CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (8): 4194-4204.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250141
• Surface and interface engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ze WANG( ), Qiong HU(
), Qiong HU( ), Yajing CHEN, Yan WANG(
), Yajing CHEN, Yan WANG( ), Jiaxu GENG, Feiran SHEN
), Jiaxu GENG, Feiran SHEN
Received:2025-02-15
Revised:2025-03-21
Online:2025-09-17
Published:2025-08-25
Contact:
Qiong HU, Yan WANG
王泽( ), 胡琼(
), 胡琼( ), 陈雅静, 王衍(
), 陈雅静, 王衍( ), 耿佳旭, 沈斐然
), 耿佳旭, 沈斐然
通讯作者:
胡琼,王衍
作者简介:王泽(2001—),男,硕士研究生,2645072370@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
Ze WANG, Qiong HU, Yajing CHEN, Yan WANG, Jiaxu GENG, Feiran SHEN. Leakage characteristics, sealing mechanism, and optimization design of self-impacting liquid seals[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4194-4204.
王泽, 胡琼, 陈雅静, 王衍, 耿佳旭, 沈斐然. 液体自冲击密封泄漏特性、密封机理与优化设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4194-4204.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| 参数 | 范围 | 相对不变量 |
|---|---|---|
| 流道宽度h/mm | 0.01~0.3 | 0.1 |
| 悬柱半径R/mm | 2.5 | — |
| 流距l/mm | 6 | — |
| 交错比k/mm | 2 | — |
| 分流角α/(°) | 48 | — |
| 入口压力Pin/MPa | 0.2~50.1 | 0.2 |
| 出口压力Pout/MPa | 0.1 | — |
| 转速N/(r/min) | 0~20000 | 0 |
| 介质黏度μ/(Pa·s) | 0.00000929~1 | 0.001 |
| 矩形宽度w/mm | 2.5 | — |
| 密封级数Z | 8~40 | 8 |
Table 1 Structural and operational parameters of three self-impact seals
| 参数 | 范围 | 相对不变量 |
|---|---|---|
| 流道宽度h/mm | 0.01~0.3 | 0.1 |
| 悬柱半径R/mm | 2.5 | — |
| 流距l/mm | 6 | — |
| 交错比k/mm | 2 | — |
| 分流角α/(°) | 48 | — |
| 入口压力Pin/MPa | 0.2~50.1 | 0.2 |
| 出口压力Pout/MPa | 0.1 | — |
| 转速N/(r/min) | 0~20000 | 0 |
| 介质黏度μ/(Pa·s) | 0.00000929~1 | 0.001 |
| 矩形宽度w/mm | 2.5 | — |
| 密封级数Z | 8~40 | 8 |
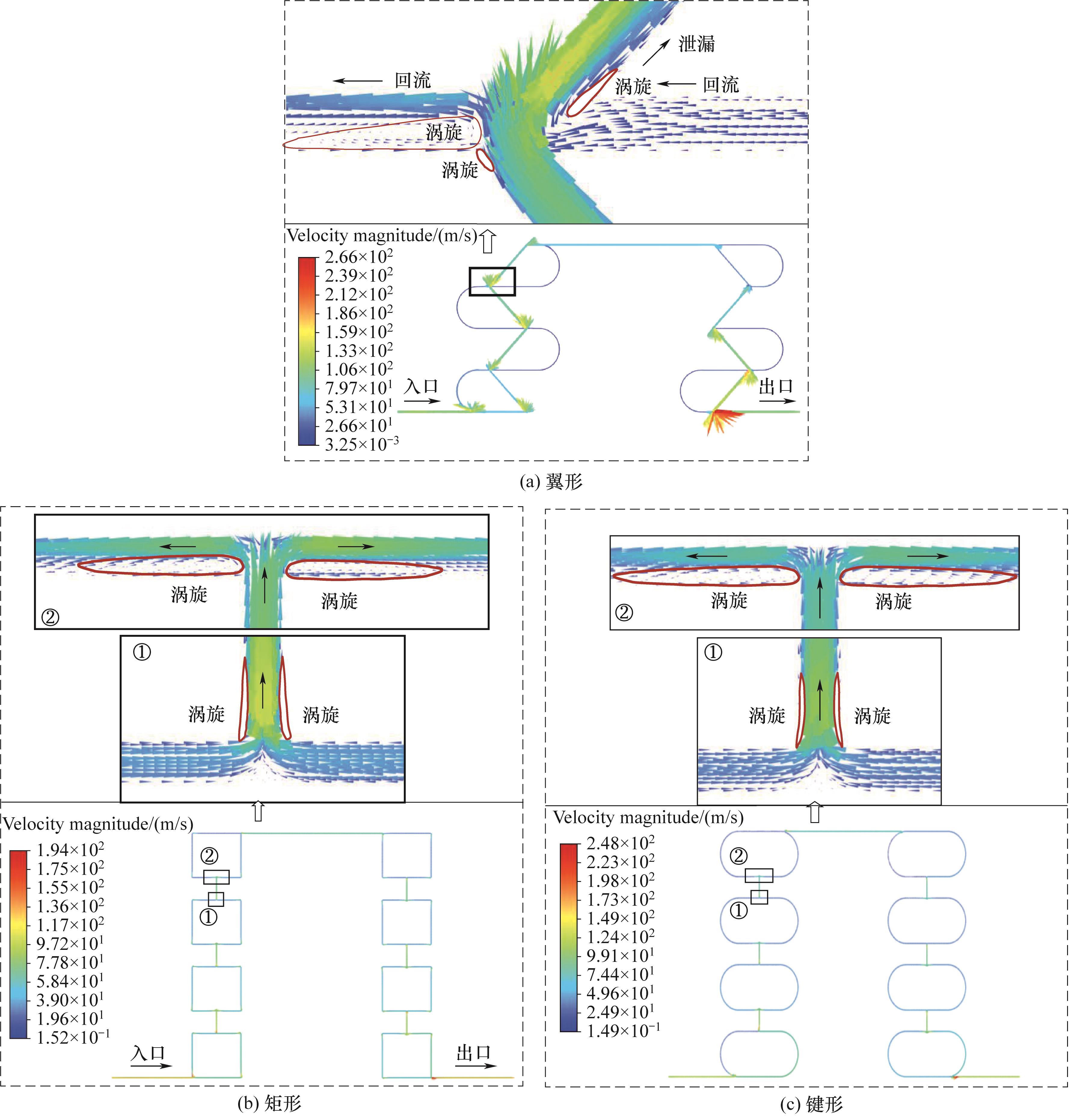
Fig.12 Velocity distribution of micro-flow field in self-impact seals with different suspension pillar shapes (water, 100 MPa pressure differential, 0.1 mm clearance and shutdown state condition)
| [1] | 勒贝克. 机械密封原理与设计[M]. 黄伟峰, 译. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2016: 11. |
| Lebeck A O. Principles and Design of Mechanical Face Seals[M]. Huang W F, trans. Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press, 2016: 11. | |
| [2] | Morad O, Viitala R, Saikko V. Behavior of marine thruster lip seals under typical operating conditions[J]. Tribology International, 2025, 201: 110195. |
| [3] | 周易文, 栗付平, 虞晓峰. 一种标准地铁单元制动缸用橡胶皮碗密封性能仿真分析研究[J]. 特种橡胶制品, 2022, 43(6): 73-78. |
| Zhou Y W, Li F P, Yu X F. Simulation analysis on sealing performance of rubber cup for a standard subway unit brake cylinder[J]. Special Purpose Rubber Products, 2022, 43(6): 73-78. | |
| [4] | 王波, 王江阳, 赵崇胜, 等. 基于有限疲劳寿命的压裂泵盘根铜套优化设计[J]. 机械设计, 2023, 40(S2): 168-174. |
| Wang B, Wang J Y, Zhao C S, et al. Optimation design of fracturing pump packing copper sleeve based on finite fatigue life[J]. Journal of Machine Design, 2023, 40(S2): 168-174. | |
| [5] | 薛婷, 王瑜, 张凯, 等. 非接触式端面密封流体动压效应的研究进展[J]. 钻探工程, 2023, 50(S1): 38-43. |
| Xue T, Wang Y, Zhang K, et al. Research on progress of hydrodynamic pressure effect of non-contact face seal[J]. Drilling Engineering, 2023, 50(S1): 38-43. | |
| [6] | 刘孟扬, 孙雪剑, 毛文元, 等. 考虑微观表面分层特征密封环接触特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1156-1169. |
| Liu M Y, Sun X J, Mao W Y, et al. Contact characterization of sealing rings considering microscopic surface delamination features[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1156-1169. | |
| [7] | Zhao Y Y, Zhang G Y, Wang J Q, et al. Tribological properties of low-temperature time-dependent pretreated graphite for mechanical seal pairs in high-speed turbopump[J]. Friction, 2024, 12(2): 305-318. |
| [8] | Gibbons N, Goyne C. Form shear stress correction in bulk flow analysis of grooved seals based on effective film thickness[J]. Journal of Tribology, 2024, 146(1): 014401. |
| [9] | Ran Y, He Q, Huang W F, et al. Analysis of the coupling mechanism of the dynamic response and mechanical-thermal deformation in mechanical seals[J]. Tribology International, 2024, 192: 109257. |
| [10] | 李双喜, 刘安, 刘志远, 等. 高速涡轮泵动静压混合式气体隔离密封扰动性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(1): 311-323. |
| Li S X, Liu A, Liu Z Y, et al. Analysis of disturbance performance of dynamic and static pressure hybrid gas isolation seal of high-speed turbopumps and experimental study[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 311-323. | |
| [11] | 张国渊, 黎旭康, 赵伟刚, 等. 低温高速动静结合型机械密封两相流仿真与实验[J]. 航空学报, 2023, 44(23): 628229. |
| Zhang G Y, Li X K, Zhao W G, et al. Theoretical and experimental on two-phase flow mechanism of low-temperature high-speed hydrodynamic mechanical seal[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(23): 628229. | |
| [12] | Migout F, Brunetière N, Tournerie B. Study of the fluid film vaporization in the interface of a mechanical face seal[J]. Tribology International, 2015, 92: 84-95. |
| [13] | 王衍, 谢雪非, 徐慧, 等. 新型非接触式自冲击密封结构设计与性能分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59(15): 204-215. |
| Wang Y, Xie X F, Xu H, et al. Design and performance analysis of a new non-contact self-impact seal[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 59(15): 204-215. | |
| [14] | 孙巍伟, 刘跃, 李永健, 等. 多因素下迷宫密封泄漏分析及实验验证[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 64(8): 1414-1423. |
| Sun W W, Liu Y, Li Y J, et al. Analysis and experimental verification on the leakage of labyrinth seals under multiple factors[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2024, 64(8): 1414-1423. | |
| [15] | 张彤, 李德才, 李艳文. 磁性液体密封与迷宫密封组合密封的结构设计及优化[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(9): 172-181. |
| Zhang T, Li D C, Li Y W. Design and optimization of combined magnetic fluid seal and labyrinth seal[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(9): 172-181. | |
| [16] | Ghosh S, Fernandez E, Kapat J. Fluid-thermal topology optimization of gas turbine blade internal cooling ducts[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2022, 144(5): 051703. |
| [17] | Wang J, Wang J B, Long Z Y, et al. Design and application of a cooling device based on peltier effect coupled with electrohydrodynamics[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2021, 162: 106761. |
| [18] | 张惠涛, 李德才. 分瓣式密封装置磁性液体平面密封研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(5): 149-155. |
| Zhang H T, Li D C. Studies of magnetic fluid plane sealing in split sealing device[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(5): 149-155. | |
| [19] | Szczech M, Horak W. Tightness testing of rotary ferromagnetic fluid seal working in water environment[J]. Industrial Lubrication and Tribology, 2015, 67(5): 455-459. |
| [20] | 靳志鸿, 李志刚, 李军, 等. 液氧涡轮泵新型螺旋阻尼密封泄漏特性研究[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2022, 56(8): 62-72. |
| Jin Z H, Li Z G, Li J, et al. Investigation on the leakage characteristics of a novel helical damper seal for the liquid oxygen turbopump[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2022, 56(8): 62-72. | |
| [21] | Nikola T. Valvular conduit: US1329559[P]. 1920-02-03. |
| [22] | 翁祥宇, 严生虎, 张跃, 等. 一种基于特斯拉阀结构的微混合器设计、模拟及其试验研究[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(8): 4173-4178. |
| Weng X Y, Yan S H, Zhang Y, et al. Design, simulation and experimental study of a micromixer based on Tesla valve structure[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(8): 4173-4178. | |
| [23] | Jang D S, Ham S H, Shin H H, et al. Thermal performance improvement of a radial pulsating heat pipe with diverging channels by adopting Tesla valves at various heat fluxes[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 237: 121799. |
| [24] | Zhang Y, He S R, Jiang X H, et al. Performance and configuration optimization of proton exchange membrane fuel cell considering dual symmetric Tesla valve flow field[J]. Energy, 2024, 288: 129791. |
| [25] | Wang P F, Hu P L, Liu L, et al. On the diodicity enhancement of multistage Tesla valves[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35(5): 052010. |
| [26] | Wahidi T, Chandavar R A, Yadav A K. Stability enhancement of supercritical CO2 based natural circulation loop using a modified Tesla valve[J]. Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 2020, 166: 105020. |
| [27] | Monika K, Chakraborty C, Roy S, et al. A numerical analysis on multi-stage Tesla valve based cold plate for cooling of pouch type Li-ion batteries[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2021, 177: 121560. |
| [28] | Zhao P C, Wang H B, Wang Y Z, et al. A time sequential microfluid sensor with Tesla valve channels[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16(9): 11667-11673. |
| [29] | 胡琼, 王锦华, 陈阳, 等. 一种具有自修复式超滑表面的高载低摩摩擦副设计方法: 202310678988.6[P]. 2024-2-2. |
| Hu Q, Wang J H, Chen Y, et al. A design method for high-load, low-friction tribo-pairs with self-healing, ultra-smooth surfaces: 202310678988.6[P]. 2024-2-2. | |
| [30] | Hu Q, Wang J H, Zhu L, et al. Numerical and experimental investigations into characteristics of liquid film seals featuring various groove shapes based on super-slip groove design[J]. Tribology International, 2024, 199: 109978. |
| [31] | 王衍, 谢雪非, 何一鸣, 等. 基于特斯拉阀的新型非接触式流体密封技术研究[J]. 摩擦学学报, 2023, 43(9): 975-985. |
| Wang Y, Xie X F, He Y M, et al. A new non-contact fluid seal technology based on Tesla valve[J]. Tribology, 2023, 43(9): 975-985. | |
| [32] | ANSYS Inc. ANSYS Fluent Theory Guide(2020 R1)[M]. Canonsburg: ANSYS Inc, 2020. |
| [33] | 胡琼, 肖洋, 卢迪, 等. 环形间隙密封泄漏率计算方法研究[J]. 流体机械, 2021, 49(12): 49-54, 61. |
| Hu Q, Xiao Y, Lu D, et al. Study on leakage calculation methods of annular clearance seals[J]. Fluid Machinery, 2021, 49(12): 49-54, 61. |
| [1] | Mengjiao WANG, Kaixue HU, Xiangkai MENG, Jinbo JIANG, Xudong PENG. Influence of micro-texture size and areal density on surface of silicon carbide on tribological properties of sliding sealing surfaces [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4165-4176. |
| [2] | Ziheng WANG, Wenhuai LI, Wei ZHOU. Application of patterned electrodes in solid oxide fuel cell [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3153-3171. |
| [3] | Jiayang PAN, Jinbo JIANG, Xudong PENG, Xiangkai MENG, Yi Ma. Study on a layered computational model of double-sided graphite circumferential seal and the effect of grooved position [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2886-2899. |
| [4] | Jiatong YU, Xiangkai MENG, Wenjing ZHAO, Lei LIU, Lihao ZHANG, Xudong PENG. Study on end face deflection of shrink-fit mechanical seals for turbo pump considering thermal-mechanical coupling effect [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2900-2912. |
| [5] | Jinbo JIANG, Zhuxin CHEN, Yangyi XIAO, Xin PENG, Yuan CHEN, Chen YU, Xiangkai MENG, Xudong PENG. Study on influence of operating conditions on thermodynamic process and steady state performance of supercritical CO2 dry gas seal [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2913-2928. |
| [6] | Mengyang LIU, Xuejian SUN, Wenyuan MAO, Xiwen DENG, Jilin LEI. Contact characterization of sealing rings considering microscopic surface delamination features [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1156-1169. |
| [7] | Panpan WEI, Yinan LIU, Chunying ZHU, Taotao FU, Xiqun GAO, Youguang MA. Preparation of aqueous two-phase droplets in improved T-shaped microchannel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 576-583. |
| [8] | Heng ZHANG, Dianlu KUI, Hong CHANG, Zhigang ZHAN. Effect of mechanical stress on the interfacial transport properties of gas diffusion layers [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(2): 637-644. |
| [9] | Yushi LI, Yuan CHEN, Yuntang LI, Xudong PENG, Bingqing WANG, Xiaolu LI. Intelligent optimization and deformation analysis of novel flexible dam foil face gas seal [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 324-334. |
| [10] | Shuangxi LI, An LIU, Zhiyuan LIU, Jiangteng ZHANG, Shicong LI. Disturbance performance of dynamic and static pressure hybrid gas isolation seal of high-speed turbopumps [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 311-323. |
| [11] | Junjie ZHANG, Yuan CHEN, Yuntang LI, Xiaolu LI, Bingqing WANG, Xudong PENG. Analysis and optimization of dynamic performance of super-elliptical hole floating seal dam compliant foil face gas seal [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(1): 296-310. |
| [12] | Liang ZHAO, Yuqiao LI, De ZHANG, Shengqiang SHEN. Experimental study of internal and external field characteristics of spiral nozzle [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(8): 2777-2786. |
| [13] | Kehao DONG, Jingzhi ZHOU, Feng ZHOU, Haijia CHEN, Xiulan HUAI, Dong LI. Experiment of gas flow pressure drop under complex boundary conditions in ultra-thin space [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(7): 2505-2521. |
| [14] | Yangyang CHAI, Xudong PENG, Jinbo JIANG, Xiangkai MENG, Yi MA. Study on friction and wear behaviors of antimony impregnated graphite with pressureless sintered SiC and 3D-printed SiC sealing materials pairs [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(5): 1966-1976. |
| [15] | Zhaoxiang ZHANG, Maokun CAI, Zhiying REN, Xiaohong JIA, Fei GUO. Numerical analysis of the effect of temperature and its fluctuations on the vulcanization process of rubber seals [J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 715-726. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||