CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (9): 4613-4629.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250145
• Special Column: Modeling and Simulation in Process Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Xu GUO( ), Jining JIA, Kejian YAO(
), Jining JIA, Kejian YAO( )
)
Received:2025-02-17
Revised:2025-04-14
Online:2025-10-23
Published:2025-09-25
Contact:
Kejian YAO
通讯作者:
姚克俭
作者简介:郭旭(1999—),男,硕士研究生,zjutGuox@outlook.com
CLC Number:
Xu GUO, Jining JIA, Kejian YAO. Modeling of batch distillation process based on optimized CNN-BiLSTM neural network[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4613-4629.
郭旭, 贾继宁, 姚克俭. 基于优化CNN-BiLSTM神经网络的间歇精馏过程建模[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4613-4629.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 色谱柱温度/℃ | 180 |
| 进样口温度/℃ | 180 |
| 热导池温度/℃ | 200 |
| 桥电流/mA | 110 |
| 氢气压力/MPa | 0.01 |
| 进样体积/μl | 1 |
| 色谱柱类型 | Porapak-Q |
Table 1 Operating parameters for FULI GC9790Ⅱ gas chromatograph
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 色谱柱温度/℃ | 180 |
| 进样口温度/℃ | 180 |
| 热导池温度/℃ | 200 |
| 桥电流/mA | 110 |
| 氢气压力/MPa | 0.01 |
| 进样体积/μl | 1 |
| 色谱柱类型 | Porapak-Q |
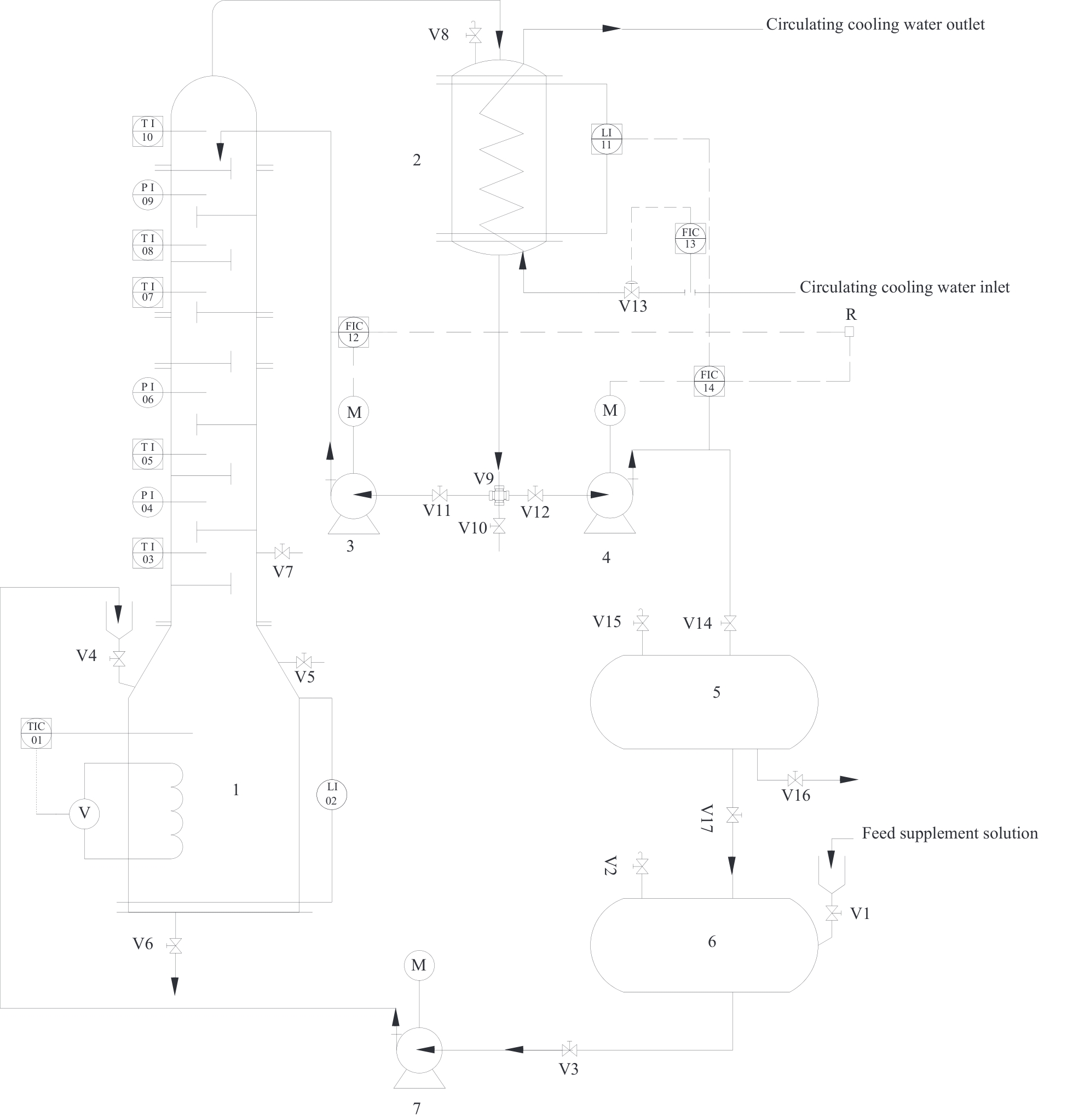
Fig.1 Process flow diagram for batch distillation1—reboiler; 2—reflux drum; 3—reflux pump; 4—distillate pump; 5—distillate storage tank; 6—feed storage tank; 7—feeding pump; V—electric heating switch; PI—pressure indicator; TI—temperature indicator; M—metering pump motor; V1—V17—control valves; LI—level indicator; R—reflux ratio controller; FIC—flow controller; TIC—temperature controller
| 批次 | 加热功率/kW | 原料乙醇质量分数 | 回流比 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.75~2.50 | 0.429 | 1.0 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.6 L/h |
| 2 | 1.70~2.50 | 0.492 | 1.0 | |
| 3 | 1.65~2.50 | 0.589 | 1.0 | |
| 4 | 1.70~2.50 | 0.652 | 1.0 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 5 | 1.73~2.50 | 0.490 | 1.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.6 L/h |
| 6 | 1.70~2.50 | 0.590 | 1.5 | |
| 7 | 1.75~2.25 | 0.650 | 1.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 8 | 1.75~2.50 | 0.493 | 2.0 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.6 L/h |
| 9 | 1.70~2.50 | 0.592 | 2.0 | |
| 10 | 1.78~2.25 | 0.654 | 2.0 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 11 | 1.77~2.50 | 0.486 | 2.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.6 L/h |
| 12 | 1.72~2.50 | 0.614 | 2.5 | |
| 13 | 1.75~2.25 | 0.685 | 2.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 14 | 2.0~2.25 | 0.674 | 2.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为8.5 L/h |
| 15 | 1.65~2.50 | 0.683 | 2.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.6 L/h |
| 16 | 1.80~2.25 | 0.677 | 3.0 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 17 | 1.75~2.50 | 0.726 | 3.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 18 | 1.60~2.50 | 0.483 | 3.3 | 恒定回流比生产操作,调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.0 L/h |
| 19 | 1.60~2.50 | 0.463 | 1.0 ~ 3.0 | 阶跃回流比生产操作,调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.0 L/h |
Table 2 Explanation of operating conditions for each batch of data
| 批次 | 加热功率/kW | 原料乙醇质量分数 | 回流比 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.75~2.50 | 0.429 | 1.0 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.6 L/h |
| 2 | 1.70~2.50 | 0.492 | 1.0 | |
| 3 | 1.65~2.50 | 0.589 | 1.0 | |
| 4 | 1.70~2.50 | 0.652 | 1.0 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 5 | 1.73~2.50 | 0.490 | 1.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.6 L/h |
| 6 | 1.70~2.50 | 0.590 | 1.5 | |
| 7 | 1.75~2.25 | 0.650 | 1.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 8 | 1.75~2.50 | 0.493 | 2.0 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.6 L/h |
| 9 | 1.70~2.50 | 0.592 | 2.0 | |
| 10 | 1.78~2.25 | 0.654 | 2.0 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 11 | 1.77~2.50 | 0.486 | 2.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.6 L/h |
| 12 | 1.72~2.50 | 0.614 | 2.5 | |
| 13 | 1.75~2.25 | 0.685 | 2.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 14 | 2.0~2.25 | 0.674 | 2.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为8.5 L/h |
| 15 | 1.65~2.50 | 0.683 | 2.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.6 L/h |
| 16 | 1.80~2.25 | 0.677 | 3.0 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 17 | 1.75~2.50 | 0.726 | 3.5 | 调节加热功率使蒸汽率为6.5 L/h |
| 18 | 1.60~2.50 | 0.483 | 3.3 | 恒定回流比生产操作,调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.0 L/h |
| 19 | 1.60~2.50 | 0.463 | 1.0 ~ 3.0 | 阶跃回流比生产操作,调节加热功率使蒸汽率为5.0 L/h |
| 序号 | 特征 | MIC | 特征 | MIC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y1 | X | Y2 | |||
| 1 | 塔釜温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.3 | 塔釜温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.7 |
| 2 | 塔节一温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.3 | 塔节一温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.7 |
| 3 | 塔节三温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.5 | 塔节三温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.4 |
| 4 | 塔节五温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.7 | 塔节五温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.2 |
| 5 | 塔节六温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.5 | 塔节六温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.2 |
| 6 | 塔顶温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 塔顶温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.2 |
| 7 | 产品温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 产品温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 8 | 冷凝水流量 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.08 | 冷凝水流量 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 9 | 馏出液体积 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.2 | 馏出液体积 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.2 |
| 10 | 原料浓度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 原料浓度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.2 |
| 11 | 回流比 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 回流比 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 12 | 塔釜液位 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.2 | 塔釜液位 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.4 |
| 13 | 塔釜压力 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 塔釜压力 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 14 | 塔节二压力 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 塔节二压力 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 15 | 塔节四压力 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.5 | 塔节四压力 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 16 | 塔节七压力 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 塔节七压力 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
Table 3 MIC values of input variables for ethanol prediction in the distillate and tower bottom
| 序号 | 特征 | MIC | 特征 | MIC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X | Y1 | X | Y2 | |||
| 1 | 塔釜温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.3 | 塔釜温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.7 |
| 2 | 塔节一温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.3 | 塔节一温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.7 |
| 3 | 塔节三温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.5 | 塔节三温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.4 |
| 4 | 塔节五温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.7 | 塔节五温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.2 |
| 5 | 塔节六温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.5 | 塔节六温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.2 |
| 6 | 塔顶温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 塔顶温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.2 |
| 7 | 产品温度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 产品温度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 8 | 冷凝水流量 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.08 | 冷凝水流量 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 9 | 馏出液体积 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.2 | 馏出液体积 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.2 |
| 10 | 原料浓度 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 原料浓度 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.2 |
| 11 | 回流比 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 回流比 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 12 | 塔釜液位 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.2 | 塔釜液位 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.4 |
| 13 | 塔釜压力 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 塔釜压力 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 14 | 塔节二压力 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 塔节二压力 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 15 | 塔节四压力 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.5 | 塔节四压力 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 16 | 塔节七压力 | 馏出液乙醇浓度 | 0.4 | 塔节七压力 | 塔釜乙醇浓度 | 0.1 |
| 模型 | 训练次数 | 学习速率 | 阈值 | 正则化参数 | 学习率下降因子 | 学习率下降开始迭代次数 | 最小输入批次 | 时间步长 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP | 1000 | 0.001 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| SVR | — | — | 0.0001 | 10 | — | — | — | — |
| LSTM | 1000 | 0.001 | — | — | 0.01 | 400 | 100 | 4 |
| BiLSTM | 1000 | 0.001 | — | — | 0.01 | 400 | 100 | 4 |
| CNN-BiLSTM | 1000 | 0.001 | — | — | 0.01 | 400 | 100 | 4 |
Table 4 Training parameters of different models
| 模型 | 训练次数 | 学习速率 | 阈值 | 正则化参数 | 学习率下降因子 | 学习率下降开始迭代次数 | 最小输入批次 | 时间步长 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP | 1000 | 0.001 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| SVR | — | — | 0.0001 | 10 | — | — | — | — |
| LSTM | 1000 | 0.001 | — | — | 0.01 | 400 | 100 | 4 |
| BiLSTM | 1000 | 0.001 | — | — | 0.01 | 400 | 100 | 4 |
| CNN-BiLSTM | 1000 | 0.001 | — | — | 0.01 | 400 | 100 | 4 |
| 折编号 | 训练集批次 | 验证集批次 | 验证集样本数 | 训练集总样本数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1折 | 4~17 | 1~3 | 71 | 530 |
| 第2折 | 1~3 & 7~17 | 4~6 | 79 | 530 |
| 第3折 | 1~6 & 10~17 | 7~9 | 108 | 530 |
| 第4折 | 1~9 & 13~17 | 10~12 | 99 | 530 |
| 第5折 | 1~12 & 16~17 | 13~15 | 90 | 530 |
| 第6折 | 1~15 | 16~17 | 68 | 530 |
Table 5 Explanation of six-fold cross-validation on the training set
| 折编号 | 训练集批次 | 验证集批次 | 验证集样本数 | 训练集总样本数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第1折 | 4~17 | 1~3 | 71 | 530 |
| 第2折 | 1~3 & 7~17 | 4~6 | 79 | 530 |
| 第3折 | 1~6 & 10~17 | 7~9 | 108 | 530 |
| 第4折 | 1~9 & 13~17 | 10~12 | 99 | 530 |
| 第5折 | 1~12 & 16~17 | 13~15 | 90 | 530 |
| 第6折 | 1~15 | 16~17 | 68 | 530 |
| 算法 | ISAO算法 |
|---|---|
| 输入 | 种群个数N,维度dim,测试函数fobj,迭代总次数tmax,迭代次数t |
| 输出 | 适应度值 |
| Begin | 初始化:生成种群X |
| 1. | while (t<tmax)do |
| 2. | For N do |
| 3. | 通过SAO算法计算种群个体的位置并计算适应度值 |
| 4. | 规范种群个体的边界 |
| 5. | 通过本文提出的位置更新策略更新个体位置并评估其适应度值 |
| 6. | if 新适应度值小于旧适应度值 |
| 7. | 新适应度所对应的种群个体将替代旧种群个体 |
| 8. | End if |
| 9. | End for |
| 10. | 更新精英池 |
| 11. | t=t+1 |
| 12. | End while |
| End |
Table 6 Pseudocode of the ISAO algorithm[24]
| 算法 | ISAO算法 |
|---|---|
| 输入 | 种群个数N,维度dim,测试函数fobj,迭代总次数tmax,迭代次数t |
| 输出 | 适应度值 |
| Begin | 初始化:生成种群X |
| 1. | while (t<tmax)do |
| 2. | For N do |
| 3. | 通过SAO算法计算种群个体的位置并计算适应度值 |
| 4. | 规范种群个体的边界 |
| 5. | 通过本文提出的位置更新策略更新个体位置并评估其适应度值 |
| 6. | if 新适应度值小于旧适应度值 |
| 7. | 新适应度所对应的种群个体将替代旧种群个体 |
| 8. | End if |
| 9. | End for |
| 10. | 更新精英池 |
| 11. | t=t+1 |
| 12. | End while |
| End |
| 项目 | 评价指标 | BP | SVR | LSTM | BiLSTM | CNN-BiLSTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 馏出液乙醇质量分数 | RMSE | 0.125 | 0.127 | 0.108 | 0.106 | 0.0677 |
| MAE | 0.0535 | 0.0529 | 0.0454 | 0.0425 | 0.0321 | |
| R2 | 0.751 | 0.746 | 0.822 | 0.863 | 0.956 | |
| 塔釜乙醇质量分数 | RMSE | 0.0649 | 0.0954 | 0.0539 | 0.0472 | 0.0250 |
| MAE | 0.0326 | 0.0477 | 0.0221 | 0.0196 | 0.0163 | |
| R2 | 0.917 | 0.899 | 0.949 | 0.969 | 0.983 |
Table 7 The average value of evaluation metrics of the training set on six-fold cross-validation for different models
| 项目 | 评价指标 | BP | SVR | LSTM | BiLSTM | CNN-BiLSTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 馏出液乙醇质量分数 | RMSE | 0.125 | 0.127 | 0.108 | 0.106 | 0.0677 |
| MAE | 0.0535 | 0.0529 | 0.0454 | 0.0425 | 0.0321 | |
| R2 | 0.751 | 0.746 | 0.822 | 0.863 | 0.956 | |
| 塔釜乙醇质量分数 | RMSE | 0.0649 | 0.0954 | 0.0539 | 0.0472 | 0.0250 |
| MAE | 0.0326 | 0.0477 | 0.0221 | 0.0196 | 0.0163 | |
| R2 | 0.917 | 0.899 | 0.949 | 0.969 | 0.983 |
| 项目 | 批次 | 指标 | BP | SVR | LSTM | BiLSTM | CNN-BiLSTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 馏出液乙醇质量分数 | 18 | RMSE | 0.00850 | 0.00850 | 0.00470 | 0.00470 | 0.00610 |
| 18 | MAE | 0.00670 | 0.00670 | 0.00380 | 0.00420 | 0.00530 | |
| 18 | R2 | 0.159 | 0.149 | 0.745 | 0.741 | 0.566 | |
| 19 | RMSE | 0.0207 | 0.0214 | 0.0139 | 0.0131 | 0.00540 | |
| 19 | MAE | 0.0198 | 0.0206 | 0.0130 | 0.0122 | 0.00460 | |
| 19 | R2 | -16.772 | -17.983 | -6.986 | -6.098 | 0.208 | |
| 塔釜乙醇质量分数 | 18 | RMSE | 0.0415 | 0.0486 | 0.0333 | 0.0173 | 0.0165 |
| 18 | MAE | 0.0385 | 0.0472 | 0.0315 | 0.0145 | 0.0141 | |
| 18 | R2 | 0.852 | 0.798 | 0.905 | 0.971 | 0.974 | |
| 19 | RMSE | 0.0338 | 0.0420 | 0.0307 | 0.0278 | 0.0258 | |
| 19 | MAE | 0.0251 | 0.0347 | 0.0283 | 0.0236 | 0.0216 | |
| 19 | R2 | 0.874 | 0.805 | 0.896 | 0.915 | 0.927 |
Table 8 Test results of two batches of test set data on different neural network models
| 项目 | 批次 | 指标 | BP | SVR | LSTM | BiLSTM | CNN-BiLSTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 馏出液乙醇质量分数 | 18 | RMSE | 0.00850 | 0.00850 | 0.00470 | 0.00470 | 0.00610 |
| 18 | MAE | 0.00670 | 0.00670 | 0.00380 | 0.00420 | 0.00530 | |
| 18 | R2 | 0.159 | 0.149 | 0.745 | 0.741 | 0.566 | |
| 19 | RMSE | 0.0207 | 0.0214 | 0.0139 | 0.0131 | 0.00540 | |
| 19 | MAE | 0.0198 | 0.0206 | 0.0130 | 0.0122 | 0.00460 | |
| 19 | R2 | -16.772 | -17.983 | -6.986 | -6.098 | 0.208 | |
| 塔釜乙醇质量分数 | 18 | RMSE | 0.0415 | 0.0486 | 0.0333 | 0.0173 | 0.0165 |
| 18 | MAE | 0.0385 | 0.0472 | 0.0315 | 0.0145 | 0.0141 | |
| 18 | R2 | 0.852 | 0.798 | 0.905 | 0.971 | 0.974 | |
| 19 | RMSE | 0.0338 | 0.0420 | 0.0307 | 0.0278 | 0.0258 | |
| 19 | MAE | 0.0251 | 0.0347 | 0.0283 | 0.0236 | 0.0216 | |
| 19 | R2 | 0.874 | 0.805 | 0.896 | 0.915 | 0.927 |
| 项目 | 批次 | 指标 | CNN-BiLSTM | SAO-CNN-BiLSTM | ISAO-CNN-BiLSTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 馏出液乙醇质量分数 | 18 | RMSE | 0.00610 | 0.00540 | 0.000900 |
| 18 | MAE | 0.00530 | 0.00440 | 0.000700 | |
| 18 | R2 | 0.255 | 0.566 | 0.981 | |
| 19 | RMSE | 0.0129 | 0.00170 | 0.00110 | |
| 19 | MAE | 0.0100 | 0.00120 | 0.00100 | |
| 19 | R2 | 0.193 | 0.811 | 0.998 | |
| 塔釜乙醇质量分数 | 18 | RMSE | 0.0165 | 0.0125 | 0.00290 |
| 18 | MAE | 0.0141 | 0.0118 | 0.00250 | |
| 18 | R2 | 0.974 | 0.986 | 0.999 | |
| 19 | RMSE | 0.0258 | 0.00940 | 0.00350 | |
| 19 | MAE | 0.0216 | 0.00710 | 0.00240 | |
| 19 | R2 | 0.927 | 0.985 | 0.998 |
Table 9 Comparison of model evaluation metrics
| 项目 | 批次 | 指标 | CNN-BiLSTM | SAO-CNN-BiLSTM | ISAO-CNN-BiLSTM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 馏出液乙醇质量分数 | 18 | RMSE | 0.00610 | 0.00540 | 0.000900 |
| 18 | MAE | 0.00530 | 0.00440 | 0.000700 | |
| 18 | R2 | 0.255 | 0.566 | 0.981 | |
| 19 | RMSE | 0.0129 | 0.00170 | 0.00110 | |
| 19 | MAE | 0.0100 | 0.00120 | 0.00100 | |
| 19 | R2 | 0.193 | 0.811 | 0.998 | |
| 塔釜乙醇质量分数 | 18 | RMSE | 0.0165 | 0.0125 | 0.00290 |
| 18 | MAE | 0.0141 | 0.0118 | 0.00250 | |
| 18 | R2 | 0.974 | 0.986 | 0.999 | |
| 19 | RMSE | 0.0258 | 0.00940 | 0.00350 | |
| 19 | MAE | 0.0216 | 0.00710 | 0.00240 | |
| 19 | R2 | 0.927 | 0.985 | 0.998 |
| [1] | 梁昕. 间歇精馏技术的优化综述[J]. 山东化工, 2016, 45(6): 41-42, 45. |
| Liang X. Summary of batch distillation technology optimization[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(6): 41-42, 45. | |
| [2] | Zavala-Loría J C, Narváez-García A. Batch Distillation: Thermodynamic Efficiency[M]. Rijeka: IntechOpen, 2012: 92-106. |
| [3] | 杨海荣, 薄翠梅, 陆爱晶, 等. 间歇精馏过程变回流比智能控制策略的研究[J]. 化工自动化及仪表, 2008, 35(1): 12-16. |
| Yang H R, Bo C M, Lu A J, et al. Study on variable reflux ratio intelligent control strategy for batch distillation process[J]. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry, 2008, 35(1): 12-16. | |
| [4] | Karacan S. Application of a non-linear long range predictive control to a packed distillation column[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 2003, 42(12): 943-953. |
| [5] | Henson M A. Nonlinear model predictive control: current status and future directions[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 1998, 23(2): 187-202. |
| [6] | 孙志军, 薛磊, 许阳明, 等. 深度学习研究综述[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2012, 29(8): 2806-2810. |
| Sun Z J, Xue L, Xu Y M, et al. Overview of deep learning[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2012, 29(8): 2806-2810. | |
| [7] | Karacan S, Hapoǧlu H, Alpbaz M. Application of optimal adaptive generalized predictive control to a packed distillation column[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2001, 84(3): 389-396. |
| [8] | Alpbaz M, Karacan S, Cabbar Y, et al. Application of model predictive control and dynamic analysis to a pilot distillation column and experimental verification[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2002, 88(1/2/3): 163-174. |
| [9] | 陈锐, 贾继宁, 姚克俭. 基于优化BP神经网络的非稳态精馏过程建模[J]. 化学工程, 2023, 51(10): 83-88. |
| Chen R, Jia J N, Yao K J. Modeling of unsteady distillation process based on optimized BP neural network[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2023, 51(10): 83-88. | |
| [10] | Gu J X, Wang Z H, Kuen J, et al. Recent advances in convolutional neural networks[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 77: 354-377. |
| [11] | Zrira N, Kamal-Idrissi A, Farssi R, et al. Time series prediction of sea surface temperature based on BiLSTM model with attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 2024, 198: 102472 . |
| [12] | Wright L G, Onodera T, Stein M M, et al. Deep physical neural networks trained with backpropagation[J]. Nature, 2022, 601(7894): 549-555. |
| [13] | Kavousi-Fard A, Samet H, Marzbani F. A new hybrid modified firefly algorithm and support vector regression model for accurate short term load forecasting[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2014, 41(13): 6047-6056. |
| [14] | Zhang Q, Wang H, Dong J Yet al. Prediction of sea surface temperature using long short-term memory[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(10): 1745-1749. |
| [15] | Deng L Y, Liu S Y. Snow ablation optimizer: a novel metaheuristic technique for numerical optimization and engineering design[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 225: 120069. |
| [16] | Sun B, Li W, Huang Y. Performance of composite PPSO on single objective bound constrained numerical optimization problems of CEC 2022[C]//2022 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC). Padua, Italy: IEEE, 2022: 1-8. |
| [17] | Hu G, Guo Y X, Wei G, et al. Genghis Khan shark optimizer: a novel nature-inspired algorithm for engineering optimization[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2023, 58: 102210. |
| [18] | 董益斌, 熊敬超, 王敬宇, 等. 融合激光雷达料位测算的锅炉燃烧优化模型预测控制 [J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 924-935. |
| Dong Y B, Xiong J C, Wang J Y, et al. LiDAR measurement based on model predictive control for boiler combustion optimization[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 924-935. | |
| [19] | Wang Z C, Xu N N, Bao X G, et al. Spatio-temporal deep learning model for accurate streamflow prediction with multi-source data fusion[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2024, 178: 106091. |
| [20] | Schmidt-Hieber J. Nonparametric regression using deep neural networks with ReLU activation function[J]. The Annals of Statistics, 2020, 48(4): 1875-1897. |
| [21] | Elfwing S, Uchibe E, Doya K. Sigmoid-weighted linear units for neural network function approximation in reinforcement learning[J]. Neural Networks, 2018, 107: 3-11. |
| [22] | 王贺琦, 王然, 刘诗琳, 等. 基于Tent映射的改进型人工蜂群算法[J]. 软件工程, 2022, 25(8): 15-19. |
| Wang H Q, Wang R, Liu S L, et al. Modified artificial bee colony algorithm based on tent mapping[J]. Software Engineering, 2022, 25(8): 15-19. | |
| [23] | 刘三阳, 张晓伟. 混合差分变异策略[J]. 智能系统学报, 2008, 3(6): 487-491. |
| Liu S Y, Zhang X W. A hybrid strategy for differential variation[J]. Caai Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2008, 3(6): 487-491. | |
| [24] | 潘恒. 基于集成学习的个人信贷违约预测方法研究与应用[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2024. |
| Pan H. Research and application of personal credit default prediction method based on integrated learning[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2024. | |
| [25] | Nadimi-Shahraki M H, Zamani H, Asghari Varzaneh Z, et al. A systematic review of the whale optimization algorithm: theoretical foundation, improvements, and hybridizations[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 2023, 30: 4113-4159. |
| [26] | Shehadeh H A. Chernobyl disaster optimizer (CDO): a novel meta-heuristic method for global optimization[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2023, 35(15): 10733-10749. |
| [27] | Trojovský P, Dehghani M. Subtraction-average-based optimizer: a new swarm-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems[J]. Biomimetics, 2023, 8(2): 149. |
| [28] | Yue Y G, Cao L, Lu D W, et al. Review and empirical analysis of sparrow search algorithm[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2023, 56(10): 10867-10919. |
| [29] | Wang D S, Tan D P, Liu L. Particle swarm optimization algorithm: an overview[J]. Soft Computing, 2018, 22(2): 387-408. |
| [30] | Xie J Y, He J C, Gao Z H, et al. An enhanced snow ablation optimizer for UAV swarm path planning and engineering design problems[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(18): e37819. |
| [1] | Biao FENG, Zhao ZHANG, Siqi LI, Bingrui WANG, Hongying WU, Miao SHI, Dan WANG, Suxia MA. Performance of flame retardant for environmentally friendly refrigerant R290 [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 462-468. |
| [2] | Hao DING, Lin WANG, Hao LIU. Comparative study on mixing rules of vapor-liquid equilibrium for R290/R245fa [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 9-16. |
| [3] | Ziqing ZANG, Xiuzhen LI, Yingying TAN, Xiaoqing LIU. Investigation on effect of fractionation on performance of two-stage separation-based auto-cascade refrigeration cycle [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 17-25. |
| [4] | Xingliang PEI, Cuiping YE, Yingli PEI, Wenying LI. Selective adsorption and separation of xylene isomers by alkali-modified MIL-53(Cr) [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 258-267. |
| [5] | Yinlong LI, Guoqiang LIU, Gang YAN. Perfromance assessment of auto-cascade cycle integrating fractionation and flash separation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 26-35. |
| [6] | Jianmin ZHANG, Meigui HE, Wanxin JIA, Jing ZHAO, Wanqin JIN. Poly(ethylene oxide)/crown ether blend membrane and performance for CO2 separation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4862-4871. |
| [7] | Jie WANG, Qucheng LIN, Xianming ZHANG. Global optimization of mixed gas multistage membrane separation system based on decomposition algorithm [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4670-4682. |
| [8] | Wenlong LI, Cheng CHANG, Xiaolin WU, Zhongli JI. Research on liquid distribution characteristics and pressure drop evolution in oil-water coalescing filters [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4850-4861. |
| [9] | Chunmeng ZHU, Zeng LI, Nan LIU, Yunpeng ZHAO, Xiaogang SHI, Xingying LAN. Fault detection of catalyst loss in FCC disengager based on autoencoder and multi-scale symbolic transfer entropy [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(9): 4512-4523. |
| [10] | Huiqin ZHANG, Hongjun ZHAO, Zhengjun FU, Li ZHUANG, Kai DONG, Tianzhi JIA, Xueli CAO, Shipeng SUN. Application of nanofiltration membrane in concentration of ionic rare earth leach solution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4095-4107. |
| [11] | Zhihong CHEN, Jiawei WU, Xiaoling LOU, Junxian YUN. Recent advances in machine learning for biomanufacturing of chemicals [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3789-3804. |
| [12] | Minghu JIANG, Fan WANG, Lei XING, Lixin ZHAO, Xinya LI, Dingwei CHEN. Influence of gas-containing on flow field characteristics and separation performance in oil-water separation string [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3361-3372. |
| [13] | Fang WANG, Suxia MA, Ying TIAN, Zhongyuan LIU. NO x emission prediction method of CFB unit based on 1D mechanism model dynamicly corrected with LSTM [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3416-3425. |
| [14] | Jinjiang WANG, Zhenjie LU, Weizheng AN, Fengyun YANG, Xiaogang QIN. Research and prospect of early warning and diagnosis technology for ORC power generation system process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3137-3152. |
| [15] | Zhao GAO, Xi WU, Dan XIA, Linzhou ZHANG. Development of thermodynamics and separation unit modules of petroleum refining molecular management platform [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3212-3225. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||