CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (4): 1705-1717.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231414
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Youming SI( ), Lingfeng ZHENG, Pengzhong CHEN, Jiangli FAN(
), Lingfeng ZHENG, Pengzhong CHEN, Jiangli FAN( ), Xiaojun PENG
), Xiaojun PENG
Received:2023-12-31
Revised:2024-03-13
Online:2024-06-06
Published:2024-04-25
Contact:
Jiangli FAN
通讯作者:
樊江莉
作者简介:司友明 (1996—),男,博士研究生,siyouming@mail.dlut.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Youming SI, Lingfeng ZHENG, Pengzhong CHEN, Jiangli FAN, Xiaojun PENG. Performance and mechanism of novel antimony oxo cluster photoresist[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1705-1717.
司友明, 郑凌峰, 陈鹏忠, 樊江莉, 彭孝军. 新型锑氧簇光刻胶的性能与机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1705-1717.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
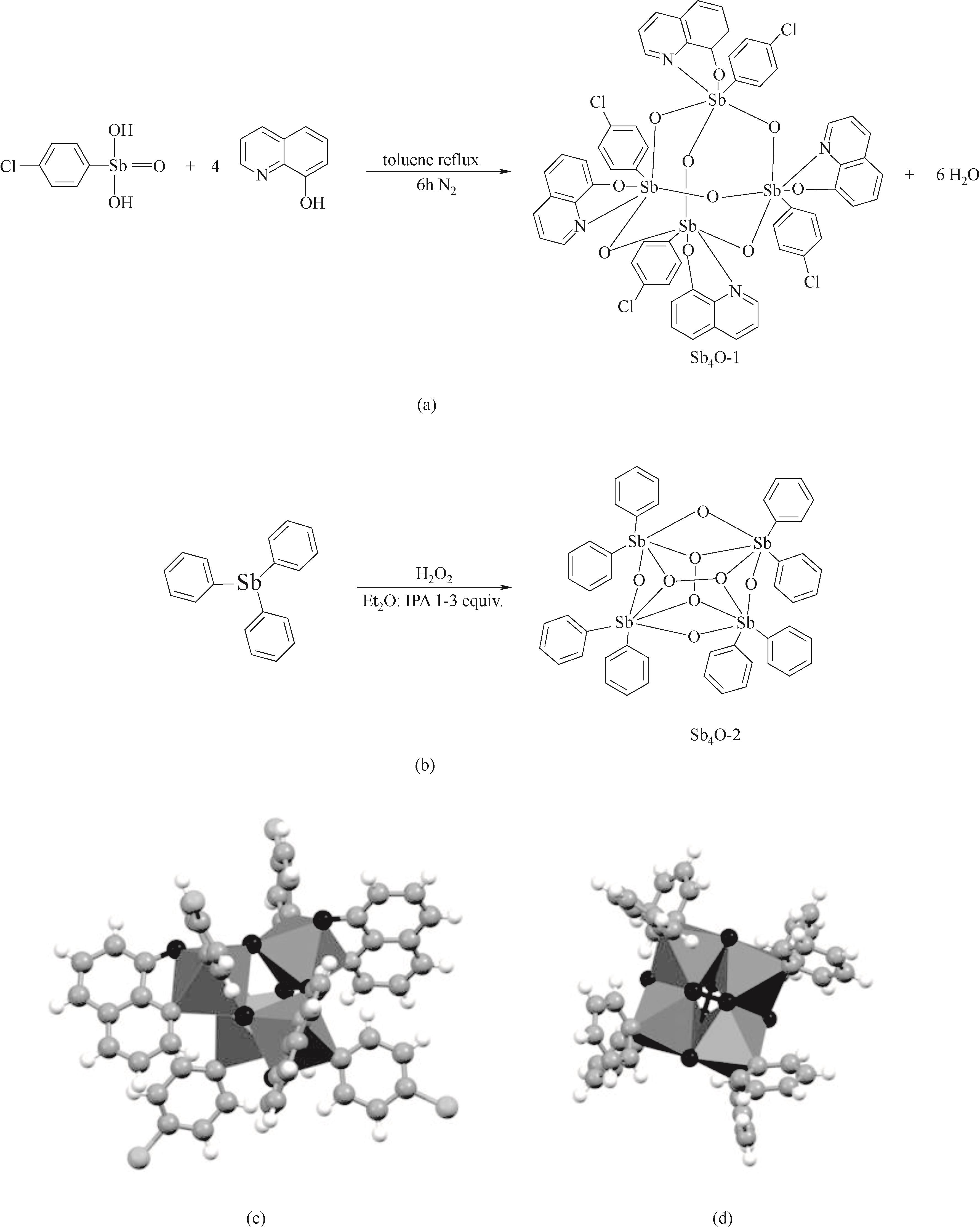
Fig.2 Synthesis routes of metal-organic assembled antimony oxo cluster Sb4O-1 (a) and self-assembled antimony oxo cluster Sb4O-2 (b), and single crystal structure of Sb4O-1 (c) and Sb4O-2 (d)
| 占空比 | 曝光剂量/(μC/cm2) | 图案高度/nm |
|---|---|---|
| L/3S | 400 | 15.5 |
| 500 | 22.8 | |
| 600 | 27.5 | |
| 700 | 24.5 | |
| 800 | 37.4 | |
| 900 | 39.7 | |
| L/4S | 400 | 26.9 |
| 500 | 32.8 | |
| 600 | 40.6 | |
| 700 | 40.9 | |
| 800 | 47.6 | |
| 900 | 49.5 | |
| L/6S | 400 | 25.2 |
| 500 | 30.2 | |
| 600 | 30.8 | |
| 700 | 35.7 | |
| 800 | 45.5 | |
| 900 | 47.6 |
Table 1 Height of Sb4O-2 pattern under different exposure doses and L/S
| 占空比 | 曝光剂量/(μC/cm2) | 图案高度/nm |
|---|---|---|
| L/3S | 400 | 15.5 |
| 500 | 22.8 | |
| 600 | 27.5 | |
| 700 | 24.5 | |
| 800 | 37.4 | |
| 900 | 39.7 | |
| L/4S | 400 | 26.9 |
| 500 | 32.8 | |
| 600 | 40.6 | |
| 700 | 40.9 | |
| 800 | 47.6 | |
| 900 | 49.5 | |
| L/6S | 400 | 25.2 |
| 500 | 30.2 | |
| 600 | 30.8 | |
| 700 | 35.7 | |
| 800 | 45.5 | |
| 900 | 47.6 |
| 占空比 | 曝光剂量/(μC/cm2) | LW/nm | LER/nm | Z/(μC·nm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L/3S | 400 | 43.0 | ||
| 500 | 46.5 | 16.3 | 1.34×10-4 | |
| 600 | 44.5 | 9.9 | 5.18×10-5 | |
| 700 | 52.3 | 10.6 | 1.13×10-4 | |
| 800 | 59.7 | 7.4 | 9.32×10-5 | |
| 900 | 64.8 | 8.9 | 1.94×10-4 | |
| L/4S | 400 | 128.5 | 12.3 | 1.28×10-3 |
| 500 | 122.6 | 9.9 | 9.03×10-4 | |
| 600 | 139.3 | 9.9 | 1.59×10-3 | |
| 700 | 146.8 | 8.3 | 1.53×10-3 | |
| 800 | 156.8 | 5.6 | 9.67×10-4 | |
| 900 | 167.0 | 9.2 | 3.55×10-3 | |
| L/6S | 400 | 73.0 | ||
| 500 | 101.2 | |||
| 600 | 51.9 | 7.1 | 4.23×10-5 | |
| 700 | 59.2 | 9.1 | 1.20×10-4 | |
| 800 | 63.5 | 5.6 | 6.42×10-5 | |
| 900 | 72.4 | 6.2 | 1.31×10-4 |
Table 2 LW, LER, and Z values of Sb4O-2 pattern under different L/S conditions
| 占空比 | 曝光剂量/(μC/cm2) | LW/nm | LER/nm | Z/(μC·nm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L/3S | 400 | 43.0 | ||
| 500 | 46.5 | 16.3 | 1.34×10-4 | |
| 600 | 44.5 | 9.9 | 5.18×10-5 | |
| 700 | 52.3 | 10.6 | 1.13×10-4 | |
| 800 | 59.7 | 7.4 | 9.32×10-5 | |
| 900 | 64.8 | 8.9 | 1.94×10-4 | |
| L/4S | 400 | 128.5 | 12.3 | 1.28×10-3 |
| 500 | 122.6 | 9.9 | 9.03×10-4 | |
| 600 | 139.3 | 9.9 | 1.59×10-3 | |
| 700 | 146.8 | 8.3 | 1.53×10-3 | |
| 800 | 156.8 | 5.6 | 9.67×10-4 | |
| 900 | 167.0 | 9.2 | 3.55×10-3 | |
| L/6S | 400 | 73.0 | ||
| 500 | 101.2 | |||
| 600 | 51.9 | 7.1 | 4.23×10-5 | |
| 700 | 59.2 | 9.1 | 1.20×10-4 | |
| 800 | 63.5 | 5.6 | 6.42×10-5 | |
| 900 | 72.4 | 6.2 | 1.31×10-4 |
曝光剂量/ (μC/cm2) | C原子浓度/% | O原子浓度/% | Sb原子浓度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 68.9 | 27.6 | 3.45 |
| 200 | 61.5 | 34 | 4.5 |
| 600 | 59.37 | 35.95 | 4.69 |
| 800 | 50.44 | 43.34 | 6.22 |
| 1000 | 50.27 | 43.42 | 6.31 |
Table 3 Atomic concentration of Sb4O-2 photoresist at different exposure doses
曝光剂量/ (μC/cm2) | C原子浓度/% | O原子浓度/% | Sb原子浓度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 68.9 | 27.6 | 3.45 |
| 200 | 61.5 | 34 | 4.5 |
| 600 | 59.37 | 35.95 | 4.69 |
| 800 | 50.44 | 43.34 | 6.22 |
| 1000 | 50.27 | 43.42 | 6.31 |
| 1 | 韦亚一. 超大规模集成电路先进光刻理论与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016. |
| Wei Y Y. Theory and Appli cation of VLSI Advanced Lithography[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. | |
| 2 | Li L, Liu X, Pal S, et al. Extreme ultraviolet resist materials for sub-7 nm patterning[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(16): 4855-4866. |
| 3 | Chen Y F. Nanofabrication by electron beam lithography and its applications: a review[J]. Microelectronic Engineering, 2015, 135: 57-72. |
| 4 | Lin Q H. Properties of Photoresist Polymers[M]//Mark JE. Physical Properties of Polymers Handbook. New York: Springer, 2007: 965-979. |
| 5 | Vollenbroek F A, Spiertz E J. Photoresist Systems for Microlithography[M]//Electronic Applications. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2005: 85-111. |
| 6 | 何颂华, 罗军益, 刘真. 辐射固化材料的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2009, 23(S1): 247-250. |
| He S H, Luo J Y, Liu Z. Development situation of radiation curing materials[J]. Materials Review, 2009, 23(S1): 247-250. | |
| 7 | 苏义旭, 马亮亮. 国内外光刻胶发展概述[J]. 化工管理, 2022(7): 62-64. |
| Su Y X, Ma L L. Summary of photoresist development at domestic and abroad[J]. Chemical Management, 2022(7): 62-64. | |
| 8 | 夏明德, 浦家诚. 抗蚀剂近年发展动态[J]. 感光材料, 1989(5): 21-25. |
| Xia M D, Pu J C. Recent development of resist[J]. Image Vision, 1989(5): 21-25. | |
| 9 | 谢常青, 陈梦真, 王玉玲, 等. 同步辐射X射线光刻中光刻胶显影速率模型研究[J]. 科学通报, 1995, 40(21): 2010-2012. |
| Xie C Q, Chen M Z, Wang Y L, et al. Development rate model of photoresist in synchrotron radiation X-ray lithography[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(21): 2010-2012. | |
| 10 | 陈昊, 陈鹏忠, 彭孝军. 金属基极紫外光刻胶[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(8): 3307-3325. |
| Chen H, Chen P Z, Peng X J. Metal-based extreme ultraviolet photoresist[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(8): 3307-3325. | |
| 11 | Si Y M, Zhao Y D, Shi G Y, et al. A novel stable zinc–oxo cluster for advanced lithography patterning[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(9): 4801-4807. |
| 12 | Wang Q Q, Cui H, Wang X L, et al. Exceptional light sensitivity by thiol-ene click lithography[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2023, 145(5): 3064-3074. |
| 13 | Lu X Y, Luo H, Wang K, et al. CO2-based dual-tone resists for electron beam lithography[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(13): 2007417. |
| 14 | Wang Z H, Chen J P, Yu T J, et al. Sulfonium-functionalized polystyrene-based nonchemically amplified resists enabling sub-13 nm nanolithography[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(1): 2289-2300. |
| 15 | 陆新宇, 马彬泽, 罗皓, 等. 二氧化碳基聚碳酸环己撑酯电子束光刻胶显影工艺优化[J]. 应用化学, 2021, 38(9): 1189-1198. |
| Lu X Y, Ma B Z, Luo H, et al. Optimization of development process for carbon dioxide-based poly(cyclohexene carbonate) electron beam resist[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2021, 38(9): 1189-1198. | |
| 16 | Kumar R, Chauhan M, Moinuddin M G, et al. Development of nickel-based negative tone metal oxide cluster resists for sub-10 nm electron beam and helium ion beam lithography[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(17): 19616-19624. |
| 17 | Wu J R, Lin T A, Wu Y R, et al. Novel hexameric tin carboxylate clusters as efficient negative-tone EUV photoresists: high resolution with well-defined patterns under low energy doses[J]. Nanoscale Advances, 2023, 5(11): 3033-3043. |
| 18 | Gangnaik A S, Georgiev Y, Holmes J. New generation electron beam resists: a review[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29: 1898-1917. |
| 19 | Gonzalez-Martinez I G, Bachmatiuk A, Bezugly V, et al. Electron-beam induced synthesis of nanostructures: a review[J]. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(22): 11340-11362. |
| 20 | Sanchez C, Belleville P, Popall M, et al. Applications of advanced hybrid organic-inorganic nanomaterials: from laboratory to market[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(2): 696-753. |
| 21 | 孔祥宇, 廖力, 卢灿忠, 等. 共价有机框架-杂多酸复合材料用于非均相催化烯烃环氧化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(12): 34-41. |
| Kong X Y, Liao L, Lu C Z, et al. Application of covalent organic framework-polyoxometalates composites in heterogeneous catalytic epoxidation of olefins[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(12): 34-41. | |
| 22 | Yu S Y, Schrodj G, Mougin K, et al. Direct laser writing of crystallized TiO2 and TiO2/carbon microstructures with tunable conductive properties[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(51): e1805093. |
| 23 | Lewis S M, DeRose G A, Alty H R, et al. Tuning the performance of negative tone electron beam resists for the next generation lithography[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(32): 2202710. |
| 24 | Sharma S K, Chauhan M, Kumar R, et al. Development of metal-organic cluster based negative tone resist: pre-screened through the helium-ion beam prelude to extreme ultraviolet lithography (EUVL) applications[C]//SPIE Advanced Lithography. Proc SPIE 11612, Advances in Patterning Materials and Processes ⅩⅩⅩⅧ, 2021, 11612: 21-28. |
| 25 | Thakur N, Vockenhuber M, Ekinci Y, et al. Fluorine-rich zinc oxoclusters as extreme ultraviolet photoresists: chemical reactions and lithography performance[J]. ACS Materials Au, 2022, 2(3): 343-355. |
| 26 | Mattson E C, Cabrera Y, Rupich S M, et al. Chemical modification mechanisms in hybrid hafnium oxo-methacrylate nanocluster photoresists for extreme ultraviolet patterning[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(17): 6192-6206. |
| 27 | Wu L J, Hilbers M F, Lugier O, et al. Fluorescent labeling to investigate nanopatterning processes in extreme ultraviolet lithography[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(43): 51790-51798. |
| 28 | 陈召勇, 李子哗, 林锋, 等. 锑/多孔碳复合材料的制备及钠离子电池负极储钠性能研究[J]. 现代化工, 2023, 43(10): 143-147. |
| Chen Z Y, Li Z H, Lin F, et al. Preparation of antimony/porous carbon composite and sodium-storing properties of sodium ion batteries[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2023, 43(10): 143-147. | |
| 29 | 冯亚莉, 马杰祎, 孙帅豪, 等. 槲皮素锑的合成、表征及生物活性研究[J]. 化学与粘合, 2023, 45(6): 494-498, 575. |
| Feng Y L, Ma J Y, Sun S H, et al. Study on the synthesis, characterization and biological activity of Sb(Ⅲ) quercetin complex[J]. Chemistry and Adhesion, 2023, 45(6): 494-498, 575. | |
| 30 | 潘飞, 马殿普, 覃德清, 等. 锡酸锌/羟基锡酸锌与三氧化二锑阻燃剂对人肺上皮细胞的毒性研究[J]. 环境工程, 2023, 41(S2): 937-940, 946. |
| Pan F, Ma D P, Qin D Q, et al. Toxicity study of zinc stannate/hydroxy zinc stannate and antimony trioxide flame retardant on human lung epithelial cells [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2023, 41(S2): 937-940, 946. | |
| 31 | 桑胜华, 邵京明, 潘贵, 等. 锑电积贫液催化氧化技术研究与应用[J]. 黄金, 2023, 44(12): 33-35. |
| Sang S H, Shao J M, Pan G, et al. Study and application of antimony electrodeposition lean liquid catalytic oxidation technology[J]. Gold, 2023, 44(12): 33-35. | |
| 32 | 张忠堂, 刘兰进, 李玉虎, 等. 复杂锑金精矿与铅精矿协同熔炼过程热力学研究[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2023(12): 9-17, 95. |
| Zhang Z T, Liu L J, Li Y H, et al. Thermodynamic study on synergistic smelting process of complex antimony gold concentrate and lead concentrate[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy), 2023(12): 9-17, 95. | |
| 33 | Liu Z Q, Ozawa Y, Yagasaki A. Oligomeric arylstibonates[J]. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2014, 87(11): 1245-1251. |
| 34 | Jami A K, Baskar V. Tetranuclear stiboxanes (RSb)4O6, exhibiting an adamantane-type structure[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2012, 41(40): 12524-12529. |
| 35 | Sharutin V V, Pakusina A P, Smirnova S A, et al. Synthesis and structure of organoantimony peroxides[J]. Russian Journal of Coordination Chemistry, 2004, 30(5): 314-321. |
| 36 | Dolomanov O V, Bourhis L J, Gildea R J, et al. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program[J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2009, 42(2): 339-341. |
| 37 | Sheldrick G M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL[J]. Acta Crystallographica. Section C, Structural Chemistry, 2015, 71(Pt 1): 3-8. |
| 38 | Spackman P R, Turner M J, McKinnon J J, et al. CrystalExplorer: a program for Hirshfeld surface analysis, visualization and quantitative analysis of molecular crystals[J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 2021, 54(Pt 3): 1006-1011. |
| 39 | Frisch M, Trucks G, Schlegel H, et al. GAUSSIAN16. Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT, USA [Z]. 2016 |
| 40 | Stephens P J, Devlin F J, Chabalowski C F, et al. Ab initio calculation of vibrational absorption and circular dichroism spectra using density functional force fields[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1994, 98(45): 11623-11627. |
| 41 | Grimme S, Antony J, Ehrlich S, et al. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2010, 132(15): 154104. |
| 42 | Grimme S, Ehrlich S, Goerigk L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2011, 32(7): 1456-1465. |
| 43 | Hariharan P C, Pople J A. The influence of polarization functions on molecular orbital hydrogenation energies[J]. Theoretica Chimica Acta, 1973, 28(3): 213-222. |
| 44 | Hehre W J, Ditchfield R, Pople J A. Self-consistent molecular orbital methods. Ⅻ. Further extensions of Gaussian-type basis sets for use in molecular orbital studies of organic molecules[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1972, 56(5): 2257-2261. |
| 45 | Lu T, Chen F W. Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2012, 33(5): 580-592. |
| 46 | Zhang J, Lu T. Efficient evaluation of electrostatic potential with computerized optimized code[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics: PCCP, 2021, 23(36): 20323-20328. |
| 47 | Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics, 1996, 14(1): 33-38, 27-28. |
| 48 | Lu T, Chen F W. Atomic dipole moment corrected hirshfeld population method[J]. Journal of Theoretical and Computational Chemistry, 2012, 11(1): 163-183. |
| 49 | Chen Z S, Wang J Y, Hao M J, et al. Tuning excited state electronic structure and charge transport in covalent organic frameworks for enhanced photocatalytic performance[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 1106. |
| [1] | Wenchao JIANG, Zhaochao XU. Fluorescent dyes for super-resolution imaging of organelles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1333-1354. |
| [2] | Yuwei YANG, Min LI, Zhiying YAO, Qinlin SUN, Yang LIU, Dan GE, Bingbing SUN. Application and prospect of organoids-on-chip in the study of nano-drug delivery systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1209-1221. |
| [3] | Jin LI, Xiaodong ZHANG, Yangting QIU, Cheng YAO, Xicun LU, Ruwei WEI, Xiao LUO, Xuhong QIAN, Youjun YANG. Dibenzoxanthene dyes with functional handles (EC5) for bioimaging [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1687-1696. |
| [4] | Xiaoqing YAN, Ying ZHAO, Yuzhe ZHANG, Honghui OU, Qizhong HUANG, Huagui HU, Guidong YANG. Preparation of five-fold twinned copper nanowires@polypyrrole and their electrocatalytic conversion of nitrate to ammonia [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1519-1532. |
| [5] | Yuxiang CHEN, Chuanlei LIU, Zijun GONG, Qiyue ZHAO, Guanchu GUO, Hao JIANG, Hui SUN, Benxian SHEN. Machine learning-assisted solvent molecule design for efficient absorption of ethanethiol [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 914-923. |
| [6] | Yu CAO, Guohui ZHANG, Ang GAO, Xinyu DU, Jing ZHOU, Yongmao CAI, Xuan YU, Xiaoming YU. Research progress of two-dimensional MXene materials in solar cells and metal-ion batteries [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 412-428. |
| [7] | Yuhua YIN, Can FANG, Qingfeng YI, Guang LI. Impact of different carbon conductive agents on performance of iron-air battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 685-694. |
| [8] | Weiqi JIN, Yuerong WU, Xia WANG, Li LI, Su QIU, Pan YUAN, Minghe WANG. Progress in infrared imaging detection technology and domestic equipment for industrial gas leakage in chemical industry parks [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 32-44. |
| [9] | Chao HU, Yuming DONG, Wei ZHANG, Hongling ZHANG, Peng ZHOU, Hongbin XU. Preparation of high-concentration positive electrolyte of vanadium redox flow battery by activating vanadium pentoxide with highly concentrated sulfuric acid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 338-345. |
| [10] | Yuanchao LIU, Bin GUAN, Jianbin ZHONG, Yifan XU, Xuhao JIANG, Duan LI. Investigation of thermoelectric transport properties of single-layer XSe2 (X=Zr/Hf) [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3968-3978. |
| [11] | Jiaqi CHEN, Wanyu ZHAO, Ruichong YAO, Daolin HOU, Sheying DONG. Synthesis of pistachio shell-based carbon dots and their corrosion inhibition behavior on Q235 carbon steel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3446-3456. |
| [12] | Xudong YU, Qi LI, Niancu CHEN, Li DU, Siying REN, Ying ZENG. Phase equilibria and calculation of aqueous ternary system KCl + CaCl2 + H2O at 298.2, 323.2, and 348.2 K [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3256-3265. |
| [13] | Yaxin CHEN, Hang YUAN, Guanzhang LIU, Lei MAO, Chun YANG, Ruifang ZHANG, Guangya ZHANG. Advances in enzyme self-immobilization mediated by protein nanocages [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [14] | Meibo XING, Zhongtian ZHANG, Dongliang JING, Hongfa ZHANG. Enhanced phase change energy storage/release properties by combining porous materials and water-based carbon nanotube under magnetic regulation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3093-3102. |
| [15] | Jiali GE, Tuxiang GUAN, Xinmin QIU, Jian WU, Liming SHEN, Ningzhong BAO. Synthesis of FeF3 nanoparticles covered by vertical porous carbon for high performance Li-ion battery cathode [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3058-3067. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||