化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (7): 3615-3625.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20241521
吴鹂霄1( ), 燕溪溪1(
), 燕溪溪1( ), 张素娜1, 徐一鸣1, 钱佳颖1, 乔永民2, 王利军1,3
), 张素娜1, 徐一鸣1, 钱佳颖1, 乔永民2, 王利军1,3
收稿日期:2024-12-30
修回日期:2025-03-07
出版日期:2025-07-25
发布日期:2025-08-13
通讯作者:
燕溪溪
作者简介:吴鹂霄(2001—),男,硕士研究生,863290955@qq.com
基金资助:
Lixiao WU1( ), Xixi YAN1(
), Xixi YAN1( ), Suna ZHANG1, Yiming XU1, Jiaying QIAN1, Yongmin QIAO2, Lijun WANG1,3
), Suna ZHANG1, Yiming XU1, Jiaying QIAN1, Yongmin QIAO2, Lijun WANG1,3
Received:2024-12-30
Revised:2025-03-07
Online:2025-07-25
Published:2025-08-13
Contact:
Xixi YAN
摘要:
现有的阳极技术已接近性能极限。微晶石墨作为阳极材料中常用的石墨类材料的一种,其在实际应用中的潜力尚未得到充分开发。开发具有高能量密度和快速充放电能力的负极材料已经成为锂离子电池领域的热点课题。采用一种简便且高效的水热合成法,通过高温煅烧,成功制备了磷掺杂的微晶石墨负极材料。通过磷酸水热法对微晶石墨进行表面改性,实现了磷元素的有效掺杂,并确保了在高温煅烧过程中掺杂元素的稳定附着和均匀分布。结果表明,磷掺杂能够显著提升微晶石墨的化学活性,初次放电比容量实现501.56 mAh/g,在3C高倍率的放电比容量仍保持在121.98 mAh/g,相较于原样提升了大约3倍。
中图分类号:
吴鹂霄, 燕溪溪, 张素娜, 徐一鸣, 钱佳颖, 乔永民, 王利军. 磷掺杂微晶石墨的制备及其在锂离子电池负极材料中的电化学性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3615-3625.
Lixiao WU, Xixi YAN, Suna ZHANG, Yiming XU, Jiaying QIAN, Yongmin QIAO, Lijun WANG. The preparation of phosphorus-doped microcrystalline graphite and its electrochemical performance as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(7): 3615-3625.
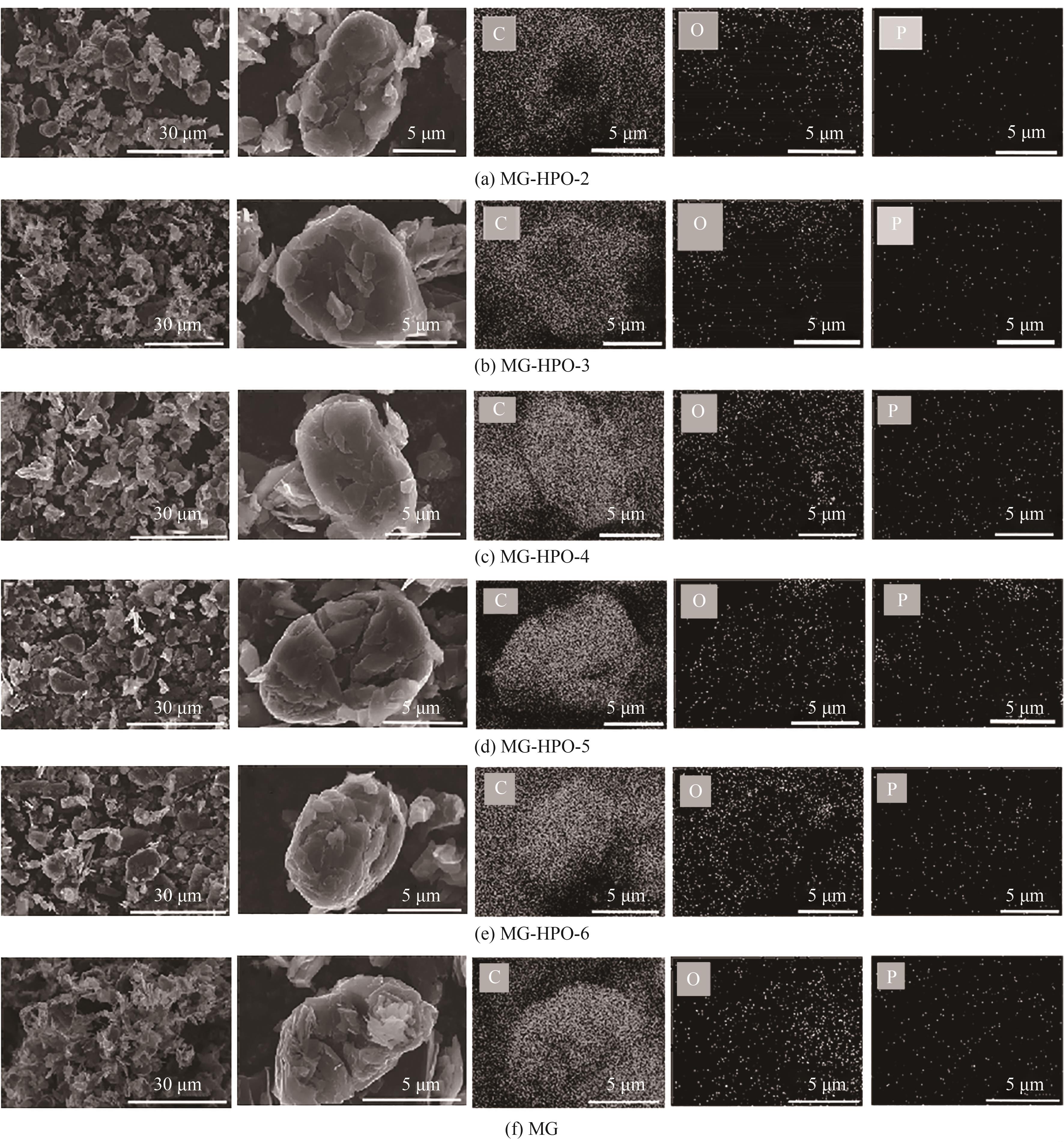
图1 MG以及不同磷酸含量样品在30 μm和5 μm下的SEM图以及对应的C、O、P元素EDS面扫能谱图
Fig.1 SEM images at 30 μm and 5 μm, and the EDS surface-scanning energy spectra of the C, O and P elements of MG and samples with different phosphoric acid contents
| 样品 | λ/Å | 2θ/(°) | 晶格间距/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| MG | 0.15406 | 26.47204 | 0.33643 |
| MG-HPO-2 | 0.15406 | 26.52727 | 0.33574 |
| MG-HPO-3 | 0.15406 | 26.51931 | 0.33584 |
| MG-HPO-4 | 0.15406 | 26.52919 | 0.33572 |
| MG-HPO-5 | 0.15406 | 26.51398 | 0.33591 |
| MG-HPO-6 | 0.15406 | 26.53285 | 0.33567 |
表1 MG以及不同磷酸含量样品(002)晶面的晶格间距
Table 1 (002) lattice spacing for MG and different phosphoric acid content samples
| 样品 | λ/Å | 2θ/(°) | 晶格间距/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| MG | 0.15406 | 26.47204 | 0.33643 |
| MG-HPO-2 | 0.15406 | 26.52727 | 0.33574 |
| MG-HPO-3 | 0.15406 | 26.51931 | 0.33584 |
| MG-HPO-4 | 0.15406 | 26.52919 | 0.33572 |
| MG-HPO-5 | 0.15406 | 26.51398 | 0.33591 |
| MG-HPO-6 | 0.15406 | 26.53285 | 0.33567 |
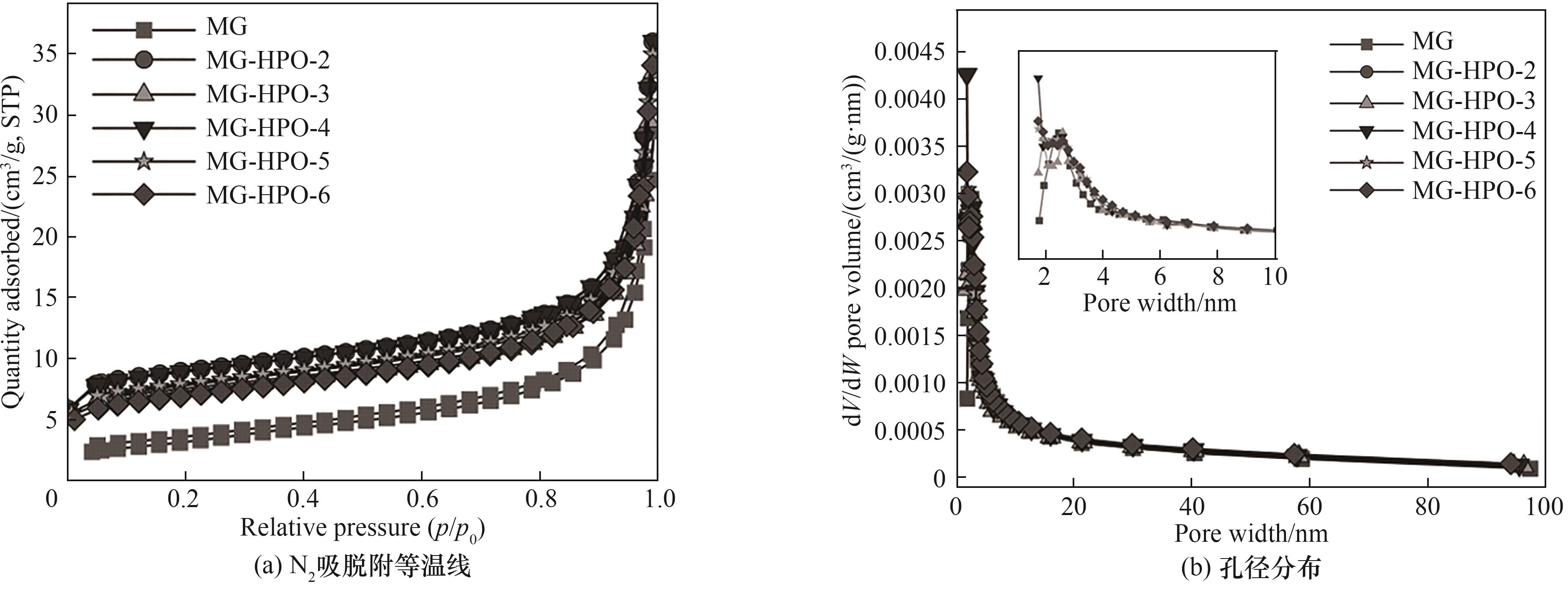
图3 MG以及不同磷酸含量样品的N2吸脱附等温线和孔径分布
Fig.3 N2 adsorption and desorption isotherm curves and pore size distribution curves for MG and samples with different phosphoric acid contents
| 样品 | P元素含量/%(质量分数) |
|---|---|
| MG | 0 |
| MG-HPO-2 | 2.630 |
| MG-HPO-3 | 2.631 |
| MG-HPO-4 | 4.963 |
| MG-HPO-5 | 3.491 |
| MG-HPO-6 | 2.847 |
表2 MG以及不同磷酸含量样品的P元素含量
Table 2 Content of element P in MG and samples with different phosphoric acid content
| 样品 | P元素含量/%(质量分数) |
|---|---|
| MG | 0 |
| MG-HPO-2 | 2.630 |
| MG-HPO-3 | 2.631 |
| MG-HPO-4 | 4.963 |
| MG-HPO-5 | 3.491 |
| MG-HPO-6 | 2.847 |
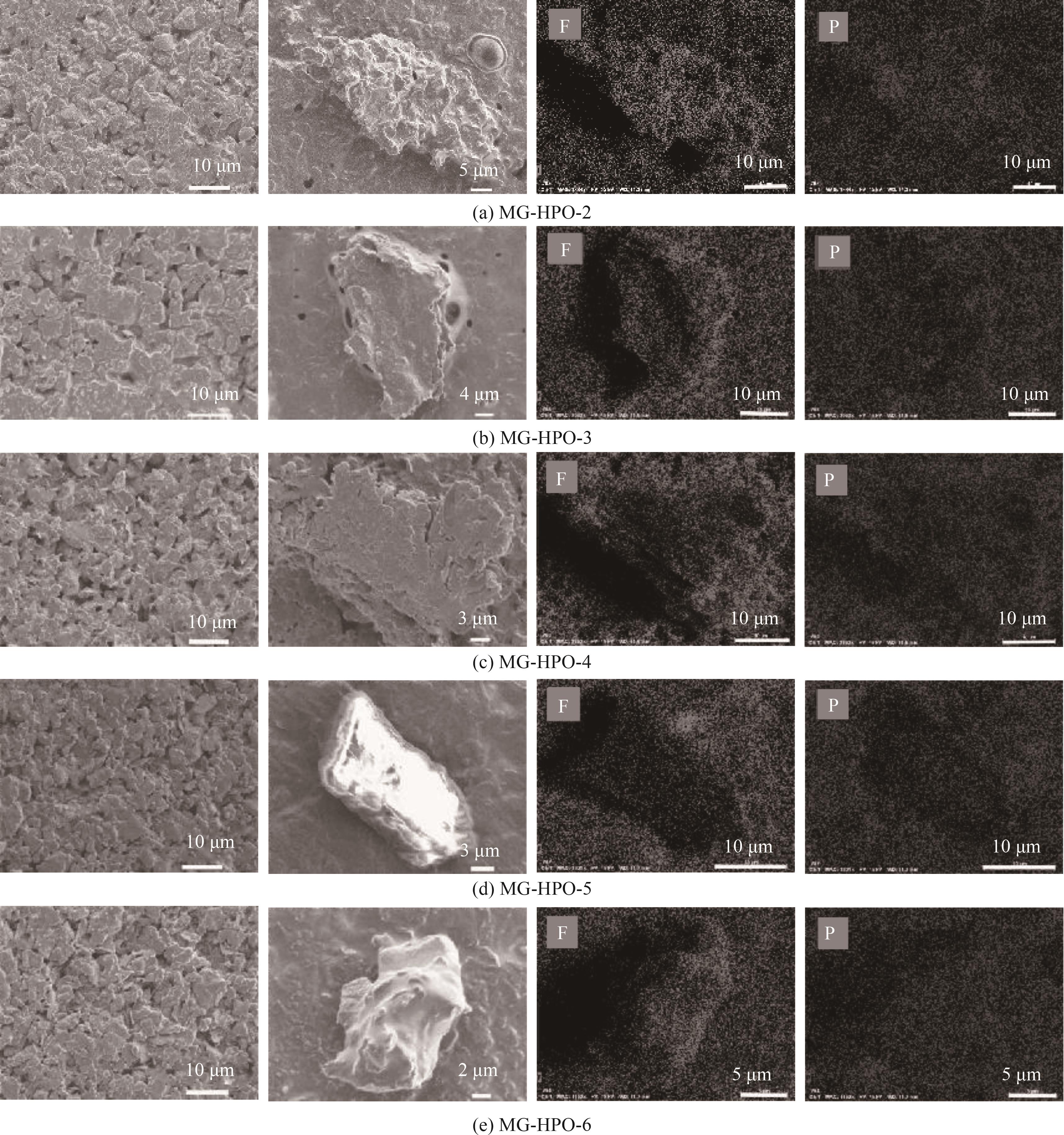
图5 不同磷酸含量样品在循环后的SEM图以及对应的P、F元素EDS面扫能谱图
Fig.5 SEM images and EDS surface scan energy spectra of P and F elements of samples with different phosphoric acid content after cycling
| 样品 | P元素含量/%(质量分数) | F元素含量/%(质量分数) |
|---|---|---|
| MG-HPO-2 | 2.0666 | 10.8394 |
| MG-HPO-3 | 2.0666 | 10.8394 |
| MG-HPO-4 | 5.2142 | 19.1342 |
| MG-HPO-5 | 2.2969 | 11.4470 |
| MG-HPO-6 | 2.2814 | 13.2386 |
表3 循环后不同磷酸含量样品的P、F元素的含量
Table 3 Mass percentage of P and F elements in samples with different phosphoric acid content after cycling
| 样品 | P元素含量/%(质量分数) | F元素含量/%(质量分数) |
|---|---|---|
| MG-HPO-2 | 2.0666 | 10.8394 |
| MG-HPO-3 | 2.0666 | 10.8394 |
| MG-HPO-4 | 5.2142 | 19.1342 |
| MG-HPO-5 | 2.2969 | 11.4470 |
| MG-HPO-6 | 2.2814 | 13.2386 |
| [6] | 吴德威, 汪郑鹏, 周玥, 等. 固定床法制备锂离子电池硅碳负极材料及其储锂性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(S1): 300-308. |
| Wu D W, Wang Z P, Zhou Y, et al. Preparation of silicon carbon anode for lithium-ion batteries by fixed bed and lithium storage properties[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(S1): 300-308. | |
| [7] | 万传云, 吴敏昌, 李辉, 等. 壳核结构改性天然石墨在电池中的应用[J]. 电池工业, 2006, 10(3): 151-153. |
| Wan C Y, Wu M C, Li H, et al. Application of micro-encapsulated modified natural graphite in Li-ion batteries[J]. Chinese Battery Industry, 2006, 10(3): 151-153. | |
| [8] | Zhang S S. The puzzles in fast charging of Li-ion batteries[J]. Energy & Environmental Materials, 2022, 5(4): 1005-1007. |
| [9] | Tang Z, Zhou S Y, Huang Y C, et al. Improving the initial coulombic efficiency of carbonaceous materials for Li/Na-ion batteries: origins, solutions, and perspectives[J]. Electrochemical Energy Reviews, 2023, 6(1): 8. |
| [10] | Yang S, Zhang S Q, Dong W, et al. Purification mechanism of microcrystalline graphite and lithium storage properties of purified graphite[J]. Materials Research Express, 2022, 9(2): 025505. |
| [11] | Zhou H Q, Zhang X W, Zhang X C, et al. N-doped microcrystalline graphite for boosting peroxymonosulfate activation with highly efficient degradation of bisphenol A[J]. Carbon, 2024, 216: 118579. |
| [12] | Kim D S, Lee J U, Kim S H, et al. Electrochemically exfoliated graphite as a highly efficient conductive additive for an anode in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Battery Energy, 2023, 2(5): 20230012. |
| [13] | Han X, Xu J X, Yu H X, et al. Highly efficient sulfur cathode built from biomass of hierarchical porous carbon for aqueous Cu-S batteries[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers, 2023, 10(13): 3844-3851. |
| [14] | Tian C X, Qin K, Suo L M. Concentrated electrolytes for rechargeable lithium metal batteries[J]. Materials Futures, 2023, 2(1): 012101. |
| [15] | Yu J F, Feng H P, Tang L, et al. Metal-free carbon materials for persulfate-based advanced oxidation process: microstructure, property and tailoring[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2020, 111: 100654. |
| [16] | Zhu D L, Yuan J C, Dai Y, et al. High-rate performance of fluorinated carbon material doped by phosphorus species for lithium-fluorinated carbon battery[J]. Energy Technology, 2022, 10(6): 2200155. |
| [17] | Zhang X, Yang S B, Chen Y H, et al. Effect of phosphorous-doped graphitic carbon nitride on electrochemical properties of lithium-sulfur battery[J]. Ionics, 2020, 26(11): 5491-5501. |
| [18] | Park H Y, Singh K P, Yang D S, et al. Simple approach to advanced binder-free nitrogen-doped graphene electrode for lithium batteries[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(5): 3881-3887. |
| [19] | Zhang H B, Liu K, Liu Y Y, et al. Observably improving initial coulombic efficiency of C/SiO x anode using -C-O-PO3Li2 groups in lithium ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2020, 447: 227400. |
| [20] | Li Y, Cao J, Wang L J, et al. Nitrogen-doped hollow carbon polyhedron derived from metal-organic frameworks for supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 55: 105485. |
| [21] | Pei S F, Cheng H M. The reduction of graphene oxide[J]. Carbon, 2012, 50(9): 3210-3228. |
| [22] | Wang J, Gao C H, Yang Z, et al. Carbon-coated mesoporous silicon shell-encapsulated silicon nano-grains for high performance lithium-ion batteries anode[J]. Carbon, 2022, 192: 277-284. |
| [23] | Valero-Romero M J, García-Mateos F J, Rodríguez-Mirasol J, et al. Role of surface phosphorus complexes on the oxidation of porous carbons[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2017, 157: 116-126. |
| [24] | Yang X Y, Zhen H G, Liu H Z, et al. Environmental-friendly and effectively regenerate anode material of spent lithium-ion batteries into high-performance P-doped graphite[J]. Waste Management, 2023, 161: 52-60. |
| [25] | Shi Q S, Zhang S N, Yan X X, et al. Acid-base encapsulation prepared N/P co-doped carbon-coated natural graphite for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2024, 952: 117990. |
| [26] | Xu Z L, Gang Y, Garakani M A, et al. Carbon-coated mesoporous silicon microsphere anodes with greatly reduced volume expansion[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(16): 6098-6106. |
| [27] | Li J B, Li J L, Ding Z B, et al. In-situ encapsulation of Ni3S2 nanoparticles into N-doped interconnected carbon networks for efficient lithium storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 378: 122108. |
| [1] | 陈昕, 赵宁, 刘桂贤, 等. 当前固体电解质与固态电池技术成熟度分析[J]. 电源技术, 2024, 48(6): 969-984. |
| Chen X, Zhao N, Liu G X, et al. Analysis of technology readiness level of solid-state electrolyte and solid-state battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 48(6): 969-984. | |
| [2] | 胡成志, 王国贤, 唐伟建, 等. 高比能锂离子电池高镍正极材料的表面包覆改性研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(11): 4020-4036. |
| Hu C Z, Wang G X, Tang W J, et al. Research progress on surface coating modification of nickel-rich cathode materials for high energy density lithium-ion battery[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(11): 4020-4036. | |
| [3] | 史淇森, 燕溪溪, 吴敏昌, 等. 锂离子电池石墨负极材料改性研究进展[J]. 电源技术, 2023, 47(7): 838-843. |
| Shi Q S, Yan X X, Wu M C, et al. Research progress on modification of graphite anode materials for lithium ion batteries[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2023, 47(7): 838-843. | |
| [4] | 赵子寿, 王家钧, 付甜甜. 锂离子电池前沿技术[J]. 电源技术, 2024, 48(5): 767-770. |
| Zhao Z S, Wang J J, Fu T T. Frontier technology of lithium ion battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2024, 48(5): 767-770. | |
| [5] | Skowroński J M, Knofczyński K. Catalytically graphitized glass-like carbon examined as anode for lithium-ion cell performing at high charge/discharge rates[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2009, 194(1): 81-87. |
| [28] | Xu K. Nonaqueous liquid electrolytes for lithium-based rechargeable batteries[J]. ChemInform, 2004, 104(10): 4303-4418. |
| [29] | Yang M M, Kong Q Q, Feng W, et al. Hierarchical porous nitrogen, oxygen, and phosphorus ternary doped hollow biomass carbon spheres for high-speed and long-life potassium storage[J]. Carbon Energy, 2022, 4(1): 45-59. |
| [30] | Yang X Y, Zhan C Z, Ren X L, et al. Nitrogen-doped hollow graphite granule as anode materials for high-performance lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2021, 303: 122500. |
| [31] | Zhou X, Liu X H, Qi F L, et al. Efficient preparation of P-doped carbon with ultra-high mesoporous ratio from furfural residue for dye removal[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2022, 292: 120954. |
| [1] | 孙国庆, 李海波, 丁志阳, 郭文辉, 徐浩, 赵艳侠. 硅基负极材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3197-3211. |
| [2] | 高凤凤, 程慧峰, 杨博, 郝晓刚. 电驱动NiFeMn LDH/CNTs/PVDF膜电极选择性提取钨酸根离子[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3350-3360. |
| [3] | 孙传付, 胡桂林, 曹俊杰, 左启斌, 陈媚, 夏玉珍. 梯度孔分布ZnO-GA锂离子电池负极材料研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3710-3718. |
| [4] | 王珺仪, 夏章讯, 景粉宁, 王素力. 基于重整气的高温聚合物电解质膜燃料电池电化学阻抗谱弛豫时间分布研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3509-3520. |
| [5] | 李欣然, 常龙娇, 罗绍华, 李永兵, 杨瑞芬, 侯增磊, 邹杰. Ho掺杂诱导NCM622局域电子重构抑制阳离子混排的改性机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3733-3741. |
| [6] | 王子恒, 李文怀, 周嵬. 图形电极在固体氧化物燃料电池中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3153-3171. |
| [7] | 陈培强, 郑群, 姜玉廷, 熊春华, 陈今茂, 王旭东, 黄龙, 阮曼, 徐万里. 电液流量及电流密度对海水激活电池输出特性的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3235-3245. |
| [8] | 张畅, 解强, 沙雨桐, 王炳杰, 梁鼎成, 刘金昌. 低灰低硅竹炭的制备及衍生硬炭的电化学性能[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3073-3083. |
| [9] | 孙文浩, 田君, 张锟, 刘娜, 曹宝森, 梁晓嫱. 锂离子电池用高热稳定性新型隔膜的研究新进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2524-2543. |
| [10] | 康佳, 刘欢, 李海燕, 罗茂亮, 姚洪. 宽温区HCl/NaOH热介质中碳钢腐蚀行为及涂层性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2872-2885. |
| [11] | 郭明钢, 杨晓航, 代岩, 米盼盼, 马世鑫, 贺高红, 肖武, 崔福军. 贫氦管输天然气提氦多元化产品耦合工艺优化设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2251-2261. |
| [12] | 李坤, 黄锐, 丛君, 马海涛, 常龙娇, 罗绍华. NCM622正极材料结构形态和储锂特性的同步演变[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1831-1840. |
| [13] | 吴迪, 刘世朋, 王文伟, 姜久春, 杨晓光. 机械压力对锂金属电池性能影响的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1422-1431. |
| [14] | 林纬, 杜建, 姚晨, 朱家豪, 汪威, 郑小涛, 徐建民, 喻九阳. 电化学水软化过程中离子输运与成核机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1788-1799. |
| [15] | 马钟琛, 魏子杰, 朱明涛, 叶恒棣, 郭学益, 谭磊. 一步氧化法制备锰酸锂正极材料用电池级四氧化三锰[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1363-1374. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号