• •
收稿日期:2025-10-09
修回日期:2025-11-27
出版日期:2025-12-12
通讯作者:
胡善伟,刘新华
作者简介:周芷康(2001—),男,硕士研究生,zhouzhikang23@ipe.ac.cn
基金资助:
Zhikang ZHOU1,2( ), Shanwei HU1,2(
), Shanwei HU1,2( ), Xinhua LIU1,2(
), Xinhua LIU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-10-09
Revised:2025-11-27
Online:2025-12-12
Contact:
Shanwei HU, Xinhua LIU
摘要:
气固流化系统中,介尺度结构的形成和动态演化对反应器的三传一反过程具有重要的影响。本文采用CFD-DEM耦合模拟与正交试验设计方法,系统研究了快速流化床中颗粒团聚物的静态(直径、浓度)与动态(寿命)特征及其影响机制。建立了基于DBSCAN和自适应大津法相结合的颗粒尺度的团聚物识别方法,提出了考虑破碎/聚并事件的团聚物寿命定义,并考察气速、颗粒通量、提升管几何结构及颗粒密度等多因素的耦合效应。分析表明气速对团聚物直径影响最大,提升管几何结构对浓度影响最显著,寿命主要由气速与几何结构共同控制;本文建立了团聚物直径预测关联式,揭示了寿命随直径呈先增后减、随浓度单调升高的非线性规律。
中图分类号:
周芷康, 胡善伟, 刘新华. 气固流化床中颗粒团聚物的静态特征和湮灭规律研究[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251102.
Zhikang ZHOU, Shanwei HU, Xinhua LIU. Investigation on the static properties and annihilation characteristics of particle clusters in gas-solid fluidized beds[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251102.
| 名称 | 符号 | 值 |
|---|---|---|
| 颗粒直径(μm) | dp | 850 |
| 气体密度(kg/m3) | ρg | 1.225 |
| 气体黏度(Pa·s) | μg | 1.8×10-5 |
| CFD步长(s) | ∆tgas | 5.0×10-5 |
| DEM步长(s) | ∆tDEM | 1/20×Tcollide |
| 网格分辨率(-) | - | 3dp |
| 弹性恢复系数(颗粒-颗粒) | ep-p | 0.96 |
| 弹性恢复系数(颗粒-墙壁) | ep-w | 0.86 |
| 摩擦系数(颗粒-颗粒) | μfr | 0.15 |
| 弹簧刚度系数(N/m) | kn | 1600 |
表1 DEM模拟参数表
Table 1 Parameters in DEM simulations
| 名称 | 符号 | 值 |
|---|---|---|
| 颗粒直径(μm) | dp | 850 |
| 气体密度(kg/m3) | ρg | 1.225 |
| 气体黏度(Pa·s) | μg | 1.8×10-5 |
| CFD步长(s) | ∆tgas | 5.0×10-5 |
| DEM步长(s) | ∆tDEM | 1/20×Tcollide |
| 网格分辨率(-) | - | 3dp |
| 弹性恢复系数(颗粒-颗粒) | ep-p | 0.96 |
| 弹性恢复系数(颗粒-墙壁) | ep-w | 0.86 |
| 摩擦系数(颗粒-颗粒) | μfr | 0.15 |
| 弹簧刚度系数(N/m) | kn | 1600 |
| 试验号 | 时均颗粒数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60 | 12 | 55 | 1600 | 6 | 27820 |
| 2 | 60 | 14 | 60 | 1800 | 8 | 36019 |
| 3 | 60 | 16 | 65 | 2000 | 10 | 39803 |
| 4 | 60 | 18 | 70 | 2200 | 12 | 45105 |
| 5 | 70 | 12 | 65 | 2200 | 8 | 38044 |
| 6 | 70 | 14 | 70 | 2000 | 6 | 26055 |
| 7 | 70 | 16 | 55 | 1800 | 12 | 71497 |
| 8 | 70 | 18 | 60 | 1600 | 10 | 60931 |
| 9 | 80 | 12 | 70 | 1800 | 10 | 41477 |
| 10 | 80 | 14 | 65 | 1600 | 12 | 50581 |
| 11 | 80 | 16 | 60 | 2200 | 6 | 79376 |
| 12 | 80 | 18 | 55 | 2000 | 8 | 95094 |
| 13 | 90 | 12 | 60 | 2000 | 12 | 80448 |
| 14 | 90 | 14 | 55 | 2200 | 10 | 125792 |
| 15 | 90 | 16 | 70 | 1600 | 8 | 46484 |
| 16 | 90 | 18 | 65 | 1800 | 6 | 74453 |
表2 无量纲工况参数
Table 2 Dimensionless operating parameters
| 试验号 | 时均颗粒数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60 | 12 | 55 | 1600 | 6 | 27820 |
| 2 | 60 | 14 | 60 | 1800 | 8 | 36019 |
| 3 | 60 | 16 | 65 | 2000 | 10 | 39803 |
| 4 | 60 | 18 | 70 | 2200 | 12 | 45105 |
| 5 | 70 | 12 | 65 | 2200 | 8 | 38044 |
| 6 | 70 | 14 | 70 | 2000 | 6 | 26055 |
| 7 | 70 | 16 | 55 | 1800 | 12 | 71497 |
| 8 | 70 | 18 | 60 | 1600 | 10 | 60931 |
| 9 | 80 | 12 | 70 | 1800 | 10 | 41477 |
| 10 | 80 | 14 | 65 | 1600 | 12 | 50581 |
| 11 | 80 | 16 | 60 | 2200 | 6 | 79376 |
| 12 | 80 | 18 | 55 | 2000 | 8 | 95094 |
| 13 | 90 | 12 | 60 | 2000 | 12 | 80448 |
| 14 | 90 | 14 | 55 | 2200 | 10 | 125792 |
| 15 | 90 | 16 | 70 | 1600 | 8 | 46484 |
| 16 | 90 | 18 | 65 | 1800 | 6 | 74453 |
| 试验号 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.051 | 0.612 | 5.0 | 1960 | 36.9 |
| 2 | 0.051 | 0.714 | 5.5 | 2205 | 53.7 |
| 3 | 0.051 | 0.816 | 5.9 | 2450 | 72.7 |
| 4 | 0.051 | 0.918 | 6.4 | 2695 | 94.0 |
| 5 | 0.060 | 0.714 | 5.9 | 2695 | 58.2 |
| 6 | 0.060 | 0.833 | 6.4 | 2450 | 47.0 |
| 7 | 0.060 | 0.952 | 5.0 | 2205 | 73.8 |
| 8 | 0.060 | 1.071 | 5.5 | 1960 | 67.1 |
| 9 | 0.068 | 0.816 | 6.4 | 2205 | 78.3 |
| 10 | 0.068 | 0.952 | 5.9 | 1960 | 87.3 |
| 11 | 0.068 | 1.088 | 5.5 | 2695 | 40.3 |
| 12 | 0.068 | 1.224 | 5.0 | 2450 | 49.2 |
| 13 | 0.077 | 0.918 | 5.5 | 2450 | 80.5 |
| 14 | 0.077 | 1.071 | 5.0 | 2695 | 61.5 |
| 15 | 0.077 | 1.224 | 6.4 | 1960 | 62.6 |
| 16 | 0.077 | 1.377 | 5.9 | 2205 | 43.6 |
表3 实际操作参数
Table 3 Operating parameters corresponding to Table 2
| 试验号 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.051 | 0.612 | 5.0 | 1960 | 36.9 |
| 2 | 0.051 | 0.714 | 5.5 | 2205 | 53.7 |
| 3 | 0.051 | 0.816 | 5.9 | 2450 | 72.7 |
| 4 | 0.051 | 0.918 | 6.4 | 2695 | 94.0 |
| 5 | 0.060 | 0.714 | 5.9 | 2695 | 58.2 |
| 6 | 0.060 | 0.833 | 6.4 | 2450 | 47.0 |
| 7 | 0.060 | 0.952 | 5.0 | 2205 | 73.8 |
| 8 | 0.060 | 1.071 | 5.5 | 1960 | 67.1 |
| 9 | 0.068 | 0.816 | 6.4 | 2205 | 78.3 |
| 10 | 0.068 | 0.952 | 5.9 | 1960 | 87.3 |
| 11 | 0.068 | 1.088 | 5.5 | 2695 | 40.3 |
| 12 | 0.068 | 1.224 | 5.0 | 2450 | 49.2 |
| 13 | 0.077 | 0.918 | 5.5 | 2450 | 80.5 |
| 14 | 0.077 | 1.071 | 5.0 | 2695 | 61.5 |
| 15 | 0.077 | 1.224 | 6.4 | 1960 | 62.6 |
| 16 | 0.077 | 1.377 | 5.9 | 2205 | 43.6 |
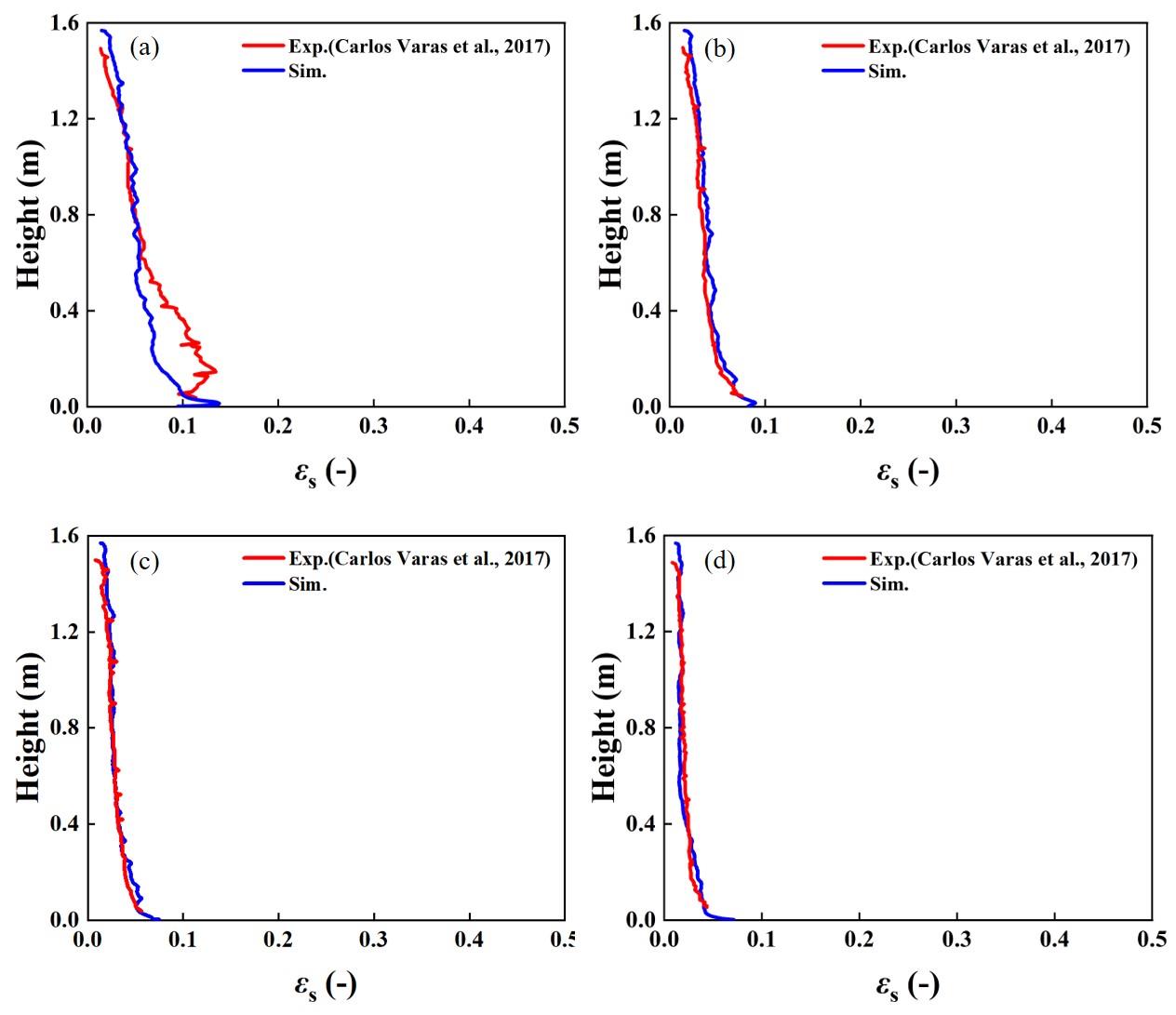
图4 不同气速下时均颗粒浓度的轴向分布注:(a) Ug=5.55 m/s (b) Ug=5.95 m/s (c) Ug=6.35 m/s (d) Ug=6.74 m/s
Fig. 4 Time-averaged axial profiles of solid volume fraction at different gas velocities
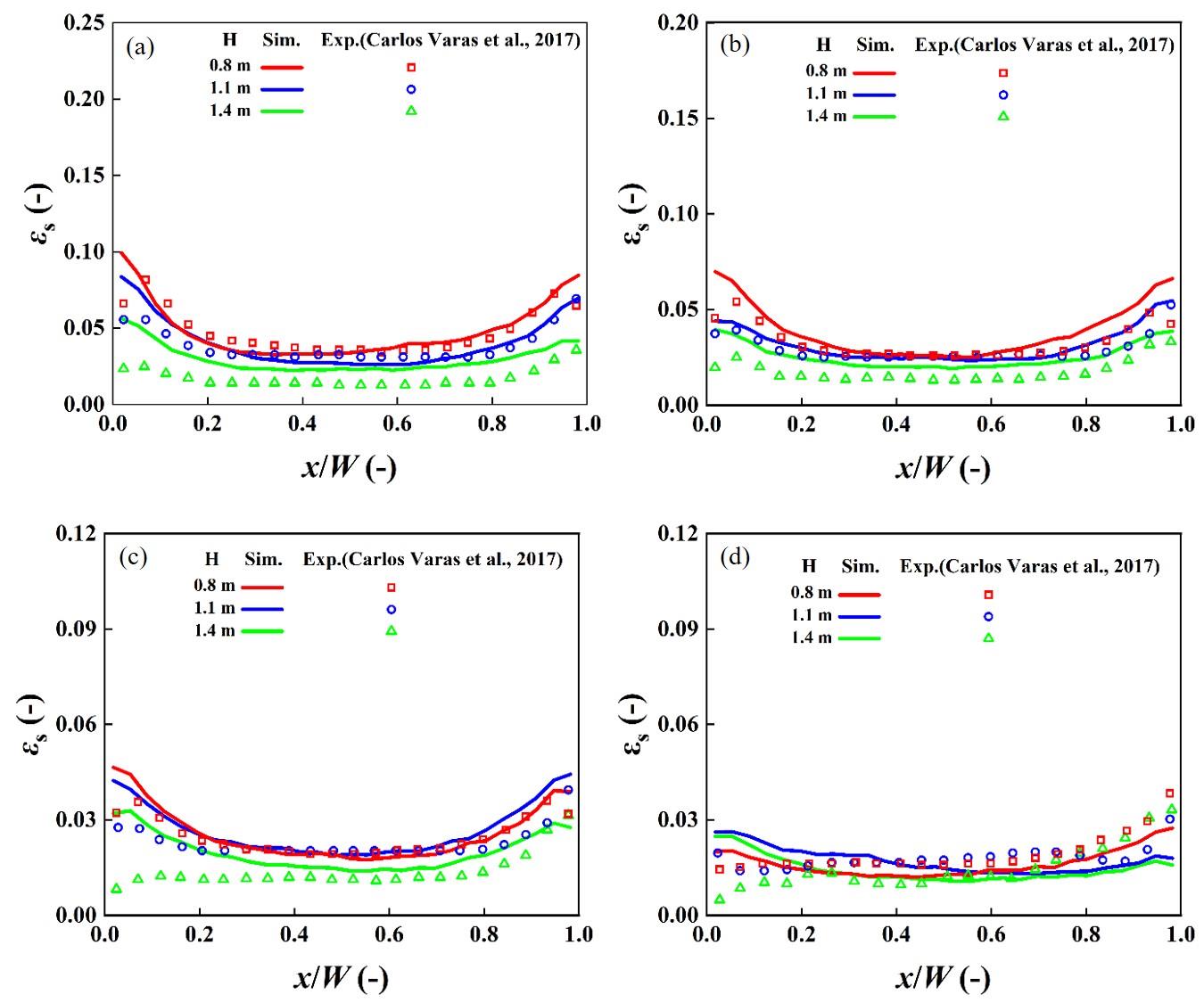
图5 不同气速下时均颗粒浓度的横向分布注:(a) Ug=5.55 m/s (b) Ug=5.95 m/s (c) Ug=6.35 m/s (d) Ug=6.74 m/s(a) Ug=5.55 m/s (b) Ug=5.95 m/s (c) Ug=6.35 m/s (d) Ug=6.74 m/s
Fig. 5 Time-averaged lateral profiles of solid volume fraction at different gas velocities
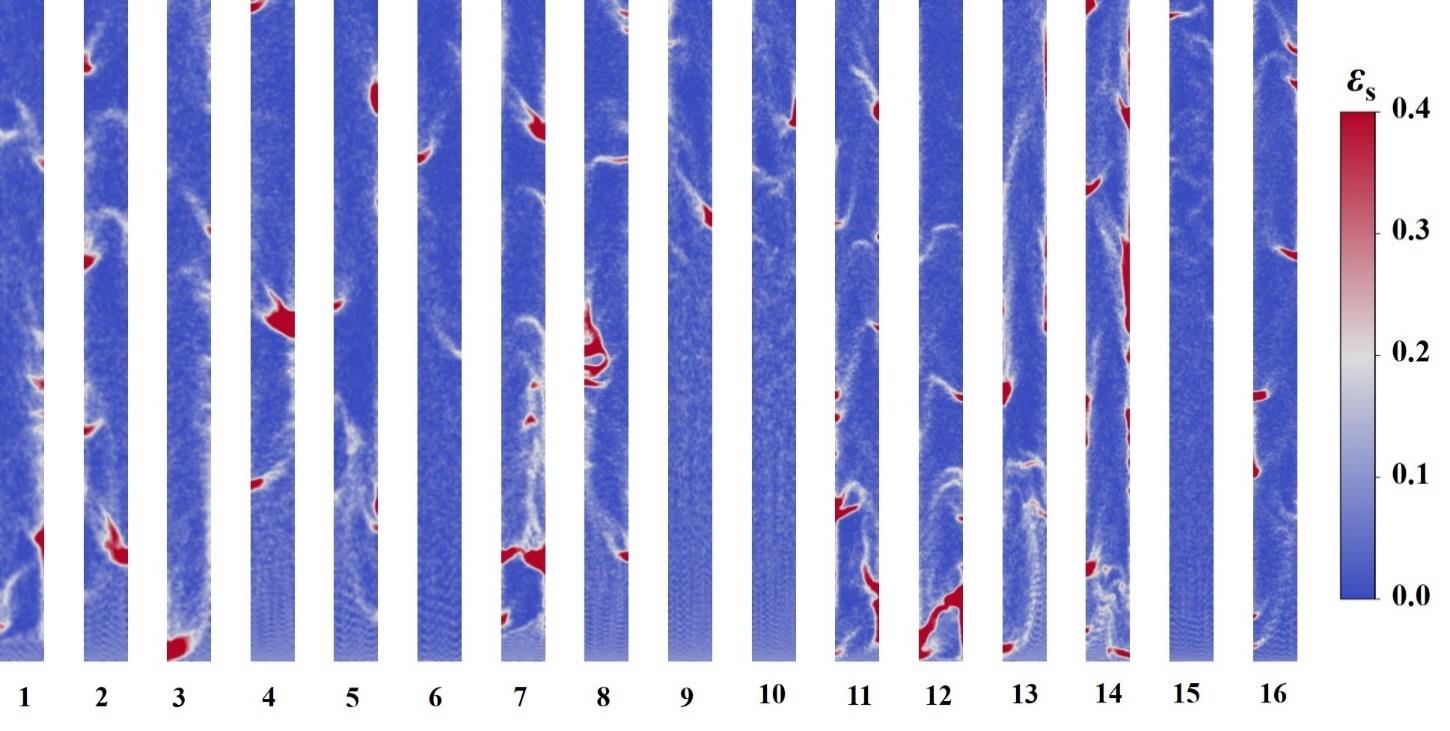
图9 正交数值模拟试验算例颗粒浓度瞬时分布(为了方便对比,对反应器大小进行了缩放)
Fig. 9 Instantaneous contours of solid volume fraction in the central plane in different cases (note the size of the reactors has been scaled).
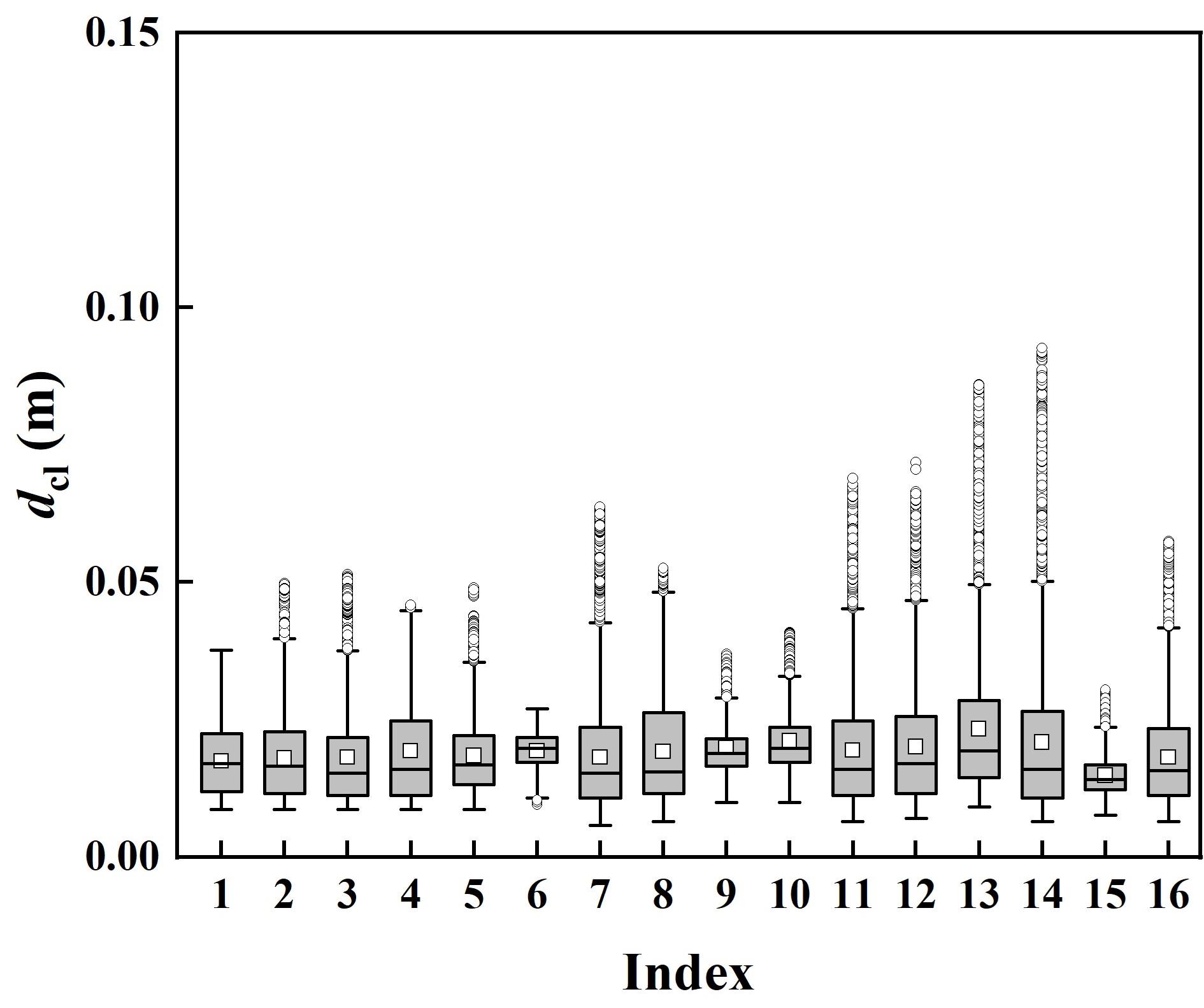
图11 团聚物直径箱线图。其中箱体内的中心线和矩形分别表示中位数和均值,箱体上下边界分别为上、下四分位数,须线延伸至1.5倍四分位距内的最值,圆点为离群值。
Fig. 11 Boxplots of cluster diameters. The center line and rectangle within the box represent the median and mean, respectively. The upper and lower boundaries of the box are the upper and lower quartiles. The whiskers extend to the maximum values within 1.5 times the interquartile range, and the dots indicate outliers.
| 式(18) | 式(19) | 式(20) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 常数项 | 29.34 | 22.42 | 22.38 |
| - | - | 0.0027 | |
| 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.44 | |
| -0.18 | -0.18 | -0.18 | |
| - | 0.0036 | 0.0036 | |
| p值 | 0.023 | 0.012 | 0.032 |
| 显著性 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 |
| Pearson系数 | 0.66 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
表4 团聚物平均直径的多元线性回归方程系数表
Table 4 Multiple linear regression equation of average cluster diameter
| 式(18) | 式(19) | 式(20) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 常数项 | 29.34 | 22.42 | 22.38 |
| - | - | 0.0027 | |
| 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.44 | |
| -0.18 | -0.18 | -0.18 | |
| - | 0.0036 | 0.0036 | |
| p值 | 0.023 | 0.012 | 0.032 |
| 显著性 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 |
| Pearson系数 | 0.66 | 0.77 | 0.77 |
| [1] | Afsahi F A, Sotudeh-Gharebagh R, Mostoufi N. Clusters identification and characterization in a gas–solid fluidized bed by the wavelet analysis[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2009, 87(3): 375-385. |
| [2] | Cocco R, Shaffer F, Hays R, et al. Particle clusters in and above fluidized beds[J]. Powder Technology, 2010, 203(1): 3-11. |
| [3] | Boyd J W R, Varley J. The uses of passive measurement of acoustic emissions from chemical engineering processes[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2001, 56(5): 1749-1767. |
| [4] | Liu X H, Gao S Q, Li J H. Characterizing particle clustering behavior by PDPA measurement for dilute gas–solid flow[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2005, 108(3): 193-202. |
| [5] | Yang T Y, Leu L P. Multiresolution analysis on identification and dynamics of clusters in a circulating fluidized bed[J]. AIChE Journal, 2009, 55(3): 612-629. |
| [6] | Liu H P, Zhang L Y, Chen T P, et al. Experimental study on the fluidization behaviors of the superfine particles[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 262: 579-587. |
| [7] | Harris A T, Davidson J F, Thorpe R B. The prediction of particle cluster properties in the near wall region of a vertical riser (200157)[J]. Powder Technology, 2002, 127(2): 128-143. |
| [8] | Teplitskii Y S. On the cluster structure of a circulating fluidized bed[J]. Journal of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics, 2005, 78(2): 316-322. |
| [9] | Horio M, Morishita K, Tachibana O, et al. Solid distribution and movement in circulating fluidized beds[M]//Circulating Fluidized Bed Technology. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1988: 147-154. |
| [10] | Mostoufi N, Chaouki J. Flow structure of the solids in gas–solid fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2004, 59(20): 4217-4227. |
| [11] | Wang C X, Lan X Y, Sun Z N, et al. Cluster identification by a k-means algorithm-assisted imaging method in a laboratory-scale circulating fluidized bed[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(1): 942-956. |
| [12] | Xu J, Zhu J. A new method for the determination of cluster velocity and size in a circulating fluidized bed[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2012, 51(4): 2143-2151. |
| [13] | Lin Q, Wei F, Jin Y. Transient density signal analysis and two-phase micro-structure flow in gas–solids fluidization[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2001, 56(6): 2179-2189. |
| [14] | Yu J H, Wang S, Luo K, et al. CFD-DEM modeling of dense gas-solid reacting flow in the framework of GPU[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 484: 149480. |
| [15] | Banaei M, Jegers J, van Sint Annaland M, et al. Tracking of particles using TFM in gas-solid fluidized beds[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2018, 29(10): 2538-2547. |
| [16] | Gao X, Li T W, Rogers W A. Assessment of mesoscale solid stress in coarse-grid TFM simulation of Geldart A particles in all fluidization regimes[J]. AIChE Journal, 2018, 64(10): 3565-3581. |
| [17] | Xiong Q G, Li B, Zhou G F, et al. Large-scale DNS of gas–solid flows on Mole-8.5 [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 71: 422-430. |
| [18] | Deen N G, Peters E A J F, Padding J T, et al. Review of direct numerical simulation of fluid–particle mass, momentum and heat transfer in dense gas–solid flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2014, 116: 710-724. |
| [19] | Yang L N, Han C X, Xu J, et al. Role of mesoscale structure in gas–solid fluidization: Comparison between continuum and discrete approaches[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 454: 139979. |
| [20] | Jin N N, Hu S W, Liu X H, et al. Machine learning assisted characterization of local bubble properties and its coupling with the EMMS bubbling drag[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2024, 63(10): 4631-4646. |
| [21] | Kumar B K, Ganesh S, Goyal H. Capturing mesoscale structures in computational fluid dynamics simulations of gas-solid flows[J]. AIChE Journal, 2024, 70(5): e18360. |
| [22] | Wang T Y, Deng A M, He Y R, et al. Artificial intelligence-based approach for cluster identification in a CFB riser[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2023, 268: 118379. |
| [23] | Yin S Y, Zhong W Q, Song T, et al. Clusters identification and meso-scale structures in a circulating fluidized bed based on image processing[J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2019, 30(12): 3010-3020. |
| [24] | Petersen A J, Baker L, Coletti F. Experimental study of inertial particles clustering and settling in homogeneous turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 864: 925-970. |
| [25] | Liu X W, Wang L M, Ge W. Meso-scale statistical properties of gas–solid flow: a direct numerical simulation (DNS) study[J]. AIChE Journal, 2017, 63(1): 3-14. |
| [26] | Kong L K, Xu J, Wang J W, et al. Nonequilibrium characteristics and spatiotemporal long-range correlations in dense gas-solid suspensions[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2021, 142: 103731. |
| [27] | Zhang H D, Sun Z N, Zhang M Z, et al. Comparison of the flow structures and regime transitions between a cylindrical fluidized bed and a square fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 376: 507-516. |
| [28] | Carlos Varas A E, Peters E A J F, Kuipers J A M. CFD-DEM simulations and experimental validation of clustering phenomena and riser hydrodynamics[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 169: 246-258. |
| [29] | Cabezas-Gómez L, da Silva R C, Navarro H A, et al. Cluster identification and characterization in the riser of a circulating fluidized bed from numerical simulation results[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2008, 32(3): 327-340. |
| [30] | Lu H L, Sun Q Q, He Y R, et al. Numerical study of particle cluster flow in risers with cluster-based approach[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2005, 60(23): 6757-6767. |
| [31] | Tsuo Y P, Gidaspow D. Computation of flow patterns in circulating fluidized beds[J]. AIChE Journal, 1990, 36(6): 885-896. |
| [32] | Tsuji Y, Tanaka T, Yonemura S. Cluster patterns in circulating fluidized beds predicted by numerical simulation (discrete particle model versus two-fluid model)[J]. Powder Technology, 1998, 95(3): 254-264. |
| [33] | Hu S W, Liu X H. A CFD-PBM-EMMS integrated model applicable for heterogeneous gas-solid flow[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 383: 123122. |
| [34] | Wang H F, Chen Y P, Wang W. Particle-level dynamics of clusters: Experiments in a gas-fluidized bed[J]. AIChE Journal, 2022, 68(3): e17525. |
| [35] | Tagawa Y, Mercado J M, Prakash V N, et al. Three-dimensional Lagrangian Voronoï analysis for clustering of particles and bubbles in turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2012, 693: 201-215. |
| [36] | Liu Y Q, Shen L, Zamansky R, et al. Life and death of inertial particle clusters in turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2020, 902: R1. |
| [37] | Kong L K, Xu J, Wang J W, et al. Characterizing particle clustering behavior in dense gas–solid suspensions[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(45): 19145-19160. |
| [38] | Niu L, Chu Z M, Cai M, et al. Modified force balance model of estimating agglomerate sizes in a gas–solid fluidized bed[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(19): 8472-8483. |
| [39] | Lu L Q, Gao X, Dietiker J F, et al. Machine learning accelerated discrete element modeling of granular flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2021, 245: 116832. |
| [40] | Cundall P A, Strack O D L. A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies[J]. Géotechnique, 1979, 29(1): 47-65. |
| [41] | Carlos Varas A E, Peters E A J F, Kuipers J A M. Experimental study of full field riser hydrodynamics by PIV/DIA coupling[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 313: 402-416. |
| [42] | Garg R, Galvin J, Li T W, et al. Open-source MFIX-DEM software for gas–solids flows: Part I: Verification studies[J]. Powder Technology, 2012, 220: 122-137. |
| [43] | Tian T, Wang H, Ge W, et al. Detecting particle clusters in particle-fluid systems by a density based method[J]. Communications in Computational Physics, 2025, 26(5): 1617-1630. |
| [44] | Fortune S. A sweepline algorithm for Voronoi diagrams[J]. Algorithmica, 1987, 2(1): 153-174. |
| [45] | Wu X, Leung D Y C. Optimization of biodiesel production from camelina oil using orthogonal experiment[J]. Applied Energy, 2011, 88(11): 3615-3624. |
| [46] | Goldhirsch I I, Zanetti G. Clustering instability in dissipative gases[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1993, 70(11): 1619-1622. |
| [47] | Fullmer W D, Hrenya C M. The clustering instability in rapid granular and gas-solid flows[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2017, 49: 485-510. |
| [1] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [2] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [3] | 陈昇, 李子争, 苗超, 白学刚, 李飞, 刘家璇, 李天天, 杨爽, 吕蓉蓉, 王江云. 大尺度密集场景高危氯气非均匀湍流扩散特性三维CFD模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4630-4643. |
| [4] | 贾志勇, 沈宪琨, 蓝晓程, 王铁峰. 气体密度对高压流态化影响的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4383-4397. |
| [5] | 解勤勤, 翁俊旗, 林振利, 叶光华, 周兴贵. 固定床反应器中甲醇制芳烃工业催化剂结构影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4487-4498. |
| [6] | 张帅, 徐嘉宇, 华蕾娜, 葛蔚. 气固系统的CG-DPM与MP-PIC耦合模拟方法[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4412-4424. |
| [7] | 曹潇风, 张华海, 王江云, 王利民. 锥形气体层流元件结构设计及流动特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4440-4448. |
| [8] | 马永丽, 安澍, 杨捷, 刘明言. 气液固流化床直接数值模拟研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3772-3788. |
| [9] | 王泽, 胡琼, 陈雅静, 王衍, 耿佳旭, 沈斐然. 液体自冲击密封泄漏特性、密封机理与优化设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4194-4204. |
| [10] | 朱紫橙, 焦云鹏, 刘梦溪, 陈建华. 三相流化床内分布器与挡板效应的模拟分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3873-3884. |
| [11] | 苏国庆, 田学梅, 李彦, 张建文, 张志军. 气力输送系统弯管三通的冲蚀分析及改进[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3894-3904. |
| [12] | 夏天炜, 王谙词, 句子涵, 孙晓霞, 胡定华. 基于三周期极小曲面结构的高密度储热器蓄放热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3605-3614. |
| [13] | 王芳, 马素霞, 田营, 刘众元. 基于LSTM动态修正一维机理模型的CFB机组NO x 排放浓度预测方法[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3416-3425. |
| [14] | 陈曦, 王淑彦, 邵宝力, 丁诺, 谢磊. 基于颗粒动态恢复系数二阶矩模型的液固流化床数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3246-3258. |
| [15] | 王富玉, 周晅毅. 结合非定常伴随方程和遗传算法的化工区反演[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3104-3114. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号