化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (11): 5753-5763.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250483
收稿日期:2025-05-06
修回日期:2025-09-22
出版日期:2025-11-25
发布日期:2025-12-19
通讯作者:
王军锋
作者简介:双舒炎(1999—),男,硕士研究生,2212206011@stmail.ujs.edu.cn
基金资助:
Shuyan SHUANG1( ), Wei ZHANG1, Jiale WANG1, Junfeng WANG1,2(
), Wei ZHANG1, Jiale WANG1, Junfeng WANG1,2( )
)
Received:2025-05-06
Revised:2025-09-22
Online:2025-11-25
Published:2025-12-19
Contact:
Junfeng WANG
摘要:
液相放电等离子体技术可突破传统热化学路径的限制,在常温常压下实现液态燃料的快速在线分解制氢。本研究设计了一种基于多孔镍材料的新型高压电极,搭建了可视化放电实验平台,系统开展了甲醇液相放电分解制氢过程的特性研究,重点分析了放电、气泡行为、能质传递特性及其对制氢性能的影响。实验结果表明,多孔电极显著增大了滑动弧放电等离子体气泡体积,并改善了放电通道的时空分布,从而有效提升了甲醇与等离子体间的反应界面与传质效率。与传统针电极相比,采用多孔电极后产氢速率提升至791.6 ml/min,增长38%;单位产氢能耗降低至1.45 kWh/m3 H2,降幅达33.78%。在长周期运行过程中,多孔电极体系的甲醇分解性能衰减率较传统系统降低超过72%,展现出优异的运行稳定性与寿命特性。研究结果为液相等离子体制氢反应器的高效化、稳定化设计提供了理论依据与关键技术支撑。
中图分类号:
双舒炎, 张伟, 王家乐, 王军锋. 基于多孔镍电极的液相放电等离子体分解甲醇制氢实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(11): 5753-5763.
Shuyan SHUANG, Wei ZHANG, Jiale WANG, Junfeng WANG. Experimental study on hydrogen production from methanol decomposition by liquid-phase discharge using porous nickel electrodes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(11): 5753-5763.
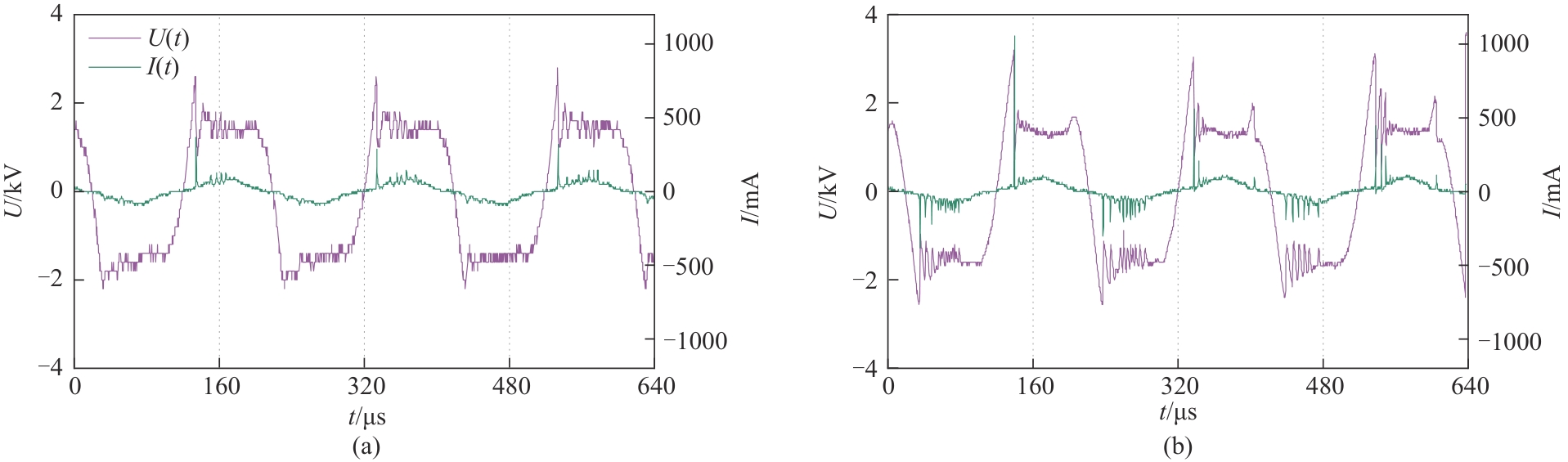
图3 滑动弧放电电压-电流波形:(a) 针电极 (61.28 W);(b)110 ppi多孔电极 (62.99 W)
Fig.3 Voltage-current wave of GAD: (a) needle electrode (61.28 W); (b) 110 ppi porous electrode (62.99 W)
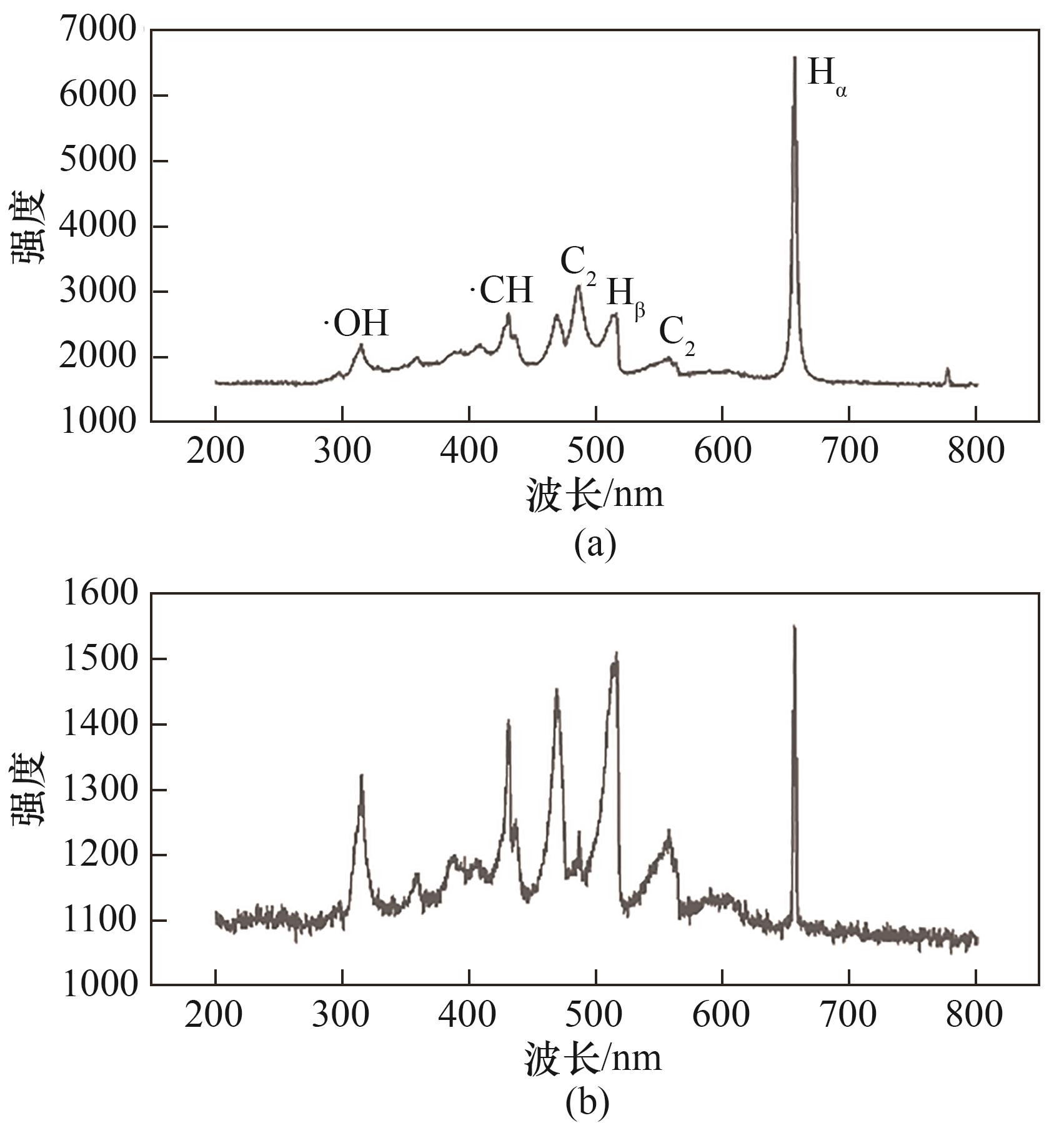
图4 不同电极分解甲醇过程中等离子体发射光谱:(a)镍针电极;(b)多孔镍电极
Fig.4 Optical emission spectra of plasma during methanol decomposition with different electrodes: (a) nickel needle electrode; (b) porous nickel electrode
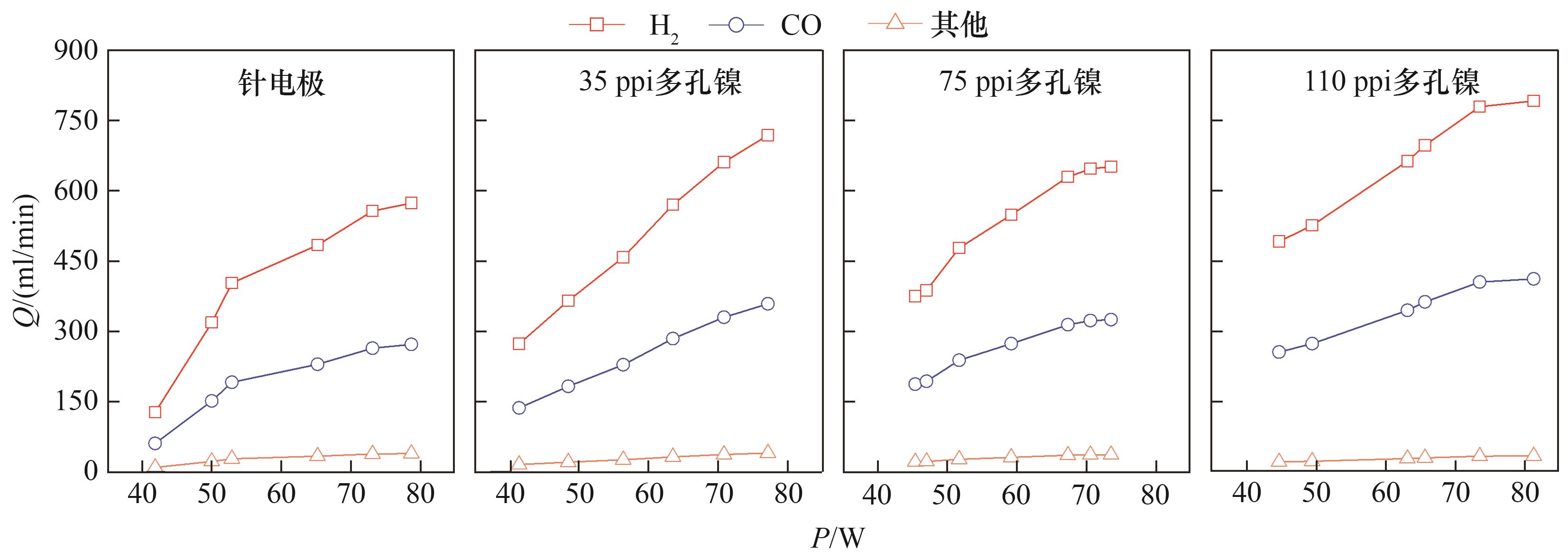
图5 不同孔隙密度多孔电极与针电极分解甲醇产气速率对比
Fig. 5 Comparison of syngas production yield from methanol decomposition by needle electrode and porous electrodes with different pore densities
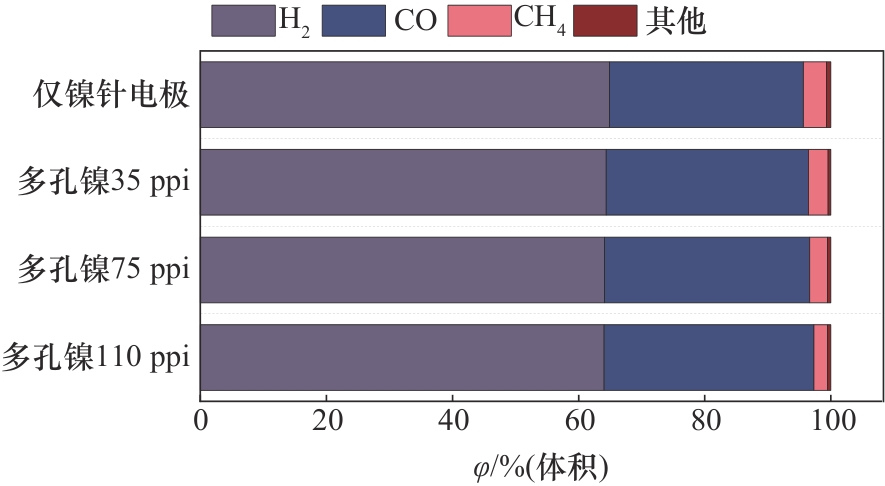
图6 不同孔隙密度多孔电极与针电极分解甲醇气相产物组分对比
Fig. 6 Comparison of gas-phase product fractions of methanol decomposition by porous electrode and needle electrode with different pore densities
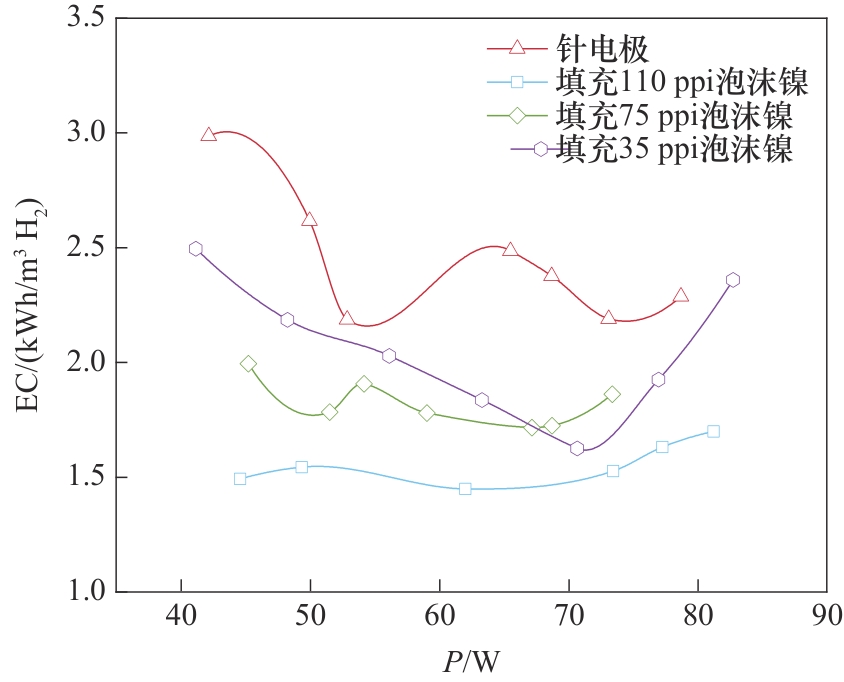
图7 不同孔隙密度多孔电极与针电极分解甲醇制氢能耗对比
Fig. 7 Comparison of energy consumption for hydrogen production from methanol decomposition by needle electrodes and porous electrodes with different pore densities
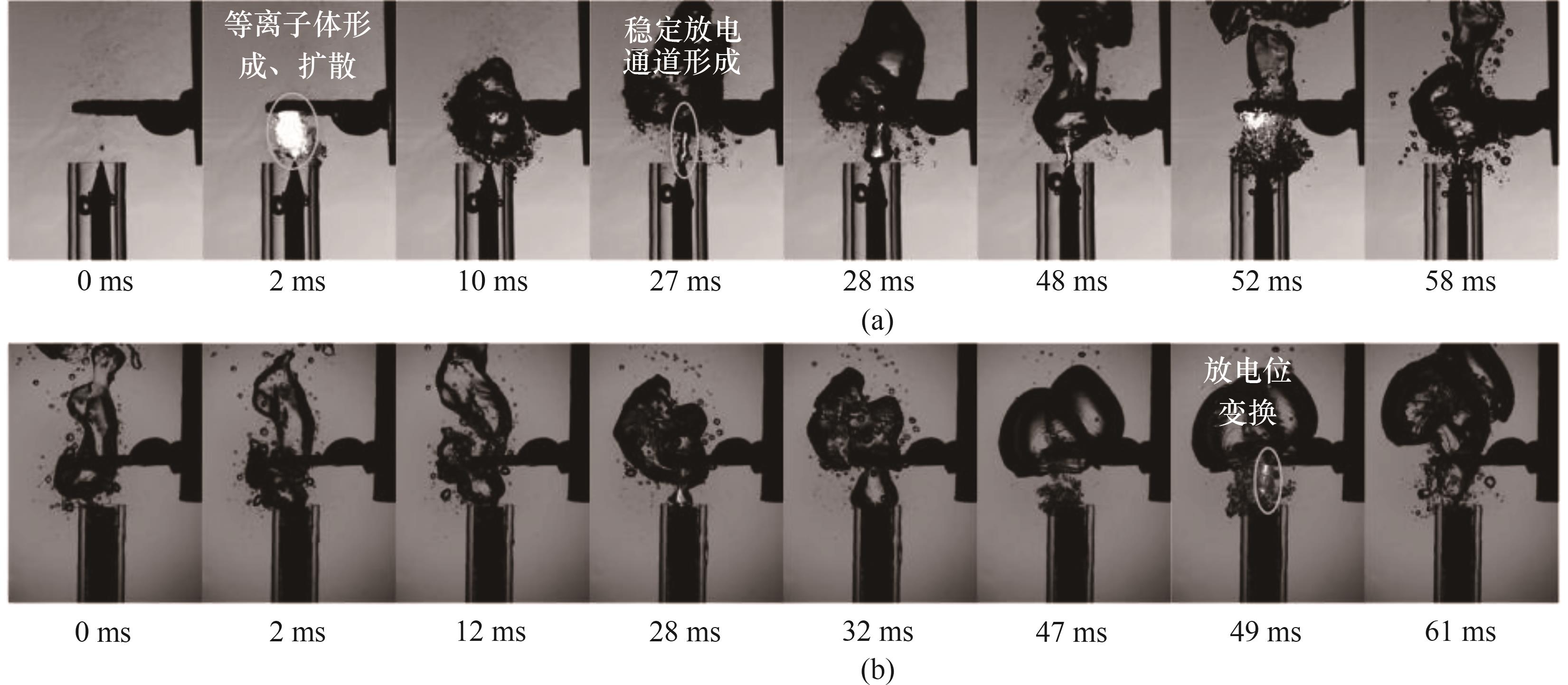
图8 不同高压电极对等离子体气泡形貌时空演变规律的影响:(a) 针电极;(b) 多孔镍电极
Fig. 8 Effects of different high-voltage electrodes on the spatial and temporal evolution of plasma bubble morphology: (a) needle electrode; (b) porous nickel electrode
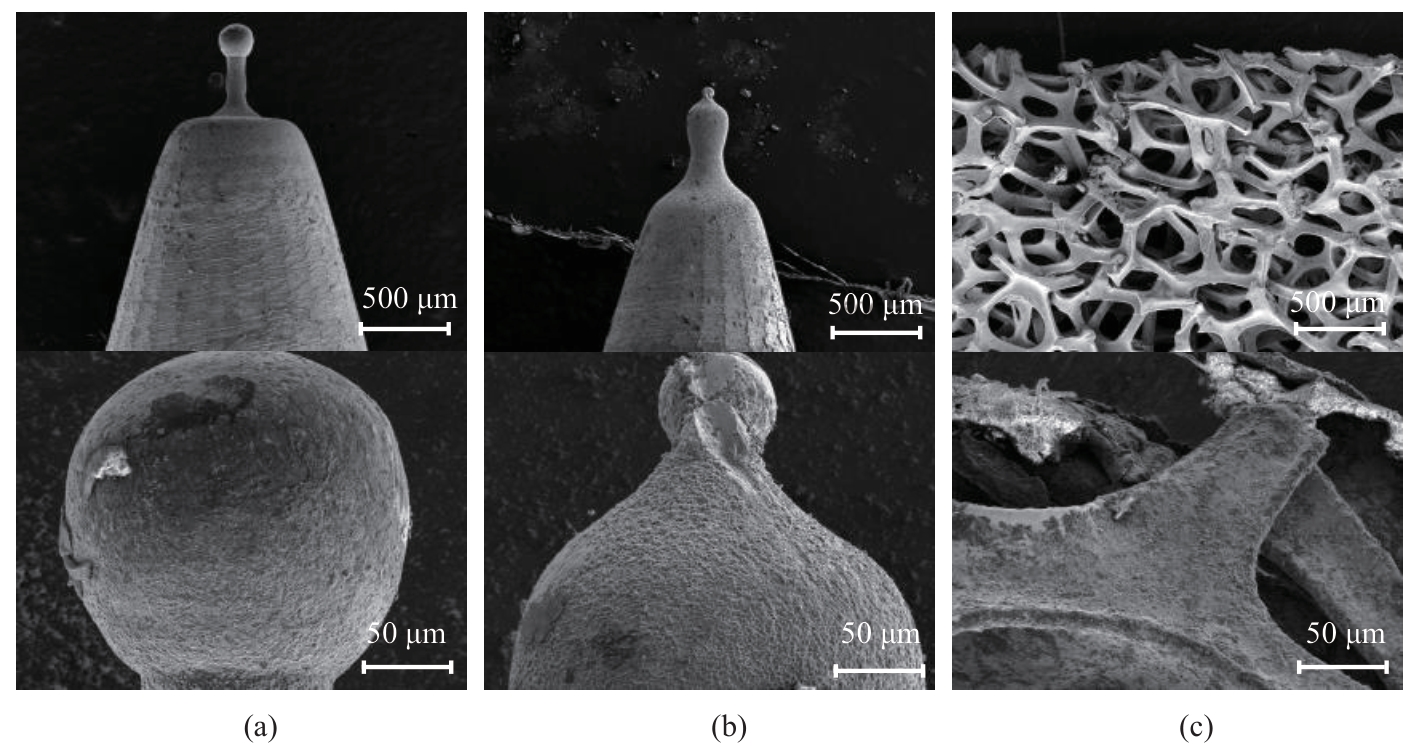
图10 高压电极放电1 h表面SEM图:(a) 针电极(无多孔镍保护);(b) 针电极(多孔镍保护);(c) 多孔镍
Fig. 10 SEM images of the surface of the high-voltage electrode discharged for 1 hour: (a) needle electrode (no porous nickel protection); (b) needle electrode (porous nickel protection); (c) porous nickel
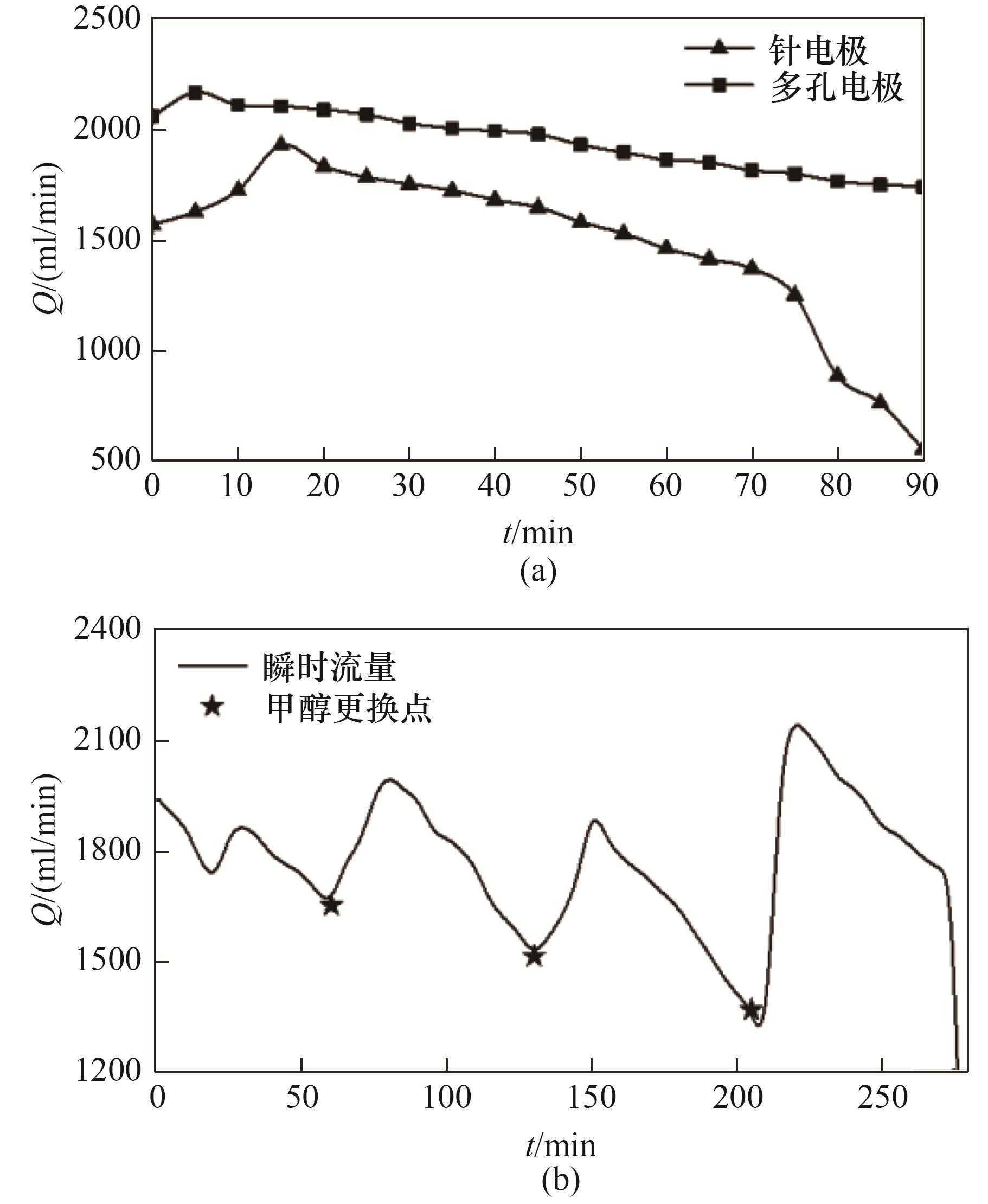
图12 持续放电过程中甲醇分解性能变化:(a) 不同电极分解甲醇稳定性对比;(b) 多孔电极产气流量变化
Fig. 12 Variation of methanol decomposition properties during continuous discharges: (a) comparison of methanol decomposition stability of different electrodes; (b) variation of syngas flow rate by porous electrodes
| [1] | 孙潇, 蔡春荣, 罗志斌,等. 70 MPa加氢站动态模拟与能耗分析[J]. 南方能源建设, 2023, 10: 150-156. |
| Sun X, Cai C R, Luo Z B, et al. Dynamic simulation and energy comsuption analysis of 70 MPa hydrogen refueling station[J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2023, 10: 150-156. | |
| [2] | 丁镠, 唐涛, 王耀萱,等. 氢储运技术研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 天然气化工—C1化学与化工, 2022, 47: 35-40. |
| Ding L, Tang T, Wang Y X, et al. Research progress and development trend of hydrogen storage and transportation technology[J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry, 2022, 47: 35-40. | |
| [3] | Lin L L, Zhou W, Gao R, et al. Low-temperature hydrogen production from water and methanol using Pt/α-MoC catalysts[J]. Nature, 2017, 544(7648): 80-83. |
| [4] | 潘光胜, 顾伟, 张会岩,等. 面向高比例可再生能源消纳的电氢能源系统[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44: 1-10. |
| Pan G S, Gu W, Zhang H Y, et al. Electricity and hydrogen energy system towards accomodation of high proportion of renewable energy[J]. Natural Gas Chemical Industry, 2020, 44: 1-10. | |
| [5] | 严从青. 西南甲醇市场研究报告[J]. 现代营销(下旬刊), 2021(3), 74-78. |
| Yan C Q. Southwest methanol market research report[J]. Marketing Management Review, 2021(3): 74-78. | |
| [6] | Lian H Y, Li X S, Liu J L, et al. Methanol steam reforming by heat-insulated warm plasma catalysis for efficient hydrogen production[J]. Catalysis Today, 2019, 337: 76-82. |
| [7] | Kamarinopoulou N S, Nguyen D K, Vlachos D G. Process-chemistry intensification using non-thermal plasmas: toward one-step chemical production[J]. Current Opinion in Green and Sustainable Chemistry, 2025, 51: 100997. |
| [8] | Chen L Y, Wang W J, Lu T R, et al. Soft template-induced deep pore structure of Cu/Al2O3 for promoting plasma-catalyzed CO2 hydrogenation to DME[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2025, 41(6): 100054. |
| [9] | Zhang H, Li X D, Zhu F S, et al. Non-oxidative decomposition of methanol into hydrogen in a rotating gliding arc plasma reactor[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(46): 15901-15912. |
| [10] | Xin Y B, Wang Q L, Sun J B, et al. Plasma in aqueous methanol: Influence of plasma initiation mechanism on hydrogen production[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 325: 119892. |
| [11] | 吴天一. 液相放电等离子体特性及强化甲醇/氨水分解制氢的实验研究[D]. 镇江:江苏大学, 2023. |
| Wu T Y. Experimental research on the characteristics of liquid-phase plasma discharge and enhanced methanol/ammonia decomposition for hydrogen production[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2023. | |
| [12] | 王军锋, 张俊杰, 张伟,等. 液相放电等离子体分解甲醇制氢:电极配置的优化[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(9): 3277-3286. |
| Wang J F, Zhang J J, Zhang W, et al. Liquid-phase discharge plasma decomposition of methanol for hydrogen production: optimization of electrode configuration[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(9): 3277-3286. | |
| [13] | Zhu T H, Liu J L, Wang Q Y, et al. Enhanced hydrogen production by microwave liquid-phase discharge plasma reforming of methanol solution without catalyst[J]. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2023, 108: 101246. |
| [14] | Xin Y B, Sun B, Liu J Y, et al. Effects of electrode configurations, solution pH, TiO2 addition on hydrogen production by in-liquid discharge plasma[J]. Renewable Energy, 2021, 171: 728-734. |
| [15] | Zhang J J, Zhang W, Wang J F, et al. Enhanced hydrogen production from methanol by liquid-phase array electrode plasma discharge[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2024, 312: 118544. |
| [16] | Li W P, Meng S J, Li Z F, et al. The function of porous working electrodes for hydrogen production from water splitting in non-thermal plasma reactor[J]. Fuel, 2022, 310: 122156. |
| [17] | Fu Y Y, Zhang P, Krek J, et al. Gas breakdown and its scaling law in microgaps with multiple concentric cathode protrusions[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2019, 114: 014102. |
| [18] | Wang H, Lin H, Tian J M, et al. Enhanced pool boiling performance of cellular metal foams by electrostatic fields for high-power thermal management[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2024, 224: 125307. |
| [19] | Srivastava S K, Krishnakumar E, Fucaloro A F, et al. Cross sections for the production of cations by electron impact on methanol[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 1996, 101(E11): 26155-26160. |
| [20] | Murphy E L, Good R H. Thermionic emission, field emission, and the transition region[J]. Physical Review, 1956, 102(6): 1464-1473. |
| [21] | 温嘉烨, 王亚桢, 肖正光,等. 水中正极性丝状流注放电发展特性[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2024, 36(10): 95-104. |
| Wen J Y, Wang Y Z, Xiao Z G, et al. Propagation characteristics of positive filamentary streamer discharges in water[J]. High Power Lazer and Particle Beams, 2024, 36(10): 95-104. | |
| [22] | 温嘉烨, 李元, 倪正全,等. 水中负极性灌木状放电特性研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2021, 41: 6108-6116. |
| Wen J Y, Li Y, Ni Z Q, et al. Study on characteristics of negative bushy discharges in water[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2021, 41: 6108-6116. | |
| [23] | Wang J F, Zhang W, Wu T Y, et al. Occurrence of giant plasma bubble in liquid[J]. Matter, 2024, 7(9): 3024-3035. |
| [24] | Wu T Y, Wang J F, Zhang W, et al. Plasma bubble characteristics and hydrogen production performance of methanol decomposition by liquid phase discharge[J]. Energy, 2023, 273: 127252. |
| [25] | Kim H H, Teramoto Y, Ogata A, et al. Plasma catalysis for environmental treatment and energy applications[J]. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 2016, 36(1): 45-72. |
| [26] | Bruggeman P J, Kushner M J, Locke B R, et al. Plasma-liquid interactions: a review and roadmap[J]. Plasma Sources Science and Technology, 2016, 25(5): 053002. |
| [27] | Boussetta N, Vorobiev E. Chapter two—Electrical discharges in water: prebreakdown and breakdown phases[M]//Boussetta N, Vorobiev E. Processing of Food Products and Wastes with High Voltage Electrical Discharges. Academic Press, 2023: 37-64. |
| [28] | Kumagai R, Kanazawa S, Ohtani K, et al. Propagation and branching process of negative streamers in water[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 124(16): 163301. |
| [29] | 李元, 温嘉烨, 李林波,等. 液体介质微/纳秒脉冲放电的特性与机理:现状及进展[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2021, 33(6): 6-18. |
| Li Y, Wen J Y, Li L B, et al. Characteristics and mechanisms of streamer discharge in liquids undermicro/nano-second pulsed voltages: status and advances [J]. High Power Lazer and Particle Beams, 2021, 33(6): 6-18. | |
| [30] | Wang X, Duan J B, Song K X, et al. Microstructure, mechanical properties and arc erosion behavior of CuW composites prepared by high energy ball milling and spark plasma sintering[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2024, 119: 106523. |
| [31] | Guseva M I, Gureev V M, Domantovskii A G, et al. Surface erosion of tungsten and the morphology of erosion products in experiments simulating plasma disruption[J]. Technical Physics, 2002, 47(7): 841-844. |
| [32] | Lukeš P, Člupek M, Babický V, et al. Erosion of needle electrodes in pulsed corona discharge in water[J]. Czechoslovak Journal of Physics, 2006, 56(2): B916-B924. |
| [33] | Kohut A, Wagner M, Seipenbusch M, et al. Surface features and energy considerations related to the erosion processes of Cu and Ni electrodes in a spark discharge nanoparticle generator[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2018, 119: 51-61. |
| [34] | Potocký, Saito N, Takai O. Needle electrode erosion in water plasma discharge[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2009, 518(3): 918-923. |
| [35] | Giraldo-Mejía H, Quintero Y M, Mery F, et al. Plasma-grafting surface modifications to enhance membrane hydrophobicity for brine membrane distillation[J]. Desalination, 2023, 567: 116942. |
| [1] | 解勤勤, 翁俊旗, 林振利, 叶光华, 周兴贵. 固定床反应器中甲醇制芳烃工业催化剂结构影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4487-4498. |
| [2] | 邹家庆, 张肇钰, 张建国, 张博宇, 刘定胜, 毛庆, 王挺, 李建军. 碱水制氢电解槽极板通道中气泡的生成及演化性质[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4786-4799. |
| [3] | 张彬怡, 孙少东, 姚谦, 蔡文河, 张惠宇, 李成新. 煤制甲醇耦合固体氧化物燃料电池混合系统研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4658-4669. |
| [4] | 周怀荣, 伊嘉伟, 曹阿波, 郭奥雪, 王东亮, 杨勇, 杨思宇. 共电解耦合CO2间接加氢制甲醇工艺集成设计与性能评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4586-4600. |
| [5] | 田鹏, 张忠林, 任超, 孟国超, 郝晓刚, 刘叶刚, 侯起旺, ABUDULA Abuliti, 官国清. 基于自热再生的一种低温甲醇洗工艺建模与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4601-4612. |
| [6] | 周奕彤, 周明熙, 刘若晨, 叶爽, 黄伟光. 光伏与电网协同驱动氢基直接还原铁炼钢的技术经济分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4318-4330. |
| [7] | 范夏雨, 孙建辰, 李可莹, 姚馨雅, 商辉. 机器学习驱动液态有机储氢技术的系统优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3805-3821. |
| [8] | 杨宁, 李皓男, LIN Xiao, GEORGIADOU Stella, LIN Wen-Feng. 从塑料废弃物到能源催化剂:塑料衍生碳@CoMoO4复合材料在电解水析氢反应中的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4081-4094. |
| [9] | 王御风, 罗小雪, 范鸿亮, 吴白婧, 李存璞, 魏子栋. 耦合电解水制氢的绿色有机电合成——电极界面调控策略综述[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3753-3771. |
| [10] | 周运桃, 崔丽凤, 张杰, 于富红, 李新刚, 田野. Ga2O3调控CuCeO催化CO2加氢制甲醇的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4042-4051. |
| [11] | 何晨, 陆明飞, 王令金, 许晓颖, 董鹏博, 赵文涛, 隆武强. 氨-甲醇高压混合气稀燃层流实验与模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4248-4258. |
| [12] | 陈佳祥, 周伟, 张学伟, 王丽杰, 黄玉明, 于洋, 孙苗婷, 李宛静, 袁骏舒, 张宏博, 孟晓晓, 高继慧, 赵广播. 脉冲电压下二维PEMWE模型的制氢特性仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3521-3530. |
| [13] | 吴天灏, 叶霆威, 林延, 黄振. 生物质化学链气化原位补氢制H2/CO可控合成气[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3498-3508. |
| [14] | 廖鹏伟, 刘庆辉, 潘安, 王嘉岳, 符小贵, 杨思宇, 余皓. 考虑不确定性的风电制氢系统:多时间尺度运行策略[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2743-2754. |
| [15] | 郭江悦, 常守金, 胡海涛. 水平管内甲醇流动冷凝数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2580-2588. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号