• •
苏敬宏1( ), 张亿宝2, 孙超2,3(
), 张亿宝2, 孙超2,3( ), 王军武1,4(
), 王军武1,4( )
)
收稿日期:2025-12-05
修回日期:2026-01-13
出版日期:2026-01-21
通讯作者:
孙超,王军武
作者简介:苏敬宏(1992—),男,博士,讲师,jhsu@cup.edu.cn
基金资助:
Jinghong SU1( ), Yi-Bao ZHANG2, Chao SUN2,3(
), Yi-Bao ZHANG2, Chao SUN2,3( ), Junwu WANG1,4(
), Junwu WANG1,4( )
)
Received:2025-12-05
Revised:2026-01-13
Online:2026-01-21
Contact:
Chao SUN, Junwu WANG
摘要:
由两种互不相溶的液体相互掺混形成的液液两相湍流系统在自然界中广泛存在,并在石油与化工等领域具有重要应用。两相界面和湍流流动之间存在多尺度的耦合作用,这使得两相湍流内的流体动力学行为比单相湍流更为复杂。本文采用界面解析的流体体积法对泰勒-库埃特系统内的液液两相湍流进行了三维直接数值模拟,研究了不同流体性质的离散液滴对湍流统计特性的影响。研究发现,当两相具有相同密度与黏度时,离散液滴将增强湍流脉动的角动量输运能力并对湍流脉动分布产生调制,具体表现为增强内外圆柱附近湍流脉动而削弱远离内外圆柱区域的湍流脉动。离散液滴密度的降低以及离散液滴黏度的进一步降低都倾向于削弱湍流脉动的强度和角动量输运能力。而对于泰勒涡结构,离散液滴的存在始终倾向于削弱泰勒涡的角动量输运能力和强度。相关研究结果有助于深入理解液液两相湍流中离散相对湍流的影响。
中图分类号:
苏敬宏, 张亿宝, 孙超, 王军武. 液液两相湍流中的统计特性分析[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251370.
Jinghong SU, Yi-Bao ZHANG, Chao SUN, Junwu WANG. Statistical characteristic analysis in turbulent emulsions[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251370.
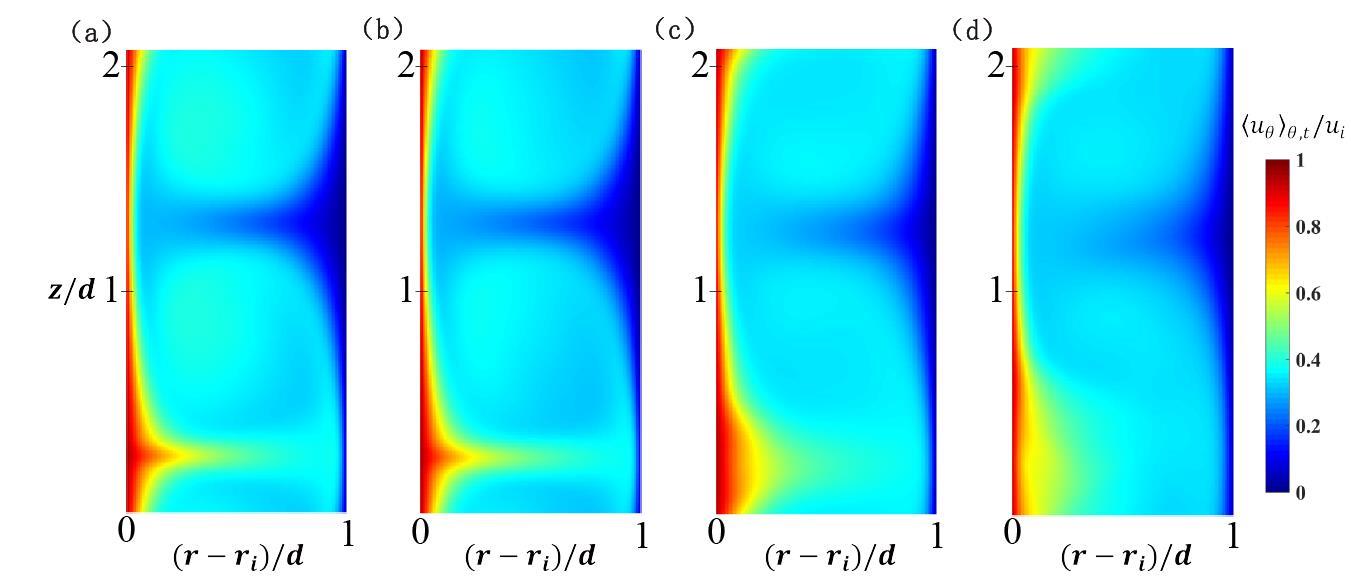
图2 不同情况下平均方位角速度uθθ,t/ui的分布云图:(a)单相情况,(b)离散相为中性液滴的两相情况,(c)离散相为轻液滴的两相情况,(d)离散相为低黏度轻液滴的两相情况。
Fig.2 Contour map of averaged azimuthal velocity uθθ,t/ui under different conditions: (a) single-phase case, (b) two-phase case with neutral buoyant droplets, (c) two-phase case with light droplets, (d) two-phase case with low-viscosity light droplets.
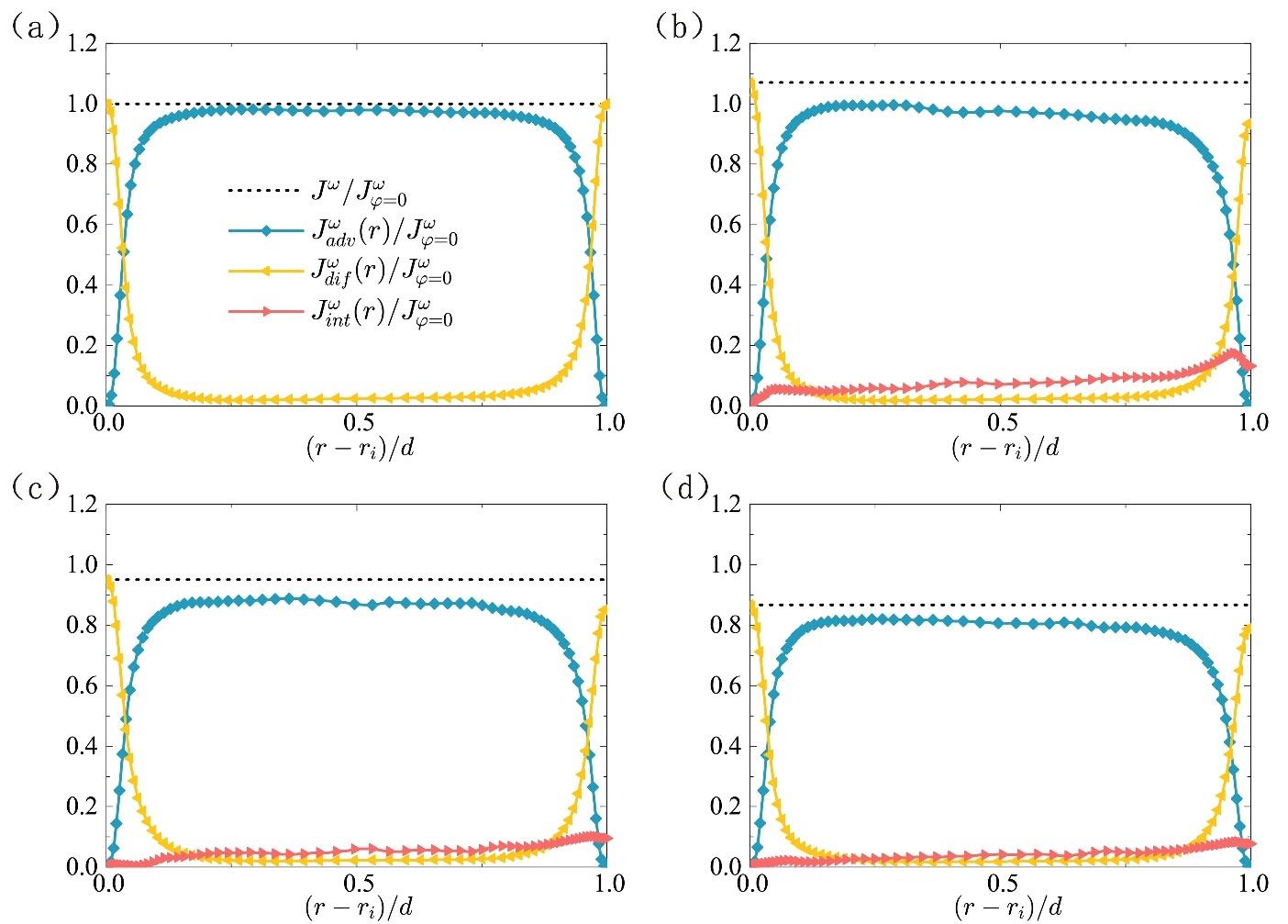
图3 角动量通量及其贡献项沿径向位置的分布:(a)单相情况,(b)离散相为中性液滴的两相情况,(c)离散相为轻液滴的两相情况,(d)离散相为低黏度轻液滴的两相情况。
Fig.3 Distribution of the angular momentum flux and its contribution terms in the radial direction: (a) single-phase case, (b) two-phase case with neutral buoyant droplets, (c) two-phase case with light droplets, (d) two-phase case with low-viscosity light droplets.
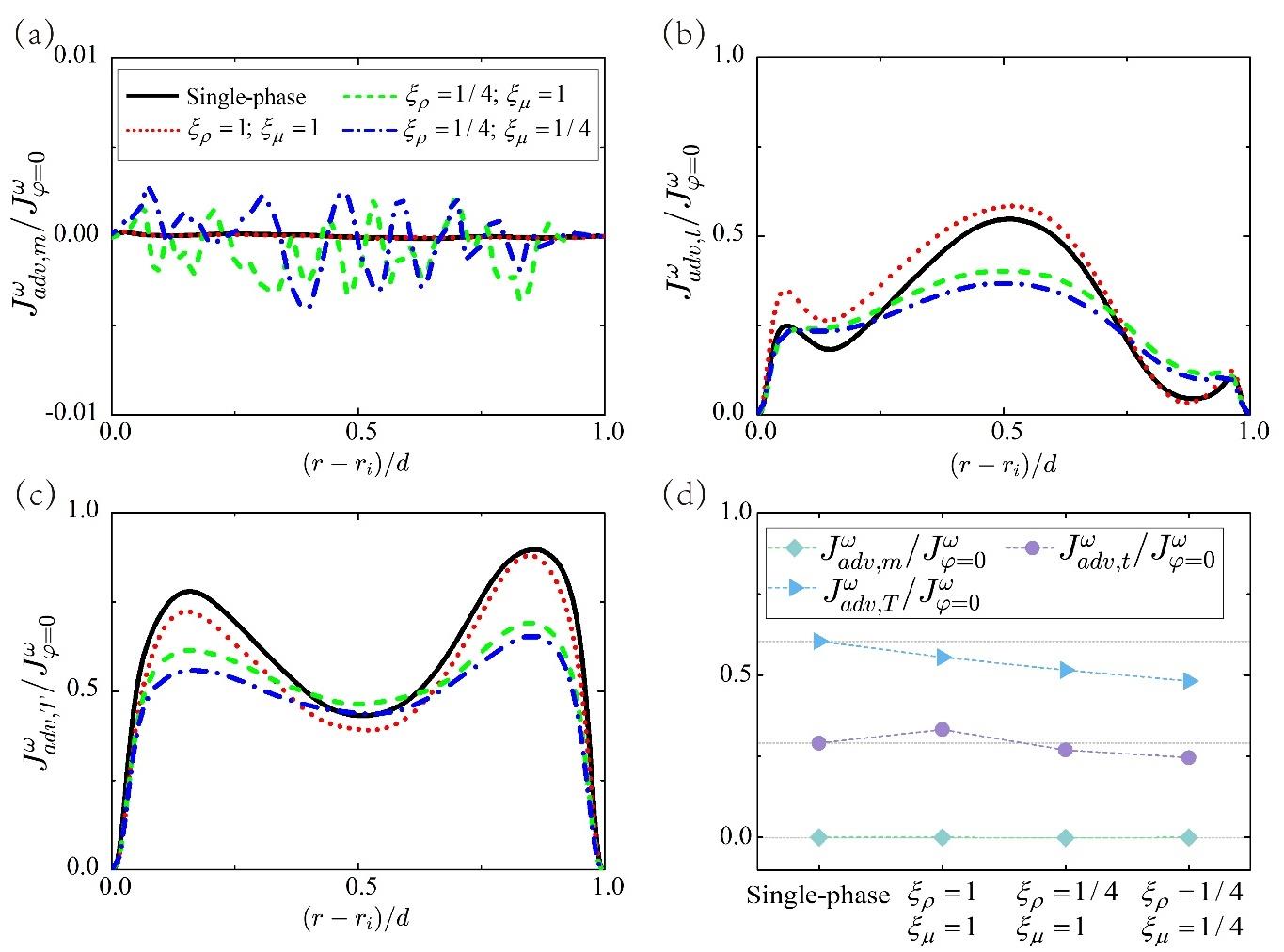
图4 对流贡献项分析:(a)平均场、(b)湍流脉动和(c)泰勒涡的贡献沿径向位置的分布。图(d)将对流贡献项及其三个子项在径向上进行了平均,以表征各项在整个系统内的均值。灰色虚线表示单相湍流情况下的均值。所有量均除以单相湍流情况下的角动量通量Jφ=0ω以便进行更直观地对比分析。图(a)的纵坐标最大值被设定为0.01,而图(b-d)的纵坐标最大值被设定为1.0。
Fig.4 Advection contribution analysis. The contributions from (a) the mean field, (b) the turbulence fluctuation, and (c) the Taylor vortex are shown as a function of the radial position. (d) The whole advection contribution and its three parts are averaged in the radial direction to characterize the corresponding total amount within the whole system. The gray dashed lines in (d) represent the averaged values for single-phase flow. All quantities are normalized by the conserved quantity Jφ=0ω. The maximum value of the ordinate of (a) is set as 0.01, while the maximum value of the ordinate of (b-d) is set as 1.0.
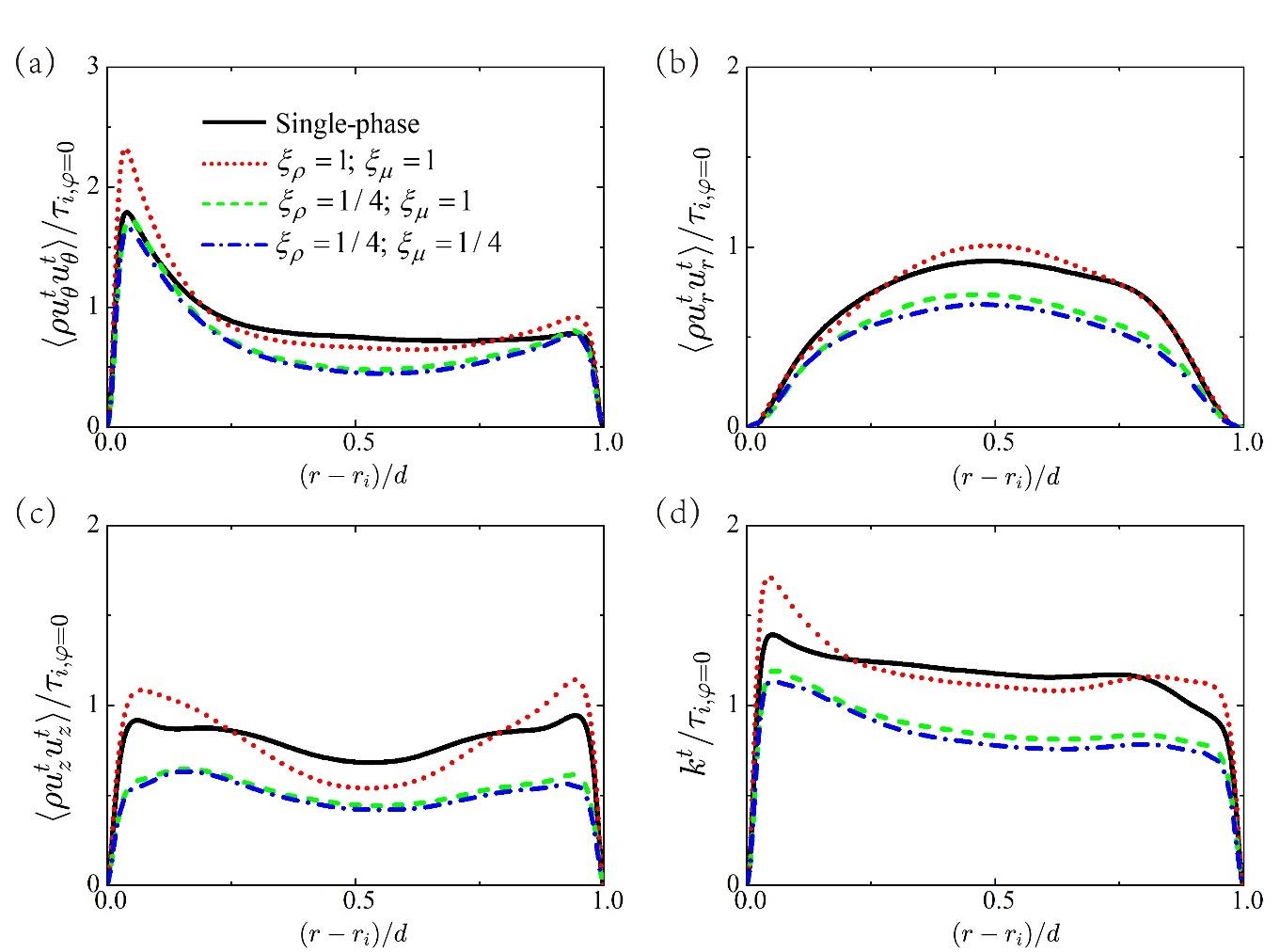
图5 离散液滴对湍流脉动的调制。图中分别显示了以下各分量随径向位置的变化:(a) ρuθtuθt(b) ρurturt,(c)ρuztuzt以及(d)湍流脉动的动能 kt=0.5ρuθtuθt+ρurturt+ρuztuzt。所有量均除以单相湍流下内圆柱上的剪切应力τi, φ=0进行无量纲化。
Fig.5 The modulation on the turbulence-induced vortices. The components (a) ρuθtuθt, (b) ρurturt, (c) ρuztuzt, and (d) the kinetic energy of turbulence fluctuation kt=0.5ρuθtuθt+ρurturt+ρuztuzt are shown as a function of the radial position. The quantities are non-dimensionalized by the shear stress τi, φ=0 at the inner cylinder in single-phase flow.
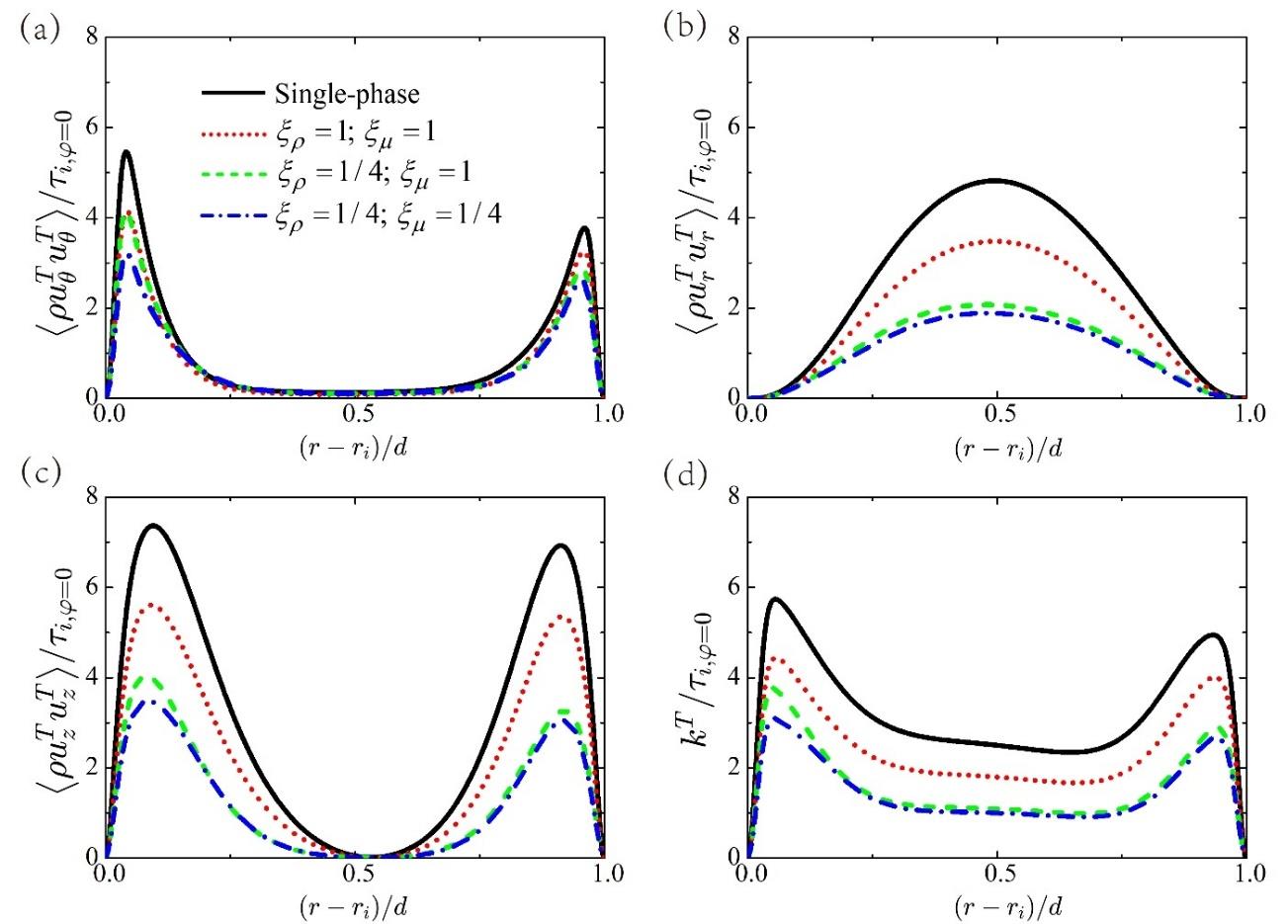
图6 离散液滴对泰勒涡强度的调制。图中分别显示了以下各分量沿径向位置的变化:(a) ρuθTuθT(b) ρurTurT,(c)ρuzTuzT以及(d)泰勒涡的动能kT=0.5ρuθTuθT+ρurTurT+ρuzTuzT。所有量均除以单相流中内圆柱壁面剪切应力τi, φ=0进行无量纲化。
Fig.6 The modulation on the Taylor vortex. The components (a) ρuθTuθT, (b) ρurTurT, (c) ρuzTuzT, and (d) the kinetic energy of Taylor vortex kT=0.5ρuθTuθT+ρurTurT+ρuzTuzT are shown as a function of the radial position. The quantities are non-dimensionalized by the shear stress τi, φ=0 at the inner cylinder in single-phase flow.
| [1] | Spernath A, Aserin A. Microemulsions as carriers for drugs and nutraceuticals[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 128: 47-64. |
| [2] | Wang L J, Li X F, Zhang G Y, et al. Oil-in-water nanoemulsions for pesticide formulations[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2007, 314(1): 230-235. |
| [3] | McClements D J. Critical review of techniques and methodologies for characterization of emulsion stability[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2007, 47(7): 611-649. |
| [4] | Kilpatrick P K. Water-in-crude oil emulsion stabilization: review and unanswered questions[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2012, 26(7): 4017-4026. |
| [5] | Lemenand T, Della Valle D, Dupont P, et al. Turbulent spectrum model for drop-breakup mechanisms in an inhomogeneous turbulent flow[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 158: 41-49. |
| [6] | Olad P, Innings F, Crialesi-Esposito M, et al. Comparison of turbulent drop breakup in an emulsification device and homogeneous isotropic turbulence: Insights from numerical experiments[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 657: 130569. |
| [7] | Ni R. Deformation and breakup of bubbles and drops in turbulence[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2024, 56: 319-347. |
| [8] | Kavehpour H P. Coalescence of drops[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2015, 47: 245-268. |
| [9] | Kamp J, Villwock J, Kraume M. Drop coalescence in technical liquid/liquid applications: a review on experimental techniques and modeling approaches[J]. Reviews in Chemical Engineering, 2017, 33(1): 1-47. |
| [10] | Håkansson A, Crialesi-Esposito M, Nilsson L, et al. A criterion for when an emulsion drop undergoing turbulent deformation has reached a critically deformed state[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2022, 648: 129213. |
| [11] | Rosti M E, De Vita F, Brandt L. Numerical simulations of emulsions in shear flows[J]. Acta Mechanica, 2019, 230(2): 667-682. |
| [12] | Rallison J. The deformation of small viscous drops and bubbles in shear flows[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1984, 16: 45-66. |
| [13] | Lohse D. Bubble puzzles: From fundamentals to applications[J]. Physical Review Fluids, 2018, 3(11): 110504. |
| [14] | Balachandar S, Eaton J K. Turbulent dispersed multiphase flow[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2010, 42: 111-133. |
| [15] | Yi L, Toschi F, Sun C. Global and local statistics in turbulent emulsions[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2021, 912: A13. |
| [16] | Yi L, Wang C, van Vuren T, et al. Physical mechanisms for droplet size and effective viscosity asymmetries in turbulent emulsions[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2022, 951: A39. |
| [17] | Boxall J A, Koh C A, Sloan E D, et al. Droplet size scaling of water-in-oil emulsions under turbulent flow[J]. Langmuir, 2012, 28(1): 104-110. |
| [18] | Yi L, Girotto I, Toschi F, et al. Divergence of critical fluctuations on approaching catastrophic phase inversion in turbulent emulsions[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2024, 133(13): 134001. |
| [19] | Yi L, Wang C, Huisman S G, et al. Recent developments of turbulent emulsions in Taylor-Couette flow[J]. Philosophical Transactions. Series A, Mathematical, Physical, and Engineering Sciences, 2023, 381(2243): 20220129. |
| [20] | Wang C, Yi L, Jiang L F, et al. Turbulence drag modulation by dispersed droplets in Taylor–Couette flow: the effects of the dispersed phase viscosity[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2022, 952: A39. |
| [21] | Bakhuis D, Ezeta R, Bullee P A, et al. Catastrophic phase inversion in high-Reynolds-number turbulent Taylor-couette flow[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2021, 126(6): 064501. |
| [22] | Fan Y N, Zhang Y B, Su J H, et al. Experimental study of velocity statistics in wall-bounded turbulent emulsions[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2025, 1011: A14. |
| [23] | Lu J C, Fernández A, Tryggvason G. The effect of bubbles on the wall drag in a turbulent channel flow[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2005, 17(9): 095102. |
| [24] | Iwasaki T, Nishimura K, Tanaka M, et al. Direct numerical simulation of turbulent Couette flow with immiscible droplets[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2001, 22(3): 332-342. |
| [25] | Dodd M S, Ferrante A. On the interaction of Taylor length scale size droplets and isotropic turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2016, 806: 356-412. |
| [26] | Lai J, Chen T, Zhang S Q, et al. A systematic study of a droplet breakup process in decaying homogeneous isotropic turbulence using a mesoscopic simulation approach[J]. Journal of Turbulence, 2022, 23(11/12): 567-614. |
| [27] | Shao C X, Luo K, Yang Y, et al. Direct numerical simulation of droplet breakup in homogeneous isotropic turbulence: The effect of the Weber number[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2018, 107: 263-274. |
| [28] | Mukherjee S, Safdari A, Shardt O, et al. Droplet–turbulence interactions and quasi-equilibrium dynamics in turbulent emulsions[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 878: 221-276. |
| [29] | Crialesi-Esposito M, Rosti M E, Chibbaro S, et al. Modulation of homogeneous and isotropic turbulence in emulsions[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2022, 940: A19. |
| [30] | Farsoiya P K, Liu Z H, Daiss A, et al. Role of viscosity in turbulent drop break-up[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2023, 972: A11. |
| [31] | Rosti M E, Ge Z Y, Jain S S, et al. Droplets in homogeneous shear turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2019, 876: 962-984. |
| [32] | Su J H, Yi L, Zhao B D, et al. Numerical study on the mechanism of drag modulation by dispersed drops in two-phase Taylor–Couette turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2024, 984: R3. |
| [33] | Su J H, Zhang Y B, Wang C, et al. How interfacial tension enhances drag in turbulent Taylor–Couette flow with neutrally buoyant and equally viscous droplets[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2025, 1002: A2. |
| [34] | Su J H, Wang C, Zhang Y B, et al. Turbulence modulation in liquid–liquid two-phase Taylor–Couette turbulence[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2024, 999: A98. |
| [35] | Brackbill J U, Kothe D B, Zemach C. A continuum method for modeling surface tension[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1992, 100(2): 335-354. |
| [36] | Weller H G. A new approach to VOF-based interface capturing methods for incompressible and compressible flow[R]. OpenCFD Ltd., 2008. |
| [37] | Brauckmann H J, Eckhardt B. Direct numerical simulations of local and global torque in Taylor–Couette flow up to Re = 30 000[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2013, 718: 398-427. |
| [38] | Spandan V, Verzicco R, Lohse D. Physical mechanisms governing drag reduction in turbulent Taylor–Couette flow with finite-size deformable bubbles[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2018, 849: R3. |
| [39] | Assen M P A, Ng C S, Will J B, et al. Strong alignment of prolate ellipsoids in Taylor–Couette flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2022, 935: A7. |
| [40] | Eckhardt B, Grossmann S, Lohse D. Torque scaling in turbulent Taylor–Couette flow between independently rotating cylinders[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2007, 581: 221-250. |
| [41] | Mathematics Holzmann T., Numerics, Derivations and OpenFOAM [M]. Loeben: Holzmann CFD, 2016: 91-112. |
| [42] | Chen S T, Zhao W W, Wan D C. Turbulent structures and characteristics of flows past a vertical surface-piercing finite circular cylinder[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2022, 34: 015115. |
| [43] | Gamet L, Scala M, Roenby J, et al. Validation of volume-of-fluid OpenFOAM® isoAdvector solvers using single bubble benchmarks[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2020, 213: 104722. |
| [44] | Picano F, Breugem W P, Brandt L. Turbulent channel flow of dense suspensions of neutrally buoyant spheres[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2015, 764: 463-487. |
| [45] | Wang G Q, Abbas M, Climent E. Modulation of large-scale structures by neutrally buoyant and inertial finite-size particles in turbulent Couette flow[J]. Physical Review Fluids, 2017, 2(8): 084302. |
| [46] | Bilson M, Bremhorst K. Direct numerical simulation of turbulent Taylor–Couette flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2007, 579: 227-270. |
| [47] | Lin F H, Song J X, Liu N S, et al. Maximum drag enhancement asymptote in turbulent Taylor–Couette flow of dilute polymeric solutions[J]. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 2024, 323: 105172. |
| [1] | 段浩磊, 陈浩远, 梁坤峰, 王林, 陈彬, 曹勇, 张晨光, 李硕鹏, 朱登宇, 何亚茹, 杨大鹏. 纯电动车热管理系统低GWP工质替代方案性能分析与综合评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 54-61. |
| [2] | 王俊鹏, 冯佳琪, 张恩搏, 白博峰. 曲折式与阵列式迷宫阀芯结构内流动与空化特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 93-105. |
| [3] | 燕子腾, 詹飞龙, 丁国良. 空调用套管式分流器结构设计及分流效果验证[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 152-159. |
| [4] | 赵子祥, 段钟弟, 孙浩然, 薛鸿祥. 大温差两相流动诱导水锤冲击的数值模型[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 170-180. |
| [5] | 黄灏, 王文, 贺隆坤. LNG船薄膜型液货舱预冷过程模拟与分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 187-194. |
| [6] | 汪思远, 刘国强, 熊通, 晏刚. 窗式空调器轴流风机的风速非均匀分布特性及其对冷凝器流路优化设计的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 205-216. |
| [7] | 曹庆泰, 郭松源, 李建强, 蒋赞, 汪彬, 耑锐, 吴静怡, 杨光. 负过载下多孔隔板对液氧贮箱蓄液性能的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 217-229. |
| [8] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [9] | 孔俊龙, 毕扬, 赵耀, 代彦军. 储能电池直冷热管理系统的模拟实验[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 289-296. |
| [10] | 何婷, 黄舒阳, 黄坤, 陈利琼. 基于余热利用的天然气化学吸收脱碳-高温热泵耦合流程研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 297-308. |
| [11] | 杨开源, 陈锡忠. 颗粒破碎的离散元及有限离散元模拟方法比较[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4398-4411. |
| [12] | 贾志勇, 沈宪琨, 蓝晓程, 王铁峰. 气体密度对高压流态化影响的CFD-DEM模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4383-4397. |
| [13] | 刘奕扬, 邢志祥, 刘烨铖, 彭明, 李玉洋, 李云浩, 沈宁舟. 加氢站液氢泄漏扩散特性与安全监测数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4694-4708. |
| [14] | 邹家庆, 张肇钰, 张建国, 张博宇, 刘定胜, 毛庆, 王挺, 李建军. 碱水制氢电解槽极板通道中气泡的生成及演化性质[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4786-4799. |
| [15] | 黄正宗, 刘科成, 李泽方, 曾平生, 刘永富, 闫红杰, 刘柳. 锌精馏炉砖砌式换热室数值模拟与场协同优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4425-4439. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号