CIESC Journal ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (8): 4259-4272.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250178
• Energy and environmental engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Zheng GAO( ), Hui WANG, Zhiguo QU(
), Hui WANG, Zhiguo QU( )
)
Received:2025-02-25
Revised:2025-05-15
Online:2025-09-17
Published:2025-08-25
Contact:
Zhiguo QU
通讯作者:
屈治国
作者简介:高正(1994—),男,博士研究生,gaozheng@stu.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:CLC Number:
Zheng GAO, Hui WANG, Zhiguo QU. Data-driven high-throughput screening of anion-pillared metal-organic frameworks for hydrogen storage[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4259-4272.
高正, 汪辉, 屈治国. 数据驱动辅助高通量筛选阴离子柱撑金属有机框架储氢[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4259-4272.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
| Atom | (ε/kB)/K | σ/Å | Atom | (ε/kB)/K | σ/Å | Atom | (ε/kB)/K | σ/Å | Charge/e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | 7.65 | 2.85 | Ti | 8.55 | 2.83 | Ge | 190.69 | 3.81 | — |
| B | 47.81 | 3.58 | V | 8.05 | 2.8 | Zr | 34.72 | 2.78 | — |
| C | 47.86 | 3.47 | Fe | 6.54 | 2.59 | Nb | 29.69 | 2.82 | — |
| N | 38.95 | 3.26 | Co | 7.05 | 2.56 | Cd | 114.73 | 2.54 | — |
| O | 48.16 | 3.03 | Ni | 7.55 | 2.52 | In | 301.43 | 3.98 | — |
| F | 36.48 | 3.09 | Cu | 2.52 | 3.11 | Sn | 285.28 | 3.91 | — |
| Al | 155.99 | 3.91 | Zn | 62.4 | 2.46 | H_H2 | — | — | 0.468 |
| Si | 156 | 3.8 | Ga | 208.84 | 3.90 | H_com | 36.7 | 2.958 | -0.936 |
Table 1 Lennard-Jones parameters of MOFs
| Atom | (ε/kB)/K | σ/Å | Atom | (ε/kB)/K | σ/Å | Atom | (ε/kB)/K | σ/Å | Charge/e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | 7.65 | 2.85 | Ti | 8.55 | 2.83 | Ge | 190.69 | 3.81 | — |
| B | 47.81 | 3.58 | V | 8.05 | 2.8 | Zr | 34.72 | 2.78 | — |
| C | 47.86 | 3.47 | Fe | 6.54 | 2.59 | Nb | 29.69 | 2.82 | — |
| N | 38.95 | 3.26 | Co | 7.05 | 2.56 | Cd | 114.73 | 2.54 | — |
| O | 48.16 | 3.03 | Ni | 7.55 | 2.52 | In | 301.43 | 3.98 | — |
| F | 36.48 | 3.09 | Cu | 2.52 | 3.11 | Sn | 285.28 | 3.91 | — |
| Al | 155.99 | 3.91 | Zn | 62.4 | 2.46 | H_H2 | — | — | 0.468 |
| Si | 156 | 3.8 | Ga | 208.84 | 3.90 | H_com | 36.7 | 2.958 | -0.936 |
| Model | Abbr. | MAE | RMSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auto-Gluon-stacking | AG | 0.2793 | 0.4004 | 0.9997 |
| H2O-stacking | H2O | 0.4745 | 0.6367 | 0.9994 |
| Extra Trees Regressor | ET | 0.9966 | 1.5235 | 0.9959 |
| Gradient Boosting Regressor | GB | 1.3043 | 1.8446 | 0.9941 |
| Random Forest Regressor | RF | 1.3000 | 1.9372 | 0.9933 |
| Light Gradient Boosting Machine | LightGBM | 1.5946 | 2.5524 | 0.9882 |
| AdaBoost Regressor | Ada | 2.1591 | 2.7458 | 0.9869 |
| Linear Regression | LR | 2.1809 | 2.7753 | 0.9867 |
| Bayesian Ridge | BR | 2.2090 | 2.7953 | 0.9865 |
| Decision Tree Regressor | DT | 1.6932 | 2.8758 | 0.9853 |
| K Neighbors Regressor | KNN | 2.2578 | 3.4469 | 0.9788 |
| Ridge Regression | Ridge | 2.9051 | 3.7187 | 0.9759 |
| Lasso Regression | Lasso | 3.5638 | 4.535 | 0.9644 |
| Lasso Least Angle Regression | LLAR | 3.5638 | 4.535 | 0.9644 |
| Elastic Net | EN | 3.5786 | 4.5482 | 0.9642 |
| Huber Regressor | Huber | 3.7659 | 4.9356 | 0.9575 |
| Orthogonal Matching Pursuit | OMP | 5.8721 | 6.6563 | 0.9237 |
| Passive Aggressive Regressor | PAR | 11.3854 | 14.1384 | 0.4173 |
| Dummy Regressor | Dummy | 20.603 | 24.2602 | -0.0084 |
Table 2 Model accuracy comparison
| Model | Abbr. | MAE | RMSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auto-Gluon-stacking | AG | 0.2793 | 0.4004 | 0.9997 |
| H2O-stacking | H2O | 0.4745 | 0.6367 | 0.9994 |
| Extra Trees Regressor | ET | 0.9966 | 1.5235 | 0.9959 |
| Gradient Boosting Regressor | GB | 1.3043 | 1.8446 | 0.9941 |
| Random Forest Regressor | RF | 1.3000 | 1.9372 | 0.9933 |
| Light Gradient Boosting Machine | LightGBM | 1.5946 | 2.5524 | 0.9882 |
| AdaBoost Regressor | Ada | 2.1591 | 2.7458 | 0.9869 |
| Linear Regression | LR | 2.1809 | 2.7753 | 0.9867 |
| Bayesian Ridge | BR | 2.2090 | 2.7953 | 0.9865 |
| Decision Tree Regressor | DT | 1.6932 | 2.8758 | 0.9853 |
| K Neighbors Regressor | KNN | 2.2578 | 3.4469 | 0.9788 |
| Ridge Regression | Ridge | 2.9051 | 3.7187 | 0.9759 |
| Lasso Regression | Lasso | 3.5638 | 4.535 | 0.9644 |
| Lasso Least Angle Regression | LLAR | 3.5638 | 4.535 | 0.9644 |
| Elastic Net | EN | 3.5786 | 4.5482 | 0.9642 |
| Huber Regressor | Huber | 3.7659 | 4.9356 | 0.9575 |
| Orthogonal Matching Pursuit | OMP | 5.8721 | 6.6563 | 0.9237 |
| Passive Aggressive Regressor | PAR | 11.3854 | 14.1384 | 0.4173 |
| Dummy Regressor | Dummy | 20.603 | 24.2602 | -0.0084 |
| No. | MOFs | ρ/(g/cm3) | GSA/(m2/g) | VP/(cm3/g) | VF | GCMC/(mg/g) | ML/(mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BFFIVE_2_Ni | 0.52 | 3943.96 | 1.42 | 0.74 | 116.9 | 113.94 |
| 2 | BFFIVE_2_Zn | 0.52 | 3765.55 | 1.40 | 0.73 | 115.95 | 114.19 |
| 3 | BFFIVE_7_Zn | 0.54 | 3551.53 | 1.34 | 0.72 | 115.7 | 114.19 |
| 4 | BFFIVE_2_Cu | 0.52 | 3882.58 | 1.40 | 0.73 | 115.12 | 114.12 |
| 5 | BFFIVE_7_Cd | 0.54 | 3533.66 | 1.37 | 0.74 | 114.85 | 114.12 |
| 6 | BFFIVE_2_Cd | 0.53 | 3695.77 | 1.40 | 0.74 | 114.41 | 114.12 |
| 7 | BFFIVE_7_Cu | 0.55 | 3568.01 | 1.31 | 0.72 | 113.38 | 113.82 |
| 8 | BFFIVE_2_Fe | 0.52 | 3737.87 | 1.40 | 0.73 | 112.88 | 113.82 |
| 9 | BFFIVE_2_Co | 0.54 | 3741.83 | 1.35 | 0.73 | 112.42 | 113.82 |
| 10 | BFFIVE_7_Co | 0.56 | 3423.04 | 1.27 | 0.71 | 111.52 | 111.00 |
| 11 | BFFIVE_7_Fe | 0.54 | 3427.77 | 1.33 | 0.72 | 109.86 | 111.25 |
| 12 | BFFIVE_7_Ni | 0.56 | 3300.72 | 1.26 | 0.71 | 107.05 | 106.65 |
| 13 | BFFIVE_16_Cu_i | 0.55 | 3715.38 | 1.22 | 0.67 | 101.39 | 101.22 |
| 14 | BFFIVE_16_Zn_i | 0.56 | 3561.92 | 1.18 | 0.66 | 97.64 | 97.50 |
| 15 | BFFIVE_16_Co_i | 0.56 | 3711.88 | 1.18 | 0.67 | 97.57 | 97.21 |
| 16 | ALFFIVE_2_Fe | 0.59 | 3203.36 | 1.18 | 0.69 | 97.51 | 97.42 |
| 17 | BFFIVE_16_Ni_i | 0.57 | 3599.53 | 1.16 | 0.66 | 97.45 | 97.36 |
| 18 | BFFIVE_16_Fe_i | 0.56 | 3632.94 | 1.18 | 0.66 | 97.31 | 97.50 |
| 19 | ALFFIVE_2_Zn | 0.6 | 3162.78 | 1.17 | 0.70 | 96.86 | 96.18 |
| 20 | ALFFIVE_2_Cd | 0.59 | 3051.31 | 1.22 | 0.72 | 96.65 | 96.12 |
Table 3 MOFs for high-performance hydrogen storage
| No. | MOFs | ρ/(g/cm3) | GSA/(m2/g) | VP/(cm3/g) | VF | GCMC/(mg/g) | ML/(mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BFFIVE_2_Ni | 0.52 | 3943.96 | 1.42 | 0.74 | 116.9 | 113.94 |
| 2 | BFFIVE_2_Zn | 0.52 | 3765.55 | 1.40 | 0.73 | 115.95 | 114.19 |
| 3 | BFFIVE_7_Zn | 0.54 | 3551.53 | 1.34 | 0.72 | 115.7 | 114.19 |
| 4 | BFFIVE_2_Cu | 0.52 | 3882.58 | 1.40 | 0.73 | 115.12 | 114.12 |
| 5 | BFFIVE_7_Cd | 0.54 | 3533.66 | 1.37 | 0.74 | 114.85 | 114.12 |
| 6 | BFFIVE_2_Cd | 0.53 | 3695.77 | 1.40 | 0.74 | 114.41 | 114.12 |
| 7 | BFFIVE_7_Cu | 0.55 | 3568.01 | 1.31 | 0.72 | 113.38 | 113.82 |
| 8 | BFFIVE_2_Fe | 0.52 | 3737.87 | 1.40 | 0.73 | 112.88 | 113.82 |
| 9 | BFFIVE_2_Co | 0.54 | 3741.83 | 1.35 | 0.73 | 112.42 | 113.82 |
| 10 | BFFIVE_7_Co | 0.56 | 3423.04 | 1.27 | 0.71 | 111.52 | 111.00 |
| 11 | BFFIVE_7_Fe | 0.54 | 3427.77 | 1.33 | 0.72 | 109.86 | 111.25 |
| 12 | BFFIVE_7_Ni | 0.56 | 3300.72 | 1.26 | 0.71 | 107.05 | 106.65 |
| 13 | BFFIVE_16_Cu_i | 0.55 | 3715.38 | 1.22 | 0.67 | 101.39 | 101.22 |
| 14 | BFFIVE_16_Zn_i | 0.56 | 3561.92 | 1.18 | 0.66 | 97.64 | 97.50 |
| 15 | BFFIVE_16_Co_i | 0.56 | 3711.88 | 1.18 | 0.67 | 97.57 | 97.21 |
| 16 | ALFFIVE_2_Fe | 0.59 | 3203.36 | 1.18 | 0.69 | 97.51 | 97.42 |
| 17 | BFFIVE_16_Ni_i | 0.57 | 3599.53 | 1.16 | 0.66 | 97.45 | 97.36 |
| 18 | BFFIVE_16_Fe_i | 0.56 | 3632.94 | 1.18 | 0.66 | 97.31 | 97.50 |
| 19 | ALFFIVE_2_Zn | 0.6 | 3162.78 | 1.17 | 0.70 | 96.86 | 96.18 |
| 20 | ALFFIVE_2_Cd | 0.59 | 3051.31 | 1.22 | 0.72 | 96.65 | 96.12 |
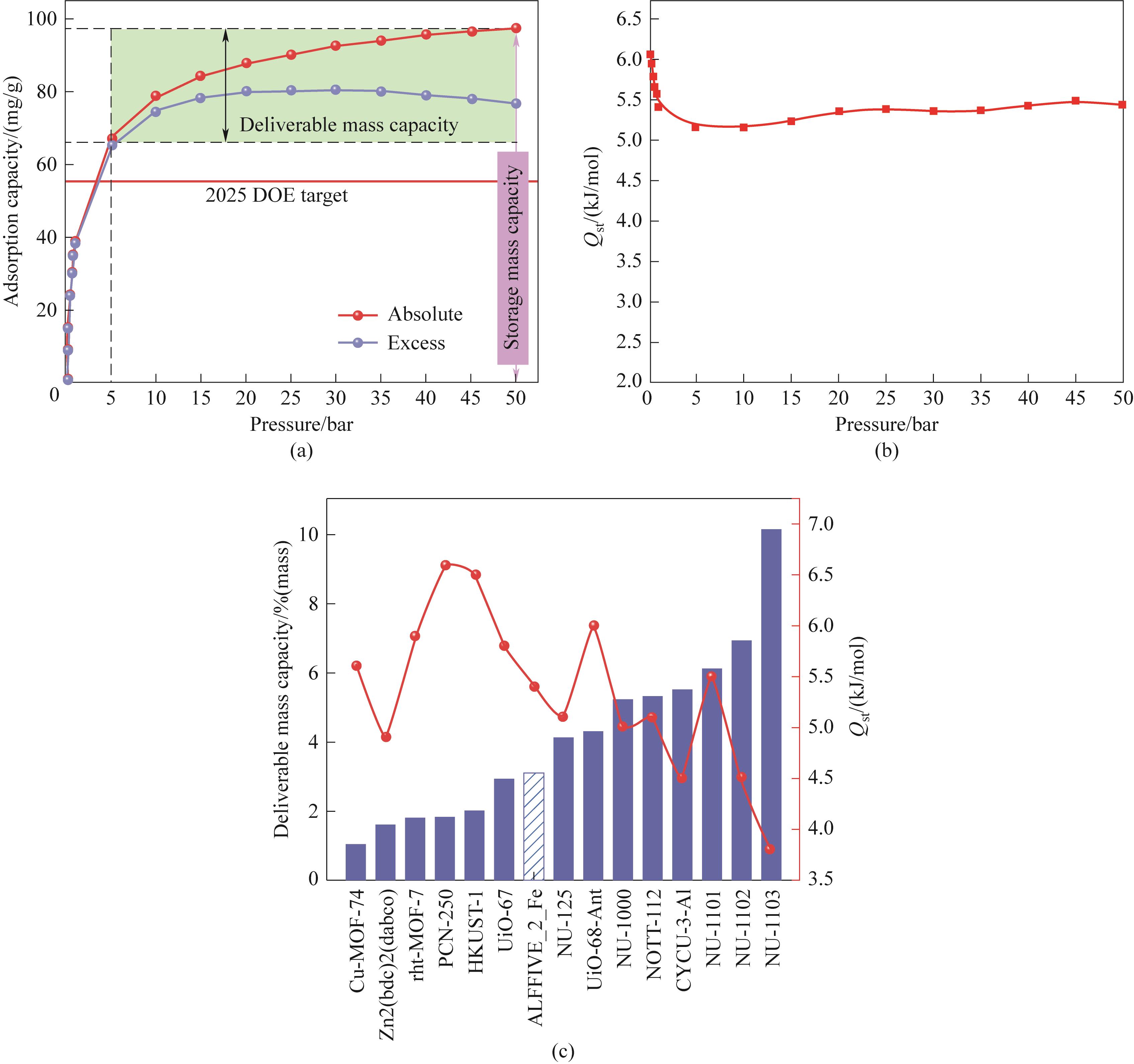
Fig.9 (a) ALFFIVE_2_Fe adsorption isotherm; (b) Adsorption heat versus pressure of ALFFIVE_2; (c) Deliverable mass capacity versus adsorption heat of a typical MOF[36]
| 位置 | 构型 | 位点 | EMOF/a.u | ΔE/(kJ/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吡啶 | 水平(H) | Fe-N | -1.166 | -3463.457 | -3464.626 | -8.590 |
| 垂直(V) | Fe-N | -1.166 | -3463.457 | -3464.625 | -7.319 | |
| 水平(H) | Hollow | -1.166 | -3463.457 | -3464.628 | -8.595 | |
| 垂直(V) | Hollow | -1.166 | -3463.457 | -3464.625 | -6.975 | |
| 乙炔 | 水平(H) | — | -1.166 | -3463.448 | -3464.624 | -4.900 |
| 垂直(V) | — | -1.166 | -3463.457 | -3464.624 | -3.067 |
Table 4 Adsorption energies at different adsorption sites
| 位置 | 构型 | 位点 | EMOF/a.u | ΔE/(kJ/mol) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 吡啶 | 水平(H) | Fe-N | -1.166 | -3463.457 | -3464.626 | -8.590 |
| 垂直(V) | Fe-N | -1.166 | -3463.457 | -3464.625 | -7.319 | |
| 水平(H) | Hollow | -1.166 | -3463.457 | -3464.628 | -8.595 | |
| 垂直(V) | Hollow | -1.166 | -3463.457 | -3464.625 | -6.975 | |
| 乙炔 | 水平(H) | — | -1.166 | -3463.448 | -3464.624 | -4.900 |
| 垂直(V) | — | -1.166 | -3463.457 | -3464.624 | -3.067 |
| [1] | Gupta A, Baron G V, Perreault P, et al. Hydrogen clathrates: next generation hydrogen storage materials[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 41: 69-107. |
| [2] | Li H L, Eddaoudi M, O'Keeffe M, et al. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework[J]. Nature, 1999, 402: 276-279. |
| [3] | Moghadam P Z, Chung Y G, Snurr R Q. Progress toward the computational discovery of new metal-organic framework adsorbents for energy applications[J]. Nature Energy, 2024, 9: 121-133. |
| [4] | Li A, Bueno-Perez R, Madden D, et al. From computational high-throughput screenings to the lab: taking metal-organic frameworks out of the computer[J]. Chemical Science, 2022, 13(27): 7990-8002. |
| [5] | Bobbitt N S, Chen J Y, Snurr R Q. High-throughput screening of metal-organic frameworks for hydrogen storage at cryogenic temperature[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(48): 27328-27341. |
| [6] | Liu K H, Chen Z J, Islamoglu T, et al. Exploring the chemical space of metal-organic frameworks with rht topology for high capacity hydrogen storage[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2024, 128(18): 7435-7446. |
| [7] | Thornton A W, Simon C M, Kim J, et al. Materials genome in action: identifying the performance limits of physical hydrogen storage[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(7): 2844-2854. |
| [8] | Xie Y Y, Li X D, Zhang H D, et al. Evaluation and screening of multivariate metal-organic frameworks for hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 87: 1356-1366. |
| [9] | Ahmed A, Seth S, Purewal J, et al. Exceptional hydrogen storage achieved by screening nearly half a million metal-organic frameworks[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1568. |
| [10] | Lu X Y, Xie Z Z, Wu X J, et al. Hydrogen storage metal-organic framework classification models based on crystal graph convolutional neural networks[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 259: 117813. |
| [11] | Wang L M, Feng S H, Zhang C J, et al. Artificial intelligence and high-throughput computational workflows empowering the fast screening of metal-organic frameworks for hydrogen storage[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(28): 36444-36452. |
| [12] | Ahmed A, Siegel D J. Predicting hydrogen storage in MOFs via machine learning[J]. Patterns, 2021, 2(7): 100291. |
| [13] | Park J, Lim Y, Lee S, et al. Computational design of metal-organic frameworks with unprecedented high hydrogen working capacity and high synthesizability[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2023, 35(1): 9-16. |
| [14] | Guo W J, Liu J, Dong F, et al. Machine learning for predicting gas adsorption capacities of metal organic framework[M]//Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Computational Toxicology. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2023: 629-654. |
| [15] | Lin J, Liu Z M, Guo Y J, et al. Machine learning accelerates the investigation of targeted MOFs: performance prediction, rational design and intelligent synthesis[J]. Nano Today, 2023, 49: 101802. |
| [16] | Altintas C, Keskin S. On the shoulders of high-throughput computational screening and machine learning: design and discovery of MOFs for H2 storage and purification[J]. Materials Today Energy, 2023, 38: 101426. |
| [17] | Neikha K, Puzari A. Metal-organic frameworks through the lens of artificial intelligence: a comprehensive review[J]. Langmuir, 2024, 40(42): 21957-21975. |
| [18] | Li Z, Bucior B J, Chen H Y, et al. Machine learning using host/guest energy histograms to predict adsorption in metal-organic frameworks: application to short alkanes and Xe/Kr mixtures[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2021, 155(1): 014701. |
| [19] | Shi K H, Li Z, Anstine D M, et al. Two-dimensional energy histograms as features for machine learning to predict adsorption in diverse nanoporous materials[J]. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2023, 19(14): 4568-4583. |
| [20] | Liu X, Wang H, Liu C, et al. Recent advances of multidentate ligand-based anion-pillared MOFs for enhanced separation and purification processes[J]. Chem & Bio Engineering, 2024, 1(6): 469-487. |
| [21] | Cui X L, Chen K J, Xing H B, et al. Pore chemistry and size control in hybrid porous materials for acetylene capture from ethylene[J]. Science, 2016, 353(6295): 141-144. |
| [22] | Gu C K, Yu Z Z, Liu J, et al. Construction of an anion-pillared MOF database and the screening of MOFs suitable for Xe/Kr separation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(9): 11039-11049. |
| [23] | Willems T F, Rycroft C H, Kazi M, et al. Algorithms and tools for high-throughput geometry-based analysis of crystalline porous materials[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2012, 149(1): 134-141. |
| [24] | Martin R L, Haranczyk M. Construction and characterization of structure models of crystalline porous polymers[J]. Crystal Growth and Design, 2014, 14(5): 2431-2440. |
| [25] | Wu Y, Duan H P, Xi H X. Machine learning-driven insights into defects of zirconium metal-organic frameworks for enhanced ethane-ethylene separation[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(7): 2986-2997. |
| [26] | Orhan I B, Daglar H, Keskin S, et al. Prediction of O2/N2 selectivity in metal-organic frameworks via high-throughput computational screening and machine learning[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(1): 736-749. |
| [27] | Xue X Y, Cheng M, Wang S H, et al. High-throughput screening of metal-organic frameworks assisted by machine learning: propane/propylene separation[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(2): 1073-1084. |
| [28] | Dubbeldam D, Calero S, Ellis D E, et al. RASPA: molecular simulation software for adsorption and diffusion in flexible nanoporous materials[J]. Molecular Simulation, 2016, 42(2): 81-101. |
| [29] | Colón Y J, Fairen-Jimenez D, Wilmer C E, et al. High-throughput screening of porous crystalline materials for hydrogen storage capacity near room temperature[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(10): 5383-5389. |
| [30] | Hutter J, Iannuzzi M, Schiffmann F, et al. cp2k: atomistic simulations of condensed matter systems[J]. WIREs Computational Molecular Science, 2014, 4(1): 15-25. |
| [31] | LeDell E, Poirier S. H2O AutoML: scalable automatic machine learning[C]//Proceedings of the AutoML Workshop at ICML. Association for Computing Machinery, 2020: 1-16. |
| [32] | Paldino G M, De Stefani J, De Caro F, et al. Does AutoML outperform naive forecasting?[J]. Engineering Proceedings, 2021, 5(1): 36. |
| [33] | Ahmed A, Liu Y Y, Purewal J, et al. Balancing gravimetric and volumetric hydrogen density in MOFs[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2017, 10(11): 2459-2471. |
| [34] | Allendorf M D, Stavila V, Snider J L, et al. Challenges to developing materials for the transport and storage of hydrogen[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2022, 14(11): 1214-1223. |
| [35] | Cadiau A, Belmabkhout Y, Adil K, et al. Hydrolytically stable fluorinated metal-organic frameworks for energy-efficient dehydration[J]. Science, 2017, 356(6339): 731-735. |
| [36] | García-Holley P, Schweitzer B, Islamoglu T, et al. Benchmark study of hydrogen storage in metal–organic frameworks under temperature and pressure swing conditions[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(3): 748-754. |
| [37] | Srivastava S, Shet S P, Shanmuga Priya S, et al. Molecular simulation of copper based metal-organic framework (Cu-MOF) for hydrogen adsorption[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(35): 15820-15831. |
| [38] | Lu T. A comprehensive electron wavefunction analysis toolbox for chemists, Multiwfn[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2024, 161(8): 082503. |
| [39] | Lu T, Chen Q X. Visualization analysis of weak interactions in chemical systems[M]//Comprehensive Computational Chemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2024: 240-264. |
| [40] | Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics[J]. Journal of Molecular Graphics, 1996, 14(1): 33-38. |
| [1] | Xiayu FAN, Jianchen SUN, Keying LI, Xinya YAO, Hui SHANG. Machine learning drives system optimization of liquid organic hydrogen storage technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [2] | Zhihong CHEN, Jiawei WU, Xiaoling LOU, Junxian YUN. Recent advances in machine learning for biomanufacturing of chemicals [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3789-3804. |
| [3] | Jiahao LIN, Fangzhong FU, Haohui YE, Jin HU, Mingcan YAO, Helin FAN, Xu WANG, Ruixiang WANG, Zhifeng XU. Effect of NdF3 content on local structure and transport properties of NdF3-LiF molten salt [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3834-3841. |
| [4] | Xiaoling WANG, Shaoqing WANG, Yungang ZHAO, Fangzhe CHANG, Ruifeng MU. Mechanism of organic Ca transformation during coal hydropyrolysis: insights from ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulations [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 4297-4309. |
| [5] | Liang QIAO, Shang LI, Xinliang LIU, Ming WANG, Pei ZHANG, Yingfei HOU. Synthesis and molecular simulation of terpolymer viscosity reducer for heavy oil [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3686-3695. |
| [6] | Zirui LI, Kai QI, Jun WANG, Guodong XIA. Molecular dynamics study of ion rejection process based on Janus nanochannel [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3531-3538. |
| [7] | Jiali WANG, Fang LIU, Wei CHEN, Xiaoying ZHANG, Shengting LI, Tian TIAN, Xiangyu XIN, Guang LIU, Yufei SONG. Recent advances in magnesium-based nanocomposites via in-situ template-confined synthesis [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3172-3184. |
| [8] | Hao QI, Yujie WANG, Shenhui LI, Qi ZOU, Yiqun LIU, Zhiping ZHAO. Molecular simulation study on adsorption and diffusion of C3H6 and C3H8 on Co/Zn-ZIFs [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2313-2326. |
| [9] | Jianbing CHEN, Hao CHANG, Ming GAO, Bing XING, Lei ZHANG, Qilei LIU. Phase separation prediction methodology for amine-based phase change absorbents based on reaction templates and molecular dynamics [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2387-2396. |
| [10] | Jialang HU, Mingyuan JIANG, Lyuming JIN, Yonggang ZHANG, Peng HU, Hongbing JI. Machine learning-assisted high-throughput computational screening of MOFs and advances in gas separation research [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 1973-1996. |
| [11] | Dandong NING, Jianhui LI, Yang CHEN, Jinping LI, Libo LI. Study on flocculation techniques in the large-scale production of MIL-101(Cr) [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2327-2336. |
| [12] | Dong GU, Xingjian PI, Die ZHANG, Ying ZHANG. Construction and H2/CO2 separation performance evaluation of CAU-1/PI mixed matrix membrane with different nanoparticle sizes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2410-2418. |
| [13] | Zijuan LI, Xiaoyan TAN, Yongsheng WU, Chenyi YANG, Hong CHEN, Xiaogang BI, Jie LIU, Faquan YU. Molecular simulation study on CO2/N2 separation via 3D-contorted catalytic arene-norbornene annulation polymer membrane [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2348-2357. |
| [14] | Haotian AN, Zhangye HAN, Muyao LU, Awu ZHOU, Jianrong LI. Promoting industrial application of MOF: scale-up preparation and shaping [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2011-2025. |
| [15] | Yaohui ZHANG, Yujie BAN, Weishen YANG. Vapor-phase synthesis and post-synthetic modification of metal-organic framework membranes [J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2070-2086. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||