化工学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 74 ›› Issue (7): 3068-3078.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20230383
王杰1,2( ), 丘晓琳1,2(
), 丘晓琳1,2( ), 赵烨1,2, 刘鑫洋1,2, 韩忠强3, 许雍3, 蒋文瀚3
), 赵烨1,2, 刘鑫洋1,2, 韩忠强3, 许雍3, 蒋文瀚3
收稿日期:2023-04-18
修回日期:2023-06-25
出版日期:2023-07-05
发布日期:2023-08-31
通讯作者:
丘晓琳
作者简介:王杰(1995—),男,硕士研究生,wangjie9535@163.com
基金资助:
Jie WANG1,2( ), Xiaolin QIU1,2(
), Xiaolin QIU1,2( ), Ye ZHAO1,2, Xinyang LIU1,2, Zhongqiang HAN3, Yong XU3, Wenhan JIANG3
), Ye ZHAO1,2, Xinyang LIU1,2, Zhongqiang HAN3, Yong XU3, Wenhan JIANG3
Received:2023-04-18
Revised:2023-06-25
Online:2023-07-05
Published:2023-08-31
Contact:
Xiaolin QIU
摘要:
食品中的过渡金属离子能够催化氧化脂质导致食品质量下降,因此开展抗氧化包装研究具有重要意义。本研究以覆盖聚丙烯酸(PAA)接枝层的聚(3-羟基丁酸酯-co-3-羟基戊酸酯)(PHBV)薄膜为基材,壳聚糖(CS)和海藻酸钠(SA)为聚电解质,通过层层自组装法制得具备金属螯合能力的PHBV-g-PAA/(CS/SA) n 非释放型抗氧化包装膜,研究聚电解质溶液浓度和pH对活性膜化学性质、微观形貌、活性基团含量以及Cu(Ⅱ)离子螯合能力的影响。结果表明:通过傅里叶变换红外光谱仪与酸性橙7染色法对活性膜进行表征,证明CS和SA聚电解质已成功交替组装到PHBV-g-PAA薄膜表面;通过SEM观察活性膜形貌结构发现,随着聚电解质溶液浓度和pH增大,组装层厚度不断增加,当CS和SA聚电解质溶液浓度为1.0 mg/ml、pH分别为5.0和7.0时,聚电解质组装层较为均匀平整;此时,活性膜表面氨基密度为136.38 nmol/cm2,Cu(Ⅱ) 离子螯合量为124.93 nmol/cm2。该活性膜具备一定的抗氧化能力且高于PHBV及PHBV-g-PAA薄膜,在食品包装领域具有广阔的应用前景。
中图分类号:
王杰, 丘晓琳, 赵烨, 刘鑫洋, 韩忠强, 许雍, 蒋文瀚. 聚电解质静电沉积改性PHBV抗氧化膜的制备与性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078.
Jie WANG, Xiaolin QIU, Ye ZHAO, Xinyang LIU, Zhongqiang HAN, Yong XU, Wenhan JIANG. Preparation and properties of polyelectrolyte electrostatic deposition modified PHBV antioxidant films[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078.
| 样品编号 | CS浓度/(mg/ml) | 溶剂 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5-3.0 | 0.5 | 稀乙酸(pH=2.8) |
| 0.5-5.0 | 0.5 | 乙酸盐缓冲液(pH=4.8) |
| 1.0-3.0 | 1.0 | 稀乙酸(pH=2.8) |
| 1.0-5.0 | 1.0 | 乙酸盐缓冲液(pH=4.8) |
| 3.0-3.5 | 3.0 | 稀乙酸(pH=2.8) |
| 5.0-3.5 | 5.0 | 稀乙酸(pH=2.8) |
| 5.0-4.5 | 5.0 | 乙酸盐缓冲液(pH=3.8) |
| 5.0-5.5 | 5.0 | 乙酸盐缓冲液(pH=4.8) |
表1 CS聚电解质溶液制备的工艺参数
Table 1 Process parameters for preparation of CS polyelectrolyte solutions
| 样品编号 | CS浓度/(mg/ml) | 溶剂 |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5-3.0 | 0.5 | 稀乙酸(pH=2.8) |
| 0.5-5.0 | 0.5 | 乙酸盐缓冲液(pH=4.8) |
| 1.0-3.0 | 1.0 | 稀乙酸(pH=2.8) |
| 1.0-5.0 | 1.0 | 乙酸盐缓冲液(pH=4.8) |
| 3.0-3.5 | 3.0 | 稀乙酸(pH=2.8) |
| 5.0-3.5 | 5.0 | 稀乙酸(pH=2.8) |
| 5.0-4.5 | 5.0 | 乙酸盐缓冲液(pH=3.8) |
| 5.0-5.5 | 5.0 | 乙酸盐缓冲液(pH=4.8) |
| 样品编号 | CS溶液pH | SA溶液pH |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5-3.0 | 3.10 ± 0.03 | 7.03 ± 0.03 |
| 0.5-5.0 | 4.82 ± 0.02 | |
| 1.0-3.0 | 3.20± 0.02 | 6.90 ± 0.04 |
| 1.0-5.0 | 4.95 ± 0.02 | |
| 3.0-3.5 | 3.61 ± 0.03 | 6.49 ± 0.03 |
| 5.0-3.5 | 3.81 ± 0.01 | 6.33 ± 0.02 |
| 5.0-4.5 | 4.47 ± 0.02 | |
| 5.0-5.5 | 5.71 ± 0.03 |
表2 聚电解质溶液pH
Table 2 pH of polyelectrolyte solution
| 样品编号 | CS溶液pH | SA溶液pH |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5-3.0 | 3.10 ± 0.03 | 7.03 ± 0.03 |
| 0.5-5.0 | 4.82 ± 0.02 | |
| 1.0-3.0 | 3.20± 0.02 | 6.90 ± 0.04 |
| 1.0-5.0 | 4.95 ± 0.02 | |
| 3.0-3.5 | 3.61 ± 0.03 | 6.49 ± 0.03 |
| 5.0-3.5 | 3.81 ± 0.01 | 6.33 ± 0.02 |
| 5.0-4.5 | 4.47 ± 0.02 | |
| 5.0-5.5 | 5.71 ± 0.03 |
| 样品编号 | CS溶液透光率/% | SA溶液透光率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5-3.0 | 99.60 ± 0.20 | 99.50 ± 0.30 |
| 0.5-5.0 | 99.60 ± 0.10 | |
| 1.0-3.0 | 99.50 ± 0.05 | 99.50 ± 0.10 |
| 1.0-5.0 | 99.50 ± 0.10 | |
| 3.0-3.5 | 98.80 ± 0.10 | 98.40 ± 0.30 |
| 5.0-3.5 | 97.90 ± 0.10 | 97.30 ± 0.20 |
| 5.0-4.5 | 97.60 ± 0.50 | |
| 5.0-5.5 | 48.60 ± 0.50 |
表3 聚电解质溶液透光率
Table 3 Light transmission of polyelectrolyte solution
| 样品编号 | CS溶液透光率/% | SA溶液透光率/% |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5-3.0 | 99.60 ± 0.20 | 99.50 ± 0.30 |
| 0.5-5.0 | 99.60 ± 0.10 | |
| 1.0-3.0 | 99.50 ± 0.05 | 99.50 ± 0.10 |
| 1.0-5.0 | 99.50 ± 0.10 | |
| 3.0-3.5 | 98.80 ± 0.10 | 98.40 ± 0.30 |
| 5.0-3.5 | 97.90 ± 0.10 | 97.30 ± 0.20 |
| 5.0-4.5 | 97.60 ± 0.50 | |
| 5.0-5.5 | 48.60 ± 0.50 |
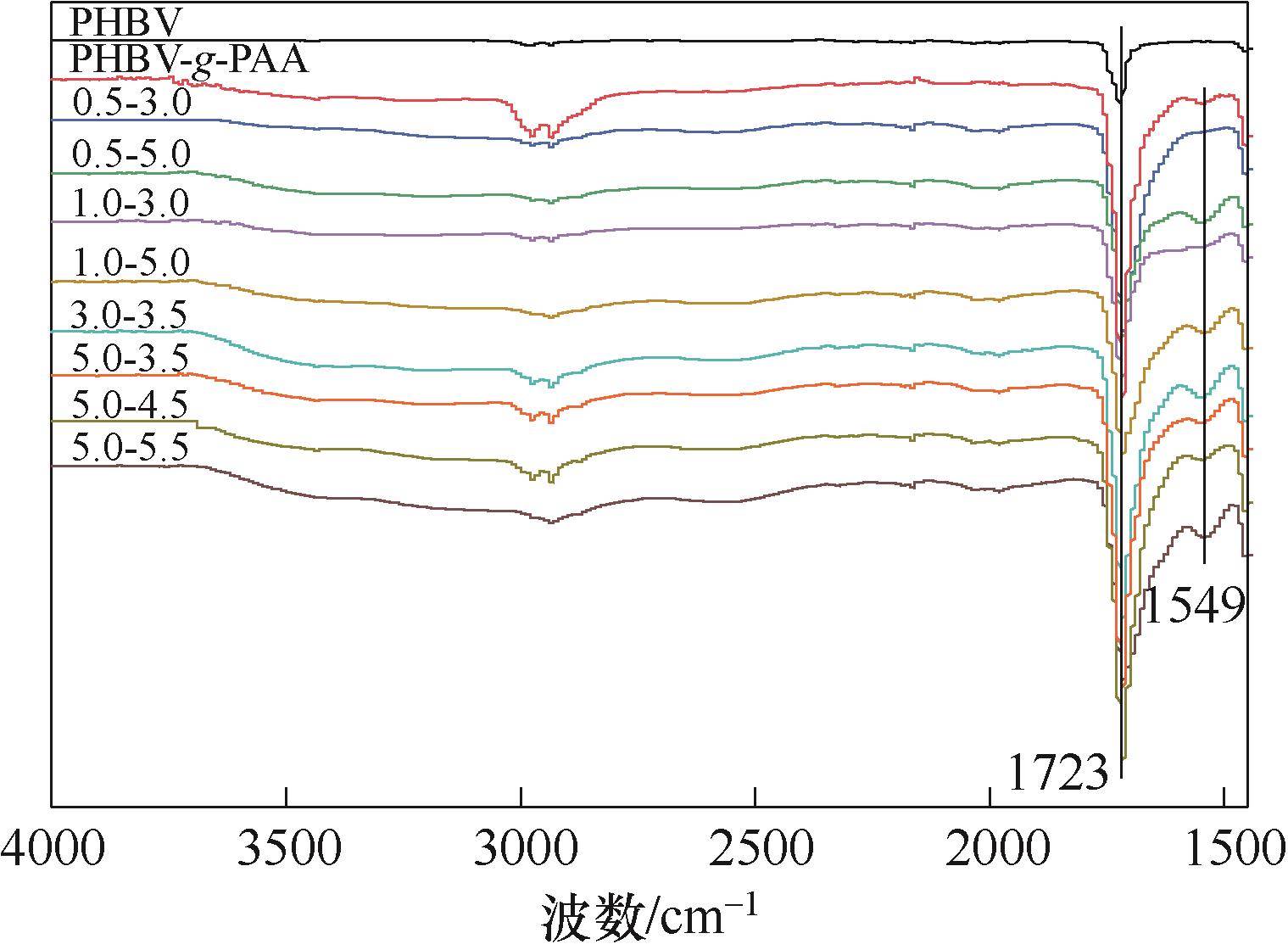
图4 不同聚电解质溶液参数制得的PHBV-g-PAA/(CS/SA)15.5活性膜的红外光谱图
Fig.4 FT-IR spectra of PHBV-g-PAA/(CS/SA)15.5 active membranes prepared with different polyelectrolyte solution parameters
| 样品编号 | 表面氨基密度/(nmol/cm2) | 标准差SD | 相对标准差RSD/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHBV-g-PAA | 8.58 | 0.79 | 9.26 |
| 0.5—3.0 | 54.75 | 3.13 | 5.73 |
| 0.5—5.0 | 81.78 | 9.46 | 11.57 |
| 1.0—3.0 | 120.57 | 14.72 | 12.21 |
| 1.0—5.0 | 136.38 | 10.85 | 7.95 |
| 3.0—3.5 | 141.41 | 15.65 | 11.07 |
| 5.0—3.5 | 253.48 | 37.88 | 14.94 |
| 5.0—4.5 | 267.84 | 46.17 | 17.24 |
| 5.0—5.5 | 405.09 | 84.54 | 20.87 |
表4 不同溶液参数制得活性膜的表面氨基含量
Table 4 Surface amino content of active membranes prepared with different solution parameters
| 样品编号 | 表面氨基密度/(nmol/cm2) | 标准差SD | 相对标准差RSD/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHBV-g-PAA | 8.58 | 0.79 | 9.26 |
| 0.5—3.0 | 54.75 | 3.13 | 5.73 |
| 0.5—5.0 | 81.78 | 9.46 | 11.57 |
| 1.0—3.0 | 120.57 | 14.72 | 12.21 |
| 1.0—5.0 | 136.38 | 10.85 | 7.95 |
| 3.0—3.5 | 141.41 | 15.65 | 11.07 |
| 5.0—3.5 | 253.48 | 37.88 | 14.94 |
| 5.0—4.5 | 267.84 | 46.17 | 17.24 |
| 5.0—5.5 | 405.09 | 84.54 | 20.87 |
| 样品编号 | Cu(Ⅱ)离子螯合量/(nmol/cm2) | 标准差SD |
|---|---|---|
| PHBV | 0 | — |
| PHBV-g-PAA | 112.64 | 6.55 |
| 0.5-3.0 | 114.56 | 4.80 |
| 0.5-5.0 | 118.90 | 6.18 |
| 1.0-3.0 | 116.64 | 5.21 |
| 1.0-5.0 | 124.93 | 4.80 |
| 3.0-3.5 | 129.97 | 9.63 |
| 5.0-3.5 | 155.95 | 11.95 |
| 5.0-4.5 | 170.14 | 18.73 |
| 5.0-5.5 | 202.40 | 23.51 |
表5 不同溶液参数制得活性膜的Cu(Ⅱ)离子螯合量
Table 5 Adsorption of Cu(Ⅱ) ions on active membranes prepared with different solution parameters
| 样品编号 | Cu(Ⅱ)离子螯合量/(nmol/cm2) | 标准差SD |
|---|---|---|
| PHBV | 0 | — |
| PHBV-g-PAA | 112.64 | 6.55 |
| 0.5-3.0 | 114.56 | 4.80 |
| 0.5-5.0 | 118.90 | 6.18 |
| 1.0-3.0 | 116.64 | 5.21 |
| 1.0-5.0 | 124.93 | 4.80 |
| 3.0-3.5 | 129.97 | 9.63 |
| 5.0-3.5 | 155.95 | 11.95 |
| 5.0-4.5 | 170.14 | 18.73 |
| 5.0-5.5 | 202.40 | 23.51 |
| 1 | Uluata S, McClements D J, Decker E A. How the multiple antioxidant properties of ascorbic acid affect lipid oxidation in oil-in-water emulsions[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2015, 63(6): 1819-1824. |
| 2 | Gómez-Estaca J, López-de-Dicastillo C, Hernández-Muñoz P, et al. Advances in antioxidant active food packaging[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2014, 35(1): 42-51. |
| 3 | Zhu P, Lin Z, Goddard J M. Performance of photo-curable metal-chelating active packaging coating in complex food matrices[J]. Food Chemistry, 2019, 286: 154-159. |
| 4 | Hong S, Kim M J, Park S, et al. Effects of hydrogen-donating or metal-chelating antioxidants on the oxidative stability of organogels made of beeswax and grapeseed oil exposed to light irradiation[J]. Journal of Food Science, 2018, 83(4): 885-891. |
| 5 | Mastromatteo M, Mastromatteo M, Conte A, et al. Advances in controlled release devices for food packaging applications[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2010, 21(12): 591-598. |
| 6 | Domínguez R, Barba F J, Gómez B, et al. Active packaging films with natural antioxidants to be used in meat industry: a review[J]. Food Research International, 2018, 113: 93-101. |
| 7 | Roman M J, Decker E A, Goddard J M. Retaining oxidative stability of emulsified foods by novel nonmigratory polyphenol coated active packaging[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2016, 64(27): 5574-5582. |
| 8 | Tian F, Decker E A, Goddard J M. Controlling lipid oxidation of food by active packaging technologies[J]. Food & Function, 2013, 4(5): 669-680. |
| 9 | Jokar M, Rahman R A, Abdullah L C. Physical and antimicrobial characterization of self assembled silver nanoparticle/chitosan onto low density polyethylene film as active packaging polymer[J]. Journal of Nano Research, 2014, 27: 53-64. |
| 10 | Arrua D, Strumia M C, Nazareno M A. Immobilization of caffeic acid on a polypropylene film: synthesis and antioxidant properties[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2010, 58(16): 9228-9234. |
| 11 | Yu Z, Lu L X, Lu L J, et al. Development and antioxidation of metal ion chelating packaging film[J]. Food Packaging and Shelf Life, 2022, 32: 100846. |
| 12 | 于振, 卢莉璟, 卢立新, 等. 聚丙烯酸表面接枝改性聚丙烯抗氧化膜的制备与性能[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2020, 36(7): 134-139, 148. |
| Yu Z, Lu L J, Lu L X, et al. Preparation and characterization of anti-oxidation packaging films based on poly (acrylic acid) grafting polypropylene surface[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering, 2020, 36(7): 134-139, 148. | |
| 13 | Tian F, Decker E A, Goddard J M. Development of an iron chelating polyethylene film for active packaging applications [J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2012, 60(8): 2046-2052. |
| 14 | Wang C Y, Liu Y, Chen W Q, et al. Critical review of global plastics stock and flow data[J]. Journal of Industrial Ecology, 2021, 25(5): 1300-1317. |
| 15 | Siracusa V, Rocculi P, Romani S, et al. Biodegradable polymers for food packaging: a review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2008, 19(12): 634-643. |
| 16 | Piontek W. The circular plastics economy and the instruments to implement it[J]. Economics and Environment, 2019, 70: 18-33. |
| 17 | Chen M, Li R, Runge T, et al. Degradable polymeric package from whole cell wall biomass[J]. Materials Today Sustainability, 2019, 3/4: 100008. |
| 18 | Guo C Y, Guo H G. Progress in the degradability of biodegradable film materials for packaging[J]. Membranes, 2022, 12(5): 500. |
| 19 | Chen J X, Wu D F, Tam K C, et al. Effect of surface modification of cellulose nanocrystal on nonisothermal crystallization of poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) composites[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2017, 157: 1821-1829. |
| 20 | López-Maldonado E A, Zavala García O G, Escobedo K C, et al. Evaluation of the chelating performance of biopolyelectrolyte green complexes (NIBPEGCs) for wastewater treatment from the metal finishing industry[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 335: 18-27. |
| 21 | Herskovitz J E, Goddard J M. Reactive extrusion of nonmigratory antioxidant poly(lactic acid) packaging[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2020, 68(7): 2164-2173. |
| 22 | Wang Y J, Ke Y, Ren L, et al. Photografting polymerization of polyacrylamide on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) films ( Ⅱ ) : Wettability and crystallization behaviors of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)-graft-polyacrylamide films[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2008, 107(6): 3765-3772. |
| 23 | Zhao X X, Liu H R, Hu Y B, et al. A novel gelatin-AgNPs coating preparing method for fabrication of antibacterial and no inflammation inducible coatings on PHBV[J]. Reactive and Functional Polymers, 2016, 107: 54-59. |
| 24 | Ali K A, Hassan M E, Elnashar M M M. Development of functionalized carrageenan, chitosan and alginate as polymeric chelating ligands for water softening[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2017, 14(9): 2009-2014. |
| 25 | Lee K Y, Mooney D J. Alginate: properties and biomedical applications[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2012, 37(1): 106-126. |
| 26 | Wang H X, Qian J, Ding F Y. Emerging chitosan-based films for food packaging applications[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2018, 66(2): 395-413. |
| 27 | Vartiainen J, Laine C, Willberg-Keyriläinen P, et al. Biobased mineral-oil barrier-coated food packaging films[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2017, 134(9): 44586. |
| 28 | Vartiainen J, Shen Y F, Kaljunen T, et al. Bio-based multilayer barrier films by extrusion, dispersion coating and atomic layer deposition[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2016, 133(2): 42260. |
| 29 | Li H, Peng L C. Antimicrobial and antioxidant surface modification of cellulose fibers using layer-by-layer deposition of chitosan and lignosulfonates [J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015, 124: 35-42. |
| 30 | Gu C H, Wang J J, Yu Y, et al. Biodegradable multilayer barrier films based on alginate/polyethyleneimine and biaxially oriented poly(lactic acid)[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2013, 92(2): 1579-1585. |
| 31 | Schoeler B, Kumaraswamy G, Caruso F. Investigation of the influence of polyelectrolyte charge density on the growth of multilayer thin films prepared by the layer-by-layer technique[J]. Macromolecules, 2002, 35(3): 889-897. |
| 32 | Caridade S G, Monge C, Gilde F, et al. Free-standing polyelectrolyte membranes made of chitosan and alginate[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2013, 14(5): 1653-1660. |
| 33 | Zhu Y X, Xuan H Y, Ren J Y, et al. Self-healing multilayer polyelectrolyte composite film with chitosan and poly(acrylic acid)[J]. Soft Matter, 2015, 11(43): 8452-8459. |
| 34 | 王杰, 丘晓琳, 赵烨, 等. 接枝聚丙烯酸改性聚(3-羟基丁酸 酯-co-3-羟基戊酸酯)抗氧化膜的制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(6): 1-10. |
| Wang J, Qiu X L, Zhao Y, et al. Preparation and properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) antioxidant film modified by graft polyacrylic acid[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(6): 1-10. | |
| 35 | Yuan W Y, Weng G M, Lipton J, et al. Weak polyelectrolyte-based multilayers via layer-by-layer assembly: approaches, properties, and applications[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 282: 102200. |
| 36 | Kiechel M A, Schauer C L. Non-covalent crosslinkers for electrospun chitosan fibers[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2013, 95(1): 123-133. |
| 37 | Ma Q Y, Du L, Yang Y, et al. Rheology of film-forming solutions and physical properties of Tara gum film reinforced with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2017, 63: 677-684. |
| 38 | Gao Q, Lei M, Zhou K M, et al. Preparation of a microfibrillated cellulose/chitosan/polypyrrole film for active food packaging [J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2020, 149: 105907. |
| 39 | Lin Z S, Goddard J. Photo-curable metal-chelating coatings offer a scalable approach to production of antioxidant active packaging[J]. Journal of Food Science, 2018, 83(2): 367-376. |
| 40 | Zheng X Y, Zheng H L, Xiong Z K, et al. Novel anionic polyacrylamide-modify-chitosan magnetic composite nanoparticles with excellent adsorption capacity for cationic dyes and pH-independent adsorption capability for metal ions [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 392: 123706. |
| [1] | 胡兴枝, 张皓焱, 庄境坤, 范雨晴, 张开银, 向军. 嵌有超小CeO2纳米粒子的碳纳米纤维的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [2] | 张澳, 罗英武. 低模量、高弹性、高剥离强度丙烯酸酯压敏胶[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3079-3092. |
| [3] | 刘杰, 吴立盛, 李锦锦, 罗正鸿, 周寅宁. 含乙烯基胺酯键聚醚类可逆交联聚合物的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3051-3057. |
| [4] | 蔡斌, 张效林, 罗倩, 党江涛, 左栗源, 刘欣梅. 导电薄膜材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2308-2321. |
| [5] | 龙臻, 王谨航, 任俊杰, 何勇, 周雪冰, 梁德青. 离子液体协同PVCap抑制天然气水合物生成实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2639-2646. |
| [6] | 崔张宁, 胡紫璇, 吴雷, 周军, 叶干, 刘田田, 张秋利, 宋永辉. 可降解纤维素基材料的耐水性能研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2296-2307. |
| [7] | 杨琴, 秦传鉴, 李明梓, 杨文晶, 赵卫杰, 刘虎. 用于柔性传感的双形状记忆MXene基水凝胶的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2699-2707. |
| [8] | 李振, 张博, 王丽伟. PEG-EG固-固相变材料的制备和性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2680-2688. |
| [9] | 代佳琳, 毕唯东, 雍玉梅, 陈文强, 莫晗旸, 孙兵, 杨超. 热物性对混合型CPCMs固液相变特性影响模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1914-1927. |
| [10] | 张建华, 陈萌萌, 孙雅雯, 彭永臻. 部分短程硝化同步除磷耦合Anammox实现生活污水高效脱氮除磷[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2147-2156. |
| [11] | 陈韶云, 徐东, 陈龙, 张禹, 张远方, 尤庆亮, 胡成龙, 陈建. 单层聚苯胺微球阵列结构的制备及其吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2228-2238. |
| [12] | 罗来明, 张劲, 郭志斌, 王海宁, 卢善富, 相艳. 1~5 kW高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池堆的理论模拟与组装测试[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1724-1734. |
| [13] | 龙臻, 王谨航, 何勇, 梁德青. 离子液体与动力学抑制剂作用下混合气体水合物生成特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1703-1711. |
| [14] | 吴学红, 栾林林, 陈亚南, 赵敏, 吕财, 刘勇. 可降解柔性相变薄膜的制备及其热性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1818-1826. |
| [15] | 吕阳光, 左培培, 杨正金, 徐铜文. 三嗪框架聚合物膜用于有机纳滤甲醇/正己烷分离[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1598-1606. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号