化工学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 73 ›› Issue (12): 5660-5671.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20221141
崔雯琦1,2( ), 杨曙光1,3, 李红周1, 罗富彬1(
), 杨曙光1,3, 李红周1, 罗富彬1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-15
修回日期:2022-10-23
出版日期:2022-12-05
发布日期:2023-01-17
通讯作者:
罗富彬
作者简介:崔雯琦(1999—),女,硕士研究生, 1992926413@qq.com
基金资助:
Wenqi CUI1,2( ), Shuguang YANG1,3, Hongzhou LI1, Fubin LUO1(
), Shuguang YANG1,3, Hongzhou LI1, Fubin LUO1( )
)
Received:2022-08-15
Revised:2022-10-23
Online:2022-12-05
Published:2023-01-17
Contact:
Fubin LUO
摘要:
利用聚乙二醇为相变组分,以氮化硼为导热填料,通过两步法络合聚丙烯酸制备了具有相变稳定性的高导热相变复合材料。系统研究了片状氮化硼以及片状/球形混杂填充对复合材料导热以及相变性能的影响,探讨了相变复合材料的定形机理。结果表明,由于紧密的堆砌结构,片状氮化硼能够有效提升复合材料导热性能。填充60%(质量)的片状氮化硼时,热导率最高达到6.437 W/(m·K)。在混杂填充时,球形氮化硼与片状氮化硼的质量比为1∶3以及1∶6时,可以更加有效提升复合材料的导热性能。热储存实验显示,所制备的复合材料具有良好的热存储能力。此外,由于聚丙烯酸与聚乙二醇形成氢键的络合以及氮化硼的片状物理阻隔作用,复合材料在高温加热条件下具有优异的相变稳定性。
中图分类号:
崔雯琦, 杨曙光, 李红周, 罗富彬. 聚乙二醇高导热定形相变复合材料的制备及其性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(12): 5660-5671.
Wenqi CUI, Shuguang YANG, Hongzhou LI, Fubin LUO. Preparation of highly thermally conductive and shape-stabilized polyethylene glycol-based phase change material[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(12): 5660-5671.
| Sample | PEG质量/g | PAA质量/g | PEG与PAA的质量比 | f-BN质量/g | s-BN质量/g | f-BN与s-BN的质量比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN3/s-BN1) | 30.0 | 10.0 | 3∶1 | 45.0 | 15.0 | 3∶1 |
| PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN6/s-BN1) | 34.3 | 5.7 | 6∶1 | 51.4 | 8.6 | 6∶1 |
| PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN9/s-BN1) | 36.0 | 4.0 | 9∶1 | 54.0 | 6.0 | 9∶1 |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN12/s-BN1) | 36.9 | 3.1 | 12∶1 | 55.4 | 4.6 | 12∶1 |
| PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 30.0 | 10.0 | 3∶1 | 60.0 | 0 | |
| PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 34.3 | 5.7 | 6∶1 | 60.0 | 0 | |
| PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 36.0 | 4.0 | 9∶1 | 60.0 | 0 | |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 36.9 | 3.1 | 12∶1 | 60.0 | 0 | |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-40) | 55.4 | 4.6 | 12∶1 | 40.0 | 0 | |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-20) | 73.8 | 6.2 | 12∶1 | 20.0 | 0 |
表1 所制备复合材料的PEG、PAA以及BN质量比例
Table 1 The mass ratio of PEG, PAA and BN in the composites
| Sample | PEG质量/g | PAA质量/g | PEG与PAA的质量比 | f-BN质量/g | s-BN质量/g | f-BN与s-BN的质量比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN3/s-BN1) | 30.0 | 10.0 | 3∶1 | 45.0 | 15.0 | 3∶1 |
| PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN6/s-BN1) | 34.3 | 5.7 | 6∶1 | 51.4 | 8.6 | 6∶1 |
| PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN9/s-BN1) | 36.0 | 4.0 | 9∶1 | 54.0 | 6.0 | 9∶1 |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN12/s-BN1) | 36.9 | 3.1 | 12∶1 | 55.4 | 4.6 | 12∶1 |
| PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 30.0 | 10.0 | 3∶1 | 60.0 | 0 | |
| PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 34.3 | 5.7 | 6∶1 | 60.0 | 0 | |
| PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 36.0 | 4.0 | 9∶1 | 60.0 | 0 | |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 36.9 | 3.1 | 12∶1 | 60.0 | 0 | |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-40) | 55.4 | 4.6 | 12∶1 | 40.0 | 0 | |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-20) | 73.8 | 6.2 | 12∶1 | 20.0 | 0 |

图2 60%(质量)片状氮化硼填充(a)、片状/球形氮化硼混杂填充(b)和不同含量片状氮化硼填充(c)的相变复合材料热导率
Fig.2 Thermal conductivity of the PCM composites filled with 60%(mass) flake-like boron nitride (a), flake-like/spherical boron nitride hybrids (b) and different content of flake-like boron nitride (c), respectively

图3 片状/球形氮化硼混杂填充相变复合材料扫描电镜图:(a)s-BN∶f-BN=1∶3, (b) s-BN∶f-BN=1∶6, (c) s-BN∶f-BN=1∶9, (d) s-BN∶f-BN=1∶12;复合材料内部结构示意图:(e) s-BN∶f-BN=1∶6, (f) s-BN∶f-BN=1/12
Fig.3 SEM images of PCM composites filled with flake-like/spherical boron nitride hybrids: (a) s-BN∶f-BN=1∶3, (b) s-BN∶f-BN=1∶6, (c) s-BN∶f-BN=1∶9, (d) s-BN∶f-BN=1∶12;Schematic diagram of thermally conductive paths: (e) s-BN∶f-BN=1∶6, (e) s-BN∶f-BN=1∶12
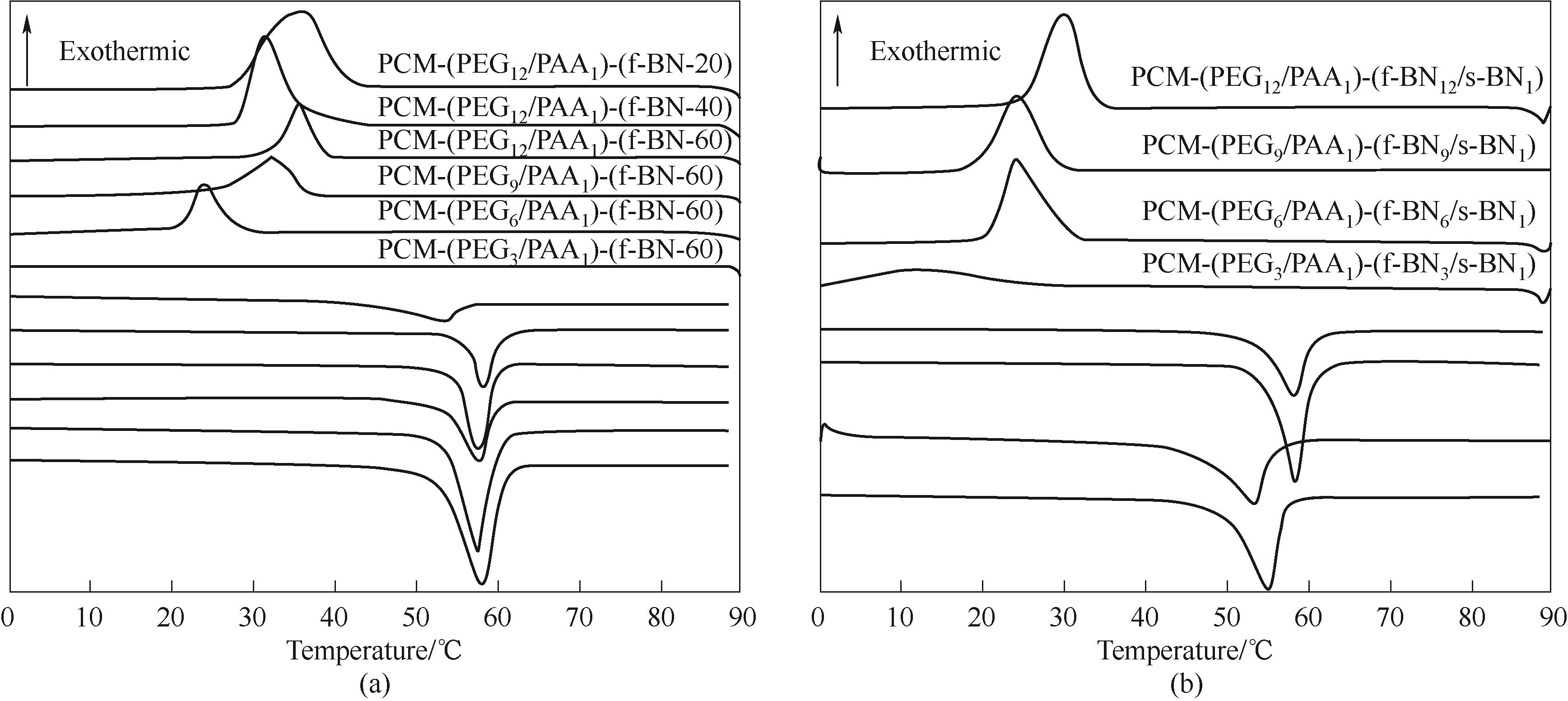
图4 片状氮化硼(a)和片状/球形氮化硼混杂(b)填充相变复合材料的DSC曲线
Fig.4 DSC curves of the PCM composites filled with flake-like boron nitride (a) and flake-like/spherical boron nitride hybrids (b)
| Sample | Tm /℃ | ΔHm /(J/g) | Theoretical Δ Hm /(J/g) | Tc/℃ | ΔHc/(J/g) | Theoretical Δ Hc/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEG | 58.93 | 141.2 | 39.48 | 139.5 | ||
| PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 53.63 | 33.91 | 42.36 | — | — | 41.85 |
| PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 58.42 | 40.18 | 48.41 | 24.28 | 37.44 | 47.83 |
| PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 57.69 | 50.70 | 50.83 | 32.55 | 49.88 | 50.22 |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 57.93 | 51.07 | 52.14 | 35.84 | 47.65 | 51.51 |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-40) | 56.70 | 90.94 | 78.22 | 30.93 | 87.45 | 77.28 |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-20) | 58.08 | 119.1 | 104.21 | 36.19 | 119.0 | 102.95 |
表2 片状氮化硼填充相变复合材料相变焓以及相转变温度
Table 2 Phase transformation enthalpy and phase transition temperature of the prepared PCM composites filled with flake-like boron nitride
| Sample | Tm /℃ | ΔHm /(J/g) | Theoretical Δ Hm /(J/g) | Tc/℃ | ΔHc/(J/g) | Theoretical Δ Hc/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEG | 58.93 | 141.2 | 39.48 | 139.5 | ||
| PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 53.63 | 33.91 | 42.36 | — | — | 41.85 |
| PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 58.42 | 40.18 | 48.41 | 24.28 | 37.44 | 47.83 |
| PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 57.69 | 50.70 | 50.83 | 32.55 | 49.88 | 50.22 |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) | 57.93 | 51.07 | 52.14 | 35.84 | 47.65 | 51.51 |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-40) | 56.70 | 90.94 | 78.22 | 30.93 | 87.45 | 77.28 |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-20) | 58.08 | 119.1 | 104.21 | 36.19 | 119.0 | 102.95 |
| Sample | Tm /℃ | Δ Hm/(J/g) | Theoretical Δ Hm /(J/g) | Tc/℃ | Δ Hc /(J/g) | Theoretical Δ Hc/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN3/s-BN1) | 58.51 | 28.69 | 42.36 | — | — | 41.85 |
| PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN6/s-BN1) | 58.83 | 37.43 | 48.41 | 24.56 | 35.89 | 47.83 |
| PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN9/s-BN1) | 53.83 | 32.72 | 50.83 | 24.57 | 32.97 | 50.22 |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN12/s-BN1) | 55.34 | 40.17 | 52.14 | 30.28 | 39.48 | 51.51 |
表3 片状/球形氮化硼(60%)混杂填充PEG/PAA复合材料相变焓以及相转变温度
Table 3 Phase transformation enthalpy and phase transition temperature of the prepared PCM composites filled with flake-like/spherical boron nitride hybrids (60%)
| Sample | Tm /℃ | Δ Hm/(J/g) | Theoretical Δ Hm /(J/g) | Tc/℃ | Δ Hc /(J/g) | Theoretical Δ Hc/(J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN3/s-BN1) | 58.51 | 28.69 | 42.36 | — | — | 41.85 |
| PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN6/s-BN1) | 58.83 | 37.43 | 48.41 | 24.56 | 35.89 | 47.83 |
| PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN9/s-BN1) | 53.83 | 32.72 | 50.83 | 24.57 | 32.97 | 50.22 |
| PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN12/s-BN1) | 55.34 | 40.17 | 52.14 | 30.28 | 39.48 | 51.51 |
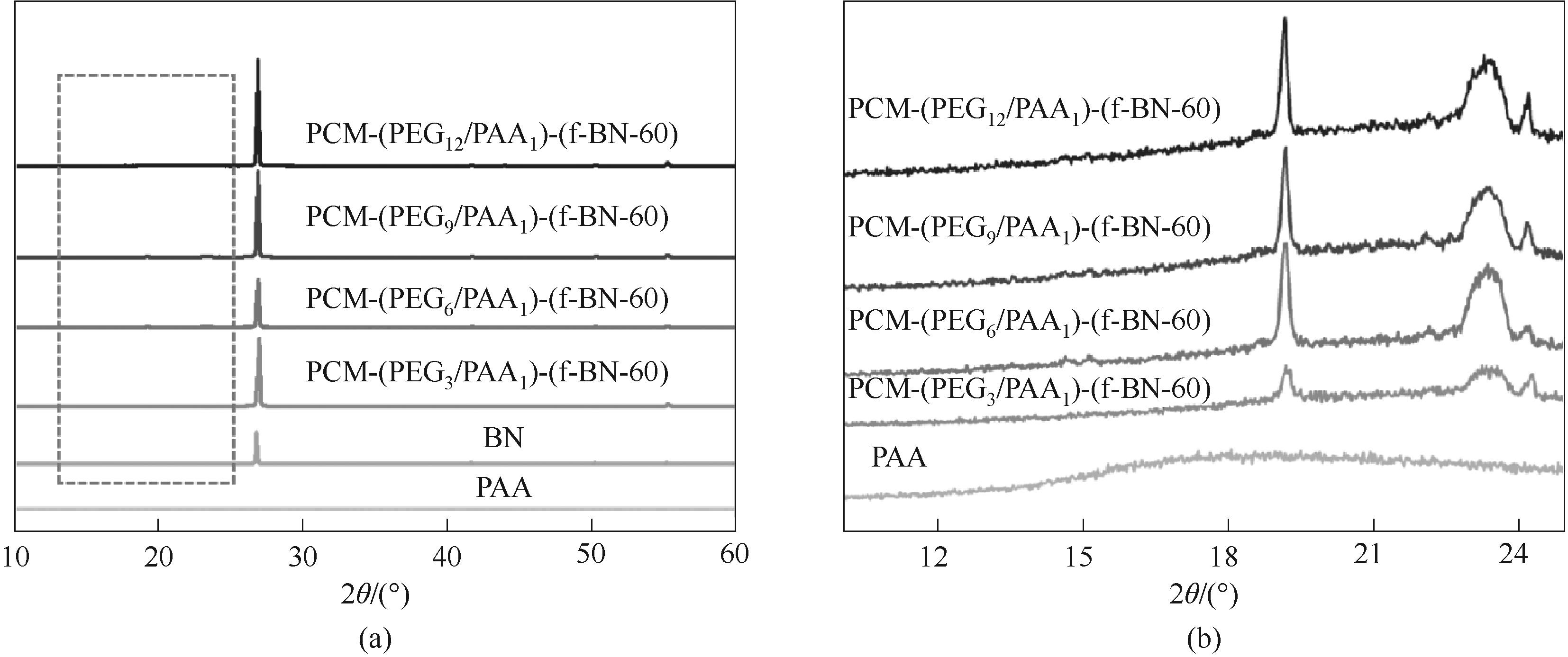
图5 片状氮化硼填充相变复合材料的XRD谱图[(b)为(a)中框线标记部分放大图]
Fig.5 XRD patterns of the PCM composites filled with flake-like boron nitride [(b) is the enlarged view of the zone marked by dotted lines in (a)]

图6 相变复合材料在加热条件下的形状稳定性观察图:(a)样品在长时间加热(100℃)条件下的变化图;(b)样品在80℃下冷热循环的变化图[样品(1)、(2)、(3)和(4)为f-BN含量为60%,PAA与PEG的比值分别为1∶3、1∶6、1∶9、1∶12的复合材料样品,对应PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)、PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)、PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)、PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60),样品(5)为仅添加60%(质量) f-BN的PEG/f-BN复合材料]
Fig.6 The shape stability performance of the prepared PCM composites: (a) digital pictures of the specimens upon heating (100℃); (b) digital pictures of the specimens upon heating and cooling cycles at 80℃ [the specimen codes (1), (2), (3) and (4) represent the PCM composite containing a PAA /PEG ratio of 1∶3, 1∶6, 1∶9, 1∶12, respectively, corresponding to PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60), PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN-60), PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN-60), PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60), the specimen code (5) refers to the PEG/f-BN PCM composite]
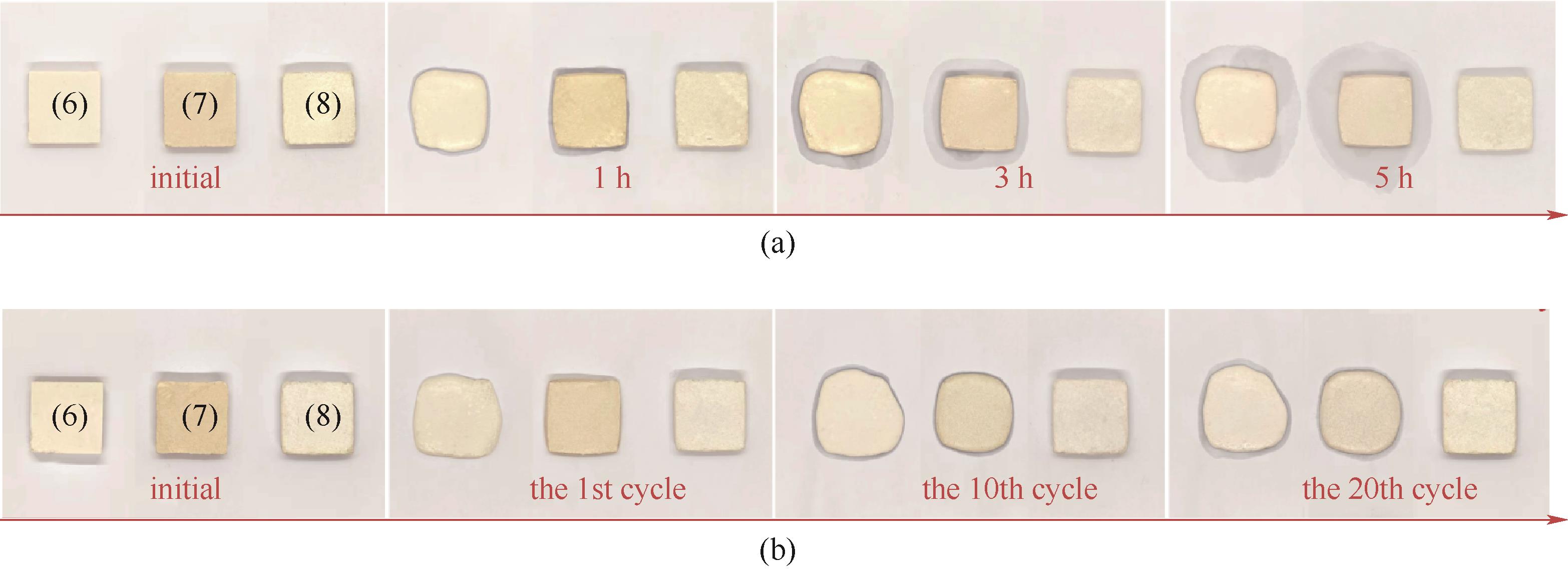
图7 相变复合材料在加热条件下的形状稳定性观察图: (a)样品在长时间加热(100℃)条件下的变化图;(b)样品在80℃下冷热循环的变化图[样品(6)、(7)和(8)为PAA与PEG的比值为1∶12,f-BN的质量分数分别为20%、40%和60%的复合材料样品,分别对应样品PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-20)、PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-40)和PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)]
Fig.7 The shape stability performance of the prepared PCM composites: (a) digital pictures of the specimens upon heating (100℃); (b) digital pictures of the specimens upon heating and cooling cycles at 80℃ [the specimen codes (6), (7) and (8) represent the PCM composite filled with 20%(mass), 40%(mass) and 60%(mass) f-BN respectively, corresponding to PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-20),PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-40) and PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)]

图8 相变复合材料的红外图(a);相变复合材料的扫描电镜图(b),其中(1)、(2)、(3)和(4)分别对应样品PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)、PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)、PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)、PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60);相变复合材料定形机理图(c)
Fig.8 FTIR of the PCM composites (a), SEM of the PCM composites (b), where (1), (2), (3) and (4) corresponding to PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60), PCM-(PEG6/PAA1)-(f-BN-60), PCM-(PEG9/PAA1)-(f-BN-60), PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60), respectively; shape stabilized mechanism diagram of the PCM composite (c)
| 编号 | 填充组分 | 填料比例 | 定形以及制备方式 | 热导率/(W/(m·K)) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 膨胀石墨/改性云母 | 3.22%(质量)/32.25%(质量) | 多孔石墨定形,真空浸渍法 | 0.56 | [ |
| 2 | 银纳米线/膨胀蛭石 | 19.3%(质量)/21.9%(质量) | 膨胀蛭石定形,物理共混和浸渍法 | 0.68 | [ |
| 3 | 氮化硼/石墨烯 | 23%(质量)/少量 | 冰模板自组装氮化硼/石墨烯多孔类气凝胶定形,真空浸渍法 | 2.36 | [ |
| 4 | 硅藻土/碳纳米管 | 36.8%(质量)/3.2%(质量) | 硅藻土孔结构定形,浸渍法 | 1.52 | [ |
| 5 | 改性二氧化硅/氧化碳纳米管 | 39.4%(质量)/0.6%(质量) | 改性二氧化硅定形,溶胶-凝胶法 | 0.41 | [ |
| 6 | 氮化硼/纳米纤维素/壳聚糖 | 47.4%(质量)/15.8%(质量)/2.4%(质量) | 纳米纤维素/壳聚糖界面相互作用定形,界面聚电解质络合纺丝法 | 4.005 | [ |
| 7 | 二氧化硅/石墨 | 10%(质量)/6%(质量) | 二氧化硅网状分子结构定形,溶胶-凝胶法和浸渍法 | 1.867 | [ |
| 8 | 聚丙烯酰胺 | 40%(质量) | 聚丙烯酰胺三维网络结构定形,化学交联法 | 0.375 | [ |
| 9 | 氮化硼/聚丙烯酸 | 60%(质量)/3.1%(质量) | 片状氮化硼阻隔及聚丙烯酸氢键络合,熔融共混浇筑法 | 6.437 | 本文 |
表4 文献报道聚乙二醇基导热相变复合材料对比
Table 4 Comparison of polyethylene glycol-based thermally conductive phase change composites reported in literature
| 编号 | 填充组分 | 填料比例 | 定形以及制备方式 | 热导率/(W/(m·K)) | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 膨胀石墨/改性云母 | 3.22%(质量)/32.25%(质量) | 多孔石墨定形,真空浸渍法 | 0.56 | [ |
| 2 | 银纳米线/膨胀蛭石 | 19.3%(质量)/21.9%(质量) | 膨胀蛭石定形,物理共混和浸渍法 | 0.68 | [ |
| 3 | 氮化硼/石墨烯 | 23%(质量)/少量 | 冰模板自组装氮化硼/石墨烯多孔类气凝胶定形,真空浸渍法 | 2.36 | [ |
| 4 | 硅藻土/碳纳米管 | 36.8%(质量)/3.2%(质量) | 硅藻土孔结构定形,浸渍法 | 1.52 | [ |
| 5 | 改性二氧化硅/氧化碳纳米管 | 39.4%(质量)/0.6%(质量) | 改性二氧化硅定形,溶胶-凝胶法 | 0.41 | [ |
| 6 | 氮化硼/纳米纤维素/壳聚糖 | 47.4%(质量)/15.8%(质量)/2.4%(质量) | 纳米纤维素/壳聚糖界面相互作用定形,界面聚电解质络合纺丝法 | 4.005 | [ |
| 7 | 二氧化硅/石墨 | 10%(质量)/6%(质量) | 二氧化硅网状分子结构定形,溶胶-凝胶法和浸渍法 | 1.867 | [ |
| 8 | 聚丙烯酰胺 | 40%(质量) | 聚丙烯酰胺三维网络结构定形,化学交联法 | 0.375 | [ |
| 9 | 氮化硼/聚丙烯酸 | 60%(质量)/3.1%(质量) | 片状氮化硼阻隔及聚丙烯酸氢键络合,熔融共混浇筑法 | 6.437 | 本文 |
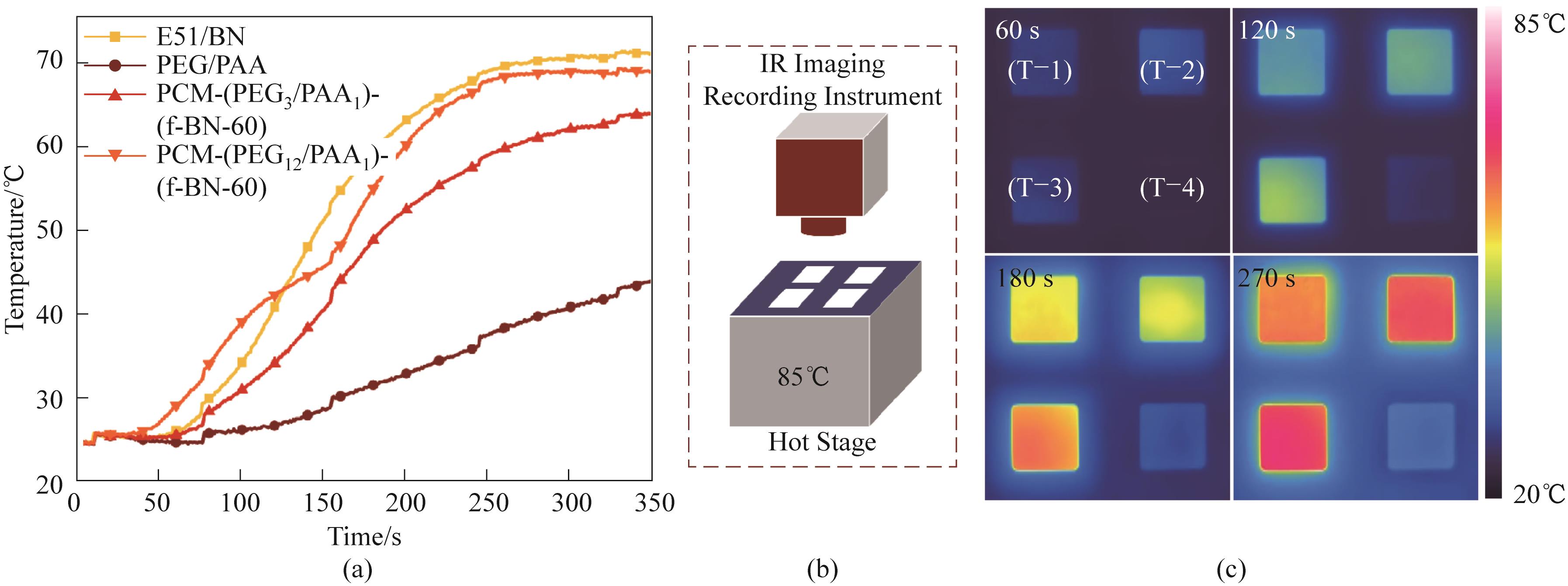
图9 样品E51/BN、PEG/PAA、PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)和PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)加热条件下表面温度变化曲线(a);加热台储能示意图(b);样品在加热时的红外热成像图(c),(T-1),(T-2),(T-3),(T-4)分别对应样品PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)、PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60)、E51/BN,PEG/PAA
Fig.9 Surface temperature variation curves of E51/BN, PEG/PAA, PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60), PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60) samples recorded by an infrared imaging devices upon heating (a); the diagram of the testing experiment (b); infrared thermal imaging of four samples upon heating (c); where (T-1), (T-2), (T-3), (T-4) are corresponding to PEG/PAA, PCM-(PEG3/PAA1)-(f-BN-60), PCM-(PEG12/PAA1)-(f-BN-60), E51/BN, PEG/PAA, respectively
| 1 | Wang R Z, Chen L F, Lei Q, et al. Preparation and characterization of polyethylene glycol/polyurea composites for shape stabilized phase change materials[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science, 2021, 62(3): 664-676. |
| 2 | Wang T J, Wang C M, Chen K, et al. Preparation, thermal, and mechanical properties of polyethylene glycol/expoxy resin composites as form-stable phase change materials[J]. Polymer Engineering and Science, 2021, 62(2): 520-529. |
| 3 | 李泽坤, 薛锋. 聚乙二醇/聚氯乙烯/废旧PCB非金属粉复合定形相变材料的制备与研究[J]. 塑料工业, 2021, 49(7): 37-41. |
| Li Z K, Xue F. Preparation and research of PEG/PVC/N-PCB composite shape-stabilized phase change materials[J]. China Plastics Industry, 2021, 49(7): 37-41. | |
| 4 | Wie J, Kim J. Thermal properties of surface-modified and cross-linked boron nitride/polyethylene glycol composite as phase change material[J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(3): 456. |
| 5 | Shi J B, Li M. Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene glycol/modified attapulgite form-stable composite phase change material for thermal energy storage[J]. Solar Energy, 2020, 205: 62-73. |
| 6 | 颜品萍, 罗富彬, 黄宝铨, 等. 导热增强聚乙二醇相变复合材料的制备及其性能[J]. 应用化学, 2020, 37(1): 46-53. |
| Yan P P, Luo F B, Huang B Q, et al. Properties of thermal conductivity enhanced polyethylene glycol-based phase change composites[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry, 2020, 37(1): 46-53. | |
| 7 | 蔡迪, 李静, 焦乃勋. 纳米石墨烯片-正十八烷复合相变材料制备及热物性研究[J]. 物理学报, 2019, 68(10): 100502. |
| Cai D, Li J, Jiao N X. Preparation and thermophysical properties of graphene nanoplatelets-octadecane phase change composite materials[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68(10): 100502. | |
| 8 | 孟新, 张焕芝, 赵梓名, 等. 三元脂肪酸/膨胀石墨复合相变材料的制备、包覆定形及热性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(3): 526-530. |
| Meng X, Zhang H Z, Zhao Z M, et al. Preparation, encapsulation and thermal properties of fatty acid/expanded graphite composites as shape-stabilized phase change materials[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(3): 526-530. | |
| 9 | 南光花, 王建平, 王艳, 等. 包含聚苯胺的相变材料纳胶囊的制备及其性能[J]. 物理化学学报, 2014, 30(2): 338-344. |
| Nan G H, Wang J P, Wang Y, et al. Preparation and properties of nanoencapsulated phase change materials containing polyaniline[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2014, 30(2): 338-344. | |
| 10 | 周建伟, 余冬梅, 赵蕴慧, 等. 有机烷烃相变材料及其微胶囊化[J]. 化学进展, 2011, 23(4): 695-703. |
| Zhou J W, Yu D M, Zhao Y H, et al. Organic alkane phase change materials and their microencapsulation[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2011, 23(4): 695-703. | |
| 11 | Li C C, Xie B S, Chen D L, et al. Ultrathin graphite sheets stabilized stearic acid as a composite phase change material for thermal energy storage[J]. Energy, 2019, 166: 246-255. |
| 12 | Feng D L, Zang Y Y, L i P, et al. Polyethylene glycol phase change material embedded in a hierarchical porous carbon with superior thermal storage capacity and excellent stability[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2021, 210(2): 108832. |
| 13 | Samani F, Bahramian A R, Sharif A. Shape-stable phenolic/polyethylene glycol phase change material: kinetics study and improvements in thermal properties of nanocomposites[J].Iranian Polymer Journal, 2018, 27(7): 495-505. |
| 14 | Chen K, Wang C M, Wang T J, et al. Preparation and performances of form-stable polyethylene glycol/methylcellulose composite phase change materials[J].Journal of Polymer Research, 2020, 27(8): 1-8. |
| 15 | Fan L W, Fang X, Wang X, et al. Effects of various carbon nanofillers on the thermal conductivity and energy storage properties of paraffin-based nanocomposite phase change materials[J]. Applied Energy, 2013, 110: 163-172. |
| 16 | Jiang L, Lei Y, Liu Q F, et al. Polyethylene glycol based self-luminous phase change materials for both thermal and light energy storage[J]. Energy, 2020, 193: 116802. |
| 17 | Li B M, Shu D, Wang R F, et al. Polyethylene glycol/silica (PEG@SiO2) composite inspired by the synthesis of mesoporous materials as shape-stabilized phase change material for energy storage[J]. Renewable Energy, 2020, 145: 84-92. |
| 18 | Yang J, Zhang E W, Li X F, et al. Cellulose/graphene aerogel supported phase change composites with high thermal conductivity and good shape stability for thermal energy storage[J]. Carbon, 2016, 98: 50-57. |
| 19 | Yang J, Tang L S, Bao R Y, et al. Hybrid network structure of boron nitride and graphene oxide in shape-stabilized composite phase change materials with enhanced thermal conductivity and light-to-electric energy conversion capability[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2018, 174: 56-64. |
| 20 | 倪凯, 潘虹, 沈勇, 等. 基分级多孔碳复合相变材料的制备与性能研究[J]. 功能材料, 2022, 53(1): 1175-1180. |
| Ni K, Pan H, Shen Y, et al. Preparation and properties of lignin based graded porous carbon composite phase change materials[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2022, 53(1): 1175-1180. | |
| 21 | Wang J F, Xie H Q, Xin Z, et al. Enhancing thermal conductivity of palmitic acid based phase change materials with carbon nanotubes as fillers[J]. Solar Energy, 2010, 84(2): 339-344. |
| 22 | Tu J Y, Li H R, Zhang J J, et al. Latent heat and thermal conductivity enhancements in polyethylene glycol/polyethylene glycol-grafted graphene oxide composites[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2019, 2(3): 471-480. |
| 23 | Wu S Y, Zhu D S, Zhang X R, et al. Preparation and melting/freezing characteristics of Cu/paraffin nanofluid as phase-change material (PCM)[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2010, 24(3): 1894-1898. |
| 24 | Gu X B, Peng L H, Liu P, et al. Enhanced thermal properties and lab-scale thermal performance of polyethylene glycol/modified halloysite nanotube form-stable phase change material cement panel[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 323(6): 126550. |
| 25 | Deng Y, Li J H, Qian T T, et al. Thermal conductivity enhancement of polyethylene glycol/expanded vermiculite shape-stabilized composite phase change materials with silver nanowire for thermal energy storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 295: 427-435. |
| 26 | 吴韶飞, 闫霆, 蒯子函, 等. 高导热膨胀石墨/棕榈酸定形复合相变材料的制备及储热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(9): 3553-3564. |
| Wu S F, Yan T, Kuai Z H, et al. Preparation and thermal energy storage properties of high heat conduction expanded graphite/palmitic acid form-stable phase change materials[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(9): 3553-3564. | |
| 27 | Tang B T, Cui J S, Wang Y M, et al. Facile synthesis and performances of PEG/SiO2 composite form-stable phase change materials[J]. Solar Energy, 2013, 97: 484-492. |
| 28 | 张正国, 邵刚, 方晓明. 石蜡/膨胀石墨复合相变储热材料的研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2005, 26(5): 698-702. |
| Zhang Z G, Shao G, Fang X M. Study on paraffin/expanded graphite composite phase change thermal energy storage material[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2005, 26(5): 698-702. | |
| 29 | Yang J, Yu P, Tang L S, et al. Hierarchically interconnected porous scaffolds for phase change materials with improved thermal conductivity and efficient solar-to-electric energy conversion[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(45): 17704-17709. |
| 30 | Li J F, Wang Z L, Wen L G, et al. Highly elastic fibers made from hydrogen-bonded polymer complex[J]. ACS Macro Letters, 2016, 5(7): 814-818. |
| 31 | 李博鑫, 杨隽阁, 尹德忠, 等. 单分散聚合物微球稳定Pickering乳液法制备大粒径微胶囊相变材料[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(9): 2085-2089. |
| Li B X, Yang J G, Yin D Z, et al. Preparation of large-sized microencapsulated phase change materials through Pickering emulsion stabilized by monodisperse polymer microspheres[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2085-2089. | |
| 32 | Zhang P X, Wang X W, Wang D, et al. Preparation and properties of photo-cured electrolyte based on poly(ethylene glycol) grafted acrylic resin[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2021, 52(1): 94-101. |
| 33 | 吴文昊, 黄心宇, 姚锐敏, 等. 煤基碳泡沫/聚氨酯相变复合材料的制备及储热性能[J]. 物理化学学报, 2017, 33(1): 255-261. |
| Wu W H, Huang X Y, Yao R M, et al. Synthesis and properties of polyurethane/coal-derived carbon foam phase change composites for thermal energy storage[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2017, 33(1): 255-261. | |
| 34 | Zhang D Y, Li C C, Lin N Z, et al. Enhanced properties of mica-based composite phase change materials for thermal energy storage[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2021, 42: 103106. |
| 35 | Qian T T, Zhu S K, Wang H L, et al. Comparative study of carbon nanoparticles and single-walled carbon nanotube for light-heat conversion and thermal conductivity enhancement of the multifunctional PEG/diatomite composite phase change material[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(33): 29698-29707. |
| 36 | 鄢冬茂, 蔡文蓉, 殷国强, 等. PEG/APS-SiO2/O-CNTs导热增强相变材料的制备及性能[J]. 精细化工, 2021, 38(4): 729-735. |
| Yan D M, Cai W R, Yin G Q, et al. Preparation and properties of PEG/APS-SiO2/O-CNTs phase change materials with enhanced thermal conductivity[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2021, 38(4): 729-735. | |
| 37 | Fang H, Lin J L, Zhang L J, et al. Fibrous form-stable phase change materials with high thermal conductivity fabricated by interfacial polyelectrolyte complex spinning[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2020, 249: 116836. |
| 38 | 仝仓, 李祥立, 端木琳. 聚乙二醇/二氧化硅/膨胀石墨相变储能材料的制备与性能研究[J]. 区域供热, 2018(3): 100-104. |
| Tong C, Li X L, Duanmu L. Preparation and properties of polyethylene glycol/silica/expanded graphite phase change energy storage materials[J]. District Heating, 2018(3): 100-104. | |
| 39 | 付维贵, 索海涛, 林贵德, 等. PEG/PAM复合定形相变材料的制备与热性能[J]. 天津工业大学学报, 2018, 37(2): 55-61. |
| Fu W G, Suo H T, Lin G D, et al. Synthesis and thermal performance of PEG/PAM shape-stabilized composite phase change materials[J]. Journal of Tianjin Polytechnic University, 2018, 37(2): 55-61. |
| [1] | 张双星, 刘舫辰, 张义飞, 杜文静. R-134a脉动热管相变蓄放热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 165-171. |
| [2] | 江河, 袁俊飞, 王林, 邢谷雨. 均流腔结构对微细通道内相变流动特性影响的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 235-244. |
| [3] | 吴延鹏, 刘乾隆, 田东民, 陈凤君. 相变材料与热管耦合的电子器件热管理研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 25-31. |
| [4] | 宋嘉豪, 王文. 斯特林发动机与高温热管耦合运行特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 287-294. |
| [5] | 刘远超, 关斌, 钟建斌, 徐一帆, 蒋旭浩, 李耑. 单层XSe2(X=Zr/Hf)的热电输运特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3968-3978. |
| [6] | 胡兴枝, 张皓焱, 庄境坤, 范雨晴, 张开银, 向军. 嵌有超小CeO2纳米粒子的碳纳米纤维的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [7] | 张贲, 王松柏, 魏子亚, 郝婷婷, 马学虎, 温荣福. 超亲水多孔金属结构驱动的毛细液膜冷凝及传热强化[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2824-2835. |
| [8] | 张澳, 罗英武. 低模量、高弹性、高剥离强度丙烯酸酯压敏胶[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3079-3092. |
| [9] | 王杰, 丘晓琳, 赵烨, 刘鑫洋, 韩忠强, 许雍, 蒋文瀚. 聚电解质静电沉积改性PHBV抗氧化膜的制备与性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [10] | 刘杰, 吴立盛, 李锦锦, 罗正鸿, 周寅宁. 含乙烯基胺酯键聚醚类可逆交联聚合物的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3051-3057. |
| [11] | 史昊鹏, 钟达文, 廉学新, 张君峰. 朝下多尺度沟槽翅片结构表面沸腾换热实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2880-2888. |
| [12] | 史方哲, 甘云华. 超薄热管启动特性和传热性能数值模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2814-2823. |
| [13] | 邢美波, 张中天, 景栋梁, 张洪发. 磁调控水基碳纳米管协同多孔材料强化相变储/释能特性[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3093-3102. |
| [14] | 蔡斌, 张效林, 罗倩, 党江涛, 左栗源, 刘欣梅. 导电薄膜材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2308-2321. |
| [15] | 龙臻, 王谨航, 任俊杰, 何勇, 周雪冰, 梁德青. 离子液体协同PVCap抑制天然气水合物生成实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2639-2646. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号