CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (9): 3742-3755.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230604
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xuejin YANG1( ), Jintao YANG1, Ping NING2, Fang WANG1, Xiaoshuang SONG1, Lijuan JIA1(
), Jintao YANG1, Ping NING2, Fang WANG1, Xiaoshuang SONG1, Lijuan JIA1( ), Jiayu FENG1(
), Jiayu FENG1( )
)
Received:2023-06-21
Revised:2023-09-01
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-09-25
Contact:
Lijuan JIA, Jiayu FENG
杨学金1( ), 杨金涛1, 宁平2, 王访1, 宋晓双1, 贾丽娟1(
), 杨金涛1, 宁平2, 王访1, 宋晓双1, 贾丽娟1( ), 冯嘉予1(
), 冯嘉予1( )
)
通讯作者:
贾丽娟,冯嘉予
作者简介:杨学金(1998—),男,硕士研究生,320731920@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Xuejin YANG, Jintao YANG, Ping NING, Fang WANG, Xiaoshuang SONG, Lijuan JIA, Jiayu FENG. Research progress in dry purification technology of highly toxic gas PH3[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755.
杨学金, 杨金涛, 宁平, 王访, 宋晓双, 贾丽娟, 冯嘉予. 剧毒气体PH3的干法净化技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3742-3755.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 材料种类 | 活性组分 | 吸附剂 比表面积/(m2/g) | 吸附剂总孔容/(cm3/g) | 吸附剂平均 孔径/nm | 气体组成 | 反应 温度/℃ | 气体总流速/(ml/min) | 质量空速/(ml/(h·g)) | 穿透标准 | 磷容/(mg/g) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce-Cu-Al | CuO | 45.8 | 0.10 | 4.5 | N2 + H2S + PH3 + 1% O2 | 70 | 500 | 10000 | — | 201.9 | [ |
| Cu-Fe-Ce | CuO | 110.27 | 0.16 | 5.64 | N2 + 456 mg/m3 H2S + 911 mg/m3 PH3 + 1% O2 | 70 | — | 30000 | — | 151.7 | [ |
| 30Cu@TiO2 | CuO | 63.77 | 0.31 | — | N2 + 1518 mg/m3 PH3 | 120 | 100 | 30000 | 90% | 135.73 | [ |
| Cu x /TiO2 | CuO | 110.3 | 0.31 | 5.7 | N2 + 1518 mg/m3 PH3+ 1% O2 | 90 | 100 | 60000 | 97% | 136.2 | [ |
| Cu/TiO2 | CuO | — | — | — | N2 + 759 mg/m3 PH3 | 25 | 100 | — | 99% | 108.48 | [ |
| Cu/γ-Al2O3 | CuO | 232 | 0.43 | — | N2 + 76 mg/m3 PH3 | 20 | 60 | — | 90% | 32.09 | [ |
Flower-shaped CuO/AC | CuO | — | — | — | N2 + PH3 + 1.6% O2 | 110 | — | 750 | — | 96.08 | [ |
| Cu x /ACF | CuO | 1768.9 | 0.57 | 0.96 | N2 + H2S + PH3 + 0.5% O2 | 90 | — | 36000 | — | 132.1 | [ |
| Modified walnut-shell ACs | CuO | 1419 | 0.70 | — | N2 + 1518 mg/m3 PH3+ 1% O2 | 120 | 250 | — | 90% | 284.12 | [ |
| Cu/HZSM-5-[S1] | CuO | 192.2 | 0.11 | 2.1 | N2 + 684 mg/m3 H2S + 911 mg/m3 PH3 + 1 % O2 | 90 | 100 | 20000 | 60% | 150.90 | [ |
| Ce1Cu30O x /HZSM-5 | CuO | 282 | 0.16 | 2.26 | N2 + 1214 mg/m3 PH3 + 1 % O2 | 90 | 100 | 15000 | 60% | 114.36 | [ |
| Cu/SBA-15 | CuO | 177.6 | 0.252 | 5.31 | N2 + 304 mg/m3 H2S + 1214 mg/m3 PH3 + 0.5 % O2 | 80 | 100 | 10000 | 60% | 104. 84 | [ |
| Cu-Fe / SBA-15 | CuO | 206.3 | — | 5.49 | N2 + 304 mg/m3 H2S + 1214 mg/m3 PH3 + 0.5 % O2 | 80 | 100 | 10000 | 60% | 120. 05 | [ |
| Cu-Fe /硅藻土 | CuO | 45.33 | 0.415 | 9.74 | N2 + 304 mg/m3 H2S + 1214 mg/m3 PH3 + 0.5 % O2 | 80 | 100 | 10000 | 60% | 29.61 | [ |
Table 1 Comparison of PH3 purification conditions for copper-based materials
| 材料种类 | 活性组分 | 吸附剂 比表面积/(m2/g) | 吸附剂总孔容/(cm3/g) | 吸附剂平均 孔径/nm | 气体组成 | 反应 温度/℃ | 气体总流速/(ml/min) | 质量空速/(ml/(h·g)) | 穿透标准 | 磷容/(mg/g) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce-Cu-Al | CuO | 45.8 | 0.10 | 4.5 | N2 + H2S + PH3 + 1% O2 | 70 | 500 | 10000 | — | 201.9 | [ |
| Cu-Fe-Ce | CuO | 110.27 | 0.16 | 5.64 | N2 + 456 mg/m3 H2S + 911 mg/m3 PH3 + 1% O2 | 70 | — | 30000 | — | 151.7 | [ |
| 30Cu@TiO2 | CuO | 63.77 | 0.31 | — | N2 + 1518 mg/m3 PH3 | 120 | 100 | 30000 | 90% | 135.73 | [ |
| Cu x /TiO2 | CuO | 110.3 | 0.31 | 5.7 | N2 + 1518 mg/m3 PH3+ 1% O2 | 90 | 100 | 60000 | 97% | 136.2 | [ |
| Cu/TiO2 | CuO | — | — | — | N2 + 759 mg/m3 PH3 | 25 | 100 | — | 99% | 108.48 | [ |
| Cu/γ-Al2O3 | CuO | 232 | 0.43 | — | N2 + 76 mg/m3 PH3 | 20 | 60 | — | 90% | 32.09 | [ |
Flower-shaped CuO/AC | CuO | — | — | — | N2 + PH3 + 1.6% O2 | 110 | — | 750 | — | 96.08 | [ |
| Cu x /ACF | CuO | 1768.9 | 0.57 | 0.96 | N2 + H2S + PH3 + 0.5% O2 | 90 | — | 36000 | — | 132.1 | [ |
| Modified walnut-shell ACs | CuO | 1419 | 0.70 | — | N2 + 1518 mg/m3 PH3+ 1% O2 | 120 | 250 | — | 90% | 284.12 | [ |
| Cu/HZSM-5-[S1] | CuO | 192.2 | 0.11 | 2.1 | N2 + 684 mg/m3 H2S + 911 mg/m3 PH3 + 1 % O2 | 90 | 100 | 20000 | 60% | 150.90 | [ |
| Ce1Cu30O x /HZSM-5 | CuO | 282 | 0.16 | 2.26 | N2 + 1214 mg/m3 PH3 + 1 % O2 | 90 | 100 | 15000 | 60% | 114.36 | [ |
| Cu/SBA-15 | CuO | 177.6 | 0.252 | 5.31 | N2 + 304 mg/m3 H2S + 1214 mg/m3 PH3 + 0.5 % O2 | 80 | 100 | 10000 | 60% | 104. 84 | [ |
| Cu-Fe / SBA-15 | CuO | 206.3 | — | 5.49 | N2 + 304 mg/m3 H2S + 1214 mg/m3 PH3 + 0.5 % O2 | 80 | 100 | 10000 | 60% | 120. 05 | [ |
| Cu-Fe /硅藻土 | CuO | 45.33 | 0.415 | 9.74 | N2 + 304 mg/m3 H2S + 1214 mg/m3 PH3 + 0.5 % O2 | 80 | 100 | 10000 | 60% | 29.61 | [ |

Fig.2 (a) Effect of different acids on the performance of Ce-Cu-Al adsorbents[42]; (b) H2-TPR profiles of three kinds of Ce-Cu-Al adsorbents[42]; (c) CO2-TPD profiles of 30Cu@TiO2 and TiO2[32]; (d) BET analysis of XCu@TiO2 at different loading levels[32]; (e) Cu x /TiO2 purification mechanism of PH3[30]; (f) XCu@TiO2 reaction mechanism for PH3 removal[32]; (g) H2-TPR profiles of Cu x /TiO2[30]; (h) CO2-TPD profiles of Cu x /TiO2[30]; (i) PH3 deactivation curves of Cu/TiO2 adsorbents under different atmospheres[27]; (j) Phosphorus capacity of CuCl2-modified γ-Al2O3 adsorbent after four regeneration cycles[28]
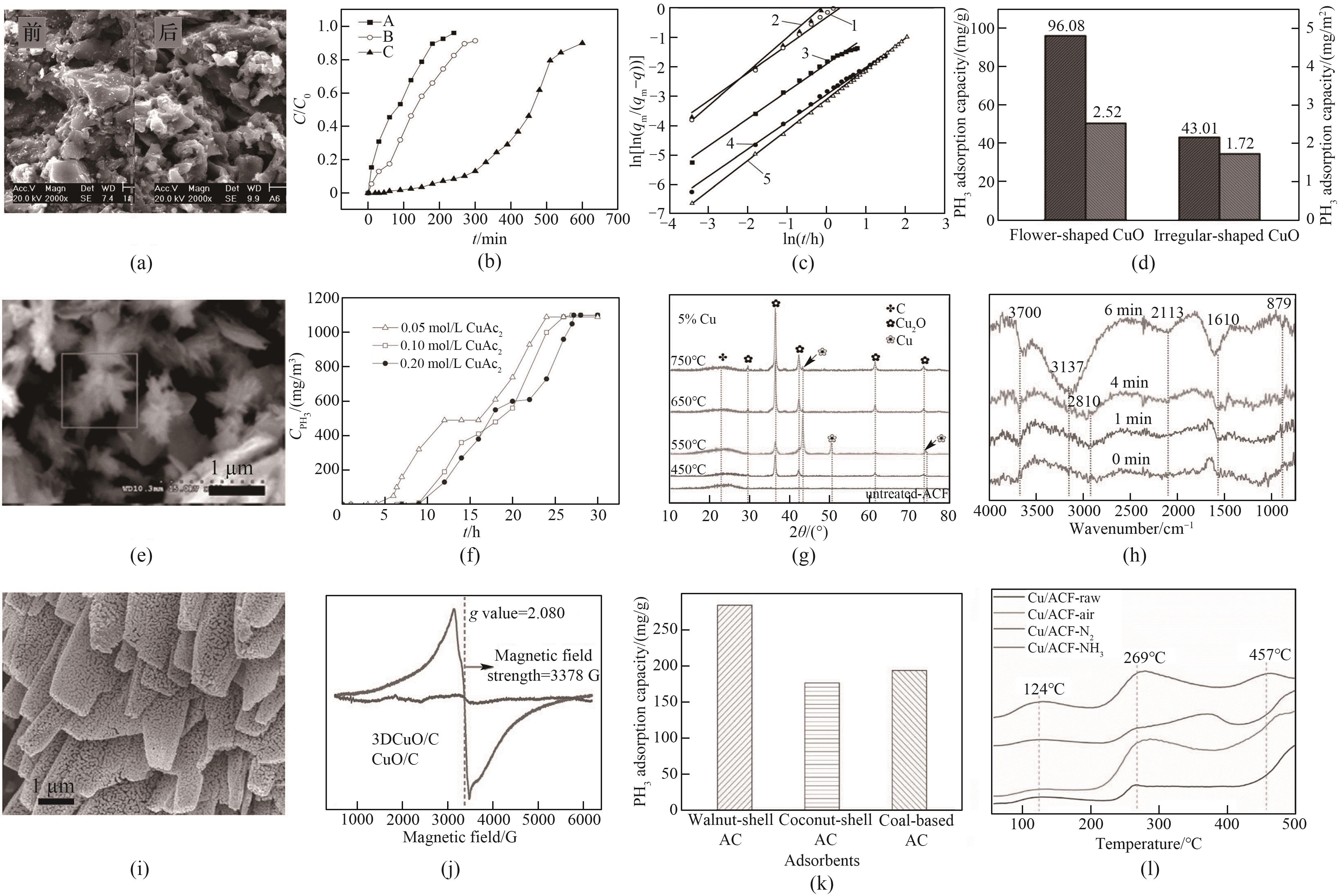
Fig.3 (a) SEM images of the adsorbent before and after the reaction[52]; (b) PH3 breakthrough curves of different activated carbon adsorbents[52]; (c) Banham adsorption kinetic curve of PH3 adsorption on impregnated activated carbon[53]; (d) Phosphorus capacity of flower-shaped and irregular CuO/AC adsorbents[44]; (e) SEM image of flower type CuO/AC adsorbent[44]; (f) PH3 breakthrough curves of AC impregnated with different concentrations of CuAc2[55]; (g) XRD patterns of Cu x /ACF adsorbents at different calcination temperatures[45]; (h) In situ infrared spectrogram of Cu0.15/ACF[45]; (i) SEM images of 3DCuO/C adsorbent[31]; (j) EPR spectrum of 3DCuO/C adsorbent[31]; (k) Comparison of phosphorus capacity of three modified adsorbents[46]; (l) CO2-TPD profiles of Cu/ACF-X[60]

Fig.4 (a) PH3 breakthrough curves for different adsorbents[47]; (b) CO2-TPD profiles of Cu/HZSM-5-[S0] and Cu/HZSM-5-[S1][47]; (c) Breakthrough curves of adsorbents at different Ce doping[29]; (d) PH3 adsorption/oxidation performance of adsorbents at different nitric acid concentrations modified with Cu/SBA-15[48]; (e) In situ IR spectra of Cu/SBA-15[48]; (f) NH3-TPD curves of different samples[49]; (g) BET analysis of Cu-Fe/SBA-15 adsorbent at different levels of Fe doping[50]; (h) Breakthrough curves of Cu-Fe/diatomite adsorbents at different levels of Fe doping[50]; (i), (j) EDS mapping (Cu and Ce) images of the adsorbent at different levels of Ce doping[29]; (k) SEM images before and after modification of 5A molecular sieve by NaCl solution[61]; (l) SEM images of Cu-Fe/diatomite adsorbent[50]
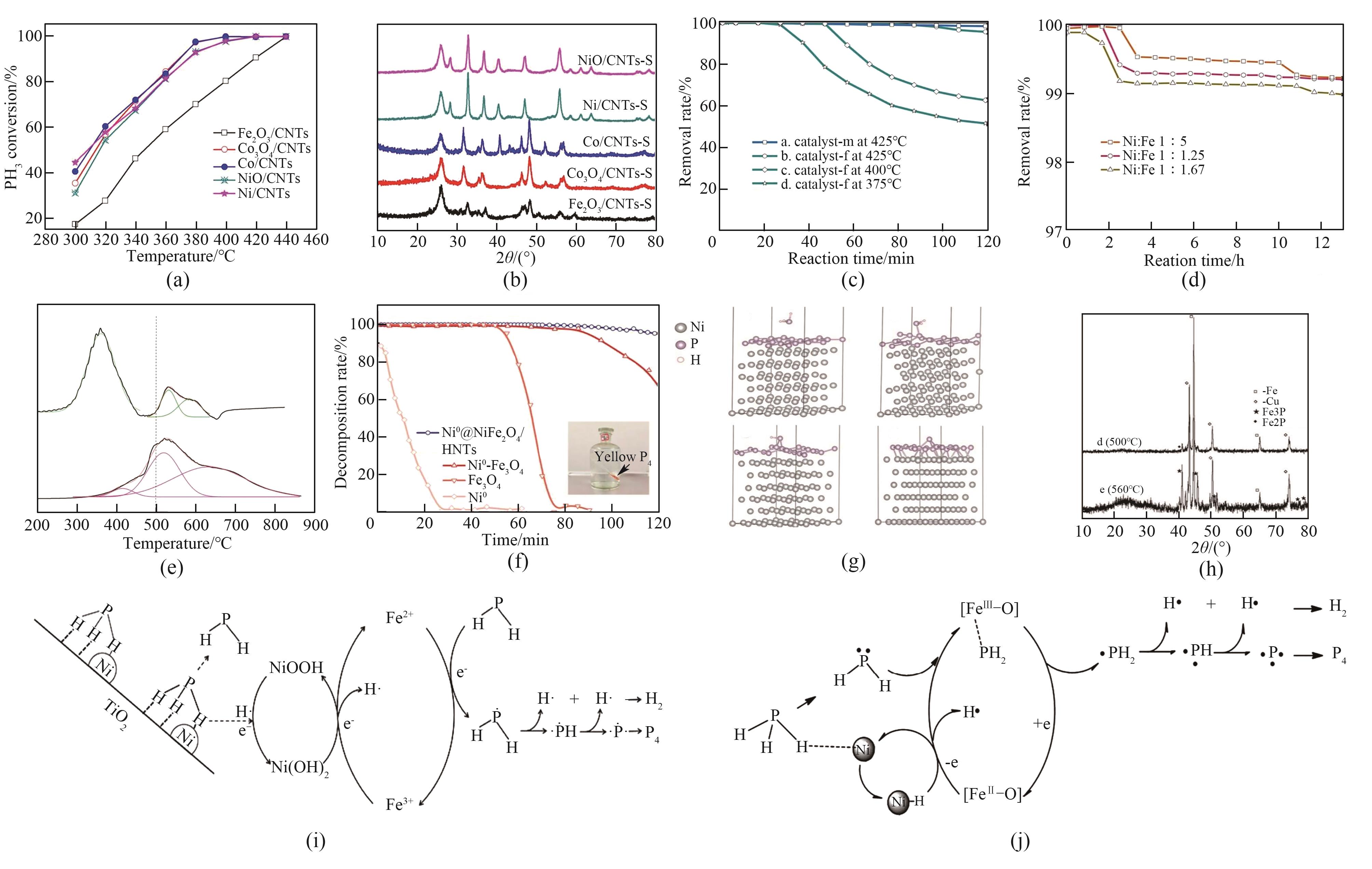
Fig.5 (a) PH3 decomposition performance of each catalyst at different temperatures[67]; (b) XRD pattern of the catalyst after reaction[67]; (c) PH3 decomposition rates of catalysts after additional calcination reduction and normal calcination reduction at 425℃ and PH3 decomposition rates of catalyst f at different temperatures[35]; (d) PH3 decomposition rates at 425℃ for catalysts m synthesized with different Ni∶Fe molar ratios[35]; (e) H2-TPR profiles of FeNiO/HNTs and BFeNiO/HNTs[9]; (f) PH3 isothermal decomposition test of different nanomaterial catalysts[36]; (g) Schematic diagram of the different states of PH3 on the surface of P-layer[36]; (h) XRD pattern of CuFeP catalyst PH3 decomposition products[34]; (i) Mechanism of catalytic decomposition of PH3 by Ni/Fe3O4/TiO2 catalyst[35]; (j) Mechanism of catalytic decomposition of PH3 by FeNi/HNTs catalysts[9]
| 纳米材料种类 | 活性组分 | 气体组成 | 气体总流速/(ml/min) | 催化剂用量/g | 质量空速/(ml/(h·g)) | 催化分解 温度/℃ | 分解 效率/% | 分解产物 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co/CNTs、Ni/CNTs、 Fe2O3/CNTs | Co3O4、NiO、Fe2O3 | N2+5% PH3 | 60 | 0.3 | 2520 | 400 | 100 | P、H2、CoP、NiP2、FeP | [ |
| Ni/Fe3O4/TiO2 | Fe3O4、Ni | N2+1% PH3 | — | 0.2 | 3000 | 425 | 100 | P4 | [ |
| FeNi/HNTs | Fe3O4、Ni | N2+5% PH3 | — | — | 2520 | 420 | 100 | P+H2 | [ |
| Ni0@Fe3O4/HNTs | Fe3O4、Ni0 | N2+1% PH3 | — | 0.1 | 1200 | 300~450 | 100 | P+H2 | [ |
| CuFeP | Fe、Cu | N2+PH3 | 88 | — | — | 400~500或>800 | 100 | Fe2P+Fe3P | [ |
| Co-P非晶合金 | CoP | N2+PH3 | 70 | — | — | 470 | 99.8 | 高纯P | [ |
Table 2 Comparison of conditions for catalytic decomposition of PH3 by several different nanomaterial catalysts
| 纳米材料种类 | 活性组分 | 气体组成 | 气体总流速/(ml/min) | 催化剂用量/g | 质量空速/(ml/(h·g)) | 催化分解 温度/℃ | 分解 效率/% | 分解产物 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co/CNTs、Ni/CNTs、 Fe2O3/CNTs | Co3O4、NiO、Fe2O3 | N2+5% PH3 | 60 | 0.3 | 2520 | 400 | 100 | P、H2、CoP、NiP2、FeP | [ |
| Ni/Fe3O4/TiO2 | Fe3O4、Ni | N2+1% PH3 | — | 0.2 | 3000 | 425 | 100 | P4 | [ |
| FeNi/HNTs | Fe3O4、Ni | N2+5% PH3 | — | — | 2520 | 420 | 100 | P+H2 | [ |
| Ni0@Fe3O4/HNTs | Fe3O4、Ni0 | N2+1% PH3 | — | 0.1 | 1200 | 300~450 | 100 | P+H2 | [ |
| CuFeP | Fe、Cu | N2+PH3 | 88 | — | — | 400~500或>800 | 100 | Fe2P+Fe3P | [ |
| Co-P非晶合金 | CoP | N2+PH3 | 70 | — | — | 470 | 99.8 | 高纯P | [ |
| 1 | Widera A, Thöny D, Aebli M, et al. Solid-state investigation, storage, and separation of pyrophoric PH3 and P2H4 with α-Mg formate[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2023, 62(13): e202217534. |
| 2 | Devai I, Delaune R D. Evidence for phosphine production and emission from Louisiana and Florida marsh soils[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1995, 23(3): 277-279. |
| 3 | Geng J J, Niu X J, Jin X C, et al. Simultaneous monitoring of phosphine and of phosphorus species in Taihu Lake sediments and phosphine emission from lake sediments[J]. Biogeochemistry, 2005, 76(2): 283-298. |
| 4 | Hong Y N, Geng J J, Qiao S, et al. Phosphorus fractions and matrix-bound phosphine in coastal surface sediments of the Southwest Yellow Sea[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 181(1/2/3): 556-564. |
| 5 | Han C, Geng J J, Hong Y N, et al. Free atmospheric phosphine concentrations and fluxes in different wetland ecosystems, China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2011, 159(2): 630-635. |
| 6 | Chen W Y, Niu X J, An S R, et al. Emission and distribution of phosphine in paddy fields and its relationship with greenhouse gases[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 599/600: 952-959. |
| 7 | Wang S, Hu Z, Zhang J, et al. Formation of phosphine and its effect on phosphorus retention in constructed wetlands: characteristic and mechanism[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2022, 28: 102653. |
| 8 | Fu W Y, Zhang X H. Global phosphorus dynamics in terms of phosphine[J]. NPJ Climate and Atmospheric Science, 2020, 3: 51. |
| 9 | Tang X J, Li L L, Shen B X, et al. Halloysite-nanotubes supported FeNi alloy nanoparticles for catalytic decomposition of toxic phosphine gas into yellow phosphorus and hydrogen[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 91(9): 1368-1373. |
| 10 | Wang Z H, Jiang M, Ning P, et al. Thermodynamic modeling and gaseous pollution prediction of the yellow phosphorus production[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(21): 12194-12202. |
| 11 | Pidakala P P B, Esfandi K, Afsar S, et al. Effects of phosphine (ECO2FUME®) on ‘Hass’ avocado fruit quality and target pest mortality[J]. New Zealand Journal of Crop and Horticultural Science, 2022: 1-11. |
| 12 | Chiluwal K, Lee B H, Kwon T H, et al. Post-fumigation sub-lethal activities of phosphine and ethyl formate on survivorship, fertility and female sex pheromone production of Callosobruchus chinensis (L.)[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13: 4333. |
| 13 | Bains W, Petkowski J J, Sousa-Silva C, et al. New environmental model for thermodynamic ecology of biological phosphine production[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 658: 521-536. |
| 14 | Roels J, Verstraete W. Occurrence and origin of phosphine in landfill gas[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2004, 327(1/2/3): 185-196. |
| 15 | Ma J L, Chen W Y, Niu X, et al. The relationship between phosphine, methane, and ozone over paddy field in Guangzhou, China[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2019, 17: e00581. |
| 16 | 刘树根, 李婷, 宁平, 等. 环境中磷化氢的产生、分布及转化研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2019, 38(2): 1085-1096. |
| Liu S G, Li T, Ning P, et al. Research progress of the release, distribution and transformation of phosphine in environment[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2019, 38(2): 1085-1096. | |
| 17 | Tuet W Y, Pierce S A, Racine M C, et al. Cardiopulmonary effects of phosphine poisoning: a preliminary evaluation of milrinone[J]. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2021, 427: 115652. |
| 18 | Yang L P, Yi H H, Tang X L, et al. Effect of rare earth addition on Cu-Fe/AC adsorbents for phosphine adsorption from yellow phosphorous tail gas[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2010, 28: 322-325. |
| 19 | 黄顺祥. 大气污染与防治的过去、现在及未来[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(10): 895-919. |
| Huang S X. Air pollution and control: past, present and future[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(10): 895-919. | |
| 20 | 王文兴, 柴发合, 任阵海, 等. 新中国成立70年来我国大气污染防治历程、成就与经验[J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(10): 1621-1635. |
| Wang W X, Chai F H, Ren Z H, et al. Process, achievements and experience of air pollution control in China since the founding of the People's Republic of China 70 years ago[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(10): 1621-1635. | |
| 21 | 吴满昌, 宁平, 任丙南, 等. 黄磷尾气中总磷及磷化氢的测定[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2004, 26(4): 317-318, 326. |
| Wu M C, Ning P, Ren B N, et al. Determination of total phosphorus and hydrogen phosphide in yellow phosphorus tail gas[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2004, 26(4): 317-318, 326. | |
| 22 | 任占冬, 陈樑. JC系列催化剂上氧化脱除黄磷尾气中PH3、H2S[J]. 天然气化工, 2004, 29(6): 19-23. |
| Ren Z D, Chen L. Oxidative removal of PH3 and H2S from yellow phosphorus tail gas by JC series catalysts[J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry (C1 Chemistry and Technology), 2004, 29(6): 19-23. | |
| 23 | 任占冬, 陈樑, 宁平, 等. 黄磷尾气净化脱除磷化氢、硫化氢中试试验[J]. 现代化工, 2005, 25(12): 48-50, 52. |
| Ren Z D, Chen L, Ning P, et al. Pilot test of removal of PH3 and H2S from yellow phosphorus tail gas[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2005, 25(12): 48-50, 52. | |
| 24 | 张永, 宁平, 徐浩东, 等. 改性活性炭吸附净化黄磷尾气中的PH3 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2007, 1(5): 74-78. |
| Zhang Y, Ning P, Xu H D, et al. Adsorptive removal of PH3 in off-gas of yellow phosphorus by modified activated carbon[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2007, 1(5): 74-78. | |
| 25 | Li W C, Bai H, Hsu J N, et al. Metal loaded zeolite adsorbents for phosphine removal[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(5): 1501-1505. |
| 26 | Hsu J N, Bai H, Li S N, et al. Copper loaded on sol-gel-derived alumina adsorbents for phosphine removal[J]. Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association, 2010, 60(5): 629-635. |
| 27 | Chang S M, Hsu Y Y, Chan T S. Chemical capture of phosphine by a sol-gel-derived Cu/TiO2 adsorbent-interaction mechanisms[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(5): 2005-2013. |
| 28 | Zhou Y M, He T F, Liu S F, et al. Adsorption of trace phosphine in circular hydrogen of a polysilicon chemical vapor deposition stove by Cu/γ-Al2O3 [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(44): 15122-15131. |
| 29 | Feng J Y, Wang F, Wang C, et al. Ce-doping CuO/HZSM-5 as a regenerable sorbent for adsorption-oxidation removal of PH3 at low temperature[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 277: 119420. |
| 30 | Feng J Y, Li K, Wang X Q, et al. Two birds with one stone: copper-based adsorbents used for photocatalytic oxidation of Hg0 (gas) after removal of PH3 [J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2023, 57(11): 4632-4642. |
| 31 | Feng J Y, Ma L X, Wang C, et al. Catalytic decomposition mechanism of PH3 on 3DCuO/C and high value utilization of deactivated catalysts[J]. Small, 2023, 19(28): 2370206. |
| 32 | Jia L J, Yang X J, Hu K Q, et al. Preparation of XCu@TiO2 adsorbent for high-efficient PH3 removal in anaerobic environment and evaluation of desulfurization activity of deactivated adsorbent[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 457: 141277. |
| 33 | 梁培玉, 韩长秀, 林徐明, 等. CoP非晶合金催化分解磷化氢制高纯磷的研究[J]. 南开大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 39(4): 20-23. |
| Liang P Y, Han C X, Lin X M, et al. Research on decomposition of phosphine to high pure phosphorus using Co-P amorphous alloy as catalyst[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Nankaiensis, 2006, 39(4): 20-23. | |
| 34 | Han C X, Ren J L, Tang X J, et al. Preparation of nanometer FeCuP alloy and its application in decomposition of PH3 [J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2007, 18(10): 1285-1288. |
| 35 | Tang X J, Xing C, Ma S H, et al. Highly active Ni/Fe3O4/TiO2 nanocatalysts with tunable interfacial interactions for PH3 decomposition[J]. Environmental Technology, 2021, 42(28): 4426-4433. |
| 36 | Tang X J, Xue J J, Xing C. Catalytic decomposition of toxic phosphine gas on the developed nickel ferrite nanocrystals supported by halloysite nanotubes[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 530: 147264. |
| 37 | 余琼粉, 易红宏, 唐晓龙, 等. 磷化氢在改性活性炭纤维上的吸附等温过程[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 41(1): 381-386. |
| Yu Q F, Yi H H, Tang X L, et al. Adsorption isotherm of phosphine onto CoCl2-modified activated carbon fiber[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2010, 41(1): 381-386. | |
| 38 | Xu X, Miao X, Liao N, et al. Breakthrough analysis for adsorption of phosphine on 5A molecular sieve[J]. Chemical Engineering & Technology, 2011, 34(1): 140-145. |
| 39 | Xu X W, Huang G Q. Effect of 13X zeolite modified with CuCl2 and ZnCl2 for removing phosphine from circular hydrogen of a polysilicon chemical vapor deposition stove[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(5): 1380-1386. |
| 40 | Xu X W, Huang G Q, Qi S. Properties of AC and 13X zeolite modified with CuCl2 and Cu(NO3)2 in phosphine removal and the adsorptive mechanisms[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 316: 563-572. |
| 41 | Wang Y W, Lin Q, Ning P, et al. Preparation of Ce0.6-Cu60/Al40-[O] catalyst and role of CeO2/CuO in simultaneous removal of H2S and PH3 [J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2018, 87: 44-53. |
| 42 | Wang Y W, Lin Q A, Ning P, et al. Effect of the acid used in the evaporation-induced self-assembly method on Ce-Cu-Al trimetallic composite catalyst for its simultaneous removal of H2S and PH3 [J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2021, 45(13): 5822-5828. |
| 43 | Wei S, Ning P, Wang C, et al. Research into the simultaneous removal process of H2S and PH3 by Cu-Fe-Ce composite metal oxide adsorbent[J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 2020, 46(9): 4017-4032. |
| 44 | Ren Z D, Quan S S, Zhu Y C, et al. Purification of yellow phosphorus tail gas for the removal of PH3 on the spot with flower-shaped CuO/AC[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(38): 29734-29740. |
| 45 | Wang Y W, Ning P, Zhao R H, et al. A Cu-modified active carbon fiber significantly promoted H2S and PH3 simultaneous removal at a low reaction temperature[J]. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 2021, 15(6): 1-10. |
| 46 | Yu Q F, Li M, Ning P, et al. Preparation and phosphine adsorption of activated carbon prepared from walnut shells by KOH chemical activation[J]. Separation Science and Technology, 2014, 49(15): 2366-2375. |
| 47 | Feng J Y, Wang F, Wang C, et al. Cu/HZSM-5 sorbent treated by NH3 plasma for low-temperature simultaneous adsorption-oxidation of H2S and PH3 [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(21): 24670-24681. |
| 48 | Li S, Li K, Hao J M, et al. Acid modified mesoporous Cu/SBA-15 for simultaneous adsorption/oxidation of hydrogen sulfide and phosphine[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 302: 69-76. |
| 49 | Song X, Li S, Li K, et al. Preparation of Cu-Fe composite metal oxide loaded SBA-15 and its capacity for simultaneous catalytic oxidation of hydrogen sulfide and phosphine[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018, 259: 89-98. |
| 50 | Li S, Hao J M, Ning P, et al. Preparation of Cu-Fe nanocomposites loaded diatomite and their excellent performance in simultaneous adsorption/oxidation of hydrogen sulfide and phosphine at low temperature[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017, 180: 23-35. |
| 51 | Rupp E C, Granite E J, Stanko D C. Laboratory scale studies of Pd/γ-Al2O3 sorbents for the removal of trace contaminants from coal-derived fuel gas at elevated temperatures[J]. Fuel, 2013, 108: 131-136. |
| 52 | 蒋明, 宁平, 王重华, 等. 改性活性炭吸附净化低浓度磷化氢[J]. 高校化学工程学报, 2012, 26(4): 685-691. |
| Jiang M, Ning P, Wang Z H, et al. Adsorption purification of low-concentration PH3 by modified activated carbon[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Chinese Universities, 2012, 26(4): 685-691. | |
| 53 | 王学谦, 宁平. 浸渍活性炭吸附低浓度PH3动力学[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 42(7): 2162-2166. |
| Wang X Q, Ning P. Kinetics of low concentration PH3 adsorption on impregnatedly activated carbon[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2011, 42(7): 2162-2166. | |
| 54 | 徐浩东, 宁平, 蒋明, 等. 净化PH3和H2S气体改性活性炭的制备与表征[J]. 环境科学学报, 2008, 28(7): 1365-1369. |
| Xu H D, Ning P, Jiang M, et al. Preparation and characterization of modified activated carbon for purification of PH3 and H2S[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2008, 28(7): 1365-1369. | |
| 55 | Ning P, Wang X Y, Bart H J, et al. Removal of phosphorus and sulfur from yellow phosphorus off-gas by metal-modified activated carbon[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2011, 19(13): 1547-1552. |
| 56 | Ning P, Yi H H, Yu Q F, et al. Effect of zinc and cerium addition on property of copper-based adsorbents for phosphine adsorption[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2010, 28(4): 581-586. |
| 57 | Yi H H, Yu Q F, Tang X L, et al. Phosphine adsorption removal from yellow phosphorus tail gas over CuO-ZnO-La2O3/activated carbon[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2011, 50(7): 3960-3965. |
| 58 | 杨丽萍, 易红宏, 唐晓龙, 等. 铜基改性活性炭吸附净化黄磷尾气中的PH3 [J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 42(5): 1489-1494. |
| Yang L P, Yi H H, Tang X L, et al. Adsorptive purification of PH3 in yellow phosphorus off-gas by Cu-based modified activated carbon[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2011, 42(5): 1489-1494. | |
| 59 | 李彬, 宁平, 王学谦. 负载酸活性炭净化黄磷尾气中磷化氢[J]. 四川化工, 2004, 7(5): 41-43. |
| Li B, Ning P, Wang X Q. Purification of phosphine from yellow phosphorus tail gas by acid-loaded activated carbon[J]. Sichuan Chemical Industry, 2004, 7(5): 41-43. | |
| 60 | Yang X Y, Li K, Wang C, et al. Cu/ACF adsorbent modified by non-thermal plasma for simultaneous adsorption-oxidation of H2S and PH3 [J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2023, 127: 641-651. |
| 61 | 黄小凤, 谭娟, 宁平. 改性5A分子筛吸附净化PH3的实验研究[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 43(2): 220-223. |
| Huang X F, Tan J, Ning P. Adsorbing purification of PH3 by modified 5A molecular sieves[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 43(2): 220-223. | |
| 62 | Feng J Y, Li K, Li S, et al. Regeneration of the exhausted mesoporous Cu/SBA-15-[N] for simultaneous adsorption-oxidation of hydrogen sulfide and phosphine[J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 2020, 46(1): 329-346. |
| 63 | Einicke W D, Enke D, Dvoyashkin M, et al. The mechanism of pseudomorphic transformation of spherical silica gel into MCM-41 studied by PFG NMR diffusometry[J]. Materials, 2013, 6(9): 3688-3709. |
| 64 | Umemoto H. Dependence of the catalytic decomposition of PH3 on wire material[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2015, 575: 9-11. |
| 65 | 李俐俐, 侯小歌, 胡春红, 等. 碳纳米管负载的镍及其氧化物对高毒气体PH3的催化分解性能[J]. 环境化学, 2013, 32(8): 1518-1523. |
| Li L L, Hou X G, Hu C H, et al. Catalytic decomposition of highly toxic PH3 gas over metal Ni and NiO supported on carbon nanotubes[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2013, 32(8): 1518-1523. | |
| 66 | 李俐俐, 盛东峰, 王进, 等. 碳纳米管负载的非晶态CoP合金和金属Co对高毒气体PH3的催化分解[J]. 环境科学学报, 2013, 33(8): 2158-2165. |
| Li L L, Sheng D F, Wang J, et al. Catalytic decomposition of highly toxic PH3 gas over amorphous CoP alloy and metal Co supported on carbon nanotubes[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2013, 33(8): 2158-2165. | |
| 67 | Li L L, Chen C, Chen L, et al. Catalytic decomposition of toxic chemicals over iron group metals supported on carbon nanotubes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2014, 48(6): 3372-3377. |
| 68 | 徐卫煌. 挥发性有机废气治理技术研究进展[J]. 化工设计通讯, 2018, 44(10): 228-229. |
| Xu W H. Research progress of treatment technology for volatile organic waste gas[J]. Chemical Engineering Design Communications, 2018, 44(10): 228-229. | |
| 69 | 王惠平, 唐忠松. 次磷酸钠生产中“三废”的综合治理[J]. 化学世界, 1999, 40(3): 159-162. |
| Wang H P, Tang Z S. Comprehensive management of waste materials in the production process of sodium hypophosphite[J]. Chemical World, 1999, 40(3): 159-162. | |
| 70 | 周为莉, 叶明华, 余锋进, 等. 有机废气处理技术研究进展[J]. 能源工程, 2018, (5): 55-61. |
| Zhou W L, Ye M H, Yu F J, et al. Research progress of organic waste gas treatment technologies[J]. Energy Engineering, 2018, (5): 55-61. | |
| 71 | Ma Y X, Wang X Q, Ning P, et al. Simultaneous removal of PH3, H2S, and dust by corona discharge[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30(11): 9580-9588. |
| 72 | 刘树根, 苏福家, 李婷, 等. 生物滴滤法净化低浓度磷化氢及其微生物群落分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2018, 12(12): 3406-3414. |
| Liu S G, Su F J, Li T, et al. Purification of low concentration phosphine by bio-trickling filter system and analysis of microbial community[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2018, 12(12): 3406-3414. | |
| 73 | 余硕, 刘树根, 李婷. 磷化氢生物净化体系及抑制作用机理[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(5): 2219-2225. |
| Yu S, Liu S G, Li T. Inhibition mechanism of phosphine biological purification system[J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(5): 2219-2225. |
| [1] | Baiyu YANG, Yue KOU, Juntao JIANG, Yali ZHAN, Qinghong WANG, Chunmao CHEN. Chemical conversion of dissolved organic matter in petrochemical spent caustic along a wet air oxidation pretreatment process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3912-3920. |
| [2] | Yihao ZHANG, Zhenlei WANG. Fault detection using grouped support vector data description based on maximum information coefficient [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3865-3878. |
| [3] | Jintong LI, Shun QIU, Wenshou SUN. Oxalic acid and UV enhanced arsenic leaching from coal in flue gas desulfurization by coal slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3522-3532. |
| [4] | Kaixuan LI, Wei TAN, Manyu ZHANG, Zhihao XU, Xuyu WANG, Hongbing JI. Design of cobalt-nitrogen-carbon/activated carbon rich in zero valent cobalt active site and application of catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3342-3352. |
| [5] | Linzheng WANG, Yubing LU, Ruizhi ZHANG, Yonghao LUO. Analysis on thermal oxidation characteristics of VOCs based on molecular dynamics simulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [6] | Bin LI, Zhenghu XU, Shuang JIANG, Tianyong ZHANG. Clean and efficient synthesis of accelerator CBS by hydrogen peroxide catalytic oxidation method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2919-2925. |
| [7] | Yuming TU, Gaoyan SHAO, Jianjie CHEN, Feng LIU, Shichao TIAN, Zhiyong ZHOU, Zhongqi REN. Advances in the design, synthesis and application of calcium-based catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2717-2734. |
| [8] | Pan LI, Junyang MA, Zhihao CHEN, Li WANG, Yun GUO. Effect of the morphology of Ru/α-MnO2 on NH3-SCO performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2908-2918. |
| [9] | Chen WANG, Xiufeng SHI, Xianfeng WU, Fangjia WEI, Haohong ZHANG, Yin CHE, Xu WU. Preparation of Mn3O4 catalyst by redox method and study on its catalytic oxidation performance and mechanism of toluene [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2447-2457. |
| [10] | Jipeng ZHOU, Wenjun HE, Tao LI. Reaction engineering calculation of deactivation kinetics for ethylene catalytic oxidation over irregular-shaped catalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2416-2426. |
| [11] | Xueyan WEI, Yong QIAN. Experimental study on the low to medium temperature oxidation characteristics and kinetics of micro-size iron powder [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2624-2638. |
| [12] | Quanbi ZHANG, Yijin YANG, Xujing GUO. Catalytic degradation of dissolved organic matter in rifampicin pharmaceutical wastewater by Fenton oxidation process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2217-2227. |
| [13] | Xu GUO, Yongzheng ZHANG, Houbing XIA, Na YANG, Zhenzhen ZHU, Jingyao QI. Research progress in the removal of water pollutants by carbon-based materials via electrooxidation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1862-1874. |
| [14] | Ruikang LI, Yingying HE, Weipeng LU, Yuanyuan WANG, Haodong DING, Yongming LUO. Study on the electrochemical enhanced cobalt-based cathode to activate peroxymonosulfate [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2207-2216. |
| [15] | Airan ZHOU, Ping LU, Jianhui XIA, Dongqin LI, Jie GUO, Ming DU, Lichun DONG. Scarring analysis and numerical simulation of TiCl4 oxidation reactor in chloride process of titanium dioxide [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1499-1508. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||