化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (6): 2770-2780.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241372
蒋敏1,2( ), 邵翔宇1,2(
), 邵翔宇1,2( ), 郑立刚1, 高建良1, 雷刚2
), 郑立刚1, 高建良1, 雷刚2
收稿日期:2024-11-28
修回日期:2025-01-09
出版日期:2025-06-25
发布日期:2025-07-09
通讯作者:
邵翔宇
作者简介:蒋敏(1999—),女,硕士研究生,212201020049@home.hpu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Min JIANG1,2( ), Xiangyu SHAO1,2(
), Xiangyu SHAO1,2( ), Ligang ZHENG1, Jianliang GAO1, Gang LEI2
), Ligang ZHENG1, Jianliang GAO1, Gang LEI2
Received:2024-11-28
Revised:2025-01-09
Online:2025-06-25
Published:2025-07-09
Contact:
Xiangyu SHAO
摘要:
氢气因低点火能、宽燃烧范围的特点,泄漏后极易发生燃爆事故。为有效控制爆炸压力,泄压措施被广泛采用,其中膜片压力被认为是影响泄压效果的关键因素。基于短管道边界效应更加明显,选取长径比为10∶1的方管,开展膜片压力(Pv)范围为0 ~ 48 kPa的爆炸实验。结果表明,膜片压力的增加显著延长火焰传播时间,火焰传播速度呈先下降后升高的趋势;管道两端最大超压差值随Pv的增加而减小,与Pv = 15 kPa相比,28、39、48 kPa时管道两端压差从30.08 kPa减小至28.96、20.68和10.44 kPa;泄爆端压力-时间曲线呈双峰结构,第二峰值Pext低于初始峰值;火焰与压力的传播在初期会受到膜抗拉强度的阻滞,膜破后压力急剧攀升,火焰呈往返振荡现象,压力振幅随膜片压力的增加而显著提升。
中图分类号:
蒋敏, 邵翔宇, 郑立刚, 高建良, 雷刚. 膜片压力对氢-空气混合气体泄爆过程的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2770-2780.
Min JIANG, Xiangyu SHAO, Ligang ZHENG, Jianliang GAO, Gang LEI. Effect of membrane pressure on the venting explosion process of premixed hydrogen-air gases[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2770-2780.
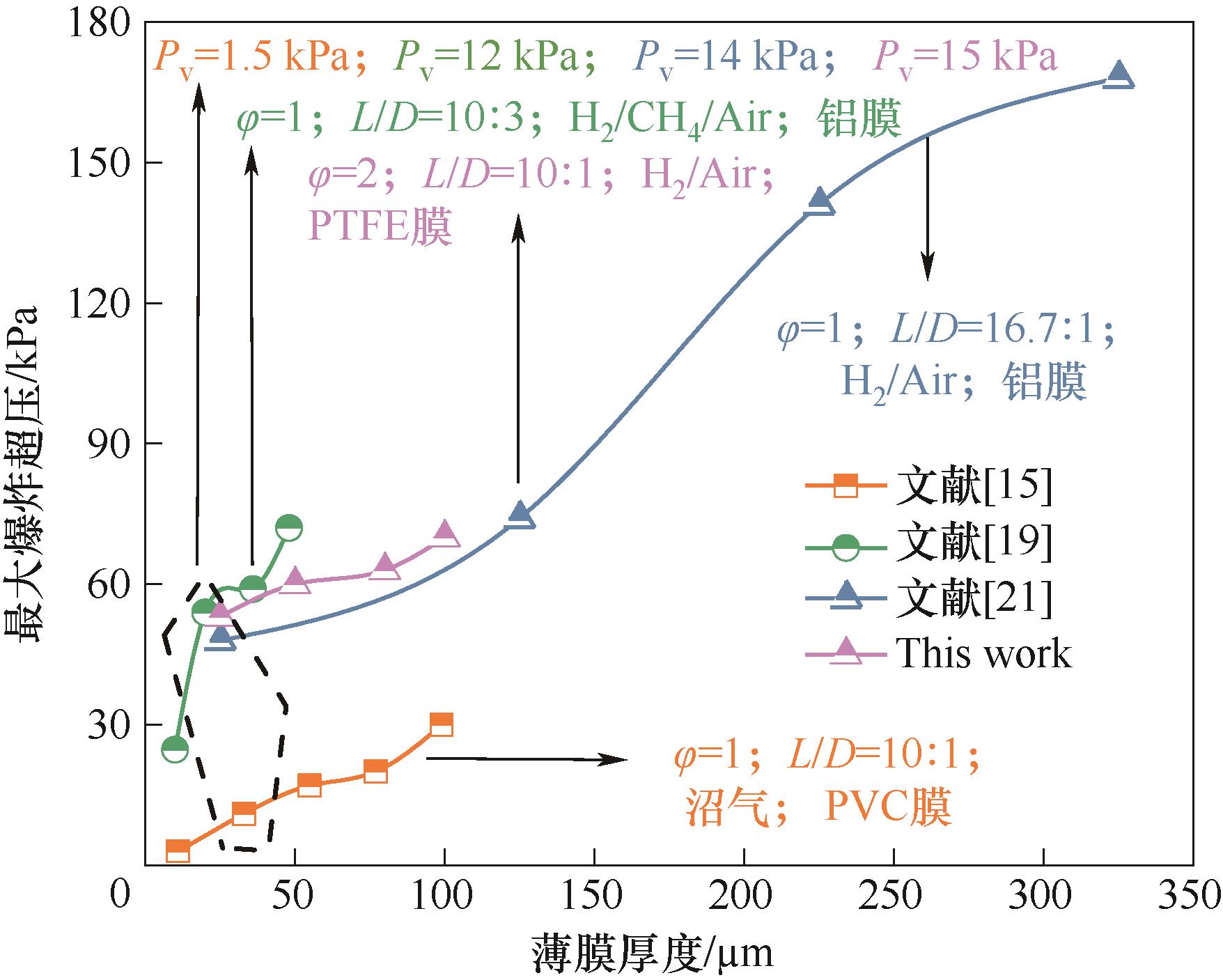
图7 膜片压力对爆炸超压的影响:本文与相关实验研究[15, 19, 21]的对比
Fig.7 Effect of rupture pressure on explosion overpressure: comparison between this study and related research[15, 19, 21]
| [16] | Cao Y, Guo J, Hu K L, et al. Effect of ignition location on external explosion in hydrogen-air explosion venting[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(15): 10547-10554. |
| [17] | Rui S C, Wang Q, Wang C J, et al. Effects of ignition location and vent area on the external explosion in vented hydrogen explosions[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024, 183: 602-616. |
| [18] | Yang Z X, Wang F, Xu C J, et al. Effects of the vent burst pressure on the duct-vented explosion of hydrogen-methane-air mixtures[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 67: 776-785. |
| [19] | 陈昊, 郭进, 王金贵, 等. 破膜压力对氢气-甲烷-空气泄爆的影响[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2022, 42(11): 161-170. |
| Chen H, Guo J, Wang J G, et al. Effects of vent burst pressure on hydrogen-methane-air deflagration in a vented duct[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2022, 42(11): 161-170. | |
| [20] | Rui S C, Guo J, Li G, et al. The effect of vent burst pressure on a vented hydrogen-air deflagration in a 1 m3 vessel[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(45): 21169-21176. |
| [21] | 杜赛枫, 张凯, 陈昊, 等. 破膜压力对氢-空气预混气体燃爆特性的影响[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2023, 43(2): 159-169. |
| Du S F, Zhang K, Chen H, et al. Effects of vent burst pressure on explosion characteristics of premixed hydrogen-air gases[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2023, 43(2): 159-169. | |
| [22] | 王晓峰, 付慧杰, 杨庆山. 气-膜耦合作用对充气薄膜管动力特性的影响[J]. 工程力学, 2023, 40(11): 46-58. |
| Wang X F, Fu H J, Yang Q S. Effect of air-membrane interaction on dynamic properties of an inflated membrane tube[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2023, 40(11): 46-58. | |
| [23] | Li Y F, Zheng L G, Wang X, et al. Effect of initial pressure on hydrogen/propane/air flames in a closed duct[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 64: 947-957. |
| [24] | Zheng L G, Miao Y X, Liu J J, et al. Effect of ignition position on the combustion instability of premixed methane-air in a semiopen duct[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2023, 143: 110830. |
| [25] | 毕明树, 李刚, 陈先锋, 等. 气体和粉尘爆炸防治工程学[M]. 2版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2017. |
| Bi M S, Li G, Chen X F, et al. Gas and Dust Explosion Prevention and Control Engineering[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2017. | |
| [26] | Luo Z M, Kang X F, Wang T, et al. Effects of an obstacle on the deflagration behavior of premixed liquefied petroleum gas-air mixtures in a closed duct[J]. Energy, 2021, 234:121291. |
| [27] | Li R K, Luo Z M, Cheng F M, et al. A comparative investigation of premixed flame propagating of combustible gases-methane mixtures across an obstructed closed tube[J]. Fuel, 2021, 289: 119766. |
| [28] | 王译晨, 朱民. 火焰动力学及其对热声稳定性的影响[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 62(4): 785-793. |
| Wang Y C, Zhu M. Flame dynamics and their effect on thermoacoustic instabilities[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2022, 62(4): 785-793. | |
| [29] | 肖华华. 管道中氢-空气预混火焰传播动力学实验与数值模拟研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2013. |
| Xiao H H. Experimental and numerical simulation study on flame propagation dynamics of hydrogen-air premixing in pipeline[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2013. | |
| [30] | Zhang K, Du S F, Chen H, et al. Effect of hydrogen concentration on the vented explosion of hydrogen-air mixtures in a 5-m-long duct[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2022, 162: 978-986. |
| [31] | 李哲, 陈先锋, 孙玮康. 浓度梯度对甲烷-空气混合气体爆炸特性参数的影响[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(11): 26-32. |
| Li Z, Chen X F, Sun W K. Effect of concentration gradient on explosion characteristic parameters of methane-air mixture[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(11):26-32. | |
| [32] | 周宁, 徐莹莹, 陈兵, 等. 泄爆条件对预混H2/空气燃爆特性影响的数值模拟[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(7): 3656-3663. |
| Zhou N, Xu Y Y, Chen B, et al. Numerical simulation of the influence of vent conditions on H2/air explosion characteristics[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(7): 3656-3663. | |
| [33] | Tavares J K, Jayachandran J. Dynamics of slowly propagating flames: role of the Rayleigh-Taylor instability[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2024, 269: 113656. |
| [34] | Sheng Y H, Luo Z M, Liu L T, et al. Experimental investigation on the vented flame and pressure behaviour of hydrogen-air mixtures[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2024, 92: 105469. |
| [35] | Yang W, Zheng L G, Wang C Z, et al. Effect of ignition position and inert gas on hydrogen/air explosions[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(12): 8820-8833. |
| [36] | Wang T, Sheng Y H, Nan F, et al. Investigation on the flame and pressure behaviors of vented hydrogen-air deflagration from a duct-connected vessel: effects of venting diameter and static activation pressure[J]. Energy, 2024, 307: 132705. |
| [37] | Huang S K, Wang F, Xu C J, et al. Effect of vent size on vented H2/N2/air deflagration[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 84: 881-888. |
| [38] | Qiu Y Y, Xing H D, Sun S, et al. Experimental study of the effects of vent area and ignition position on internal and external pressure characteristics of venting explosion[J]. Fuel, 2021, 300: 120935. |
| [39] | Cao Y, Wang Z Y, Zeng M Y, et al. Experimental and numerical study of the influence of vent burst pressure on venting characteristic of hydrogen-air explosion[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 2022, 394: 111844. |
| [40] | 曹勇, 郭进, 胡坤伦, 等. 点火位置对氢气-空气预混气体泄爆过程的影响[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2016, 36(6): 847-852. |
| Cao Y, Guo J, Hu K L, et al. Effect of ignition locations on vented explosion of premixed hydrogen-air mixtures[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2016, 36(6): 847-852. | |
| [41] | 王亚军, 蒋曙光, 王磊, 等. 含弱约束结构受限空间甲烷爆炸及传播特征实验研究[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(2): 502-508. |
| Wang Y J, Jiang S G, Wang L, et al. Experimental study on the characteristics of methane explosion and propagation in closed space with weak constraint structure[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(2): 502-508. | |
| [42] | Rui S C, Wang C J, Luo X J, et al. Experimental study on the effects of ignition location and vent burst pressure on vented hydrogen-air deflagrations in a cubic vessel[J]. Fuel, 2020, 278: 118342. |
| [43] | 张新民, 李米瑶, 温小萍, 等. 变截面管道内瓦斯爆炸火焰与压力耦合趋势[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2022, 22(6): 3104-3110. |
| Zhang X M, Li M Y, Wen X P, et al. Gas explosion characteristics in the presence of flow cross-section variations[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2022, 22(6): 3104-3110. | |
| [44] | 温小萍, 武建军, 解茂昭. 瓦斯爆炸火焰结构与压力波的耦合规律[J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(10): 3871-3877. |
| Wen X P, Wu J J, Xie M Z. Coupled relationship between flame structure and pressure wave of gas explosion[J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(10): 3871-3877. | |
| [45] | Wen X P, Yu M G, Liu Z C, et al. Large eddy simulation of methane-air deflagration in an obstructed chamber using different combustion models[J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2012, 25(4): 730-738. |
| [46] | 时高龙, 温小萍, 王发辉, 等. 预混气体爆炸火焰与压力的耦合振荡特性[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(7): 2811-2818. |
| Shi G L, Wen X P, Wang F H, et al. Coupling oscillation characteristics of premixed gas explosion flame and pressure[J]. CIESC Journal, 2019, 70(7): 2811-2818. | |
| [1] | Shao X Y, Shi W Y, Jia H L, et al. Flameback identification and air intrusion prevention in small flow hydrogen flare stack emissions[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 53: 717-727. |
| [2] | Cheng X M, Ye K T, Du A M, et al. Dual carbon goals and renewable energy innovations[J]. Research in International Business and Finance, 2024, 70: 102406. |
| [3] | 黄晟, 杨振丽, 李振宇. 氢产业链发展的路径分析[J]. 化工进展, 2024, 43(2): 882-893. |
| Huang S, Yang Z L, Li Z Y. Analysis of optimization path of developing China's hydrogen industry[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2024, 43(2): 882-893. | |
| [4] | Shao X Y, Shi W Y, Li P P, et al. Explosion-prevention strategies of airflow controlling and closed-inerting for hydrogen dilution in utility tunnel[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(37): 14095-14111. |
| [5] | Patonia A. Green hydrogen and its unspoken challenges for energy justice[J]. Applied Energy, 2025, 377: 124674. |
| [6] | Martins F P, De-León Almaraz S, Botelho A B, et al. Hydrogen and the sustainable development goals: synergies and trade-offs[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2024, 204: 114796. |
| [7] | Gao X W, An R C. Research on the coordinated development capacity of China's hydrogen energy industry chain[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 377: 134177. |
| [8] | Hui Y Z, Wang M T, Guo S R, et al. Comprehensive review of development and applications of hydrogen energy technologies in China for carbon neutrality: technology advances and challenges[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 315: 118776. |
| [9] | Muhammed N S, Gbadamosi A O, Epelle E I, et al. Hydrogen production, transportation, utilization, and storage: recent advances towards sustainable energy[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2023, 73: 109207. |
| [10] | Moradi R, Groth K M. Hydrogen storage and delivery: review of the state of the art technologies and risk and reliability analysis[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(23): 12254-12269. |
| [11] | Rasul M G, Hazrat M A, Sattar M A, et al. The future of hydrogen: challenges on production, storage and applications[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 272: 116326. |
| [12] | Liu W J, Sun L, Li Z L, et al. Trends and future challenges in hydrogen production and storage research[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2020, 27(25): 31092-31104. |
| [13] | Zhuang C J, Zhang L J, Tao G, et al. Effect of concentration, obstacles, and ignition location on the explosion overpressure of hydrogen-air in a closed-vessel[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(61): 23737-23747. |
| [14] | Ma X Y, Nie B S, Wang W L, et al. Effect of hydrogen concentration, initial pressure and temperature on mechanisms of hydrogen explosion in confined spaces[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2024, 269: 113696. |
| [15] | Dou Z G, Zheng L G, Zheng K, et al. Effect of film thickness and methane fraction on explosion characteristics of biogas/air mixture in a duct[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2020, 139: 26-35. |
| [1] | 彭建斌, 李明, 谢军龙, 陈建业. 液氢接收终端液氢泄漏扩散及爆炸超压研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 453-461. |
| [2] | 冯彪, 张昭, 李思琪, 王秉睿, 吴红颖, 史淼, 王丹, 马素霞. 适配环保制冷剂R290的阻燃剂性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 462-468. |
| [3] | 丁昊, 王林, 刘豪. R290/R245fa汽液相平衡混合规则对比研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 9-16. |
| [4] | 吴与伦, 王振雷, 王昕. 基于对比学习的乙烯裂解炉运行工况识别方法[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2733-2742. |
| [5] | 廖鹏伟, 刘庆辉, 潘安, 王嘉岳, 符小贵, 杨思宇, 余皓. 考虑不确定性的风电制氢系统:多时间尺度运行策略[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2743-2754. |
| [6] | 王富玉, 周晅毅. 结合非定常伴随方程和遗传算法的化工区反演[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3104-3114. |
| [7] | 李芳, 王怡然, 张鹏鹤, 刘月明, 何鸣元. 烃转化过程中的氢转移反应[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2483-2504. |
| [8] | 王一非, 任婧杰, 毕明树, 叶昊天. 基于本质安全与经济性的环己烷氧化工艺参数多目标优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2722-2732. |
| [9] | 赵清萍, 张敏, 赵辉, 王刚, 邱永福. 乙烯氢甲酯化合成丙酸甲酯的氢键作用机制及反应动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2701-2713. |
| [10] | 王智超, 刘冬妹, 熊敏, 周利, 吉旭, 党亚固. 可再生能源发电制氢与炼油企业氢气网络耦合系统的多周期调度优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2802-2812. |
| [11] | 宋粉红, 王文光, 郭亮, 范晶. C元素修饰g-C3N4对TiO2的调控及复合材料光催化产氢性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2983-2994. |
| [12] | 姬海燕, 刘家印, 吴海军, 何璟琳, 靳紫恒, 魏钿航, 江霞. 低温等离子体在生物质气化制氢中的应用研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2419-2433. |
| [13] | 安昊天, 韩章烨, 陆慕瑶, 周阿武, 李建荣. 推进MOF产业化应用:宏量制备与成型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2011-2025. |
| [14] | 郭明钢, 杨晓航, 代岩, 米盼盼, 马世鑫, 贺高红, 肖武, 崔福军. 贫氦管输天然气提氦多元化产品耦合工艺优化设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2251-2261. |
| [15] | 张赵雪, 李正宇, 崔文慧, 王倩, 王志平, 龚领会. 基于液氖液氮梯级蓄冷的液氢储能中冷能回收利用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1731-1741. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号