化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (11): 5779-5789.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210835
许劲1,2( ),朱杰东1,2,李卷利1,2,刘孟秋1,2,龚河洛1,2
),朱杰东1,2,李卷利1,2,刘孟秋1,2,龚河洛1,2
收稿日期:2021-06-21
修回日期:2021-08-20
出版日期:2021-11-05
发布日期:2021-11-12
通讯作者:
许劲
作者简介:许劲(1968—),女,博士,教授,基金资助:
Jin XU1,2( ),Jiedong ZHU1,2,Juanli LI1,2,Mengqiu LIU1,2,Heluo GONG1,2
),Jiedong ZHU1,2,Juanli LI1,2,Mengqiu LIU1,2,Heluo GONG1,2
Received:2021-06-21
Revised:2021-08-20
Online:2021-11-05
Published:2021-11-12
Contact:
Jin XU
摘要:
以富含磷的污泥水热炭为研究对象,用SMT法分析磷的形态分布,以盐酸和柠檬酸为浸提剂,探究湿化学法回收磷的潜能。结果表明,污泥经水热碳化后,总磷含量上升,有机磷朝着无机磷转化,非磷灰石无机磷朝着磷灰石无机磷转化,水热炭中磷形态以无机磷和非磷灰石磷为主。适宜酸浸条件下(盐酸浓度0.3 mol/L、液固比50 ml/g、酸浸时间240 min,柠檬酸浓度0.1 mol/L、液固比50 ml/g、酸浸时间600 min),盐酸和柠檬酸对磷的浸出效率分别可达94.34%、88.78%,准二级动力学模型能较好地拟合磷的浸出过程;同时,金属浸出能力随酸浸时间延长而逐渐上升,与磷浸出能力呈线性相关,由大到小依次为Fe>Ca>Al>Mg;重金属浸出能力由大到小依次为Zn>Mn>Cr>Cu>Pb;酸浸残渣有望成为性能良好的吸附材料。
中图分类号:
许劲, 朱杰东, 李卷利, 刘孟秋, 龚河洛. 湿化学法回收污泥水热炭中磷的潜能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(11): 5779-5789.
Jin XU, Jiedong ZHU, Juanli LI, Mengqiu LIU, Heluo GONG. Potential of phosphorus recovery from sludge-based hydrochar by wet chemical method[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(11): 5779-5789.
| 样品 | 工业分析①/%(质量) | 元素分析①/%(质量) | H/C | O/C | 炭产率/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ash | VM | FC | C | H | N | S | O | ||||
| 污泥 | 56.48 | 40.57 | 2.95 | 20.16 | 3.5 | 2.9 | 0.9 | 16.07 | 2.08 | 0.6 | — |
| 水热炭 | 72.86 | 24.32 | 2.82 | 14.59 | 2.31 | 1.47 | 0.53 | 8.24 | 1.9 | 0.42 | 74.67 |
表1 污泥和水热炭的基本理化性质
Table 1 Basic physicochemical properties of sludge and hydrochar
| 样品 | 工业分析①/%(质量) | 元素分析①/%(质量) | H/C | O/C | 炭产率/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ash | VM | FC | C | H | N | S | O | ||||
| 污泥 | 56.48 | 40.57 | 2.95 | 20.16 | 3.5 | 2.9 | 0.9 | 16.07 | 2.08 | 0.6 | — |
| 水热炭 | 72.86 | 24.32 | 2.82 | 14.59 | 2.31 | 1.47 | 0.53 | 8.24 | 1.9 | 0.42 | 74.67 |
| 样品 | 金属含量/(mg/g)① | 重金属含量/(mg/kg)① | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Al | Ca | Mg | Pb | Cu | Cr | Mn | Zn | |
| 污泥 | 92.15 | 41.84 | 18.99 | 10.58 | 29.04 | 73.12 | 50.11 | 552.53 | 474.62 |
| 水热炭 | 98.97 | 47.53 | 20.35 | 11.23 | 37.66 | 94.54 | 61.54 | 669.73 | 589.24 |
表2 污泥和水热炭中金属和重金属含量
Table 2 Contents of metals and heavy metals in sludge and hydrochar
| 样品 | 金属含量/(mg/g)① | 重金属含量/(mg/kg)① | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Al | Ca | Mg | Pb | Cu | Cr | Mn | Zn | |
| 污泥 | 92.15 | 41.84 | 18.99 | 10.58 | 29.04 | 73.12 | 50.11 | 552.53 | 474.62 |
| 水热炭 | 98.97 | 47.53 | 20.35 | 11.23 | 37.66 | 94.54 | 61.54 | 669.73 | 589.24 |
| 酸类型 | 相关参数 | 单因素 | 变量 |
|---|---|---|---|
盐酸 柠檬酸 | 水热炭质量:0.4 g 液固比:50 ml/g 酸浸时间:720 min | 酸浓度 | 0.01、0.05、0.1、0.15、0.3、0.5、0.8、1 mol/L |
酸体积:20 ml 盐酸浓度:0.3 mol/L 柠檬酸浓度:0.1 mol/L 酸浸时间:720 min | 液固比 | 10、15、25、50、100 ml/g | |
液固比:50 ml/g 盐酸浓度:0.3 mol/L 柠檬酸浓度:0.1 mol/L | 酸浸时间 | 15、30、45、60、90、120、180、240、360、480、600、720 min |
表3 单因素实验设计
Table 3 Single factor experimental design
| 酸类型 | 相关参数 | 单因素 | 变量 |
|---|---|---|---|
盐酸 柠檬酸 | 水热炭质量:0.4 g 液固比:50 ml/g 酸浸时间:720 min | 酸浓度 | 0.01、0.05、0.1、0.15、0.3、0.5、0.8、1 mol/L |
酸体积:20 ml 盐酸浓度:0.3 mol/L 柠檬酸浓度:0.1 mol/L 酸浸时间:720 min | 液固比 | 10、15、25、50、100 ml/g | |
液固比:50 ml/g 盐酸浓度:0.3 mol/L 柠檬酸浓度:0.1 mol/L | 酸浸时间 | 15、30、45、60、90、120、180、240、360、480、600、720 min |
| 样品 | 含量/(mg/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | IP | NAIP | AP | 总磷回收率R/% | |
| 污泥 | 22.89±0.18 | 20.70±0.38 | 15.77±0.27 | 5.59±0.21 | — |
| 水热炭 | 30.31±0.28 | 28.29±0.17 | 20.39±0.10 | 7.85±0.01 | 98.81 |
表4 污泥和水热炭中不同形态磷的含量
Table 4 Contents of different forms of phosphorus in sludge and hydrochar
| 样品 | 含量/(mg/g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP | IP | NAIP | AP | 总磷回收率R/% | |
| 污泥 | 22.89±0.18 | 20.70±0.38 | 15.77±0.27 | 5.59±0.21 | — |
| 水热炭 | 30.31±0.28 | 28.29±0.17 | 20.39±0.10 | 7.85±0.01 | 98.81 |
| 数学模型 | 酸浸体系 | 表达式 | 相关参数值 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elovich模型 | 柠檬酸 | α=0.3264; β=4.2571 | 0.9856 | |
| 盐酸 | α=401.71; β=10.06 | 0.7775 | ||
| 准二级动力学模型 | 柠檬酸 | qe=32.89; k2=1.9839×10-4 | 0.9861 | |
| 盐酸 | qe=28.49; k2=2.6448×10-4 | 0.9999 |
表5 水热炭中磷浸出动力学模型的拟合参数
Table 5 Fit parameters of phosphorus release kinetics model in hydrochar
| 数学模型 | 酸浸体系 | 表达式 | 相关参数值 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elovich模型 | 柠檬酸 | α=0.3264; β=4.2571 | 0.9856 | |
| 盐酸 | α=401.71; β=10.06 | 0.7775 | ||
| 准二级动力学模型 | 柠檬酸 | qe=32.89; k2=1.9839×10-4 | 0.9861 | |
| 盐酸 | qe=28.49; k2=2.6448×10-4 | 0.9999 |

图8 酸浸时间对磷与金属元素浸出能力的影响(a)柠檬酸酸浸体系;(b)盐酸酸浸体系
Fig.8 Influence of acid leaching time on the leaching capacity of phosphorus and metal elements(a) lemon acid leaching system; (b) hydrochloric acid leaching system
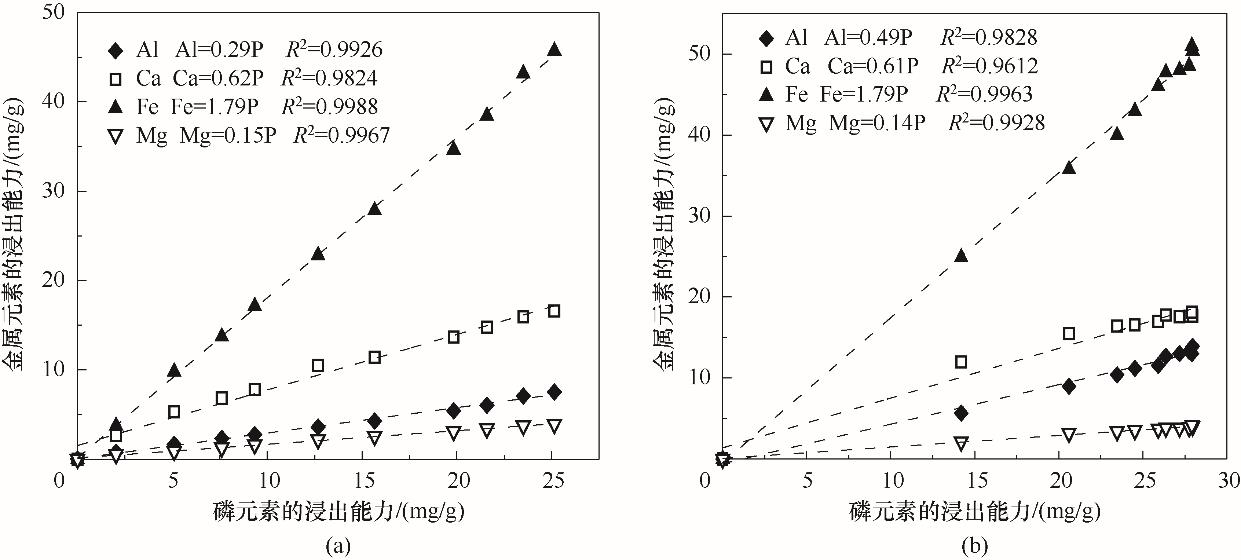
图9 金属元素与磷元素浸出能力的关系(a) 柠檬酸酸浸体系;(b) 盐酸酸浸体系
Fig.9 Relationship between leaching capacity of metal elements and phosphorus elements(a) lemon acid leaching system; (b) hydrochloric acid leaching system
| 酸浸体系 | 浸出浓度/(mg/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Cu | Cr | Mn | Zn | |
| 柠檬酸 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 3.36 | 6.36 | 8.66 |
| 盐酸 | 0.41 | 1.46 | 3.60 | 6.43 | 12.02 |
表6 适宜酸浸条件下重金属的浸出浓度
Table 6 Leaching concentration of heavy metals under optimum acid leaching conditions
| 酸浸体系 | 浸出浓度/(mg/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Cu | Cr | Mn | Zn | |
| 柠檬酸 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 3.36 | 6.36 | 8.66 |
| 盐酸 | 0.41 | 1.46 | 3.60 | 6.43 | 12.02 |

图11 水热炭(a)、盐酸酸浸残渣(b)、柠檬酸酸浸残渣(c)的SEM-EDS分析结果
Fig.11 SEM-EDS analysis results of hydrothermal carbon (a), acid leaching residue of hydrochloric acid (b) and acid leaching residue of citric acid (c) respectively
| 1 | Cordell D, Drangert J O, White S. The story of phosphorus: global food security and food for thought[J]. Global Environmental Change, 2009, 19(2): 292-305. |
| 2 | Sørensen B L, Dall O L, Habib K. Environmental and resource implications of phosphorus recovery from waste activated sludge[J]. Waste Management, 2015, 45: 391-399. |
| 3 | Cieślik B, Konieczka P. A review of phosphorus recovery methods at various steps of wastewater treatment and sewage sludge management. The concept of “no solid waste generation” and analytical methods[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2017, 142: 1728-1740. |
| 4 | Law K P, Pagilla K R. Reclaimed phosphorus commodity reserve from water resource recovery facilities—a strategic regional concept towards phosphorus recovery[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2019, 150: 104429. |
| 5 | 崔荣国, 张艳飞, 郭娟, 等. 资源全球配置下的中国磷矿发展策略[J]. 中国工程科学, 2019, 21(1): 128-132. |
| Cui R G, Zhang Y F, Guo J, et al. Development strategy of phosphate rock in China under global allocation of resources[J]. Engineering Science, 2019, 21(1): 128-132. | |
| 6 | Tarayre C, De Clercq L, Charlier R, et al. New perspectives for the design of sustainable bioprocesses for phosphorus recovery from waste[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2016, 206: 264-274. |
| 7 | Cornel P, Schaum C. Phosphorus recovery from wastewater: needs, technologies and costs[J]. Water Science and Technology, 2009, 59(6): 1069-1076. |
| 8 | Havukainen J, Nguyen M T, Hermann L, et al. Potential of phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge and manure ash by thermochemical treatment[J]. Waste Management, 2016, 49: 221-229. |
| 9 | Egle L, Rechberger H, Zessner M. Overview and description of technologies for recovering phosphorus from municipal wastewater[J]. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 2015, 105: 325-346. |
| 10 | Wang L P, Li A M, Chang Y Z. Relationship between enhanced dewaterability and structural properties of hydrothermal sludge after hydrothermal treatment of excess sludge[J]. Water Research, 2017, 112: 72-82. |
| 11 | Wang L P, Li A M. Hydrothermal treatment coupled with mechanical expression at increased temperature for excess sludge dewatering: the dewatering performance and the characteristics of products[J]. Water Research, 2015, 68: 291-303. |
| 12 | Wang L P, Zhang L, Li A M. Hydrothermal treatment coupled with mechanical expression at increased temperature for excess sludge dewatering: influence of operating conditions and the process energetics[J]. Water Research, 2014, 65: 85-97. |
| 26 | Liu H K, Xu F, Xie Y L, et al. Effect of modified coconut shell biochar on availability of heavy metals and biochemical characteristics of soil in multiple heavy metals contaminated soil[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 645: 702-709. |
| 27 | Peiris C, Nayanathara O, Navarathna C M, et al. The influence of three acid modifications on the physicochemical characteristics of tea-waste biochar pyrolyzed at different temperatures: a comparative study[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(31): 17612-17622. |
| 28 | Rashid U S, Bezbaruah A N. Citric acid modified granular activated carbon for enhanced defluoridation[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 252: 126639. |
| 13 | 郑晓园, 蒋正伟, 陈伟, 等. 污水污泥水热炭化过程中磷的迁移转化特性[J]. 化工进展, 2020, 39(5): 2017-2025. |
| Zheng X Y, Jiang Z W, Chen W, et al. Migration and transformation of phosphorus in sewage sludge during hydrothermal carbonization process[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2020, 39(5): 2017-2025. | |
| 14 | 郝晓地, 于晶伦, 刘然彬, 等. 剩余污泥焚烧灰分磷回收及其技术进展[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(4): 1149-1159. |
| Hao X D, Yu J L, Liu R B, et al. Advances of phosphorus recovery from the incineration ashes of excess sludge and its associated technologies[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(4): 1149-1159. | |
| 15 | Yan W, Wu J Y, Chen Y, et al. Short reaction times coupled with alkalization improves the release of phosphorus from Al-waste activated sludge[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2021, 333: 125168. |
| 16 | Ruban V, López-Sánchez J F, Pardo P, et al. Harmonized protocol and certified reference material for the determination of extractable contents of phosphorus in freshwater sediments — a synthesis of recent works[J]. Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2001, 370(2/3): 224-228. |
| 17 | Pardo P, López-Sánchez J F, Rauret G. Relationships between phosphorus fractionation and major components in sediments using the SMT harmonised extraction procedure[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2003, 376(2): 248-254. |
| 18 | García-Albacete M, Martín A, Cartagena M C. Fractionation of phosphorus biowastes: characterisation and environmental risk[J]. Waste Management, 2012, 32(6): 1061-1068. |
| 19 | 龙加洪, 谭菊, 吴银菊, 等. 土壤重金属含量测定不同消解方法比较研究[J]. 中国环境监测, 2013, 29(1): 123-126. |
| Long J H, Tan J, Wu Y J, et al. A comparative study on the detection of heavy metal in soil with different digestion methods[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2013, 29(1): 123-126. | |
| 20 | 徐杰,黄群星,孟详东, 等. 钙基添加剂对污水污泥在水热炭化过程中磷形态及生物有效性的影响[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(6):3507-3514. |
| Xu J, Huang Q X, Meng X D, et al. Effect of calcium based additives on phosphorus form and bioavailability of sewage sludge during hydrothermal carbonization[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2021, 40(6):3507-3514. | |
| 21 | Shi Y, Luo G, Rao Y, et al. Hydrothermal conversion of dewatered sewage sludge: focusing on the transformation mechanism and recovery of phosphorus[J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 228: 619-628. |
| 22 | 方俊华, 唐琦, 李杨, 等. 污泥水热碳化中磷的形态变化及金属浸出行为[J]. 化工学报, 2020, 71(7): 3288-3295. |
| Fang J H, Tang Q, Li Y, et al. Morphology of phosphorus and metal extraction behavior in sewage sludge during hydrothermal carbonization treatment[J]. CIESC Journal, 2020, 71(7): 3288-3295. | |
| 23 | 王涛. 城市污泥(水)热处理固体产物中磷的迁移转化及释放回收研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2018. |
| Wang T. Hydrothermal carbonization of municipal sewage sludge: invesgation on the transformation release and recovery of phosphorus in hydrochar[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2018. | |
| 24 | Barca C, Martino M, Hennebert P, et al. Kinetics and capacity of phosphorus extraction from solid residues obtained from wet air oxidation of sewage sludge[J]. Waste Management, 2019, 89: 275-283. |
| 25 | Wang S Y, Ai S Y, Nzediegwu C, et al. Carboxyl and hydroxyl groups enhance ammonium adsorption capacity of iron (Ⅲ) chloride and hydrochloric acid modified biochars[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 309: 123390. |
| 29 | Liu M M, Zhao Z Y, Yu W Z. Citric acid modified wood membranes for efficient adsorption of tetracycline: effect of alkali pretreatment concentration and adsorption mechanism[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 393: 124748. |
| 30 | Liu G F, Liao L, Dai Z M, et al. Organic adsorbents modified with citric acid and Fe3O4 enhance the removal of Cd and Pb in contaminated solutions[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 395: 125108. |
| [1] | 刘春雨, 周桓宇, 马跃, 岳长涛. CaO调质含油污泥干燥特性及数学模型[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3018-3027. |
| [2] | 屈园浩, 邓文义, 谢晓丹, 苏亚欣. 活性炭/石墨辅助污泥电渗脱水研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 3038-3050. |
| [3] | 陈宇豪, 陈晓平, 马吉亮, 梁财. 市政污泥回转窑焚烧气态污染物排放特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2170-2178. |
| [4] | 张兰河, 赖青燚, 王铁铮, 关潇卓, 张明爽, 程欣, 徐小惠, 贾艳萍. H2O2对SBR脱氮效率和污泥性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 2186-2196. |
| [5] | 陈号, 田仪娟, 全学军, 蒋子文, 李纲. 铬铁矿在HCl-HF体系中的分解行为[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1161-1174. |
| [6] | 沈嘉辉, 王侃宏, 郁达伟, 胡大洲, 魏源送. 游离氨调理污泥厌氧消化优化产甲烷过程与强化有机物释放[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4147-4155. |
| [7] | 罗欣宜, 冯超, 刘晶, 乔瑜. 污泥不同热处理工艺产物磷的浸出回收实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(9): 4034-4044. |
| [8] | 张军, 胡升, 顾菁, 袁浩然, 陈勇. 甲醇体系电镀污泥衍生磁性多金属材料催化糠醛加氢转化[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(7): 2996-3006. |
| [9] | 陈冠益, 童图军, 李瑞, 王燕杉, 颜蓓蓓, 李宁, 侯立安. 热解时间对污泥生物炭活化过硫酸盐的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2111-2119. |
| [10] | 宋超宇, 熊亚选, 张金花, 金宇贺, 药晨华, 王辉祥, 丁玉龙. 污泥焚烧炉渣基定型复合相变储热材料的制备和性能[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(5): 2279-2287. |
| [11] | 王燕杉, 朱小超, 宋英今, 李易航. 草屑厌氧消化预处理耦合水热炭化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(2): 904-913. |
| [12] | 成珊, 罗睿, 田红, 王振琦, 黄经春, 乔瑜. 水热碳化温度对污泥有机氮固液相迁移转化路径影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5220-5229. |
| [13] | 杨晓阳, 王宝凤, 宋旭涛, 杨凤玲, 程芳琴. 污泥与高硫煤共水热碳化过程中硫氮形态转化规律[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5211-5219. |
| [14] | 张立, 吴建华, 崔舒惠, 严锋, 孙浩, 钱飞跃. PN/A颗粒污泥-固相反硝化组合工艺的菌群功能解析[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(11): 5128-5137. |
| [15] | 张兰河, 汪露, 李梓萌, 唐宏, 郭静波, 贾艳萍, 张明爽. 电极超滤膜生物反应器处理阴离子表面活性剂废水[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(10): 4679-4691. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号