CIESC Journal ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (10): 3783-3792.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240453
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yingying LIU1( ), Yue QIAN1, Xinyu DONG1, Xinlong QIAN1, Yuan HE1, Meijun LIU1, Haifeng ZHANG1(
), Yue QIAN1, Xinyu DONG1, Xinlong QIAN1, Yuan HE1, Meijun LIU1, Haifeng ZHANG1( ), Zhi WANG2(
), Zhi WANG2( )
)
Received:2024-04-25
Revised:2024-06-30
Online:2024-11-04
Published:2024-10-25
Contact:
Haifeng ZHANG, Zhi WANG
刘莹莹1( ), 钱月1, 董鑫宇1, 乾鑫龙1, 何媛1, 刘美君1, 张海丰1(
), 钱月1, 董鑫宇1, 乾鑫龙1, 何媛1, 刘美君1, 张海丰1( ), 王志2(
), 王志2( )
)
通讯作者:
张海丰,王志
作者简介:刘莹莹(1991—),女,博士研究生,讲师,liuyingying@tju.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Yingying LIU, Yue QIAN, Xinyu DONG, Xinlong QIAN, Yuan HE, Meijun LIU, Haifeng ZHANG, Zhi WANG. Preparation of anti-biofouling reverse osmosis membrane by surface modification with quorum sensing inhibitor[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3783-3792.
刘莹莹, 钱月, 董鑫宇, 乾鑫龙, 何媛, 刘美君, 张海丰, 王志. 利用群体感应抑制剂表面改性制备抗生物污染反渗透膜[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3783-3792.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 膜 | 元素组成/% | O/N比 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | O | ||
| RO-VG | 76.81 | 11.60 | 11.35 | 0.978 |
| RO-0MA | 77.00 | 10.31 | 12.42 | 1.205 |
| MA | 72.73 | 9.09 | 18.18 | 2.00 |
| RO-5MA | 76.67 | 10.46 | 12.68 | 1.212 |
| RO-10MA | 76.97 | 11.15 | 11.61 | 1.041 |
| RO-15MA | 77.51 | 10.18 | 12.00 | 1.179 |
Table 1 Composition of chemical elements on surface of original membrane and modified membranes prepared with different MA concentrations
| 膜 | 元素组成/% | O/N比 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | N | O | ||
| RO-VG | 76.81 | 11.60 | 11.35 | 0.978 |
| RO-0MA | 77.00 | 10.31 | 12.42 | 1.205 |
| MA | 72.73 | 9.09 | 18.18 | 2.00 |
| RO-5MA | 76.67 | 10.46 | 12.68 | 1.212 |
| RO-10MA | 76.97 | 11.15 | 11.61 | 1.041 |
| RO-15MA | 77.51 | 10.18 | 12.00 | 1.179 |
| 膜 | 平均粗糙度/nm | 均方根粗糙度/nm |
|---|---|---|
| RO-VG | 42.71±0.76 | 54.36±0.39 |
| RO-0MA | 35.11±0.29 | 44.54±0.51 |
| RO-5MA | 32.89±0.30 | 41.53±2.38 |
| RO-10MA | 33.04±0.17 | 42.19±1.42 |
| RO-15MA | 37.09±0.57 | 47.60±0.89 |
Table 2 Surface roughness of reverse osmosis membranes
| 膜 | 平均粗糙度/nm | 均方根粗糙度/nm |
|---|---|---|
| RO-VG | 42.71±0.76 | 54.36±0.39 |
| RO-0MA | 35.11±0.29 | 44.54±0.51 |
| RO-5MA | 32.89±0.30 | 41.53±2.38 |
| RO-10MA | 33.04±0.17 | 42.19±1.42 |
| RO-15MA | 37.09±0.57 | 47.60±0.89 |
| 膜 | 相对表面积 | 界面自由能/(mJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|
| RO-VG | 1.393±0.011 | 97.39 |
| RO-0MA | 1.342±0.009 | 106.43 |
| RO-5MA | 1.309±0.022 | 103.29 |
| RO-10MA | 1.316±0.006 | 99.82 |
| RO-15MA | 1.338±0.005 | 96.29 |
Table 3 Relative surface area and interfacial free energy of reverse osmosis membranes
| 膜 | 相对表面积 | 界面自由能/(mJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|
| RO-VG | 1.393±0.011 | 97.39 |
| RO-0MA | 1.342±0.009 | 106.43 |
| RO-5MA | 1.309±0.022 | 103.29 |
| RO-10MA | 1.316±0.006 | 99.82 |
| RO-15MA | 1.338±0.005 | 96.29 |
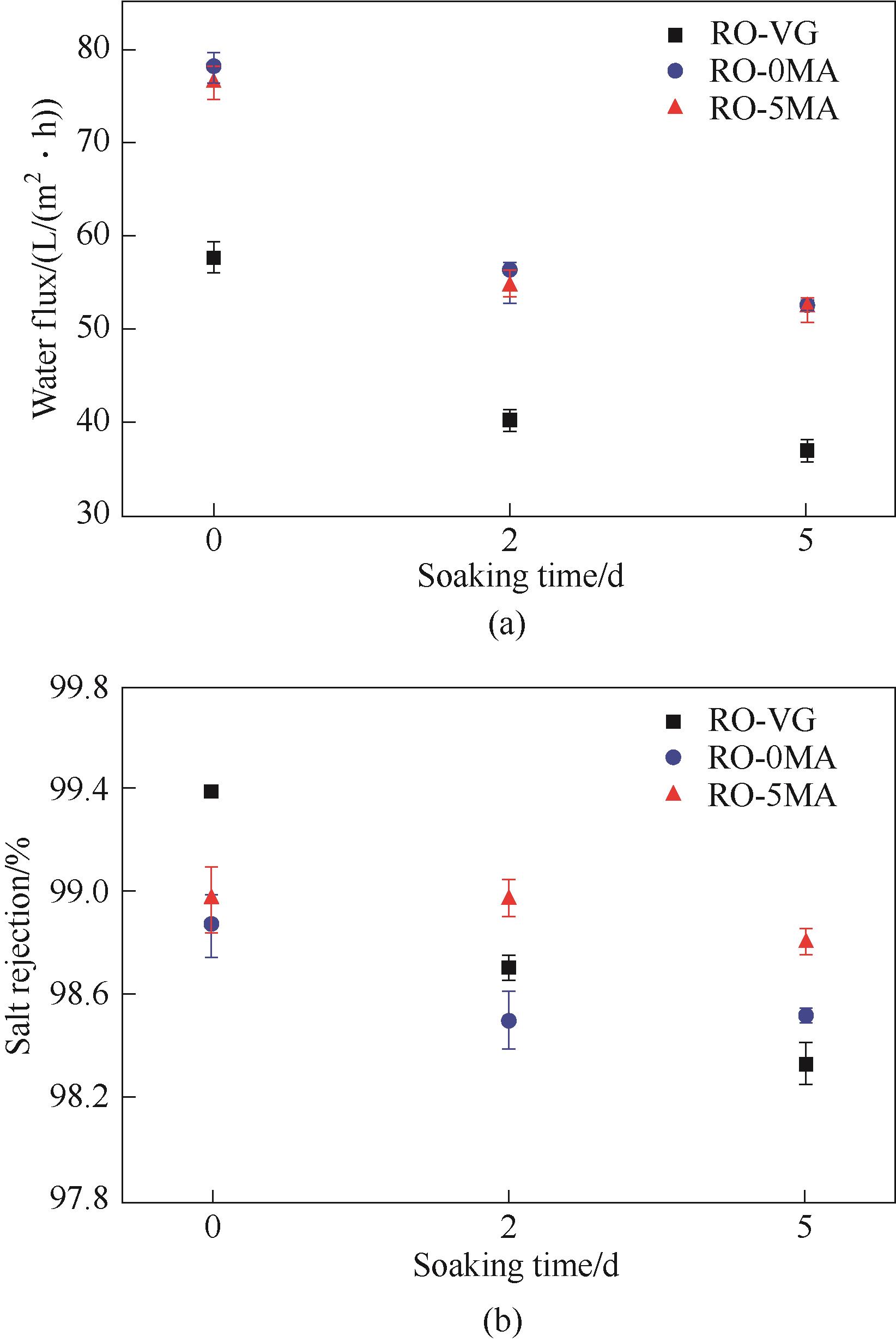
Fig.12 Changes of water flux and salt rejection of reverse osmosis membranes (membranes were immersed with Songhua River water containing nutrient solution for 2 d and 5 d)
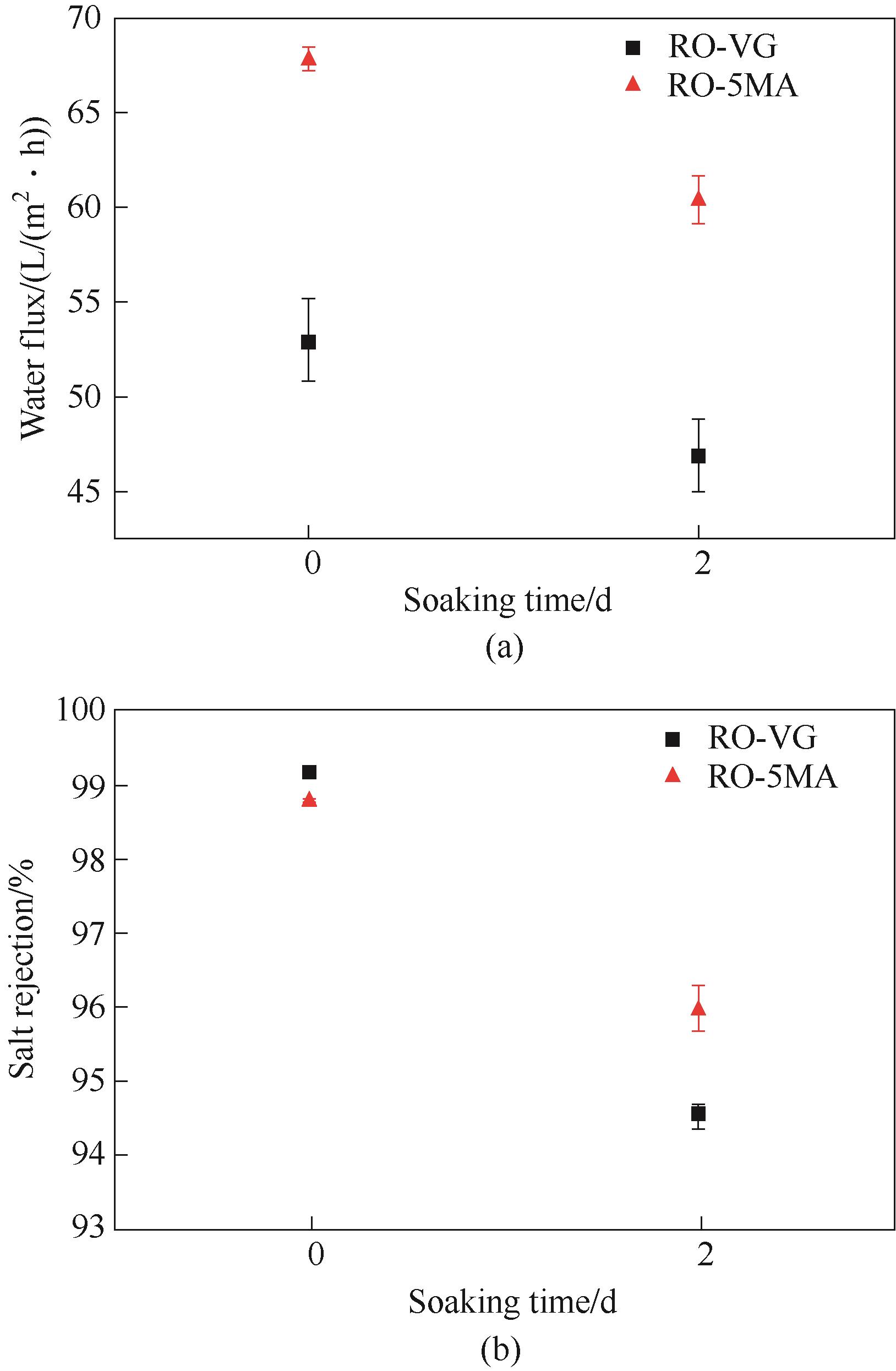
Fig.13 Changes of water flux and salt rejection of reverse osmosis membranes (membranes were immersed with Songhua River water containing nutrient solution and shaked for 2 d)
| 1 | Wang H S, Yang J X, Zhang H, et al. Membrane-based technology in water and resources recovery from the perspective of water social circulation: a review[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 908: 168277. |
| 2 | 高从堦, 周勇, 刘立芬. 反渗透海水淡化技术现状和展望[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2016, 35(1): 1-14. |
| Gao C J, Zhou Y, Liu L F. Recent development and prospect of seawater reverse osmosis desalination technology[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2016, 35(1): 1-14. | |
| 3 | Lim Y J, Goh K, Kurihara M, et al. Seawater desalination by reverse osmosis: current development and future challenges in membrane fabrication — a review[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 629: 119292. |
| 4 | Werber J R, Deshmukh A, Elimelech M. The critical need for increased selectivity, not increased water permeability, for desalination membranes[J]. Environmental Science & Technology Letters, 2016, 3(4): 112-120. |
| 5 | Li X, Wang Z, Han X L, et al. Regulating the interfacial polymerization process toward high-performance polyamide thin-film composite reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes: a review[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 640: 119765. |
| 6 | Gorgojo P, Jimenez-Solomon M F, Livingston A G. Polyamide thin film composite membranes on cross-linked polyimide supports: improvement of RO performance via activating solvent[J]. Desalination, 2014, 344: 181-188. |
| 7 | Cui Y, Liu X Y, Chung T S. Enhanced osmotic energy generation from salinity gradients by modifying thin film composite membranes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2014, 242: 195-203. |
| 8 | Chong C Y, Lau W J, Yusof N, et al. Studies on the properties of RO membranes for salt and boron removal: influence of thermal treatment methods and rinsing treatments[J]. Desalination, 2018, 428: 218-226. |
| 9 | Liu Y Y, Xin Z, Wang M, et al. Optimizing separation layer structure of polyamide composite membrane for high permselectivity based on post-treatment: a review[J]. Desalination, 2024, 580: 117585. |
| 10 | Mukherjee D, Kulkarni A, Gill W N. Flux enhancement of reverse osmosis membranes by chemical surface modification[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 1994, 97: 231-249. |
| 11 | Shin M G, Park S H, Kwon S J, et al. Facile performance enhancement of reverse osmosis membranes via solvent activation with benzyl alcohol[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 578: 220-229. |
| 12 | Zhao S F, Liao Z P, Fane A, et al. Engineering antifouling reverse osmosis membranes: a review[J]. Desalination, 2021, 499: 114857. |
| 13 | Liu C, Wang W J, Yang B, et al. Separation, anti-fouling, and chlorine resistance of the polyamide reverse osmosis membrane: from mechanisms to mitigation strategies[J]. Water Research, 2021, 195: 116976. |
| 14 | 任六一, 赵颂, 王志, 等. 抗污染芳香聚酰胺反渗透膜研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(2): 475-486. |
| Ren L Y, Zhao S, Wang Z, et al. Research progress of antifouling aromatic polyamide reverse osmosis membrane[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(2): 475-486. | |
| 15 | Li T T, Sun X J, Chen H T, et al. Methyl anthranilate: a novel quorum sensing inhibitor and anti-biofilm agent against Aeromonas sobria [J]. Food Microbiology, 2020, 86: 103356. |
| 16 | Chen C, Yang Y, Lee C H, et al. Functionalization of seawater reverse osmosis membrane with quorum sensing inhibitor to regulate microbial community and mitigate membrane biofouling[J]. Water Research, 2024, 253: 121358. |
| 17 | Katebian L, Gomez E, Skillman L, et al. Inhibiting quorum sensing pathways to mitigate seawater desalination RO membrane biofouling[J]. Desalination, 2016, 393: 135-143. |
| 18 | Feng Y R, Liang J, Liu X H, et al. Graphene oxide / methyl anthranilate modified anti-biofouling membrane possesses dual functions of anti-adhesion and quorum quenching[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 668: 121265. |
| 19 | Li C, Liang J, Yang Y, et al. Novel insights into the role of Pseudomonas quinolone signal in the control of reverse osmosis membrane biofouling[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 563: 505-512. |
| 20 | Si X R, Quan X C. Prevention of multi-species wastewater biofilm formation using vanillin and EPS disruptors through non-microbicidal mechanisms[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2017, 116: 211-218. |
| 21 | Katebian L, Hoffmann M R, Jiang S C. Incorporation of quorum sensing inhibitors onto reverse osmosis membranes for biofouling prevention in seawater desalination[J]. Environmental Engineering Science, 2018, 35(4): 261-269. |
| 22 | Chen C, Yang Y, Choo K H, et al. Cracking the code of seasonal seawater biofouling: enhanced biofouling control with quorum sensing inhibitor-functionalized membranes[J]. NPJ Clean Water, 2024, 7: 12. |
| 23 | Liu Y Y, Yan W T, Wang Z, et al. 1-Methylimidazole as a novel additive for reverse osmosis membrane with high flux-rejection combinations and good stability[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 599: 117830. |
| 24 | Liu Y Y, Du J, Wu H W, et al. Antifouling streptomycin-based nanofiltration membrane with high permselectivity for dye/salt separation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 297: 121443. |
| 25 | Guo S J, Du J, Yan F Z, et al. Fabrication of anti-fouling polyamide nanofiltration membrane by incorporating streptomycin as a novel co-monomer[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2022, 50: 185-196. |
| 26 | Liu Y Y, Wu H W, Wang Z, et al. Regulating solvent activation by the mechanical force for the fabrication of reverse osmosis membranes with high permeability and selectivity[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 638: 119732. |
| 27 | Liu Y Y, Wu H W, Guo S J, et al. Is the solvent activation strategy before heat treatment applicable to all reverse osmosis membranes?[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2023, 665: 121123. |
| 28 | Khan A A P, Khan A, Alam M A, et al. Chemical sensing platform for the Zn+2 ions based on poly(o-anisidine-co-methyl anthranilate) copolymer composites and their environmental remediation in real samples[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(28): 27899-27911. |
| 29 | Zhang S, Fu F J, Chung T S. Substrate modifications and alcohol treatment on thin film composite membranes for osmotic power[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 87: 40-50. |
| 30 | Zhang Y, Li X, Wang Z, et al. A novel method of fabricating anti-biofouling nanofiltration membrane with almost no potential to induce antimicrobial resistance in bacteria[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 288: 120710. |
| 31 | Shi M Q, Yan W T, Dong C X, et al. Solvent activation before heat-treatment for improving reverse osmosis membrane performance[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 595: 117565. |
| 32 | Guo S W, Chen X R, Wan Y H, et al. Custom-tailoring loose nanofiltration membrane for precise biomolecule fractionation: new insight into post-treatment mechanisms[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(11): 13327-13337. |
| 33 | Sukitpaneenit P, Chung T S. Fabrication and use of hollow fiber thin film composite membranes for ethanol dehydration[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014, 450: 124-137. |
| 34 | Wang X C, Zhang Q. Role of surface roughness in the wettability, surface energy and flotation kinetics of calcite[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 371: 55-63. |
| 35 | Yan W T, Shi M Q, Wang Z, et al. Confined growth of skin layer for high performance reverse osmosis membrane[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 585: 208-217. |
| 36 | Freger V. Nanoscale heterogeneity of polyamide membranes formed by interfacial polymerization[J]. Langmuir, 2003, 19(11): 4791-4797. |
| 37 | Wang C, Wang Z, Yang F R, et al. Improving the permselectivity and antifouling performance of reverse osmosis membrane based on a semi-interpenetrating polymer network[J]. Desalination, 2021, 502: 114910. |
| 38 | Chu K H, Mang J S, Lim J, et al. Variation of free volume and thickness by high pressure applied on thin film composite reverse osmosis membrane[J]. Desalination, 2021, 520: 115365. |
| 39 | Liu J, Sun X H, Ma Y T, et al. Quorum quenching mediated bacteria interruption as a probable strategy for drinking water treatment against bacterial pollution[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2020, 17(24): 9539. |
| 40 | Park C, Kim J O. Performance of biofouling mitigating feed spacer by surface modification using quorum sensing inhibitor[J]. Desalination, 2022, 538: 115904. |
| [1] | Wenfang GAO, Han CUI, Yiran SUN, Jiaqing PENG, Rui ZHU, Ran XIA, Xinyu ZHANG, Jiaqi LI, Xueliang WANG, Zhi SUN, Longyi LYU. A critical review on environmental impact assessment of typical metal production processes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3056-3073. |
| [2] | Qianqian WANG, Bing LI, Weibo ZHENG, Guomin CUI, Bingtao ZHAO, Pingwen MING. Three-dimensional modeling of local dynamic characteristics in hydrogen fuel cells [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2812-2820. |
| [3] | Mingjun YANG, Guangjun GONG, Jianan ZHENG, Yongchen SONG. Production characteristics and model of muddy hydrates with low permeability by depressurization [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2909-2916. |
| [4] | Wenxuan ZHOU, Zhen LIU, Fujian ZHANG, Zhongqiang ZHANG. Mechanism of water treatment by high permeability-selectivity time dimension membrane method [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2583-2593. |
| [5] | Zongwei HUO, Yabin NIU, Yanqiu PAN. Behavior of high viscosity oil droplets in oil-water membrane separation and its influencing factors [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(6): 2262-2273. |
| [6] | Wenyan ZHANG, Hao LIU, Weilong SONG, Pin ZHAO, Xinhua WANG. Construction and performance evaluation of TFN-FO membranes incorporated with UiO-66 nanoparticles of different sizes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 1920-1928. |
| [7] | Zijia ZHANG, Xinyue QIU, Xiang SUN, Zhibin LUO, Haizhong LUO, Gaohong HE, Xuehua RUAN. Progress in molecular structure design for polyimide membrane materials to enhance CO2 permeation ability [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1137-1152. |
| [8] | Binyu MO, Yaxin ZHANG, Guozhen LIU, Gongping LIU, Wanqin JIN. Recent progress of metal-organic framework membranes for mono/divalent ions separation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(4): 1183-1197. |
| [9] | Lingxian ZHANG, Bin LIU, Lin DENG, Yuhang REN. PEMFC fault diagnosis based on improved TSO optimized Xception [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 945-955. |
| [10] | Yaowen TAN, Panxing JIANG, Qing DU, Wanqiu YU, Xiaofei WEN, Zhigang ZHAN. Numerical study of the effects of operating voltage on the degradation of membrane electrodes of PEMFC [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 974-986. |
| [11] | Xinrui ZHANG, Xuemei CHEN. CNT/PVA@carbon-cloth membrane for performance study of solar and electric-driven interfacial evaporation [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 1028-1039. |
| [12] | Pei WANG, Ruiming DUAN, Guangru ZHANG, Wanqin JIN. Modeling and simulation analysis of solar driven membrane separation biomethane hydrogen production process [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 967-973. |
| [13] | Lingjie WANG, Hailong GAO, Jipeng JIN, Zhihao WANG, Jianbo LI. Influence of pollutants in seawater on performance of reverse electrodialysis stacks [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 695-705. |
| [14] | Hong CHEN, Kun JIANG, Tingjiang TANG, Yiyuan HUANG, Bin CHI, Shijun LIAO. Research on membrane electrode assembly consistency of high-power proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 637-646. |
| [15] | Ruijiao YU, Hang GUO, Fang YE, Hao CHEN. Effect of gas diffusion layer porosity on fuel cell performance [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3752-3762. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||