化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (12): 6587-6600.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250447
周晨阳( ), 商浩杰, 胡杨, 曹天航, 姚尔人(
), 商浩杰, 胡杨, 曹天航, 姚尔人( ), 席光
), 席光
收稿日期:2025-04-27
修回日期:2025-07-06
出版日期:2025-12-31
发布日期:2026-01-23
通讯作者:
姚尔人
作者简介:周晨阳(2004—),男,本科生,zcy2789866672@stu.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Chenyang ZHOU( ), Haojie SHANG, Yang HU, Tianhang CAO, Erren YAO(
), Haojie SHANG, Yang HU, Tianhang CAO, Erren YAO( ), Guang XI
), Guang XI
Received:2025-04-27
Revised:2025-07-06
Online:2025-12-31
Published:2026-01-23
Contact:
Erren YAO
摘要:
热泵储电是实现高比例新能源电力系统稳定运行的大规模长时物理储能技术,而推动大规模高效储能应用以及改善火电深度调峰能力是保障新能源电力充分消纳与煤电低碳转型的重要途径。为此,开发了一种集成余热回收的多压超临界CO2热泵储电系统,不仅可以实现火电厂低品位烟气余热的高效回收与利用,并且通过引入多级储热拓扑与分布式回热装置,大幅降低了热泵储电系统在换热过程由于温度滑移问题导致的不可逆损失,实现了火电机组灵活调峰和可再生能源安全并网。在建立系统热力学与经济学模型的基础上,采用敏感性分析方法研究了关键运行参数对系统热力学性能与经济性能的影响规律,进而采用遗传算法开展了系统的热经济学多目标优化分析。结果表明,系统在设计工况下的性能指标㶲效率为53.83%,平准化度电成本为2063.26 CNY·MWh-1;在关键参数中,放电膨胀机等熵效率对系统热力学性能影响最显著,而充电膨胀机等熵效率对系统经济学性能影响最显著。根据TOPSIS方法在Pareto最优前沿解集中获得的最优工况㶲效率为58.20%、平准化度电成本为1142.24 CNY·MWh-1,较设计工况分别提升8.12%与降低44.64%。
中图分类号:
周晨阳, 商浩杰, 胡杨, 曹天航, 姚尔人, 席光. 集成余热回收的多压超临界CO2热泵储电系统热经济学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(12): 6587-6600.
Chenyang ZHOU, Haojie SHANG, Yang HU, Tianhang CAO, Erren YAO, Guang XI. Thermo-economic analysis of a multi-pressure supercritical CO₂ pumped thermal energy storage system integrated with waste heat recovery[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(12): 6587-6600.
| 设备 | 成本函数 |
|---|---|
| 充电压缩机 | |
| 放电压缩机 | |
| 充电膨胀机 | |
| 放电膨胀机 | |
| 换热器 | |
| 储罐 | |
| 冷凝器 | |
| 烟气换热器 | |
| 回热器 |
表1 系统设备的采购成本方程[24-26]
Table 1 The procurement cost equation of system equipment[24-26]
| 设备 | 成本函数 |
|---|---|
| 充电压缩机 | |
| 放电压缩机 | |
| 充电膨胀机 | |
| 放电膨胀机 | |
| 换热器 | |
| 储罐 | |
| 冷凝器 | |
| 烟气换热器 | |
| 回热器 |
| 流股点 | 压力/kPa | 温度/K | 相对误差/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 本文 | |||
| 1 | 1500 | 523.15 | 523.15 | 0 |
| 2 | 8000 | 739.95 | 736.22 | 0.50 |
| 3 | 8000 | 545.45 | 546.51 | 0.19 |
| 4 | 8000 | 373.15 | 373.15 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 1500 | 251.94 | 254.97 | 1.20 |
| 6 | 1500 | 319.15 | 319.15 | 0 |
| 7 | 8000 | 729.95 | 726.22 | 0.51 |
| 8 | 1500 | 558.05 | 557.45 | 0.11 |
| 9 | 1500 | 408.85 | 410.22 | 0.34 |
| 10 | 1500 | 327.45 | 327.99 | 0.16 |
| 11 | 1500 | 259.94 | 262.97 | 1.17 |
| 12 | 8000 | 403.75 | 404.76 | 0.25 |
| 13 | 8000 | 535.15 | 536.09 | 0.18 |
表2 模型验证
Table 2 Model validation
| 流股点 | 压力/kPa | 温度/K | 相对误差/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 本文 | |||
| 1 | 1500 | 523.15 | 523.15 | 0 |
| 2 | 8000 | 739.95 | 736.22 | 0.50 |
| 3 | 8000 | 545.45 | 546.51 | 0.19 |
| 4 | 8000 | 373.15 | 373.15 | 0.00 |
| 5 | 1500 | 251.94 | 254.97 | 1.20 |
| 6 | 1500 | 319.15 | 319.15 | 0 |
| 7 | 8000 | 729.95 | 726.22 | 0.51 |
| 8 | 1500 | 558.05 | 557.45 | 0.11 |
| 9 | 1500 | 408.85 | 410.22 | 0.34 |
| 10 | 1500 | 327.45 | 327.99 | 0.16 |
| 11 | 1500 | 259.94 | 262.97 | 1.17 |
| 12 | 8000 | 403.75 | 404.76 | 0.25 |
| 13 | 8000 | 535.15 | 536.09 | 0.18 |
| 参数 | 数值 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 环境温度/℃ | 25 | [ |
| 环境压力/kPa | 101.325 | [ |
| 压缩机进口压力/kPa | 7600 | [ |
| 压缩机出口压力/kPa | 25000 | [ |
| 充电压缩机进口温度/℃ | 220 | [ |
| 放电压缩机进口温度/℃ | 32 | [ |
| 充电循环质量流量/(kg·s-1) | 100 | [ |
| 放电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5 | [ |
| 充电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5 | [ |
| 充电压缩机等熵效率/% | 85 | [ |
| 充电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 90 | [ |
| 放电压缩机等熵效率/% | 80 | [ |
| 放电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 90 | [ |
表3 充放电初始参数
Table 3 Charge and discharge initial parameters
| 参数 | 数值 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|
| 环境温度/℃ | 25 | [ |
| 环境压力/kPa | 101.325 | [ |
| 压缩机进口压力/kPa | 7600 | [ |
| 压缩机出口压力/kPa | 25000 | [ |
| 充电压缩机进口温度/℃ | 220 | [ |
| 放电压缩机进口温度/℃ | 32 | [ |
| 充电循环质量流量/(kg·s-1) | 100 | [ |
| 放电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5 | [ |
| 充电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5 | [ |
| 充电压缩机等熵效率/% | 85 | [ |
| 充电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 90 | [ |
| 放电压缩机等熵效率/% | 80 | [ |
| 放电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 90 | [ |
| 流股 | 温度/K | 压力/kPa | 比焓/(kJ·kg-1) | 比熵/(kJ·(kg·K) -1) | 质量流量/(kg·s-1) | 㶲/MW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 306.28 | 7600 | 372.27 | 1.563 | 100 | 21.640 |
| 2 | 322.32 | 7600 | 442.00 | 1.787 | 100 | 21.947 |
| 3 | 413.06 | 7600 | 572.08 | 2.146 | 100 | 24.225 |
| 4 | 493.15 | 7600 | 663.65 | 2.349 | 100 | 27.337 |
| 5 | 642.03 | 25000 | 805.59 | 2.383 | 100 | 40.529 |
| 6 | 528.87 | 25000 | 660.43 | 2.134 | 100 | 33.436 |
| 7 | 463.73 | 25000 | 568.86 | 1.949 | 100 | 29.795 |
| 8 | 373.15 | 25000 | 404.40 | 1.551 | 100 | 25.199 |
| 9 | 305.15 | 7600 | 315.08 | 1.376 | 80 | 17.200 |
| 10 | 348.01 | 25000 | 348.00 | 1.395 | 80 | 19.380 |
| 11 | 453.73 | 25000 | 553.58 | 1.916 | 80 | 23.408 |
| 12 | 493.15 | 25000 | 611.59 | 2.038 | 80 | 25.123 |
| 13 | 632.03 | 25000 | 793.04 | 2.363 | 80 | 31.889 |
| 14 | 510.19 | 7600 | 682.80 | 2.387 | 80 | 22.491 |
| 15 | 458.73 | 7600 | 624.80 | 2.268 | 80 | 20.709 |
| 16 | 332.32 | 7600 | 462.19 | 1.848 | 80 | 17.701 |
| 17 | 360.58 | 2000 | 114.61 | 0.345 | 85.26 | 1.003 |
| 18 | 458.73 | 2000 | 307.50 | 0.817 | 85.26 | 5.465 |
| 19 | 511.01 | 2000 | 424.33 | 1.058 | 44.83 | 4.890 |
| 20 | 637.03 | 2000 | 748.13 | 1.622 | 44.83 | 11.862 |
| 21 | 435.90 | 2000 | 259.58 | 0.709 | 64.17 | 3.088 |
| 22 | 327.32 | 2000 | 56.87 | 0.177 | 64.17 | 0.263 |
| 23 | 332.32 | 101.325 | 332.86 | 6.970 | 328.94 | 0.603 |
| 24 | 311.28 | 101.325 | 311.67 | 6.904 | 328.94 | 0.093 |
表4 流股参数
Table 4 Flow stock parameters
| 流股 | 温度/K | 压力/kPa | 比焓/(kJ·kg-1) | 比熵/(kJ·(kg·K) -1) | 质量流量/(kg·s-1) | 㶲/MW |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 306.28 | 7600 | 372.27 | 1.563 | 100 | 21.640 |
| 2 | 322.32 | 7600 | 442.00 | 1.787 | 100 | 21.947 |
| 3 | 413.06 | 7600 | 572.08 | 2.146 | 100 | 24.225 |
| 4 | 493.15 | 7600 | 663.65 | 2.349 | 100 | 27.337 |
| 5 | 642.03 | 25000 | 805.59 | 2.383 | 100 | 40.529 |
| 6 | 528.87 | 25000 | 660.43 | 2.134 | 100 | 33.436 |
| 7 | 463.73 | 25000 | 568.86 | 1.949 | 100 | 29.795 |
| 8 | 373.15 | 25000 | 404.40 | 1.551 | 100 | 25.199 |
| 9 | 305.15 | 7600 | 315.08 | 1.376 | 80 | 17.200 |
| 10 | 348.01 | 25000 | 348.00 | 1.395 | 80 | 19.380 |
| 11 | 453.73 | 25000 | 553.58 | 1.916 | 80 | 23.408 |
| 12 | 493.15 | 25000 | 611.59 | 2.038 | 80 | 25.123 |
| 13 | 632.03 | 25000 | 793.04 | 2.363 | 80 | 31.889 |
| 14 | 510.19 | 7600 | 682.80 | 2.387 | 80 | 22.491 |
| 15 | 458.73 | 7600 | 624.80 | 2.268 | 80 | 20.709 |
| 16 | 332.32 | 7600 | 462.19 | 1.848 | 80 | 17.701 |
| 17 | 360.58 | 2000 | 114.61 | 0.345 | 85.26 | 1.003 |
| 18 | 458.73 | 2000 | 307.50 | 0.817 | 85.26 | 5.465 |
| 19 | 511.01 | 2000 | 424.33 | 1.058 | 44.83 | 4.890 |
| 20 | 637.03 | 2000 | 748.13 | 1.622 | 44.83 | 11.862 |
| 21 | 435.90 | 2000 | 259.58 | 0.709 | 64.17 | 3.088 |
| 22 | 327.32 | 2000 | 56.87 | 0.177 | 64.17 | 0.263 |
| 23 | 332.32 | 101.325 | 332.86 | 6.970 | 328.94 | 0.603 |
| 24 | 311.28 | 101.325 | 311.67 | 6.904 | 328.94 | 0.093 |
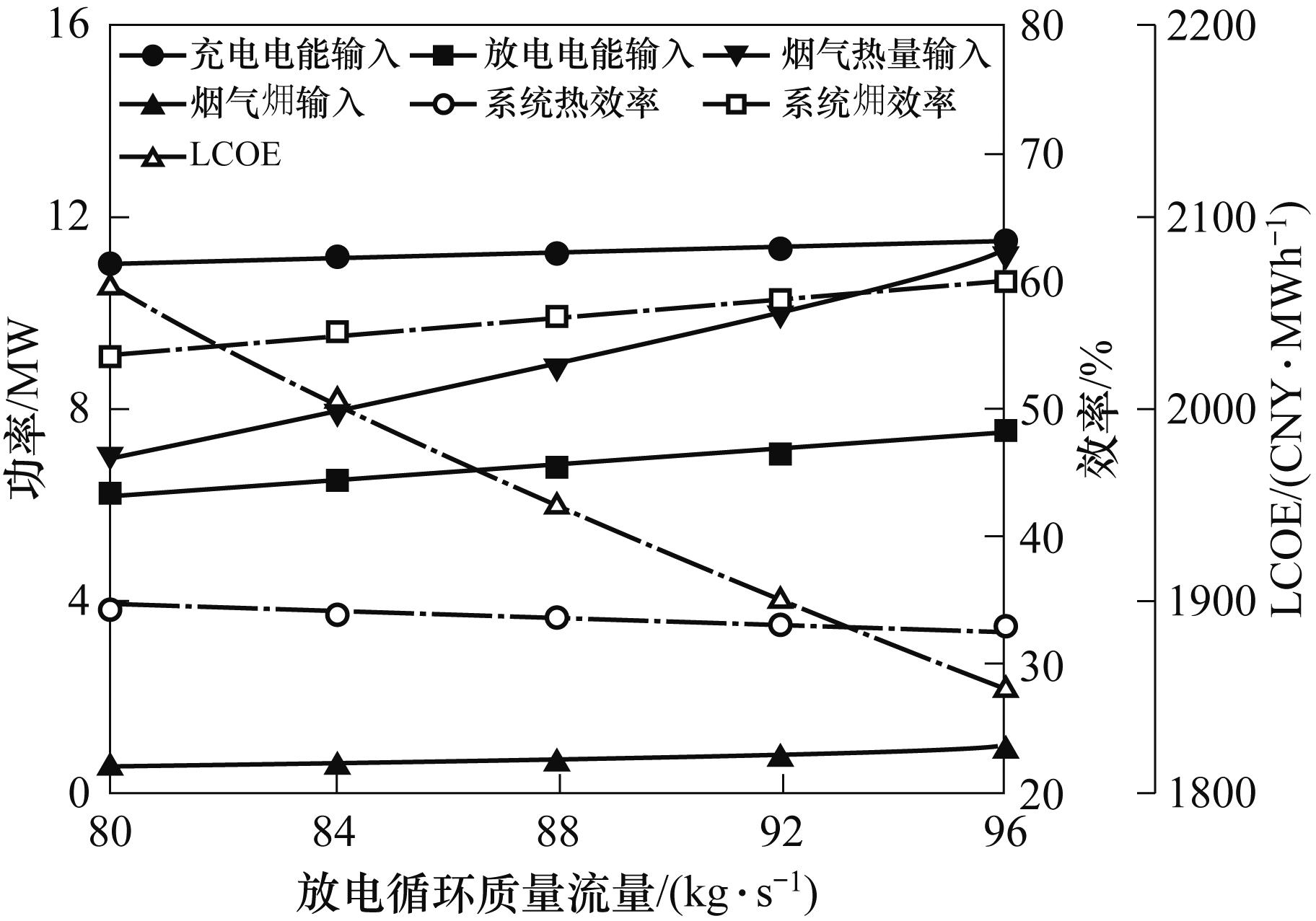
图4 放电循环质量流量对能量输入、能量输出、系统效率和LCOE的影响
Fig.4 Effect of mass flow rate during discharging process on energy input, energy output, system efficiency and LCOE
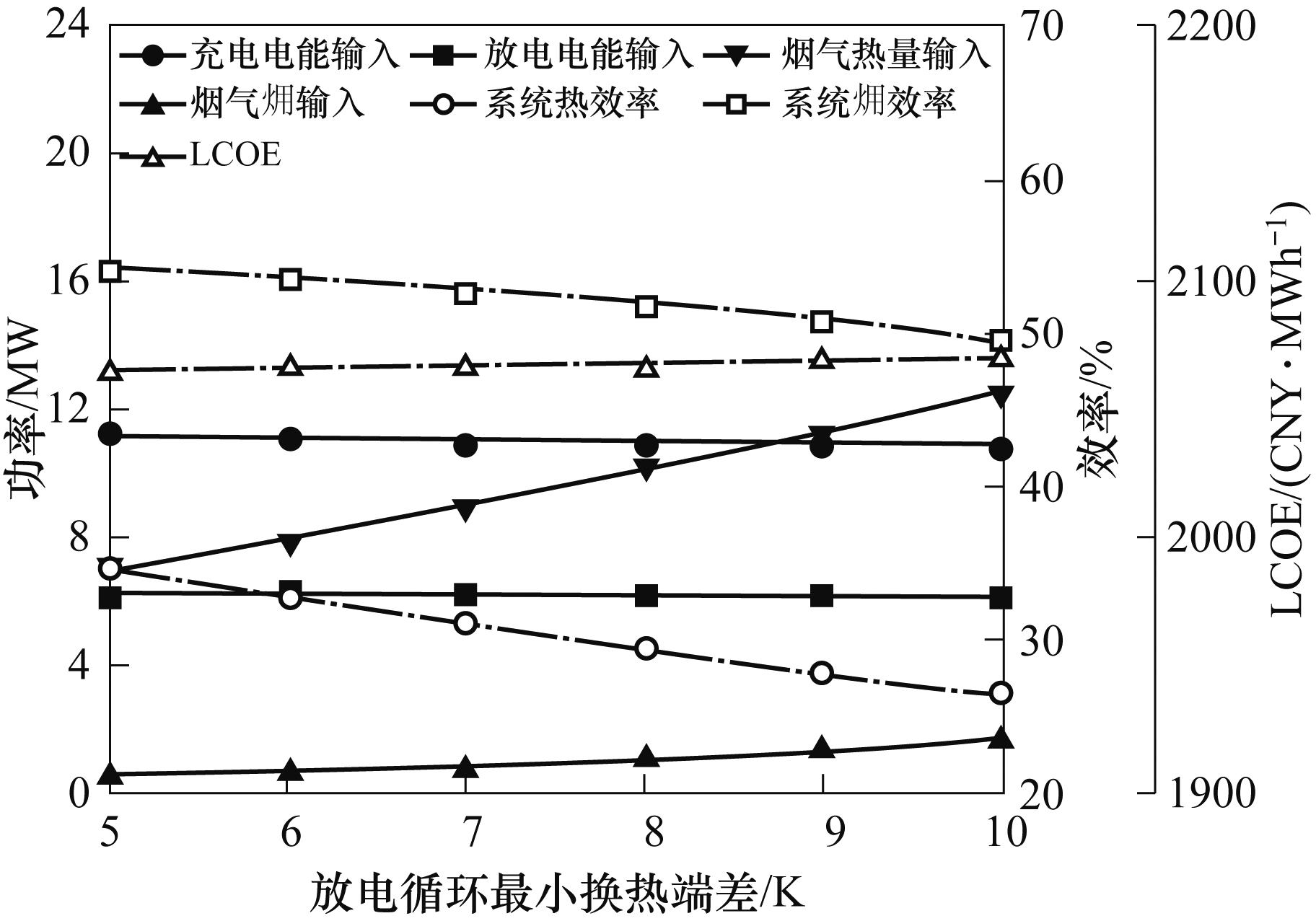
图7 放电循环最小换热端差对能量输入、能量输出、系统效率和LCOE的影响
Fig.7 Effect of minimum heat exchange temperature difference during discharging cycle on energy input, energy output, system efficiency and LCOE
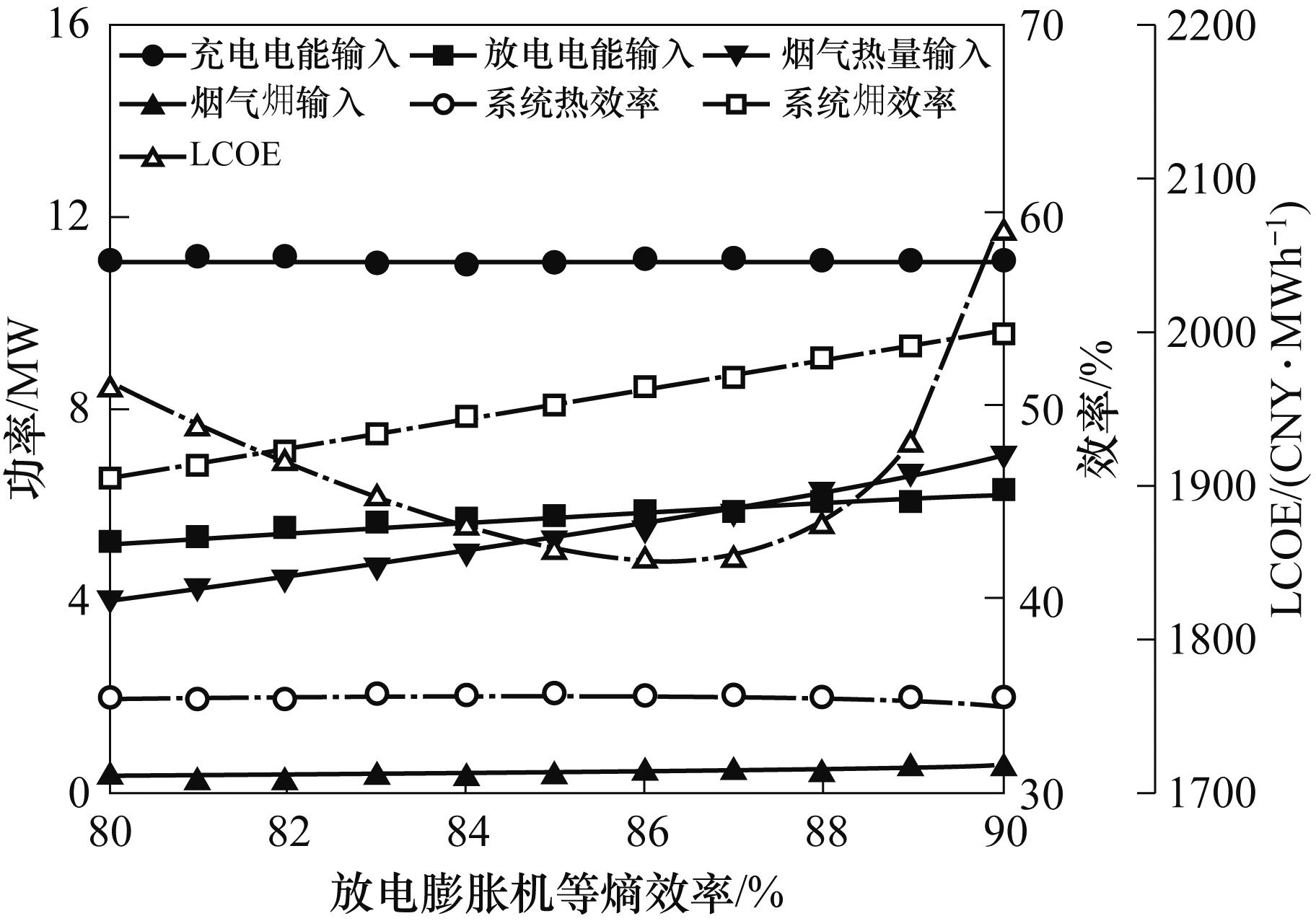
图8 放电膨胀机等熵效率对能量输入、能量输出、系统效率和LCOE的影响
Fig.8 Effect of discharging expander isentropic efficiency on energy input, energy output, system efficiency and LCOE
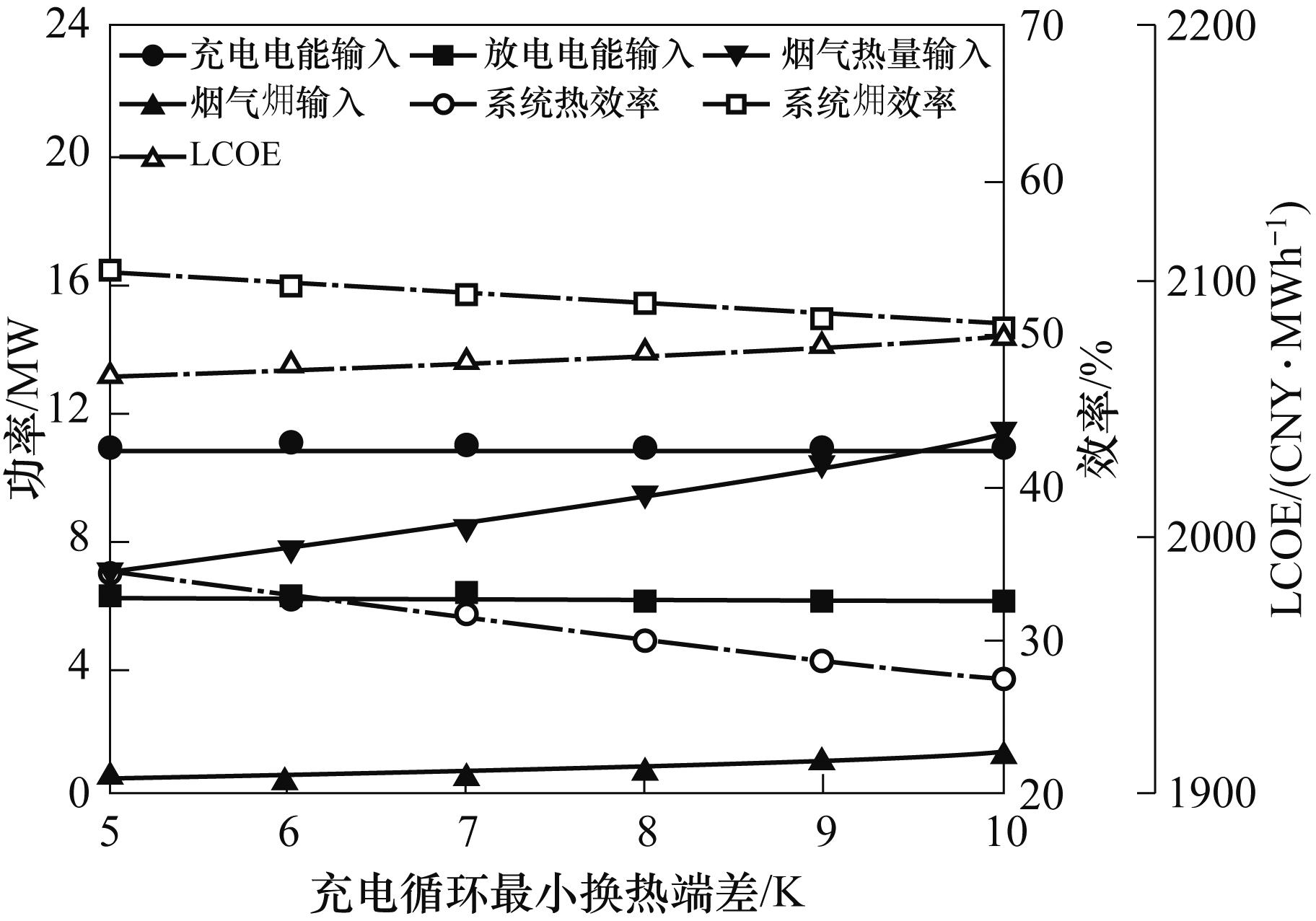
图9 充电循环最小换热端差对能量输入、能量输出、系统效率和LCOE的影响
Fig.9 Effect of minimum heat exchange temperature difference during charging cycle on energy input, energy output, system efficiency and LCOE
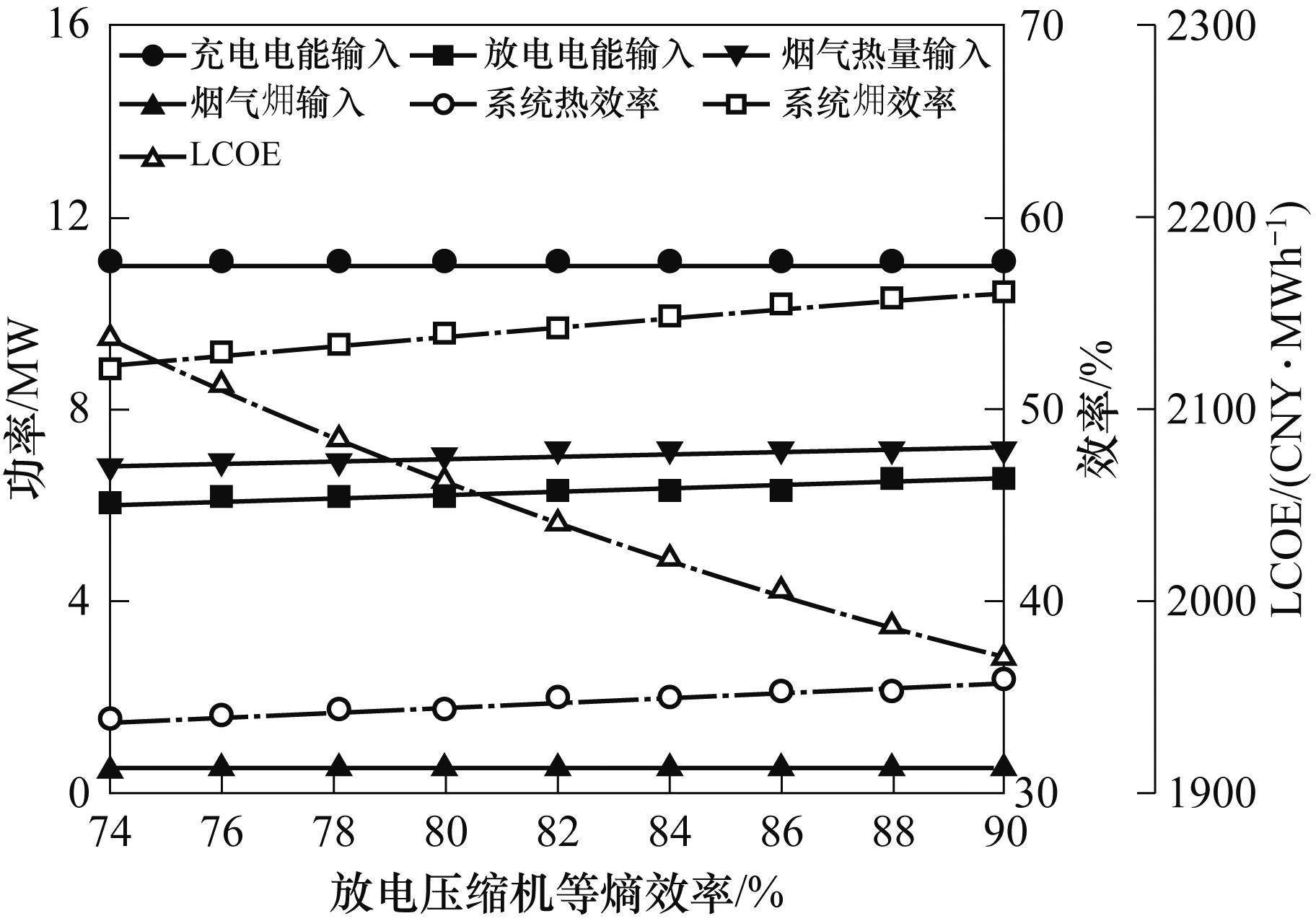
图10 放电压缩机等熵效率对能量输入、能量输出、系统效率和LCOE的影响
Fig.10 Effect of discharging compressor isentropic efficiency on energy input, energy output, system efficiency and LCOE
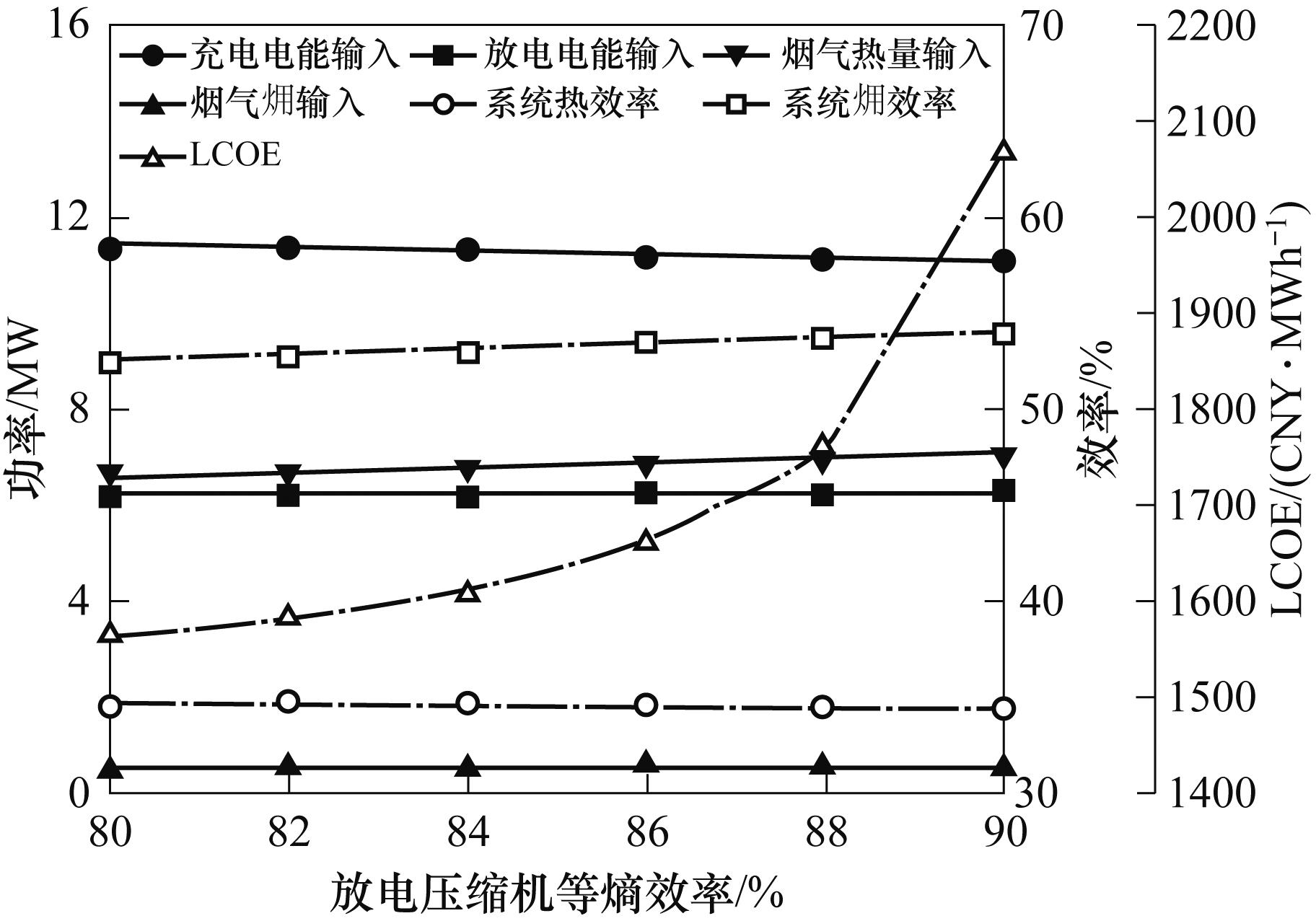
图11 充电膨胀机等熵效率对能量输入、能量输出、系统效率和LCOE的影响
Fig.11 Effect of charging expander isentropic efficiency on energy input, energy output, system efficiency and LCOE
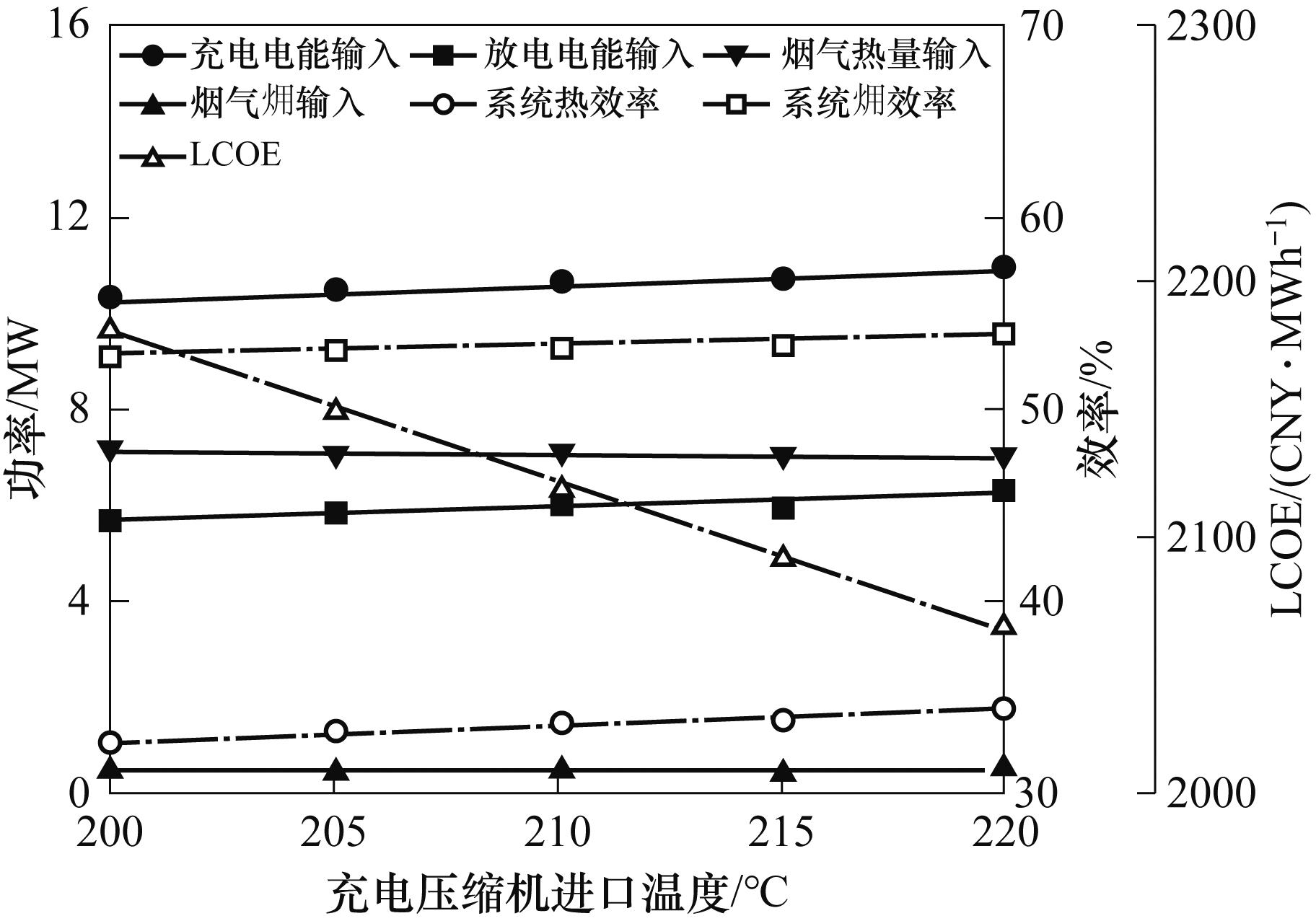
图12 充电压缩机进口温度对能量输入、能量输出、系统效率和LCOE的影响
Fig.12 Effect of charging compressor inlet temperature on energy input, energy output, system efficiency and LCOE
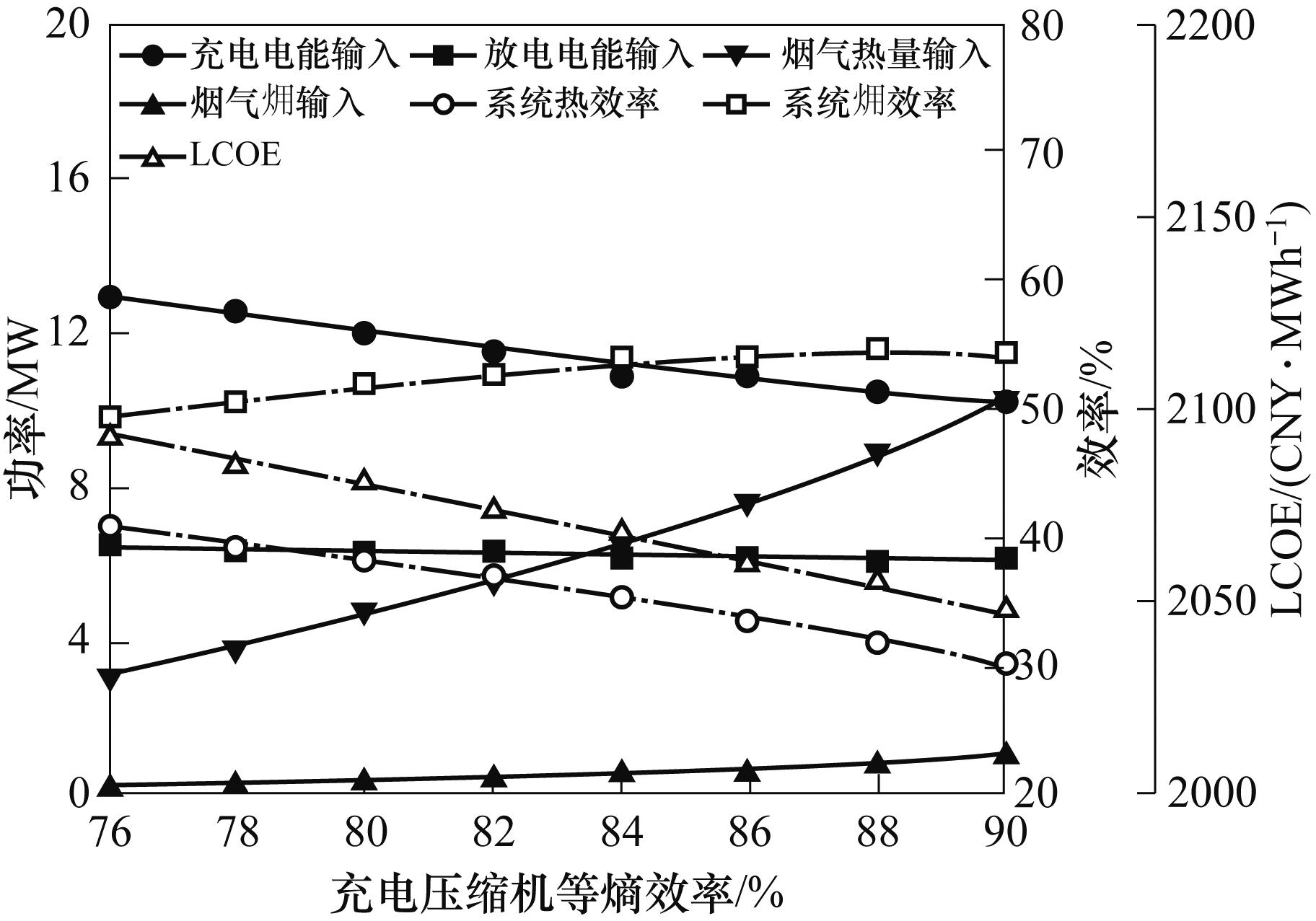
图13 充电压缩机等熵效率对能量输入、能量输出、系统效率和LCOE的影响
Fig.13 Effect of charging compressor isentropic efficiency on energy input, energy output, system efficiency and LCOE
| 决策变量 | 取值 |
|---|---|
| 种群数量 | 150 |
| 迭代次数 | 200 |
| 选择函数 | Tournament |
| 突变函数 | Constraint dependent |
| 超参数组合规模 | 2 |
| 交叉函数 | Intermediate |
| 交叉分数 | 0.8 |
| Pareto分数 | 0.8 |
表5 多目标优化参数设置
Table 5 Settings for system multi-objective optimization
| 决策变量 | 取值 |
|---|---|
| 种群数量 | 150 |
| 迭代次数 | 200 |
| 选择函数 | Tournament |
| 突变函数 | Constraint dependent |
| 超参数组合规模 | 2 |
| 交叉函数 | Intermediate |
| 交叉分数 | 0.8 |
| Pareto分数 | 0.8 |
| 决策变量 | 取值范围 |
|---|---|
| 充电压缩机进口温度/℃ | 200~220 |
| 压缩机出口压力/kPa | 19000~25000 |
| 压缩机进口压力/kPa | 7600~9000 |
| 充电压缩机等熵效率/% | 76~90 |
| 充电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 80~90 |
| 放电压缩机等熵效率/% | 74~90 |
| 放电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 80~90 |
| 放电循环质量流量/(kg·s-1) | 80~96 |
| 充电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5~10 |
| 放电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5~10 |
表6 决策变量的取值范围
Table 6 The range of the value of the decision variable
| 决策变量 | 取值范围 |
|---|---|
| 充电压缩机进口温度/℃ | 200~220 |
| 压缩机出口压力/kPa | 19000~25000 |
| 压缩机进口压力/kPa | 7600~9000 |
| 充电压缩机等熵效率/% | 76~90 |
| 充电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 80~90 |
| 放电压缩机等熵效率/% | 74~90 |
| 放电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 80~90 |
| 放电循环质量流量/(kg·s-1) | 80~96 |
| 充电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5~10 |
| 放电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5~10 |
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 充电压缩机进口温度/℃ | 219.84 |
| 压缩机出口压力/kPa | 24250 |
| 压缩机进口压力/kPa | 7818 |
| 充电压缩机等熵效率/% | 85.66 |
| 充电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 81.93 |
| 放电压缩机等熵效率/% | 89.66 |
| 放电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 86.74 |
| 放电循环质量流量/(kg·s-1) | 95.93 |
| 充电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5.04 |
| 放电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5.05 |
表7 最优点决策变量的取值
Table 7 Optimal solution of decision variables
| 参数 | 数值 |
|---|---|
| 充电压缩机进口温度/℃ | 219.84 |
| 压缩机出口压力/kPa | 24250 |
| 压缩机进口压力/kPa | 7818 |
| 充电压缩机等熵效率/% | 85.66 |
| 充电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 81.93 |
| 放电压缩机等熵效率/% | 89.66 |
| 放电膨胀机等熵效率/% | 86.74 |
| 放电循环质量流量/(kg·s-1) | 95.93 |
| 充电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5.04 |
| 放电循环最小换热端差/℃ | 5.05 |
| [1] | Kerschbaum A, Trentmann L, Hanel A, et al. Methods for analysing renewable energy potentials in energy system modelling: a review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2025, 215: 115559. |
| [2] | Lin Y C, Chong C H, Ma L W, et al. Quantification of waste heat potential in China: a top-down societal waste heat accounting model[J]. Energy, 2022, 261: 125194. |
| [3] | 卢昕悦, 陈锐莹, 姜夏雪, 等. 耦合LNG冷能的液态空气储能系统和液态CO2储能系统对比分析[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3297-3309. |
| Lu X Y, Chen R Y, Jiang X X, et al. Comparative study on liquid air energy storage system and liquid carbon dioxide energy storage system coupled with liquefied natural gas cold energy[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3297-3309. | |
| [4] | 郑林烽, 缪源诚, 滕晓毕, 等. 考虑配储的火电机组灵活性改造模型与方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2025, 45(4): 1501-1513. |
| Zheng L F, Miao Y C, Teng X B, et al. Model and method for flexible retrofit of thermal power units considering energy storage configuration[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2025, 45(4): 1501-1513. | |
| [5] | 孙健, 陶建龙, 胡芸蓉, 等. 基于热泵型储电技术国内外研究综述[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2024, 13(6): 1963-1976. |
| Sun J, Tao J L, Hu Y R, et al. Summary of research on power storage technology based on heat pump at home and abroad[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2024, 13(6): 1963-1976. | |
| [6] | Smallbone A, Jülch V, Wardle R, et al. Levelised cost of storage for pumped heat energy storage in comparison with other energy storage technologies[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 152: 221-228. |
| [7] | 卢沛, 王晋, 陈锴煌, 等. 新型全时段耦合余热的卡诺电池系统构建及热-经济性评估[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2023, 44(11): 3084-3090. |
| Lu P, Wang J, Cheng K H, et al. Thermo-economic evaluation of a novel Carnot battery with thermal integration during charging and discharging process[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2023, 44(11): 3084-3090. | |
| [8] | 赵永亮, 王朝阳, 刘明, 等. 基于跨临界循环的卡诺电池储能系统构型优化[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2021, 42(7): 1659-1666. |
| Zhao Y L, Wang C Y, Liu M, et al. Configuration optimization of Carnot battery energy storage system based on transcritical cycles[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2021, 42(7): 1659-1666. | |
| [9] | Wang K, Shi X P, He Q. Thermodynamic analysis of novel carbon dioxide pumped-thermal energy storage system[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 255: 123969. |
| [10] | 张涵, 王亮, 林曦鹏, 等. 基于逆/正布雷顿循环的热泵储电系统性能[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2021, 10(5): 1796-1805. |
| Zhang H, Wang L, Lin X P, et al. Performance of pumped thermal electricity storage system based on reverse/forward Brayton cycle[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2021, 10(5): 1796-1805. | |
| [11] | Liu Y P, Wang Y, Huang D G. Supercritical CO2 Brayton cycle: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Energy, 2019, 189: 115900. |
| [12] | 刘明, 张旭伟, 王朝阳, 等. 集成SCO2动力循环的燃煤电站余热回收系统研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2017, 38(8): 1613-1618. |
| Liu M, Zhang X W, Wang C Y, et al. Study on heat recovery system of coal-fired power plant integrated with SCO2 power cycle[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2017, 38(8): 1613-1618. | |
| [13] | 孙瑞强, 李延兵, 刘明, 等. 集成外热源的超临界二氧化碳热泵储电系统性能研究[J]. 动力工程学报, 2023, 43(11): 1469-1476. |
| Sun R Q, Li Y B, Liu M, et al. Performance evaluation on supercritical carbon dioxide pumped thermal electricity storage system integrated with external thermal source[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2023, 43(11): 1469-1476. | |
| [14] | Sun R Q, Zhao Y L, Liu M, et al. Thermodynamic design and optimization of pumped thermal electricity storage systems using supercritical carbon dioxide as the working fluid[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2022, 271: 116322. |
| [15] | Tauveron N, Macchi E, Nguyen D, et al. Experimental study of supercritical CO2 heat transfer in a thermo-electric energy storage based on Rankine and heat-pump cycles[J]. Energy Procedia, 2017, 129: 939-946. |
| [16] | Sharma S, Mortazavi M. Pumped thermal energy storage: a review[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2023, 213: 124286. |
| [17] | Breidenbach N, Martin C, Jockenhöfer H, et al. Thermal energy storage in molten salts: overview of novel concepts and the DLR test facility TESIS[J]. Energy Procedia, 2016, 99: 120-129. |
| [18] | 于博旭, 韩瑞, 刘倩, 等. 耦合火电厂灵活改造的卡诺电池储能系统热力学性能研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2025, 14(4): 1461. |
| Yu B X, Han R, Liu Q, et al. Thermodynamic performance of flexible retrofit Carnot battery energy storage system in coupled thermal power plant[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2025, 14(4): 1461. | |
| [19] | 韩瑞, 廖志荣, 于博旭, 等. 面向火电厂改造的熔盐卡诺电池储能系统仿真研究[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2023, 12(12): 3605-3615. |
| Han R, Liao Z R, Yu B X, et al. Simulation study of a molten-salt Carnot battery energy storage system for retrofitting a thermal power plant[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2023, 12(12): 3605-3615. | |
| [20] | Vinnemeier P, Wirsum M, Malpiece D, et al. Integration of heat pumps into thermal plants for creation of large-scale electricity storage capacities[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 184: 506-522. |
| [21] | 邵明轩, 孙杨, 张祥, 等. 依托低阶煤电站的提质储热卡诺电池及其性能分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2023, 43(14): 5525-5537. |
| Shao M X, Sun Y, Zhang X, et al. Carnot battery integrated with low-rank coal power plant for the stored heat upgrading and its performance analysis[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2023, 43(14): 5525-5537. | |
| [22] | 吴志斌, 邵轩, 郑普. 基于燃煤电厂烟气余热利用场景下的卡诺电池系统性能分析[J]. 建模与仿真, 2023, 12(4): 3481-3490. |
| Wu Z B, Shao X, Zheng P. Performance analysis of Carnot battery system based on flue gas waste heat utilization scenario in coal-fired power plants[J]. Modeling and Simulation, 2023, 12(4): 3481-3490. | |
| [23] | Forman C, Muritala I K, Pardemann R, et al. Estimating the global waste heat potential[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 57: 1568-1579. |
| [24] | Yao E R, Wang H R, Wang L G, et al. Multi-objective optimization and exergoeconomic analysis of a combined cooling, heating and power based compressed air energy storage system[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2017, 138: 199-209. |
| [25] | Mazloum Y, Sayah H, Nemer M. Exergy analysis and exergoeconomic optimization of a constant-pressure adiabatic compressed air energy storage system[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2017, 14: 192-202. |
| [26] | Geissbühler L, Becattini V, Zanganeh G, et al. Pilot-scale demonstration of advanced adiabatic compressed air energy storage(part 1): Plant description and tests with sensible thermal-energy storage[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2018, 17: 129-139. |
| [27] | Hu Y, Yao E R, Zhong L K, et al. Techno-economic analysis of thermochemical-integrated pumped thermal energy storage system[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2024, 104: 114394. |
| [28] | 仲理科. 基于固体氧化物电池的新型能量系统构建与热管理研究[D]. 西安: 西安交通大学,2023. |
| Zhong L K. Investigation on novel energy system constructions and thermal management based on solid oxide cell[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2023. | |
| [29] | Zhu H T, Xie G N, Yuan H, et al. Thermodynamic assessment of combined supercritical CO2 cycle power systems with organic Rankine cycle or Kalina cycle[J]. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 2022, 52: 102166. |
| [30] | Vecchi A, Knobloch K, Liang T, et al. Carnot battery development: a review on system performance, applications and commercial state-of-the-art[J]. Journal of Energy Storage, 2022, 55: 105782. |
| [31] | Sadni E E, Salhi I, Belhora F, et al. Multi-objective optimization of energy and exergy efficiencies in ORC configurations using NSGA-Ⅱ and TOPSIS[J]. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2025, 63: 103606. |
| [32] | 王群, 姜悦茂, 王哲, 等. 船载GT-sCO2双布雷顿联合循环经济分析与多目标优化[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2023, 57(1): 87-99. |
| Wang Q, Jiang Y M, Wang Z, et al. Exergoeconomic analysis and multi-objective optimization of a marine GT-sCO2 dual brayton combined cycle[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2023, 57(1): 87-99. | |
| [33] | Wang Z, Liu H, Jiang C H, et al. Assessment and optimization of a novel combined heat and power system through an energy nexus approach: enhancing energy storage and sustainability[J]. Energy, 2025, 322: 135575. |
| [34] | Hao J H, Ju C Z, Ma T Y, et al. Integrated modeling and exergy evaluation of an advanced solar-driven supercritical carbon dioxide-heat pump cogeneration system by standard thermal resistance[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 307: 118357. |
| [35] | Alsagri A S, Rahbari H R, Wang L N, et al. Thermo-economic optimization of an innovative integration of thermal energy storage and supercritical CO2 cycle using artificial intelligence techniques[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2024, 186: 1373-1386. |
| [1] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [2] | 郭纪超, 徐肖肖, 孙云龙. 基于植物工厂中的CO2浓度气流模拟及优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 237-245. |
| [3] | 孔繁臣, 张硕, 唐明生, 邹慧明, 胡舟航, 田长青. 二氧化碳直线压缩机气体轴承模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 281-288. |
| [4] | 燕子腾, 詹飞龙, 丁国良. 空调用套管式分流器结构设计及分流效果验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [5] | 赵婧, 董书辰, 李高洋, 黄友科, 石浩森, 缪舒文, 谭辰妍, 朱唐琦, 李永帅, 潘慧, 凌昊. 基于电化学模型的电池性能模拟与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4922-4932. |
| [6] | 李雪雯, 王治红, 高阳, 吴明鸥, 马文皓, 谭仁敏. 基于热泵技术的醇胺法脱硫再生系统多目标优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4563-4577. |
| [7] | 田鹏, 张忠林, 任超, 孟国超, 郝晓刚, 刘叶刚, 侯起旺, ABUDULA Abuliti, 官国清. 基于自热再生的一种低温甲醇洗工艺建模与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4601-4612. |
| [8] | 王杰, 林渠成, 张先明. 基于分解算法的混合气体多级膜分离系统全局优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4670-4682. |
| [9] | 曹潇风, 张华海, 王江云, 王利民. 锥形气体层流元件结构设计及流动特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4440-4448. |
| [10] | 刘璐, 王文玥, 王腾, 王太, 董新宇, 汤建成, 王少恒. 基于双混合工质深冷的氢液化工艺优化与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4933-4943. |
| [11] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [12] | 李科, 谢昊琳, 文键. 耦合多重蒸气冷却屏的液氢储罐绝热性能的多目标遗传算法优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4217-4227. |
| [13] | 王涛, 李光明, 胡秋霞, 徐静. 基于时序演变粒子群算法的双色注射产品翘曲工艺优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3403-3415. |
| [14] | 吴小龙, 黄晓璜, 肖媛, 单灵海, 叶家慧, 崔国民. 一种预留节点策略应用于换热网络优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3388-3402. |
| [15] | 丁宏鑫, 干文翔, 赵雍洋, 贾润泽, 康子祺, 赵玉隆, 向勇. X65钢焊接接头在超临界CO2相及富H2O相中的腐蚀机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3426-3435. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号