化工学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 71 ›› Issue (7): 3151-3164.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20191139
收稿日期:2019-10-08
修回日期:2019-12-24
出版日期:2020-07-05
发布日期:2020-07-05
通讯作者:
巫江虹
作者简介:于仙毅(1994—),男,硕士研究生,基金资助:
Xianyi YU1( ),Jianghong WU1(
),Jianghong WU1( ),Yunhui GAO2
),Yunhui GAO2
Received:2019-10-08
Revised:2019-12-24
Online:2020-07-05
Published:2020-07-05
Contact:
Jianghong WU
摘要:
为了研究热泵系统制冷剂泄漏识别的数据挖掘理论方法和实验验证,首先建立空气源热泵系统制冷剂泄漏实验台,进行热泵系统正常工况、干扰工况、泄漏工况的实验参数测试;其次,采用主成分分析法对测试数据进行特征提取处理,采用支持向量机对数据进行分类识别,建立了用于热泵系统的制冷剂泄漏识别的主成分分析-支持向量机模型,在二分类和多分类模式下验证了模型的性能,并研究了泄漏速率和不同故障工况对模型的影响。采用RefliefF特征选择算法对原始特征参数进行筛选,简化了识别模型的特征参数。研究结果表明:对于空气源热泵热水系统,PCA-SVM泄漏识别模型在多种验证集中对泄漏工况的识别准确度达100%,缓慢泄漏的诊断识别性能弱于快速泄漏,同一模型在不同故障诊断识别中性能不同,对系统运行影响轻微的故障诊断识别性能弱于其他故障。RefliefF特征选择方法将原始41个系统特征参数精简至10个特征参数,参数筛选优化后的泄漏识别模型识别精度也维持在较高水平,优化的泄漏识别模型更利于实际应用。
中图分类号:
于仙毅, 巫江虹, 高云辉. 基于主成分分析与支持向量机的热泵系统制冷剂泄漏识别研究[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(7): 3151-3164.
Xianyi YU, Jianghong WU, Yunhui GAO. Research on refrigerant leakage identification for heat pump system based on PCA-SVM models[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(7): 3151-3164.
| 系统 | 部件 | 规格型号 |
|---|---|---|
| 制冷循环系统 | 压缩机 | BSA645CV-R1EN型 R134a制冷剂 |
| 冷凝器 | U型套管式 | |
| 节流阀 | 丹佛斯TN2型热力膨胀阀 | |
| 蒸发器(含小型风扇组) | 单流层微通道换热器 | |
| 水路循环系统 | 保温水箱 | 30 L、?20 mm进出水口 |
| 水泵 | 1个 自吸式磁力循环泵 | |
| 水流量计 | 1个 LWGY型涡轮流量计 | |
| 制冷剂泄漏控制及收集部件 | 手阀 | 4个 |
| 开度阀 | 4个 | |
| 气体收集袋 | 1个 20 L超高密封袋 | |
| 测试部件 | 热电偶 | 若干 J型热电偶 |
| 压力变送器 | 8个 0~0.6 MPa、0~4 MPa | |
| 电子秤 | 100 g/0.02 g 15 kg/0.2 g | |
| 功率仪 | 1个 HOPI型 | |
| 安捷伦 | 1台 34972型 | |
| 计算机 | 1台 |
表1 制冷剂泄漏实验系统部件信息
Table 1 Refrigerant leak test system component information
| 系统 | 部件 | 规格型号 |
|---|---|---|
| 制冷循环系统 | 压缩机 | BSA645CV-R1EN型 R134a制冷剂 |
| 冷凝器 | U型套管式 | |
| 节流阀 | 丹佛斯TN2型热力膨胀阀 | |
| 蒸发器(含小型风扇组) | 单流层微通道换热器 | |
| 水路循环系统 | 保温水箱 | 30 L、?20 mm进出水口 |
| 水泵 | 1个 自吸式磁力循环泵 | |
| 水流量计 | 1个 LWGY型涡轮流量计 | |
| 制冷剂泄漏控制及收集部件 | 手阀 | 4个 |
| 开度阀 | 4个 | |
| 气体收集袋 | 1个 20 L超高密封袋 | |
| 测试部件 | 热电偶 | 若干 J型热电偶 |
| 压力变送器 | 8个 0~0.6 MPa、0~4 MPa | |
| 电子秤 | 100 g/0.02 g 15 kg/0.2 g | |
| 功率仪 | 1个 HOPI型 | |
| 安捷伦 | 1台 34972型 | |
| 计算机 | 1台 |
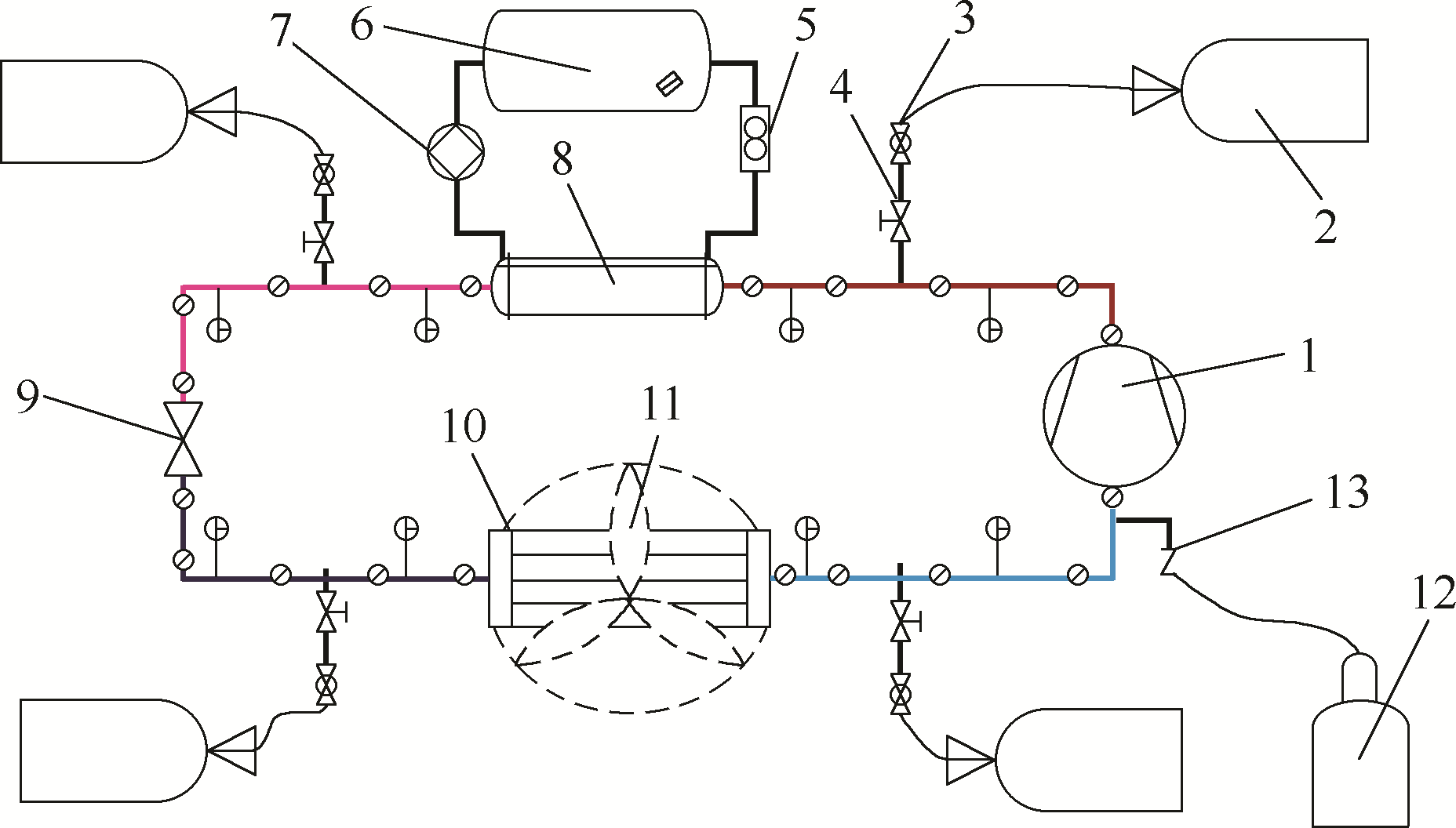
图1 泄漏实验系统及测点布置示意图温度测点; 压力测点;1—压缩机;2—防爆气囊;3—可调开度阀;4—开度阀;5—水流量计;6—水箱;7—水泵;8—套管冷凝器;9—热力膨胀阀;10—蒸发器;11—风机;12—制冷剂气瓶;13—开度阀
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of leakage test system and arrangement of measurement points
| 工况类型 | 工况详情及引入方法 |
|---|---|
| 正常工况(normal) | 系统开机后,恒定30℃水温,系统稳定运行 |
| 泄漏工况(Refleak) | 以正常工况为基准,在其开机平稳运行一小段时间后,系统趋于稳定的一个时间点作为泄漏工况的开始点,开始控制泄漏口阀门开度 |
| 冷凝器脏污工况(ReduCF) | 调节冷凝器水泵,降低冷凝器水流量 |
| 蒸发器脏污工况(ReduEF) | 通过遮挡蒸发器,降低蒸发器换热面积 |
| 热力膨胀阀预紧力过小工况(loosTV) | 人为调松热力膨胀阀预紧弹簧 |
| 热力膨胀阀预紧力过大工况(ClosTV) | 人为调紧热力膨胀阀预紧弹簧 |
| 冷凝温度变化工况(IncrTW)(DecrTW) | 分别恒定6号大水箱内的水温为25℃和35℃ |
表2 恒定水温热泵系统测试工况
Table 2 Test conditions of the heat pump system with constant water temperature
| 工况类型 | 工况详情及引入方法 |
|---|---|
| 正常工况(normal) | 系统开机后,恒定30℃水温,系统稳定运行 |
| 泄漏工况(Refleak) | 以正常工况为基准,在其开机平稳运行一小段时间后,系统趋于稳定的一个时间点作为泄漏工况的开始点,开始控制泄漏口阀门开度 |
| 冷凝器脏污工况(ReduCF) | 调节冷凝器水泵,降低冷凝器水流量 |
| 蒸发器脏污工况(ReduEF) | 通过遮挡蒸发器,降低蒸发器换热面积 |
| 热力膨胀阀预紧力过小工况(loosTV) | 人为调松热力膨胀阀预紧弹簧 |
| 热力膨胀阀预紧力过大工况(ClosTV) | 人为调紧热力膨胀阀预紧弹簧 |
| 冷凝温度变化工况(IncrTW)(DecrTW) | 分别恒定6号大水箱内的水温为25℃和35℃ |
| 序号 | 变量 符号 | 变量名称 | 意义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tci1 | 冷凝器进口温度1 | 测点温度 |
| 2 | Tci2 | 冷凝器进口温度2 | 测点温度 |
| 3 | Tci3 | 冷凝器进口温度3 | 测点温度 |
| 4 | Tci4 | 冷凝器进口温度4 | 测点温度 |
| 5 | Tci5 | 冷凝器进口温度5 | 测点温度 |
| 6 | Tco1 | 冷凝器出口温度1 | 测点温度 |
| 7 | Tco2 | 冷凝器出口温度2 | 测点温度 |
| 8 | Tco3 | 冷凝器出口温度3 | 测点温度 |
| 9 | Tco4 | 冷凝器出口温度4 | 测点温度 |
| 10 | Tco5 | 冷凝器出口温度5 | 测点温度 |
| 11 | Tei1 | 蒸发器进口温度1 | 测点温度 |
| 12 | Tei2 | 蒸发器进口温度2 | 测点温度 |
| 13 | Tei3 | 蒸发器进口温度3 | 测点温度 |
| 14 | Tei4 | 蒸发器进口温度4 | 测点温度 |
| 15 | Tei5 | 蒸发器进口温度5 | 测点温度 |
| 16 | Teo1 | 蒸发器出口温度1 | 测点温度 |
| 17 | Teo2 | 蒸发器出口温度2 | 测点温度 |
| 18 | Teo3 | 蒸发器出口温度3 | 测点温度 |
| 19 | Teo4 | 蒸发器出口温度4 | 测点温度 |
| 20 | Teo5 | 蒸发器出口温度5 | 测点温度 |
| 21 | Tesu | 蒸发器风冷出口环温 | 蒸发端环境温度 |
| 22 | Twat | 水箱水温 | 冷凝端环境温度 |
| 23 | POcom | 压缩机耗功 | 系统输入耗功 |
| 24 | Tesub | 过热度 | Teo1-Tgsat |
| 25 | Tcsub | 过冷度 | Tlsat-Tco1 |
| 26 | P01 | 压缩机出口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 27 | P02 | 冷凝器进口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 28 | P03 | 冷凝器出口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 29 | P04 | 节流阀入口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 30 | P05 | 节流阀出口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 31 | P06 | 蒸发器进口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 32 | P07 | 蒸发器出口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 33 | P08 | 压缩机进口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 34 | ΔTcom | 压缩机进出口温差 | Tci1-Teo5 |
| 35 | ΔTcon | 冷凝器进出口温差 | Tci5-Tco1 |
| 36 | ΔTvel | 节流阀温差 | Tco5-Tei1 |
| 37 | ΔPcom | 压缩机进出口压差 | P01-P08 |
| 38 | ΔPcon | 冷凝器进出口压差 | P02-P03 |
| 39 | ΔPvel | 节流阀压差 | P04-P05 |
| 40 | ΔPeva | 蒸发器进出口压差 | P06-P07 |
| 41 | ΔHcon | 冷凝器进出口焓差 | Hci-Hco |
表3 特征变量名称符号及对应的系统表征含义
Table 3 Name symbols of characteristic variables and their corresponding system representation meanings
| 序号 | 变量 符号 | 变量名称 | 意义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tci1 | 冷凝器进口温度1 | 测点温度 |
| 2 | Tci2 | 冷凝器进口温度2 | 测点温度 |
| 3 | Tci3 | 冷凝器进口温度3 | 测点温度 |
| 4 | Tci4 | 冷凝器进口温度4 | 测点温度 |
| 5 | Tci5 | 冷凝器进口温度5 | 测点温度 |
| 6 | Tco1 | 冷凝器出口温度1 | 测点温度 |
| 7 | Tco2 | 冷凝器出口温度2 | 测点温度 |
| 8 | Tco3 | 冷凝器出口温度3 | 测点温度 |
| 9 | Tco4 | 冷凝器出口温度4 | 测点温度 |
| 10 | Tco5 | 冷凝器出口温度5 | 测点温度 |
| 11 | Tei1 | 蒸发器进口温度1 | 测点温度 |
| 12 | Tei2 | 蒸发器进口温度2 | 测点温度 |
| 13 | Tei3 | 蒸发器进口温度3 | 测点温度 |
| 14 | Tei4 | 蒸发器进口温度4 | 测点温度 |
| 15 | Tei5 | 蒸发器进口温度5 | 测点温度 |
| 16 | Teo1 | 蒸发器出口温度1 | 测点温度 |
| 17 | Teo2 | 蒸发器出口温度2 | 测点温度 |
| 18 | Teo3 | 蒸发器出口温度3 | 测点温度 |
| 19 | Teo4 | 蒸发器出口温度4 | 测点温度 |
| 20 | Teo5 | 蒸发器出口温度5 | 测点温度 |
| 21 | Tesu | 蒸发器风冷出口环温 | 蒸发端环境温度 |
| 22 | Twat | 水箱水温 | 冷凝端环境温度 |
| 23 | POcom | 压缩机耗功 | 系统输入耗功 |
| 24 | Tesub | 过热度 | Teo1-Tgsat |
| 25 | Tcsub | 过冷度 | Tlsat-Tco1 |
| 26 | P01 | 压缩机出口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 27 | P02 | 冷凝器进口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 28 | P03 | 冷凝器出口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 29 | P04 | 节流阀入口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 30 | P05 | 节流阀出口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 31 | P06 | 蒸发器进口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 32 | P07 | 蒸发器出口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 33 | P08 | 压缩机进口压力 | 压力测点 |
| 34 | ΔTcom | 压缩机进出口温差 | Tci1-Teo5 |
| 35 | ΔTcon | 冷凝器进出口温差 | Tci5-Tco1 |
| 36 | ΔTvel | 节流阀温差 | Tco5-Tei1 |
| 37 | ΔPcom | 压缩机进出口压差 | P01-P08 |
| 38 | ΔPcon | 冷凝器进出口压差 | P02-P03 |
| 39 | ΔPvel | 节流阀压差 | P04-P05 |
| 40 | ΔPeva | 蒸发器进出口压差 | P06-P07 |
| 41 | ΔHcon | 冷凝器进出口焓差 | Hci-Hco |
| 名称 | 表达式 | 参数 |
|---|---|---|
| 线性核 | ||
| 多项式核 | ||
| 高斯核 | ||
| 拉普拉斯核 | ||
| Sigmoid核 |
表4 不同核函数类型的SVM模型表达式及其参数
Table 4 SVM model expressions and parameters of different kernel function types
| 名称 | 表达式 | 参数 |
|---|---|---|
| 线性核 | ||
| 多项式核 | ||
| 高斯核 | ||
| 拉普拉斯核 | ||
| Sigmoid核 |
| 真实结果 | 识别结果 | |
|---|---|---|
| 泄漏 | 非泄漏 | |
| 泄漏 | TP | FN |
| 非泄露 | FP | TN |
表5 二分类结果的混淆矩阵
Table 5 Confusion matrix of binary classification results
| 真实结果 | 识别结果 | |
|---|---|---|
| 泄漏 | 非泄漏 | |
| 泄漏 | TP | FN |
| 非泄露 | FP | TN |
| 评价指标 | 定义 | 计算公式 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 按类性能 | 命中率TPR | 对于给定类,发生且正确预测的样本占总发生样本的比率 | |
| 虚警率FPR | 对于给定类,没发生但被预测为发生的样本占没发生样本总数的比率 | ||
| 总体性能 | 准确率Acc | 正确分类数占总样本数的比率 | |
| 错误分类率Mcr | 错误分类样本数占总样本数的比率 | ||
表6 泄漏识别模型评级评价指标及其定义
Table 6 Leak identification model rating evaluation index and its definition
| 评价指标 | 定义 | 计算公式 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 按类性能 | 命中率TPR | 对于给定类,发生且正确预测的样本占总发生样本的比率 | |
| 虚警率FPR | 对于给定类,没发生但被预测为发生的样本占没发生样本总数的比率 | ||
| 总体性能 | 准确率Acc | 正确分类数占总样本数的比率 | |
| 错误分类率Mcr | 错误分类样本数占总样本数的比率 | ||
| 主元编号 | 特征值 | 主元方差贡献率/% | 累计方差贡献率/% | Tci1 | Tci2 | Tci3 | Tci4 | … | ΔPvel | ΔPeva | ΔHcon | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.80 | 38.55 | 38.55 | 0.052 | 0.220 | 0.246 | -0.135 | … | -0.289 | 0.249 | 0.112 | |
| 2 | 9.64 | 23.51 | 62.06 | 0.048 | 0.213 | 0.253 | -0.143 | … | -0.000 | 0.000 | -0.000 | |
| 3 | 7.12 | 17.36 | 79.42 | 0.048 | 0.216 | 0.250 | -0.142 | … | -0.000 | 0.000 | -0.000 | |
| 4 | 3.12 | 7.61 | 87.03 | 0.045 | 0.213 | 0.254 | -0.145 | … | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 5 | 2.37 | 5.78 | 92.81 | 0.034 | 0.216 | 0.254 | -0.148 | … | -0.121 | 0.312 | 0.446 | |
| 6 | 0.82 | 2.01 | 94.82 | -0.173 | 0.214 | -0.072 | 0.036 | … | 0.054 | -0.140 | -0.200 | |
| 7 | 0.71 | 1.74 | 96.56 | -0.208 | 0.157 | -0.052 | 0.036 | … | -0.000 | -0.000 | -0.000 | |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | |
表7 泄漏特征的主成分分析结果
Table 7 Principal component analysis results of leakage characteristics
| 主元编号 | 特征值 | 主元方差贡献率/% | 累计方差贡献率/% | Tci1 | Tci2 | Tci3 | Tci4 | … | ΔPvel | ΔPeva | ΔHcon | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.80 | 38.55 | 38.55 | 0.052 | 0.220 | 0.246 | -0.135 | … | -0.289 | 0.249 | 0.112 | |
| 2 | 9.64 | 23.51 | 62.06 | 0.048 | 0.213 | 0.253 | -0.143 | … | -0.000 | 0.000 | -0.000 | |
| 3 | 7.12 | 17.36 | 79.42 | 0.048 | 0.216 | 0.250 | -0.142 | … | -0.000 | 0.000 | -0.000 | |
| 4 | 3.12 | 7.61 | 87.03 | 0.045 | 0.213 | 0.254 | -0.145 | … | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |
| 5 | 2.37 | 5.78 | 92.81 | 0.034 | 0.216 | 0.254 | -0.148 | … | -0.121 | 0.312 | 0.446 | |
| 6 | 0.82 | 2.01 | 94.82 | -0.173 | 0.214 | -0.072 | 0.036 | … | 0.054 | -0.140 | -0.200 | |
| 7 | 0.71 | 1.74 | 96.56 | -0.208 | 0.157 | -0.052 | 0.036 | … | -0.000 | -0.000 | -0.000 | |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … | |
| SVM模型编号 | 名称 | 意义 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Linear SVM | 线性核函数 |
| 2 | Quadratic SVM | 二次多项式核函数 d=2 |
| 3 | Cubic SVM | 三次多项式核函数 d=3 |
| 4 | Fine Gaussian SVM | 精细高斯核函数 |
| 5 | Medium Gaussian SVM | 中位高斯核函数 |
| 6 | Coarse Gaussisn SVM | 粗糙高斯核函数 |
表8 不同核函数类型的SVM模型信息
Table 8 SVM model information of different kernel function types
| SVM模型编号 | 名称 | 意义 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Linear SVM | 线性核函数 |
| 2 | Quadratic SVM | 二次多项式核函数 d=2 |
| 3 | Cubic SVM | 三次多项式核函数 d=3 |
| 4 | Fine Gaussian SVM | 精细高斯核函数 |
| 5 | Medium Gaussian SVM | 中位高斯核函数 |
| 6 | Coarse Gaussisn SVM | 粗糙高斯核函数 |
| CPVa | 主元组合 | SVM核函数 | Acc/% | Mcr/% | TPR/% | FPR/% | 测试集混淆矩阵 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 87.02% | [1,2,3,4] | Fine Gaussian SVM | 100 | 0 | 99.5 | 0 |
表9 泄漏/非泄漏模式下PCA-SVM识别模型及性能
Table 9 PCA-SVM leak identification model and performance
| CPVa | 主元组合 | SVM核函数 | Acc/% | Mcr/% | TPR/% | FPR/% | 测试集混淆矩阵 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 87.02% | [1,2,3,4] | Fine Gaussian SVM | 100 | 0 | 99.5 | 0 |
| 工况 | Model-o | Model-pca4 |
|---|---|---|
Refleak normal ReduCF ReduEF loosTV ClosTV IncrTW DecrTW | ||
| 工况 | Model-pca5 | Model-pca6 |
Refleak normal ReduCF ReduEF loosTV ClosTV IncrTW DecrTW | ||
| 工况 | Model-pca7 | |
Refleak normal ReduCF ReduEF loosTV ClosTV IncrTW DecrTW |
表10 不同模型在各个故障的诊断识别的混淆矩阵
Table 10 Confusion matrix of different models in each fault diagnosis identification
| 工况 | Model-o | Model-pca4 |
|---|---|---|
Refleak normal ReduCF ReduEF loosTV ClosTV IncrTW DecrTW | ||
| 工况 | Model-pca5 | Model-pca6 |
Refleak normal ReduCF ReduEF loosTV ClosTV IncrTW DecrTW | ||
| 工况 | Model-pca7 | |
Refleak normal ReduCF ReduEF loosTV ClosTV IncrTW DecrTW |
| 工况 | Model-pca4 | Model-pca5 | Model-pca6 | Model-pca7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Refleak_slow Refleak_fast normal |
表11 四种模型在相同数据集的各泄漏诊断识别结果混淆矩阵
Table 11 Confusion matrix of leakage diagnosis and identification results of four models in the same data set
| 工况 | Model-pca4 | Model-pca5 | Model-pca6 | Model-pca7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Refleak_slow Refleak_fast normal |
| 方式 | 序号 | 主元组合 | SVM核函数 | Acc/% | Mcr/% | TPR/% | FPR/% | 测试集混淆矩阵 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA-SVM | 1 | [ | Fine Gaussian SVM | 100 | 0 | 99.5 | 0 | |
| 2 | [ | 100 | 0 | 99.5 | 0 | |||
| 3 | [ | 99.1 | 0.9 | 97.6 | 0.2 | |||
RefliefF PCA-SVM | 4 | [1r,2r,3r,4r] | Fine Gaussian SVM | 97.8 | 2.2 | 97.1 | 1.8 | |
| 5 | [1r,2r,3r,4r,5r] | 97.4 | 2.6 | 95.6 | 1.8 | |||
| 6 | [1r,2r,3r,4r,5r,6r] | 97.4 | 2.6 | 93.7 | 0.9 |
表12 RefliefF特征选择前后的PCA-SVM泄漏识别模型及性能结果对比
Table 12 Comparison of PCA-SVM leak identification model and performance results before and after RefliefF FS
| 方式 | 序号 | 主元组合 | SVM核函数 | Acc/% | Mcr/% | TPR/% | FPR/% | 测试集混淆矩阵 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA-SVM | 1 | [ | Fine Gaussian SVM | 100 | 0 | 99.5 | 0 | |
| 2 | [ | 100 | 0 | 99.5 | 0 | |||
| 3 | [ | 99.1 | 0.9 | 97.6 | 0.2 | |||
RefliefF PCA-SVM | 4 | [1r,2r,3r,4r] | Fine Gaussian SVM | 97.8 | 2.2 | 97.1 | 1.8 | |
| 5 | [1r,2r,3r,4r,5r] | 97.4 | 2.6 | 95.6 | 1.8 | |||
| 6 | [1r,2r,3r,4r,5r,6r] | 97.4 | 2.6 | 93.7 | 0.9 |
| 1 | Mohanraj M, Muraleedharan C, Jayaraj S. A review on recent developments in new refrigerant mixtures for vapour compression-based refrigeration, air-conditioning and heat pump units[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2011, 35(8): 647-669. |
| 2 | 王晓明. 制冷系统故障先兆分析和故障预报技术研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 1998. |
| Wang X M. Analysis of refrigeration system failure predication and failure prediction technology [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 1998. | |
| 3 | Koronaki I P, Cowan D, Maidment G, et al. Refrigerant emissions and leakage prevention across Europe-results from the RealSkillsEurope project[J]. Energy, 2012, 45(1): 71-80. |
| 4 | Francis C, Maidment G, Davies G. An investigation of refrigerant leakage in commercial refrigeration[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2017, 74: 12-21. |
| 5 | Cowan D, Maidment G, Churchyard B, et al. Maintenance and long-term operation of supermarkets and minimizing refrigerant leakage[M]// Sustainable Retail Refrigeration. New York: John Wiley & Sons Ltd., 2015: 14-20. |
| 6 | Chantant M, Lambert R, Gargiulo L, et al. Leak tightness tests on actively cooled plasma facing components: lessons learned from Tore Supra experience and perspectives for the new fusion machines[J]. Fusion Engineering & Design, 2015, 98: 92-96. |
| 7 | Tassou S A, Grace I N. Fault diagnosis and refrigerant leak detection in vapour compression refrigeration systems[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2005, 28(5): 680-688. |
| 8 | 任能. 制冷系统故障检测、诊断及预测研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2008. |
| Ren N. Fault detection, diagnosis and prediction of refrigeration system [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2008. | |
| 9 | Beshr M, Aute V, Sharma V, et al. A comparative study on the environmental impact of supermarket refrigeration systems using low GWP refrigerants[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2015, 56: 154-164. |
| 10 | Coulomb D. Refrigeration and cold chain serving the global food industry and creating a better future: two key IIR challenges for improved health and environment[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2008, 19(8): 409-417. |
| 11 | 郭军峰. 汽车空调性能衰减研究[D].重庆: 重庆大学, 2012. |
| Guo J F. Research on performance attenuation of automobile air conditioner [D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2012. | |
| 12 | Yoo J W, Hong S B, Kim M S. Refrigerant leakage detection in an EEV installed residential air conditioner with limited sensor installations[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2017, 78: 157-165. |
| 13 | Yu Y, Woradechjumroen D, Yu D. A review of fault detection and diagnosis methodologies on air-handling units[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2014, 82: 550-562. |
| 14 | Grace I N, Datta D, Tassou S A. Sensitivity of refrigeration system performance to charge levels and parameters for on-line leak detection[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2005, 25(4): 557-566. |
| 15 | Grace I N, Datta D, Tassou S A. Sensitivity of refrigeration system performance to charge levels and parameters for on-line leak detection[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2005, 25(4): 557-566. |
| 16 | Yoon S H, Payne W V, Domanski P A. Residential heat pump heating performance with single faults imposed[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2011, 31(5): 765-771. |
| 17 | Han H, Gu B, Wang T, et al. Important sensors for chiller fault detection and diagnosis (FDD) from the perspective of feature selection and machine learning[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2011, 34(2): 586-599. |
| 18 | Han H, Cao Z, Gu B, et al. PCA-SVM-based automated fault detection and diagnosis (AFDD) for vapor-compression refrigeration systems[J]. HVAC&R Research, 2010, 16(3): 295-313. |
| 19 | 齐咏生, 张海利, 王林, 等.基于MSPCA-KECA的冷水机组故障监测及诊断[J].化工学报, 2017, 68(4): 1499-1508. |
| Qi Y S, Zhang H L, Wang L, et al. Fault monitoring and diagnosis of chiller based on MSPCA-KECA [J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(4): 1499-1508. | |
| 20 | 韩华, 谷波, 任能. 基于主元分析与支持向量机的制冷系统故障诊断方法[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2011, (9): 108-114+126. |
| Han H, Gu B, Ren N. Fault diagnosis method of refrigeration system based on principal component analysis and support vector machine [J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2011, (9): 108-114+126. | |
| 21 | 洪迎春. 基于多变量统计分析的制冷系统故障检测与诊断[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2012. |
| Hong Y C. Fault detection and diagnosis of refrigeration system based on multivariate statistical analysis [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2012. | |
| 22 | 梁晴晴, 韩华, 崔晓钰, 等. 基于主元分析-概率神经网络的制冷系统故障诊断[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(3): 1022-1031. |
| Liang Q Q, Han H, Cui X Y, et al. Fault diagnosis of refrigeration system based on PCA-PNN [J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(3): 1022-1031. | |
| 23 | 王路瑶, 吴斌, 杜志敏, 等.基于长短期记忆神经网络的数据中心空调系统传感器故障诊断[J].化工学报, 2018, 69: 252-259. |
| Wang L Y, Wu B, Du Z M, et al. Sensor fault diagnosis of air conditioning system in data center based on neural network of long and short term memory [J]. CIESC Journal, 2018, 69: 252-259. | |
| 24 | 韩华. 基于顺序集成方法的制冷系统故障检测与诊断研究[D].上海: 上海交通大学, 2012. |
| Han H. Study on fault detection and diagnosis of refrigeration system based on sequential integration method [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2012. | |
| 25 | 赵旭, 阎威武, 邵惠鹤, 等. 基于核Fisher判别分析方法的非线性统计过程监控与故障诊断[J]. 化工学报, 2007, 58(4): 951-956. |
| Zhao X, Yan W W, Shao H H, et al. Nonlinear statistical process monitoring and fault diagnosis based on nuclear Fisher discriminant analysis [J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering(China), 2007, 58(4): 951-956. | |
| 26 | 周志华, 王珏. 机器学习及其应用2009[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2009. |
| Zhou Z H, Wang J. Machine Learning and Its Application 2009[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2009. | |
| 27 | Valle S, Li W, Qin S J. Selection of the number of principal components: the variance of the reconstruction error criterion with a comparison to other methods[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 1999, 38(11): 4389-4401. |
| 28 | Jos B, Draper B A. Feature selection from huge feature sets[C]// Proceedings. Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE, 2001. |
| 29 | Robnik M, Kononenko I. Theoretical and empirical analysis of ReliefF and RReliefF[J]. Machine Learning, 2003, 53(1/2): 23-69. |
| 30 | Deng X, Li Y, Weng J, et al. Feature selection for text classification: a review[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2018, 78: 3797-3816. |
| [1] | 曹跃, 余冲, 李智, 杨明磊. 工业数据驱动的加氢裂化装置多工况切换过渡状态检测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3841-3854. |
| [2] | 尹刚, 李伊惠, 何飞, 曹文琦, 王民, 颜非亚, 向禹, 卢剑, 罗斌, 卢润廷. 基于KPCA和SVM的铝电解槽漏槽事故预警方法[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3419-3428. |
| [3] | 诸程瑛, 王振雷. 基于改进深度强化学习的乙烯裂解炉操作优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3429-3437. |
| [4] | 高学金, 姚玉卓, 韩华云, 齐咏生. 基于注意力动态卷积自编码器的发酵过程故障监测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2503-2521. |
| [5] | 周继鹏, 何文军, 李涛. 异形催化剂上乙烯催化氧化失活动力学反应工程计算[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2416-2426. |
| [6] | 郑书闽, 郭鹏程, 颜建国, 王帅, 李文博, 周淇. 微小通道内过冷流动沸腾阻力特性实验及预测研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1549-1560. |
| [7] | 顾学荣, 刘硕士, 杨思宇. 基于并行EGO和代理模型辅助的多参数优化方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1205-1215. |
| [8] | 张生安, 刘桂莲. 高效太阳能电解水制氢系统及其性能的多目标优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1260-1274. |
| [9] | 陈家辉, 杨鑫泽, 陈顾中, 宋震, 漆志文. 以离子液体密度为例的分子性质预测模型建模方法探讨[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 630-641. |
| [10] | 袁海鸥, 叶方俊, 张硕, 罗祎青, 袁希钢. 考虑中间换热器的能量集成精馏序列合成[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 796-806. |
| [11] | 高学金, 程琨, 韩华云, 高慧慧, 齐咏生. 基于中心损失的条件生成式对抗网络的冷水机组故障诊断[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3950-3962. |
| [12] | 王雅琳, 潘雨晴, 刘晨亮. 基于GSA-LSTM动态结构特征提取的间歇过程监测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 3994-4002. |
| [13] | 王琨, 侍洪波, 谭帅, 宋冰, 陶阳. 局部时差约束邻域保持嵌入算法在故障检测中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3109-3119. |
| [14] | 孙哲, 金华强, 李康, 顾江萍, 黄跃进, 沈希. 基于知识数据化表达的制冷空调系统故障诊断方法[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3131-3144. |
| [15] | 杨岭, 崔国民, 周志强, 肖媛. 精细搜索策略应用于质量交换网络综合[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3145-3155. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号