化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (3): 1040-1051.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231133
丁相斐1,2( ), 丘晓琳1,2(
), 丘晓琳1,2( ), 朱喜成1,2, 张佳伟1,2, 陈锦华1,2
), 朱喜成1,2, 张佳伟1,2, 陈锦华1,2
收稿日期:2023-11-06
修回日期:2024-01-26
出版日期:2024-03-25
发布日期:2024-05-11
通讯作者:
丘晓琳
作者简介:丁相斐(1999—),男,硕士研究生,dxfcom@163.com
基金资助:
Xiangfei DING1,2( ), Xiaolin QIU1,2(
), Xiaolin QIU1,2( ), Xicheng ZHU1,2, Jiawei ZHANG1,2, Jinhua CHEN1,2
), Xicheng ZHU1,2, Jiawei ZHANG1,2, Jinhua CHEN1,2
Received:2023-11-06
Revised:2024-01-26
Online:2024-03-25
Published:2024-05-11
Contact:
Xiaolin QIU
摘要:
具有可调控气体渗透的薄膜对包装保鲜领域发展具有重要意义,而设计具有pH响应性渗透和高力学性能的薄膜仍然是一个挑战。设计琥珀酸酐酯化与二乙烯三胺酰胺化的两步取代反应,实现纤维素纳米晶表面胺基(A-CNC)与羧基(S-CNC)功能化修饰,进一步与聚对苯二甲酸-己二酸丁二醇酯(PBAT)复合,制备具有互反pH响应性气体渗透的复合薄膜。结果表明,通过扫描电镜(SEM)、红外光谱(FTIR)和核磁共振13C谱(13C NMR)对纤维素纳米晶及其功能化修饰进行表征,证实改性成功。对复合薄膜性能表征:在力学性能方面,S-CNC/PBAT(3/97)与A-CNC/PBAT(5/95)复合薄膜拉伸强度达到最高,比PBAT分别增加40.44%与50.56%,但断裂伸长率下降,断裂模式由韧性向脆性断裂转变。在气体渗透性方面,复合薄膜展现出互反pH响应渗透特征。S-CNC/PBAT(5/95)复合薄膜渗透性出现正响应变化趋势,随着缓冲液pH(3~12)升高,CO2与O2渗透性分别增加67.98%和48.34%,水蒸气渗透性从2.467×10-13变化到3.039×10-13 g·cm/(cm2·s·Pa);而A-CNC/PBAT(5/95)复合薄膜渗透出现pH负响应性现象,CO2与O2渗透性分别降低63.00%与54.61%,水蒸气渗透性从2.747×10-13变化到2.043×10-13 g·cm/(cm2·s·Pa)。这种具有pH响应性渗透的复合薄膜在智能包装领域具有广阔的前景。
中图分类号:
丁相斐, 丘晓琳, 朱喜成, 张佳伟, 陈锦华. pH响应性气体渗透CNC/PBAT复合膜的制备与性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 1040-1051.
Xiangfei DING, Xiaolin QIU, Xicheng ZHU, Jiawei ZHANG, Jinhua CHEN. Preparation and properties of pH-responsive gas permeable CNC/PBAT composite membranes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(3): 1040-1051.
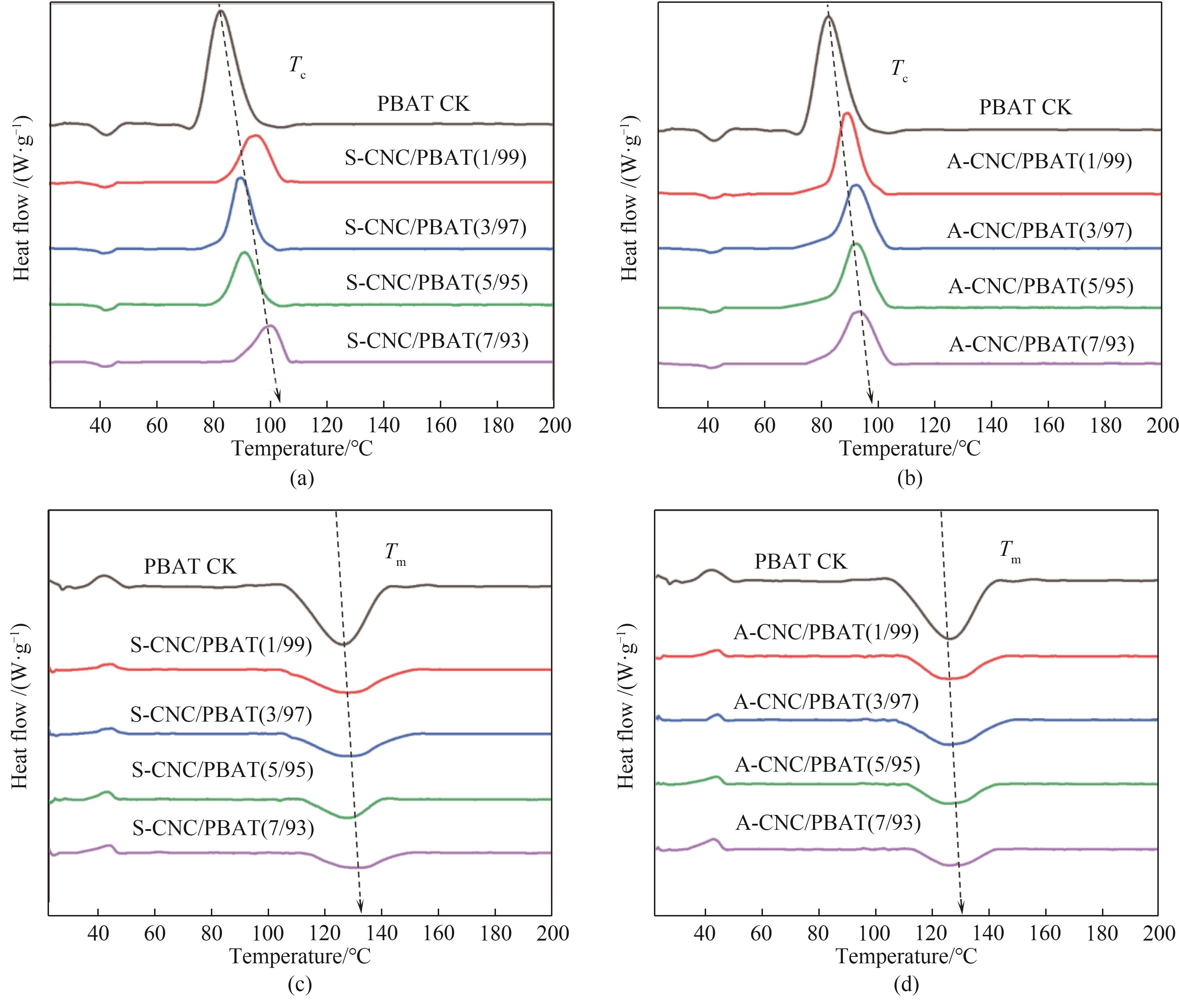
图5 不同含量的功能化CNC/PBAT复合薄膜的DSC测试:(a)、(b)一次降温曲线;(c)、(d)二次升温曲线
Fig.5 DSC tests of functionalized CNC/PBAT composite films with different contents: (a), (b) primary cooling curves; (c), (d) secondary heating curves
| 样品名称 | Tm/℃ | Tc/℃ | Tc-onset/℃ | ΔHm/(J/g) | ΔXc/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBAT | 125.51 | 82.43 | 93.04 | 13.32 | 11.68 |
| S-CNC/PBAT(1/99) | 128.29 | 94.86 | 103.89 | 9.261 | 8.21 |
| S-CNC/PBAT(3/97) | 127.43 | 89.48 | 96.82 | 9.505 | 8.60 |
| S-CNC/PBAT(5/95) | 126.45 | 91.08 | 104.18 | 8.143 | 7.52 |
| S-CNC/PBAT(7/93) | 128.95 | 98.70 | 107.31 | 7.296 | 6.88 |
| A-CNC/PBAT(1/99) | 126.96 | 89.31 | 97.16 | 10.94 | 9.69 |
| A-CNC/PBAT(3/97) | 127.60 | 92.43 | 101.54 | 10.39 | 9.59 |
| A-CNC/PBAT(5/95) | 127.84 | 92.66 | 101.76 | 9.858 | 8.91 |
| A-CNC/PBAT(7/93) | 128.53 | 93.21 | 103.23 | 9.36 | 8.83 |
表1 功能化CNC/PBAT复合薄膜的DSC曲线参数
Table 1 The DSC curve parameters of functionalized CNC /PBAT composite films
| 样品名称 | Tm/℃ | Tc/℃ | Tc-onset/℃ | ΔHm/(J/g) | ΔXc/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBAT | 125.51 | 82.43 | 93.04 | 13.32 | 11.68 |
| S-CNC/PBAT(1/99) | 128.29 | 94.86 | 103.89 | 9.261 | 8.21 |
| S-CNC/PBAT(3/97) | 127.43 | 89.48 | 96.82 | 9.505 | 8.60 |
| S-CNC/PBAT(5/95) | 126.45 | 91.08 | 104.18 | 8.143 | 7.52 |
| S-CNC/PBAT(7/93) | 128.95 | 98.70 | 107.31 | 7.296 | 6.88 |
| A-CNC/PBAT(1/99) | 126.96 | 89.31 | 97.16 | 10.94 | 9.69 |
| A-CNC/PBAT(3/97) | 127.60 | 92.43 | 101.54 | 10.39 | 9.59 |
| A-CNC/PBAT(5/95) | 127.84 | 92.66 | 101.76 | 9.858 | 8.91 |
| A-CNC/PBAT(7/93) | 128.53 | 93.21 | 103.23 | 9.36 | 8.83 |
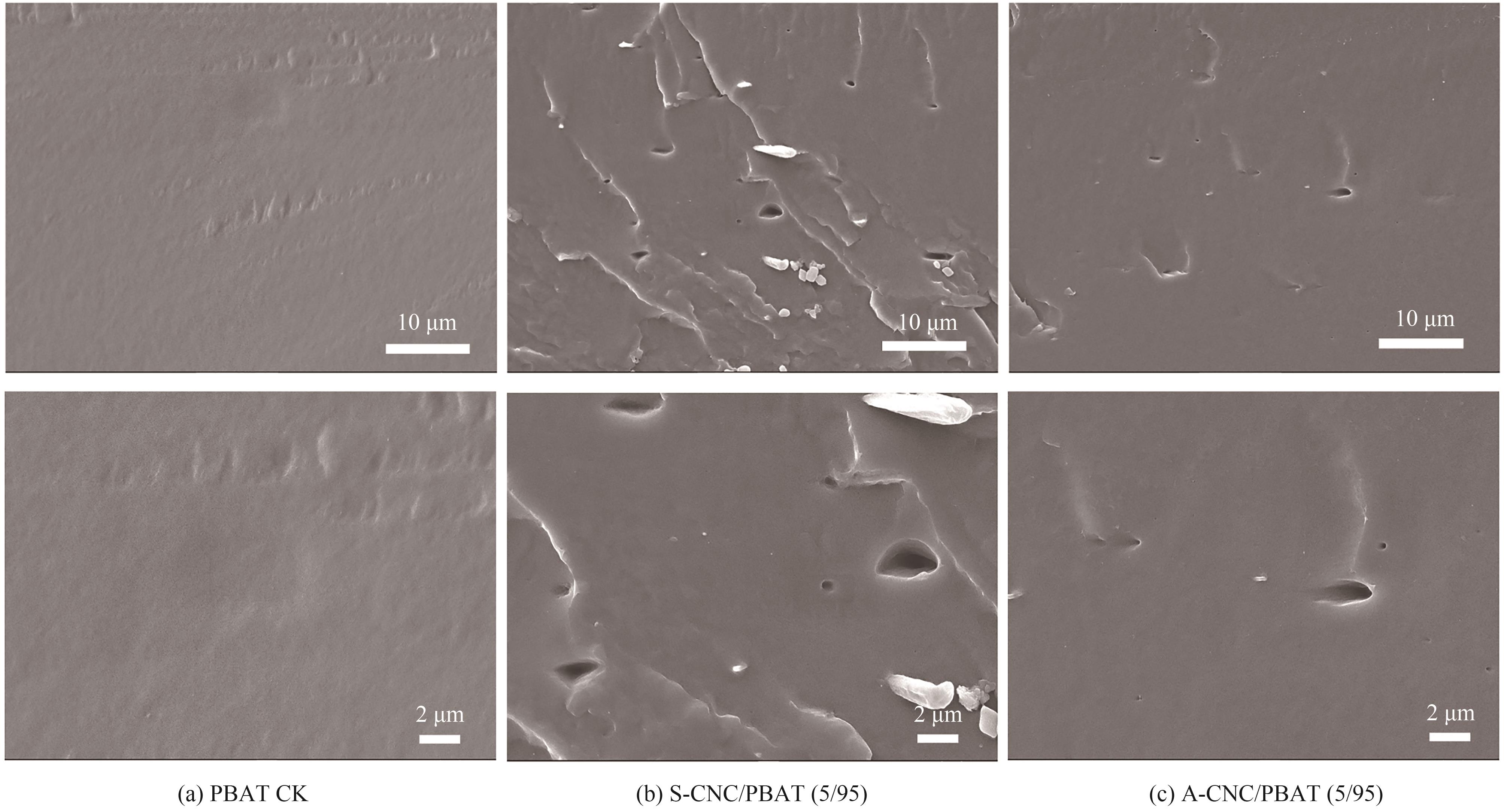
图7 功能化CNC/PBAT复合薄膜截面的低、高倍下扫描电镜SEM表征结果
Fig.7 SEM characterisation results at low and high magnification of functionalised CNC/PBAT composite film cross section
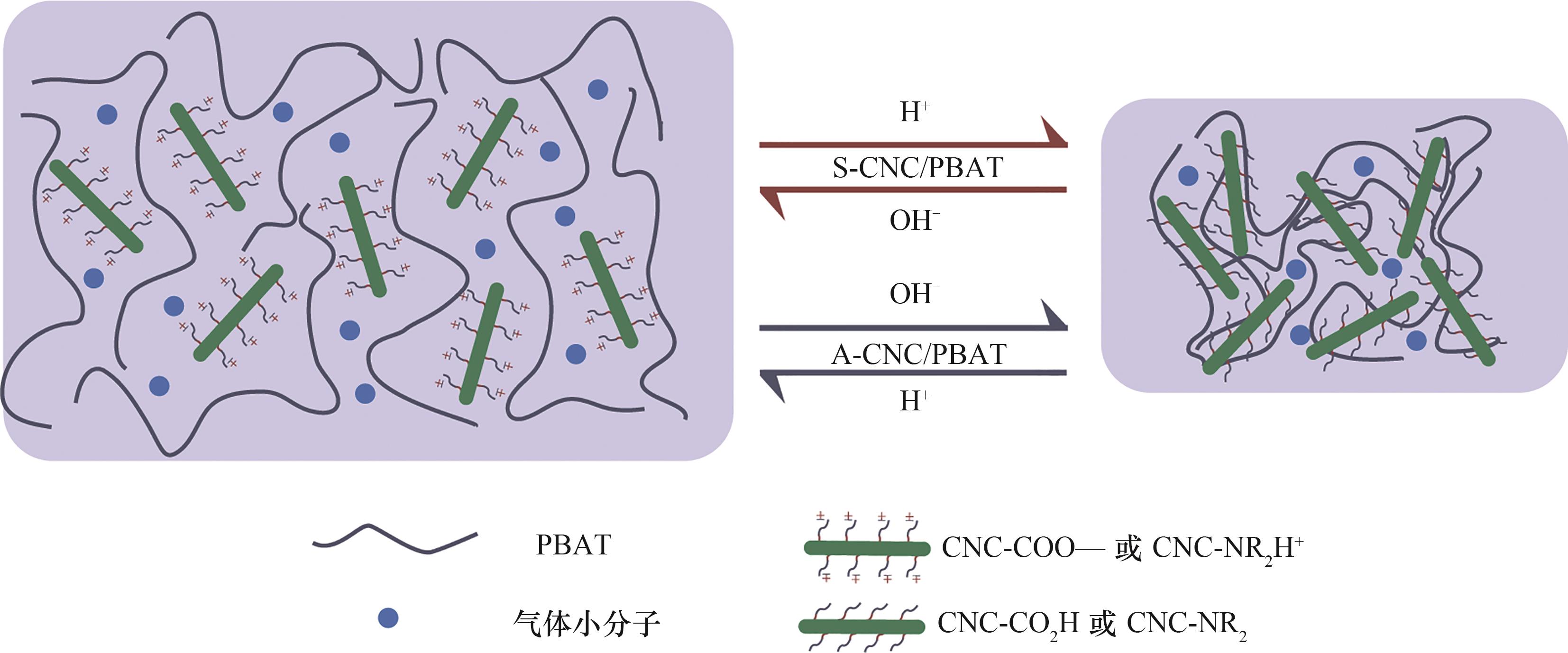
图8 功能化CNC/PBAT复合薄膜的pH响应性气体渗透原理示意图
Fig.8 Schematic representation of the principle of pH-responsive gas permeation of functionalized CNC/PBAT composite films
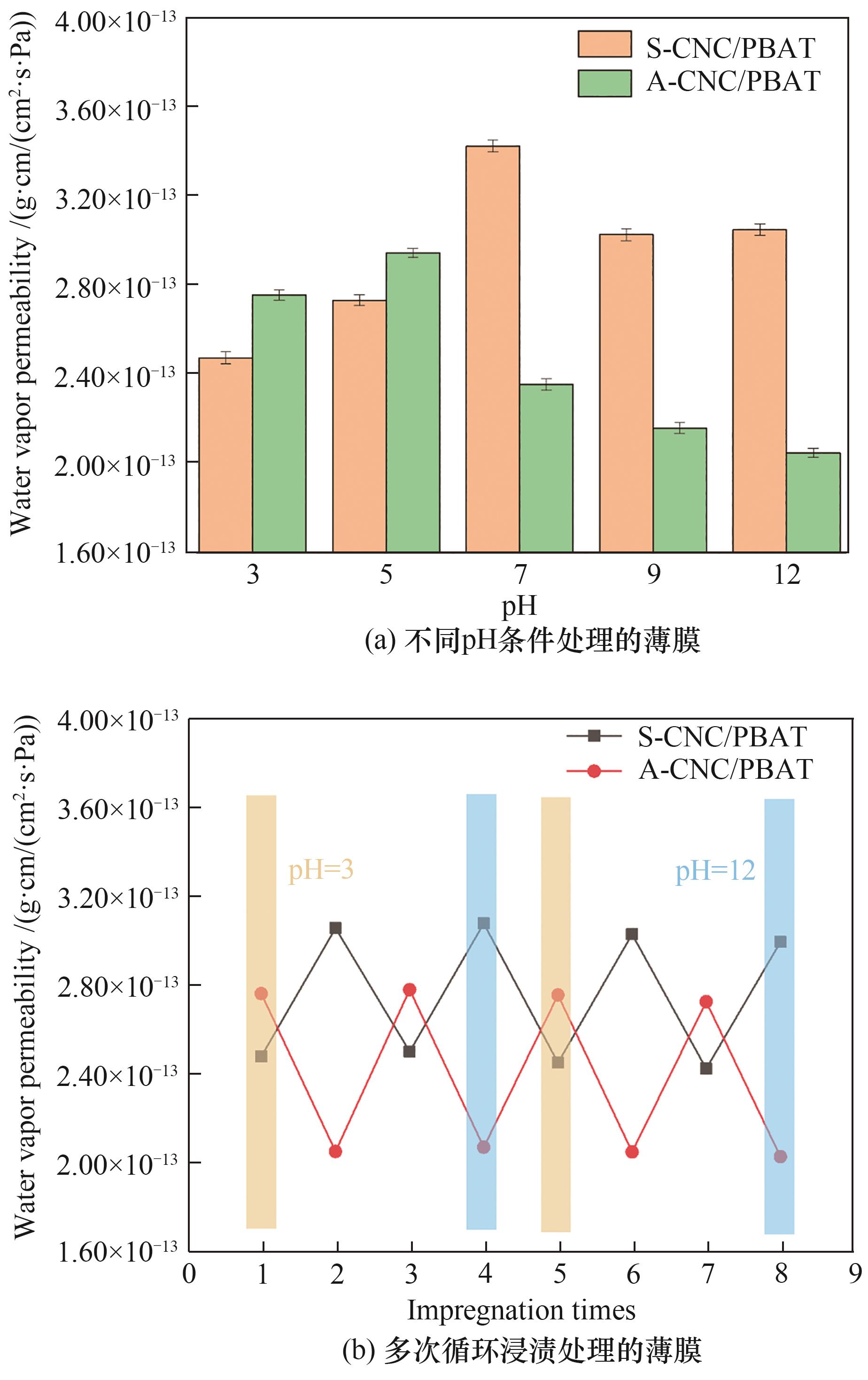
图10 S-CNC/PBAT(5/95)与A-CNC/PBAT(5/95)复合薄膜的pH响应性水蒸气渗透的测试结果
Fig.10 Test results of pH-responsive water vapor permeability of S-CNC/PBAT (5/95) and A-CNC/PBAT (5/95) composite films
| 1 | Opara U L, Caleb O J, Belay Z A. Modified atmosphere packaging for food preservation[M]//Food Quality and Shelf Life. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 235-259. |
| 2 | Turan D, Sängerlaub S, Stramm C, et al. Gas permeabilities of polyurethane films for fresh produce packaging: response of O2 permeability to temperature and relative humidity[J]. Polymer Testing, 2017, 59: 237-244. |
| 3 | Zhao Y, Qiu X L, Wang J, et al. Preparation and characterization of CO2/O2 selective facilitated transport films by coating polyvinyl alcohol/polyethylene glycol/aminated sodium lignosulfonate on TiO2/ZnO-modified LDPE[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2023, 140(21): e53877. |
| 4 | Kim D, Seo J. A review: breathable films for packaging applications[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2018, 76: 15-27. |
| 5 | Osada Y, Honda K, Ohta M. Control of water permeability by mechanochemical contraction of poly(methacrylic acid)-grafted membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 1986, 27(3): 327-338. |
| 6 | Tufani A, Ozaydin Ince G. Smart membranes with pH-responsive control of macromolecule permeability[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 537: 255-262. |
| 7 | Houben S J A, Kloos J, Borneman Z, et al. Switchable gas permeability of a polypropylene-liquid crystalline composite film[J]. Journal of Polymer Science, 2022, 60(5): 803-811. |
| 8 | Siracusa V, Rocculi P, Romani S, et al. Biodegradable polymers for food packaging: a review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2008, 19(12): 634-643. |
| 9 | Sousa F M, Cavalcanti F B, Marinho V A D, et al. Effect of composition on permeability, mechanical properties and biodegradation of PBAT/PCL blends films[J]. Polymer Bulletin, 2022, 79(7): 5327-5338. |
| 10 | Kian L K, Jawaid M, Mahmoud M H, et al. PBAT/PBS blends membranes filled with nanocrystalline cellulose for heavy metal ion separation[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 2022, 30(12): 5263-5273. |
| 11 | Lamsaf H, Singh S, Pereira J, et al. Multifunctional properties of PBAT with hemp (Cannabis sativa) micronised fibres for food packaging: cast films and coated paper[J]. Coatings, 2023, 13(7): 1195. |
| 12 | Sonchaeng U, Promsorn J, Bumbudsanpharoke N, et al. Polyesters incorporating Gallic acid as oxygen scavenger in biodegradable packaging[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(23): 5296. |
| 13 | Pagno V, Módenes A N, Dragunski D C, et al. Heat treatment of polymeric PBAT/PCL membranes containing activated carbon from Brazil nutshell biomass obtained by electrospinning and applied in drug removal[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2020, 8(5): 104159. |
| 14 | Thangudu S. Next generation nanomaterials: smart nanomaterials, significance, and biomedical applications[M]//Khan F. Applications of Nanomaterials in Human Health. Singapore: Springer, 2020: 287-312. |
| 15 | Fourati Y, Tarrés Q, Delgado-Aguilar M, et al. Cellulose nanofibrils reinforced PBAT/TPS blends: mechanical and rheological properties[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2021, 183: 267-275. |
| 16 | Hung Y J, Chiang M Y, Wang E T, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and physical properties of maleic acid-grafted poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/cellulose nanocrystal composites[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(13): 2742. |
| 17 | Isogai A. Emerging nanocellulose technologies: recent developments[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(28): 2000630. |
| 18 | Nasseri R, Deutschman C P, Han L, et al. Cellulose nanocrystals in smart and stimuli-responsive materials: a review[J]. Materials Today Advances, 2020, 5: 100055. |
| 19 | Way A E, Hsu L, Shanmuganathan K, et al. pH-responsive cellulose nanocrystal gels and nanocomposites[J]. ACS Macro Letters, 2012, 1(8): 1001-1006. |
| 20 | Li Y, Chen H M, Liu D, et al. pH-responsive shape memory poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(ε-caprolactone)-based polyurethane/cellulose nanocrystals nanocomposite[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(23): 12988-12999. |
| 21 | Chen Y X, Abdalkarim S Y H, Yu H Y, et al. Double stimuli-responsive cellulose nanocrystals reinforced electrospun PHBV composites membrane for intelligent drug release[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 155: 330-339. |
| 22 | Luo Q Y, Hossen A, Sameen D E, et al. Recent advances in the fabrication of pH-sensitive indicators films and their application for food quality evaluation[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2023, 63(8): 1102-1118. |
| 23 | Thambiraj S, Ravi Shankaran D. Preparation and physicochemical characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from industrial waste cotton[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 412: 405-416. |
| 24 | Mazlita Y, Lee H V, Hamid S B A. Preparation of cellulose nanocrystals bio-polymer from agro-industrial wastes: separation and characterization[J]. Polymers and Polymer Composites, 2016, 24(9): 719-728. |
| 25 | Habibi Y, Lucia L A, Rojas O J. Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2010, 110(6): 3479-3500. |
| 26 | Hu Y, Tang L R, Lu Q L, et al. Preparation of cellulose nanocrystals and carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals from borer powder of bamboo[J]. Cellulose, 2014, 21(3): 1611-1618. |
| 27 | Zafari R, Mendonça F G, Baker R T, et al. Technology, efficient SO2 capture using an amine-functionalized, nanocrystalline cellulose-based adsorbent[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2023, 308: 122917. |
| 28 | Chatterjee S, Nafezarefi F, Tai N H, et al. Size and synergy effects of nanofiller hybrids including graphene nanoplatelets and carbon nanotubes in mechanical properties of epoxy composites[J]. Carbon, 2012, 50(15): 5380-5386. |
| 29 | Wu C Q, Zhang X Z, Wang X H, et al. Surface modification of cellulose nanocrystal using succinic anhydride and its effects on poly(butylene succinate) based composites[J]. Cellulose, 2019, 26(5): 3167-3181. |
| 30 | Liu X, Shao X Y, Fang G B, et al. Preparation and properties of chemically reduced graphene oxide/copolymer-polyamide nanocomposites[J]. e-Polymers, 2017, 17(1): 3-14. |
| 31 | Huang W J, Lv G F, Wei L J, et al. Preparation and performance study of pbat/microcrystalline cellulose composite materials[J]. 2021, 49(9): 12-16. |
| 32 | Wang Z F, Wang B, Qi N, et al. Influence of fillers on free volume and gas barrier properties in styrene-butadiene rubber studied by positrons[J]. Polymer, 2005, 46(3): 719-724. |
| 33 | Torstensen J Ø, Liu M, Jin S A, et al. Swelling and free-volume characteristics of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibril films[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2018, 19(3): 1016-1025. |
| 34 | Moon J D, Borjigin H, Liu R, et al. Impact of humidity on gas transport in polybenzimidazole membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 639: 119758. |
| 35 | Kedia P, Badhe Y, Gupta R, et al. Modeling the effect of pH on the permeability of dried chitosan film[J]. Journal of Food Engineering, 2023, 358: 111682. |
| 36 | Zhang F, Yu L J, Liu J, et al. pH-responsive laminar WSe2 membrane with photocatalytic antifouling property for ultrafast water transport[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 435:135159. |
| [1] | 徐文杰, 贾献峰, 王际童, 乔文明, 凌立成, 王任平, 余子舰, 张寅旭. 有机硅/酚醛杂化气凝胶的制备和性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3572-3583. |
| [2] | 胡兴枝, 张皓焱, 庄境坤, 范雨晴, 张开银, 向军. 嵌有超小CeO2纳米粒子的碳纳米纤维的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3584-3596. |
| [3] | 张澳, 罗英武. 低模量、高弹性、高剥离强度丙烯酸酯压敏胶[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3079-3092. |
| [4] | 王杰, 丘晓琳, 赵烨, 刘鑫洋, 韩忠强, 许雍, 蒋文瀚. 聚电解质静电沉积改性PHBV抗氧化膜的制备与性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3068-3078. |
| [5] | 刘杰, 吴立盛, 李锦锦, 罗正鸿, 周寅宁. 含乙烯基胺酯键聚醚类可逆交联聚合物的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3051-3057. |
| [6] | 蔡斌, 张效林, 罗倩, 党江涛, 左栗源, 刘欣梅. 导电薄膜材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2308-2321. |
| [7] | 崔张宁, 胡紫璇, 吴雷, 周军, 叶干, 刘田田, 张秋利, 宋永辉. 可降解纤维素基材料的耐水性能研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2296-2307. |
| [8] | 杨琴, 秦传鉴, 李明梓, 杨文晶, 赵卫杰, 刘虎. 用于柔性传感的双形状记忆MXene基水凝胶的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2699-2707. |
| [9] | 李振, 张博, 王丽伟. PEG-EG固-固相变材料的制备和性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2680-2688. |
| [10] | 代佳琳, 毕唯东, 雍玉梅, 陈文强, 莫晗旸, 孙兵, 杨超. 热物性对混合型CPCMs固液相变特性影响模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1914-1927. |
| [11] | 陈韶云, 徐东, 陈龙, 张禹, 张远方, 尤庆亮, 胡成龙, 陈建. 单层聚苯胺微球阵列结构的制备及其吸附性能[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2228-2238. |
| [12] | 刘瑞琪, 周栖桐, 张悦, 贺莹, 高静, 马丽. 基于金纳米颗粒修饰二氧化硅纳米花的生物传感器构建及应用[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1247-1259. |
| [13] | 徐东, 田杜, 陈龙, 张禹, 尤庆亮, 胡成龙, 陈韶云, 陈建. 聚苯胺/二氧化锰/聚吡咯复合纳米球的制备及其电化学储能性[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1379-1389. |
| [14] | 陈瑞哲, 程磊磊, 顾菁, 袁浩然, 陈勇. 纤维增强树脂复合材料化学回收技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 981-994. |
| [15] | 王帅, 杨富凯, 徐新宇. 阻燃型全生物基多元醇聚氨酯泡沫的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1399-1408. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号