CIESC Journal ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (1): 397-408.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20191249
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2019-10-23
Revised:2019-11-15
Online:2020-01-05
Published:2020-01-05
Contact:
Jianhua HUANG
通讯作者:
黄建花
作者简介:陈克龙(1993—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:CLC Number:
Kelong CHEN, Jianhua HUANG. g-C3N4-CdS-NiS2 composite nanotube: synthesis and its photocatalytic activity for H2 generation under visible light[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(1): 397-408.
陈克龙, 黄建花. g-C3N4-CdS-NiS2复合纳米管的制备及可见光催化分解水制氢[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(1): 397-408.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 光催化剂 | SBET/(m2·g-1) | 平均孔径/nm | 孔体积/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| g-C3N4 | 77.9 | 19.5 | 0.397 |
| g-C3N4-0.1CdS | 73.8 | 18.8 | 0.368 |
| g-C3N4-0.1CdS-NiS2 | 47.1 | 16.8 | 0.247 |
Table 1 Pore structure parameters of g-C3N4, g-C3N4-0.1CdS and g-C3N4-0.1CdS-NiS2
| 光催化剂 | SBET/(m2·g-1) | 平均孔径/nm | 孔体积/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| g-C3N4 | 77.9 | 19.5 | 0.397 |
| g-C3N4-0.1CdS | 73.8 | 18.8 | 0.368 |
| g-C3N4-0.1CdS-NiS2 | 47.1 | 16.8 | 0.247 |
| 光催化剂 | 助催化剂 | 氙灯功率,波长 | 催化剂用量/mg | 性能/(μmol·h-1) | 稳定性 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g-C3N4 纳米管/CdS | NiS2 | 300 W,λ>420 nm | 50 | 50.9 | 25 h/100% | this work |
| CdS 纳米棒/g-C3N4 纳米片 | NiS | 300W,λ>420 nm | 50 | 128 | 12 h/80% | [ |
| CdS 纳米棒/g-C3N4 纳米片 | CoP | 300 W,λ>400 nm | 5 | 118 | 20 h/100% | [ |
| 块体g-C3N4 /CdS量子点 | Pt | 300 W,λ>400 nm | 100 | 17.3 | 30 h/100% | [ |
| CdS/g-C3N4 | CuS | 350 W,λ>400 nm | 50 | 57.6 | - | [ |
| g-C3N4纳米片/CdS量子点 | WS2 | 300 W,λ>420 nm | 10 | 11.7 | 20 h/90% | [ |
| g-C3N4纳米片/炭黑 | NiS | 300 W,λ>420 nm | 50 | 18.3 | 12 h/90% | [ |
| CdS/碳量子点 | NiS | 350 W,λ>420 nm | 100 | 144.5 | 15 h/100% | [ |
Table 2 Comparison of H2 production rate between g-C3N4-0.1CdS-NiS2 and some reported composite photocatalysts
| 光催化剂 | 助催化剂 | 氙灯功率,波长 | 催化剂用量/mg | 性能/(μmol·h-1) | 稳定性 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| g-C3N4 纳米管/CdS | NiS2 | 300 W,λ>420 nm | 50 | 50.9 | 25 h/100% | this work |
| CdS 纳米棒/g-C3N4 纳米片 | NiS | 300W,λ>420 nm | 50 | 128 | 12 h/80% | [ |
| CdS 纳米棒/g-C3N4 纳米片 | CoP | 300 W,λ>400 nm | 5 | 118 | 20 h/100% | [ |
| 块体g-C3N4 /CdS量子点 | Pt | 300 W,λ>400 nm | 100 | 17.3 | 30 h/100% | [ |
| CdS/g-C3N4 | CuS | 350 W,λ>400 nm | 50 | 57.6 | - | [ |
| g-C3N4纳米片/CdS量子点 | WS2 | 300 W,λ>420 nm | 10 | 11.7 | 20 h/90% | [ |
| g-C3N4纳米片/炭黑 | NiS | 300 W,λ>420 nm | 50 | 18.3 | 12 h/90% | [ |
| CdS/碳量子点 | NiS | 350 W,λ>420 nm | 100 | 144.5 | 15 h/100% | [ |
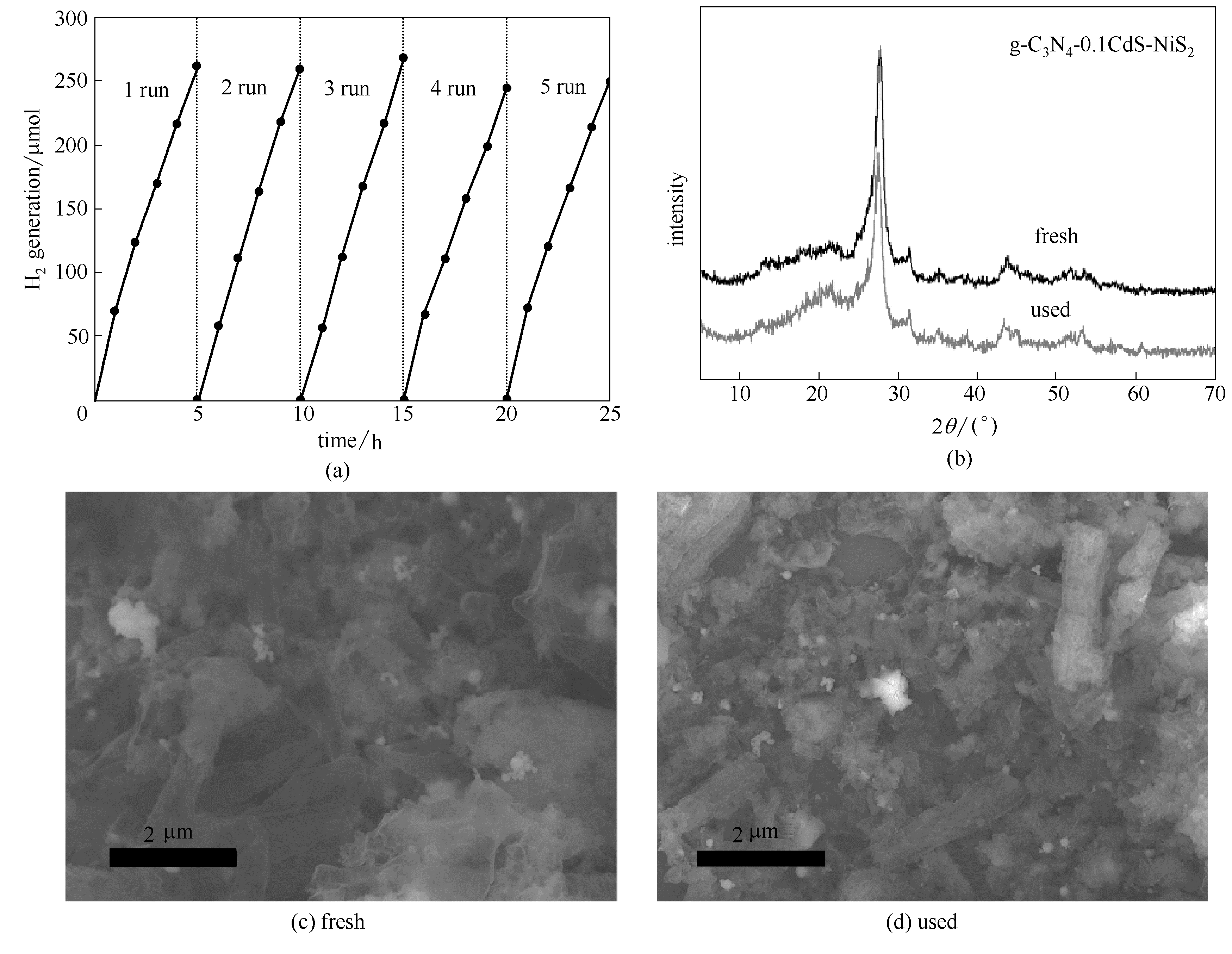
Fig.9 Cyclic photocatalytic H2 evolution over g-C3N4-0.1CdS-NiS2 (a), XRD patterns (b) and SEM images (c, d) of g-C3N4-0.1CdS-NiS2 before and after cyclic H2 generation
| 1 | Fujishima A, Honda K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode[J]. Nature, 1972, 238(5358): 37. |
| 2 | Kapilashrami M, Zhang Y, Liu Y S, et al. Probing the optical property and electronic structure of TiO2 nanomaterials for renewable energy applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(19): 9662-9707. |
| 3 | Li H, Zhou Y, Tu W, et al. State of the art progress in diverse heterostructured photocatalysts toward promoting photocatalytic performance[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(7): 998-1013. |
| 4 | Yao T, An X, Han H, et al. Photoelectrocatalytic materials for solar water splitting[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(21): 1800210. |
| 5 | Mamba G, Mishra A K. Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanocomposites: a new and exciting generation of visible light driven photocatalysts for environmental pollution remediation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 198: 347-377. |
| 6 | Wang X, Maeda K, Thomas A, et al. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light[J]. Nature Materials, 2009, 8(1): 76-80. |
| 7 | Xu D, Cheng B, Wang W, et al. Ag2CrO4/g-C3N4/graphene oxide ternary nanocomposite Z-scheme photocatalyst with enhanced CO2 reduction activity[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 231: 368-380. |
| 8 | Liu S, Chen F, Li S, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic conversion of greenhouse gas CO2 into solar fuels over g-C3N4 nanotubes with decorated transparent ZIF-8 nanoclusters[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 211: 1-10. |
| 9 | Zhang P, Deng J, Mao J, et al. Selective aerobic oxidation of alcohols by a mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride/N-hydroxyphthalimide system under visible-light illumination at room temperature[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 36: 1580-1586. |
| 10 | Lang X, Chen X, Zhao J. Heterogeneous visible light photocatalysis for selective organic transformations[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2014, 43(1): 473-486. |
| 11 | Ong W J, Tan L L, Ng Y H, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-based photocatalysts for artificial photosynthesis and environmental remediation: are we a step closer to achieving sustainability?[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2016, 116(12): 7159-7329. |
| 12 | Inagaki M, Tsumura T, Kinumoto T, et al. Graphitic carbon nitrides (g-C3N4) with comparative discussion to carbon materials[J]. Carbon, 2019, 141: 580-607. |
| 13 | Zhang S, Gu P, Ma R, et al. Recent developments in fabrication and structure regulation of visible-light-driven g-C3N4-based photocatalysts towards water purification: a critical review[J]. Catalysis Today, 2019, 335: 65-77. |
| 14 | 柳璐,张文,王宇新, 等. 石墨相氮化碳的可控制备及其在能源催化中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2018, 69(11): 4577-4591. |
| Liu L, Zhang W, Wang Y X, et al. Graphitic carbon nitride materials: controllable preparations and applications in energy catalysis[J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69(11): 4577-4591. | |
| 15 | Wang S, Li C, Wang T, et al. Controllable synthesis of nanotube-type graphitic C3N4 and their visible-light photocatalytic and fluorescent properties[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(9): 2885-2890. |
| 16 | Yan S C, Li Z S, Zou Z G. Photodegradation of rhodamine B and methyl orange over boron-doped g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation[J]. Langmuir, 2010, 26(6): 3894-3901. |
| 17 | Zhang J, Hu S, Wang Y. A convenient method to prepare a novel alkali metal sodium doped carbon nitride photocatalyst with a tunable band structure[J]. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(108): 62912-62919. |
| 18 | Wang Y, Li H, Yao J, et al. Synthesis of boron doped polymeric carbon nitride solids and their use as metal-free catalysts for aliphatic C—H bond oxidation[J]. Chemical Science, 2011, 2(3): 446-450. |
| 19 | Wang P, Wu T, Wang C, et al. Combining heterojunction engineering with surface cocatalyst modification to synergistically enhance the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of cadmium sulfide nanorods[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(9): 7670-7677. |
| 20 | Yuan J, Wen J, Zhong Y, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic H2 evolution over noble-metal-free NiS cocatalyst modified CdS nanorods/g-C3N4 heterojunctions[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(35): 18244-18255. |
| 21 | 何志桥, 陈锦萍, 童丽丽, 等. BiOCl/g-C3N4异质结催化剂可见光催化还原CO2[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(11): 4634-4642. |
| He Z Q, Chen J P, Tong L L, et al. BiOCl/g-C3N4 heterojunction catalyst for efficient photocatalytic reduction of CO2 under visible light [J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(11): 4634-4642. | |
| 22 | Gong Y, Wang J, Wei Z, et al. Combination of carbon nitride and carbon nanotubes: synergistic catalysts for energy conversion[J]. ChemSusChem, 2014, 7(8): 2303-2309. |
| 23 | Ge L, Zuo F, Liu J, et al. Synthesis and efficient visible light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution of polymeric g-C3N4 coupled with CdS quantum dots[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(25): 13708-13714. |
| 24 | Cheng F, Yin H, Xiang Q. Low-temperature solid-state preparation of ternary CdS/g-C3N4/CuS nanocomposites for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic H2-production activity[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 391: 432-439. |
| 25 | Wen J, Xie J, Yang Z, et al. Fabricating the robust g-C3N4 nanosheets/carbons/NiS multiple heterojunctions for enhanced photocatalytic H2 generation: an insight into the trifunctional roles of nanocarbons[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2017, 5(3): 2224-2236. |
| 26 | Chen D, Zhao J, Zhang P, et al. Mechanochemical synthesis of metal-organic frameworks[J]. Polyhedron, 2019, 162: 59-64. |
| 27 | Zhao J, Shu Y, Zhang P. Solid-state CTAB-assisted synthesis of mesoporous Fe3O4 and Au@Fe3O4 by mechanochemistry[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2019, 40(7): 1078-1084. |
| 28 | Zhao J, Shan W, Zhang P, et al. Solvent-free and mechanochemical synthesis of N-doped mesoporous carbon from tannin and related gas sorption property[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 381: 122579. |
| 29 | Peng W, Zhang S S, Shao Y B, et al. Bimetallic PtNi/g-C3N4 nanotubes with enhanced photocatalytic activity for H2 evolution under visible light irradiation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(49): 22215-22225. |
| 30 | Cao S W, Yuan Y P, Fang J, et al. In-situ growth of CdS quantum dots on g-C3N4 nanosheets for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen generation under visible light irradiation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(3): 1258-1266. |
| 31 | Zhao T, Xing Z, Xiu Z, et al. CdS quantum dots/Ti3+-TiO2 nanobelts heterojunctions as efficient visible-light-driven photocatalysts[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2018, 103: 114-121. |
| 32 | Chen F, Yang H, Wang X, et al. Facile synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic H2-evolution performance of NiS2-modified g-C3N4 photocatalysts[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 38(2): 296-304. |
| 33 | Cao S, Low J, Yu J, et al. Polymeric photocatalysts based on graphitic carbon nitride[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(13): 2150-2176. |
| 34 | Wu T, Wang P, Qian J, et al. Noble-metal-free nickel phosphide modified CdS/C3N4 nanorods for dramatically enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light irradiation[J]. Dalton Transactions, 2017, 46(40): 13793-13801. |
| 35 | Zou Y, Shi J W, Ma D, et al. WS2/graphitic carbon nitride heterojunction nanosheets decorated with CdS quantum dots for photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. ChemSusChem, 2018, 11(7): 1187-1197. |
| 36 | Lu X, Xie J, Chen X, et al. Engineering MPx (M = Fe, Co or Ni) interface electron transfer channels for boosting photocatalytic H2 evolution over g-C3N4/MoS2 layered heterojunctions[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 252: 250-259. |
| 37 | Mishra I K, Zhou H, Sun J, et al. Highly efficient hydrogen evolution by self-standing nickel phosphide-based hybrid nanosheet arrays electrocatalyst[J]. Materials Today Physics, 2018, 4: 1-6. |
| 38 | Pan J, Wang B, Dong Z, et al. The 2D RGO-NiS2 dual co-catalyst synergistic modified g-C3N4 aerogel towards enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(36): 19942-19952. |
| 39 | Shao B, Liu X, Liu Z, et al. Synthesis and characterization of 2D/0D g-C3N4/MoS2/CdS-nitrogen doped hollow carbon spheres (NHCs) composites with enhanced visible light photodegradation activity for antibiotic[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 374: 479-493. |
| 40 | Lin H, Deng W, Zhou T, et al. Iodine-modified nanocrystalline titania for photo-catalytic antibacterial application under visible light illumination[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015, 176: 36-43. |
| 41 | Di T, Zhu B, Cheng B, et al. A direct Z-scheme g-C3N4/MoS2/SnS2 photocatalyst with superior visible-light CO2 reduction performance[J]. Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 352: 532-541. |
| 42 | Yu H, Zhong W, Huang X, et al. Suspensible cubic-phase CdS nanocrystal photocatalyst: facile synthesis and highly efficient H2-evolution performance in a sulfur-rich system[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(4): 5513-5523. |
| 43 | Ma S, Xu X, Xie J, et al. Improved visible-light photocatalytic H2 generation over CdS nanosheets decorated by NiS2 and metallic carbon black as dual earth-abundant cocatalysts[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2017, 38(12): 1970-1980. |
| 44 | Wei R B, Huang Z L, Gu G H, et al. Dual-cocatalysts decorated rimous CdS spheres advancing highly-efficient visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 231: 101-107. |
| 45 | Yan S C, Li Z S, Zou Z G. Photodegradation performance of g-C3N4 fabricated by directly heating melamine[J]. Langmuir, 2009, 25(17): 10397-10401. |
| 46 | Zhang Y, Peng Z, Guan S, et al. Novel β-NiS film modified CdS nanoflowers heterostructure nanocomposite: extraordinarily highly efficient photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 224: 1000-1008. |
| 47 | He H, Cao J, Guo M, et al. Distinctive ternary CdS/Ni2P/g-C3N4 composite for overall water splitting: Ni2P accelerating separation of photocarriers[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 249: 246-256. |
| 48 | Huang H B, Wang Y, Jiao W B, et al. Lotus-leaf-derived activated-carbon-supported nano-CdS as energy-efficient photocatalysts under visible irradiation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 6(6): 7871-7879. |
| [1] | Congqi HUANG, Yimei WU, Jianye CHEN, Shuangquan SHAO. Simulation study of thermal management system of alkaline water electrolysis device for hydrogen production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| [2] | Lei WU, Jiao LIU, Changcong LI, Jun ZHOU, Gan YE, Tiantian LIU, Ruiyu ZHU, Qiuli ZHANG, Yonghui SONG. Catalytic microwave pyrolysis of low-rank pulverized coal for preparation of high value-added modified bluecoke powders containing carbon nanotubes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3956-3967. |
| [3] | Yepin CHENG, Daqing HU, Yisha XU, Huayan LIU, Hanfeng LU, Guokai CUI. Application of ionic liquid-based deep eutectic solvents for CO2 conversion [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3640-3653. |
| [4] | Yaxin CHEN, Hang YUAN, Guanzhang LIU, Lei MAO, Chun YANG, Ruifang ZHANG, Guangya ZHANG. Advances in enzyme self-immobilization mediated by protein nanocages [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [5] | Xiaoling TANG, Jiarui WANG, Xuanye ZHU, Renchao ZHENG. Biosynthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin by halohydrin dehalogenase based on Pickering emulsion system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2926-2934. |
| [6] | Tan ZHANG, Guang LIU, Jinping LI, Yuhan SUN. Performance regulation strategies of Ru-based nitrogen reduction electrocatalysts [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2264-2280. |
| [7] | Xiaowen ZHOU, Jie DU, Zhanguo ZHANG, Guangwen XU. Study on the methane-pulsing reduction characteristics of Fe2O3-Al2O3 oxygen carrier [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2611-2623. |
| [8] | Yong LI, Jiaqi GAO, Chao DU, Yali ZHAO, Boqiong LI, Qianqian SHEN, Husheng JIA, Jinbo XUE. Construction of Ni@C@TiO2 core-shell dual-heterojunctions for advanced photo-thermal catalytic hydrogen generation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2458-2467. |
| [9] | Lei MAO, Guanzhang LIU, Hang YUAN, Guangya ZHANG. Efficient preparation of carbon anhydrase nanoparticles capable of capturing CO2 and their characteristics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [10] | Zijian WANG, Ming KE, Jiahan LI, Shuting LI, Jinru SUN, Yanbing TONG, Zhiping ZHAO, Jiaying LIU, Lu REN. Progress in preparation and application of short b-axis ZSM-5 molecular sieve [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1457-1473. |
| [11] | Tianhao BAI, Xiaowen WANG, Mengzi YANG, Xinwei DUAN, Jie MI, Mengmeng WU. Study on release and inhibition behavior of COS during high-temperature gas desulfurization process using Zn-based oxide derived from hydrotalcite [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(4): 1772-1780. |
| [12] | Yin XU, Jie CAI, Lu CHEN, Yu PENG, Fuzhen LIU, Hui ZHANG. Advances in heterogeneous visible light photocatalysis coupled with persulfate activation for water pollution control [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 995-1009. |
| [13] | Sheng’an ZHANG, Guilian LIU. Multi-objective optimization of high-efficiency solar water electrolysis hydrogen production system and its performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1260-1274. |
| [14] | Runzhu LIU, Tiantian CHU, Xiaoa ZHANG, Chengzhong WANG, Junying ZHANG. Synthesis and properties of phenylene-containing α,ω-hydroxy-terminated fluorosilicone polymers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1360-1369. |
| [15] | Mengxin LIANG, Yan GUO, Shidong WANG, Hongwei ZHANG, Pei YUAN, Xiaojun BAO. Study on preparation of Pd catalyst supported on carbon nitride for the selective hydrogenation of SBS [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 766-775. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
