化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (10): 5162-5175.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250182
王燕子1( ), 代佳楠1,2, 马晶1(
), 代佳楠1,2, 马晶1( ), 张腾月1, 梁子莉1
), 张腾月1, 梁子莉1
收稿日期:2025-02-26
修回日期:2025-04-23
出版日期:2025-10-25
发布日期:2025-11-25
通讯作者:
马晶
作者简介:王燕子(1998—),女,硕士研究生,1139338723@qq.com
基金资助:
Yanzi WANG1( ), Jia’nan DAI1,2, Jing MA1(
), Jia’nan DAI1,2, Jing MA1( ), Tengyue ZHANG1, Zili LIANG1
), Tengyue ZHANG1, Zili LIANG1
Received:2025-02-26
Revised:2025-04-23
Online:2025-10-25
Published:2025-11-25
Contact:
Jing MA
摘要:
近年来,稀土元素改性二氧化钛(TiO2)在环境催化领域展现出巨大潜力。采用溶剂热法制备了一系列稀土元素修饰的RE-B-TiO2(RE:Nd、Sm、Eu、Er、Tm)纳米催化剂,并系统探究了其在可见光下降解盐酸四环素(TCH)的性能与机理。其中Er-B-TiO2展现出最优的可见光催化性能。多尺度表征技术(XRD、TEM、XPS等)证实,Er-B-TiO2由具有双晶面暴露特征的双锥体纳米单元自组装形成纳米棒结构,这种独特的晶体构型显著促进了光生载流子的空间分离效率。在可见光照射下,Er-B-TiO2对TCH的降解效率在120 min内达到93.2%。深入研究表明,Er3+掺杂通过以下协同效应显著提升催化性能:(1)引入丰富的氧空位缺陷;(2)有效抑制光生电子-空穴复合;(3)通过4f能级调控将光响应范围扩展至可见光区。系统考察了环境因素对降解效率的影响,发现溶液pH和特定阴离子(如Cl-、
中图分类号:
王燕子, 代佳楠, 马晶, 张腾月, 梁子莉. 稀土元素(RE: Nd、Sm、Eu、Er、Tm)修饰B-TiO2氧空位特性及其催化性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(10): 5162-5175.
Yanzi WANG, Jia’nan DAI, Jing MA, Tengyue ZHANG, Zili LIANG. Oxygen vacancy characteristics and photocatalytic performance of rare earth elements (RE: Nd, Sm, Eu, Er, Tm) doped B-TiO₂[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(10): 5162-5175.
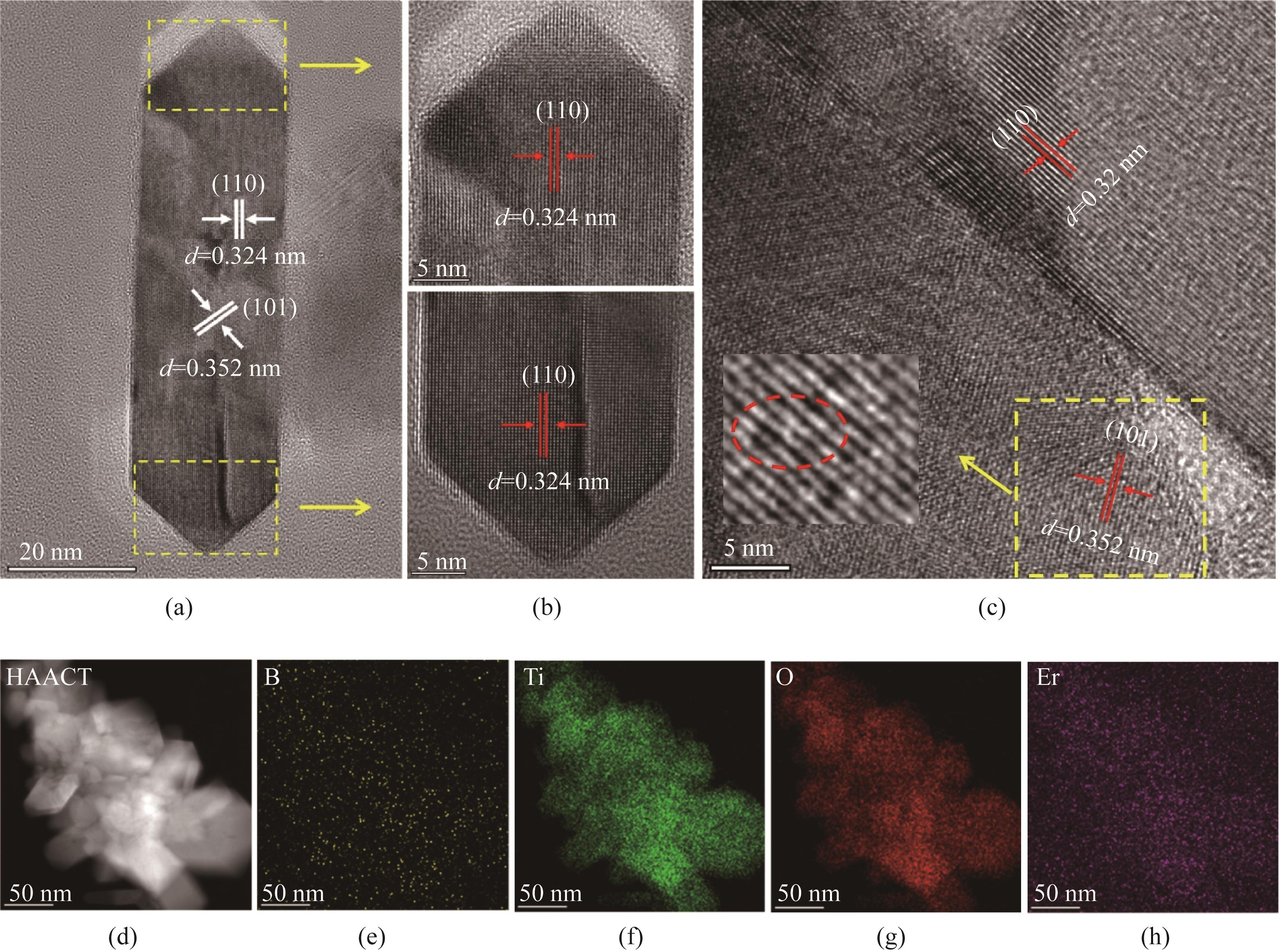
图4 (a)~(c) Er-B-TiO2的TEM谱图;Er-B-TiO2的元素分布图:(d) HAACT, (e) B, (f) Ti, (g) O, (h) Er
Fig.4 (a)—(c) TEM images of Er-B-TiO2; Element mapping of Er-B-TiO2:(d) HAACT, (e) B, (f) Ti, (g) O, (h) Er

图9 (a) 光催化降解TCH循环实验;(b) 循环前后的XRD谱图
Fig.9 (a) Cycling experiments of photocatalytic degradation of TCH and (b) XRD patterns before and after reaction of Er-B-TiO2
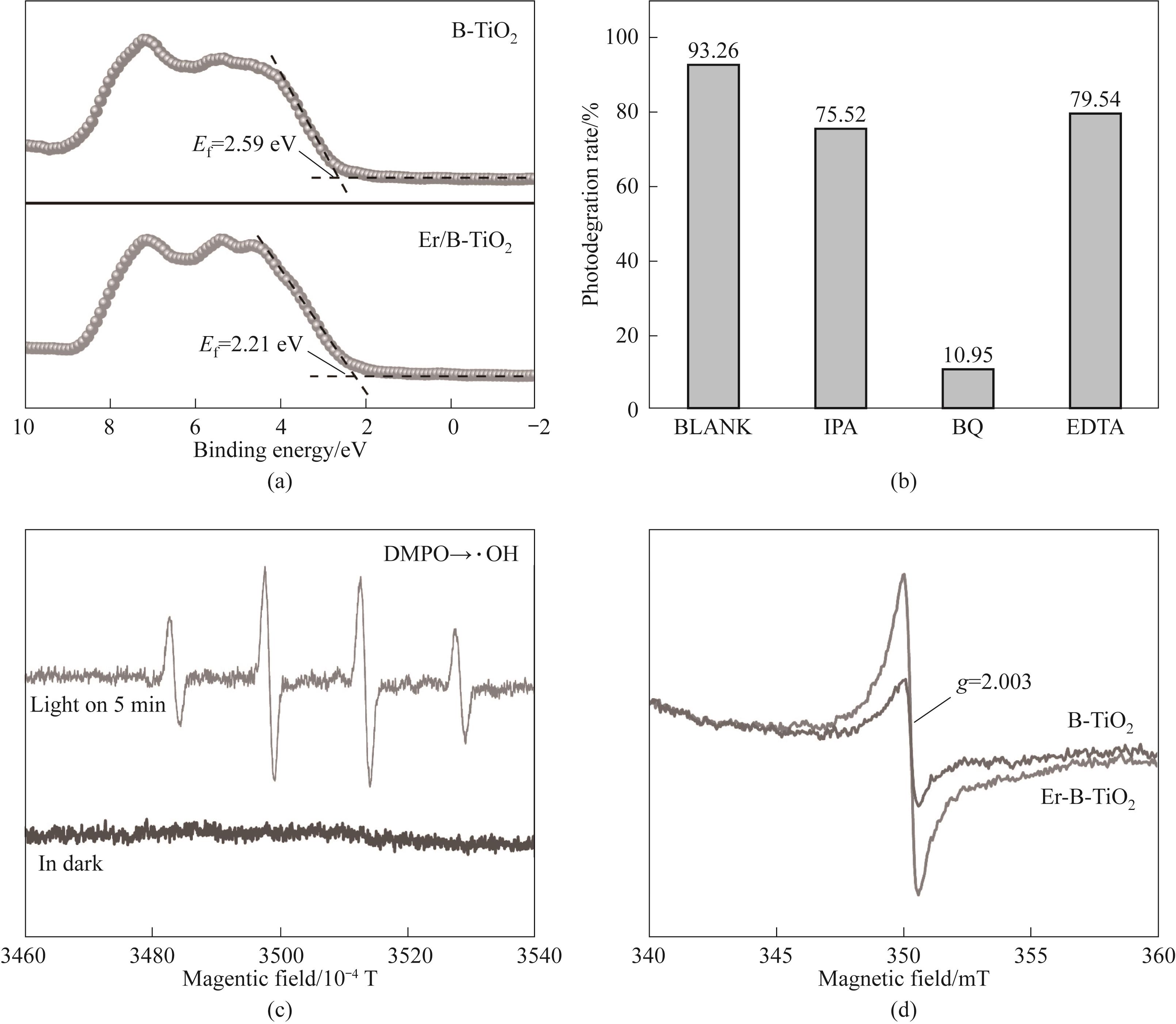
图11 (a) B-TiO2和Er-B-TiO2的价带谱;(b) TCH降解的自由基捕获实验;(c) RE-B-TiO2的EPR谱图;(d) B-TiO2和Er-B-TiO2的氧空位谱图
Fig.11 (a) Valence band spectrum of B-TiO2 and Er-B-TiO2; (b) Free radical capture experiment for degradation of TCH; (c) EPR spectra of RE-B-TiO2; (d) OVs spectra of B-TiO2 and Er-B-TiO2

图13 (a)水蚤大LC50(48 h)、(b)诱变性、(c)发育毒性和(d)生物积累因子对Er-B-TiO2的降解中间体的毒性评价
Fig.13 Toxicity evaluation of TCH and its degradation intermediates for Er-B-TiO2: (a) Daphnia magna LC50 (48 h), (b) mutagenicity, (c) development toxicity, and (d) bioaccumulation factor
| [1] | Gao Y W, Chen Z H, Zhu Y, et al. New insights into the generation of singlet oxygen in the metal-free peroxymonosulfate activation process: important role of electron-deficient carbon atoms[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 54(2): 1232-1241. |
| [2] | Zhan X Y, Zeng Y X, Zhang H, et al. The coral-like carbon nitride array: rational design for efficient photodegradation of tetracycline under visible light[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2023, 11(1): 109201. |
| [3] | Mustafa F S, Aziz K H H. Heterogeneous catalytic activation of persulfate for the removal of rhodamine B and diclofenac pollutants from water using iron-impregnated biochar derived from the waste of black seed pomace[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2023, 170: 436-448. |
| [4] | Du S W, Zou H, Bao Y F, et al. Homogeneous nitrogen-doped (111)-type layered Sr5Nb4O15– x N x as a visible-light-responsive photocatalyst for water oxidation[J]. Nano Research, 2022, 15(12): 9976-9984. |
| [5] | Wang L J, Zhang Z, Guan R Q, et al. Synergistic CO2 reduction and tetracycline degradation by CuInZnS-Ti3C2T x in one photoredox cycle[J]. Nano Research, 2022, 15(9): 8010-8018. |
| [6] | 梁梦欣,郭艳,王世栋,等.氮化碳负载钯催化剂的制备及对SBS选择性催化加氢性能的研究[J].化工学报,2023,74(2):766-775. |
| Liang M X, Guo Y, Wang S D, et al. Study on preparation of Pd catalyst supported on carbon nitride for the selective hydrogenation of SBS[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(2): 766-775. | |
| [7] | 谈朋, 李雪梅, 刘晓勤,等. 基于柔性MOFs的磁响应复合材料及其丙烯吸附性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2230-2240. |
| Tan P, Li X M, Liu X Q, et al. Study on magnetically responsive composite materials based on flexible MOFs and their propylene adsorption performance[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(5): 2230-2240. | |
| [8] | Hu D K, Qiu D P, Zeng L W, et al. Solar-driven nitrogen fixation catalyzed by stable radical-containing MOFs: improved efficiency induced by a structural transformation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(46): 20666-20671. |
| [9] | Liang P L, Yuan L Y, Du K, et al. Photocatalytic reduction of uranium(Ⅵ) under visible light with 2D/1D Ti3C2/CdS[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 420: 129831. |
| [10] | Zhang J, Gao M T, Wang R Y, et al. Switching of CO2 hydrogenation selectivity via chlorine poisoning over Ru/TiO2 catalyst[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16(4): 4786-4792. |
| [11] | 吴云, 龚海峰. 疏水改性羰基铁负载TiO2光催化降解石油烃污染物[J]. 化工学报, 2024: 75(12): 4555-4562. |
| Wu Y, Gong H F. Carbonyl iron loaded TiO2 photocatalyst by hydrophobic modification for degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants in water[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(12): 4555-4562. | |
| [12] | Yavuz C, Ela S E. Fabrication of g-C3N4-reinforced CdS nanosphere-decorated TiO2 nanotablet composite material for photocatalytic hydrogen production and dye-sensitized solar cell application[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 936: 168209. |
| [13] | Mazierski P, Mikolajczyk A, Bajorowicz B, et al. The role of lanthanides in TiO2-based photocatalysis: a review[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 233: 301-317. |
| [14] | Ru Y X, Chen Y J, Yu X Y, et al. Enhanced charge separation of Cu-BTC@CuSe@TiO2 hollow octahedrons for efficient CO2 photoreduction with superior CO selectivity[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 349: 127784. |
| [15] | Kumaravel V, Mathew S, Bartlett J, et al. Photocatalytic hydrogen production using metal doped TiO2: a review of recent advances[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 244: 1021-1064. |
| [16] | Bilgin Simsek E. Solvothermal synthesized boron doped TiO2 catalysts: photocatalytic degradation of endocrine disrupting compounds and pharmaceuticals under visible light irradiation[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2017, 200: 309-322. |
| [17] | Feng N, Zheng A, Wang Q, et al. Boron environments in B-doped and (B, N)-codoped TiO2 photocatalysts: a combined solid-state NMR and theoretical calculation study[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(6): 2709-2719. |
| [18] | Christoforidis D K C, Montini D T, Fittipaldi D M, et al. Photocatalytic hydrogen production by boron modified TiO2/carbon nitride heterojunctions[J]. ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(24): 6408-6416. |
| [19] | Wu D P, Guo J, Wang H J, et al. Green synthesis of boron and nitrogen co-doped TiO2 with rich BN motifs as Lewis acid-base couples for the effective artificial CO2 photoreduction under simulated sunlight[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 585: 95-107. |
| [20] | Liu C W, Hao D, Ye J, et al. Knowledge-driven design and lab-based evaluation of B-doped TiO2 photocatalysts for ammonia synthesis[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2023, 13(8): 2204126. |
| [21] | Mo Z, Miao Z H, Yan P C, et al. Electronic and energy level structural engineering of graphitic carbon nitride nanotubes with B and S co-doping for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 645: 525-532. |
| [22] | Rong W, Ding M, Wang Y, et al. Porous biochar with a tubular structure for photothermal CO2 cycloaddition: one-step doping versus two-step doping[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 353: 128427. |
| [23] | Zheng B Z, Fan J Y, Chen B, et al. Rare-earth doping in nanostructured inorganic materials[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2022, 122(6): 5519-5603. |
| [24] | Tiwari D, Lee S M, Kim D J, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of amoxicillin and tetracycline by template synthesized nano-structured Ce3+@TiO2 thin film catalyst[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 210: 112914. |
| [25] | Prakash J, Samriti, Kumar A, et al. Novel rare earth metal–doped one-dimensional TiO2 nanostructures: fundamentals and multifunctional applications[J]. Materials Today Sustainability, 2021, 13: 100066. |
| [26] | Wu Q, Zhang Q, Li W P, et al. Tailoring of visible light driven photocatalytic activities of Bi2MoO6 flower-like microspheres via synergistic effect of doping and surface Plasmon resonance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 475: 146192. |
| [27] | Chen L Y, Zhang P K, Kuo D H, et al. Synergism of heterovalent valence state and oxygen vacancy defect engineering in Co/S co-doped TiO2 for nitrogen photoreduction to ammonia[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2024, 12(16): 9871-9885. |
| [28] | Chen Y, Liu K R. Fabrication of Ce/N co-doped TiO2/diatomite granule catalyst and its improved visible-light-driven photoactivity[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 324: 139-150. |
| [29] | Ma K W, Zhang M Y, Sun W J, et al. Revealing different depth boron substitution on interfacial charge transfer in TiO2 for enhanced visible-light H2 production[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2022, 315: 121570. |
| [30] | Das D, Shyam S. Reduced work function in anatase <101> TiO2 films self-doped by O-vacancy-dependent Ti3+ bonds controlling the photocatalytic dye degradation performance[J]. Langmuir, 2024, 40(20): 10502-10517. |
| [31] | Wang R, Xu M, Xie J W, et al. A spherical TiO2-Bi2WO6 composite photocatalyst for visible-light photocatalytic degradation of ethylene[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2020, 602: 125048. |
| [32] | Acharya L, Pattnaik S P, Behera A, et al. Exfoliated boron nitride (e-BN) tailored exfoliated graphitic carbon nitride (e-CN): an improved visible light mediated photocatalytic approach towards TCH degradation and H2 evolution[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2021, 60(7): 5021-5033. |
| [33] | Mikolajczyk A, Wyrzykowska E, Mazierski P, et al. Visible-light photocatalytic activity of rare-earth-metal-doped TiO2: experimental analysis and machine learning for virtual design[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environment and Energy, 2024, 346: 123744. |
| [34] | 张佳颖, 王聪, 王雅君. CNT-Co/Bi2O3催化剂光催化协同过硫酸盐活化高效降解四环素[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3163-3175. |
| Zhang J Y, Wang C, Wang Y J. CNT-Co/Bi2O3 catalyst photocatalytic synergistic activation of persulfate for efficient degradation of tetracycline[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3163-3175. | |
| [35] | Sengottiyan S, Mikolajczyk A, Jagiełło K, et al. Core, coating, or corona? The importance of considering protein coronas in nano-QSPR modeling of zeta potential[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(3): 1989-1997. |
| [36] | Ren X H, Yao H, Tang R, et al. Modification of TiO2 by Er3+ and rGO enhancing visible photocatalytic degradation of arsanilic acid[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2023, 30(12): 35023-35033. |
| [37] | Parnicka P, Lisowski W, Klimczuk T, et al. Visible-light-driven lanthanide-organic-frameworks modified TiO2 photocatalysts utilizing up-conversion effect[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2021, 291: 120056. |
| [38] | Zhang S Q, Zhang J, Sun J, et al. Capillary microphotoreactor packed with TiO2-coated glass beads: an efficient tool for photocatalytic reaction[J]. Chemical Engineering and Processing - Process Intensification, 2020, 147: 107746. |
| [39] | Parrino F, Bellardita M, García-López E I, et al. Heterogeneous photocatalysis for selective formation of high-value-added molecules: some chemical and engineering aspects[J]. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(12): 11191-11225. |
| [40] | 皮若冰, 周云龙. 直接Z型异质结体系光催化还原二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(10): 3379-3400. |
| Pi R B, Zhou Y L. Research progress on photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide in direct Z-scheme heterojunctions system[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(10): 3379-3400. | |
| [41] | Lin Z T, Ye S J, Xu Y B, et al. Construction of a novel efficient Z-scheme BiVO4/EAQ heterojunction for the photocatalytic inactivation of antibiotic-resistant pathogens: Performance and mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 453: 139747. |
| [42] | Reszczyńska J, Grzyb T, Wei Z S, et al. Photocatalytic activity and luminescence properties of RE3+-TiO2 nanocrystals prepared by sol-gel and hydrothermal methods[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 181: 825-837. |
| [43] | Tian K G, Jin L J, Mahmood A, et al. Lattice distortion promotes carrier separation to improve the photoelectrochemical water splitting performance of bismuth vanadate photoanode[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(51): 2410548. |
| [44] | Fang W J, Yan J W, Wei Z D, et al. Account of doping photocatalyst for water splitting[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2024, 60: 1-24. |
| [45] | Zhao D X, Cai C. Layered Ti3C2 MXene modified two-dimensional Bi2WO6 composites with enhanced visible light photocatalytic performance[J]. Materials Chemistry Frontiers, 2019, 3(11): 2521-2528. |
| [46] | Liu F, Feng N D, Wang Q, et al. Transfer channel of photoinduced holes on a TiO2 surface As revealed by solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance and electron spin resonance spectroscopy[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017, 139(29): 10020-10028. |
| [47] | Zhang L, Tan L, Yuan Z X, et al. Engineering of Bi2O2CO3/Ti3C2T x heterojunctions co-embedded with surface and interface oxygen vacancies for boosted photocatalytic degradation of levofloxacin[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 452: 139327. |
| [48] | Chen L, Ji H D, Qi J J, et al. Degradation of acetaminophen by activated peroxymonosulfate using Co(OH)2 hollow microsphere supported titanate nanotubes: insights into sulfate radical production pathway through CoOH+ activation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 406: 126877. |
| [49] | Mao S, Zhao P, Wu Y, et al. Promoting charge migration of Co(OH)2/ g-C3N4 by hydroxylation for improved PMS activation: catalyst design, DFT calculation and mechanism analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 451: 138503. |
| [50] | Li H, Ji H D, Liu J J, et al. Interfacial modulation of ZnIn2S4 with high active Zr-S4 sites for boosting photocatalytic activation of oxygen and degradation of emerging contaminant[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2023, 328: 122481. |
| [1] | 张圣美, 李明, 张莹, 易茜, 杨依婷, 刘雅莉. 乳化剂和温度对相变微胶囊性能的影响分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 444-452. |
| [2] | 赵维, 邢文乐, 韩朝旭, 袁兴中, 蒋龙波. g-C3N4基非金属异质结光催化降解水中有机污染物的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4752-4769. |
| [3] | 钱慧慧, 王文婕, 陈文尧, 周兴贵, 张晶, 段学志. 聚丙烯定向转化制芳烃:金属-分子筛协同催化机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4838-4849. |
| [4] | 佟丽丽, 陈英, 艾敏华, 舒玉美, 张香文, 邹吉军, 潘伦. ZnO/WO3异质结光催化环烯烃[2+2]环加成制备高能量密度燃料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4882-4892. |
| [5] | 巢欣旖, 陈文尧, 张晶, 钱刚, 周兴贵, 段学志. 甲醇和乙酸甲酯一步法制丙酸甲酯催化剂的可控制备与性能调控[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4030-4041. |
| [6] | 张荟钦, 赵泓竣, 付正军, 庄力, 董凯, 贾添智, 曹雪丽, 孙世鹏. 纳滤膜在离子型稀土浸出液提浓中的应用研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4095-4107. |
| [7] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [8] | 杨宁, 李皓男, LIN Xiao, GEORGIADOU Stella, LIN Wen-Feng. 从塑料废弃物到能源催化剂:塑料衍生碳@CoMoO4复合材料在电解水析氢反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [9] | 林嘉豪, 付芳忠, 叶昊辉, 胡金, 姚明灿, 范鹤林, 王旭, 王瑞祥, 徐志峰. NdF3含量对NdF3-LiF熔盐局域结构和输运性质的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3834-3841. |
| [10] | 陆学瑞, 周帼彦, 方琦, 俞孟正, 张秀成, 涂善东. 固体氧化物燃料电池外重整器积炭效应数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3295-3304. |
| [11] | 赵世颖, 左志帅, 贺梦颖, 安华良, 赵新强, 王延吉. Co-Pt/HAP的制备及其催化1,2-丙二醇氨化反应[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3305-3315. |
| [12] | 李愽龙, 蒋雨希, 任傲天, 秦雯琪, 傅杰, 吕秀阳. TS-1/In-TS-1催化果糖一步法醇解制备乳酸甲酯连续化试验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2678-2686. |
| [13] | 何军, 李勇, 赵楠, 何孝军. 碳负载硒掺杂硫化钴在锂硫电池中的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2995-3008. |
| [14] | 宋粉红, 王文光, 郭亮, 范晶. C元素修饰g-C3N4对TiO2的调控及复合材料光催化产氢性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2983-2994. |
| [15] | 茅雨洁, 路晓飞, 锁显, 杨立峰, 崔希利, 邢华斌. 工业气体中微量氧深度脱除催化剂研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 1997-2010. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号