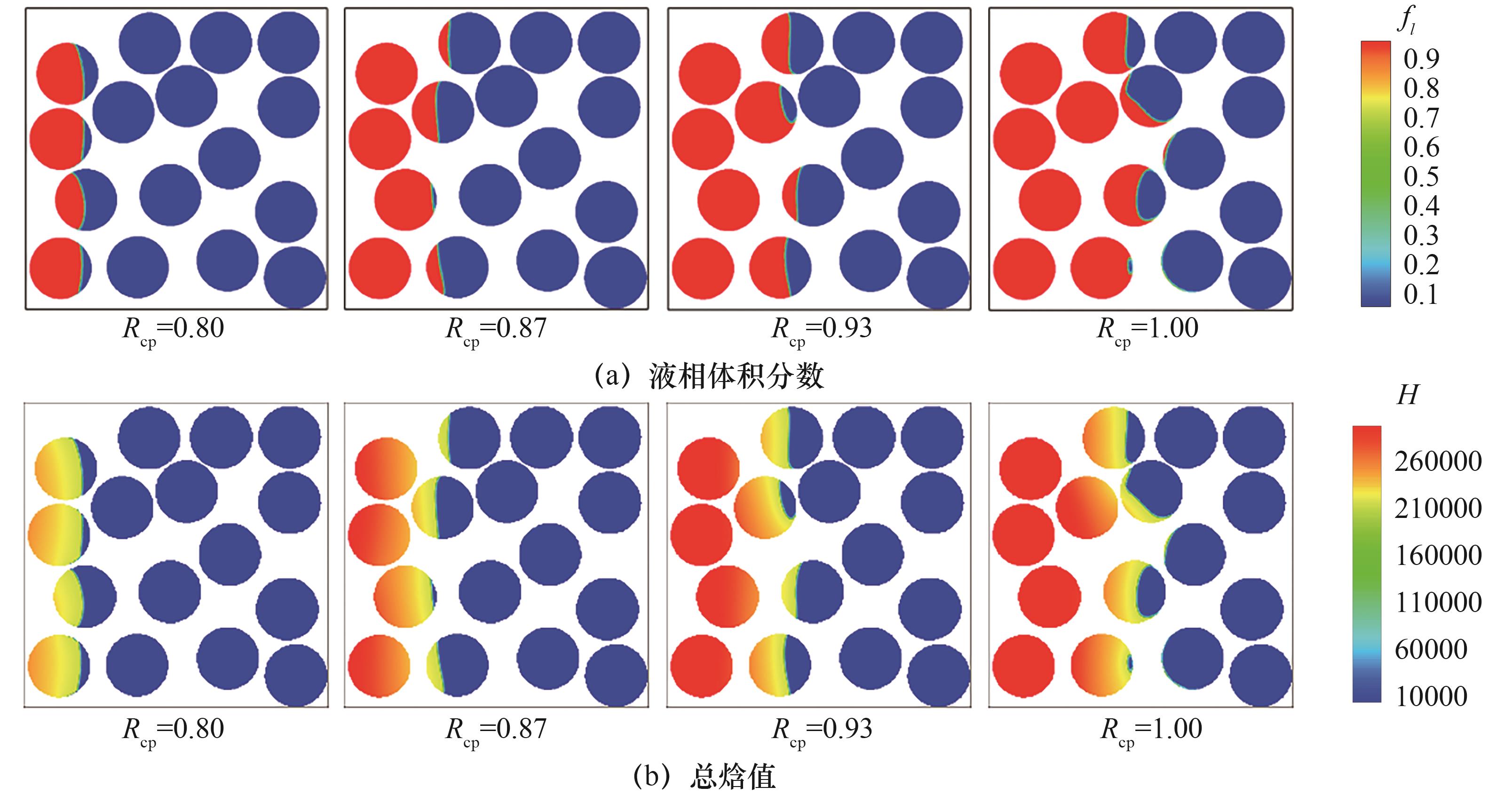
Fig.7 Distribution of liquid volume fraction and enthalpy under different specific heat capacities of base and PCMs(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.1, St=1, Rs=Rfcp=Rfs=1, Fo=0.1)
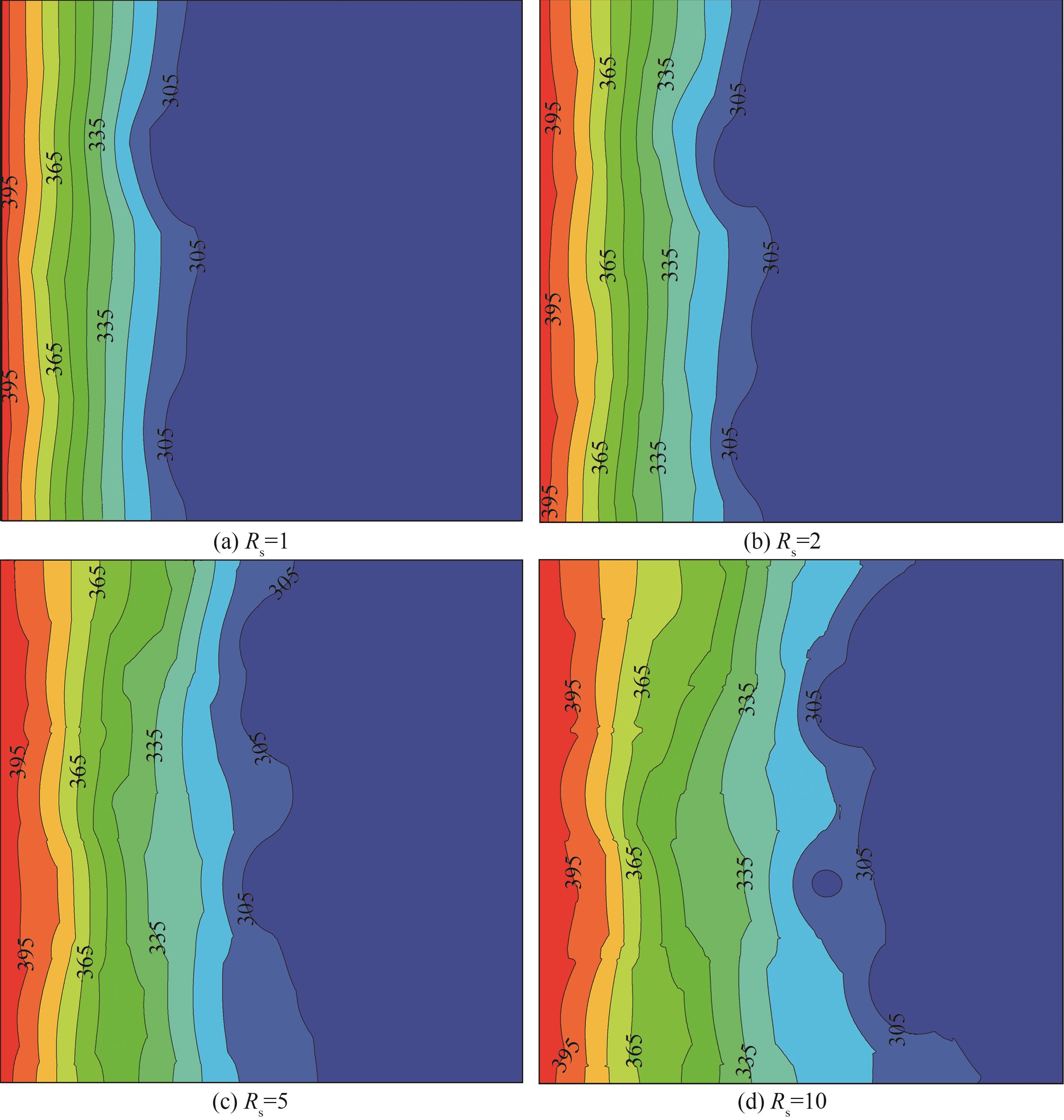
Fig.9 Temperature distribution at different ratios of thermal conductivity coefficient of substrate to PCMs(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.1, St=1, Rcp=Rfcp=Rfs=1, Fo=0.05)

Fig.12 Phase distribution and enthalpy distribution under different specific heat capacities of solid phase PCMs(Ra=2.5×104, Pr=0.1, St=1, Rs=Rcp=Rfs=1, Fo=0.1)
| 1 | Oró E, De Gracia A, Castell A, et al. Review on phase change materials (PCMs) for cold thermal energy storage applications[J]. Applied Energy, 2012, 99: 513-533. |
| 2 | 刘亮, 吴爱枝, 黄云, 等. 两类复合无机相变储热材料高温热稳定性和安全性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(S2): 513-320. |
| Liu L, Wu A Z, Huang Y, et al. Research on high temperature thermal stability and safety of two types of composite inorganic phase change thermal storage materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(S2): 513-320. | |
| 3 | Banu D, Feldman D, Haghighat F, et al. Energy-storing wallboard: flammability tests[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 1998, 10(2): 98-105. |
| 4 | Huang X, Sun C, Chen Z, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on melting process of phase change materials (PCMs) embedded in open-cells metal foams[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2021, 170: 107151. |
| 5 | 张自仕. 含多孔骨架的储能材料固液相变界面传递机理研究[D]. 济南: 山东建筑大学, 2019. |
| Zhang Z S. Study on solid-liquid interface transfer mechanism of energy storage materials with porous skeleton[D]. Jinan: Shandong Jianzhu University, 2019. | |
| 6 | Gokon N, Nakamura S, Hatamachi T, et al. Steam reforming of methane using double-walled reformer tubes containing high-temperature thermal storage Na2CO3/MgO composites for solar fuel production[J]. Energy, 2014, 68: 773-782. |
| 7 | 王君雷, 张第玲, 王昆, 等. 碳酸盐/高炉矿渣定型复合相变储热材料的制备与性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(9): 3028-3034. |
| Wang J L, Zhang D L, Wang K, et al. Carbonates/blast furnace slag form-stable phase change materials[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(9): 3028-3034. | |
| 8 | Atinafu D G, Yun B Y, Wi S, et al. A comparative analysis of biochar, activated carbon, expanded graphite, and multi-walled carbon nanotubes with respect to PCM loading and energy-storage capacities[J]. Environmental Research, 2021, 195: 110853. |
| 9 | 杲东彦, 陈振乾, 陈凌海. 开孔泡沫铝内石蜡融化相变过程的可视化实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(S1): 95-100. |
| Gao D Y, Chen Q Z, Chen L H. Visualized experiment of melting of paraffin waxin aluminum foam with open cells[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(S1): 95-100. | |
| 10 | Palazzolo M A, Dourges M-A, Magueresse A, et al. Preparation of lignosulfonate-based carbon foams by pyrolysis and their use in the microencapsulation of a phase change material[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(2): 2453-2461. |
| 11 | Liu Q, Feng X-B, He Y-L, et al. Three-dimensional multiple-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann models for single-phase and solid-liquid phase-change heat transfer in porous media at the REV scale[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2019, 152: 319-337. |
| 12 | Liu Q, He Y L. Double multiple-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann model for solid-liquid phase change with natural convection in porous media[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2015, 438: 94-106. |
| 13 | Xu Y, Ren Q L, Zheng Z J, et al. Evaluation and optimization of melting performance for a latent heat thermal energy storage unit partially filled with porous media[J]. Applied Energy, 2017, 193: 84-95. |
| 14 | Yang J L, Yang L J, Xu C, et al. Numerical analysis on thermal behavior of solid-liquid phase change within copper foam with varying porosity[J]. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 2015, 84: 1008-1018. |
| 15 | Beckermann C, Viskanta R. Natural convection solid/liquid phase change in porous media[J]. International Journal of Heat & Mass Transfer, 1988, 31(1): 35-46. |
| 16 | Gong X Z, Mujumdar A S. Finite-element analysis of cyclic heat transfer in a shell-and-tube latent heat energy storage exchanger[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 1997, 17(6): 583-591. |
| 17 | Cornubert R, d'Humières D, Levermore D. A Knudsen layer theory for lattice gases[J]. Physica D: Nonlinear Phenomena, 1991, 47(1): 241-259. |
| 18 | Ziegler D P. Boundary conditions for lattice Boltzmann simulations[J]. Journal of Statistical Physics, 1993, 71(5): 1171-1177. |
| 19 | Ginzbourg I, Adler P M. Boundary flow condition analysis for the three-dimensional lattice Boltzmann model[J]. Journal de Physique Ⅱ, 1994, 4(2): 191-214. |
| 20 | He X Y, Zou Q S, Luo L S, et al. Analytic solutions of simple flows and analysis of nonslip boundary conditions for the lattice Boltzmann BGK model[J]. Journal of Statistical Physics, 1997, 87(1): 115-136. |
| 21 | Pan C X, Luo L S, Miller C T. An evaluation of lattice Boltzmann schemes for porous medium flow simulation[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2006, 35(8): 898-909. |
| 22 | de Fabritiis G, Mancini A, Mansutti D, et al. Mesoscopic models of liquid/solid phase transitions[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics C, 1998, 09(8): 1405-1415. |
| 23 | Miller W, Succi S, Mansutti D. Lattice Boltzmann model for anisotropic liquid-solid phase transition[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2001, 86(16): 3578-3581. |
| 24 | Jiaung W S, Ho J R, Kuo C P. Lattice Boltzmann method for the heat conduction problem with phase change[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part B: Fundamentals, 2001, 39(2): 167-187. |
| 25 | Chakraborty S, Chatterjee D. An enthalpy-based hybrid lattice-Boltzmann method for modelling solid-liquid phase transition in the presence of convective transport[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2007, 592: 155-175. |
| 26 | Chatterjee D, Chakraborty S. An enthalpy-based lattice Boltzmann model for diffusion dominated solid-liquid phase transformation[J]. Physics Letters A, 2005, 341(1/2/3/4): 320-330. |
| 27 | Chatterjee D, Chakraborty S. An enthalpy-source based lattice Boltzmann model for conduction dominated phase change of pure substances[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2008, 47(5): 552-559. |
| 28 | Chatterjee D. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of incompressible transport phenomena in macroscopic solidification processes[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part B: Fundamentals, 2010, 58(1): 55-72. |
| 29 | Chatterjee D, Chakraborty S. A hybrid lattice Boltzmann model for solid-liquid phase transition in presence of fluid flow[J]. Physics Letters A, 2006, 351(4/5): 359-367. |
| 30 | Chatterjee D. An enthalpy-based thermal lattice Boltzmann model for non-isothermal systems[J]. Europhysics Letters, 2009, 86(1): 14004. |
| 31 | Luo K, Yao F J, Yi H L, et al. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of convection melting in complex heat storage systems filled with phase change materials[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 86: 238-250. |
| 32 | Li X Y, Ma T, Liu J, et al. Pore-scale investigation of gravity effects on phase change heat transfer characteristics using lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 222: 92-103. |
| 33 | 杲东彦. 基于格子Boltzmann方法的泡沫金属内固液相变传热过程的研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2011. |
| Gao D Y. Study on the effect of thermal properties of porous skeleton on solid-liquid phase change based on LBM[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2011. | |
| 34 | 宋林泉, 陈宝明, 郜凯凯. 基于LBM的多孔骨架热物性对固液相变的影响研究[J]. 山东建筑大学学报, 2017, 32(4): 356-364. |
| Song L Q, Chen B M, Gao K K. Research on the influence of solid liquid phase change in porous skeleton media based on LBM method[J]. Journal of Shandong Jianzhu University, 2017, 32(4): 356-364. | |
| 35 | Dardis O, McCloskey J. Lattice Boltzmann scheme with real numbered solid density for the simulation of flow in porous media[J]. Physical Review E, 1998, 57(4): 4834-4837. |
| 36 | Luo L S, Liao W, Chen X W, et al. Numerics of the lattice Boltzmann method: effects of collision models on the lattice Boltzmann simulations[J]. Physical Review E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2011, 83(5Pt2): 056710. |
| 37 | Lallemand P, Luo L S. Lattice Boltzmann method for moving boundaries[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2003, 184(2): 406-421. |
| 38 | Huang R Z, Wu H Y, Cheng P. A new lattice Boltzmann model for solid-liquid phase change[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2013, 59: 295-301. |
| 39 | Mencinger J. Numerical simulation of melting in two-dimensional cavity using adaptive grid[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2004, 198(1): 243-264. |
| 40 | Gallivan M A, Noble D R, Georgiadis J G, et al. An evaluation of the bounce-back boundary condition for lattice Boltzmann simulations[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 1997, 25(3): 249-263. |
| 41 | House J M, Beckermann C, Smith T F. Effect of a centered conducting body on natural convection heat transfer in an enclosure[J]. Numerical Heat Transfer, Part A: Applications, 1990, 18(2): 213-225. |
| 42 | Das M K, Reddy K S K. Conjugate natural convection heat transfer in an inclined square cavity containing a conducting block[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2006, 49(25): 4987-5000. |
| 43 | 林琦. 微胶囊悬浮液双尺度建模及管内换热特性研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2019. |
| Lin Q. Two-scale modeling of microcapsule suspension and study on heat transfer characteristics in tube[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||