CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (3): 1239-1246.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221603
• Biochemical engineering and technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Lufan JIA( ), Yiying WANG, Yuman DONG, Qinyuan LI, Xin XIE, Hao YUAN, Tao MENG(
), Yiying WANG, Yuman DONG, Qinyuan LI, Xin XIE, Hao YUAN, Tao MENG( )
)
Received:2022-12-13
Revised:2023-02-14
Online:2023-04-19
Published:2023-03-05
Contact:
Tao MENG
贾露凡( ), 王艺颖, 董钰漫, 李沁园, 谢鑫, 苑昊, 孟涛(
), 王艺颖, 董钰漫, 李沁园, 谢鑫, 苑昊, 孟涛( )
)
通讯作者:
孟涛
作者简介:贾露凡(1998—),女,硕士研究生,18838936617@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Lufan JIA, Yiying WANG, Yuman DONG, Qinyuan LI, Xin XIE, Hao YUAN, Tao MENG. Aqueous two-phase system based adherent droplet microfluidics for enhanced enzymatic reaction[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(3): 1239-1246.
贾露凡, 王艺颖, 董钰漫, 李沁园, 谢鑫, 苑昊, 孟涛. 微流控双水相贴壁液滴流动强化酶促反应研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1239-1246.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
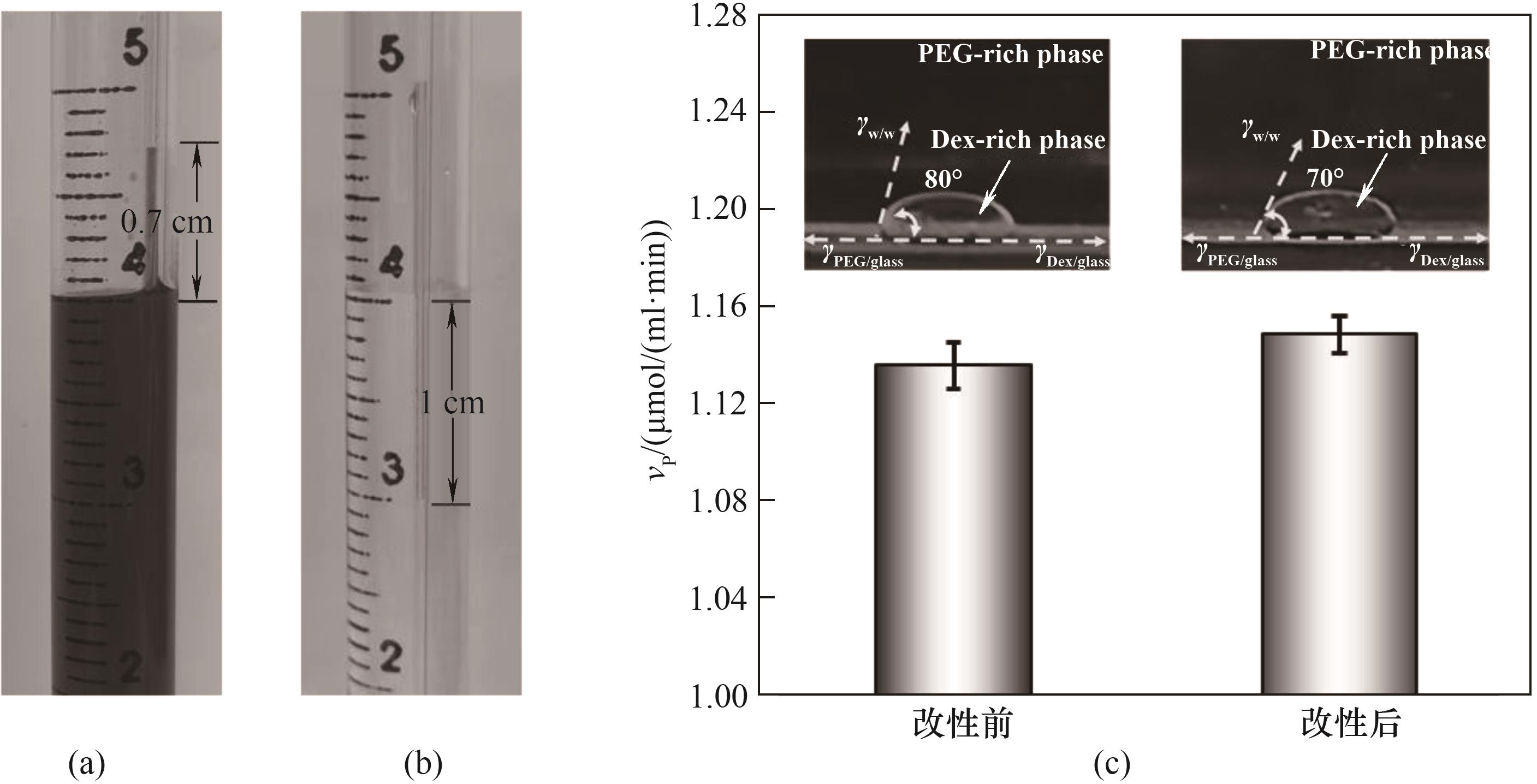
Fig.9 Effect of hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of the microchannel on the reaction rate: the height of water in microchannels before (a) and after (b) microchannel surface modification; (c) the reaction rate of the catalysis performed in microchannel before and after microchannel surface modification (the insets show the corresponding three-phase contact angle)
| 16 | Ge J, Lu D N, Zhu J Y, et al. Advances in preparation of nanostructured enzyme catalysts[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(7): 2668-2675. |
| 17 | Bussamra B C, Gomes J C, Freitas S, et al. A robotic platform to screen aqueous two-phase systems for overcoming inhibition in enzymatic reactions[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 280: 37-50. |
| 18 | Zou S P, Hua D G, Jiang Z T, et al. A integrated process for nitrilase-catalyzed asymmetric hydrolysis and easy biocatalyst recycling by introducing biocompatible biphasic system[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 320: 124392. |
| 19 | Kim T H, Kang S H, Han J E, et al. Multilayer engineering of enzyme cascade catalysis for one-pot preparation of nylon monomers from renewable fatty acids[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2020, 10(9): 4871-4878. |
| 20 | Yang J, Zhang X P, Yong Q A, et al. Three-stage enzymatic hydrolysis of steam-exploded corn stover at high substrate concentration[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2011, 102(7): 4905-4908. |
| 21 | Meng S X, Xue L H, Xie C Y, et al. Enhanced enzymatic reaction by aqueous two-phase systems using parallel-laminar flow in a double Y-branched microfluidic device[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 335: 392-400. |
| 22 | Vobecka L, Romanov A, Slouka Z, et al. Optimization of aqueous two-phase systems for the production of 6-aminopenicillanic acid in integrated microfluidic reactors-separators[J]. New Biotechnology, 2018, 47: 73-79. |
| 23 | Wei D Z, Zhu J H, Cao X J. Enzymatic synthesis of cephalexin in aqueous two-phase systems[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2002, 11(2/3): 95-99. |
| 24 | Zijlstra G M, Gooijer C D, Tramper J. Extractive bioconversions in aqueous two-phase systems[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 1998, 9(2): 171-176. |
| 25 | 朱建航, 魏东芝, 曹学君, 等. 酶法合成头孢氨苄的反应-双水相萃取耦合过程[J]. 化工学报, 2003, 54(1): 95-99. |
| Zhu J H, Wei D Z, Cao X J, et al. Enzymatic synthesis of cephalexin integrated with aqueous two-phase systems[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2003, 54(1): 95-99. | |
| 26 | Aguirre C, Concha I, Vergara J, et al. Partition and substrate concentration effect in the enzymatic synthesis of cephalexin in aqueous two-phase systems[J]. Process Biochemistry, 2010, 45(7): 1163-1167. |
| 27 | Lu Y C, Xia Y, Luo G S. Phase separation of parallel laminar flow for aqueous two phase systems in branched microchannel[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2011, 10(5): 1079-1086. |
| 1 | 陈光文, 袁权. 微化工技术[J]. 化工学报, 2003, 54(4): 427-439. |
| Chen G W, Yuan Q. Micro-chemical technology[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2003, 54(4): 427-439. | |
| 2 | Service R F. Miniaturization puts chemical plants where you want them[J]. Science, 1998, 282(5388): 400. |
| 3 | Gemoets H P L, Su Y H, Shang M J, et al. Liquid phase oxidation chemistry in continuous-flow microreactors[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(1): 83-117. |
| 4 | Peyman S A, Abou-Saleh R H, McLaughlan J R, et al. Expanding 3D geometry for enhanced on-chip microbubble production and single step formation of liposome modified microbubbles[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2012, 12(21): 4544-4552. |
| 5 | Adamson D N, Mustafi D, Zhang J X J, et al. Production of arrays of chemically distinct nanolitre plugs via repeated splitting in microfluidic devices[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2006, 6(9): 1178-1186. |
| 6 | 黄心童, 耿宇昊, 刘恒源, 等. 微流控制备新型功能纳米粒子研究进展[J].化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 355-364. |
| Huang X T, Geng Y H, Liu H Y, et al. Research progress on new functional nanoparticles prepared by microfluidic technology[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(1): 355-364. | |
| 7 | 苏瑶瑶, 李平凡, 汪伟, 等. 微流控液滴模板法可控构建功能微颗粒材料[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 42-60. |
| Su Y Y, Li P F, Wang W, et al. Controllable fabrication of functional microparticle materials from microfluidic droplet templates[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 42-60. | |
| 8 | Abolhasani M, Günther A, Kumacheva E. Microfluidic studies of carbon dioxide[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 2014, 53(31): 7992-8002. |
| 9 | 邓传富, 汪伟, 谢锐, 等. 液滴微流控的集成化放大方法研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(12): 5965-5974. |
| Deng C F, Wang W, Xie R, et al. Recent progress in scale-up integration of microfluidic droplet generators[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(12): 5965-5974. | |
| 10 | Ji J, Nie L, Qiao L, et al. Proteolysis in microfluidic droplets: an approach to interface protein separation and peptide mass spectrometry[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2012, 12(15): 2625-2629. |
| 11 | Xu J H, Tan J, Li S W, et al. Enhancement of mass transfer performance of liquid-liquid system by droplet flow in microchannels[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2007, 141(1): 242-249. |
| 12 | Song H, Tice J D, Ismagilov R F. A microfluidic system for controlling reaction networks in time[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 2003, 42(7): 768-772. |
| 13 | 李光晓, 刘塞尔, 苏远海. 微尺度内液-液传质及反应过程强化的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(1): 452-467. |
| Li G X, Liu S E, Su Y H. Research progress on micro-scale internal liquid-liquid mass transfer and reaction process enhancement[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(1): 452-467. | |
| 14 | Schmid A, Dordick J S, Hauer B, et al. Industrial biocatalysis today and tomorrow[J]. Nature, 2001, 409(6817): 258-268. |
| 15 | Klibanov A M. Improving enzymes by using them in organic solvents[J]. Nature, 2001, 409(6817): 241-246. |
| 16 | 戈钧, 卢滇楠, 朱晶莹, 等. 纳米酶催化剂制备方法研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(7): 2668-2675. |
| 28 | 林东强, 朱自强, 姚善泾, 等. 生化分离过程的新探索:双水相分配与相关技术的集成化[J]. 化工学报, 2000, 51(1): 1-6. |
| Lin D Q, Zhu Z Q, Yao S J, et al. Novel technology in bioseparation process integration of aqueous two-phase partitioning with related techniques[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2000, 51(1): 1-6. | |
| 29 | Wang Y Y, Dong Y M, Liu H Y, et al. Compartmentalized aqueous-in-aqueous droplets for flow biocatalysis[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(4):5009-5016. |
| 30 | Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1976, 72(1/2): 248-254. |
| 31 | Asenjo J A, Andrews B A. Aqueous two-phase systems for protein separation: a perspective[J]. Journal of Chromatography. A, 2011, 1218(49): 8826-8835. |
| 32 | Dewey D C, Strulson C A, Cacace D N, et al. Bioreactor droplets from liposome-stabilized all-aqueous emulsions[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4670. |
| 33 | Kurt S K, Gursel I V, Hessel V, et al. Liquid-liquid extraction system with microstructured coiled flow inverter and other capillary setups for single-stage extraction applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 284: 764-777. |
| 34 | Kojima T, Takayama S. Membraneless compartmentalization facilitates enzymatic cascade reactions and reduces substrate inhibition[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(38): 32782-32791. |
| 35 | Malsch D, Gleichmann N, Kielpinski M, et al. Effects of fluid and interface interaction on droplet internal flow in all-glass micro channels[C]//Proceedings of ASME 2008 6th International Conference on Nanochannels, Microchannels, and Minichannels. Darmstadt, Germany, 2009: 1571-1578. |
| 36 | Picardo J R, Pushpavanam S. Core-annular two-phase flow in a gently curved circular channel[J]. AIChE Journal, 2013, 59(12): 4871-4886. |
| 37 | Song H, Chen D L, Ismagilov R F. Reactions in droplets in microfluidic channels[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English), 2006, 45(44): 7336-7356. |
| [1] | Xin WU, Jianying GONG, Long JIN, Yutao WANG, Ruining HUANG. Study on the transportation characteristics of droplets on the aluminium surface under ultrasonic excitation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 104-112. |
| [2] | Xiaoqing ZHOU, Chunyu LI, Guang YANG, Aifeng CAI, Jingyi WU. Icing kinetics and mechanism of droplet impinging on supercooled corrugated plates with different curvature [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 141-153. |
| [3] | Lisen BI, Bin LIU, Hengxiang HU, Tao ZENG, Zhuorui LI, Jianfei SONG, Hanming WU. Molecular dynamics study on evaporation modes of nanodroplets at rough interfaces [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 172-178. |
| [4] | He JIANG, Junfei YUAN, Lin WANG, Guyu XING. Experimental study on the effect of flow sharing cavity structure on phase change flow characteristics in microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [5] | Jingwei CHAO, Jiaxing XU, Tingxian LI. Investigation on the heating performance of the tube-free-evaporation based sorption thermal battery [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 302-310. |
| [6] | Yitong LI, Hang GUO, Hao CHEN, Fang YE. Study on operating conditions of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform catalyst distributions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [7] | Lingding MENG, Ruqing CHONG, Feixue SUN, Zihui MENG, Wenfang LIU. Immobilization of carbonic anhydrase on modified polyethylene membrane and silica [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3472-3484. |
| [8] | Wenzhu LIU, Heming YUN, Baoxue WANG, Mingzhe HU, Chonglong ZHONG. Research on topology optimization of microchannel based on field synergy and entransy dissipation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3329-3341. |
| [9] | Yaxin CHEN, Hang YUAN, Guanzhang LIU, Lei MAO, Chun YANG, Ruifang ZHANG, Guangya ZHANG. Advances in enzyme self-immobilization mediated by protein nanocages [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2773-2782. |
| [10] | Xiaoling TANG, Jiarui WANG, Xuanye ZHU, Renchao ZHENG. Biosynthesis of chiral epichlorohydrin by halohydrin dehalogenase based on Pickering emulsion system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2926-2934. |
| [11] | Xuanzhi HE, Yongqing HE, Guiye WEN, Feng JIAO. Ferrofluid droplet neck self-similar breakup behavior [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 2889-2897. |
| [12] | Yuanyuan ZHANG, Jiangyuan QU, Xinxin SU, Jing YANG, Kai ZHANG. Gas-liquid mass transfer and reaction characteristics of SNCR denitration in CFB coal-fired unit [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2404-2415. |
| [13] | Lei MAO, Guanzhang LIU, Hang YUAN, Guangya ZHANG. Efficient preparation of carbon anhydrase nanoparticles capable of capturing CO2 and their characteristics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [14] | Zhengtao LI, Zhijie YUAN, Gaohong HE, Xiaobin JIANG. Study of the mechanism of internal circulation regulation during evaporation of NaCl droplets on hydrophobic interface [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 1904-1913. |
| [15] | Lanhe ZHANG, Qingyi LAI, Tiezheng WANG, Xiaozhuo GUAN, Mingshuang ZHANG, Xin CHENG, Xiaohui XU, Yanping JIA. Effect of H2O2 on nitrogen removal and sludge properties in SBR [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2186-2196. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||