CIESC Journal ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (12): 5006-5015.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231188
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Peipei CHEN( ), Qiuying WANG(
), Qiuying WANG( ), Zeqing XIAO, Sijia ZHOU, Xiaoliang ZHANG(
), Zeqing XIAO, Sijia ZHOU, Xiaoliang ZHANG( )
)
Received:2023-11-17
Revised:2023-12-22
Online:2024-02-19
Published:2023-12-25
Contact:
Qiuying WANG, Xiaoliang ZHANG
通讯作者:
汪秋英,张小亮
作者简介:陈佩佩(1998—),女,硕士研究生,chenpeipei17@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Peipei CHEN, Qiuying WANG, Zeqing XIAO, Sijia ZHOU, Xiaoliang ZHANG. Tailoring preparation of graphene quantum dot composite membranes: influence of precursors[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(12): 5006-5015.
陈佩佩, 汪秋英, 肖泽卿, 周思佳, 张小亮. 石墨烯量子点复合膜的调控制备:前体的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(12): 5006-5015.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
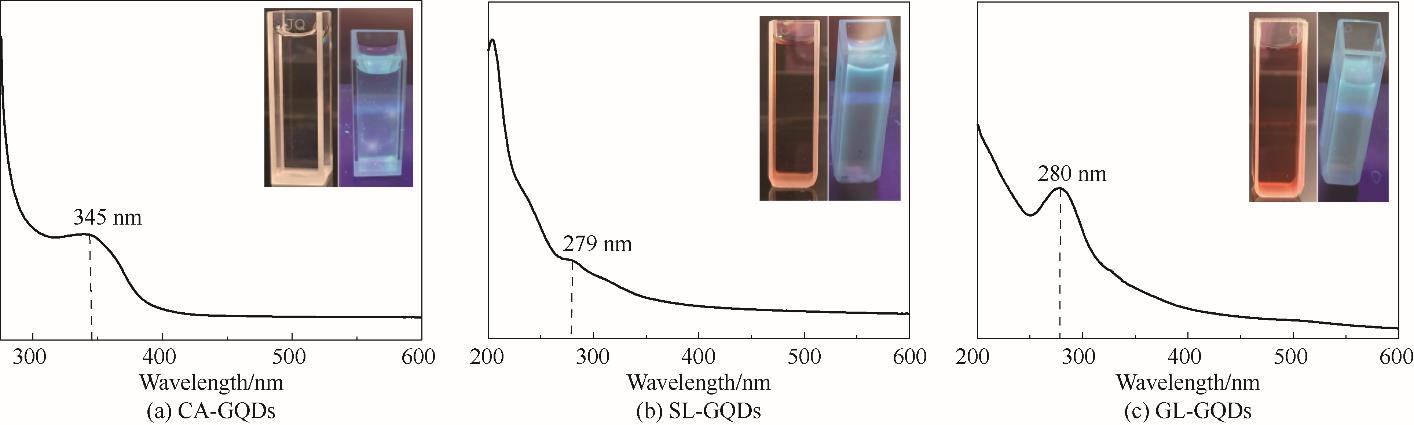
Fig.2 UV-Vis spectra and photoluminescence photos of GQDs solutions prepared with different precursors [incandescent lamp (left) and 365 nm UV light (right) in the illustrations]
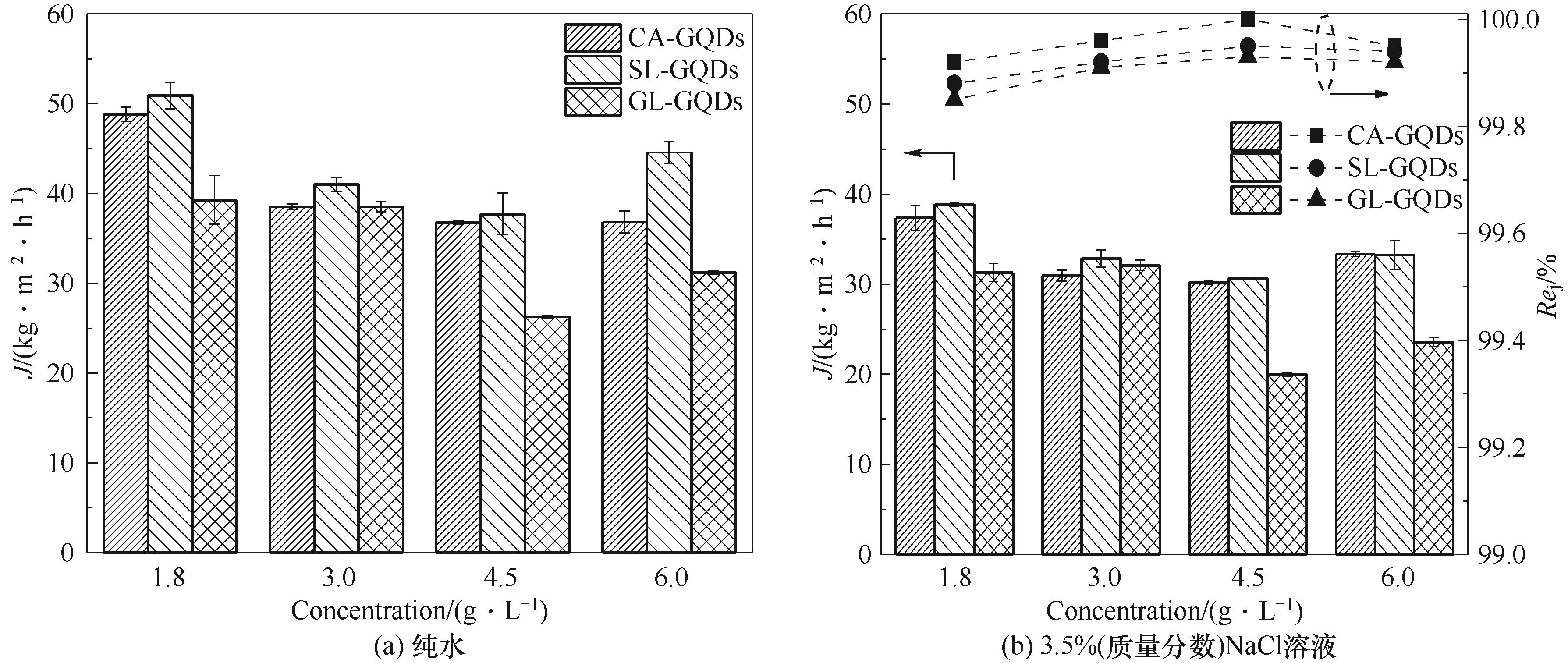
Fig.6 Effect of precursors and dip-coating concentrations on the desalination performance of GQDs composite membranes towards pure water and 3.5% (mass) NaCl solution at 30℃

Fig.7 Effect of dip-coating times and pH in dip-coating solution on the desalination performance of CA-GQDs composite membranes towards pure water and 3.5% (mass) NaCl solution at 30℃
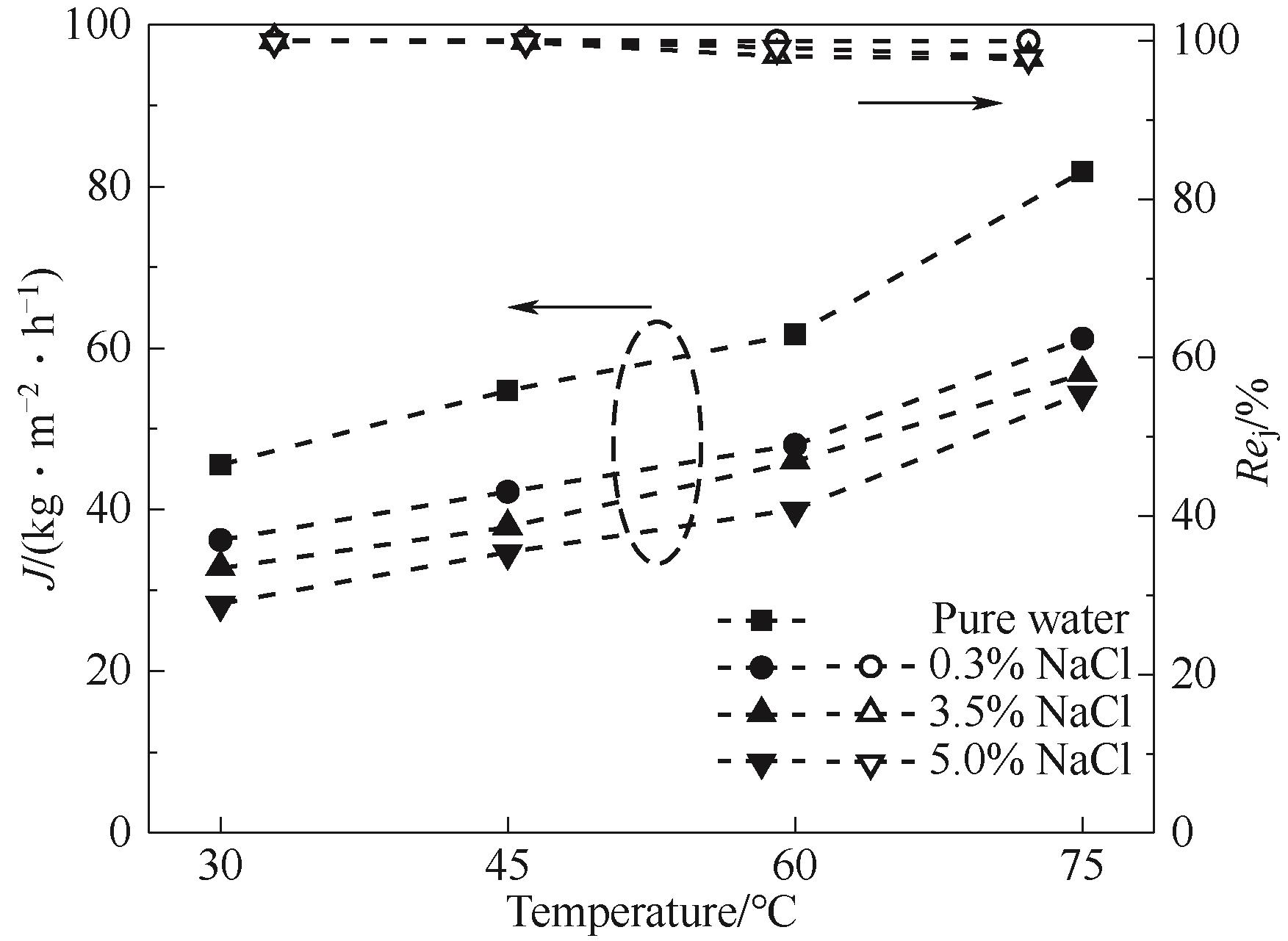
Fig.8 Effect of feed temperature on the desalination performance of CA-GQDs composite membranes towards pure water and NaCl solutions with different concentrations
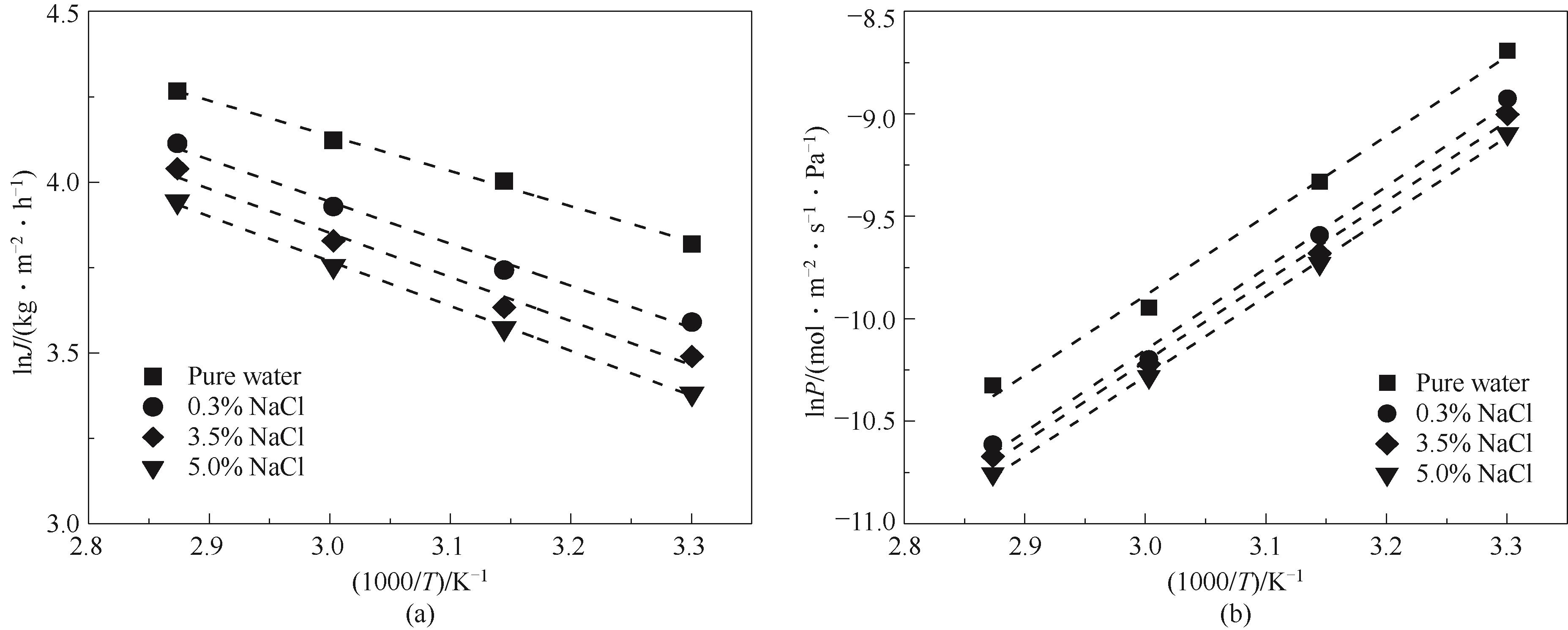
Fig.9 Arrhenius plots of temperature dependent permeation flux and permeance of GQDs composite membranes towards pure water and NaCl solutions with different concentrations
| Solution | Ej/(kJ·mol-1) | Ep/(kJ·mol-1) | (Ej-Ep)/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔHv/(kJ·mol-1)[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure water | 8.57±0.38 | -32.33±1.73 | 40.90 | 40.71—46.48 |
| 0.3% NaCl | 10.24±0.62 | -33.22±1.45 | 43.46 | 40.69—46.34 |
| 3.5% NaCl | 10.73±0.95 | -32.49±1.16 | 43.22 | 40.67—45.96 |
| 5.0% NaCl | 10.91±0.30 | -32.37±0.54 | 43.28 | 40.66—45.74 |
Table 1 Activation energy of CA-GQDs composite membranes for pervaporation desalination processes
| Solution | Ej/(kJ·mol-1) | Ep/(kJ·mol-1) | (Ej-Ep)/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔHv/(kJ·mol-1)[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure water | 8.57±0.38 | -32.33±1.73 | 40.90 | 40.71—46.48 |
| 0.3% NaCl | 10.24±0.62 | -33.22±1.45 | 43.46 | 40.69—46.34 |
| 3.5% NaCl | 10.73±0.95 | -32.49±1.16 | 43.22 | 40.67—45.96 |
| 5.0% NaCl | 10.91±0.30 | -32.37±0.54 | 43.28 | 40.66—45.74 |
| 1 | Yan Y X, Manickam S, Lester E, et al. Synthesis of graphene oxide and graphene quantum dots from miscanthus via ultrasound-assisted mechano-chemical cracking method[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2021, 73: 105519. |
| 2 | Li X M, Rui M C, Song J Z, et al. Carbon and graphene quantum dots for optoelectronic and energy devices: a review[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(31): 4929-4947. |
| 3 | 刘嘉玮, 郝雨峰, 苏延磊. 石墨烯量子点纳滤膜的仿生修饰及稳定性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(6): 3390-3398. |
| Liu J W, Hao Y F, Su Y L. Biomimetic modification and stability of graphene quantum dots nanofiltration membranes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(6): 3390-3398. | |
| 4 | Li H T, Kang Z H, Liu Y, et al. Carbon nanodots: synthesis, properties and applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(46): 24230-24253. |
| 5 | 韩威, 詹俊, 石红, 等. 氮和硫双掺杂石墨烯量子点的合成及其性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(S1): 530-538. |
| Han W, Zhan J, Shi H, et al. Synthesis and properties of nitrogen and sulfur codoped graphene quantum dots[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(S1): 530-538. | |
| 6 | Chen W F, Lv G, Hu W M, et al. Synthesis and applications of graphene quantum dots: a review[J]. Nanotechnology Reviews, 2018, 7(2): 157-185. |
| 7 | Sun J W, Jia W, Guo J X, et al. Amino-embedded carbon quantum dots incorporated thin-film nanocomposite membrane for desalination by pervaporation[J]. Desalination, 2022, 533: 115742. |
| 8 | Zhang Y, Song J, Shi B B, et al. Graphene oxide membranes with an enlarged interlaminar nanochannel through functionalized quantum dots for pervaporative water-selective transport[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 292: 120975. |
| 9 | Shao D D, Wang L, Yan X Y, et al. Amine-carbon quantum dots (CQDs-NH2) tailored polymeric loose nanofiltration membrane for precise molecular separation[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2021, 171: 237-246. |
| 10 | Sun W G, Zhang N, Li Q, et al. Bioinspired lignin-based loose nanofiltration membrane with excellent acid, fouling, and chlorine resistances toward dye/salt separation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 670: 121372. |
| 11 | 任炼, 张鑫涛, 赵丽萍, 等. 碳源选择对荧光碳量子点光致发光性能的影响[J]. 化学与黏合, 2016, 38(5): 366-368. |
| Ren L, Zhang X T, Zhao L P, et al. Effect of different carbon sources on the photoluminescence properties of fluorescent carbon quantum dots[J]. Chemistry and Adhesion, 2016, 38(5): 366-368. | |
| 12 | Zhu Y, Zhang X J, Zhang L M, et al. Membranes constructed with zero-dimension carbon quantum dots for CO2 separation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2022, 664: 121086. |
| 13 | Liu W, Ning C X, Sang R R, et al. Lignin-derived graphene quantum dots from phosphous acid-assisted hydrothermal pretreatment and their application in photocatalysis[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2021, 171: 113963. |
| 14 | Behzadi F, Saievar-Iranizad E, Bayat A. One step synthesis of graphene quantum dots, graphene nanosheets and carbon nanospheres: investigation of photoluminescence properties[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019, 6(10): 105615. |
| 15 | 张锐, 邵琦, 张华宇, 等. 硼掺杂二氧化硅杂化膜的制备及渗透汽化脱盐性能[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(4): 2317-2327. |
| Zhang R, Shao Q, Zhang H Y, et al. Fabrication of boron-doped hybrid silica membranes for pervaporation desalination[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(4): 2317-2327. | |
| 16 | Zhang H Y, Wen J L, Shao Q, et al. Fabrication of La/Y-codoped microporous organosilica membranes for high-performance pervaporation desalination[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 584: 353-363. |
| 17 | Dong Y Q, Shao J W, Chen C Q, et al. Blue luminescent graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide prepared by tuning the carbonization degree of citric acid[J]. Carbon, 2012, 50(12): 4738-4743. |
| 18 | Shehab M, Ebrahim S, Soliman M. Graphene quantum dots prepared from glucose as optical sensor for glucose[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 2017, 184: 110-116. |
| 19 | Achadu O J, Nyokong T. Interaction of graphene quantum dots with 4-acetamido-2, 2, 6, 6-tetramethylpiperidine-oxyl free radicals: a spectroscopic and fluorimetric study[J]. Journal of Fluorescence, 2016, 26(1):283-295. |
| 20 | Gu W T, Zhang W, Li X M, et al. Graphene sheets from worm-like exfoliated graphite[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2009, 19(21): 3367-3369. |
| 21 | Li L L, Wu G H, Yang G H, et al. Focusing on luminescent graphene quantum dots: current status and future perspectives[J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(10): 4015-4039. |
| 22 | Zheng H, Mou Z H, Lim Y J, et al. Incorporating ionic carbon dots in polyamide nanofiltration membranes for high perm-selectivity and antifouling performance[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 672: 121401. |
| 23 | Wu D H, Gao A R, Zhao H T, et al. Pervaporative desalination of high-salinity water[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2018, 136: 154-164. |
| 24 | Halakoo E, Feng X S. Layer-by-layer assembly of polyethyleneimine/graphene oxide membranes for desalination of high-salinity water via pervaporation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 234: 116077. |
| 25 | Baker R W, Wijmans J G, Huang Y. Permeability, permeance and selectivity: a preferred way of reporting pervaporation performance data[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 348(1/2): 346-352. |
| 26 | Yang G, Xie Z L, Cran M, et al. Enhanced desalination performance of poly(vinyl alcohol)/carbon nanotube composite pervaporation membranes via interfacial engineering[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 579: 40-51. |
| 27 | Feng B, Xu K, Huang A S. Covalent synthesis of three-dimensional graphene oxide framework (GOF) membrane for seawater desalination[J]. Desalination, 2016, 394: 123-130. |
| 28 | Zhao X Y, Tong Z Q, Liu X F, et al. Facile preparation of polyamide-graphene oxide composite membranes for upgrading pervaporation desalination performances of hypersaline solutions[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(26): 12232-12238. |
| 29 | Liang B, Zhan W, Qi G G, et al. High performance graphene oxide/polyacrylonitrile composite pervaporation membranes for desalination applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(9): 5140-5147. |
| 30 | Song Y M, Li R, Pan F S, et al. Ultrapermeable graphene oxide membranes with tunable interlayer distances via vein-like supramolecular dendrimers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(31): 18642-18652. |
| 31 | Sun J W, Qian X W, Wang Z H, et al. Tailoring the microstructure of poly(vinyl alcohol)-intercalated graphene oxide membranes for enhanced desalination performance of high-salinity water by pervaporation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 599: 117838. |
| 32 | Cao Z S, Zeng S X, Xu Z, et al. Ultrathin ZSM-5 zeolite nanosheet laminated membrane for high-flux desalination of concentrated brines[J]. Science Advances, 2018, 4(11): eaau8634. |
| 33 | Liang B, Pan K, Li L, et al. High performance hydrophilic pervaporation composite membranes for water desalination[J]. Desalination, 2014, 347: 199-206. |
| 34 | Li L, Hou J W, Ye Y, et al. Composite PVA/PVDF pervaporation membrane for concentrated brine desalination: salt rejection, membrane fouling and defect control[J]. Desalination, 2017, 422: 49-58. |
| 35 | Prihatiningtyas I, Gebreslase G A, van der Bruggen B. Incorporation of Al2O3 into cellulose triacetate membranes to enhance the performance of pervaporation for desalination of hypersaline solutions[J]. Desalination, 2020, 474: 114198. |
| 36 | Wang Q Z, Lu Y Y, Li N. Preparation, characterization and performance of sulfonated poly(styrene-ethylene/butylene-styrene) block copolymer membranes for water desalination by pervaporation[J]. Desalination, 2016, 390: 33-46. |
| 37 | Prihatiningtyas I, Li Y, Hartanto Y, et al. Effect of solvent on the morphology and performance of cellulose triacetate membrane/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposite pervaporation desalination membranes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388: 124216. |
| 38 | Drobek M, Yacou C, Motuzas J, et al. Long term pervaporation desalination of tubular MFI zeolite membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012, 415/416: 816-823. |
| 39 | He Y, Cui X M, Liu X D, et al. Preparation of self-supporting NaA zeolite membranes using geopolymers[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013, 447: 66-72. |
| 40 | Reino Olegário da Silva D A, Bosmuler Zuge L C, de Paula Scheer A. Preparation and characterization of a novel green silica/PVA membrane for water desalination by pervaporation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 247: 116852. |
| 41 | Xie Z L, Hoang M, Duong T, et al. Sol-gel derived poly(vinyl alcohol)/maleic acid/silica hybrid membrane for desalination by pervaporation[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011, 383(1/2): 96-103. |
| [1] | He JIANG, Junfei YUAN, Lin WANG, Guyu XING. Experimental study on the effect of flow sharing cavity structure on phase change flow characteristics in microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [2] | Yanpeng WU, Xiaoyu LI, Qiaoyang ZHONG. Experimental analysis on filtration performance of electrospun nanofibers with amphiphobic membrane of oily fine particles [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 259-264. |
| [3] | Yitong LI, Hang GUO, Hao CHEN, Fang YE. Study on operating conditions of proton exchange membrane fuel cells with non-uniform catalyst distributions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(9): 3831-3840. |
| [4] | Jiayi ZHANG, Jiali HE, Jiangpeng XIE, Jian WANG, Yu ZHAO, Dongqiang ZHANG. Research progress of pervaporation technology for N-methylpyrrolidone recovery in lithium battery production [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [5] | Yuyuan ZHENG, Zhiwei GE, Xiangyu HAN, Liang WANG, Haisheng CHEN. Progress and prospect of medium and high temperature thermochemical energy storage of calcium-based materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3171-3192. |
| [6] | Yali HU, Junyong HU, Suxia MA, Yukun SUN, Xueyi TAN, Jiaxin HUANG, Fengyuan YANG. Development of novel working fluid and study on electrochemical characteristics of reverse electrodialysis heat engine [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [7] | Lingding MENG, Ruqing CHONG, Feixue SUN, Zihui MENG, Wenfang LIU. Immobilization of carbonic anhydrase on modified polyethylene membrane and silica [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(8): 3472-3484. |
| [8] | Lei MAO, Guanzhang LIU, Hang YUAN, Guangya ZHANG. Efficient preparation of carbon anhydrase nanoparticles capable of capturing CO2 and their characteristics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2589-2598. |
| [9] | Kuikui HAN, Xianglong TAN, Jinzhi LI, Ting YANG, Chun ZHANG, Yongfen ZHANG, Hongquan LIU, Zhongwei YU, Xuehong GU. Four-channel hollow fiber MFI zeolite membrane for the separation of xylene isomers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2468-2476. |
| [10] | Bin CAI, Xiaolin ZHANG, Qian LUO, Jiangtao DANG, Liyuan ZUO, Xinmei LIU. Research progress of conductive thin film materials [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2308-2321. |
| [11] | Zhaoguang CHEN, Yuxiang JIA, Meng WANG. Modeling neutralization dialysis desalination driven by low concentration waste acid and its validation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(6): 2486-2494. |
| [12] | Lei WANG, Lei WANG, Yunlong BAI, Liuliu HE. Preparation of SA lithium ion sieve membrane and its adsorptive properties [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2046-2056. |
| [13] | Wenchao XU, Zhigao SUN, Cuimin LI, Juan LI, Haifeng HUANG. Effect of surfactant E-1310 on the formation of HCFC-141b hydrate under static conditions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2179-2185. |
| [14] | Hao GU, Fujian ZHANG, Zhen LIU, Wenxuan ZHOU, Peng ZHANG, Zhongqiang ZHANG. Desalination performance and mechanism of porous graphene membrane in temporal dimension under mechanical-electrical coupling [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2067-2074. |
| [15] | Yongyao SUN, Qiuying GAO, Wenguang ZENG, Jiaming WANG, Yifei CHEN, Yongzhe ZHOU, Gaohong HE, Xuehua RUAN. Design and optimization of membrane-based integration process for advanced utilization of associated gases in N2-EOR oilfields [J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(5): 2034-2045. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||