化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (7): 3026-3037.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220341
陈永安1,2( ),周安宁1,2(
),周安宁1,2( ),李云龙1,3,石智伟1,2,贺新福1,2,焦卫红1,2
),李云龙1,3,石智伟1,2,贺新福1,2,焦卫红1,2
收稿日期:2022-03-06
修回日期:2022-04-24
出版日期:2022-07-05
发布日期:2022-08-01
通讯作者:
周安宁
作者简介:陈永安(1997—),男,硕士研究生, 基金资助:
Yong’an CHEN1,2( ),Anning ZHOU1,2(
),Anning ZHOU1,2( ),Yunlong LI1,3,Zhiwei SHI1,2,Xinfu HE1,2,Weihong JIAO1,2
),Yunlong LI1,3,Zhiwei SHI1,2,Xinfu HE1,2,Weihong JIAO1,2
Received:2022-03-06
Revised:2022-04-24
Online:2022-07-05
Published:2022-08-01
Contact:
Anning ZHOU
摘要:
采用溶胶-凝胶法制得MgFe2O4前体,经焙烧得到MgFe2O4催化剂,再经St?ber法制得核壳结构催化剂MgFe2O4@SiO2和MgFe2O4@SiO2@HZSM-5(MSH),利用VSM、XRD、SEM、FT-IR、N2物理吸附等手段研究了催化剂的磁性能和结构特征;在固定床反应器上,考察了N2气氛下磁性催化剂对补连塔富油煤的催化热解特性及回收再生性能。结果表明:MgFe2O4为立方尖晶石结构,饱和磁化强度达到181.50 emu/g,具有良好热稳定性能。上述系列磁性催化剂均呈现出良好的催化活性,其中MSH催化活性最好。与非催化热解相比,MSH催化热解焦油产率提高了57.7%,焦油中脂肪烃和苯类含量增加约2倍,稠环芳烃含量下降8.6%~9.8%。采用磁选方法可有效实现催化剂回收,经700℃下焙烧处理,可实现回收催化剂的再生。SiO2包覆有助于提高核壳结构催化剂的磁热稳定性和催化寿命。
中图分类号:
陈永安, 周安宁, 李云龙, 石智伟, 贺新福, 焦卫红. 磁性MgFe2O4及其核壳催化剂制备与煤热解性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 3026-3037.
Yong’an CHEN, Anning ZHOU, Yunlong LI, Zhiwei SHI, Xinfu HE, Weihong JIAO. Preparation and coal pyrolysis performance of magnetic MgFe2O4 and its core-shell catalysts[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(7): 3026-3037.
| Proximate analysis/%(mass,ad) | Ultimate analysis/%(mass,ad) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | A | V | FC① | C | H | N | S | O① |
| 9.58 | 4.4 | 30.42 | 55.6 | 82.42 | 5.16 | 1.23 | 0.26 | 10.93 |
表1 补连塔煤的工业分析与元素分析
Table 1 Proximate analysis and ultimate analysis of BLT-coal
| Proximate analysis/%(mass,ad) | Ultimate analysis/%(mass,ad) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | A | V | FC① | C | H | N | S | O① |
| 9.58 | 4.4 | 30.42 | 55.6 | 82.42 | 5.16 | 1.23 | 0.26 | 10.93 |

图5 磁性催化剂的XRD谱图、 N2吸脱附等温曲线、FT-IR谱图和VSM磁化曲线
Fig.5 XRD patterns, N2 adsorption and desorption isotherm curve, FT-IR spectra and VSM magnetization curve of magnetic catalyst
| 催化剂 | SBET/(m2/g) | DBJH/nm | Vtotal/(10-2 cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MgFe2O4 | 9.94 | 26.19 | 7.32 |
| MgFe2O4@SiO2 | 35.35 | 14.01 | 14.82 |
| MSH | 321.13 | 4.20 | 7.32 |
表2 磁性催化剂的比表面积和孔结构参数
Table 2 Specific surface area and pore structure parameters of magnetic catalyst
| 催化剂 | SBET/(m2/g) | DBJH/nm | Vtotal/(10-2 cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MgFe2O4 | 9.94 | 26.19 | 7.32 |
| MgFe2O4@SiO2 | 35.35 | 14.01 | 14.82 |
| MSH | 321.13 | 4.20 | 7.32 |
| 催化剂 | 半焦产率/% | 焦油产率/% | 气体产率/% | 水产率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| none | 68.13 65.76 64.94 65.67 | 9.42 14.25 12.16 14.86 | 16.19 14.46 16.73 14.82 | 6.26 5.53 6.17 4.61 |
| MgFe2O4 | ||||
| MgFe2O4@SiO2 | ||||
| MSH |
表3 磁性催化剂对热解产物分布的影响
Table 3 Effect of magnetic catalyst on distribution of pyrolysis products
| 催化剂 | 半焦产率/% | 焦油产率/% | 气体产率/% | 水产率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| none | 68.13 65.76 64.94 65.67 | 9.42 14.25 12.16 14.86 | 16.19 14.46 16.73 14.82 | 6.26 5.53 6.17 4.61 |
| MgFe2O4 | ||||
| MgFe2O4@SiO2 | ||||
| MSH |
| 催化剂 | 苯类/% | 酚类/% | 脂肪 烃类/% | 稠环芳 烃类/% | 其他/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| none | 1.37 | 18.04 | 12.85 | 34.22 | 33.52 |
| MgFe2O4 | 4.18 | 18.58 | 18.28 | 28.67 | 30.29 |
| MgFe2O4@SiO2 | 4.02 | 18.21 | 17.98 | 28.91 | 30.88 |
| MSH | 4.12 | 17.84 | 23.53 | 25.63 | 29.88 |
表4 不同催化剂上BLT-coal热解焦油组分含量
Table 4 Content of BLT-coal pyrolysis tar on different catalysts
| 催化剂 | 苯类/% | 酚类/% | 脂肪 烃类/% | 稠环芳 烃类/% | 其他/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| none | 1.37 | 18.04 | 12.85 | 34.22 | 33.52 |
| MgFe2O4 | 4.18 | 18.58 | 18.28 | 28.67 | 30.29 |
| MgFe2O4@SiO2 | 4.02 | 18.21 | 17.98 | 28.91 | 30.88 |
| MSH | 4.12 | 17.84 | 23.53 | 25.63 | 29.88 |
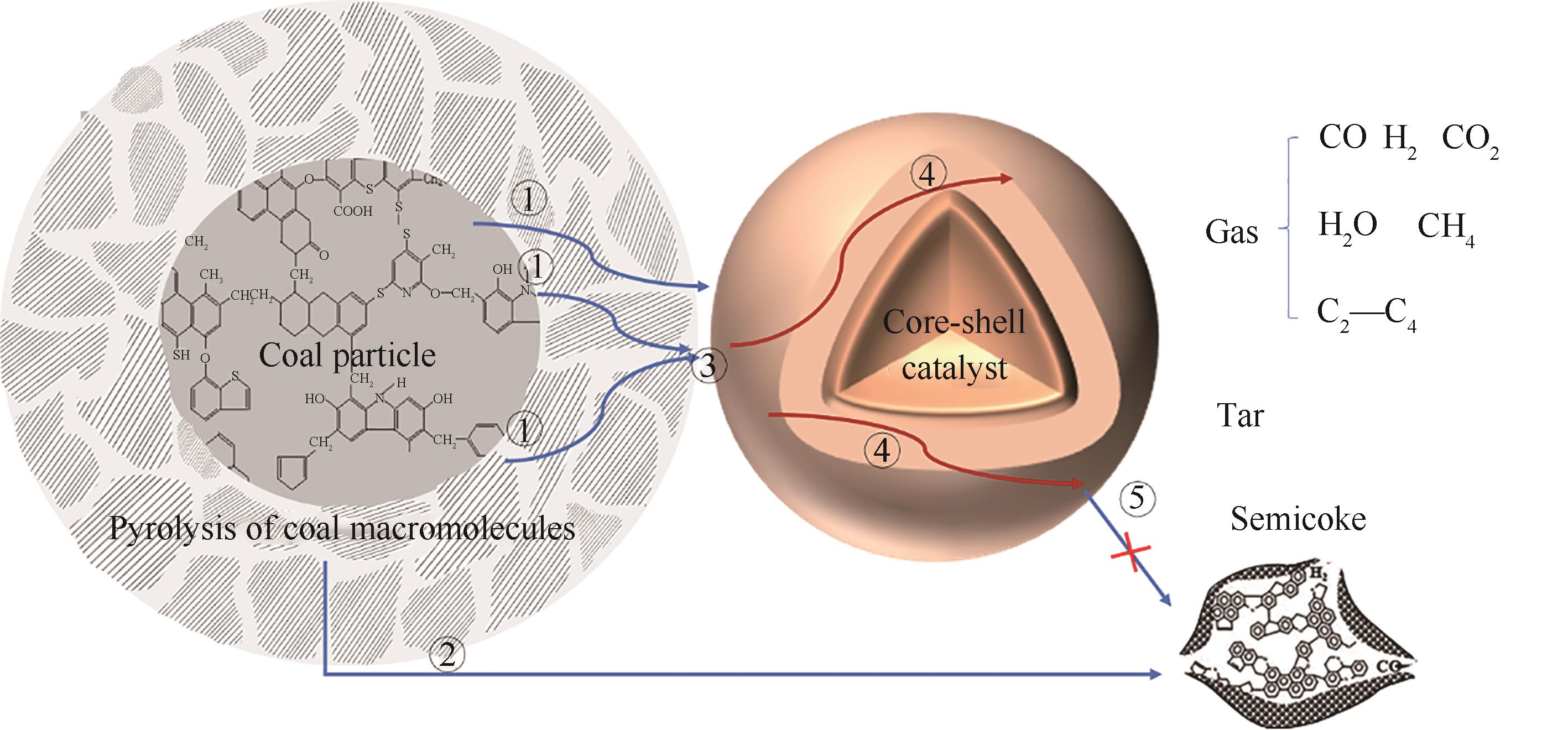
图7 磁性催化剂催化热解机理① 煤常规裂解及油气内扩散过程;② 煤常规热解生成的自由基之间的缩聚脱氢形成半焦;③ 煤大分子界面催化裂解形成油气;④ 油气扩散与催化裂化反应形成轻质油及煤气;⑤ 裂解自由基二次缩聚形成半焦或在催化剂表面积炭
Fig.7 Catalytic pyrolysis mechanism of magnetic catalyst
| 催化剂 | 半焦产率/% | 焦油产率/% | 气体产率/% | 水产率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1R-MgFe2O4 | 65.97 | 13.23 | 14.98 | 5.82 |
| 1R-MgFe2O4@SiO2 | 65.01 | 11.54 | 16.98 | 6.47 |
| 1R-MSH | 66.63 | 13.08 | 15.12 | 5.17 |
表5 再生磁性催化剂对热解产物分布的影响
Table 5 Effect of recovery of magnetic catalyst on distribution of pyrolysis products
| 催化剂 | 半焦产率/% | 焦油产率/% | 气体产率/% | 水产率/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1R-MgFe2O4 | 65.97 | 13.23 | 14.98 | 5.82 |
| 1R-MgFe2O4@SiO2 | 65.01 | 11.54 | 16.98 | 6.47 |
| 1R-MSH | 66.63 | 13.08 | 15.12 | 5.17 |
| 1 | 王双明, 师庆民, 王生全, 等. 富油煤的油气资源属性与绿色低碳开发[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(5): 1365-1377. |
| Wang S M, Shi Q M, Wang S Q, et al. Resource property and exploitation concepts with green and low-carbon of tar-rich coal as coal-based oil and gas[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(5): 1365-1377. | |
| 2 | 马丽, 拓宝生. 陕西富油煤资源量居全国之首 榆林可“再造一个大庆油田”[J]. 陕西煤炭, 2020, 39(1): 220-222. |
| Ma L, Tuo B S. Shaanxi’s oil-rich coal resources rank first in the country. Yulin can “rebuild a Daqing Oilfield”[J]. Shaanxi Coal, 2020, 39(1): 220-222. | |
| 3 | 煤炭资讯网. 推进富油煤合理开发利用[EB/OL]. [2022-03-24]. . |
| Coal Information Network. Promoting the rational development and utilization of oil-rich coal[EB/OL]. [2022-03-24]. . | |
| 4 | 李勇, 闫伦靖, 李晓荣, 等. 酸/碱催化剂对低阶煤热解挥发分转化行为的作用机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(3): 1173-1183. |
| Li Y, Yan L J, Li X R, et al. Study on the mechanism of acid/base catalyst on the release behavior of volatiles during low rank coal pyrolysis[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(3): 1173-1183. | |
| 5 | 陈兆辉, 高士秋, 许光文. 煤热解过程分析与工艺调控方法[J]. 化工学报, 2017, 68(10): 3693-3707. |
| Chen Z H, Gao S Q, Xu G W. Analysis and control methods of coal pyrolysis process[J]. CIESC Journal, 2017, 68(10): 3693-3707. | |
| 6 | Deng X L, Deng J, He R Z, et al. Effects of Ba and Mg promoters on gas release from Fe catalyzed coal pyrolysis: effects of different precursors[J]. Fuel, 2022, 308: 121977. |
| 7 | Zhang C, Wu R C, Xu G W. Coal pyrolysis for high-quality tar in a fixed-bed pyrolyzer enhanced with internals[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(1): 236-244. |
| 8 | Wang D, Chen Z H, Li C M, et al. High-quality tar production from coal in an integrated reactor: rapid pyrolysis in a drop tube and downstream volatiles upgrading over char in a moving bed[J]. Fuel, 2021, 285: 119156. |
| 9 | Niu B, Liu R C, Zhang J T, et al. Effect of O2/CH4 atmosphere on tar production during coal pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2021, 159: 105317. |
| 10 | Zhang X H, Zhu J L, Ban Y P, et al. Effect of Fe2O3 on the pyrolysis of two demineralized coal using in-situ pyrolysis photoionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2021, 49(5): 589-597. |
| 11 | Yang Z, Cao J P, Liu T L, et al. Controllable hollow HZSM-5 for high shape-selectivity to light aromatics from catalytic reforming of lignite pyrolysis volatiles[J]. Fuel, 2021, 294: 120427. |
| 12 | Liu T L, Cao J P, Zhao X Y, et al. In situ upgrading of Shengli lignite pyrolysis vapors over metal-loaded HZSM-5 catalyst[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2017, 160: 19-26. |
| 13 | Han J Z, Liu X X, Yue J R, et al. Catalytic upgrading of in situ coal pyrolysis tar over Ni-char catalyst with different additives[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(8): 4934-4941. |
| 14 | Liguori F, Moreno-Marrodan C, Barbaro P. Metal nanoparticles immobilized on ion-exchange resins: a versatile and effective catalyst platform for sustainable chemistry[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2015, 36(8): 1157-1169. |
| 15 | 施达. 磁性双功能催化剂的制备、结构表征及其甲醇催化转化反应性能研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2017. |
| Shi D. Preparation of magnetic difunctional catalysts, characterization of structure and their catalytic performance for methanol catalysis activity[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2017. | |
| 16 | 姜少宁, 雷建民, 张敏刚, 等. 铁基非晶软磁合金的制备及磁性能研究[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2009, 28(7): 30-32. |
| Jiang S N, Lei J M, Zhang M G, et al. Preparation and magnetic properties study of Fe-based amorphous soft magnetic alloys[J]. Electronic Components and Materials, 2009, 28(7): 30-32. | |
| 17 | 惠希东, 吕旷, 斯佳佳, 等. 高饱和磁化强度铁基非晶纳米晶软磁合金发展概况[J]. 工程科学学报, 2018, 40(10): 1158-1167. |
| Hui X D, Lyu K, Si J J, et al. Development of Fe-based amorphous and nanocrystalline alloys with high saturation flux density[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2018, 40(10): 1158-1167. | |
| 18 | Shakir I, Sarfraz M, Ali Z, et al. Magnetically separable and recyclable graphene-MgFe2O4 nanocomposites for enhanced photocatalytic applications[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 660: 450-455. |
| 19 | Oladipo A A, Ifebajo A O, Gazi M. Magnetic LDH-based CoO-NiFe2O4 catalyst with enhanced performance and recyclability for efficient decolorization of azo dye via Fenton-like reactions[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 243: 243-252. |
| 20 | Zhang E L, Wu J Y, Wang G S, et al. Efficient Fenton oxidation of Congo red dye by magnetic MgFe2O4 nanorods[J]. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 2016, 16(5): 4727-4732. |
| 21 | Rath C, Anand S, Das R P, et al. Dependence on cation distribution of particle size, lattice parameter, and magnetic properties in nanosize Mn-Zn ferrite[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 91(4): 2211-2215. |
| 22 | Roumaih K. Effect of temperature on the dielectric and magnetic properties of NiFe2O4@MgFe2O4 and ZnFe2O4@MgFe2O4 core-shell[J]. Physica Scripta, 2021, 96(12): 125809. |
| 23 | Puspitarum D L, Hermawan A, Suharyadi E. The influence of PEG-4000 and silica on crystal structure and magnetic properties of magnesium ferrite (MgFe2O4) nanoparticles[C/OL]// AIP Conference Proceedings. Semarang, Indonesia, 2016. |
| 24 | Thakare J G, Pandey C, Mahapatra M M, et al. Thermal barrier coatings—a state of the art review[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2021, 27(7): 1947-1968. |
| 25 | 张军兴, 周安宁, 闫宁, 等. 磁性Mo/HZSM-5@SiO2@Fe3O4催化剂可控制备及煤催化热解[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(6): 1985-1994. |
| Zhang J X, Zhou A N, Yan N, et al. Controlled preparation and catalytic pyrolysis of coal over magnetic Mo/HZSM-5@SiO2@Fe3O4 catalyst[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(6): 1985-1994. | |
| 26 | Zhao W R, Gu J L, Zhang L X, et al. Fabrication of uniform magnetic nanocomposite spheres with a magnetic core/mesoporous silica shell structure[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2005, 127(25): 8916-8917. |
| 27 | 孙冬, 孙博, 裴燕, 等. 壳层厚度对骨架Fe@HZSM-5核壳催化剂费托合成催化性能的影响[J]. 化学学报, 2021, 79(6): 771-777. |
| Sun D, Sun B, Pei Y, et al. Effect of shell thickness on skeletal Fe@HZSM-5 core-shell catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch synthesis[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2021, 79(6): 771-777 | |
| 28 | Wang J, Liu X, Li L . et al. Performance improvement of Fe-6.5Si soft magnetic composites with hybrid phosphate-silica insulation coatings[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(4): 1266-1278. |
| 29 | 濮思菁, 刘汝庚, 刘国柱, 等. 表面性质对HZSM-5分子筛涂层结构的影响[C]//第十七届全国分子筛学术大会. 宁夏, 2013. |
| Pu S J, Liu R G, Liu G Z, et al. Effect of surface properties on the structure of HZSM-5 molecular sieve coating[C]//The 17th Chinese Zeolite Conference. Ningxia, 2013. | |
| 30 | Tang W S, Su Y, Li Q, et al. Superparamagnetic magnesium ferrite nano-adsorbent for effective arsenic (Ⅲ, Ⅴ) removal and easy magnetic separation[J]. Water Research: A Journal of the International Water Association, 2013, 47(11): 3624-3634. |
| 31 | 张淑平. CoFe2O4/SiO2材料的制备及其磁性的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2005. |
| Zhang S P. Preparation and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4/SiO2 materials[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2005. | |
| 32 | 李云龙, 周安宁, 石智伟, 等. 磁性Mo-Ni/HZSM-5@SiO2@Fe3O4催化剂对补连塔煤热解的影响[J]. 煤炭转化, 2021, 44(6): 26-33. |
| Li Y L, Zhou A N, Shi Z W, et al. Effects of magnetic Mo-Ni/HZSM-5@SiO2@Fe3O4 catalyst on pyrolysis of bulianta coal[J]. Coal Conversion, 2021, 44(6): 26-33. | |
| 33 | 杨珍, 曹景沛, 朱陈, 等. B-ZSM-5酸调控及催化褐煤热解挥发分制轻质芳烃研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5633-5642. |
| Yang Z, Cao J P, Zhu C, et al. Catalytic conversion of lignite pyrolysis volatiles for enriching light aromatics over B-ZSM-5[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(11): 5633-5642. | |
| 34 | Yousefi A, Almasi Kashi M, Afghahi S S S. Enhancement and recovery of magnetic exchange coupling properties in SrFe11AlO19@NiFe2O4 core-shell structure by multiple TiO2 and SiO2 nanolayer shells[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2021, 530: 167932. |
| 35 | 王俊丽, 吕婧, 李淑英, 等.基于贝壳衍生CaO的低阶煤催化热解特性及热解机理研究[J/OL]. 煤炭转化, 2022, [2022-04-20]. . |
| Wang J L, Lyu J, Li S Y, et al. Catalytic pyrolysis characteristics and pyrolysis mechanism of low rank coal with shell-derived CaO[J/OL]. Coal Conversion,2022, [2022-04-20]. . | |
| 36 | 刘芸, 张源, 郭娅男, 等. 不同煤阶煤热解气化特性及机理研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(18): 7672-7677. |
| Liu Y, Zhang Y, Guo Y N, et al. Pyrolysis and gasification of coal with different ranks: characteristics and mechanism[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(18): 7672-7677. | |
| 37 | 刘振宇. 重质有机资源热解过程中的自由基化学[J]. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 45(5): 8-24. |
| Liu Z Y. Radical chemistry in the pyrolysis of heavy organics[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 45(5): 8-24. | |
| 38 | 刘振宇. 煤快速热解制油技术问题的化学反应工程根源: 逆向传热与传质[J]. 化工学报, 2016, 67(1): 1-5. |
| Liu Z Y. Origin of common problems in fast coal pyrolysis technologies for tar: the countercurrent flow of heat and volatiles[J]. CIESC Journal, 2016, 67(1): 1-5. | |
| 39 | 陈冠益, 杨会军, 姚金刚, 等. 两段式固定床芦竹催化热解实验研究[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 2017, 50(1): 59-64. |
| Chen G Y, Yang H J, Yao J G, et al. Catalytic pyrolysis of arundo donax in a two-stage fixed-bed reactor[J]. Journal of Tianjin University (Science and Technology), 2017, 50(1): 59-64. | |
| 40 | Zhang Y, Zheng Y. Co-gasification of coal and biomass in a fixed bed reactor with separate and mixed bed configurations[J]. Fuel, 2016, 183: 132-138. |
| 41 | 潘庆谊, 张中太. MgFe2O4尖晶石型固溶体的导电性和缺陷结构[J]. 无机材料学报, 1988, 3(3): 245-250. |
| Pan Q Y, Zhang Z T. Defect structure and conduction in magnesium ferrite[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1988, 3(3): 245-250. | |
| 42 | Song Q, Zhao H Y, Chang S Q, et al. Study on the catalytic pyrolysis of coal volatiles over hematite for the production of light tar[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2020, 151: 104927. |
| 43 | 杨英杰, 杨赫, 朱家龙, 等. 淖毛湖煤慢速热解过程官能团相互作用[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 865-875. |
| Yang Y J, Yang H, Zhu J L, et al. Interaction between functional groups during slow pyrolysis of Naomaohu coal[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(2): 865-875. | |
| 44 | 宋超, 叶茂, 刘中民. 甲醇制烯烃工艺催化剂再生过程的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 中国粉体技术, 2020, 26(3): 39-45. |
| Song C, Ye M, Liu Z M. CFD-DEM simulation of catalyst regeneration in methanol to olefins process[J]. China Powder Science and Technology, 2020, 26(3): 39-45. | |
| 45 | 任雪宇, 曹景沛, 赵小燕, 等. ZSM-5分子筛孔道调控及催化褐煤热解挥发物制轻质芳烃的研究[C]//第三届能源转化化学与技术研讨会. 厦门, 2018. |
| Ren X Y, Cao J P, Zhao X Y, et al. Study on ZSM-5 molecular sieve pore channel regulation and catalytic pyrolysis of lignite to produce light aromatics[C]// The 3rd Energy Conversion Chemistry and Technology Symposium. Xiamen, 2018. |
| [1] | 黄琮琪, 吴一梅, 陈建业, 邵双全. 碱性电解水制氢装置热管理系统仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| [2] | 车睿敏, 郑文秋, 王小宇, 李鑫, 许凤. 基于离子液体的纤维素均相加工研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3615-3627. |
| [3] | 张佳怡, 何佳莉, 谢江鹏, 王健, 赵鹬, 张栋强. 渗透汽化技术用于锂电池生产中N-甲基吡咯烷酮回收的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [4] | 张瑞航, 曹潘, 杨锋, 李昆, 肖朋, 邓春, 刘蓓, 孙长宇, 陈光进. ZIF-8纳米流体天然气乙烷回收工艺的产品纯度关键影响因素分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [5] | 文兆伦, 李沛睿, 张忠林, 杜晓, 侯起旺, 刘叶刚, 郝晓刚, 官国清. 基于自热再生的隔壁塔深冷空分工艺设计及优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2988-2998. |
| [6] | 卫雪岩, 钱勇. 微米级铁粉燃料中低温氧化反应特性及其动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2624-2638. |
| [7] | 肖忠良, 尹碧露, 宋刘斌, 匡尹杰, 赵亭亭, 刘成, 袁荣耀. 废旧锂离子电池回收工艺研究进展及其安全风险分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1446-1456. |
| [8] | 陈瑞哲, 程磊磊, 顾菁, 袁浩然, 陈勇. 纤维增强树脂复合材料化学回收技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 981-994. |
| [9] | 潘煜, 王子航, 王佳韵, 王如竹, 张华. 基于可得然-氯化锂复合吸附剂的除湿换热器热湿性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1352-1359. |
| [10] | 许万, 陈振斌, 张慧娟, 牛昉昉, 火婷, 刘兴盛. 线性温敏性聚合物嵌段调控的 |
| [11] | 黄宽, 马永德, 蔡镇平, 曹彦宁, 江莉龙. 油脂催化加氢转化制备第二代生物柴油研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 380-396. |
| [12] | 鲁文静, 李先锋. 液流电池多孔离子传导膜研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(1): 192-204. |
| [13] | 郝泽光, 张乾, 高增林, 张宏文, 彭泽宇, 杨凯, 梁丽彤, 黄伟. 生物质与催化裂化油浆共热解协同作用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4070-4078. |
| [14] | 罗欣宜, 冯超, 刘晶, 乔瑜. 污泥不同热处理工艺产物磷的浸出回收实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4034-4044. |
| [15] | 马语峻, 刘向军. 多孔陶瓷膜烟气水分回收理论与模型研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4103-4112. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号