• •
梁丹曦1,2( ), 俎焱敏2, 宋洁1,2, 柯绍杰2, 徐桂芝1,2, 侯坤2, 梁立晓2, 赵子泰2, 张永生1(
), 俎焱敏2, 宋洁1,2, 柯绍杰2, 徐桂芝1,2, 侯坤2, 梁立晓2, 赵子泰2, 张永生1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-08-20
修回日期:2025-12-09
出版日期:2025-12-10
通讯作者:
张永生
作者简介:梁丹曦(1992—),女,博士研究生,高级工程师,liangdanxi@sina.com
基金资助:
Danxi LIANG1,2( ), Yanmin ZU2, Jie Song1,2, Shaojie KE2, Guizhi XU1,2, Kun HOU2, Lixiao LIANG2, Zitai ZHAO2, Yongsheng ZHANG1(
), Yanmin ZU2, Jie Song1,2, Shaojie KE2, Guizhi XU1,2, Kun HOU2, Lixiao LIANG2, Zitai ZHAO2, Yongsheng ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2025-08-20
Revised:2025-12-09
Online:2025-12-10
Contact:
Yongsheng ZHANG
摘要:
质子交换膜(PEM)电解制氢具有效率高、响应快、电流密度高、可调范围广的优点,是适应可再生能源波动制氢的重要技术。温度控制是直接影响PEM电解制氢耐久性、输出性能及可靠运行的关键因素。为实现电解制氢温度和温差的快速精确控制,建立了面向控制的PEM电解制氢系统时滞数学模型并进行线性化和频域模型转化,针对电解槽温度和温差控制强耦合、动态响应慢的问题,提出了基于前馈解耦的自适应模糊PID优化控制策略,并基于100kW电解制氢装置完成了系统模型验证和控制策略仿真对比分析。结果表明,所提控制策略在波动工况下能使电解制氢温度和温差保持稳定,温度/温差调节时间分别加快65.75s与66.5s,并且具备较强的抗干扰能力,最大偏差在±0.5℃内。
中图分类号:
梁丹曦, 俎焱敏, 宋洁, 柯绍杰, 徐桂芝, 侯坤, 梁立晓, 赵子泰, 张永生. PEM电解制氢热管理建模及解耦控制设计与优化[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250937.
Danxi LIANG, Yanmin ZU, Jie Song, Shaojie KE, Guizhi XU, Kun HOU, Lixiao LIANG, Zitai ZHAO, Yongsheng ZHANG. Thermal management modeling and decoupling control design and optimization for PEM electrolytic hydrogen production system[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250937.
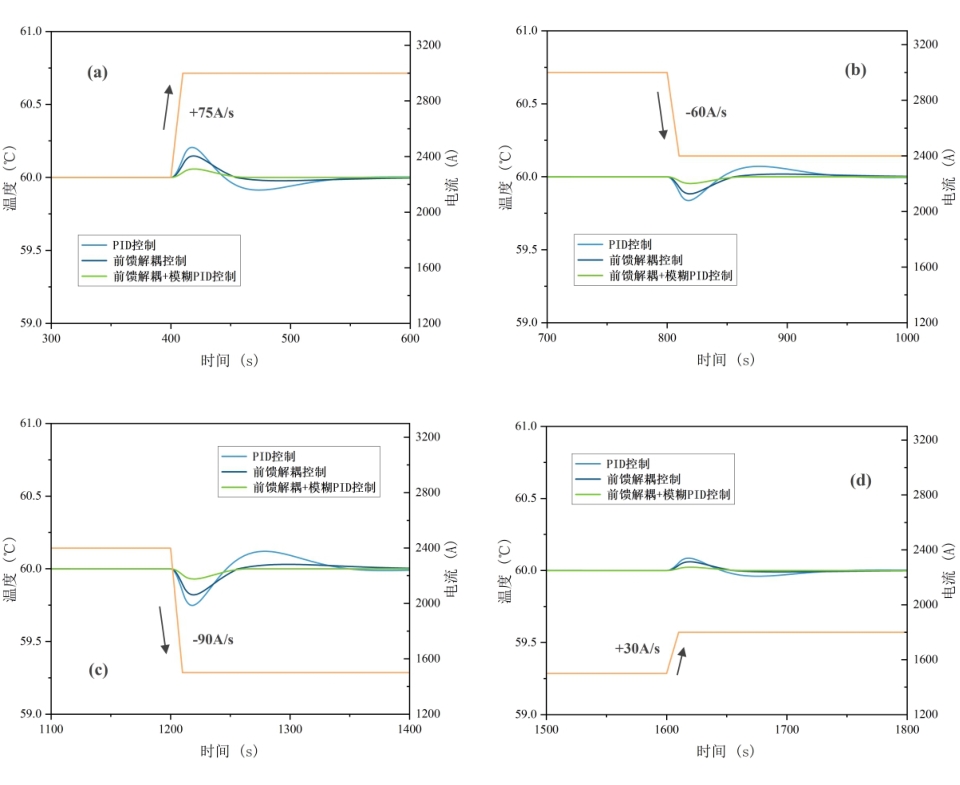
图11 不同控制策略电解槽入口温度变化放大: (a)400s;(b)800s;(c)1200s;(d)1600s
Fig.11 Amplification of inlet temperature changes in electrolytic cells with different control strategies: (a)400s;(b)800s;(c)1200s;(d)1600s
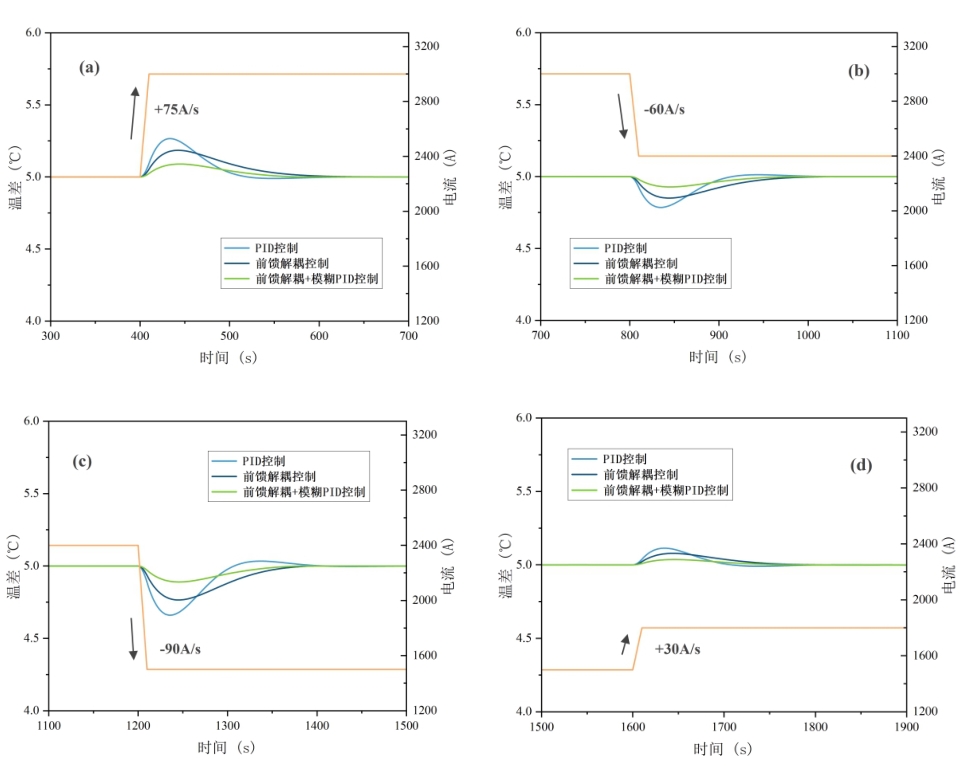
图12 不同控制策略电解槽温差变化放大: (a)400s;(b)800s;(c)1200s;(d)1600s
Fig.12 Amplification of temperature difference changes in electrolytic cells with different control strategies: (a)400s;(b)800s;(c)1200s;(d)1600s
| 目标 | 指标 | 控制策略 | 升载一 t=400s | 降载一 t=800s | 降载二 t=1200s | 升载二 t=1600s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 入口温度 | 60℃ | 超调量 (℃) | PID | 0.206 | -0.163 | -0.252 | 0.085 |
| 前馈解耦 | 0.147 | -0.112 | -0.173 | 0.06 | |||
| 前馈+模糊PID | 0.061 | -0.043 | -0.069 | 0.023 | |||
| 调节时间(s) | PID | 122 | 118 | 129 | 101 | ||
| 前馈解耦 | 99 | 96 | 105 | 53 | |||
| 前馈+模糊PID | 52 | 51 | 58 | 46 | |||
| 温差 | 5℃ | 超调量 (℃) | PID | 0.266 | -0.215 | -0.34 | 0.113 |
| 前馈解耦 | 0.185 | -0.149 | -0.235 | 0.078 | |||
| 前馈+模糊PID | 0.089 | -0.072 | -0.109 | 0.036 | |||
| 调节时间(s) | PID | 168 | 155 | 181 | 157 | ||
| 前馈解耦 | 142 | 136 | 164 | 119 | |||
| 前馈+模糊PID | 107 | 92 | 120 | 76 | |||
表1 电解制氢系统在波动工况下温度和温差动态响应指标
Table 1 Dynamic response indicators of temperature and temperature difference in electrolytic hydrogen production system under fluctuating operating conditions
| 目标 | 指标 | 控制策略 | 升载一 t=400s | 降载一 t=800s | 降载二 t=1200s | 升载二 t=1600s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 入口温度 | 60℃ | 超调量 (℃) | PID | 0.206 | -0.163 | -0.252 | 0.085 |
| 前馈解耦 | 0.147 | -0.112 | -0.173 | 0.06 | |||
| 前馈+模糊PID | 0.061 | -0.043 | -0.069 | 0.023 | |||
| 调节时间(s) | PID | 122 | 118 | 129 | 101 | ||
| 前馈解耦 | 99 | 96 | 105 | 53 | |||
| 前馈+模糊PID | 52 | 51 | 58 | 46 | |||
| 温差 | 5℃ | 超调量 (℃) | PID | 0.266 | -0.215 | -0.34 | 0.113 |
| 前馈解耦 | 0.185 | -0.149 | -0.235 | 0.078 | |||
| 前馈+模糊PID | 0.089 | -0.072 | -0.109 | 0.036 | |||
| 调节时间(s) | PID | 168 | 155 | 181 | 157 | ||
| 前馈解耦 | 142 | 136 | 164 | 119 | |||
| 前馈+模糊PID | 107 | 92 | 120 | 76 | |||
| [1] | 罗进成, 李锁华, 商玮珂, 等. 化石资源与新能源融合下的制氢技术发展及展望[J]. 应用化工, 2024, 53(11): 2777-2782. |
| Luo J C, Li S H, Shang W K, et al. Development and prospect of hydrogen production technology under the integration of fossil resources and new energy[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2024, 53(11): 2777-2782. | |
| [2] | 中国氢能联盟.中国氢能源及燃料电池产业白皮书[M]北京:人民日报出版社.2019. |
| China Hydrogen Alliance. White Paper on China's Hydrogen Energy and Fuel Cell Industry [M]. Beijing: People's Daily Press.2019. | |
| [3] | 赵雪莹, 李根蒂, 孙晓彤, 等. "双碳"目标下电解制氢关键技术及其应用进展[J]. 全球能源互联网, 2021(5): 436-446. |
| Zhao X Y, Li G D, Sun X T, et al. Key technology and application progress of hydrogen production by electrolysis under peaking carbon dioxide emissions and carbon neutrality targets[J]. Journal of Global Energy Interconnection, 2021(5): 436-446. | |
| [4] | 宋洁, 郜捷, 梁丹曦, 等. 质子交换膜电解制氢系统建模研究综述[J]. 电力建设, 2024, 45(2): 58-78. |
| Song J, Gao J, Liang D X, et al. A review on modeling of hydrogen production system with proton exchange membrane electrolysis[J]. Electric Power Construction, 2024, 45(2): 58-78. | |
| [5] | 车秀波,姚京裕,徐久盛.新型高性能大产能电解水制氢装置的研究与应用[J].模具制造,2024,24(05):169-171+176. |
| Research and Application of New High Performance Water Hydrogen Production Device[J]. Die Mould Manufacture, 2024,24(05):169-171+176. | |
| [6] | 宋洁, 邓占锋, 徐桂芝, 等. 煤炭制氢替代技术: 质子交换膜水电解制氢技术及其衰减机理[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2022, 50(6): 136-144. |
| Song J, Deng Z F, Xu G Z, et al. Substitution technology for hydrogen production from coal: proton exchange membrane water electrolysis technology for hydrogen production and its attenuation mechanism[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(6): 136-144. | |
| [7] | 李微微, 谢晓峰, 王树博. 固体聚合物电解水制氢性能衰减分析[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(S2): 168-174. |
| Li W W, Xie X F, Wang S B. Performance degradation analysis of solid polymer electrolyte water electrolysis[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(S2): 168-174. | |
| [8] | 宋洁, 宗正, 梁丹曦, 等. PEM电解制氢系统压力抗干扰控制策略研究[J]. 动力工程学报, 2025, 45(3): 431-442. |
| Song J, Zong Z, Liang D X, et al. Research on pressure anti-disturbance control strategy of hydrogen production by PEM electrolysis system[J]. Journal of Chinese Society of Power Engineering, 2025, 45(3): 431-442. | |
| [9] | Hammoudi M, Henao C, Agbossou K, et al. New multi-physics approach for modelling and design of alkaline electrolyzers[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(19): 13895-13913. |
| [10] | Milewski J, Guandalini G, Campanari S. Modeling an alkaline electrolysis cell through reduced-order and loss-estimate approaches[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 269: 203-211. |
| [11] | Amores E, Rodríguez J, Carreras C. Influence of operation parameters in the modeling of alkaline water electrolyzers for hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39(25): 13063-13078. |
| [12] | 方明.大功率燃料电池测试系统耦合建模及温湿度控制研究[D].电子科技大学,2023. |
| Fang M. Coupling modelling of high-power fuel cell test system and temperature & humidity control study[D]. University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2023. | |
| [13] | Rizwan M, Alstad V, Jäschke J. Design considerations for industrial water electrolyzer plants[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(75): 37120-37136. |
| [14] | 黄琮琪, 吴一梅, 陈建业, 等. 碱性电解水制氢装置热管理系统仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| Huang C Q, Wu Y M, Chen J Y, et al. Simulation study on thermal management system of alkaline electrolyzed water hydrogen production plant[J]. CIESC Journal, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. | |
| [15] | Keller R, Rauls E, Hehemann M, et al. An adaptive model-based feedforward temperature control of a 100 kW PEM electrolyzer[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2022, 120: 104992. |
| [16] | 尹柄桢, 刘小珠, 朱文超, 等. 50 kW PEMEC动态建模及变论域温度控制优化[J]. 太阳能学报, 2025, 46(5): 44-52. |
| Yin B Z, Liu X Z, Zhu W C, et al. 50 kW pemec dynamic modeling and variable universe temperature control optimization[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2025, 46(5): 44-52. | |
| [17] | Ogumerem G S, Pistikopoulos E N. Parametric optimization and control for a smart Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis (PEMWE) system[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2020, 91: 37-49. |
| [18] | 曹威, 石祥建, 蔡丹, 等. 模糊内模控制在电解水制氢温度控制中的应用[J]. 南方能源建设, 2023, 10(3): 120-127. |
| Cao W, Shi X J, Cai D, et al. Application of fuzzy internal model control in temperature control in hydrogen production by water electrolysis[J]. Southern Energy Construction, 2023, 10(3): 120-127. | |
| [19] | 韩鹏飞, 徐潇源, 王晗, 等. 基于功率-温度自适应控制的多堆质子交换膜电解制氢系统效率优化[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(7): 2236-2248. |
| Han P F, Xu X Y, Wang H, et al. Operational efficiency enhancement of multi-stack proton exchange membrane electrolyzer systems with power-temperature adaptive control[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39(7): 2236-2248. | |
| [20] | Scheepers F, Sthler M, Sthler A, et al. Temperature optimization for improving polymer electrolyte membrane-water electrolysis system efficiency[J]. Applied Energy, 2020:116270. |
| [21] | Ren Z B, Wang J Y, Yu Z Y, et al. Experimental studies and modeling of a 250-kW alkaline water electrolyzer for hydrogen production[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 544: 231886. |
| [22] | Qi R M, Li J R, Lin J, et al. Thermal modeling and controller design of an alkaline electrolysis system under dynamic operating conditions[J]. Applied Energy, 2023, 332: 120551. |
| [23] | 李建林, 梁忠豪, 李光辉, 等. 质子交换膜电解槽控制策略研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2023, 38(17): 4787-4799. |
| Li J L, Liang Z H, Li G H, et al. Research on control strategy of proton exchange membrane electrolyzer[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2023, 38(17): 4787-4799. | |
| [24] | Qi R M, Li J R, Lin J, et al. Design of the PID temperature controller for an alkaline electrolysis system with time delays[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(50): 19008-19021. |
| [25] | 朱仲文, 程谭龙, 江维海, 等. 燃料电池氢气系统自适应滑模解耦控制研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2025, 47(1): 85-95, 126. |
| Zhu Z W, Cheng T L, Jiang W H, et al. Research on adaptive sliding mode decoupling control of FC hydrogen system[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2025, 47(1): 85-95, 126. | |
| [26] | 高金武, 王义琳, 刘华洋, 等. 基于滑模观测器的质子交换膜燃料电池阴极进气系统解耦控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2156-2167. |
| Gao J W, Wang Y L, Liu H Y, et al. Decoupling control for proton exchange membrane fuel cell air supply system based on sliding mode observer[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(9): 2156-2167. | |
| [27] | Xing Y S, Costa-Castelló R, Na J. Temperature control for a proton-exchange membrane fuel cell system with unknown dynamic compensations[J]. Complexity, 2020, 2020(1): 8822835. |
| [28] | Xue W C, Zhang X C, Sun L, et al. Extended state filter based disturbance and uncertainty mitigation for nonlinear uncertain systems with application to fuel cell temperature control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(12): 10682-10692. |
| [29] | T/CES 382-2025, 高比例新能源电网中质子交换膜水电解制氢典型测试工况 [S].北京: 中国电工技术学会,2025. |
| T/CES 382-2025, Typical Testing Cycle of Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis for Hydrogen Production in High Penetration Renewable Energy Integrated Power Grid [S]. Beijing: China Electrotechnical Society, 2025. | |
| [30] | 徐衍会, 陈浩维, 胡俊杰. 光伏电解水制氢典型工况及质子交换膜电解堆性能衰减研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2024, 39(19): 6228-6243. |
| Xu Y H, Chen H W, Hu J J. Study on Typical Working Conditions of Hydrogen Production by Photovoltaic Electrolysis of Water and Performance Degradation of Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolytic Stacks[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2024, 39(19): 6228-6243. |
| [1] | 刘豪, 王林, 丁昊, 耿嘉怡. R1150+R1234ze(E)二元体系223.15~253.15 K汽液相平衡研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 1-8. |
| [2] | 密晓光, 孙国刚, 程昊, 张晓慧. 印刷电路板式天然气冷却器性能仿真模型和验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 426-434. |
| [3] | 黄灏, 王文, 李沛昀. 三角转子膨胀机串联运行特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 435-443. |
| [4] | 张文锋, 郭玮, 张新玉, 曹昊敏, 丁国良. 铝管铝翅片换热器模型开发及软件实现[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 84-92. |
| [5] | 郭纪超, 徐肖肖, 孙云龙. 基于植物工厂中的CO2浓度气流模拟及优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 237-245. |
| [6] | 石一帆, 柯钢, 陈浩, 黄孝胜, 叶芳, 李成娇, 郭航. 大型高低温环境实验室温度控制仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 268-280. |
| [7] | 马爱华, 赵帅, 王林, 常明慧. 太阳能吸收制冷循环动态特性仿真方法研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 318-325. |
| [8] | 吴成云, 孙浩然. 民用飞机空调系统性能仿真与燃油代偿损失研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 351-359. |
| [9] | 李卫, 陈浩, 柯钢, 黄孝胜, 李成娇, 郭航, 叶芳. 高原环境适应性试验室模拟平台新风系统仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 360-369. |
| [10] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| [11] | 王偲凡, 栗一帆, 陈江波, 周桓. 碳酸盐型卤水Li+, Na+, K+, CO |
| [12] | 娄岚浩, 杨立鹏, 杨晓光. 锂离子电池电化学机理模型参数辨识研究综述[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4369-4382. |
| [13] | 周轶磊, 李智, 彭鑫. 基于代理模型的连续重整反应过程自优化控制结构设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4499-4511. |
| [14] | 罗海梅, 王泓, 孙照明, 尹艳华. 同向双螺杆传热系数计算模型的分析与验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4809-4823. |
| [15] | 邹家庆, 张肇钰, 张建国, 张博宇, 刘定胜, 毛庆, 王挺, 李建军. 碱水制氢电解槽极板通道中气泡的生成及演化性质[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4786-4799. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号