CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (11): 3835-3856.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241241
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Cheng ZHANG1,2( ), Xue LI1(
), Xue LI1( ), Mao YE1(
), Mao YE1( ), Zhongmin LIU1
), Zhongmin LIU1
Received:2024-11-01
Revised:2024-11-10
Online:2024-12-26
Published:2024-11-25
Contact:
Xue LI, Mao YE
通讯作者:
李雪,叶茂
作者简介:张橙(1996—),女,博士研究生,chengzhang@dicp.ac.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Cheng ZHANG, Xue LI, Mao YE, Zhongmin LIU. Application of physics-informed neural network in two-phase flow[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 3835-3856.
张橙, 李雪, 叶茂, 刘中民. 物理信息神经网络在两相流中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(11): 3835-3856.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
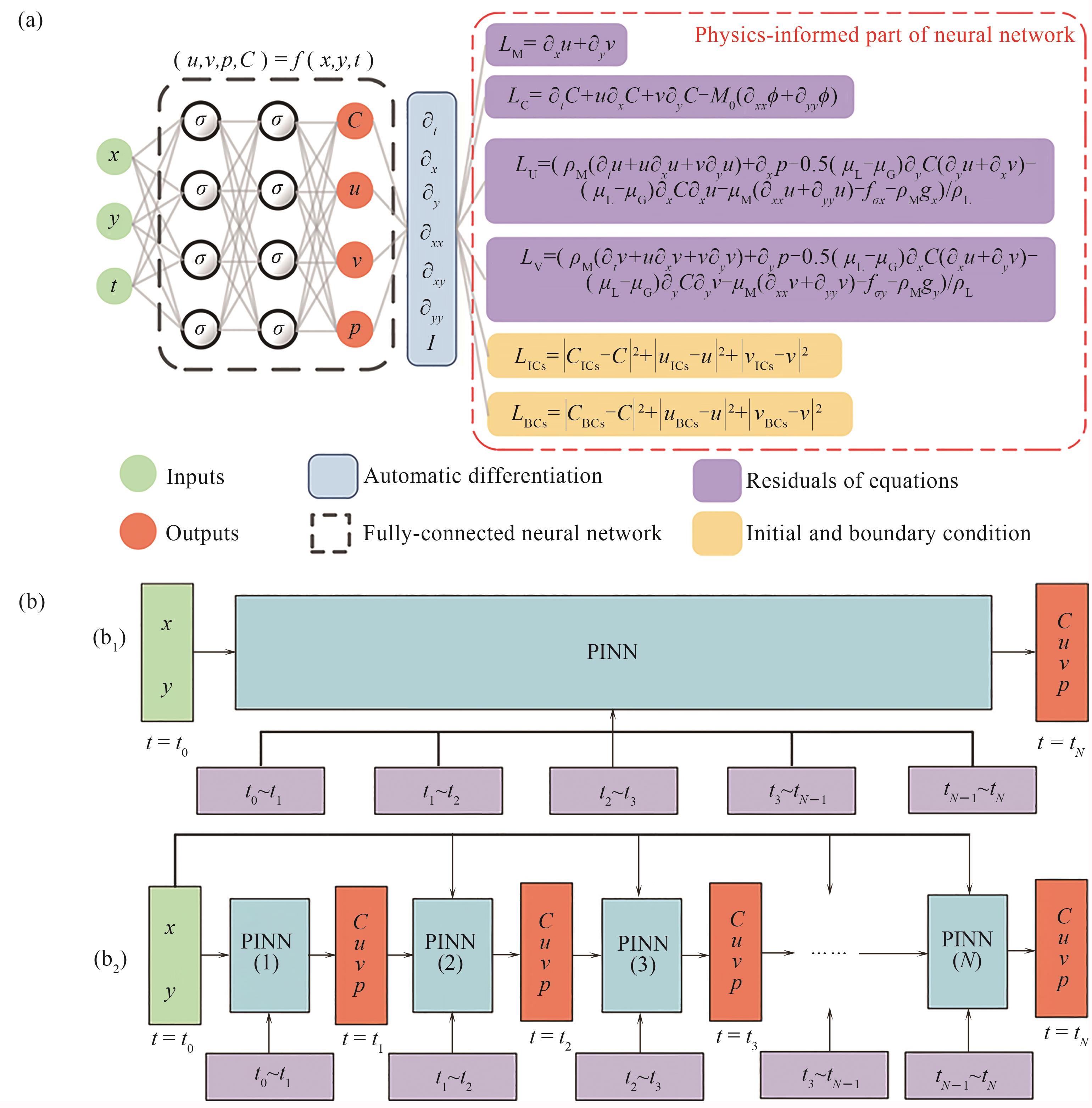
Fig.2 (a) Illustration of physics-informed neural network for the phase-field method; (b) Different time marching strategies of physics-informed neural networks for the phase-field method: (b1) single network training in the whole time domain, (b2) multiple-networks training in various time sequences[64]
| 界面演化方程 | 显式形式 | 损失函数 |
|---|---|---|
| 普通形式 | ||
| 深度混合残差形式 |
Table 1 Differences between a normal neural network and a deep mixed residual method network in interface evolution equation[67]
| 界面演化方程 | 显式形式 | 损失函数 |
|---|---|---|
| 普通形式 | ||
| 深度混合残差形式 |

Fig.5 (a) Predicted results of phase-field variable C at a reverse single vortex based on physics-informed neural network for the phase-field method: (a1) t=0 s, (a2) t=0.5 s, (a3) t=1.0 s, (a4) t=1.5 s, (a5) t=2.0 s; (b) At bubble-rising problem: temporal evolution of bubble center of mass (b1) and rising velocity (b2) (the red solid lines correspond to the present result, while the blue dashed lines correspond to the reference result obtained from Aland and Voigt)[64]

Fig.6 (a) Computational domain and initial condition of RT instability; (b) Comparison of evolution of volume fraction of RT instability : (b1) results from modified PF-PINNs, (b2) results from reference[67]
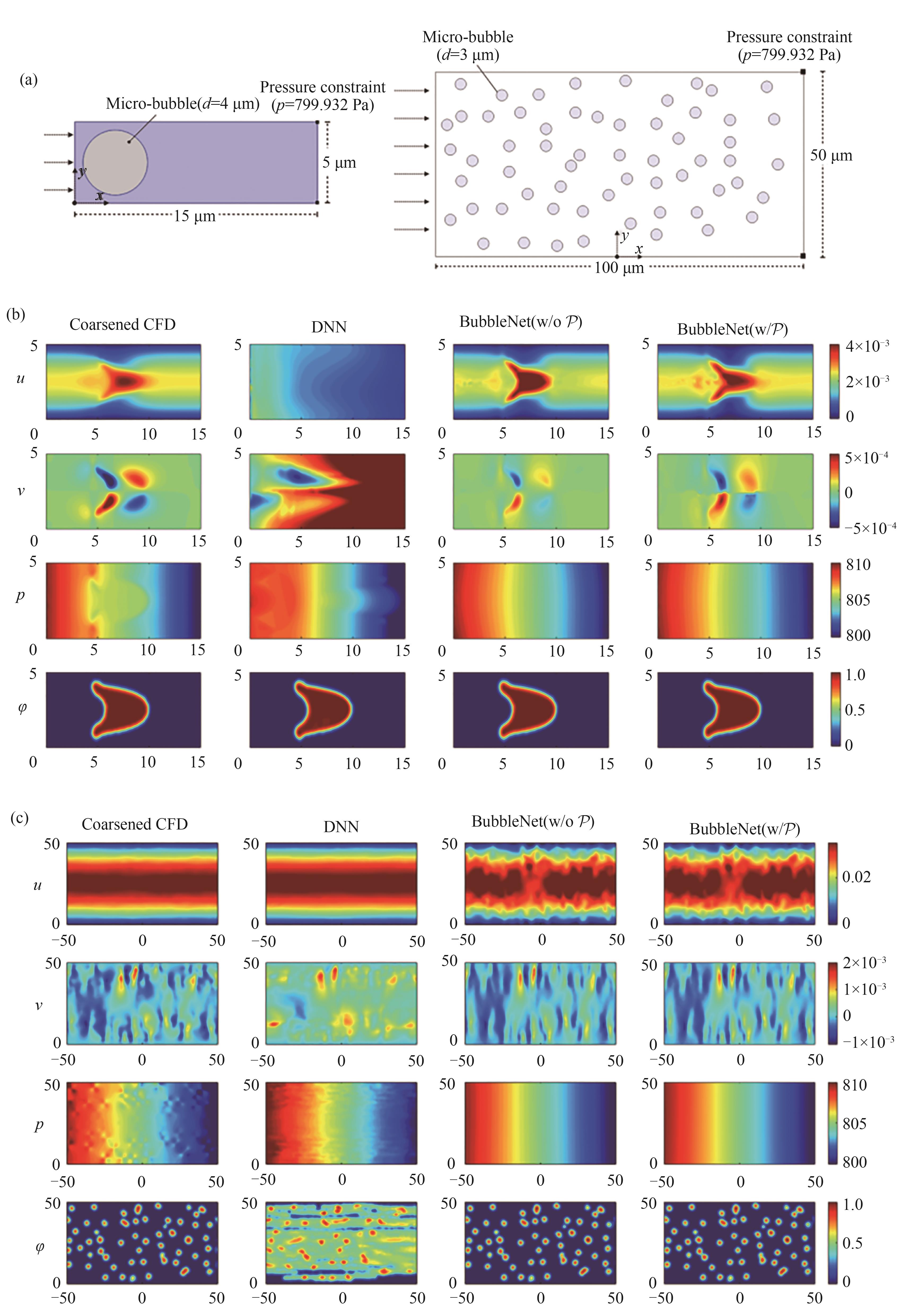
Fig.7 (a) Computational domain and initial condition of single bubble flow case and multiple bubble flow case; (b) At single flow case: comparison of physical quantity u, v, p, φ between CFD, DNN, BubbleNet (without Poisson equation) and BubbleNet (with Poisson equation); (c) At multiple bubble flow case: comparison of physical quantity u, v, p, φ between CFD, DNN, BubbleNet (without Poisson equation) and BubbleNet (with Poisson equation)[69]

Fig.8 (a) Initial condition of one-dimensional computational domain; (b) Initial condition of two-dimensional computational domain; (c) Evolution of collocation points with new adaptivity (from left to right represent different governing equations and new collocation points after each adaptation step are shown in red)[58]

Fig.9 (a) An illustration of the reservoir model with injector, producer and boundary conditions; (b) The permeability field for the heterogeneous test case; (c) The pressure (c1) and water saturation fields (c2) at the end of simulation for the heterogeneous test case; (d) The change of well-block and bottom-hole pressures of the producer obtained by PICNN for the heterogeneous reservoir, compared to reference solution by the conventional FV approach[68]

Fig.10 (a) Physics-informed neural network with observed values for prediction of pressure, gas saturation and water production;A comparison between the ground truth and predicted value together with the corresponding relative error for (b) gas saturation and (c) pressure field: multi-output data-driven model (top), physics-informed model without interpolated points (middle) and physics-informed model with interpolated points (bottom)[71]
| 场 | 产水率 | 压力 | 气体饱和度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| STT | 1.05 | 0.13 | |
| MTT | |||
| PI w/o interp | |||
| PI with interp |
Table 2 Recorded MSE values (original un-normalized scale) for STT (single-output training), MTT (multi-output training), PI w/o interp(physics-informed without interpolated points), PI with interp(physics-informed with interpolated points) for water production rate, pressure field and gas saturation field[71]
| 场 | 产水率 | 压力 | 气体饱和度 |
|---|---|---|---|
| STT | 1.05 | 0.13 | |
| MTT | |||
| PI w/o interp | |||
| PI with interp |

Fig.12 (a) PINN predicted average normalized water flux for transient spontaneous imbibition; (b) PINN predicted capillary dimensionless group for transient spontaneous imbibition; (c) Absolute difference in average normalized water flux between PINN and FD results for transient spontaneous imbibition; (d) Absolute difference in capillary dimensionless group between PINN and FD results for transient spontaneous imbibition [73]

Fig.13 Schematic diagram of training the PINN system for solving two-phase steady state flow with capillary heterogeneity at various flow conditions[74]

Fig.14 1D saturation profiles of the actual core-flooding experiment (red crosses) and PINNs predictions (dotted black lines) at fractional flows of 0.50 (a), 0.80 (b), 0.90 (c), and 0.95 (d)[74]

Fig.15 Configuration and training strategy of the PINN algorithm for heat transfer in two-phase flow: (a) network architecture; (b) training strategy[75]
| 1 | Dillard L A, Essaid H I, Herkelrath W N. Multiphase flow modeling of a crude-oil spill site with a bimodal permeability distribution[J]. Water Resources Research, 1997, 33(7): 1617-1632. |
| 2 | Gerritsen M G, Durlofsky L J. Modeling fluid flow in oil reservoirs[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2005, 37(1): 211-238. |
| 3 | Ferdian E, Marlevi D, Schollenberger J, et al. Cerebrovascular super-resolution 4D Flow MRI-sequential combination of resolution enhancement by deep learning and physics-informed image processing to non-invasively quantify intracranial velocity, flow, and relative pressure[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2023, 88: 102831. |
| 4 | Magnaudet J, Mercier M J. Particles, drops, and bubbles moving across sharp interfaces and stratified layers[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2020, 52: 61-91. |
| 5 | Hirt C W, Nichols B D. Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1981, 39(1): 201-225. |
| 6 | Chen L Q. Phase-field models for microstructure evolution[J]. Annual Review of Materials Research, 2002, 32: 113-140. |
| 7 | Karniadakis G E, Kevrekidis I G, Lu L, et al. Physics-informed machine learning[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2021, 3: 422-440. |
| 8 | Moreno Z, Paster A. Prediction of pollutant remediation in a heterogeneous aquifer in Israel: reducing uncertainty by incorporating lithological, head and concentration data[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 564: 651-666. |
| 9 | Moreno Z. Fine-scale heterogeneous structure impact on the scale-dependency of the effective hydro-electrical relations of unsaturated soils[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2022, 162: 104156. |
| 10 | Moreno Z, Rabinovich A. Evaluating numerical simulation errors of CO2-brine flow with capillary heterogeneity using a 1D semi-analytical solution[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2021, 110: 103416. |
| 11 | Brunton S L, Noack B R, Koumoutsakos P. Machine learning for fluid mechanics[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2020, 52: 477-508. |
| 12 | Chang C W, Dinh N T. Classification of machine learning frameworks for data-driven thermal fluid models[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2019, 135: 559-579. |
| 13 | Yan B C, Chen B L, Robert Harp D, et al. A robust deep learning workflow to predict multiphase flow behavior during geological CO2 sequestration injection and Post-Injection periods[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 607: 127542. |
| 14 | Zhang K, Zuo Y D, Zhao H J, et al. Fourier neural operator for solving subsurface oil/water two-phase flow partial differential equation[J]. SPE Journal, 2022, 27(3): 1815-1830. |
| 15 | Montañez-Barrera J A, Barroso-Maldonado J M, Bedoya-Santacruz A F, et al. Correlated-informed neural networks: a new machine learning framework to predict pressure drop in micro-channels[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 194: 123017. |
| 16 | Li W, Bazant M Z, Zhu J E. Phase-Field DeepONet: physics-informed deep operator neural network for fast simulations of pattern formation governed by gradient flows of free-energy functionals[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 416: 116299. |
| 17 | Zhao X G, Shirvan K, Salko R K, et al. On the prediction of critical heat flux using a physics-informed machine learning-aided framework[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2020, 164: 114540. |
| 18 | Seyed-Ahmadi A, Wachs A. Physics-inspired architecture for neural network modeling of forces and torques in particle-laden flows[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2022, 238: 105379. |
| 19 | Quintino A M, Da Rocha D L L N, Fonseca Junior R, et al. Flow pattern transition in pipes using data-driven and physics-informed machine learning. Journal of Fluids Engineering-Transactions of the Asme. 2021;143(3): 031401. |
| 20 | Wu Y Q, Sun S Y. Removing the performance bottleneck of pressure-temperature flash calculations during both the online and offline stages by using physics-informed neural networks[J]. 2023, 35(4): 043326. |
| 21 | Cheng Z H, Wachs A. Physics-informed neural network for modeling force and torque fluctuations in a random array of bidisperse spheres[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2023, 169: 104603. |
| 22 | Dang Z R, Ishii M. Towards stochastic modeling for two-phase flow interfacial area predictions: a physics-informed reinforcement learning approach[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 192: 122919. |
| 23 | Sirovich L. Turbulence and the dynamics of coherent structures (Ⅰ): Coherent structures[J]. Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 1987, 45(3): 561-571. |
| 24 | Sirovich L, Kirby M. Low-dimensional procedure for the characterization of human faces[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1987, 4(3): 519-524. |
| 25 | Kaiser E, Noack B R, Cordier L, et al. Cluster-based reduced-order modelling of a mixing layer[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2014, 754: 365-414. |
| 26 | Colabrese S, Gustavsson K, Celani A, et al. Smart inertial particles[J]. Physical Review Fluids, 2018, 3(8): 084301. |
| 27 | Manohar K, Brunton B W, Kutz J N, et al. Data-driven sparse sensor placement for reconstruction: demonstrating the benefits of exploiting known patterns[J]. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2018, 38(3): 63-86. |
| 28 | Halko N, Martinsson P G, Tropp J A. Finding structure with randomness: probabilistic algorithms for constructing approximate matrix decompositions[J]. SIAM Review, 2011, 53(2): 217-288. |
| 29 | Dong C, Loy C C, He K M, et al. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[M]//Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2014: 184-199. |
| 30 | Lee Y, Yang H, Yin Z P. PIV-DCNN: cascaded deep convolutional neural networks for particle image velocimetry[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2017, 58(12): 171. |
| 31 | Xie Y, Franz E, Chu M Y, et al. tempoGAN: a temporally coherent, volumetric GAN for super-resolution fluid flow[EB/OL]. 2018: 1801.09710. |
| 32 | Mezić I. Analysis of fluid flows via spectral properties of the koopman operator[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2013, 45: 357-378. |
| 33 | Schmid P J. Dynamic mode decomposition of numerical and experimental data[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2010, 656: 5-28. |
| 34 | Raissi M, Karniadakis G E. Hidden physics models: machine learning of nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2018, 357: 125-141. |
| 35 | Schmidt M, Lipson H. Distilling free-form natural laws from experimental data[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5923): 81-85. |
| 36 | Ling J L, Jones R, Templeton J. Machine learning strategies for systems with invariance properties[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2016, 318: 22-35. |
| 37 | Ling J L, Kurzawski A, Templeton J. Reynolds averaged turbulence modelling using deep neural networks with embedded invariance[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2016, 807: 155-166. |
| 38 | Raissi M, Wang Z C, Triantafyllou M S, et al. Deep learning of vortex-induced vibrations[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 861: 119-137. |
| 39 | Raissi M, Perdikaris P, Karniadakis G E. Physics-informed neural networks: a deep learning framework for solving forward and inverse problems involving nonlinear partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2019, 378: 686-707. |
| 40 | Huang Y, Zhang Z Y, Zhang X. A direct-forcing immersed boundary method for incompressible flows based on physics-informed neural network[J]. Fluids, 2022, 7(2): 56. |
| 41 | Shukla K, Jagtap A D, Karniadakis G E. Parallel physics-informed neural networks via domain decomposition[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 447: 110683. |
| 42 | Raissi M, Yazdani A, Karniadakis G E. Hidden fluid mechanics: learning velocity and pressure fields from flow visualizations[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6481): 1026-1030. |
| 43 | Bararnia H, Esmaeilpour M. On the application of physics informed neural networks (PINN) to solve boundary layer thermal-fluid problems[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 132: 105890. |
| 44 | Cai S Z, Wang Z C, Fuest F, et al. Flow over an espresso cup: inferring 3-D velocity and pressure fields from tomographic background oriented schlieren via physics-informed neural networks[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 915: A102. |
| 45 | Laubscher R. Simulation of multi-species flow and heat transfer using physics-informed neural networks[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2021, 33(8): 087101. |
| 46 | Laubscher R, Rousseau P. Application of a mixed variable physics-informed neural network to solve the incompressible steady-state and transient mass, momentum, and energy conservation equations for flow over in-line heated tubes[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2022, 114: 108050. |
| 47 | Cai S Z, Mao Z P, Wang Z C, et al. Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for fluid mechanics: a review[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2021, 37(12): 1727-1738. |
| 48 | Bradley W, Kim J, Kilwein Z, et al. Perspectives on the integration between first-principles and data-driven modeling[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2022, 166: 107898. |
| 49 | Díez P, Huerta A. A unified approach to remeshing strategies for finite element h-adaptivity[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1999, 176(1/2/3/4): 215-229. |
| 50 | Askes H, Rodríguez-Ferran A. A combined rh-adaptive scheme based on domain subdivision. Formulation and linear examples[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2001, 51(3): 253-273. |
| 51 | Babuška I, Suri M. The p and h-p versions of the finite element method, basic principles and properties[J]. SIAM Review, 1994, 36(4): 578-632. |
| 52 | Zhang X D, Trépanier J Y, Camarero R. A posteriori error estimation for finite-volume solutions of hyperbolic conservation laws[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 185(1): 1-19. |
| 53 | McRae D S. R-Refinement grid adaptation algorithms and issues[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 189(4): 1161-1182. |
| 54 | Lee D, Tsuei Y M. A formula for estimation of truncation errors of convection terms in a curvilinear coordinate system[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1992, 98(1): 90-100. |
| 55 | Choudhary A, Roy C. Efficient residual-based mesh adaptation for 1D and 2D CFD applications[C]∥49th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. Florida, 2011. |
| 56 | Roy C. Strategies for driving mesh adaptation in CFD[C]∥47th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting Including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition. Florida, 2009. |
| 57 | Lu L, Meng X H, Mao Z P, et al. Deep XDE: a deep learning library for solving differential equations[J]. SIAM Review, 2021, 63(1): 208-228. |
| 58 | Hanna J M, Aguado J V, Comas-Cardona S, et al. Residual-based adaptivity for two-phase flow simulation in porous media using Physics-informed Neural Networks[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 396: 115100. |
| 59 | Gurtin M E, Polignone D, Viñals J. Two-phase binary fluids and immiscible fluids described by an order parameter[J]. Mathematical Models and Methods in Applied Sciences, 1996, 6(6): 815-831. |
| 60 | Ma C, Wu J, Zhang T W. A high order spectral difference-based phase field lattice Boltzmann method for incompressible two-phase flows[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2020, 32(12): 122113. |
| 61 | Kou J S, Wang X H, Zeng M L, et al. Energy stable and mass conservative numerical method for a generalized hydrodynamic phase-field model with different densities[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2020, 32(11): 117103. |
| 62 | Dadvand A, Bagheri M, Samkhaniani N, et al. Advected phase-field method for bounded solution of the Cahn-Hilliard Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2021, 33(5): 053311. |
| 63 | De Rosis A, Enan E. A three-dimensional phase-field lattice Boltzmann method for incompressible two-components flows[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2021, 33(4): 043315. |
| 64 | Qiu R D, Huang R F, Xiao Y, et al. Physics-informed neural networks for phase-field method in two-phase flow[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2022, 34(5): 052109. |
| 65 | Zhao C L W, Jia. Solving Allen-cahn and cahn-Hilliard equations using the adaptive physics informed neural networks[J]. Communications in Computational Physics, 2021, 29(3): 930-954. |
| 66 | Lyu L Y, Zhang Z, Chen M X, et al. MIM: a deep mixed residual method for solving high-order partial differential equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 452: 110930. |
| 67 | 丘润荻, 王静竹, 黄仁芳, 等. 改进的物理融合神经网络在瑞利-泰勒不稳定性问题中的应用[J]. 力学学报, 2022, 54(8): 2224-2234. |
| Qiu R D, Wang J Z, Huang R F, et al. The application of modified physics-informed neural networks in Rayleigh-Taylor instability[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2022, 54(8): 2224-2234. | |
| 68 | Zhang Z, Yan X, Liu P Y, et al. A physics-informed convolutional neural network for the simulation and prediction of two-phase Darcy flows in heterogeneous porous media[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2023, 477: 111919. |
| 69 | Zhai H F, Zhou Q, Hu G H. Predicting micro-bubble dynamics with semi-physics-informed deep learning[J]. AIP Advances, 2022, 12(3): 035153. |
| 70 | Yan X, Lin J Q, Wang S, et al. Physics-informed neural network simulation of two-phase flow in heterogeneous and fractured porous media[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2024, 189: 104731. |
| 71 | Shokouhi P, Kumar V, Prathipati S, et al. Physics-informed deep learning for prediction of CO2 storage site response[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2021, 241: 103835. |
| 72 | Sheremetov L, Lopez-Peña L A, Díaz-Cortes G B, et al. Deep learning model of two-phase fluid transport through fractured media: a real-world case study[M]//Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2024: 55-68. |
| 73 | Deng L C, Pan Y W. Application of physics-informed neural networks for self-similar and transient solutions of spontaneous imbibition[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 203: 108644. |
| 74 | Chakraborty A, Rabinovich A, Moreno Z. Physics-informed neural networks for modeling two-phase steady state flow with capillary heterogeneity at varying flow conditions[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2024, 185: 104639. |
| 75 | Jalili D, Jang S, Jadidi M, et al. Physics-informed neural networks for heat transfer prediction in two-phase flows[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 221: 125089. |
| [1] | Guanyu REN, Yifei ZHANG, Xinze LI, Wenjing DU. Numerical study on flow and heat transfer characteristics of airfoil printed circuit heat exchangers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 108-117. |
| [2] | Yong YANG, Zixuan ZU, Yukun LI, Dongliang WANG, Zongliang FAN, Huairong ZHOU. Numerical simulation of CO2 absorption by alkali liquor in T-junction cylindrical microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 135-142. |
| [3] | Junhao HUANG, Keliang PANG, Fangyuan SUN, Fujun LIU, Zhiyuan GU, Long HAN, Yanquan DUAN, Yanhui FENG. Influence of bell structure of coke dry quenching furnace on coke distribution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 158-169. |
| [4] | Xinyu DONG, Longfei BIAN, Yiyi YANG, Yuxuan ZHANG, Lu LIU, Teng WANG. Study on flow and heat transfer mechanism of supercritical CO2 in inclined upward tube under cooling conditions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 195-205. |
| [5] | Qirui GUO, Liyuan REN, Kang CHEN, Xiangyu HUANG, Weihua MA, Leqin XIAO, Weiliang ZHOU. Numerical simulation of static mixing tubes for HTPB propellant slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 206-216. |
| [6] | Kuangxi LI, Peiqian YU, Jiangyun WANG, Haoran WEI, Zhigang ZHENG, Liuhai FENG. Flow analysis and structure optimization of micro-bubble swirling air flotation device [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 223-234. |
| [7] | Zhangzhou WANG, Tianqi TANG, Jiajun XIA, Yurong HE. Battery thermal management performance simulation based on composite phase change material [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 329-338. |
| [8] | Jian HU, Jinghua JIANG, Shengjun FAN, Jianhao LIU, Haijiang ZOU, Wanlong CAI, Fenghao WANG. Research on heat extraction performance of deep U-type borehole heat exchanger [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 76-84. |
| [9] | Juhui CHEN, Tong SU, Dan LI, Liwei CHEN, Wensheng LYU, Fanqi MENG. Study on the heat transfer characteristics of microchannels under the action of fin-shaped spoilers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3122-3132. |
| [10] | Shuyue LI, Huan WANG, Shaoqiang ZHOU, Zhihong MAO, Yongmin ZHANG, Junwu WANG, Xiuhua WU. Numerical simulation of hydrogen reduction of U3O8 in fluidized bed reactors using CPFD method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3133-3151. |
| [11] | Lei ZUO, Junfeng WANG, Jian GAO, Daorui WANG. Electric field-regulating combustion behavior of biodiesel droplet [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2983-2990. |
| [12] | Shaojun DOU, Liang HAO. Mesoscale simulation of coupled gas charge transfer process in PEMFC catalyst layer [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 3002-3010. |
| [13] | Xiaoyu QIAN, Xuan RUAN, Shuiqing LI. Structural reconstruction and levitation of dielectric particle layers in electric fields [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2756-2762. |
| [14] | Ziliang ZHU, Shuang WANG, Yu'ang JIANG, Mei LIN, Qiuwang WANG. Solid-liquid phase change algorithm with Euler-Lagrange iteration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2763-2776. |
| [15] | Aiming DENG, Yurong HE, Tianqi TANG, Yanwei HU. Simulation of effect of draft plate on particle growth process in spray fluidized beds [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2787-2799. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||