CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (7): 3477-3486.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241029
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zeming DONG( ), Juwei LOU, Nan WANG, Liangqi CHEN, Jiangfeng WANG(
), Juwei LOU, Nan WANG, Liangqi CHEN, Jiangfeng WANG( ), Pan ZHAO
), Pan ZHAO
Received:2024-09-13
Revised:2025-03-18
Online:2025-08-13
Published:2025-07-25
Contact:
Jiangfeng WANG
董泽明( ), 娄聚伟, 王楠, 陈良奇, 王江峰(
), 娄聚伟, 王楠, 陈良奇, 王江峰( ), 赵攀
), 赵攀
通讯作者:
王江峰
作者简介:董泽明(2001—),男,硕士研究生,18223737710@stu.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Zeming DONG, Juwei LOU, Nan WANG, Liangqi CHEN, Jiangfeng WANG, Pan ZHAO. Research on thermodynamic properties of supercritical compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system with waste heat recovery[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3477-3486.
董泽明, 娄聚伟, 王楠, 陈良奇, 王江峰, 赵攀. 含余热回收的超临界压缩二氧化碳储能系统热力学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3477-3486.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
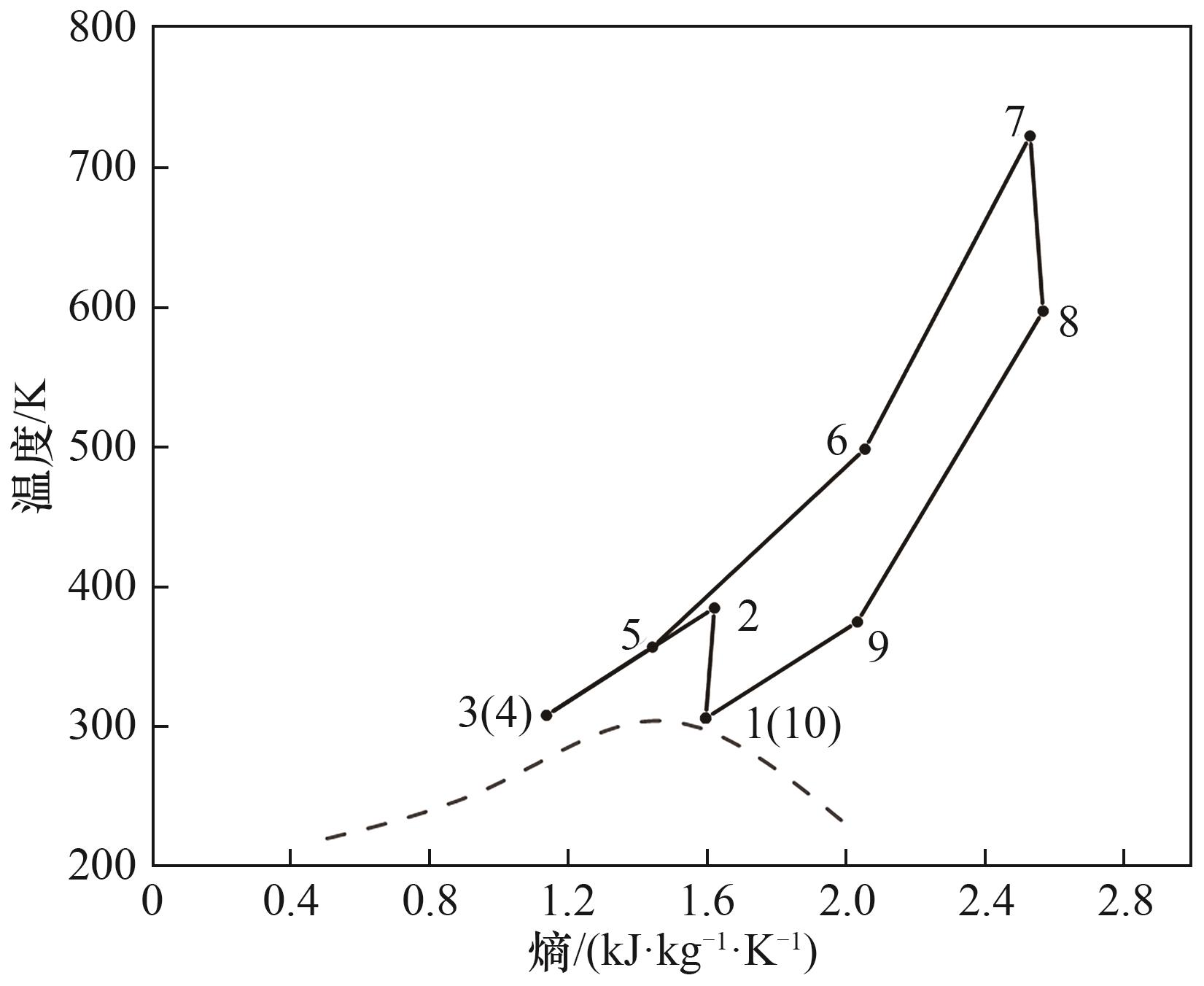
Fig.3 Temperature entropy diagram of supercritical compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system (dashed line represents saturation curve of carbon dioxide)
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 环境温度/℃ | 32 |
| 环境压力/MPa | 0.1 |
| 高压储罐压力/MPa | 25.0 |
| 低压储罐压力/MPa | 7.5 |
| 透平进口温度/℃ | 450 |
| 压缩机进口温度/℃ | 33 |
| 透平等熵效率/% | 85 |
| 压缩机等熵效率/% | 80 |
| 水泵等熵效率/% | 75 |
| 燃烧室内温度/℃ | 727 |
| 回热器端差/℃ | 20 |
| 燃烧室加热功率/kW | 5000 |
Table 1 Initial parameters of supercritical compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 环境温度/℃ | 32 |
| 环境压力/MPa | 0.1 |
| 高压储罐压力/MPa | 25.0 |
| 低压储罐压力/MPa | 7.5 |
| 透平进口温度/℃ | 450 |
| 压缩机进口温度/℃ | 33 |
| 透平等熵效率/% | 85 |
| 压缩机等熵效率/% | 80 |
| 水泵等熵效率/% | 75 |
| 燃烧室内温度/℃ | 727 |
| 回热器端差/℃ | 20 |
| 燃烧室加热功率/kW | 5000 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 压缩机耗功/kW | 525.91 |
| 膨胀透平输出功/kW | 1349.34 |
| 往返效率/% | 37.21 |
| 㶲效率/% | 33.44 |
| 储能密度/(kW∙h∙m-3) | 8.13 |
Table 2 Calculation results of energy parameters of supercritical compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 压缩机耗功/kW | 525.91 |
| 膨胀透平输出功/kW | 1349.34 |
| 往返效率/% | 37.21 |
| 㶲效率/% | 33.44 |
| 储能密度/(kW∙h∙m-3) | 8.13 |
| 参数 | 下限 | 上限 |
|---|---|---|
| 压缩机进口温度/℃ | 32 | 45 |
| 透平进口温度/℃ | 350 | 550 |
| 低压储罐压力/MPa | 7.4 | 15.0 |
| 高压储罐压力/MPa | 15.0 | 30.0 |
Table 3 Parameter range of supercritical compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system
| 参数 | 下限 | 上限 |
|---|---|---|
| 压缩机进口温度/℃ | 32 | 45 |
| 透平进口温度/℃ | 350 | 550 |
| 低压储罐压力/MPa | 7.4 | 15.0 |
| 高压储罐压力/MPa | 15.0 | 30.0 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 压缩机进口温度/℃ | 32.00 |
| 透平进口温度/℃ | 550.00 |
| 低压储罐压力/MPa | 13.42 |
| 高压储罐压力/MPa | 24.77 |
| 系统的往返效率/% | 52.69 |
Table 4 Optimized round-trip efficiency and key parameters
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 压缩机进口温度/℃ | 32.00 |
| 透平进口温度/℃ | 550.00 |
| 低压储罐压力/MPa | 13.42 |
| 高压储罐压力/MPa | 24.77 |
| 系统的往返效率/% | 52.69 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 压缩机进口温度/℃ | 32.00 |
| 透平进口温度/℃ | 550.00 |
| 低压储罐压力/MPa | 8.05 |
| 高压储罐压力/MPa | 29.94 |
| 储能密度/(kW∙h∙m-3) | 17.16 |
Table 5 Optimized energy storage density and design parameters
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 压缩机进口温度/℃ | 32.00 |
| 透平进口温度/℃ | 550.00 |
| 低压储罐压力/MPa | 8.05 |
| 高压储罐压力/MPa | 29.94 |
| 储能密度/(kW∙h∙m-3) | 17.16 |
| [1] | Jafari M, Botterud A, Sakti A. Decarbonizing power systems: a critical review of the role of energy storage[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2022, 158: 112077. |
| [2] | Ali S, Stewart R A, Sahin O. Drivers and barriers to the deployment of pumped hydro energy storage applications: systematic literature review[J]. Cleaner Engineering and Technology, 2021, 5: 100281. |
| [3] | 王伟. 可再生能源并网系统中电池储能系统特性及优化[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2022. |
| Wang W. Characteristics and optimization of battery energy storage system in renewable energy grid-connected system[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2022. | |
| [4] | 万明忠, 王元媛, 李峻, 等. 压缩空气储能技术研究进展及未来展望[J]. 综合智慧能源, 2023, 45(9): 26-31. |
| Wan M Z, Wang Y Y, Li J, et al. Research progress and future prospect of compressed air energy storage technology[J]. Integrated Intelligent Energy, 2023, 45(9): 26-31. | |
| [5] | 何青, 王珂. 等温压缩空气储能技术及其研究进展[J]. 热力发电, 2022, 51(8): 11-19. |
| He Q, Wang K. Research progress of isothermal compressed air energy storage technology[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2022, 51(8): 11-19. | |
| [6] | 傅昊, 张毓颖, 崔岩, 等. 压缩空气储能技术研究进展[J]. 科技导报, 2016, 34(23): 81-87. |
| Fu H, Zhang Y Y, Cui Y, et al. Research progress of compressed air energy storage systems[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2016, 34(23): 81-87. | |
| [7] | 赵攀, 张仕强, 许文盼, 等. 具备近似等压放电过程的近似等温压缩CO2储能系统特性研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2023, 57(1): 34-44. |
| Zhao P, Zhang S Q, Xu W P, et al. Performance analysis of a near-isothermal compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system with near constant discharge process[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2023, 57(1): 34-44. | |
| [8] | 高超. 超临界二氧化碳储能发电系统设计优化[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2023. |
| Gao C. Design optimization of supercritical carbon dioxide energy storage power generation system[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2023. | |
| [9] | 张家俊, 李晓琼, 张振涛, 等. 压缩二氧化碳储能系统研究进展[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(6): 1928-1945. |
| Zhang J J, Li X Q, Zhang Z T, et al. Research progress of compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(6): 1928-1945. | |
| [10] | 郝佳豪, 越云凯, 张家俊, 等. 二氧化碳储能技术研究现状与发展前景[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(10): 3285-3296. |
| Hao J H, Yue Y K, Zhang J J, et al. Research status and development prospect of carbon dioxide energy-storage technology[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(10): 3285-3296. | |
| [11] | 李玉平. 压缩二氧化碳储能系统的热力学性能分析[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2018. |
| Li Y P. Thermodynamic performance analysis of compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2018. | |
| [12] | 吴毅, 胡东帅, 王明坤, 等. 一种新型的跨临界CO2储能系统[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2016, 50(3): 45-49, 100. |
| Wu Y, Hu D S, Wang M K, et al. A novel transcritical CO2 energy storage system[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2016, 50(3): 45-49, 100. | |
| [13] | 郝银萍. 跨临界压缩二氧化碳储能系统热力学特性及技术经济性研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021. |
| Hao Y P. Study on thermodynamic characteristics and technical economy of transcritical compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021. | |
| [14] | 赵俊朋. 含二氧化碳储能的冷热电联产系统运行优化研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2020. |
| Zhao J P. Study on operation optimization of CCHP system with carbon dioxide energy storage[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2020. | |
| [15] | Ahmadi M H, Mehrpooya M, Pourfayaz F. Thermodynamic and exergy analysis and optimization of a transcritical CO2 power cycle driven by geothermal energy with liquefied natural gas as its heat sink[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2016, 109: 640-652. |
| [16] | Ahmadi M H, Mehrpooya M, Pourfayaz F. Exergoeconomic analysis and multi objective optimization of performance of a carbon dioxide power cycle driven by geothermal energy with liquefied natural gas as its heat sink[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2016, 119: 422-434. |
| [17] | Naseri A, Bidi M, Ahmadi M H, et al. Exergy analysis of a hydrogen and water production process by a solar-driven transcritical CO2 power cycle with Stirling engine[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 158: 165-181. |
| [18] | Kim Y M, Shin D G, Lee S Y, et al. Isothermal transcritical CO2 cycles with TES (thermal energy storage) for electricity storage[J]. Energy, 2013, 49: 484-501. |
| [19] | Ghazizade-Ahsaee H, Ameri M. Energy and exergy investigation of a carbon dioxide direct-expansion geothermal heat pump[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2018, 129: 165-178. |
| [20] | Bai T, Yu J L, Yan G. Advanced exergy analyses of an ejector expansion transcritical CO2 refrigeration system[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2016, 126: 850-861. |
| [21] | Tian H, Chang L W, Shu G Q, et al. Multi-objective optimization of the carbon dioxide transcritical power cycle with various configurations for engine waste heat recovery[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 148: 477-488. |
| [22] | Enriquez L C, Munoz-Anton J, Penalosa J M M V. Thermodynamic optimization of supercritical CO2 Brayton power cycles coupled to line-focusing solar fields[J]. Journal of Solar Energy Engineering, 2017, 139(6):061005. |
| [23] | Morandin M, Maréchal F, Mercangöz M, et al. Conceptual design of a thermo-electrical energy storage system based on heat integration of thermodynamic cycles (Part B): Alternative system configurations[J]. Energy, 2012, 45(1): 386-396. |
| [24] | 张远. 风电与先进绝热压缩空气储能技术的系统集成与仿真研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院工程热物理研究所, 2014. |
| Zhang Y. System integration and simulation of wind power and advanced adiabatic compressed air energy storage technology[D]. Beijing: Institute of Engineering Thermophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2014. | |
| [25] | Wang M K, Zhao P, Wu Y, et al. Performance analysis of a novel energy storage system based on liquid carbon dioxide[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2015, 91: 812-823. |
| [26] | Liu Z, Liu Z H, Xin X, et al. Proposal and assessment of a novel carbon dioxide energy storage system with electrical thermal storage and ejector condensing cycle: energy and exergy analysis[J]. Applied Energy, 2020, 269: 115067. |
| [27] | 刘辉. 超临界压缩二氧化碳储能系统热力学特性与热经济性研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2017. |
| Liu H. Study on thermodynamic characteristics and thermal economy of supercritical compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2017. | |
| [28] | Span R, Wagner W. A new equation of state for carbon dioxide covering the fluid region from the triple-point temperature to 1100 K at pressures up to 800 MPa[J]. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data, 1996, 25(6): 1509-1596. |
| [29] | 傅秦生. 能量系统的热力学分析方法[M]. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 2005: 289. |
| Fu Q S. Thermodynamic Analysis Method of Energy System[M]. Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University Press, 2005: 289. | |
| [30] | Liu X, Yan X W, Liu X L, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of a novel liquid carbon dioxide energy storage system with cold recuperator: energy, conventional exergy and advanced exergy analysis[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 250: 114909. |
| [31] | Zhao P, Xu W P, Zhang S Q, et al. Components design and performance analysis of a novel compressed carbon dioxide energy storage system: a pathway towards realizability[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 229: 113679. |
| [1] | Haolei DUAN, Haoyuan CHEN, Kunfeng LIANG, Lin WANG, Bin CHEN, Yong CAO, Chenguang ZHANG, Shuopeng LI, Dengyu ZHU, Yaru HE, Dapeng YANG. Performance analysis and comprehensive evaluation of thermal management system schemes with low GWP refrigerants [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [2] | Songyuan GUO, Xiaoqing ZHOU, Wubing MIAO, Bin WANG, Rui ZHUAN, Qingtai CAO, Chengcheng CHEN, Guang YANG, Jingyi WU. Numerical study on characteristics of pressurized discharge in liquid oxygen tank equipped with porous plate in the ascent period of rocket [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [3] | Xinquan SHA, Ran HU, Lei DING, Zhenhua JIANG, Yinong WU. Development and testing of an independent two-stage valved linear compressor for space applications [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 114-122. |
| [4] | Wei SU, Dahai ZHAO, Xu JIN, Zhongyan LIU, Jing LI, Xiaosong ZHANG. Delaying condensation frosting using biphilic surfaces coupled with spatial control of liquid desiccant [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 140-151. |
| [5] |
Jichao GUO, Xiaoxiao XU, Yunlong SUN.
Airflow simulation and optimization based on |
| [6] | Yifan SHI, Gang KE, Hao CHEN, Xiaosheng HUANG, Fang YE, Chengjiao LI, Hang GUO. Simulation of temperature control in large-scale high and low temperature environmental laboratory [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 268-280. |
| [7] | Fanchen KONG, Shuo ZHANG, Mingsheng TANG, Huiming ZOU, Zhouhang HU, Changqing TIAN. Simulation of gas bearings in carbon dioxide linear compressors [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 281-288. |
| [8] | Congqi HUANG, Shuangquan SHAO. Research on characteristics of compression-absorption refrigeration system driven by waste heat in liquid-cooled data center [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 326-335. |
| [9] | Tengfei ZHU, Ye LIU. Performance analysis of low GWP refrigerant used in new energy vehicle air conditioning [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 343-350. |
| [10] | Di WU, Bin HU, Jiatong JIANG. Experimental study and application analysis of R1233zd(E) high temperature heat pump [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 377-383. |
| [11] | Xin XIAO, Geng YANG, Yunfeng WANG. Simulation of solar heat pump system integration of cascade latent heat thermal energy storage based on TRNSYS [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 393-400. |
| [12] | Guorui HUANG, Yao ZHAO, Mingxi XIE, Erjian CHEN, Yanjun DAI. Experimental study on a novel waste heat recovery system based on desiccant coated exchanger in data center [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 409-417. |
| [13] | Ting HE, Kai ZHANG, Wensheng LIN, Liqiong CHEN, Jiafu CHEN. Research on integrated process of cryogenic CO2 removal under supercritical pressure and liquefaction for biogas [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(S1): 418-425. |
| [14] | Hongxin DING, Wenxiang GAN, Yongyang ZHAO, Runze JIA, Ziqi KANG, Yulong ZHAO, Yong XIANG. Corrosion mechanisms of X65 steel welded joints in supercritical CO2 and H2O-rich phases [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3426-3435. |
| [15] | Yu GONG, Shengli WANG, Jinju SUN, Kuo HAI, Wen HUANG. Thermodynamic model and exploration of micro multi-stage compressor inflation system [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3626-3638. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||