化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (9): 4034-4044.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20220340
收稿日期:2022-03-07
修回日期:2022-05-29
出版日期:2022-09-05
发布日期:2022-10-09
通讯作者:
刘晶,乔瑜
作者简介:罗欣宜(1996—),女,硕士研究生,luoxinyi@hust.edu.cn
基金资助:
Xinyi LUO1,2( ), Chao FENG1, Jing LIU1(
), Chao FENG1, Jing LIU1( ), Yu QIAO1(
), Yu QIAO1( )
)
Received:2022-03-07
Revised:2022-05-29
Online:2022-09-05
Published:2022-10-09
Contact:
Jing LIU, Yu QIAO
摘要:
针对污泥阴燃处理灰渣开展了关于磷浸出回收性能的实验研究,并与传统焚烧和热解处理工艺所产生的焚烧灰和热解焦的磷浸出回收性能进行了分析对比。结果表明,热产物中磷含量与残碳含量有关,而热处理过程中磷留存率与反应剧烈程度等因素有关。热处理会降低污泥中磷的生物有效性,尤其是焚烧。污泥阴燃灰、焚烧灰和热解焦的磷浸出过程主要受反应物浓度和产物层扩散控制,浸出时间不应超过8 h。通过硫酸浸出污泥热处理产物的方法,单位质量热产物的磷浸出量为25.72~34.42 mg/g,可将原污泥中的磷回收59.30%~84.21%。进一步对浸出工艺进行工况优选,可在保持较高污泥磷回收率的同时大幅降低硫酸单位消耗量。
中图分类号:
罗欣宜, 冯超, 刘晶, 乔瑜. 污泥不同热处理工艺产物磷的浸出回收实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4034-4044.
Xinyi LUO, Chao FENG, Jing LIU, Yu QIAO. Phosphorus recovery from products of sewage sludge via different thermal treatment processes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(9): 4034-4044.
| 工业分析①/%(质量) | 元素分析②/%(质量) | 高位热值/(MJ/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水分③ | 挥发分 | 灰分 | 固定碳 | C | H | N | S | O④ | |
| 51.32 | 43.66 | 56.14 | 0.20 | 50.26 | 8.18 | 9.39 | 1.12 | 31.05 | 8.73 |
表1 污泥的工业分析和元素分析
Table 1 Proximate analysis and ultimate analysis of sewage sludge
| 工业分析①/%(质量) | 元素分析②/%(质量) | 高位热值/(MJ/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 水分③ | 挥发分 | 灰分 | 固定碳 | C | H | N | S | O④ | |
| 51.32 | 43.66 | 56.14 | 0.20 | 50.26 | 8.18 | 9.39 | 1.12 | 31.05 | 8.73 |
| 样品 | 含量/%(质量) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | P2O5 | Fe2O3 | SO3 | CaO | K2O | MgO | C | |
| 污泥 | 24.69 | 8.26 | 5.96 | 3.68 | 3.18 | 1.92 | 1.74 | 1.55 | 21.24 |
| 阴燃灰 | 54.73 | 17.56 | 9.44 | 5.85 | 1.94 | 3.46 | 3.15 | 1.68 | 0.60 |
| 焚烧灰 | 51.37 | 18.18 | 9.60 | 7.21 | 0.33 | 4.15 | 2.98 | 2.25 | 0 |
| 热解焦 | 49.83 | 18.86 | 8.75 | 6.59 | 1.18 | 4.05 | 3.17 | 2.12 | 13.74 |
表2 污泥(SS)、阴燃灰(SA)、焚烧灰(IA)和热解焦(PC)的元素组成和碳含量
Table 2 Chemical composition and carbon content of sewage sludge (SS), smouldered ash (SA), incinerated ash (IA) and pyrolysis char (PC)
| 样品 | 含量/%(质量) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | P2O5 | Fe2O3 | SO3 | CaO | K2O | MgO | C | |
| 污泥 | 24.69 | 8.26 | 5.96 | 3.68 | 3.18 | 1.92 | 1.74 | 1.55 | 21.24 |
| 阴燃灰 | 54.73 | 17.56 | 9.44 | 5.85 | 1.94 | 3.46 | 3.15 | 1.68 | 0.60 |
| 焚烧灰 | 51.37 | 18.18 | 9.60 | 7.21 | 0.33 | 4.15 | 2.98 | 2.25 | 0 |
| 热解焦 | 49.83 | 18.86 | 8.75 | 6.59 | 1.18 | 4.05 | 3.17 | 2.12 | 13.74 |
| 样品 | Y/ (g/g) | P/ (mg P/g) | R/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 阴燃灰 | 0.58 | 41.22 | 92.50 |
| 焚烧灰 | 0.54 | 41.93 | 87.02 |
| 热解焦 | 0.66 | 38.20 | 96.89 |
表3 阴燃灰(SA)、焚烧灰(IA)和热解焦(PC)的灰(焦)产率、磷含量和磷留存率
Table 3 Ash/char yield, P content and P retention rate of smouldered ash (SA), incinerated ash (IA) and pyrolysis char (PC)
| 样品 | Y/ (g/g) | P/ (mg P/g) | R/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 阴燃灰 | 0.58 | 41.22 | 92.50 |
| 焚烧灰 | 0.54 | 41.93 | 87.02 |
| 热解焦 | 0.66 | 38.20 | 96.89 |
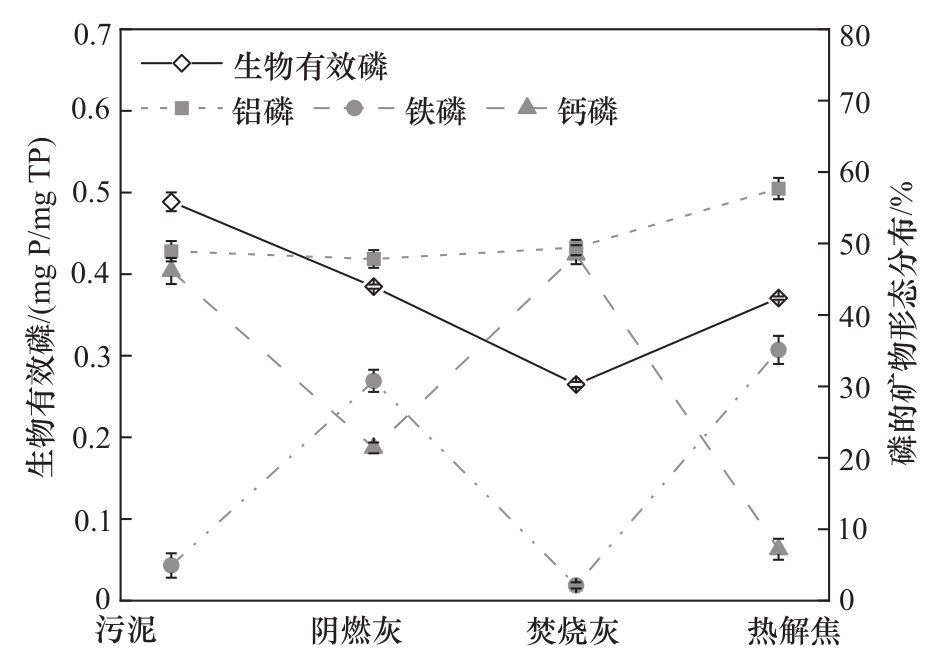
图5 污泥(SS)、阴燃灰(SA)、焚烧灰(IA)和热解焦(PC)的磷矿物形态分布及生物有效性
Fig.5 P mineral species distribution and Bio-P in sewage sludge (SS), smouldered ash (SA), incinerated ash (IA) and pyrolysis char (PC)
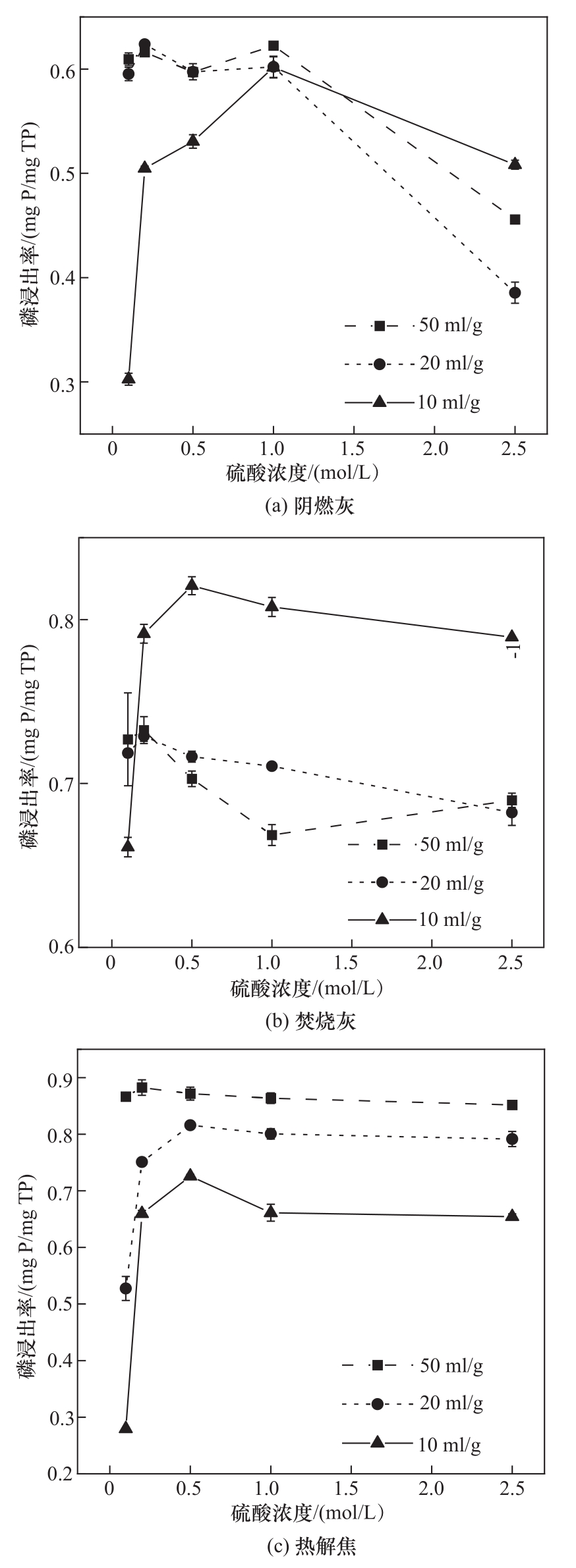
图6 硫酸浓度及液固比对阴燃灰(SA)、焚烧灰(IA)和热解焦(PC)中磷浸出率的影响
Fig.6 Phosphorus leaching proportion of smouldered ash (SA), incineration ash (IA) and pyrolysis char (PC) under different H2SO4 concentrations and liquid/solid ratios
| 动力学模型 | 阴燃灰 | 焚烧灰 | 热解焦 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | K/s-1 | R2 | K/s-1 | R2 | K/s-1 | ||
| Ⅰ | 0.9587 | 0.0086 | 0.9100 | 0.0296 | 0.9120 | 0.0077 | |
| Ⅱ | 0.9706 | 0.0030 | 0.9195 | 0.0125 | 0.9177 | 0.0036 | |
| Ⅲ | 0.9812 | 0.0033 | 0.9415 | 0.0192 | 0.9393 | 0.0073 | |
| Ⅳ | 0.9893 | 0.0095 | 0.9655 | 0.0875 | 0.9616 | 0.0474 | |
表4 模型的拟合系数(R2 )和速率常数(K)
Table 4 R2and K of the kinetic models
| 动力学模型 | 阴燃灰 | 焚烧灰 | 热解焦 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | K/s-1 | R2 | K/s-1 | R2 | K/s-1 | ||
| Ⅰ | 0.9587 | 0.0086 | 0.9100 | 0.0296 | 0.9120 | 0.0077 | |
| Ⅱ | 0.9706 | 0.0030 | 0.9195 | 0.0125 | 0.9177 | 0.0036 | |
| Ⅲ | 0.9812 | 0.0033 | 0.9415 | 0.0192 | 0.9393 | 0.0073 | |
| Ⅳ | 0.9893 | 0.0095 | 0.9655 | 0.0875 | 0.9616 | 0.0474 | |
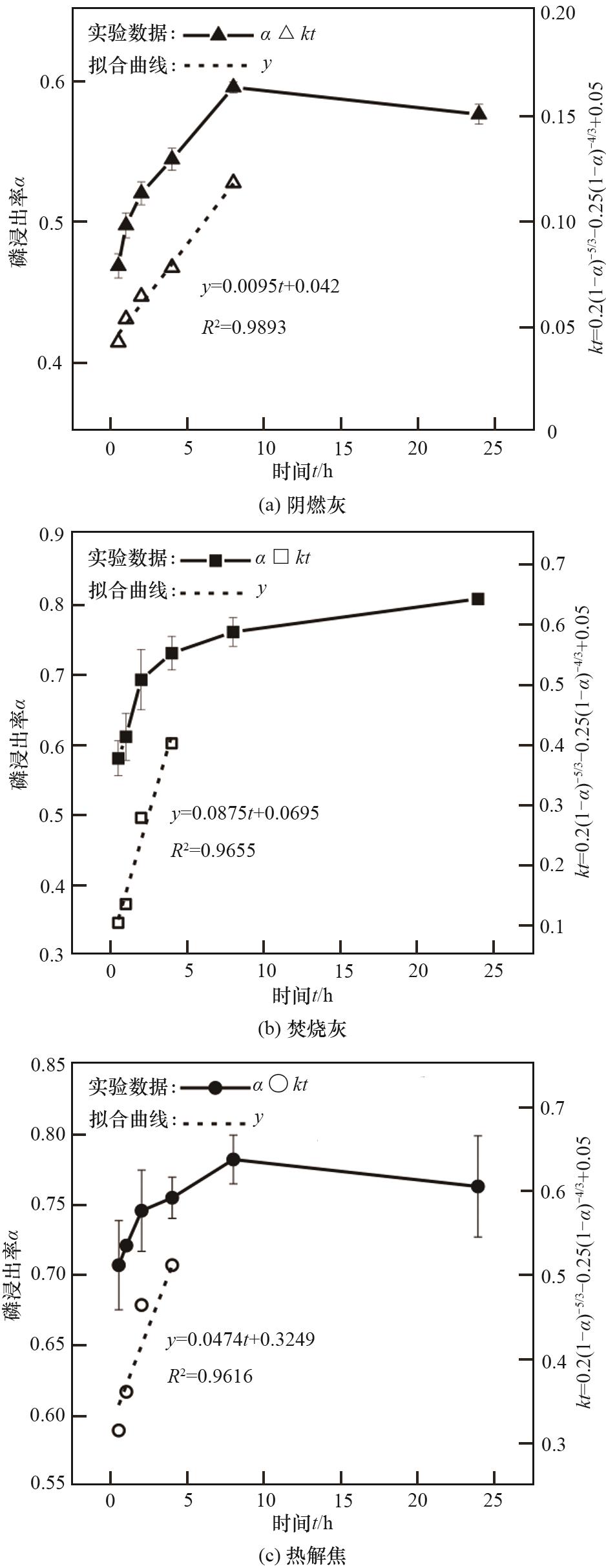
图7 阴燃灰(SA)、焚烧灰(IA)和热解焦(PC)的磷浸出动力学模拟
Fig.7 Kinetic simulation of phosphorus leaching from smouldered ash (SA), incineration ash (IA) and pyrolysis char (PC)
| 样品 | 最高磷浸出工况 | 优选工况 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 磷回收率①/%(质量) | 磷浸出量/(mg P/g) | 硫酸单位消耗量/mmol | 磷回收率①/%(质量) | 磷浸出量/(mg P/g) | 硫酸单位消耗量/mmol | ||
| 阴燃灰 | 59.30 | 25.72 | 0.16 | 56.58 | 24.54 | 0.082 | |
| 焚烧灰 | 70.10 | 34.42 | 0.15 | 67.59 | 33.19 | 0.060 | |
| 热解焦 | 84.21 | 33.71 | 0.30 | 62.96 | 25.20 | 0.079 | |
表5 阴燃灰(SA)、焚烧灰(IA)和热解焦(PC)的磷回收性能和提取剂消耗
Table 5 P recovery capability and leaching agent consumption of smouldered ash (SA), incinerated ash (IA) and pyrolysis char (PC)
| 样品 | 最高磷浸出工况 | 优选工况 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 磷回收率①/%(质量) | 磷浸出量/(mg P/g) | 硫酸单位消耗量/mmol | 磷回收率①/%(质量) | 磷浸出量/(mg P/g) | 硫酸单位消耗量/mmol | ||
| 阴燃灰 | 59.30 | 25.72 | 0.16 | 56.58 | 24.54 | 0.082 | |
| 焚烧灰 | 70.10 | 34.42 | 0.15 | 67.59 | 33.19 | 0.060 | |
| 热解焦 | 84.21 | 33.71 | 0.30 | 62.96 | 25.20 | 0.079 | |
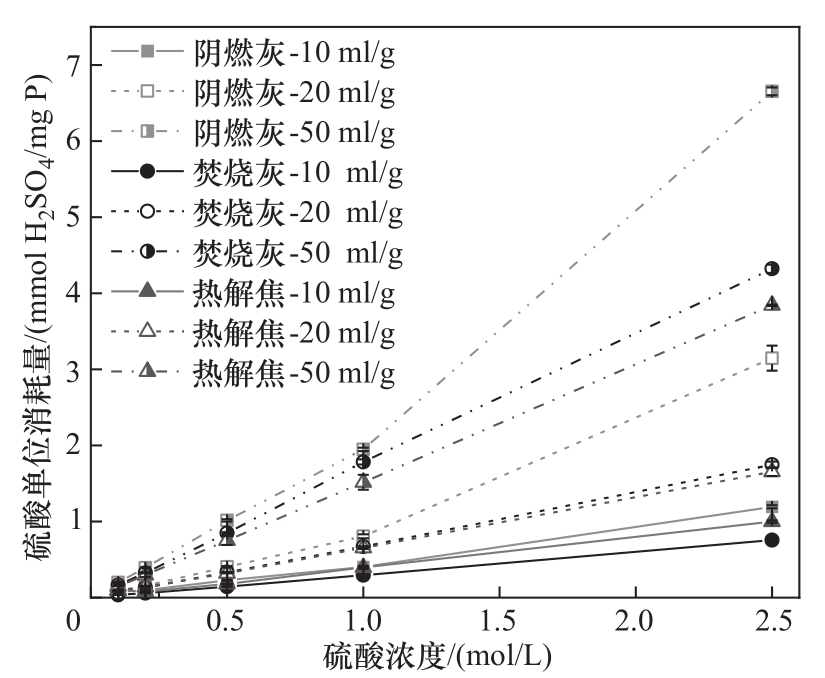
图8 各浸出工况下阴燃灰(SA)、焚烧灰(IA)和热解焦(PC)的硫酸单位消耗量
Fig.8 H2SO4 unit consumption of smouldered ash (SA), incineration ash (IA) and pyrolysis char (PC) under leaching conditions
| 1 | Fang L, Wang Q M, Li J S, et al. Feasibility of wet-extraction of phosphorus from incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA) for phosphate fertilizer production: a critical review[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 51(9): 939-971. |
| 2 | 旦增, 王旭彤, 颜蓓蓓, 等. 西藏生活垃圾掺烧市政污泥的焚烧特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(8): 3151-3159. |
| Dan Z, Wang X T, Yan B B, et al. Study on incineration characteristics of Tibetan municipal solid wastes mixed with sewage sludge[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(8): 3151-3159. | |
| 3 | Syed-Hassan S S A, Wang Y, Hu S, et al. Thermochemical processing of sewage sludge to energy and fuel: fundamentals, challenges and considerations[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 80: 888-913. |
| 4 | Schnell M, Horst T, Quicker P. Thermal treatment of sewage sludge in Germany: a review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2020, 263: 110367. |
| 5 | Wyn H K, Konarova M, Beltramini J, et al. Self-sustaining smouldering combustion of waste: a review on applications, key parameters and potential resource recovery[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2020, 205: 106425. |
| 6 | Rashwan T L, Gerhard J I, Grant G P. Application of self-sustaining smouldering combustion for the destruction of wastewater biosolids[J]. Waste Management, 2016, 50: 201-212. |
| 7 | Fabris I, Cormier D, Gerhard J I, et al. Continuous, self-sustaining smouldering destruction of simulated faeces[J]. Fuel, 2017, 190: 58-66. |
| 8 | Meng X D, Huang Q X, Gao H P, et al. Improved utilization of phosphorous from sewage sludge (as fertilizer) after treatment by low-temperature combustion[J]. Waste Management, 2018, 80: 349-358. |
| 9 | Fang L, Li J S, Guo M Z, et al. Phosphorus recovery and leaching of trace elements from incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA)[J]. Chemosphere, 2018, 193: 278-287. |
| 10 | Kleemann R, Chenoweth J, Clift R, et al. Comparison of phosphorus recovery from incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA) and pyrolysed sewage sludge char (PSSC)[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 60: 201-210. |
| 11 | Donatello S, Cheeseman C R. Recycling and recovery routes for incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA): a review[J]. Waste Management, 2013, 33(11): 2328-2340. |
| 12 | Adam C, Peplinski B, Michaelis M, et al. Thermochemical treatment of sewage sludge ashes for phosphorus recovery[J]. Waste Management, 2009, 29(3): 1122-1128. |
| 43 | Fu X, Liu M, Chen Y. Research progresses on recovery of phosphorus from sewage sludge ash by wet chemical method[J]. Environmental Protection of Chemical Industry, 2017, 37(3): 276-281. |
| 44 | Zhang P Z, Zhang X X, Li Y F, et al. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on chemical speciation, leaching ability, and environmental risk of heavy metals in biochar derived from cow manure[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 302: 122850. |
| 45 | Baba A A, Adekola F A. A study of dissolution kinetics of a Nigerian galena ore in hydrochloric acid[J]. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society, 2012, 16(4): 377-386. |
| 46 | Dickinson C F, Heal G R. Solid-liquid diffusion controlled rate equations[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 1999, 340/341: 89-103. |
| 47 | Ottosen L M, Kirkelund G M, Jensen P E. Extracting phosphorous from incinerated sewage sludge ash rich in iron or aluminum[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 91(7): 963-969. |
| 48 | 李伟新. 浸提时间对城市污泥重金属浸出特性的影响[J]. 水科学与工程技术, 2012(2): 43-45. |
| Li W X. Experimental study on the effects of extraction time on the leachability of heavy metals in sewage sludge[J]. Water Sciences and Engineering Technology, 2012(2): 43-45. | |
| 13 | 郝晓地, 于晶伦, 刘然彬, 等. 剩余污泥焚烧灰分磷回收及其技术进展[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(4): 1149-1159. |
| Hao X D, Yu J L, Liu R B, et al. Advances of phosphorus recovery from the incineration ashes of excess sludge and its associated technologies[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(4): 1149-1159. | |
| 14 | Zhu Y, Zhai Y B, Li S H, et al. Thermal treatment of sewage sludge: a comparative review of the conversion principle, recovery methods and bioavailability-predicting of phosphorus[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 291: 133053. |
| 15 | Fahimi A, Federici S, Depero L E, et al. Evaluation of the sustainability of technologies to recover phosphorus from sewage sludge ash based on embodied energy and CO2 footprint[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2021, 289: 125762. |
| 16 | Liang S, Chen H M, Zeng X H, et al. A comparison between sulfuric acid and oxalic acid leaching with subsequent purification and precipitation for phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge incineration ash[J]. Water Research, 2019, 159: 242-251. |
| 17 | Zhang F S, Yamasaki S I, Nanzyo M. Application of waste ashes to agricultural land—effect of incineration temperature on chemical characteristics[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2001, 264(3): 205-214. |
| 18 | Reuna S, Väisänen A. To incinerate or not?—Effects of incineration on the concentrations of heavy metals and leaching efficiency of post-precipitated sewage sludge (RAVITATM)[J]. Waste Management, 2020, 118: 241-246. |
| 19 | 何天澄, 朱学良, 范浩然, 等. 城市固废自维持阴燃处理的调控因素实验研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2020, 41(9): 2333-2344. |
| He T C, Zhu X L, Fan H R, et al. Self-sustaining smoldering treatment of municipal solid wastes: controlling parameters[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2020, 41(9): 2333-2344. | |
| 20 | 邓文义, 严建华, 李晓东, 等. 流化床内干化污泥燃烧污染物排放特性研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2008, 42(10): 1805-1811. |
| Deng W Y, Yan J H, Li X D, et al. Emission characteristics of pollutants during fluidized-bed incineration of pre-dried sewage sludge[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2008, 42(10): 1805-1811. | |
| 21 | 廖艳芬, 漆雅庆, 马晓茜.城市污水污泥焚烧处理环境影响分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2009, 29(11): 2359-2365. |
| Liao Y F, Qi Y Q, Ma X Q. Environmental impact assessment of sewage sludge incineration treatments[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2009, 29(11): 2359-2365. | |
| 22 | Shao J G, Lee D H, Yan R, et al. Agglomeration characteristics of sludge combustion in a bench-scale fluidized bed combustor[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2007, 21(5): 2608-2614. |
| 23 | Wang L, Skjevrak G, Hustad J E, et al. Sintering characteristics of sewage sludge ashes at elevated temperatures[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2012, 96: 88-97. |
| 24 | 金正宇, 张国臣, 王凯军. 热解技术资源化处理城市污泥的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2012, 31(1): 1-9. |
| Jin Z Y, Zhang G C, Wang K J. Research advance in resource recovery treatment of sewage sludge by pyrolysis[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2012, 31(1): 1-9. | |
| 25 | Shiba N C, Ntuli F. Extraction and precipitation of phosphorus from sewage sludge[J]. Waste Management, 2017, 60: 191-200. |
| 26 | 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. 4版. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社,2008. |
| China Environmental Protection Administration. Monitoring and Determination Methods for Water and Wastewater[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2008. | |
| 27 | Yang F, Chen J Y, Yang M, et al. Phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge via incineration with chlorine-based additives[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 95: 644-651. |
| 28 | de Figueiredo C C, de Souza Prado Junqueira Reis A, de Araujo A S, et al. Assessing the potential of sewage sludge-derived biochar as a novel phosphorus fertilizer: influence of extractant solutions and pyrolysis temperatures[J]. Waste Management, 2021, 124: 144-153. |
| 29 | Falayi T. Alkaline recovery of phosphorous from sewage sludge and stabilisation of sewage sludge residue[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 84: 166-172. |
| 30 | Lim B H, Kim D J. Selective acidic elution of Ca from sewage sludge ash for phosphorus recovery under pH control[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2017, 46: 62-67. |
| 31 | 许劲, 朱杰东, 李卷利, 等. 湿化学法回收污泥水热炭中磷的潜能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5779-5789. |
| Xu J, Zhu J D, Li J L, et al. Potential of phosphorus recovery from sludge-based hydrochar by wet chemical method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(11): 5779-5789. | |
| 32 | Feng C, Huang J C, Yang C H, et al. Smouldering combustion of sewage sludge: volumetric scale-up, product characterization, and economic analysis[J]. Fuel, 2021, 305: 121485. |
| 33 | Yermán L, Cormier D, Fabris I, et al. Potential bio-oil production from smouldering combustion of faeces[J]. Waste and Biomass Valorization, 2017, 8(2): 329-338. |
| 34 | Feng C, Cheng M K, Gao X P, et al. Occurrence forms and leachability of inorganic species in ash residues from self-sustaining smouldering combustion of sewage sludge[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2021, 38(3): 4327-4334. |
| 35 | Atienza-Martínez M, Gea G, Arauzo J, et al. Phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge char ash[J]. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2014, 65(2): 42-50. |
| 36 | Wu H, Castro M, Jensen P A, et al. Release and transformation of inorganic elements in combustion of a high-phosphorus fuel[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2011, 25(7): 2874-2886. |
| 37 | 沈雪莲, 周振, 任伟超, 等. 城镇污水处理厂污泥中磷的形态分布及生物可利用性分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2016, 10(3): 1200-1204. |
| Shen X L, Zhou Z, Ren W C, et al. Fractionation and bioavailability of phosphorus in sludge from municipal wastewater treatment plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2016, 10(3): 1200-1204. | |
| 38 | 王超, 刘清伟, 职音, 等. 中国市政污泥中磷的含量与形态分布[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(4): 1922-1930. |
| Wang C, Liu Q W, Zhi Y, et al. Contents and forms of phosphorous in the municipal sewage sludge of China[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(4): 1922-1930. | |
| 39 | Sevim F, Saraç H, Kocakerim M M, et al. Dissolution kinetics of phosphate ore in H2SO4 solutions[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2003, 42(10): 2052-2057. |
| 40 | Lee M S, Kim D J. Identification of phosphorus forms in sewage sludge ash during acid pre-treatment for phosphorus recovery by chemical fractionation and spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2017, 51: 64-70. |
| 41 | 王贤华, 鞠付栋, 陈汉平, 等. 污泥热解过程中焦的表面孔隙结构分形生长[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2010, 38(3): 374-379. |
| Wang X H, Ju F D, Chen H P, et al. Fractal growth of char surface pore structure during sewage sluge pyrolysis[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2010, 38(3): 374-379. | |
| 42 | Robinson J S, Baumann K, Hu Y F, et al. Phosphorus transformations in plant-based and bio-waste materials induced by pyrolysis[J]. Ambio, 2018, 47(): 73-82. |
| 43 | 付雄, 刘敏, 陈滢. 污泥灰中磷的湿化学法回收技术研究进展[J]. 化工环保, 2017, 37(3): 276-281. |
| [1] | 毕丽森, 刘斌, 胡恒祥, 曾涛, 李卓睿, 宋健飞, 吴翰铭. 粗糙界面上纳米液滴蒸发模式的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 172-178. |
| [2] | 于宏鑫, 邵双全. 水结晶过程的分子动力学模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 250-258. |
| [3] | 金正浩, 封立杰, 李舒宏. 氨水溶液交叉型再吸收式热泵的能量及 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. 分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 53-63. |
| [4] | 程成, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 胡海涛, 薛鸿祥. 表面微结构对析晶沉积特性影响的格子Boltzmann模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 74-86. |
| [5] | 肖明堃, 杨光, 黄永华, 吴静怡. 浸没孔液氧气泡动力学数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 87-95. |
| [6] | 郑佳丽, 李志会, 赵新强, 王延吉. 离子液体催化合成2-氰基呋喃反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3708-3715. |
| [7] | 范孝雄, 郝丽芳, 范垂钢, 李松庚. LaMnO3/生物炭催化剂低温NH3-SCR催化脱硝性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3821-3830. |
| [8] | 韩晨, 司徒友珉, 朱斌, 许建良, 郭晓镭, 刘海峰. 协同处理废液的多喷嘴粉煤气化炉内反应流动研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3266-3278. |
| [9] | 杨越, 张丹, 郑巨淦, 涂茂萍, 杨庆忠. NaCl水溶液喷射闪蒸-掺混蒸发的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3279-3291. |
| [10] | 张曼铮, 肖猛, 闫沛伟, 苗政, 徐进良, 纪献兵. 危废焚烧处理耦合有机朗肯循环系统工质筛选与热力学优化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3502-3512. |
| [11] | 汪林正, 陆俞冰, 张睿智, 罗永浩. 基于分子动力学模拟的VOCs热氧化特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3242-3255. |
| [12] | 曾如宾, 沈中杰, 梁钦锋, 许建良, 代正华, 刘海峰. 基于分子动力学模拟的Fe2O3纳米颗粒烧结机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3353-3365. |
| [13] | 李锦潼, 邱顺, 孙文寿. 煤浆法烟气脱硫中草酸和紫外线强化煤砷浸出过程[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3522-3532. |
| [14] | 张蒙蒙, 颜冬, 沈永峰, 李文翠. 电解液类型对双离子电池阴阳离子储存行为的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3116-3126. |
| [15] | 何宣志, 何永清, 闻桂叶, 焦凤. 磁液液滴颈部自相似破裂行为[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2889-2897. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号