CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (12): 4825-4832.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240399
• Material science and engineering, nanotechnology • Previous Articles
Yifan XU( ), Yuanchao LIU(
), Yuanchao LIU( ), Duan LI, Xuhao JIANG, Xinhao LIU, Zishuo LI
), Duan LI, Xuhao JIANG, Xinhao LIU, Zishuo LI
Received:2024-04-10
Revised:2024-08-21
Online:2025-01-03
Published:2024-12-25
Contact:
Yuanchao LIU
徐一帆( ), 刘远超(
), 刘远超( ), 李耑, 蒋旭浩, 刘新昊, 李梓硕
), 李耑, 蒋旭浩, 刘新昊, 李梓硕
通讯作者:
刘远超
作者简介:徐一帆(1997—),男,硕士研究生,m18232668085@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yifan XU, Yuanchao LIU, Duan LI, Xuhao JIANG, Xinhao LIU, Zishuo LI. Thermoelectric transport properties of double layers phosphorene heterostructure[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(12): 4825-4832.
徐一帆, 刘远超, 李耑, 蒋旭浩, 刘新昊, 李梓硕. 双层异向磷烯异质结构的热电输运特性[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(12): 4825-4832.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
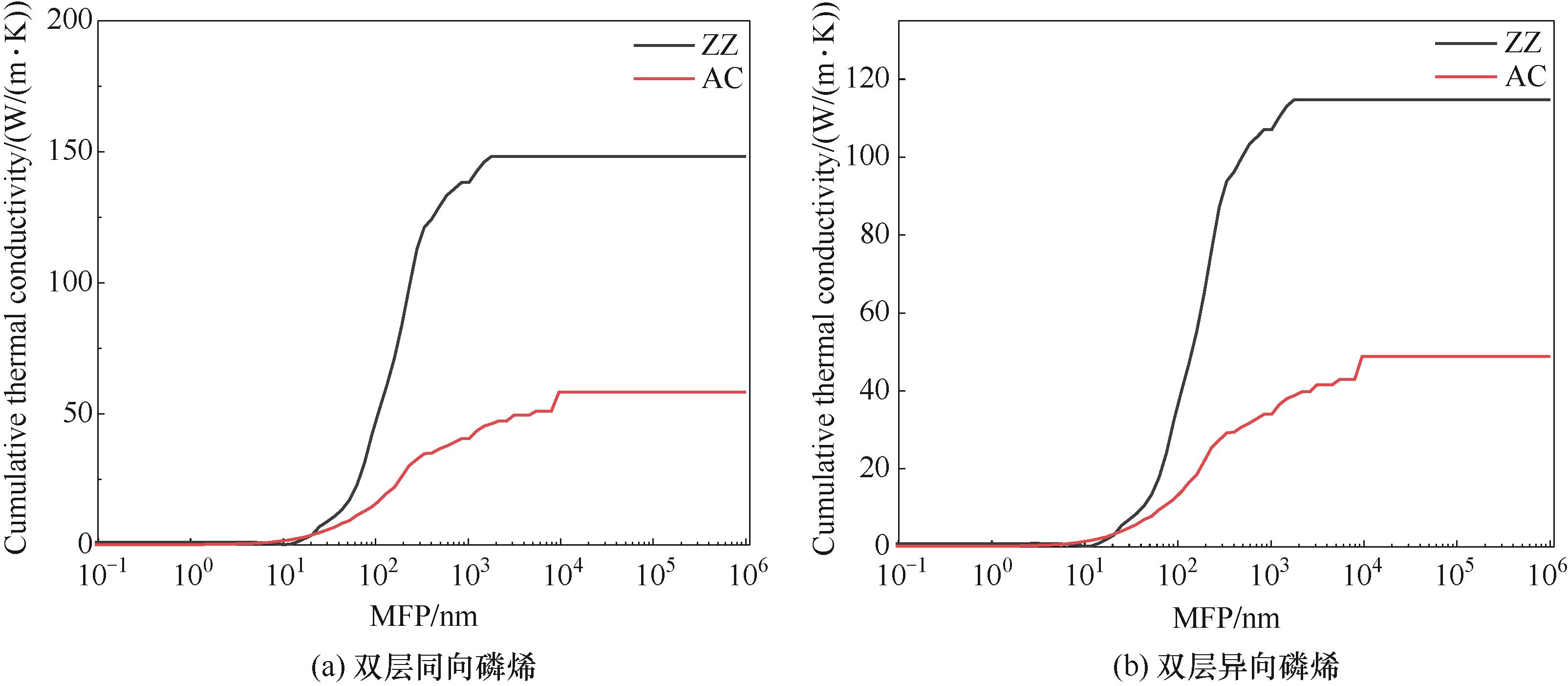
Fig.6 Cumulative thermal conductivity of phosphorene with respect to phonon MFP for homo-directional bilayer phosphorene and iso-directional bilayer phosphorene at different direction
| 1 | Xu Y J, Shi Z, Shi X Y, et al. Recent progress in black phosphorus and black-phosphorus-analogue materials: properties, synthesis and applications[J]. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(31): 14491-14527. |
| 2 | Li C, Tian Z T. Thermal transport properties of black phosphorus: a topical review[J]. Nanoscale and Microscale Thermophysical Engineering, 2017, 21(1): 45-57. |
| 3 | Xia F N, Wang H, Jia Y C. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4458. |
| 4 | Tran V, Soklaski R, Liang Y F, et al. Layer-controlled band gap and anisotropic excitons in few-layer black phosphorus[J]. Physical Review B, 2014, 89(23): 235319. |
| 5 | Qiao J S, Kong X H, Hu Z X, et al. High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 4475. |
| 6 | Zhu J, Park H, Chen J Y, et al. Revealing the origins of 3D anisotropic thermal conductivities of black phosphorus[J]. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2016, 2(5): 1600040. |
| 7 | Miao J S, Cai L, Zhang S M, et al. Air-stable humidity sensor using few-layer black phosphorus[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(11): 10019-10026. |
| 8 | Favron A, Gaufrès E, Fossard F, et al. Photooxidation and quantum confinement effects in exfoliated black phosphorus[J]. Nature Materials, 2015, 14(8): 826-832. |
| 9 | Cui Y F, Duan S, Chen X, et al. Prediction of enhanced thermoelectric performance in two-dimensional black phosphorus nanosheets[J]. Vacuum, 2021, 183: 109790. |
| 10 | Sun B, Gu X K, Zeng Q S, et al. Temperature dependence of anisotropic thermal-conductivity tensor of bulk black phosphorus[J]. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(3): 1603297.1-1603297.8. |
| 11 | Devi A, Singh A. Thermal properties of black phosphorene and doped phosphorene (C, N & O): a DFT study[C]//AIP Conference Proceedings, Mumbai, India, 2018, 1942(1): 090042.1-090042.4. |
| 12 | Hu W, Yang J L. Defects in phosphorene[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119(35): 20474-20480. |
| 13 | Zhao Y S, Zhang G, Nai M H, et al. Probing the physical origin of anisotropic thermal transport in black phosphorus nanoribbons[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(50): 1804928. |
| 14 | Qi P F, Liu K, Bi S P, et al. The abnormally excellent figure of merit of 14,14,18-graphyne at room temperature: a study on the thermoelectric characteristic of graphyne[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(5): 6363-6372. |
| 15 | Wang V, Xu N, Liu J C, et al. VASPKIT: a user-friendly interface facilitating high-throughput computing and analysis using VASP code[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2021, 267: 108033. |
| 16 | Tao J M, Perdew J P, Staroverov V N, et al. Climbing the density functional ladder: nonempirical meta-generalized gradient approximation designed for molecules and solids[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 91(14): 146401. |
| 17 | Baroni S, De Gironcoli S, Dal Corso A, et al. Phonons and related crystal properties from density-functional perturbation theory[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 2001, 73(2): 515-562. |
| 18 | He X Y, Luo L S. Theory of the lattice Boltzmann method: from the Boltzmann equation to the lattice Boltzmann equation[J]. Physical Review E, 1997, 56(6): 6811-6817. |
| 19 | Li W, Carrete J, Katcho N A, et al. ShengBTE: a solver of the Boltzmann transport equation for phonons[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2014, 185(6): 1747-1758. |
| 20 | Madsen G K H, Carrete J, Verstraete M J. BoltzTraP2, a program for interpolating band structures and calculating semi-classical transport coefficients[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2018, 231: 140-145. |
| 21 | Bardeen J, Shockley W. Deformation potentials and mobilities in non-polar crystals[J]. Physical Review, 1950, 80(1): 72-80. |
| 22 | Gao Y, Liu Q C, Xu B X. Lattice mismatch dominant yet mechanically tunable thermal conductivity in bilayer heterostructures[J]. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(5): 5431-5439. |
| 23 | Zhang F, Zheng X, Wang H M, et al. Anisotropy of thermal transport in phosphorene: a comparative first-principles study using different exchange–correlation functionals[J]. Materials Advances, 2022, 3(12): 5108-5117. |
| 24 | Liu T H, Chang C C. Anisotropic thermal transport in phosphorene: effects of crystal orientation[J]. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(24): 10648-10654. |
| 25 | Zhang X, Sun S, Xu T, et al. Temperature dependent Grüneisen parameter[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2019, 62(9): 1565-1576. |
| 26 | Schelling P K, Phillpot S R, Keblinski P. Comparison of atomic-level simulation methods for computing thermal conductivity[J]. Physical Review B, 2002, 65(14): 144306. |
| 27 | Goldsmid H J, Sharp J W. Estimation of the thermal band gap of a semiconductor from Seebeck measurements[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 1999, 28(7): 869-872. |
| 28 | Snyder G J, Toberer E S. Complex thermoelectric materials[J]. Nature Materials, 2008, 7(2): 105-114. |
| 29 | Hu R, Zhou Z Z, Sheng C Y, et al. Surprisingly good thermoelectric performance of a black phosphorus/blue phosphorus van der Waals heterostructure[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2020, 22(39): 22390-22398. |
| 30 | Zhang J, Liu H J, Cheng L, et al. High thermoelectric performance can be achieved in black phosphorus[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(5): 991-998. |
| [1] | Guanyu REN, Yifei ZHANG, Xinze LI, Wenjing DU. Numerical study on flow and heat transfer characteristics of airfoil printed circuit heat exchangers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 108-117. |
| [2] | Yong YANG, Zixuan ZU, Yukun LI, Dongliang WANG, Zongliang FAN, Huairong ZHOU. Numerical simulation of CO2 absorption by alkali liquor in T-junction cylindrical microchannels [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 135-142. |
| [3] | Junhao HUANG, Keliang PANG, Fangyuan SUN, Fujun LIU, Zhiyuan GU, Long HAN, Yanquan DUAN, Yanhui FENG. Influence of bell structure of coke dry quenching furnace on coke distribution [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 158-169. |
| [4] | Xinyu DONG, Longfei BIAN, Yiyi YANG, Yuxuan ZHANG, Lu LIU, Teng WANG. Study on flow and heat transfer mechanism of supercritical CO2 in inclined upward tube under cooling conditions [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 195-205. |
| [5] | Qirui GUO, Liyuan REN, Kang CHEN, Xiangyu HUANG, Weihua MA, Leqin XIAO, Weiliang ZHOU. Numerical simulation of static mixing tubes for HTPB propellant slurry [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 206-216. |
| [6] | Kuangxi LI, Peiqian YU, Jiangyun WANG, Haoran WEI, Zhigang ZHENG, Liuhai FENG. Flow analysis and structure optimization of micro-bubble swirling air flotation device [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 223-234. |
| [7] | Zhangzhou WANG, Tianqi TANG, Jiajun XIA, Yurong HE. Battery thermal management performance simulation based on composite phase change material [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 329-338. |
| [8] | Jian HU, Jinghua JIANG, Shengjun FAN, Jianhao LIU, Haijiang ZOU, Wanlong CAI, Fenghao WANG. Research on heat extraction performance of deep U-type borehole heat exchanger [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 76-84. |
| [9] | Shugang HU, Guoqing TIAN, Wenjuan LIU, Guangfei XU, Huaqing LIU, Jian ZHANG, Yanlong WANG. Preparation of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its application of reduction and oxidation technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3041-3055. |
| [10] | Juhui CHEN, Tong SU, Dan LI, Liwei CHEN, Wensheng LYU, Fanqi MENG. Study on the heat transfer characteristics of microchannels under the action of fin-shaped spoilers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3122-3132. |
| [11] | Shuyue LI, Huan WANG, Shaoqiang ZHOU, Zhihong MAO, Yongmin ZHANG, Junwu WANG, Xiuhua WU. Numerical simulation of hydrogen reduction of U3O8 in fluidized bed reactors using CPFD method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3133-3151. |
| [12] | Xiaoyu QIAN, Xuan RUAN, Shuiqing LI. Structural reconstruction and levitation of dielectric particle layers in electric fields [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2756-2762. |
| [13] | Ziliang ZHU, Shuang WANG, Yu'ang JIANG, Mei LIN, Qiuwang WANG. Solid-liquid phase change algorithm with Euler-Lagrange iteration [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2763-2776. |
| [14] | Aiming DENG, Yurong HE, Tianqi TANG, Yanwei HU. Simulation of effect of draft plate on particle growth process in spray fluidized beds [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2787-2799. |
| [15] | Hu JIN, Fan YANG, Mengyao DAI. The motion process of a droplet on a circular cylinder based on the lattice Boltzmann method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2897-2908. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||