CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2524-2543.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241344
• Reviews and monographs • Previous Articles Next Articles
Wenhao SUN( ), Jun TIAN, Kun ZHANG, Na LIU, Baosen CAO, Xiaoqiang LIANG
), Jun TIAN, Kun ZHANG, Na LIU, Baosen CAO, Xiaoqiang LIANG
Received:2024-11-22
Revised:2025-01-14
Online:2025-07-09
Published:2025-06-25
Contact:
Wenhao SUN
通讯作者:
孙文浩
作者简介:孙文浩(1995—),男,博士,工程师,563729367@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Wenhao SUN, Jun TIAN, Kun ZHANG, Na LIU, Baosen CAO, Xiaoqiang LIANG. New development of novel separators with high thermal stability for lithium-ion batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2524-2543.
孙文浩, 田君, 张锟, 刘娜, 曹宝森, 梁晓嫱. 锂离子电池用高热稳定性新型隔膜的研究新进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2524-2543.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
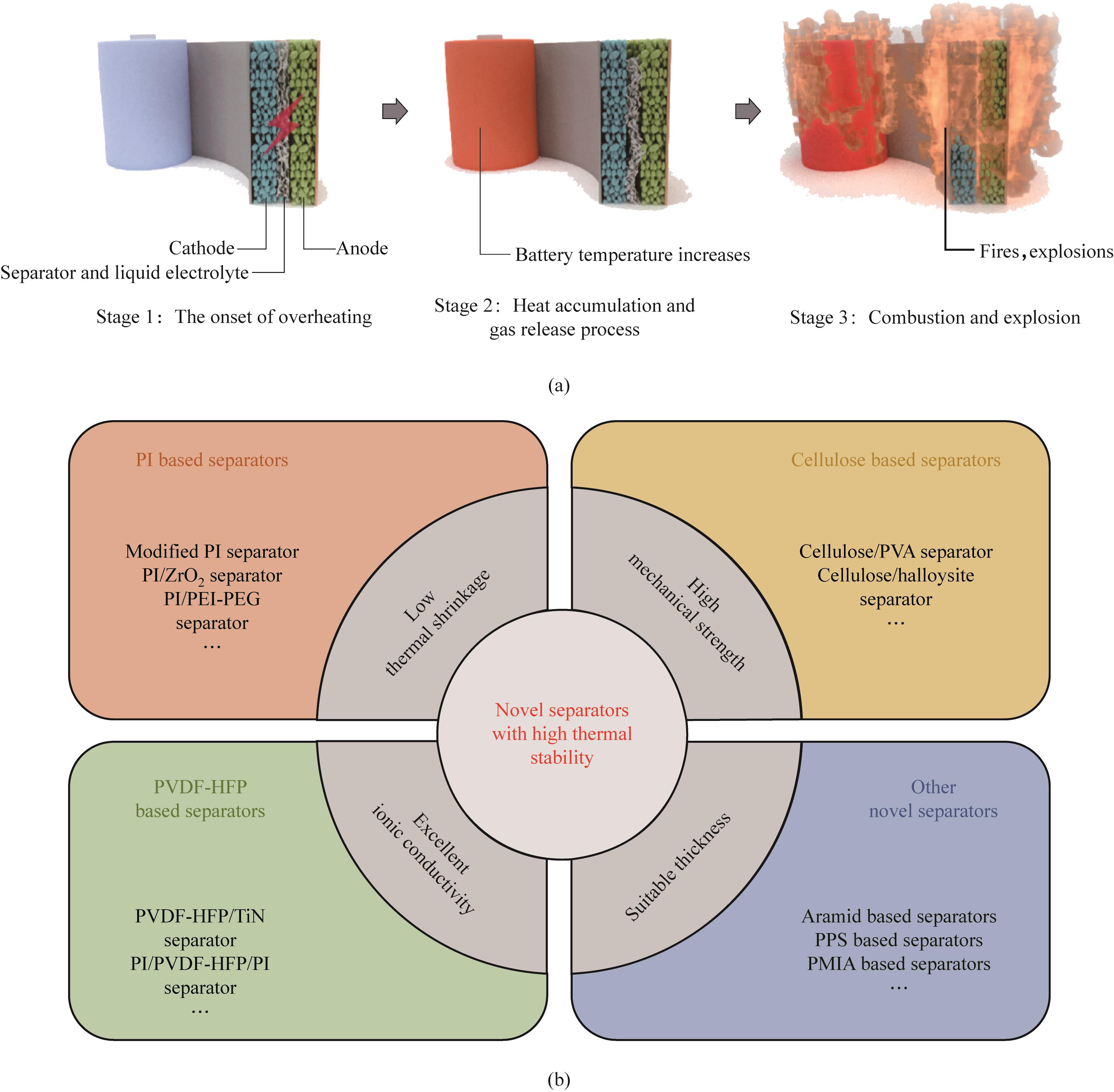
Fig.1 (a) The thermal runaway process of lithium-ion battery[20]; (b) Common types and performance requirements of novel separators with high thermal stability
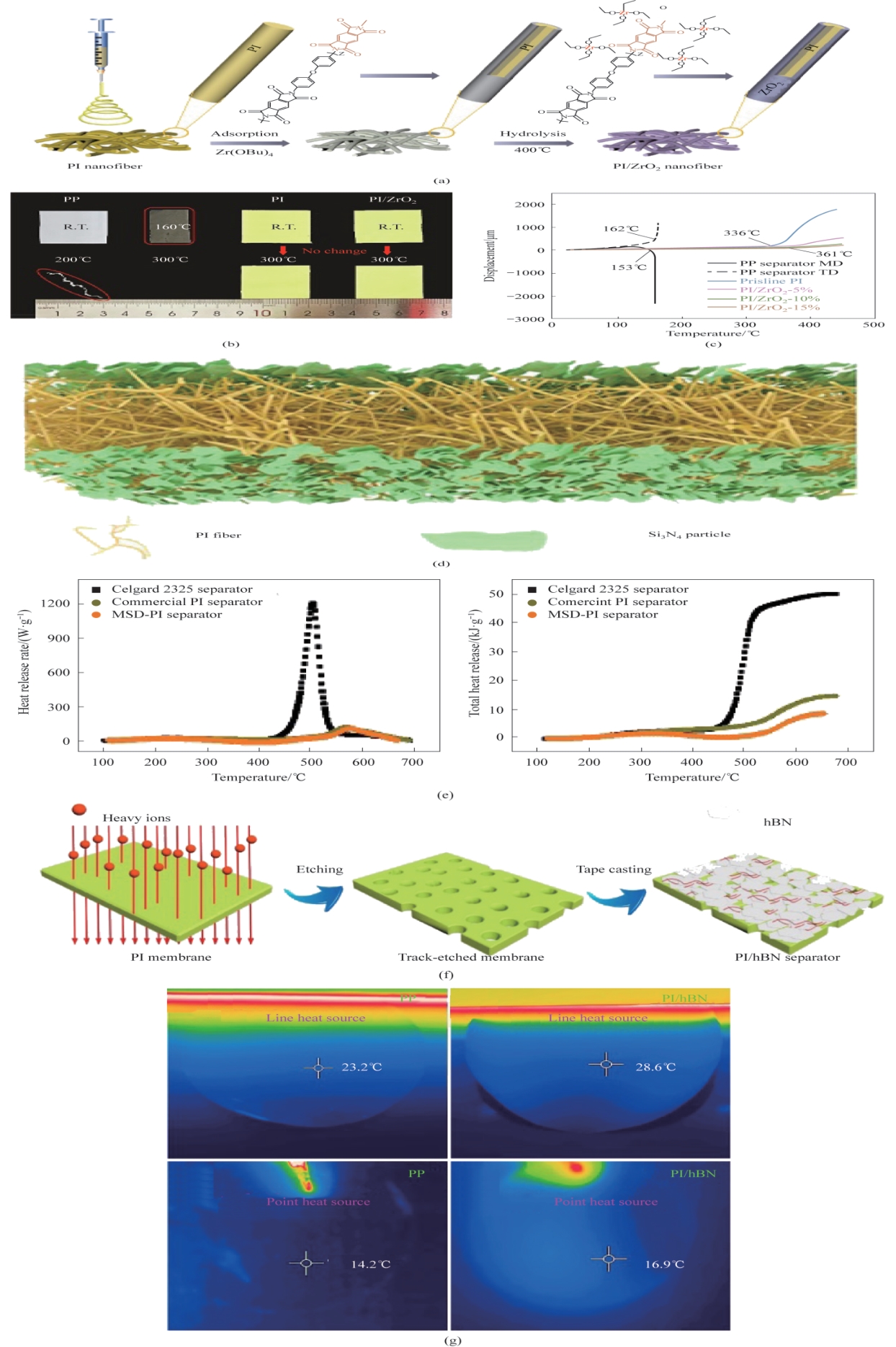
Fig.2 (a) Schematic diagram of the fabrication process and structure of PI/ZrO2 separator; (b) Photographs of PP separator, PI separator and PI/ZrO2 separator after heat treatment at different temperatures; (c) Thermal mechanical analysis (TMA) curves of PP separator, PI separator and PI/ZrO2 separator[21]; (d) Schematic structure of MSD-PI separator; (e) Heat release rate and total heat release curves of Celgard 2325 separator, PI separator and MSD-PI separator[22]; (f) Schematic diagram of the fabrication process and structure of PI/hBN separator; (g) Infrared thermal images of PP separator and PI/hBN separator using a line heat source and a point heat source[23]
| Material | Preparation method | Thickness/μm | Tensile strength/MPa | Porosity/% | Ionic conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | Electrolyte uptake/% | Thermal shrinkage/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI/CNFs/DPDBE | casting | 18 | 25.4 | 78 | 0.45 | 192 | 0 (200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP@PI | electrospinning | 22 | — | 80 | 1.79 | 800 | 0 (140℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/PEI-PEG | impregnation | 28 | 39 | 66.4 | 2.33 | 168 | —(200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| Si3N4/PI | casting | 约48 | 18.2 | 72.2 | 0.66 | 180 | —(400℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PI/PVDF-HFP | electrospinning | 25 | 19 | 86.7 | 1.24 | 366.6 | —(400℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cross-linked PI | electrospinning | 24 | — | 81 | 1.1 | 540.2 | —(250℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PI/PEI | electrospinning | 12.3 | 95.7 | 75 | 1.42 | 210.6 | —(200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/montmorillonite | electrospinning | 50 | 14.7 | 72 | 0.77 | 1615 | —(250℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/hBN | ion etching and coating | 14 | 220.1 | 44.5 | — | 62.7 | 0 (280℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/ZrO2 | electrospinning and pyrolysis | 33 | 25.7 | 86 | 1.32 | 456 | 0 (300℃, —) | [ |
| PI/AlOOH | impregnation | 31.7 | 35.21 | 80 | 2.04 | 392 | 0 (250℃, —) | [ |
| PI containing carboxyl groups | casting | 26 | 16.55 | 75.2 | 0.717 | 344 | 0 (200℃, —) | [ |
| TiO2@PI | electrospinning | 26.5 | — | 89.1 | 2.52 | 721 | —(160℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI aerogel | casting | — | 13.7 | 74.38 | 0.524 | 329.1 | 约3 (300℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/carboxylated PI | electrospinning and pyrolysis | 20 | 34.2 | 78 | 0.51 | 638 | 0 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/SiO2 | electrospinning and pyrolysis | 19 | 73.69 | 61 | 1.55 | 264 | 0 (200℃, —) | [ |
| PI/A-POSS | electrospinning | 41 | 13.58 | 83.8 | 2.617 | 1149 | —(280℃, —) | [ |
| Si3N4/PI/Si3N4 | magnetron sputtering deposition | 21.4 | — | 61.35 | 0.6631 | 321.66 | 0 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/PAALi | electrospinning and impregnation | 40 | 16.1 | 67.6 | 1.37 | — | 0 (160℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of PI based separators
| Material | Preparation method | Thickness/μm | Tensile strength/MPa | Porosity/% | Ionic conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | Electrolyte uptake/% | Thermal shrinkage/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PI/CNFs/DPDBE | casting | 18 | 25.4 | 78 | 0.45 | 192 | 0 (200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP@PI | electrospinning | 22 | — | 80 | 1.79 | 800 | 0 (140℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/PEI-PEG | impregnation | 28 | 39 | 66.4 | 2.33 | 168 | —(200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| Si3N4/PI | casting | 约48 | 18.2 | 72.2 | 0.66 | 180 | —(400℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PI/PVDF-HFP | electrospinning | 25 | 19 | 86.7 | 1.24 | 366.6 | —(400℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cross-linked PI | electrospinning | 24 | — | 81 | 1.1 | 540.2 | —(250℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PI/PEI | electrospinning | 12.3 | 95.7 | 75 | 1.42 | 210.6 | —(200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/montmorillonite | electrospinning | 50 | 14.7 | 72 | 0.77 | 1615 | —(250℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/hBN | ion etching and coating | 14 | 220.1 | 44.5 | — | 62.7 | 0 (280℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/ZrO2 | electrospinning and pyrolysis | 33 | 25.7 | 86 | 1.32 | 456 | 0 (300℃, —) | [ |
| PI/AlOOH | impregnation | 31.7 | 35.21 | 80 | 2.04 | 392 | 0 (250℃, —) | [ |
| PI containing carboxyl groups | casting | 26 | 16.55 | 75.2 | 0.717 | 344 | 0 (200℃, —) | [ |
| TiO2@PI | electrospinning | 26.5 | — | 89.1 | 2.52 | 721 | —(160℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI aerogel | casting | — | 13.7 | 74.38 | 0.524 | 329.1 | 约3 (300℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/carboxylated PI | electrospinning and pyrolysis | 20 | 34.2 | 78 | 0.51 | 638 | 0 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/SiO2 | electrospinning and pyrolysis | 19 | 73.69 | 61 | 1.55 | 264 | 0 (200℃, —) | [ |
| PI/A-POSS | electrospinning | 41 | 13.58 | 83.8 | 2.617 | 1149 | —(280℃, —) | [ |
| Si3N4/PI/Si3N4 | magnetron sputtering deposition | 21.4 | — | 61.35 | 0.6631 | 321.66 | 0 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PI/PAALi | electrospinning and impregnation | 40 | 16.1 | 67.6 | 1.37 | — | 0 (160℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
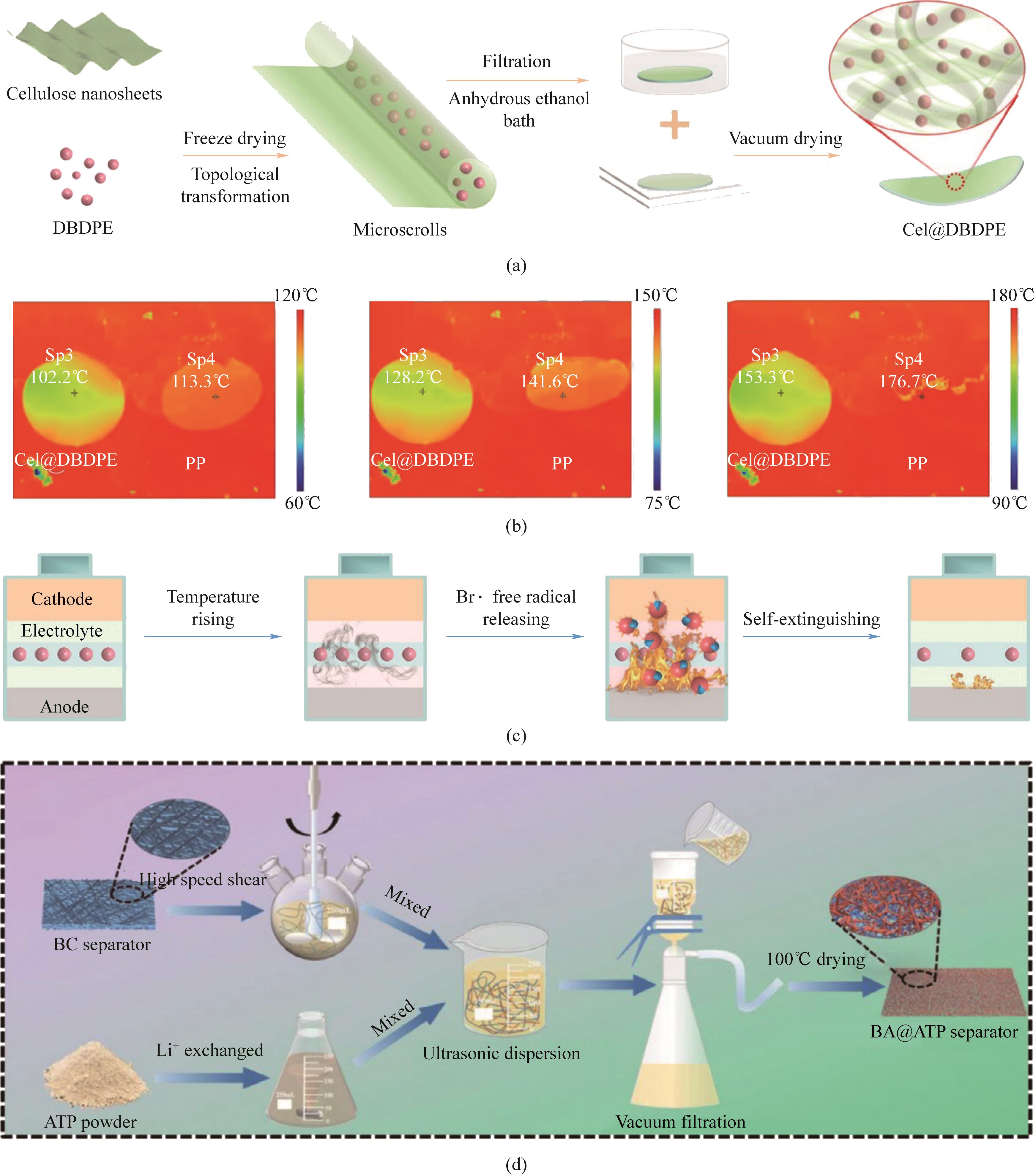
Fig.3 (a) Schematic diagram of the fabrication process and structure of Cel@DBDPE separator; (b) Infrared thermal images of Cel@DBDPE separator and PP separator at different temperatures; (c) Flame retardant mechanism of Cel@DBDPE separator[48]; (d) Schematic diagram of the fabrication process and structure of BA@ATP separator[49]
| Material | Preparation method | Thickness/μm | Tensile strength/MPa | Porosity/% | Ionic conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | Electrolyte uptake/% | Thermal shrinkage/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cellulose/PPNBs | co-extrusion | 20 | 50 | 78.4 | 1.04 | 326 | 30 (260℃, —) | [ |
| cellulose/APP/LPC | casting | 85 | 12.9 | 70 | 2.45 | 446 | 0 (210℃, 1 h) | [ |
| cellulose/PVA | casting and impregnation | 45 | 50.1 | 63.3 | 1.81 | 397 | —(300℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/hydroxyapatite | filtration | 28 | 9.94 | 76 | 0.81 | 162 | 0 (250℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/DBDPE | filtration | 15 | 20 | — | 0.27 | 244 | 0 (210℃, —) | [ |
| cellulose/PVDF/BaTiO3/SBR | sizing, impregnation and lamination | 20 | 50.15 | — | 0.19 | 270.21 | 0 (200℃, —) | [ |
| ZIF-8@cellulose/ANFs | filtration and extrusion | — | 70.7 | 62.4 | 1.6 | 267.8 | —(200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/ANFs | filtration and extrusion | 40 | 33 | 49.5 | 0.75 | 157.4 | 0 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/PVDF-HFP/PEI/SiO2 | impregnation | 49 | 9.9 | 71 | 0.69 | 254 | 0 (250℃, 1 h) | [ |
| cellulose/chitosan/PVA/BaTiO3 | coating | 70 | 41.31 | — | — | 约140 | 0 (200℃, 0.167 h) | [ |
| cellulose/attapulgite | filtration | — | 3.71 | 58.08 | 1.734 | 470.03 | 0 (250℃, —) | [ |
| cellulose/halloysite nanotubes | coating | 120 | 20.1 | 76.8 | 0.42 | 295 | —(200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/PVDF-HFP/PEI/PDMSDGE | impregnation | 55 | 19.9 | 70 | 0.59 | 230 | —(200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| cellulose | filtration | — | 45.3 | 61.5 | 1.08 | 225.8 | 0 (160℃, 0.167 h) | [ |
| cellulose/chitosan/PVA/SiO2 | coating | 70 | 34.86 | — | 0.58 | 147 | 0 (200℃, —) | [ |
| cellulose/laponite/PEG | dry | — | 143.3 | 68 | 0.977 | 260 | 0 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose | filtration | 35 | 49 | 63.4 | 0.71 | 136.4 | 0 (150℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
Table 2 Physicochemical properties of cellulose based separators
| Material | Preparation method | Thickness/μm | Tensile strength/MPa | Porosity/% | Ionic conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | Electrolyte uptake/% | Thermal shrinkage/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cellulose/PPNBs | co-extrusion | 20 | 50 | 78.4 | 1.04 | 326 | 30 (260℃, —) | [ |
| cellulose/APP/LPC | casting | 85 | 12.9 | 70 | 2.45 | 446 | 0 (210℃, 1 h) | [ |
| cellulose/PVA | casting and impregnation | 45 | 50.1 | 63.3 | 1.81 | 397 | —(300℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/hydroxyapatite | filtration | 28 | 9.94 | 76 | 0.81 | 162 | 0 (250℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/DBDPE | filtration | 15 | 20 | — | 0.27 | 244 | 0 (210℃, —) | [ |
| cellulose/PVDF/BaTiO3/SBR | sizing, impregnation and lamination | 20 | 50.15 | — | 0.19 | 270.21 | 0 (200℃, —) | [ |
| ZIF-8@cellulose/ANFs | filtration and extrusion | — | 70.7 | 62.4 | 1.6 | 267.8 | —(200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/ANFs | filtration and extrusion | 40 | 33 | 49.5 | 0.75 | 157.4 | 0 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/PVDF-HFP/PEI/SiO2 | impregnation | 49 | 9.9 | 71 | 0.69 | 254 | 0 (250℃, 1 h) | [ |
| cellulose/chitosan/PVA/BaTiO3 | coating | 70 | 41.31 | — | — | 约140 | 0 (200℃, 0.167 h) | [ |
| cellulose/attapulgite | filtration | — | 3.71 | 58.08 | 1.734 | 470.03 | 0 (250℃, —) | [ |
| cellulose/halloysite nanotubes | coating | 120 | 20.1 | 76.8 | 0.42 | 295 | —(200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose/PVDF-HFP/PEI/PDMSDGE | impregnation | 55 | 19.9 | 70 | 0.59 | 230 | —(200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| cellulose | filtration | — | 45.3 | 61.5 | 1.08 | 225.8 | 0 (160℃, 0.167 h) | [ |
| cellulose/chitosan/PVA/SiO2 | coating | 70 | 34.86 | — | 0.58 | 147 | 0 (200℃, —) | [ |
| cellulose/laponite/PEG | dry | — | 143.3 | 68 | 0.977 | 260 | 0 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| cellulose | filtration | 35 | 49 | 63.4 | 0.71 | 136.4 | 0 (150℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
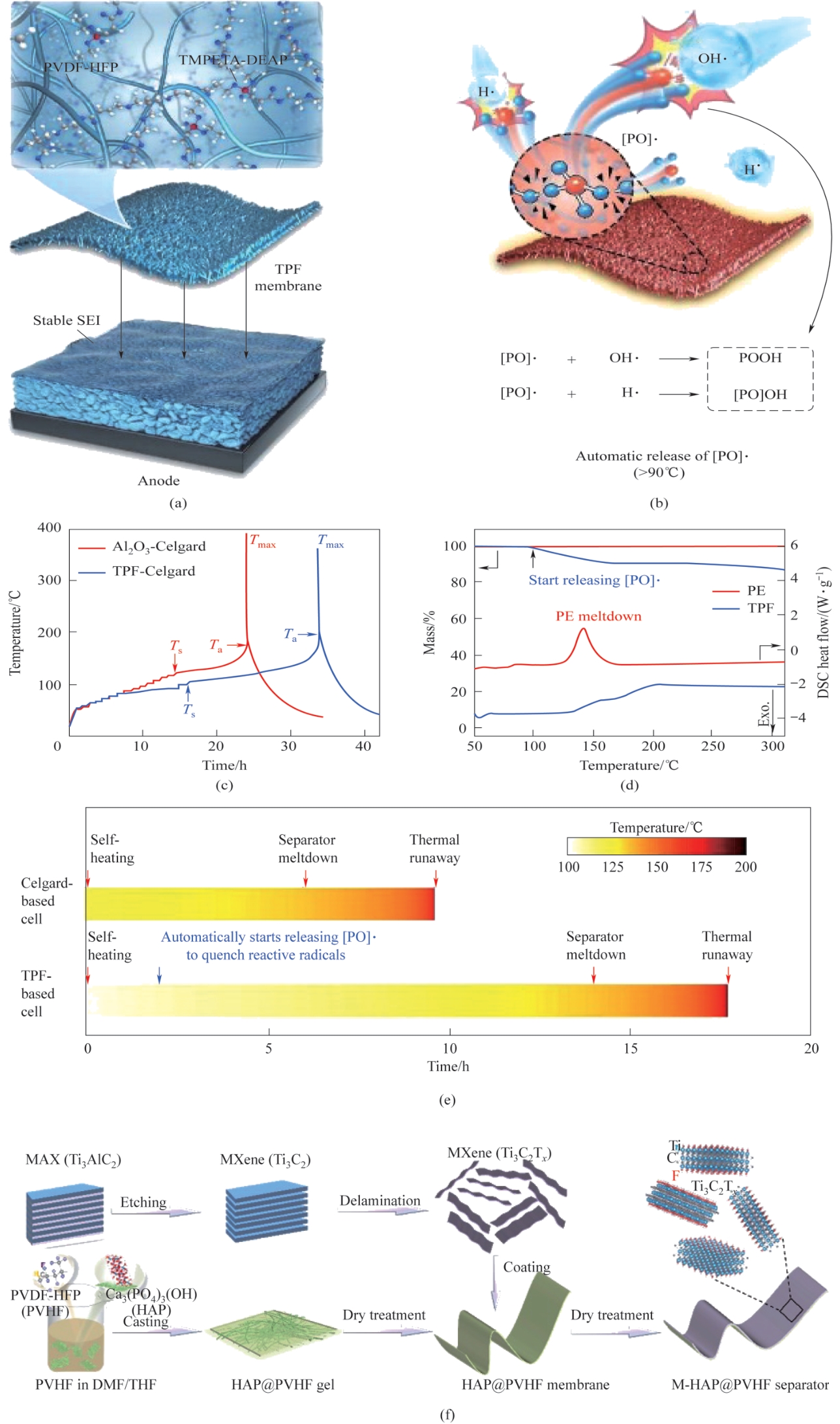
Fig.4 Structure diagram (a) and flame retardant mechanism (b) of TPF separator; (C) ARC profiles of pouch cells with Al2O3-Celgard separator and TPF separator; (d) Thermogravimetry (TG) and DSC profiles of PE separator and TPF separator; (e) Temperature-time axis after self-heating of pouch cells with Al2O3-Celgard separator and TPF separator[71]; (f) Schematic diagram of the fabrication process and structure of M-HAP@PVHF separator[72]
| Material | Preparation method | Thickness/μm | Tensile strength/MPa | Porosity/% | Ionic conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | Electrolyte uptake/% | Thermal shrinkage/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF-HFP/TiN | casting | 25 | 12.1 | — | 1.02 | 192 | 约6 (175℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/SiC | casting | — | 14.6 | — | 1.32 | 249 | 5 (150℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/TPP | casting | 约35 | — | — | 0.28 | 115.2 | 15 (140℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/Fyrol DMMP | casting | 25 | — | 约48.9 | — | 2213 | 0 (220℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/MPP | casting | 25 | — | 44.6 | 0.327 | 429.4 | —(200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/TMPETA-DEAP | casting | 44 | — | — | 2.8 | — | 约2 (160℃, —) | [ |
| PI/PVDF-HFP/PI | electrospinning, extrusion and heat | 46 | 19.09 | 71.57 | 1.23 | 529 | 2 (220℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/CaCO3 | casting | 20 | 3 | — | 0.18 | 约113 | 0 (300℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/Si3N4 | casting | 72 | 3.13 | 75.2 | 0.884 | 230 | —(200℃, —) | [ |
Table 3 Physicochemical properties of PVDF-HFP-based separators
| Material | Preparation method | Thickness/μm | Tensile strength/MPa | Porosity/% | Ionic conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | Electrolyte uptake/% | Thermal shrinkage/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF-HFP/TiN | casting | 25 | 12.1 | — | 1.02 | 192 | 约6 (175℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/SiC | casting | — | 14.6 | — | 1.32 | 249 | 5 (150℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/TPP | casting | 约35 | — | — | 0.28 | 115.2 | 15 (140℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/Fyrol DMMP | casting | 25 | — | 约48.9 | — | 2213 | 0 (220℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/MPP | casting | 25 | — | 44.6 | 0.327 | 429.4 | —(200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/TMPETA-DEAP | casting | 44 | — | — | 2.8 | — | 约2 (160℃, —) | [ |
| PI/PVDF-HFP/PI | electrospinning, extrusion and heat | 46 | 19.09 | 71.57 | 1.23 | 529 | 2 (220℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/CaCO3 | casting | 20 | 3 | — | 0.18 | 约113 | 0 (300℃, 1 h) | [ |
| PVDF-HFP/Si3N4 | casting | 72 | 3.13 | 75.2 | 0.884 | 230 | —(200℃, —) | [ |
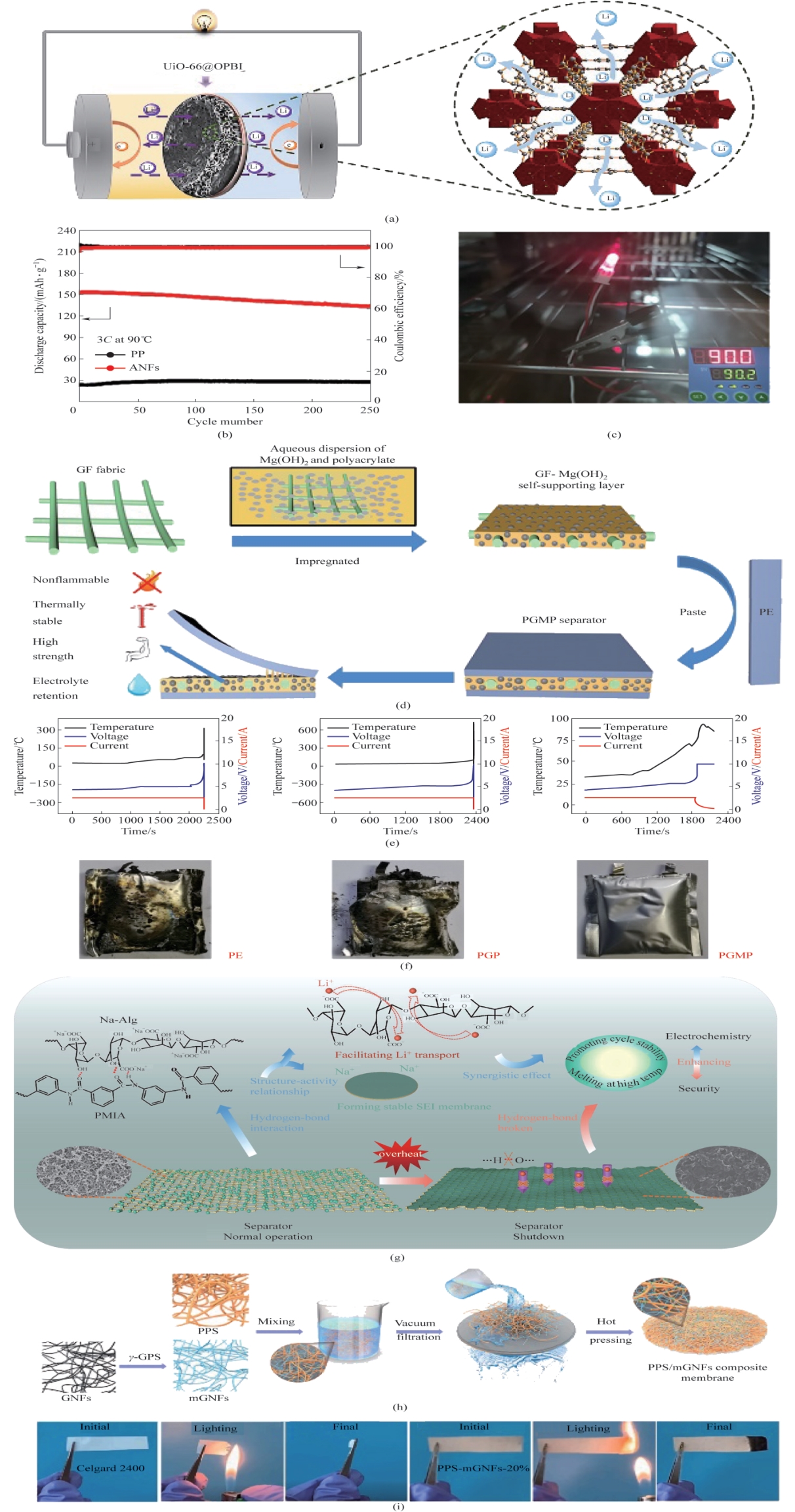
Fig.5 (a) Structure diagram of UiO-66@OPBI separator[82]; (b) Cycling performance of batteries with ANFs separator and PP separator at 90℃; (c) Photographs of a battery with ANFs separator lighting a light bulb at 90℃[83]; (d) Schematic diagram of the fabrication process and work mechanism of PGMP separator; Temperature, voltage and current curves (e) and digital images after the test (f) of batteries with PE separator, PGP separator and PGMP separator during overcharge test[84]; (g) Schematic diagram of the fabrication process and work mechanism of Na-Alg/PMIA separator[85]; (h) Fabrication process of PPS-mGNFs separator; (i) The flammability test of Celgard 2400 separator and PPS-mGNFs separator[86]
| Material | Preparation method | Thickness/μm | Tensile strength/MPa | Porosity/% | Ionic conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | Electrolyte uptake/% | Thermal shrinkage/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCOF@Li/OPBI | casting | 36 | 23.2 | 51 | 1.363 | 391 | —(200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| SCOF/OPBI | casting | 34 | 8.9 | 58 | 1.76 | 439 | 0 (200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| UiO-66-S-Li@OPBI | casting | 31 | 13.5 | 58 | 1.46 | 249 | 0 (200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| OPBI@COF | casting | 26 | 15.4 | 60 | 1.214 | 428 | —(200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| UiO-66@OPBI | casting | 25 | 10.3 | 63 | 1.74 | 213 | —(200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| GF/PPS | electrospinning, filtration and press | 34 | 22.2 | 65.4 | 1.43 | 270.7 | 0 (250℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PE/GF-Mg(OH)2/PE | impregnation and press | 65 | 250 | 61 | 0.93 | 86 | —(350℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| GF/polyacrylate | impregnation and press | 150 | 20 | 75.8 | 2.16 | 335 | —(350℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| GF/PEGDMA/Al2O3 | casting | 50 | 12.7 | — | — | 约326 | 0 (458℃, —) | [ |
| ANFs/CNF/diatomite/PI | filtration, impregnation and extrusion | — | 23.74 | 69.34 | 1.04 | 237.16 | 0.31 (200℃, 0.67 h) | [ |
| ANFs | casting | — | 0.75 | 86.5 | 1.04 | 695 | 0 (300℃, 1 h) | [ |
| ANFs/ZIF-8 | filtration | — | 52.8 | 61.6 | 1.37 | 224 | —(200℃, —) | [ |
| ANFs/PEO | electrospinning | — | 41.52 | 75.85 | 4.33 | 650 | 0 (200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| chitosan nanofibers | filtration | 25 | 22 | 65 | 1.15 | 281 | 0 (160℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| polyimine aerogel | casting | 50 | — | 78 | 0.92 | 591 | 0 (210℃, 0.167 h) | [ |
| PPS/PAMAM/PVDF-HFP | impregnation | 51 | 10.2 | 85 | 0.92 | 236 | 0 (200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| sodium-alginate/PMIA | coating | — | — | 52.5 | 1.26 | 252.3 | —(250℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| fluoride TiO2/PMIA | casting | 40 | 24.6 | 73 | 1.3 | 322 | —(250℃, —) | [ |
| Al2O3/PEI | casting | 30 | 16.2 | 62 | 1.07 | 165 | —(350℃, /) | [ |
| PBS/Mxene/SiO2 | filtration | 45 | 约4.15 | 54.3 | 3.386 | 633 | —(160℃, 0.25 h) | [ |
| PEEK | electrospinning and extrusion | 40 | 15.8 | 71.2 | 1.48 | 245.5 | 3.4 (300℃, —) | [ |
| Alginate fiber-PEA | filtration | 85 | — | — | 1.8 | — | — (200℃, 2 h) | [ |
| sulfonated cellulose/PLA/PBS | coating | 35 | — | 87.7 | 3.24 | 290.6 | 0 (150℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PEN@PDA-PEI | casting | 约30 | 20.6 | 75 | 1.5 | 618 | 0 (200℃, —) | [ |
| cellulose/PPS | filtration | 60 | 约18 | 62.7 | 1.55 | 216.2 | 0 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| Ca6Si6O17(OH)2 | filtration and freeze drying | 6~15 | — | 82 | 3.08 | — | 约2.6 (150℃, —) | [ |
| PEN-IPA | casting and impregnation | 30 | — | 73.1 | 1.47 | 400 | 0 (180℃, 1 h) | [ |
| Li-SPEOD | electrospinning | — | 6.7 | 65.52 | 3.57 | 476.2 | 0 (400℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PPS | plasma-assisted mechanochemical treatment, compression moulding and etching | 50 | — | — | — | — | 0 (250℃, —) | [ |
| PAEK | casting | 40 | 21.1 | 85 | — | 310 | 约12 (300℃, —) | [ |
| electrospinning and impregnation | — | 5.3 | 38.7 | 0.28 | 195 | 2 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
Table 4 Physicochemical properties of other separators
| Material | Preparation method | Thickness/μm | Tensile strength/MPa | Porosity/% | Ionic conductivity/(mS·cm-1) | Electrolyte uptake/% | Thermal shrinkage/% | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCOF@Li/OPBI | casting | 36 | 23.2 | 51 | 1.363 | 391 | —(200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| SCOF/OPBI | casting | 34 | 8.9 | 58 | 1.76 | 439 | 0 (200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| UiO-66-S-Li@OPBI | casting | 31 | 13.5 | 58 | 1.46 | 249 | 0 (200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| OPBI@COF | casting | 26 | 15.4 | 60 | 1.214 | 428 | —(200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| UiO-66@OPBI | casting | 25 | 10.3 | 63 | 1.74 | 213 | —(200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| GF/PPS | electrospinning, filtration and press | 34 | 22.2 | 65.4 | 1.43 | 270.7 | 0 (250℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PE/GF-Mg(OH)2/PE | impregnation and press | 65 | 250 | 61 | 0.93 | 86 | —(350℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| GF/polyacrylate | impregnation and press | 150 | 20 | 75.8 | 2.16 | 335 | —(350℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| GF/PEGDMA/Al2O3 | casting | 50 | 12.7 | — | — | 约326 | 0 (458℃, —) | [ |
| ANFs/CNF/diatomite/PI | filtration, impregnation and extrusion | — | 23.74 | 69.34 | 1.04 | 237.16 | 0.31 (200℃, 0.67 h) | [ |
| ANFs | casting | — | 0.75 | 86.5 | 1.04 | 695 | 0 (300℃, 1 h) | [ |
| ANFs/ZIF-8 | filtration | — | 52.8 | 61.6 | 1.37 | 224 | —(200℃, —) | [ |
| ANFs/PEO | electrospinning | — | 41.52 | 75.85 | 4.33 | 650 | 0 (200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| chitosan nanofibers | filtration | 25 | 22 | 65 | 1.15 | 281 | 0 (160℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| polyimine aerogel | casting | 50 | — | 78 | 0.92 | 591 | 0 (210℃, 0.167 h) | [ |
| PPS/PAMAM/PVDF-HFP | impregnation | 51 | 10.2 | 85 | 0.92 | 236 | 0 (200℃, 1 h) | [ |
| sodium-alginate/PMIA | coating | — | — | 52.5 | 1.26 | 252.3 | —(250℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| fluoride TiO2/PMIA | casting | 40 | 24.6 | 73 | 1.3 | 322 | —(250℃, —) | [ |
| Al2O3/PEI | casting | 30 | 16.2 | 62 | 1.07 | 165 | —(350℃, /) | [ |
| PBS/Mxene/SiO2 | filtration | 45 | 约4.15 | 54.3 | 3.386 | 633 | —(160℃, 0.25 h) | [ |
| PEEK | electrospinning and extrusion | 40 | 15.8 | 71.2 | 1.48 | 245.5 | 3.4 (300℃, —) | [ |
| Alginate fiber-PEA | filtration | 85 | — | — | 1.8 | — | — (200℃, 2 h) | [ |
| sulfonated cellulose/PLA/PBS | coating | 35 | — | 87.7 | 3.24 | 290.6 | 0 (150℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PEN@PDA-PEI | casting | 约30 | 20.6 | 75 | 1.5 | 618 | 0 (200℃, —) | [ |
| cellulose/PPS | filtration | 60 | 约18 | 62.7 | 1.55 | 216.2 | 0 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| Ca6Si6O17(OH)2 | filtration and freeze drying | 6~15 | — | 82 | 3.08 | — | 约2.6 (150℃, —) | [ |
| PEN-IPA | casting and impregnation | 30 | — | 73.1 | 1.47 | 400 | 0 (180℃, 1 h) | [ |
| Li-SPEOD | electrospinning | — | 6.7 | 65.52 | 3.57 | 476.2 | 0 (400℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| PPS | plasma-assisted mechanochemical treatment, compression moulding and etching | 50 | — | — | — | — | 0 (250℃, —) | [ |
| PAEK | casting | 40 | 21.1 | 85 | — | 310 | 约12 (300℃, —) | [ |
| electrospinning and impregnation | — | 5.3 | 38.7 | 0.28 | 195 | 2 (200℃, 0.5 h) | [ |
| [14] | McKerracher R D, Guzman-Guemez J, Wills R G A, et al. Advances in prevention of thermal runaway in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy and Sustainability Research, 2021, 2(5): 2000059. |
| [15] | Zhu L M, Ding G C, Han Q, et al. Review—recent developments in safety-enhancing separators for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2021, 168(10): 100524. |
| [16] | Lagadec M F, Zahn R, Wood V. Characterization and performance evaluation of lithium-ion battery separators[J]. Nature Energy, 2019, 4: 16-25. |
| [17] | Zhang L P, Li X L, Yang M R, et al. High-safety separators for lithium-ion batteries and sodium-ion batteries: advances and perspective[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 41: 522-545. |
| [18] | Liu S L, Fan B, Shi Z, et al. High-safety lithium-ion battery separator with adjustable temperature function inspired by the sugar gourd structure[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(23): 30284-30295. |
| [19] | Park B J, Yu J S, Shin K, et al. Polysiloxane-coated PI nonwoven separators with higher thermal and electrochemical stability for lithium ion battery application[J]. Next Energy, 2024, 3: 100090. |
| [20] | Liu K, Liu Y Y, Lin D C, et al. Materials for lithium-ion battery safety[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(6): eaas9820. |
| [21] | Li X G, Liu K F, Yan Y, et al. Thermostable and nonflammable polyimide/zirconia compound separator for lithium-ion batteries with superior electrochemical and safe properties[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 625: 936-945. |
| [22] | Liao C, Wang W, Wang J L, et al. Magnetron sputtering deposition of silicon nitride on polyimide separator for high-temperature lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2021, 56: 1-10. |
| [23] | Liu J D, Cao D L, Yao H J, et al. Hexagonal boron nitride-coated polyimide ion track etched separator with enhanced thermal conductivity and high-temperature stability for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(7): 8639-8649. |
| [24] | Zhang Q Z, Chen L J, Li X L, et al. Robust, high-temperature-resistant polyimide separators with vertically aligned uniform nanochannels for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Nano, 2024, 18(46): 32162-32174. |
| [25] | Huang X X, Cheng S, Huang C, et al. Superspreading-based fabrication of thermostable nanoporous polyimide membranes for high safety separators of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Small, 2024, 20(27): 2311219. |
| [26] | Zhang M Y, Wang L, Xu H, et al. Polyimides as promising materials for lithium-ion batteries: a review[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2023, 15(1): 135. |
| [27] | Yu B, Chen X M, Jin X L, et al. Heat-resistant lithium-ion-battery separator using synchronous thermal stabilization/imidization[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2024, 6(5): 2464-2473. |
| [28] | Liu Q, Wang Z Y, Xie L L, et al. A polyimide separator inlaid by methylsilyl-modified silica aerogels for high thermal safety and low polarization lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 607: 234585. |
| [29] | Deng Y R, Pan Y L, Li C H, et al. Advanced polyimide separator via co-precursor method for lithium-ion batteries with low thermal runaway risks[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 56: 106100. |
| [30] | Gu J P, Zhang K Y, Li X T, et al. Construction of safety and non-flammable polyimide separator containing carboxyl groups for advanced fast charing lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 2022, 40(4): 345-354. |
| [31] | Deng J H, Cao D Q, Yang X Q, et al. Cross-linked cellulose/carboxylated polyimide nanofiber separator for lithium-ion battery application[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 433: 133934. |
| [32] | Liu Y, Li C, Li C X, et al. Porous, robust, thermally stable, and flame retardant nanocellulose/polyimide separators for safe lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11(43): 23360-23369. |
| [33] | Sun G H, Jiang S J, Feng X X, et al. Ultra-robust polyimide nanofiber separators with shutdown function for advanced lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2022, 645: 120208. |
| [34] | Yang K C, Liu Z L, Chai J C, et al. High performance polyimide-based separator for 4.5V high voltage LiCoO2 battery with superior safety[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 282: 125975. |
| [35] | Li M N, Wang K M, Shen F, et al. An electrolyte-locked thermally stable composite separator for safe lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 938: 168543. |
| [36] | Huang H T, Zhou Z X, Qian C, et al. Grafting polyethyleneimine-poly(ethylene glycol) gel onto a heat-resistant polyimide nanofiber separator for improving lithium-ion transporting ability in lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(25): 30913-30923. |
| [37] | Palanisamy M, Lin K W, Lo C T, et al. In situ thermal safety aspect of the electrospun polyimide-Al2O3 separator reveals less exothermic heat energies than polypropylene at the thermal runaway event of lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(24): 28310-28320. |
| [38] | Qiao M Y, Zhang G Q, Deng J H, et al. Electrospun polyimide@organic-montmorillonite composite separator with enhanced mechanical and thermal performances for high-safety lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2022, 57(25): 11796-11808. |
| [39] | Liu K F, Yang C Y, Li X G, et al. Controllable coaxial coating of boehmite on the surface of polyimide nanofiber membrane and its application as a separator for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Technology, 2022, 10(4): 2100982. |
| [40] | Dong N X, Wang J, Tian G F, et al. Inorganic-shell reinforcement: TiO2-coated polyimide nanofibers membrane as advanced separator for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2021, 167(16): 160560. |
| [41] | Deng J H, Cao D Q, Li L J, et al. Electrospun nanofiber separator derived from nano-SiO2-modified polyimide with superior mechanical flexibility for high-performance lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2021, 56(27): 15215-15228. |
| [42] | Zhou P L, Yao D X, Liang H Q, et al. Highly connective spongy polyimide separators blended with inorganic whiskers for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(2): 2011-2023. |
| [43] | Wang Y, Guo M H, Fu H, et al. Thermotolerant separator of cross-linked polyimide fibers with narrowed pore size for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2022, 662: 121004. |
| [44] | Gao X X, Sheng L, Li M L, et al. Flame-retardant nano-TiO2/polyimide composite separator for the safety of a lithium-ion battery[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2022, 4(7): 5125-5133. |
| [45] | Wu D Y, Dong N X, Wang R H, et al. In situ construction of high-safety and non-flammable polyimide “Ceramic” lithium-ion battery separator via SiO2 nano-encapsulation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 420: 129992. |
| [46] | Song X Y, Wang Z, Zhao F Z, et al. A separator with a novel thermal crosslinking structure based on electrospun PI/A-POSS for lithium-ion battery with high safety and outstanding electrochemical performance[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2021, 8(24): 2100458. |
| [47] | Li M L, Sheng L, Xu R, et al. Enhanced the mechanical strength of polyimide (PI) nanofiber separator via PAALi binder for lithium ion battery[J]. Composites Communications, 2021, 24: 100607. |
| [48] | Fu J Z, Wang H W, Du Z C, et al. A high-safety, flame-retardant cellulose-based separator with encapsulation structure for lithium-ion battery[J]. SmartMat, 2023, 4(5): e1182. |
| [49] | Liao C, Mu X W, Han L F, et al. A flame-retardant, high ionic-conductivity and eco-friendly separator prepared by papermaking method for high-performance and superior safety lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 48: 123-132. |
| [50] | Chen H Z, Wang Z C, Feng Y T, et al. Cellulose-based separators for lithium batteries: source, preparation and performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 471: 144593. |
| [51] | Wang L F, Wang Y R, Yang J, et al. An eco-friendly and flame-retardant bio-based fibers separator with fast lithium-ion transport towards high-safety lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 613: 234950. |
| [52] | Zhang S F, Luo J, Du M, et al. Safety and cycling stability enhancement of cellulose paper-based lithium-ion battery separator by aramid nanofibers[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2022, 171: 111222. |
| [53] | Zou Z H, Hu Z Y, Pu H T. Lithium-ion battery separators based-on nanolayer co-extrusion prepared polypropylene nanobelts reinforced cellulose[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 666: 121120. |
| [54] | Wang Z N, Hu M L, Yu X Y, et al. Uniform and porous nacre-like cellulose nanofibrils/nanoclay composite membrane as separator for highly safe and advanced Li-ion battery[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 637: 119622. |
| [55] | Liu Y, Li C X, Li C, et al. Highly thermally stable, highly electrolyte-wettable hydroxyapatite/cellulose nanofiber hybrid separators for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2023, 6(7): 3862-3871. |
| [56] | Liu J X, Qin D J, Chen K, et al. The preparation of intrinsic DOPO-Cinnamic flame-retardant cellulose and its application for lithium-ion battery separator[J]. Materials Research Express, 2021, 8(7): 076404. |
| [57] | Miao W W, Wang J X, Li G X, et al. Superior thermal stability of PVA/cellulose composite membranes for lithium-ion battery separators prepared by impregnation method with noncovalent cross-linking of intermolecular multiple hydrogen-bonds[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 66: 107353. |
| [58] | Delaporte N, Perea A, Paolella A, et al. Alumina-flame retardant separators toward safe high voltage Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 506: 230189. |
| [59] | Hu Y Q, Zhu G B, Zeng X Y, et al. Tissue paper-based composite separator using double-crosslinked polymer electrolyte as coating layer for lithium-ion battery with superior ion transport and cyclic stability[J]. Cellulose, 2023, 30(1): 247-261. |
| [60] | Huang J H, Jiang H, Wu F X, et al. Natural halloysite nanotubes coated commercial paper or waste newspaper as highly-thermal-stable separator for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials Technologies, 2022, 7(11): 2200075. |
| [61] | Raja M W, Basu R N, Pramanik N C, et al. Paperator: the paper-based ceramic separator for lithium-ion batteries and the process scale-up strategy[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(5): 5841-5854. |
| [62] | Das M, Das P S, Basu R N, et al. Cellulose-ceramic composite flexible paper separator with improved wettability and flame retardant properties for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Cellulose, 2022, 29(18): 9899-9917. |
| [63] | He X H, Wang J R, Zhong X Q, et al. Multifunctional separators with high safety and regulated ion transport for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2025, 626: 235794. |
| [64] | Zhang K, Chen H Z, Huang H Q, et al. Water-soluble ammonium polyphosphate synchronously enables mechanically robust and flame-retardant cellulose composite separator for high safety lithium batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 558: 232627. |
| [65] | Yang Y L, Chen Z L, Lv T, et al. Ultrafast self-assembly of supramolecular hydrogels toward novel flame-retardant separator for safe lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 649: 591-600. |
| [66] | Zhang S F, Luo J, Zhang F J, et al. A porous, mechanically strong and thermally stable zeolitic imidazolate framework-8@bacterial cellulose/aramid nanofibers composite separator for advanced lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2022, 652: 120461. |
| [67] | Das M, Das P S, Pramanik N C, et al. Advanced sustainable trilayer cellulosic “paper separator” functionalized with nano-BaTiO3 for applications in Li-ion batteries and supercapacitors[J]. ACS Omega, 2023, 8(23): 21315-21331. |
| [68] | Zeng X Y, Liu Y, He R L, et al. Tissue paper-based composite separator using nano-SiO2 hybrid crosslinked polymer electrolyte as coating layer for lithium ion battery with superior security and cycle stability[J]. Cellulose, 2022, 29(7): 3985-4000. |
| [69] | Gou J R, Liu W Y, Tang A M, et al. Interfacially stable and high-safety lithium batteries enabled by porosity engineering toward cellulose separators[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2022, 659: 120807. |
| [70] | Lv D, Chai J C, Wang P, et al. Pure cellulose lithium-ion battery separator with tunable pore size and improved working stability by cellulose nanofibrils[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 251: 116975. |
| [71] | Zhang Y, Yu L, Zhang X D, et al. A smart risk-responding polymer membrane for safer batteries[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(5): eade5802. |
| [72] | Hou Y, Huang Z D, Chen Z, et al. Bifunctional separators design for safe lithium-ion batteries: suppressed lithium dendrites and fire retardance[J]. Nano Energy, 2022, 97: 107204. |
| [73] | Yuan B T, Feng Y H, Qiu X H, et al. A safe separator with heat-dispersing channels for high-rate lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(9): 2308929. |
| [74] | Parsaei S, Zebarjad S M, Moghim M H. Fabrication and post-processing of PI/PVDF-HFP/PI electrospun sandwich separators for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2022, 62(11): 3641-3651. |
| [75] | Kim T. Multifunctional separator enabled by a high phosphorus content additive for Ni-rich transition metal oxide batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2023, 6(20): 10487-10498. |
| [76] | Han C Y, Cao Y, Zhang S J, et al. Separator with nitrogen-phosphorus flame-retardant for LiNi x Co y Mn1- x- y O2 cathode-based lithium-ion batteries[J]. Small, 2023, 19(26): 2207453. |
| [77] | Long M C, Duan P H, Gao Y, et al. Boosting safety and performance of lithium-ion battery enabled by cooperation of thermotolerant fire-retardant composite membrane and nonflammable electrolyte[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 432: 134394. |
| [78] | Zhao Q, Wu X L, Li S H, et al. Boosting thermal and mechanical properties: achieving high-safety separator chemically bonded with nano TiN particles for high performance lithium‐ion batteries[J]. Small, 2023, 19(30): 2300378. |
| [79] | Zhao Q, Ma L, Xu Y, et al. An upgraded polymeric composite with interparticle chemical bonding microstructure toward lithium-ion battery separators with enhanced safety and electrochemical performances[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023, 84: 402-413. |
| [80] | Li J M, Meng D Y, Xiao P D. Multi-functional membrane for air-proof and high temperature-stable Li metal batteries[J]. ChemElectroChem, 2023, 10(4): e202200983. |
| [81] | Zhou P L, Yao D X, Zuo K H, et al. Highly dispersible silicon nitride whiskers in asymmetric porous separators for high-performance lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 621: 119001. |
| [82] | Liu X T, Wu Y N, Yang F, et al. An effective dual-channel strategy for preparation of polybenzimidazole separator for advanced-safety and high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 626: 119190. |
| [83] | Liu M C, Chen H J, Wu G, et al. Multifunctional robust aerogel separator towards high-temperature, large-rate, long-cycle lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2023, 34(5): 107546. |
| [84] | Chen J H, Kang T X, Cui Y, et al. A nonflammable and thermally stable polyethylene/glass fiber-magnesium hydroxide/polyethylene composite separator with high mechanical strength and electrolyte retention to enhance the performance of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Energy Technology, 2022, 10(3): 2101040. |
| [85] | Hu X, Li Y H, Chen Z, et al. Facile fabrication of PMIA composite separator with bi-functional sodium-alginate coating layer for synergistically increasing performance of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 648: 951-962. |
| [86] | Yu Y, Jia G S, Zhao L, et al. Flexible and heat-resistant polyphenylene sulfide ultrafine fiber hybrid separators for high-safety lithium-ion batteries[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452: 139112. |
| [87] | Min Y, Guo L, Wei G Y, et al. Enhancing the safety and cyclic performance of lithium-ion batteries using heat resistant and wettable separator based on covalent organic framework and polybenzimidazole[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 443: 136480. |
| [88] | Min Y, Liu T D, Zhang B, et al. Inhibition of lithium dendrite growth by high-thermal-stability separator containing sulfonated covalent organic frameworks and polybenzimidazole[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 677: 121617. |
| [89] | Parekh M H, Oka S, Lutkenhaus J, et al. Critical-point-dried, porous, and safer aramid nanofiber separator for high-performance durable lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(25): 29176-29187. |
| [90] | Zhang S F, Luo J, Zhang F J, et al. Highly porous and thermally stable zeolitic imidazolate framework-8/aramid nanofibers composite separator for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Composites Communications, 2022, 32: 101183. |
| [91] | Liu X, Qin M H, Sun W, et al. Study on cellulose nanofibers/aramid fibers lithium-ion battery separators by the heterogeneous preparation method[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2023, 225: 1476-1486. |
| [92] | Tang W, Liu Q Q, Luo N, et al. High safety and electrochemical performance electrospun para-aramid nanofiber composite separator for lithium-ion battery[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2022, 225: 109479. |
| [93] | Chafi F Z, Qi R X, Ma L J, et al. Thermosetting high-rate and high-safety polymer/inorganic composite separator for lithium-ion battery through a fast scalable photo cross-linking process[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2021, 35(22): 18746-18755. |
| [94] | Hu X, Li Y H, Chen Z, et al. Anchoring porous F-TiO2 particles by directed-assembly on PMIA separators for enhancing safety and electrochemical performances of Li-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2023, 443: 141926. |
| [95] | Kim M, Hong S Y, Bang J, et al. Highly sustainable polyphenylene sulfide membrane of tailored porous architecture for high-performance lithium-ion battery applications[J]. Materials Today Advances, 2021, 12: 100186. |
| [96] | Hu Y Q, Zhu G B, Wang C, et al. Poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-induced 3D crosslinked network constructed on polyphenylene sulfide nonwoven as a battery separator: effect of generation number on cell performance[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 663: 131100. |
| [97] | Zhu C Q, Zhang J X, Qiu S Y, et al. Tailoring the pore size of polyphenylene sulfide nonwoven with bacterial cellulose (BC) for heat-resistant and high-wettability separator in lithium-ion battery[J]. Composites Communications, 2021, 24: 100659. |
| [98] | Lin G, Bai Z X, Liu C C, et al. Mechanically robust, nonflammable and surface cross-linking composite membranes with high wettability for dendrite-proof and high-safety lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2022, 647: 120262. |
| [99] | Lin G, Cao T, Bai Z X, et al. Poly(arylene ether nitrile) porous membranes with adjustable pore size for high temperature resistance and high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2021, 324: 111276. |
| [100] | Ding L Y, Yue X Y, Zhang X H, et al. A polyimine aerogel separator with electron cloud design to boost Li-ion transport for stable Li metal batteries[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2023, 120(51): e2314264120. |
| [101] | Hu W Q, Fu W B, Jhulki S, et al. Heat-resistant Al2O3 nanowire-polyetherimide separator for safer and faster lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023, 142: 112-120. |
| [102] | Dai X K, Yu F S, Wen J W, et al. Robust and high-wettability pristine poly(ether ether ketone) nanofiber separator for heat-resistant and safe lithium-ion battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 2023, 41(12): 1937-1946. |
| [103] | Gu J Y, Feng Y T, Wei X, et al. Flexible fibrous separator asymmetrically coated by silica and MXene for high performance lithium batteries with enhanced safety[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 581: 233515. |
| [104] | Thiangtham S, Saito N, Manuspiya H. Asymmetric porous and highly hydrophilic sulfonated cellulose/biomembrane functioning as a separator in a lithium-ion battery[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(5): 6206-6218. |
| [105] | Xian D X, Min Y, Liu T D, et al. Effective strategy to improve safety of lithium-ion batteries by constructing ion transport modes and employing a cross-linking structure in the separator[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2023, 6(18): 9716-9725. |
| [106] | Min Y, Liu X T, Guo L, et al. Construction of diversified ion channels in lithium-ion battery separator using polybenzimidazole and ion-modified metal-organic framework[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(7): 9131-9140. |
| [107] | Chen J H, Kang T X, Cui Y, et al. Nonflammable and thermally stable glass fiber/polyacrylate (GFP) separator for lithium-ion batteries with enhanced safety and lifespan[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2021, 496: 229862. |
| [108] | Song Y H, Zhao G L, Zhang S H, et al. Chitosan nanofiber paper used as separator for high performance and sustainable lithium-ion batteries[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2024, 329: 121530. |
| [109] | Wang Y R, Fang T M, Wang S Y, et al. Alginate fiber-grafted polyetheramine-driven high ion-conductive and flame-retardant separator and solid polymer electrolyte for lithium metal batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(51): 56780-56789. |
| [110] | Liu Y J, Wu Y X, Zheng J L, et al. Silicious nanowires enabled dendrites suppression and flame retardancy for advanced lithium metal anodes[J]. Nano Energy, 2021, 82: 105723. |
| [111] | Li D Z, Wang H, Luo L B, et al. Electrospun separator based on sulfonated polyoxadiazole with outstanding thermal stability and electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2021, 4(1): 879-887. |
| [112] | Huang Z H, Chen J M, Huo Y P, et al. Heat resistant microporous membranes based on soluble poly(aryl ether ketone) copolymers for lithium ion battery separator[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2021, 138(35): 50895. |
| [113] | Hu W, Liang X X, Yang X, et al. Sulfophenylated poly (ether ether ketone ketone) nanofiber composite separator with excellent electrochemical performance and dimensional thermal stability for lithium-ion battery via electrospinning[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2021, 306(7): 2100118. |
| [1] | Xu J J, Cai X Y, Cai S M, et al. High‐energy lithium‐ion batteries: recent progress and a promising future in applications[J]. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2023, 6(5): e12450. |
| [2] | Shahjalal M, Roy P K, Shams T, et al. A review on second-life of Li-ion batteries: prospects, challenges, and issues[J]. Energy, 2022, 241: 122881. |
| [3] | Wulandari T, Fawcett D, Majumder S B, et al. Lithium‐based batteries, history, current status, challenges, and future perspectives[J]. Battery Energy, 2023, 2(6): 20230030. |
| [4] | 曹宇, 张国辉, 高昂, 等. 二维MXene材料在太阳能电池和金属离子电池中的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 412-428. |
| Cao Y, Zhang G H, Gao A, et al. Research progress of two-dimensional MXene materials in solar cells and metal-ion batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 412-428. | |
| [5] | Wang N M, Tang G W. A review on environmental efficiency evaluation of new energy vehicles using life cycle analysis[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(6): 3371. |
| [6] | Xia X N, Li P W. A review of the life cycle assessment of electric vehicles: considering the influence of batteries[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 814: 152870. |
| [7] | Rangarajan S S, Sunddararaj S P, Sudhakar A, et al. Lithium-ion batteries—the crux of electric vehicles with opportunities and challenges[J]. Clean Technologies, 2022, 4(4): 908-930. |
| [8] | Yang Y, Wang R J, Shen Z J, et al. Towards a safer lithium-ion batteries: a critical review on cause, characteristics, warning and disposal strategy for thermal runaway[J]. Advances in Applied Energy, 2023, 11: 100146. |
| [9] | 刘邦金, 汪林威, 吴月月, 等. 锂离子电池热管理研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(12): 4413-4431. |
| Liu B J, Wang L W, Wu Y Y, et al. Advances in thermal management of lithium-ion batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(12): 4413-4431. | |
| [10] | Lingappan N, Lee W, Passerini S, et al. A comprehensive review of separator membranes in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2023, 187: 113726. |
| [11] | Tong B L, Li X F. Towards separator safety of lithium-ion batteries: a review[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2024, 8(2): 309-340. |
| [12] | 王振华, 彭代冲, 孙克宁. 锂离子电池隔膜材料研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(1): 282-294. |
| Wang Z H, Peng D C, Sun K N. Research progress of separator materials for lithium ion batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(1): 282-294. | |
| [13] | Mallick S, Gayen D. Thermal behaviour and thermal runaway propagation in lithium-ion battery systems—a critical review[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 62: 106894. |
| [1] | Ziyang LI, Peixin SHEN, Xiao'a ZHANG, Chengzhong WANG, Ling SHI, Junying ZHANG. Synthesis and thermal stability of α, ω-hydroxy-terminated phenyl/phenylene-containing polysiloxanes with high vinyl content [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 3041-3052. |
| [2] | Xin LIU, Haoren ZHENG, Qiang CHEN, Jingyi DING, Kang HUANG, Zhi XU. Cellulose nanocrystals-doped hybrid matrix membranes for vanadium flow battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2294-2303. |
| [3] | Hongbin NIU, Li QIU, Jingxuan YANG, Zhonglin ZHANG, Xiaogang HAO, Zhongkai ZHAO, Abuliti ABUDULA, Guoqing GUAN. Effect of cylinder diameter on cyclone performance and its flow field mechanism [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2367-2376. |
| [4] | Jiashun LI, Wang LI, Zuzeng QIN, Tongming SU, Xinling XIE, Hongbing JI. Preparation of polyimide-reinforced lignocellulosic nanofibril aerogel and its oil-water separation performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2169-2185. |
| [5] | Jiayuan FAN, Wenhui ZENG, Zhichao REN, Wentao ZHANG, Shuang LYU. Preparation and heat transfer enhancement of phase change slurry with multi-phase change temperature [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(4): 1863-1874. |
| [6] | Siwen ZHANG, Haiming GU, Shanhui ZHAO. Molecular mechanism study on chemical looping gasification of cellulose over iron oxide nanocluster [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 363-373. |
| [7] | Jijun ZOU, Baohong LIU, Chengxiang SHI, Lun PAN, Xiangwen ZHANG. Research progress of heterogeneous catalysts for conversion of holocellulose derivatives into bio-aviation fuels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 1-17. |
| [8] | Wuling ZHAO, Yi MAN. Research on framework of nanocellulose molecular structure prediction model based on variational encoder [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3221-3230. |
| [9] | Dan PENG, Junjie LU, Wenjing NI, Yuan YANG, Jinglun WANG. Research progress of functional electrolyte for high-voltage LiCoO2 battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3028-3040. |
| [10] | Xianggang ZHANG, Yulong CHANG, Hualin WANG, Xia JIANG. Low energy consumption non-phase change second drying of waste straw and other biomass [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2433-2445. |
| [11] | Wenya WANG, Wei ZHANG, Xiaoling LOU, Ruofei ZHONG, Bingbing CHEN, Junxian YUN. Multi-microtubes formation and simulation of nanocellulose-embedded cryogel microspheres [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 2060-2071. |
| [12] | Zijia ZHANG, Xinyue QIU, Xiang SUN, Zhibin LUO, Haizhong LUO, Gaohong HE, Xuehua RUAN. Progress in molecular structure design for polyimide membrane materials to enhance CO2 permeation ability [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1137-1152. |
| [13] | Bangjun GUO, Linan JIA, Xi ZHANG. A review of NCM cathode and interface characteristics in all-solid-state lithium-ion battery with sulfide electrolytes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 743-759. |
| [14] | Xiangfei DING, Xiaolin QIU, Xicheng ZHU, Jiawei ZHANG, Jinhua CHEN. Preparation and properties of pH-responsive gas permeable CNC/PBAT composite membranes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 1040-1051. |
| [15] | Mingqing TAO, Minghao MU, Teng CHENG, Bo WANG. Research on spray coupled cooling to enhance the removal of fine particles by cyclone separator [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 584-592. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||