CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (3): 914-923.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231370
• Process system engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yuxiang CHEN1( ), Chuanlei LIU1, Zijun GONG2, Qiyue ZHAO1, Guanchu GUO1, Hao JIANG1, Hui SUN1,3,4(
), Chuanlei LIU1, Zijun GONG2, Qiyue ZHAO1, Guanchu GUO1, Hao JIANG1, Hui SUN1,3,4( ), Benxian SHEN1
), Benxian SHEN1
Received:2023-12-25
Revised:2024-02-06
Online:2024-05-11
Published:2024-03-25
Contact:
Hui SUN
陈宇翔1( ), 刘传磊1, 龚子君2, 赵起越1, 郭冠初1, 姜豪1, 孙辉1,3,4(
), 刘传磊1, 龚子君2, 赵起越1, 郭冠初1, 姜豪1, 孙辉1,3,4( ), 沈本贤1
), 沈本贤1
通讯作者:
孙辉
作者简介:陈宇翔(1996—),男,博士研究生,chenyuxiang0425@gmail.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yuxiang CHEN, Chuanlei LIU, Zijun GONG, Qiyue ZHAO, Guanchu GUO, Hao JIANG, Hui SUN, Benxian SHEN. Machine learning-assisted solvent molecule design for efficient absorption of ethanethiol[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 914-923.
陈宇翔, 刘传磊, 龚子君, 赵起越, 郭冠初, 姜豪, 孙辉, 沈本贤. 机器学习辅助乙硫醇高效吸收溶剂分子设计[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 914-923.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 原料 | 含量 | 生产厂家 |
|---|---|---|
| 3-乙氧基丙胺 | 99.0% | 北京华威锐科化工有限公司 |
| 3-丁氧基丙胺 | 98.0% | 上海恩拿马生物科技有限公司 |
| 3-二乙胺基丙胺 | 99.0% | 上海迈瑞尔生化科技有限公司 |
| 1,4-二甲基哌嗪 | 98.0% | 上海迈瑞尔生化科技有限公司 |
| 环丁砜 | 99.7% | 上海新铂化学技术有限公司 |
| 混合气 | 上海伟创标准气体有限公司 | |
| 乙硫醇 | 5578.2 mg/m3(标准工况) | |
| 氮气 | 余量 |
Table 1 Raw materials used for equilibrium solubility determination experiment
| 原料 | 含量 | 生产厂家 |
|---|---|---|
| 3-乙氧基丙胺 | 99.0% | 北京华威锐科化工有限公司 |
| 3-丁氧基丙胺 | 98.0% | 上海恩拿马生物科技有限公司 |
| 3-二乙胺基丙胺 | 99.0% | 上海迈瑞尔生化科技有限公司 |
| 1,4-二甲基哌嗪 | 98.0% | 上海迈瑞尔生化科技有限公司 |
| 环丁砜 | 99.7% | 上海新铂化学技术有限公司 |
| 混合气 | 上海伟创标准气体有限公司 | |
| 乙硫醇 | 5578.2 mg/m3(标准工况) | |
| 氮气 | 余量 |
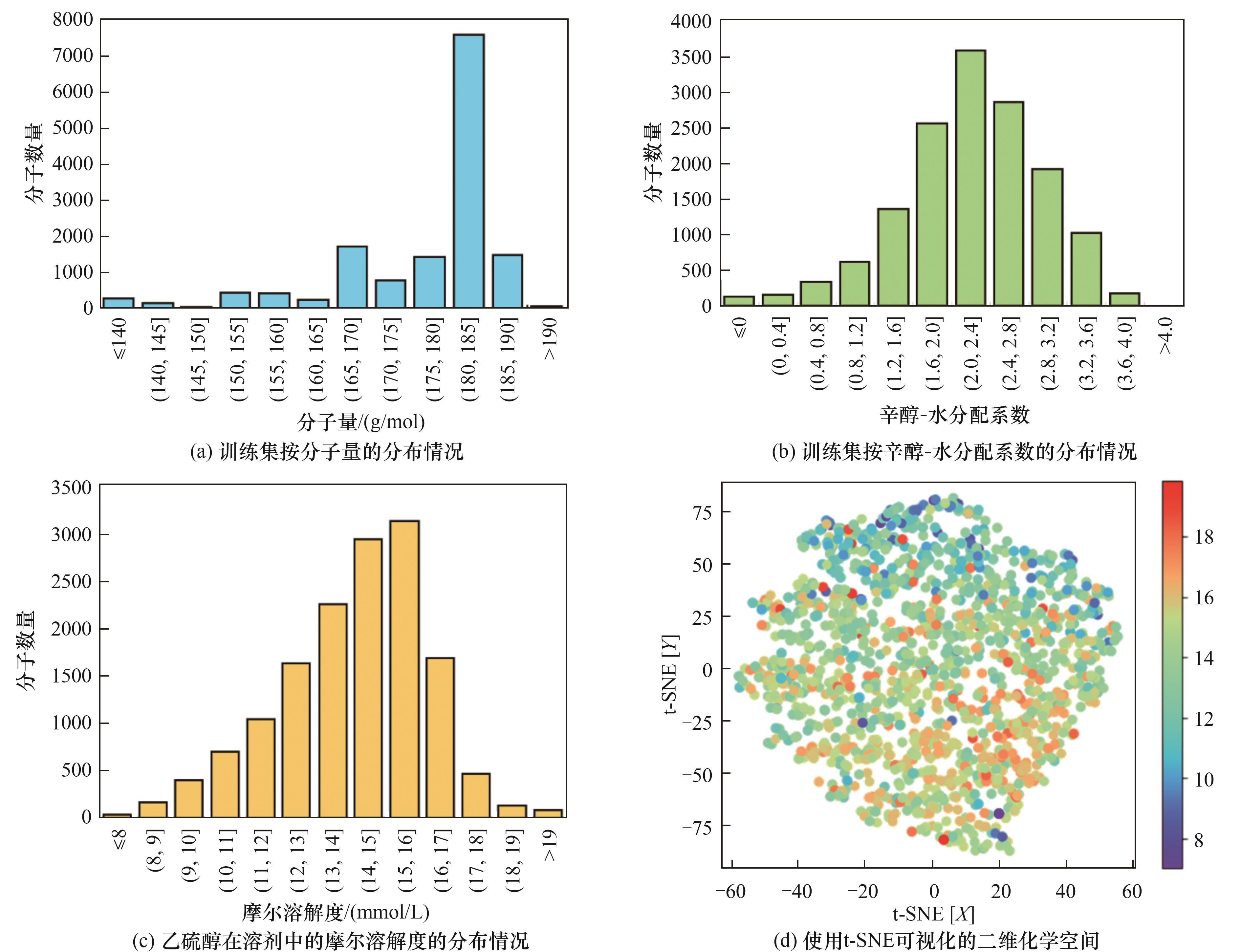
Fig.2 Distribution of molecular weight, octanol-water partition coefficient, and molar solubility of ethanethiol in the initial training set, and the two-dimensional chemical space of the initial training set
| 算法 | 超参数 | 搜索空间 | 优化后的参数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLR | default | — | default |
| RR | alpha | logspace(-5,3,20) | 0.16 |
| LR | alpha | logspace(-5,3,20) | 0.12 |
| KNN | n_neighbors | [ | 8 |
| DT | max_depth | [ | 100 |
| RF | max_depth | [ | 100 |
| max_features | [sqrt, log2, none] | sqrt | |
| n_estimators | [ | 10000 | |
| XGBoost | learning_rate | [0.001,0.01,0.1,1,10] | 0.01 |
| max_depth | [ | 100 | |
| n_estimators | [ | 10000 |
Table 2 Hyperparameter of different algorithms
| 算法 | 超参数 | 搜索空间 | 优化后的参数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLR | default | — | default |
| RR | alpha | logspace(-5,3,20) | 0.16 |
| LR | alpha | logspace(-5,3,20) | 0.12 |
| KNN | n_neighbors | [ | 8 |
| DT | max_depth | [ | 100 |
| RF | max_depth | [ | 100 |
| max_features | [sqrt, log2, none] | sqrt | |
| n_estimators | [ | 10000 | |
| XGBoost | learning_rate | [0.001,0.01,0.1,1,10] | 0.01 |
| max_depth | [ | 100 | |
| n_estimators | [ | 10000 |
| 算法 | RMSE | MAE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLR | 0.66 | 0.65 | 1.23 | 0.87 |
| RR | 0.66 | 0.65 | 1.24 | 0.87 |
| LR | 0.64 | 0.63 | 1.27 | 0.90 |
| KNN | 0.57 | 0.36 | 1.67 | 1.25 |
| DT | 0.75 | 0.48 | 1.50 | 1.04 |
| RF | 0.95 | 0.65 | 1.23 | 0.86 |
| XGBoost | 0.98 | 0.66 | 1.22 | 0.84 |
Table 3 Metrics of ethanethiol solubility prediction model using different algorithms
| 算法 | RMSE | MAE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLR | 0.66 | 0.65 | 1.23 | 0.87 |
| RR | 0.66 | 0.65 | 1.24 | 0.87 |
| LR | 0.64 | 0.63 | 1.27 | 0.90 |
| KNN | 0.57 | 0.36 | 1.67 | 1.25 |
| DT | 0.75 | 0.48 | 1.50 | 1.04 |
| RF | 0.95 | 0.65 | 1.23 | 0.86 |
| XGBoost | 0.98 | 0.66 | 1.22 | 0.84 |
| 分子结构 | 分子名称 | CAS号 | 沸点/℃ | 熔点/℃ | 水溶性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
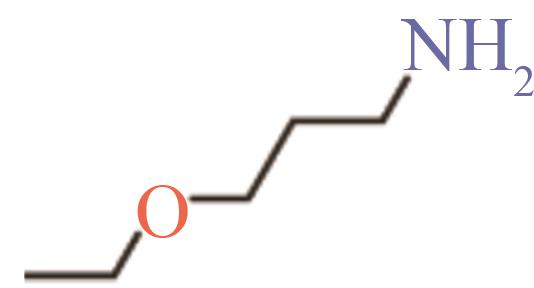 | 3-乙氧基丙胺 | 6291-85-6 | 136~138 | -24 | 可溶 |
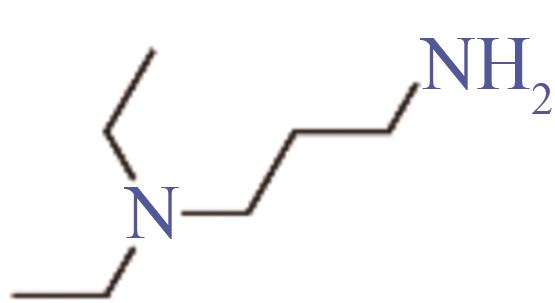 | 3-二乙胺基丙胺 | 104-78-9 | 168~171 | -60 | 可溶 |
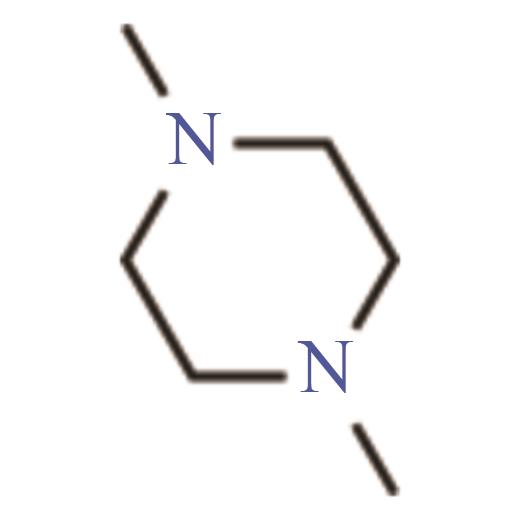 | 1,4-二甲基哌嗪 | 106-58-1 | 131~132 | -1 | 可溶 |
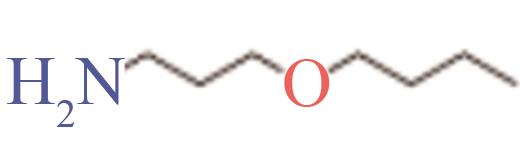 | 3-丁氧基丙胺 | 16499-88-0 | 169~170 | -65 | 可溶 |
Table 4 Properties of the four selected molecules
| 分子结构 | 分子名称 | CAS号 | 沸点/℃ | 熔点/℃ | 水溶性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 3-乙氧基丙胺 | 6291-85-6 | 136~138 | -24 | 可溶 |
 | 3-二乙胺基丙胺 | 104-78-9 | 168~171 | -60 | 可溶 |
 | 1,4-二甲基哌嗪 | 106-58-1 | 131~132 | -1 | 可溶 |
 | 3-丁氧基丙胺 | 16499-88-0 | 169~170 | -65 | 可溶 |
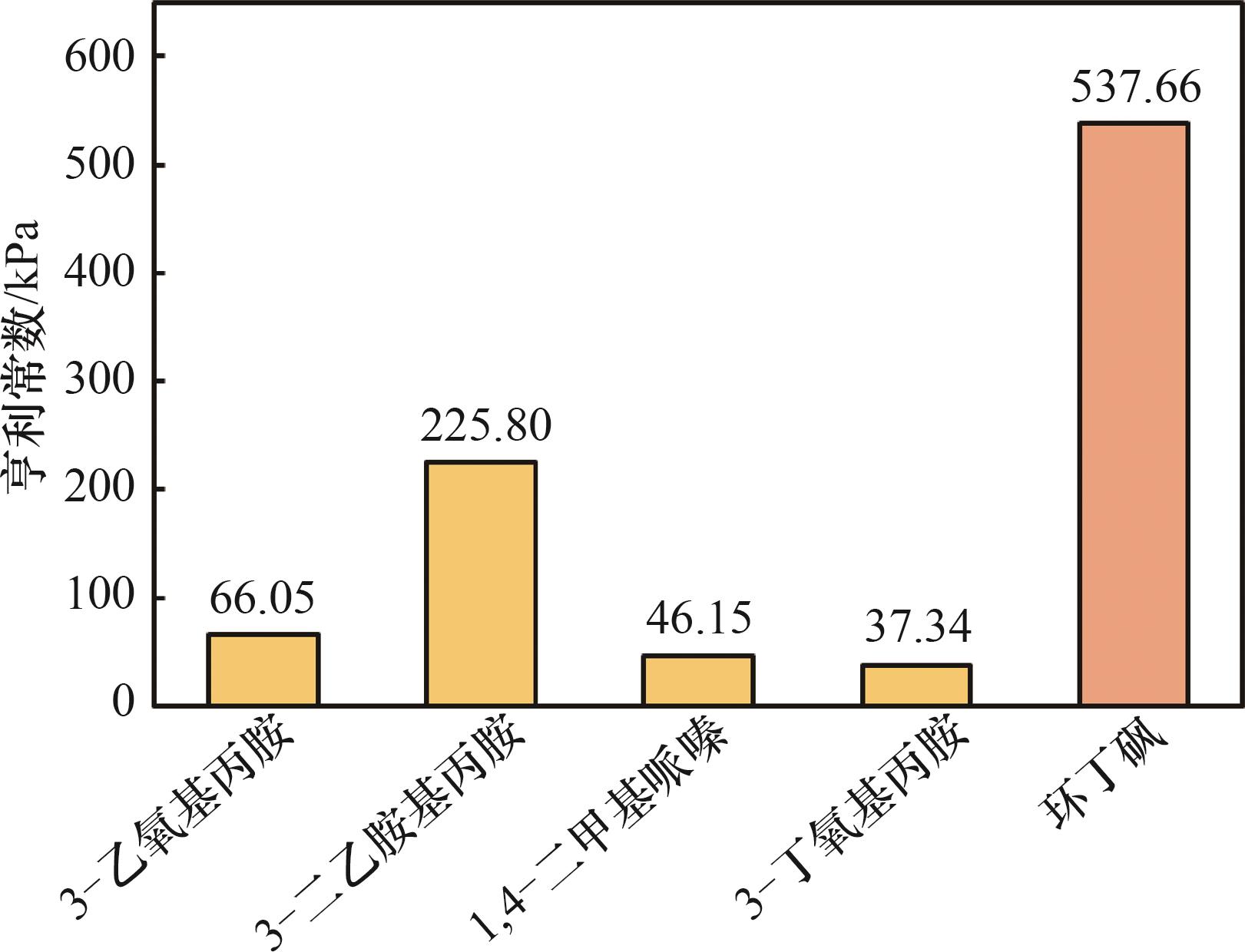
Fig. 6 The experimental Henry’s constants of ethanethiol in 3-ethoxypropylamine, 3-diethylaminopropylamine, 1,4-dimethylpiperazine, 3-butoxypropylamine and sulfolane at 40℃
| 1 | 中国石油国家高端智库研究中心. 中国天然气发展报告(2023) [M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2023. |
| PetroChina National Research Center for High-End Think Tank. China Natural Gas Development Report (2023) [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2023. | |
| 2 | de Angelis A. Natural gas removal of hydrogen sulphide and mercaptans[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2012, 113/114: 37-42. |
| 3 | Iliuta M C, Larachi F. Solubility of total reduced sulfurs (hydrogen sulfide, methyl mercaptan, dimethyl sulfide, and dimethyl disulfide) in liquids[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2007, 52(1): 2-19. |
| 4 | Petit C, Mendoza B, Bandosz T J. Hydrogen sulfide adsorption on MOFs and MOF/graphite oxide composites[J]. Chemphyschem: a European Journal of Chemical Physics and Physical Chemistry, 2010, 11(17): 3678-3684. |
| 5 | Nemestóthy N, Bakonyi P, Lajtai-Szabó P, et al. The impact of various natural gas contaminant exposures on CO2/CH4 separation by a polyimide membrane[J]. Membranes, 2020, 10(11): 324. |
| 6 | Gągol M, Soltani R D C, Przyjazny A, et al. Effective degradation of sulfide ions and organic sulfides in cavitation-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs)[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2019, 58: 104610. |
| 7 | Aghel B, Janati S, Wongwises S, et al. Review on CO2 capture by blended amine solutions[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2022, 119: 103715. |
| 8 | 陈颖, 杨鹤, 梁宏宝, 等. 天然气脱硫脱碳方法的研究进展[J]. 石油化工, 2011, 40: 565-570. |
| Chen Y, Yang H, Liang H B, et al. Advances in research of decarbonization and desulfurization for natural gas[J]. Petrochemical Technology, 2011, 40: 565-570. | |
| 9 | Al-Baghli N A, Pruess S A, Yesavage V F, et al. A rate-based model for the design of gas absorbers for the removal of CO2 and H2S using aqueous solutions of MEA and DEA[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 2001, 185(1/2): 31-43. |
| 10 | 王开岳. 天然气脱硫脱碳工艺发展进程的回顾: 甲基二乙醇胺现居一支独秀地位[J]. 天然气与石油, 2011, 29(1): 15-21. |
| Wang K Y. Review on development process of gas desulfurization and decarburization technique—methyldiethanolamine (MDEA for short) outshines others[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2011, 29(1): 15-21. | |
| 11 | 王开岳. 天然气净化工艺: 脱硫脱碳、脱水、硫黄回收及尾气处理[M]. 2版. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2015. |
| Wang K Y. Natural Gas Purification Process: Desulfurization and Decarbonization, Dehydration, Sulfur Recovery and Tail Gas Treatment[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2015. | |
| 12 | Hochgesand G. Rectisol and purisol[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 1970, 62(7): 37-43. |
| 13 | Murrieta-Guevara F, Rebolledo-Libreros E, Trejo A. Gas solubility of hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide in mixtures of sulfolane with diethanolamine at different temperatures[J]. Fluid Phase Equilibria, 1994, 95: 163-174. |
| 14 | Bucklin R W, Schendel R. Comparison of fluor solvent and selexol processes[J]. Energy Progress, 1984, 4: 137-142. |
| 15 | Luo Q L, Feng B, Liu Z H, et al. Experimental study on simultaneous absorption and desorption of CO2, SO2, and NO x using aqueous N-methyldiethanolamine and dimethyl sulfoxide solutions[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32(3): 3647-3659. |
| 16 | Orlov A A, Marcou G, Horvath D, et al. Computer-aided design of new physical solvents for hydrogen sulfide absorption[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(23): 8588-8596. |
| 17 | Shokouhi M, Farahani H, Vahidi M, et al. Experimental solubility of carbonyl sulfide in sulfolane and γ-butyrolactone[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2017, 62(10): 3401-3408. |
| 18 | Abduesslam M, Kayi H K. Capture of carbonyl sulfide by organic liquid mixtures: a systematic DFT investigation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2021, 60(3): 1366-1374. |
| 19 | Rivera-Tinoco R, Bouallou C. Reaction kinetics of carbonyl sulfide (COS) with diethanolamine in methanolic solutions[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008, 47(19): 7375-7380. |
| 20 | Fisher R A. Design of experiments[J]. BMJ, 1936, 1(3923): 554. |
| 21 | 于惠波, 沈本贤, 孙辉, 等. 改性UDS溶剂提高天然气中甲硫醇脱除效率的研究[J]. 石油炼制与化工, 2017, 48: 28-33. |
| Yu H B, Shen B X, Sun H, et al. Study of improving MeSH removal efficiency by modified UDS solvent from natural gas[J]. Petroleum Processing and Petrochemicals, 2017, 48: 28-33. | |
| 22 | 段思慧. 脱硫醇吸收剂的量化计算及溶解机理研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2020. |
| Duan S H. Study on quantitative calculation and dissolution mechanism of desulfurized alcohol absorbent[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2020. | |
| 23 | Francoeur P G, Koes D R. SolTranNet—a machine learning tool for fast aqueous solubility prediction[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2021, 61(6): 2530-2536. |
| 24 | Chen Y X, Liu C L, Guo G C, et al. Machine-learning-guided reaction kinetics prediction towards solvent identification for chemical absorption of carbonyl sulfide[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 444: 136662. |
| 25 | Boobier S, Liu Y F, Sharma K, et al. Predicting solvent-dependent nucleophilicity parameter with a causal structure property relationship[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2021, 61(10): 4890-4899. |
| 26 | Maskeri M A, Fernandes A J, Di Mauro G, et al. Taming keteniminium reactivity by steering reaction pathways: computational predictions and experimental validations[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2022, 144(51): 23358-23367. |
| 27 | LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521: 436-444. |
| 28 | 王彦旭. 基于机器学习的低共熔溶剂的物性预测及其在CO2吸收中的应用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2023. |
| Wang Y X. Physical property prediction of deep eutectic solvents based on machine learning and its application in CO2 absorption[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2023. | |
| 29 | Blum L C, Reymond J L. 970 million druglike small molecules for virtual screening in the chemical universe database GDB-13[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(25): 8732-8733. |
| 30 | Tropsha A. Best practices for QSAR model development, validation, and exploitation[J]. Molecular Informatics, 2010, 29(6/7): 476-488. |
| 31 | Boobier S, Hose D R J, Blacker A J, et al. Machine learning with physicochemical relationships: solubility prediction in organic solvents and water[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 5753. |
| 32 | Sorkun M C, Khetan A, Er S. AqSolDB, a curated reference set of aqueous solubility and 2D descriptors for a diverse set of compounds[J]. Scientific Data, 2019, 6: 143. |
| 33 | Moriwaki H, Tian Y S, Kawashita N, et al. Mordred: a molecular descriptor calculator[J]. Journal of Cheminformatics, 2018, 10(1): 4. |
| 34 | Liu C L, Chen Y X, Jiang H, et al. Revealing the structure-interaction-dissolubility relationships through computational investigation coupled with solubility measurement: toward solvent design for organosulfide capture[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(20): 7183-7192. |
| 35 | Tomasulo P. ChemIDplus—super source for chemical and drug information[J]. Medical Reference Services Quarterly, 2002, 21(1): 53-59. |
| 36 | Wang J M, Krudy G, Hou T J, et al. Development of reliable aqueous solubility models and their application in druglike analysis[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2007, 47(4): 1395-1404. |
| 37 | Sayers E W, Bolton E E, Brister J R, et al. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2022, 50(D1): D20-D26. |
| [1] | Yujiao ZENG, Xin XIAO, Gang YANG, Yibo ZHANG, Guangming ZHENG, Fang LI, Fengling WANG. Surrogate modeling and optimization of wet phosphoric acid production process based on mechanism and data hybrid driven [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 936-944. |
| [2] | Wenjun LI, Zhongyang ZHAO, Zhen NI, Can ZHOU, Chenghang ZHENG, Xiang GAO. CFD numerical simulation of wet flue gas desulfurization:performance improvement based on gas-liquid mass transfer enhancement [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 505-519. |
| [3] | Congqi HUANG, Yimei WU, Jianye CHEN, Shuangquan SHAO. Simulation study of thermal management system of alkaline water electrolysis device for hydrogen production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| [4] | Chao HU, Yuming DONG, Wei ZHANG, Hongling ZHANG, Peng ZHOU, Hongbin XU. Preparation of high-concentration positive electrolyte of vanadium redox flow battery by activating vanadium pentoxide with highly concentrated sulfuric acid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 338-345. |
| [5] | Zhenghao JIN, Lijie FENG, Shuhong LI. Energy and exergy analysis of a solution cross-type absorption-resorption heat pump using NH3/H2O as working fluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [6] | Zehao MI, Er HUA. DFT and COSMO-RS theoretical analysis of SO2 absorption by polyamines type ionic liquids [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3681-3696. |
| [7] | Xudong YU, Qi LI, Niancu CHEN, Li DU, Siying REN, Ying ZENG. Phase equilibria and calculation of aqueous ternary system KCl + CaCl2 + H2O at 298.2, 323.2, and 348.2 K [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3256-3265. |
| [8] | Ruihang ZHANG, Pan CAO, Feng YANG, Kun LI, Peng XIAO, Chun DENG, Bei LIU, Changyu SUN, Guangjin CHEN. Analysis of key parameters affecting product purity of natural gas ethane recovery process via ZIF-8 nanofluid [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [9] | Xingzhi HU, Haoyan ZHANG, Jingkun ZHUANG, Yuqing FAN, Kaiyin ZHANG, Jun XIANG. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of carbon nanofibers embedded with ultra-small CeO2 nanoparticles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [10] | Xinyue WANG, Junjie WANG, Sixian CAO, Cui WANG, Lingkun LI, Hongyu WU, Jing HAN, Hao WU. Effect of glass primary container surface modification on monoclonal antibody aggregates induced by mechanical stress [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2580-2588. |
| [11] | Lei WANG, Lei WANG, Yunlong BAI, Liuliu HE. Preparation of SA lithium ion sieve membrane and its adsorptive properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2046-2056. |
| [12] | Ke CHEN, Li DU, Ying ZENG, Siying REN, Xudong YU. Phase equilibria and calculation of quaternary system LiCl+MgCl2+CaCl2+H2O at 323.2 K [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1896-1903. |
| [13] | Shanghao LIU, Shengkun JIA, Yiqing LUO, Xigang YUAN. Optimization of ternary-distillation sequence based on gradient boosting decision tree [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2075-2087. |
| [14] | Can YANG, Xueqi SUN, Minghua SHANG, Jian ZHANG, Xiangping ZHANG, Shaojuan ZENG. Research status and prospect of CO2 absorption and separation by phase-change ionic liquid systems [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1419-1432. |
| [15] | Mujin LI, Song HU, Depan SHI, Peng ZHAO, Rui GAO, Jinlong LI. A process for offgas absorption and purification of 1,2-butylene oxide [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1607-1618. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||