化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (9): 3242-3254.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20240324
郭鑫1,2,3,4( ), 李文静2,3,4, 乔俊飞2,3,4
), 李文静2,3,4, 乔俊飞2,3,4
收稿日期:2024-03-20
修回日期:2024-05-21
出版日期:2024-09-25
发布日期:2024-10-10
通讯作者:
郭鑫
作者简介:郭鑫(1990—),男,博士,讲师,guo_xin@haut.edu.cn
基金资助:
Xin GUO1,2,3,4( ), Wenjing LI2,3,4, Junfei QIAO2,3,4
), Wenjing LI2,3,4, Junfei QIAO2,3,4
Received:2024-03-20
Revised:2024-05-21
Online:2024-09-25
Published:2024-10-10
Contact:
Xin GUO
摘要:
针对城市污水处理过程关键出水水质一些参数难以在线测量的问题,提出了一种基于经验模态分解(EMD)的自组织模块化神经网络(MNN)出水参数软测量模型。首先设计一种基于EMD的任务分解方法,将复杂的时间序列分解为若干子序列,并采用样本熵和欧氏距离分别计算子序列的复杂性及相似性,自适应调整子网络模块。然后针对子网络模块初始结构难以确定的问题提出一种前馈神经网络的结构自组织算法,实现子网络模型根据分配的子任务动态调整自身网络结构,更有效地对各子序列进行预测。最后通过基准时间序列预测和实际污水处理厂中出水水质参数检测实验验证了所提出的模型具有较好的预测精度和自适应性。
中图分类号:
郭鑫, 李文静, 乔俊飞. 基于自组织模块化神经网络的污水处理过程出水参数预测[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3242-3254.
Xin GUO, Wenjing LI, Junfei QIAO. Prediction of effluent parameters in wastewater treatment process using self-organizing modular neural network[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3242-3254.
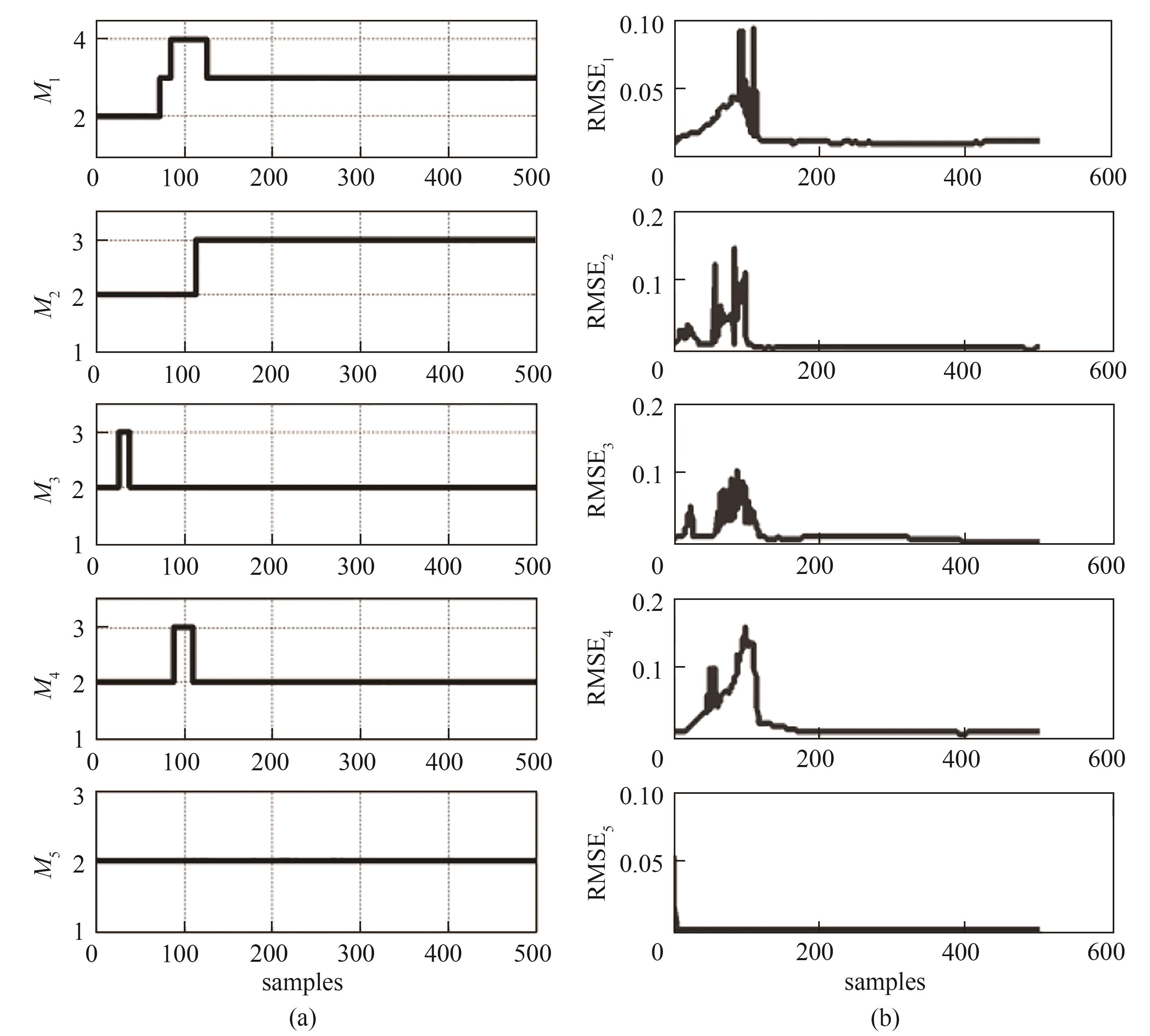
图5 子网络模型学习Mackey-Glass时间序列各子序列过程:(a)子网络模型结构动态变化;(b)子网络模型训练RMSE
Fig.5 Learning process of subseries of Mackey-Glass time series by sub-networks: (a) dynamic change of structure; (b) training RMSE of sub-networks
| 子网络模型 | 预测RMSE×103 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | |
| EMD-SMNN | 2.3 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| EMD-MNN | 3.0 | 5.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
表1 子网络模型的预测RMSE
Table 1 Prediction RMSE of sub-networks
| 子网络模型 | 预测RMSE×103 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | |
| EMD-SMNN | 2.3 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| EMD-MNN | 3.0 | 5.7 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| 网络类型 | 模块数 | 隐含层节点数 | RMSE | NMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMD-SMNN | 5 | 12 | 4.0×10-3 | 3.1×10-4 |
| EMD-MNN | 5 | 15 | 4.5×10-3 | 3.3×10-4 |
| SWEMD-MNN[ | 5 | 15 | 7.0×10-3 | 9.8×10-4 |
| OAMNN[ | 5 | 25 | 8.6×10-3 | — |
| CMNN[ | 4 | 12 | 1.9×10-2 | 5.5×10-3 |
| OSAMNN[ | 7 | 35 | 3.1×10-2 | — |
| FNN | 1 | 15 | 4.1×10-2 | 6.1×10-3 |
| CCRNN[ | 1 | 11 | 9.3×10-3 | 6.3×10-4 |
| CICC[ | 1 | 9 | 8.5×10-3 | — |
| CCPSO[ | 1 | — | 8.2×10-3 | — |
表2 不同模型的Mackey-Glass时间序列预测结果
Table 2 Prediction results of different models for Mackey-Glass time series
| 网络类型 | 模块数 | 隐含层节点数 | RMSE | NMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMD-SMNN | 5 | 12 | 4.0×10-3 | 3.1×10-4 |
| EMD-MNN | 5 | 15 | 4.5×10-3 | 3.3×10-4 |
| SWEMD-MNN[ | 5 | 15 | 7.0×10-3 | 9.8×10-4 |
| OAMNN[ | 5 | 25 | 8.6×10-3 | — |
| CMNN[ | 4 | 12 | 1.9×10-2 | 5.5×10-3 |
| OSAMNN[ | 7 | 35 | 3.1×10-2 | — |
| FNN | 1 | 15 | 4.1×10-2 | 6.1×10-3 |
| CCRNN[ | 1 | 11 | 9.3×10-3 | 6.3×10-4 |
| CICC[ | 1 | 9 | 8.5×10-3 | — |
| CCPSO[ | 1 | — | 8.2×10-3 | — |
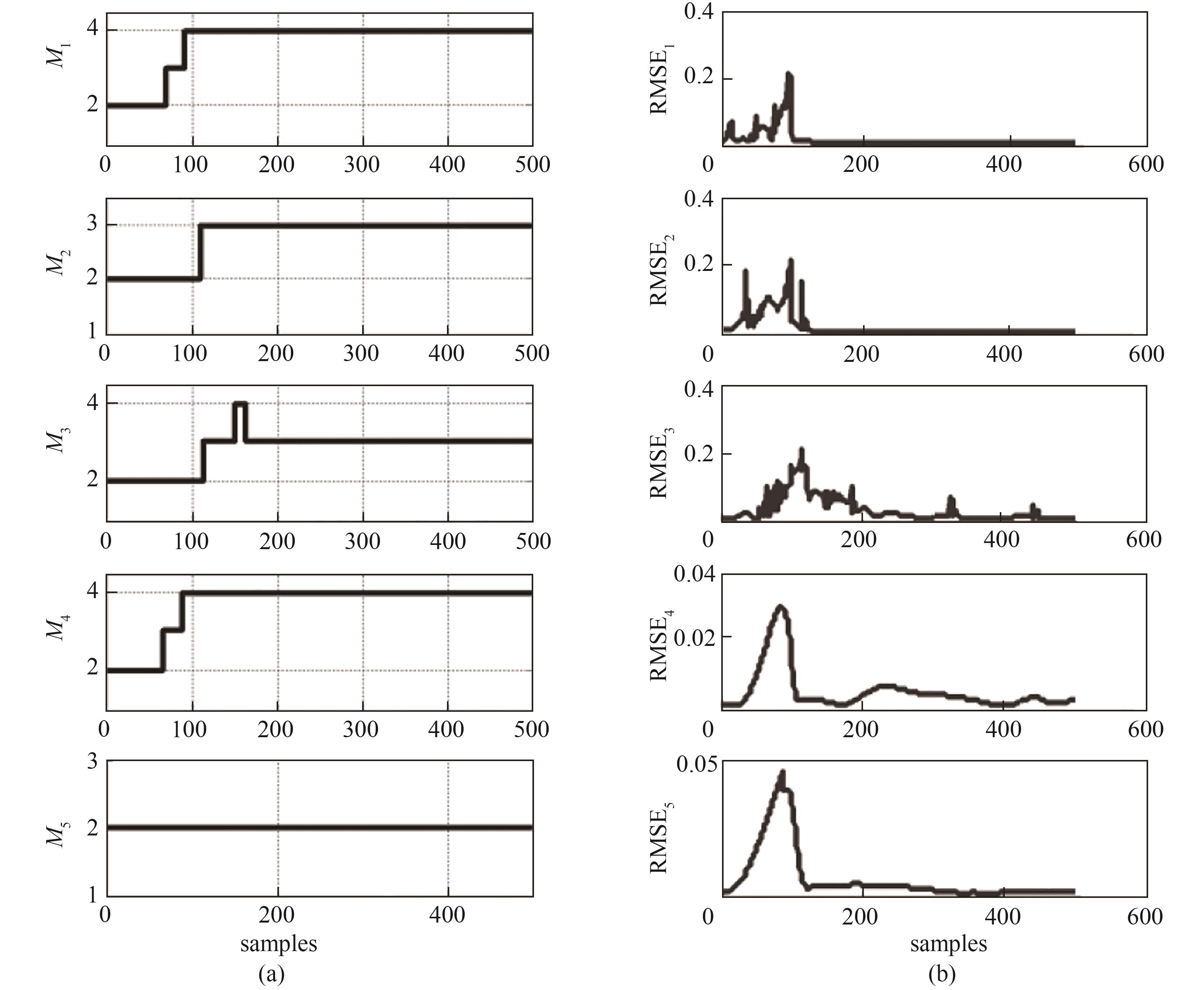
图9 子网络模型学习Lorenz时间序列各子序列过程:(a)子网络模型结构动态变化;(b)子网络模型训练RMSE
Fig.9 Learning process of subseries of Lorenz time series by sub-networks: (a) dynamic change of structure; (b) training RMSE of sub-networks
| 子网络模型 | 预测RMSE×102 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | |
| EMD-SMNN | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| EMD-MNN | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.1 |
表3 子网络模型的预测RMSE
Table 3 Prediction RMSE of sub-networks
| 子网络模型 | 预测RMSE×102 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | |
| EMD-SMNN | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| EMD-MNN | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.1 |
| 网络类型 | 模块数 | 隐含层节点数 | RMSE | NMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMD-SMNN | 5 | 16 | 0.8×10-3 | 1.1×10-4 |
| EMD-MNN | 5 | 15 | 1.1×10-2 | 1.3×10-4 |
| CMNN[ | 4 | 12 | 2.1×10-2 | 2.0×10-3 |
| OAMNN[ | 4 | 20 | 1.3×10-2 | — |
| FNN | 1 | 15 | 7.3×10-2 | 2.2×10-2 |
| CCRNN[ | 1 | 13 | 1.9×10-2 | 8.2×10-3 |
| CICC[ | 1 | 9 | 2.4×10-2 | — |
| MLP-BLM[ | 1 | 37 | — | 9.6×10-4 |
表4 不同模型的Lorenz时间序列预测结果
Table 4 Pediction results of different models for Lorenz time series
| 网络类型 | 模块数 | 隐含层节点数 | RMSE | NMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMD-SMNN | 5 | 16 | 0.8×10-3 | 1.1×10-4 |
| EMD-MNN | 5 | 15 | 1.1×10-2 | 1.3×10-4 |
| CMNN[ | 4 | 12 | 2.1×10-2 | 2.0×10-3 |
| OAMNN[ | 4 | 20 | 1.3×10-2 | — |
| FNN | 1 | 15 | 7.3×10-2 | 2.2×10-2 |
| CCRNN[ | 1 | 13 | 1.9×10-2 | 8.2×10-3 |
| CICC[ | 1 | 9 | 2.4×10-2 | — |
| MLP-BLM[ | 1 | 37 | — | 9.6×10-4 |

图13 子网络模型学习出水氨氮浓度各子序列过程:(a)子网络模型结构动态变化;(b)子网络模型训练RMSE
Fig.13 Learning process of subseries of effluent NH4-N by sub-networks: (a) dynamic change of structure; (b) training RMSE of sub-networks
| 子网络模型 | 预测RMSE×102 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 | |
| EMD-SMNN | 1.8 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| EMD-MNN | 2.3 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
表5 子网络模型的预测RMSE
Table 5 Prediction RMSE of sub-networks
| 子网络模型 | 预测RMSE×102 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 | |
| EMD-SMNN | 1.8 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| EMD-MNN | 2.3 | 1.0 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.4 |
| 网络类型 | 模块数 | 隐含层节点数 | RMSE | NMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMD-SMNN | 8 | 24 | 1.0×10-1 | 1.0×10-2 |
| EMD-MNN | 8 | 24 | 1.5×10-1 | 1.6×10-2 |
| SWEMD-MNN[ | 8 | 24 | 1.4×10-1 | 2.4×10-2 |
| OAMNN[ | 5 | 25 | 2.1×10-1 | — |
| CMNN[ | 8 | 40 | 2.5×10-1 | 7.4×10-2 |
| OSAMNN[ | 7 | 35 | 2.6×10-1 | — |
| FNN | 1 | 20 | 7.4×10-1 | 8.4×10-2 |
表6 不同模型的出水氨氮浓度预测结果
Table 6 Prediction results of different models for effluent NH4-N
| 网络类型 | 模块数 | 隐含层节点数 | RMSE | NMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMD-SMNN | 8 | 24 | 1.0×10-1 | 1.0×10-2 |
| EMD-MNN | 8 | 24 | 1.5×10-1 | 1.6×10-2 |
| SWEMD-MNN[ | 8 | 24 | 1.4×10-1 | 2.4×10-2 |
| OAMNN[ | 5 | 25 | 2.1×10-1 | — |
| CMNN[ | 8 | 40 | 2.5×10-1 | 7.4×10-2 |
| OSAMNN[ | 7 | 35 | 2.6×10-1 | — |
| FNN | 1 | 20 | 7.4×10-1 | 8.4×10-2 |
| 1 | 韩红桂, 张琳琳, 伍小龙, 等. 数据和知识驱动的城市污水处理过程多目标优化控制[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(11): 2538-2546. |
| Han H G, Zhang L L, Wu X L, et al. Data-knowledge driven multiobjective optimal control for municipal wastewater treatment process[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(11): 2538-2546. | |
| 2 | 付鹏波, 田金乙, 吕文杰, 等. 物理法水处理技术[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(1): 59-72. |
| Fu P B, Tian J Y, Lyu W J, et al. Physical water treatment technology[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(1): 59-72. | |
| 3 | Li D, Liu Y Q, Huang D P, et al. Development of an adversarial transfer learning-based soft sensor in industrial systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: 3000610. |
| 4 | Wang Z Y, Liao C M, Zhong Z H, et al. Design, optimization and application of a highly sensitive microbial electrolytic cell-based BOD biosensor[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 216: 114533. |
| 5 | 刘壮壮, 鞠然, 刘崇涛, 等. 电化学膜生物反应器处理污水性能提升策略及研究现状[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(11): 4433-4444. |
| Liu Z Z, Ju R, Liu C T, et al. Strategies for performance enhancement of electrochemical membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment and current research status[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(11): 4433-4444. | |
| 6 | Kolb M, Bahadir M, Teichgräber B. Determination of chemical oxygen demand (COD) using an alternative wet chemical method free of mercury and dichromate[J]. Water Research, 2017, 122: 645-654. |
| 7 | Zhang R, Li Y S, Luo Y X, et al. A carbon-dot fluorescence capillary sensor for the determination of chemical oxygen demand[J]. Microchemical Journal, 2023, 187: 108445. |
| 8 | Zhu J J, Kang L L, Anderson P R. Predicting influent biochemical oxygen demand: balancing energy demand and risk management[J]. Water Research, 2018, 128: 304-313. |
| 9 | 杨翠丽, 武战红, 韩红桂, 等. 城市污水处理过程优化设定方法研究进展[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(10): 2092-2108. |
| Yang C L, Wu Z H, Han H G, et al. Perspectives on optimal setting methods for municipal wastewater treatment processes[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(10): 2092-2108. | |
| 10 | Li X, Bi F R, Yang X, et al. An echo state network with improved topology for time series prediction[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(6): 5869-5878. |
| 11 | 闻超垚, 周平. 污水处理过程出水水质稀疏鲁棒建模[J]. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(6): 1469-1481. |
| Wen C Y, Zhou P. Sparse robust modeling of effluent quality indices in wastewater treatment process[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(6): 1469-1481. | |
| 12 | Meng X, Zhang Y, Qiao J F. An adaptive task-oriented RBF network for key water quality parameters prediction in wastewater treatment process[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33(17): 11401-11414. |
| 13 | Fernandez de Canete J, Del Saz-Orozco P, Baratti R, et al. Soft-sensing estimation of plant effluent concentrations in a biological wastewater treatment plant using an optimal neural network[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2016, 63: 8-19. |
| 14 | Zhu J R, Jiang Z Z, Feng L. Improved neural network with least square support vector machine for wastewater treatment process[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 308: 136116. |
| 15 | Qiao J F, Guo X, Li W J. An online self-organizing algorithm for feedforward neural network[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32(23): 17505-17518. |
| 16 | 韩红桂, 乔俊飞, 薄迎春. 基于信息强度的RBF神经网络结构设计研究[J]. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(7): 1083-1090. |
| Han H G, Qiao J F, Bo Y C. On structure design for RBF neural network based on information strength[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(7): 1083-1090. | |
| 17 | Meng X, Zhang Y, Quan L M, et al. A self-organizing fuzzy neural network with hybrid learning algorithm for nonlinear system modeling[J]. Information Sciences, 2023, 642: 119145. |
| 18 | 廉小亲, 王俐伟, 安飒, 等. 基于SOM-RBF神经网络的COD软测量方法[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(9): 3465-3472. |
| Lian X Q, Wang L W, An S, et al. On soft sensor of chemical oxygen demand by SOM-RBF neural network[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(9): 3465-3472. | |
| 19 | 蒙西, 王岩, 孙子健, 等. 基于注意力模块化神经网络的城市固废焚烧过程氮氧化物排放预测[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 593-603. |
| Meng X, Wang Y, Sun Z J, et al. Prediction of NO x emissions for municipal solid waste incineration processes using attention modular neural network[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 593-603. | |
| 20 | Qiao J F, Guo X, Li W J. An online self-organizing modular neural network for nonlinear system modeling[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 97: 106777. |
| 21 | Ünlü R, Xanthopoulos P. Estimating the number of clusters in a dataset via consensus clustering[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 125: 33-39. |
| 22 | 蒙西, 乔俊飞, 韩红桂. 基于类脑模块化神经网络的污水处理过程关键出水参数软测量[J]. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(5): 906-919. |
| Meng X, Qiao J F, Han H G. Soft measurement of key effluent parameters in wastewater treatment process using brain-like modular neural networks[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(5): 906-919. | |
| 23 | 丛秋梅, 邓淑贤, 赵宇, 等. 稳定RBF神经网络的在线软测量建模方法[J]. 控制工程, 2018, 25(5): 823-828. |
| Cong Q M, Deng S X, Zhao Y, et al. Stable soft sensor based on RBF neural network and its applications[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2018, 25(5): 823-828. | |
| 24 | Duan H S, Meng X, Tang J, et al. Prediction of NO x concentration using modular long short-term memory neural network for municipal solid waste incineration[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2023, 56: 46-57. |
| 25 | Li M, Li W J, Qiao J F. Design of a modular neural network based on an improved soft subspace clustering algorithm[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 209: 118219. |
| 26 | Guo X, Li W J, Qiao J F. A modular neural network with empirical mode decomposition and multi-view learning for time series prediction[J]. Soft Computing, 2023, 27(17): 12609-12624. |
| 27 | Guo X, Li W J, Qiao J F. A self-organizing modular neural network based on empirical mode decomposition with sliding window for time series prediction[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2023, 145: 110559. |
| 28 | 郭鑫, 李文静, 乔俊飞. 一种改进的在线自适应模块化神经网络[J]. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(7): 1597-1605. |
| Guo X, Li W J, Qiao J F. An improved online adaptive modular neural network[J]. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(7): 1597-1605. | |
| 29 | Méndez E, Lugo O, Melin P. A competitive modular neural network for long-term time series forecasting[M]//Melin P, Castillo O, Kacprzyk J. Nature-inspired Design of Hybrid Intelligent Systems. Cham: Springer, 2017: 243-254. |
| 30 | Qiao J F, Zhang Z Z, Bo Y C. An online self-adaptive modular neural network for time-varying systems[J]. Neurocomputing, 2014, 125: 7-16. |
| 31 | Chandra R, Zhang M J. Cooperative coevolution of Elman recurrent neural networks for chaotic time series prediction[J]. Neurocomputing, 2012, 86: 116-123. |
| 32 | Chandra R. Competition and collaboration in cooperative coevolution of Elman recurrent neural networks for time-series prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2015, 26(12): 3123-3136. |
| 33 | Lin C J, Chen C H, Lin C T. A hybrid of cooperative particle swarm optimization and cultural algorithm for neural fuzzy networks and its prediction applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part C:Applications and Reviews, 2009, 39(1): 55-68. |
| 34 | Mirikitani D T, Nikolaev N. Recursive Bayesian recurrent neural networks for time-series modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2010, 21(2): 262-274. |
| [1] | 王倩倩, 李冰, 郑伟波, 崔国民, 赵兵涛, 明平文. 氢燃料电池局部动态特征三维模型[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(8): 2812-2820. |
| [2] | 马林峰, 欧爱彤, 李志远, 李垚, 刘润泽, 吴晓乐, 徐景涛. Na2S改性生物炭高效吸附重金属离子:制备及吸附机理[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(7): 2594-2603. |
| [3] | 王岩, 周佳文, 孙培亮, 陈勇, 齐元红, 彭冲. 磁性聚氨基噻唑吸附剂脱除水体Hg2+性能[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(6): 2283-2298. |
| [4] | 汪威, 白旭, 赵翔, 马学良, 林纬, 喻九阳. 基于响应面法的气浮旋流分离条件优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 1929-1938. |
| [5] | 高磊, 戴闻, 杨忠莲, 李淑萍, 闫刚印, 孙琪, 陆勇泽, 朱光灿. 汞对低气压条件下污水处理系统脱氮性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(5): 2036-2046. |
| [6] | 孟园, 倪善, 刘亚锋, 王文杰, 赵越, 朱育丹, 杨良嵘. 功能化多孔氮化碳材料对铀的吸附性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(4): 1616-1629. |
| [7] | 王沛, 段睿明, 张广儒, 金万勤. 光热驱动的膜分离生物甲烷制氢过程建模与仿真分析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 967-973. |
| [8] | 张天永, 张晶怡, 姜爽, 李彬, 吕东军, 陈都民, 陈雪. 弱酸性蓝AS染料排放的废盐制碳基吸附剂及利用[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 890-899. |
| [9] | 董益斌, 熊敬超, 王敬宇, 汪守康, 王亚飞, 黄群星. 融合激光雷达料位测算的锅炉燃烧优化模型预测控制[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 924-935. |
| [10] | 李琢宇, 金鹏, 陈孝彦, 赵泽玉, 王庆宏, 陈春茂, 詹亚力. 零价铁活化过氧乙酸降解水中双酚A的效果与机制[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 987-999. |
| [11] | 邓志诚, 许世峰, 王淇冬, 王家瑞, 王斯民. 浸没燃烧处理高盐高化学需氧量废水过程与能耗分析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(3): 1000-1008. |
| [12] | 蒙西, 王岩, 孙子健, 乔俊飞. 基于注意力模块化神经网络的城市固废焚烧过程氮氧化物排放预测[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 593-603. |
| [13] | 杨百玉, 寇悦, 姜峻韬, 詹亚力, 王庆宏, 陈春茂. 炼化碱渣湿式氧化预处理过程DOM的化学转化特征[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(9): 3912-3920. |
| [14] | 杨欣, 彭啸, 薛凯茹, 苏梦威, 吴燕. 分子印迹-TiO2光电催化降解增溶PHE废水性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3564-3571. |
| [15] | 张艳梅, 袁涛, 李江, 刘亚洁, 孙占学. 高效SRB混合菌群构建及其在酸胁迫条件下的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2599-2610. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号