化工学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 72 ›› Issue (7): 3823-3831.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20210014
收稿日期:2021-01-05
修回日期:2021-05-07
出版日期:2021-07-05
发布日期:2021-07-05
通讯作者:
王凯
作者简介:董晓锐(1995—),男,博士研究生,基金资助:
DONG Xiaorui( ),WANG Kai(
),WANG Kai( ),LUO Guangsheng
),LUO Guangsheng
Received:2021-01-05
Revised:2021-05-07
Online:2021-07-05
Published:2021-07-05
Contact:
WANG Kai
摘要:
金纳米颗粒具有特征性紫外-可见吸收光谱,在分析检测领域被广泛应用。为了突破间歇搅拌反应制备金纳米颗粒的技术局限,提出了一种连续流微反应方法。该方法在酸性条件下借助螺纹管实施HAuCl4和Na3Ct水溶液的快速均匀混合,引入惰性溶剂避免颗粒在反应器内沉积,利用膜分相装置完成油水在线相分离,实现了金纳米颗粒的连续稳定制备。探索了反应物摩尔比、浓度、停留时间、水油体积比、pH等因素对于颗粒粒径分布和吸收光谱的影响规律,成功制备了平均粒径20~24 nm、分散因子小于10%的窄分布金纳米颗粒。
中图分类号:
董晓锐, 王凯, 骆广生. 金纳米颗粒的微反应连续合成[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(7): 3823-3831.
DONG Xiaorui, WANG Kai, LUO Guangsheng. Microreaction continuous synthesis of gold nanoparticles[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(7): 3823-3831.

图2 Na3Ct/ HAuCl4摩尔比对金颗粒特征吸收峰的影响和窄分布金颗粒的透射电镜照片
Fig.2 Effect of Na3Ct/ HAuCl4 molar ratio on the characteristic absorption peak of Au particles and the TEM images of narrow-distributed Au particles
| pH (25℃) | Qtotal=400 μl·min-1 | Qtotal=800 μl·min-1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d50 / nm | PDI/% | d50/nm | PDI/% | ||
| 1.5 | 4.8 | 27.3 | 34.8 | 28.2 | 31.1 |
| 2.0 | 5.2 | 28.4 | 23.2 | 28 | 23.4 |
| 2.5 | 5.6 | 25.3 | 10.7 | 25 | 12.7 |
| 3.0 | 5.8 | 23.7 | 7.7 | 23 | 5.9 |
| 3.5 | 6.2 | 24.2 | 7.3 | 22.9 | 6.5 |
表1 反应体系pH和颗粒粒径分布结果
Table 1 pH of the reaction system and particle size distribution results
| pH (25℃) | Qtotal=400 μl·min-1 | Qtotal=800 μl·min-1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d50 / nm | PDI/% | d50/nm | PDI/% | ||
| 1.5 | 4.8 | 27.3 | 34.8 | 28.2 | 31.1 |
| 2.0 | 5.2 | 28.4 | 23.2 | 28 | 23.4 |
| 2.5 | 5.6 | 25.3 | 10.7 | 25 | 12.7 |
| 3.0 | 5.8 | 23.7 | 7.7 | 23 | 5.9 |
| 3.5 | 6.2 | 24.2 | 7.3 | 22.9 | 6.5 |
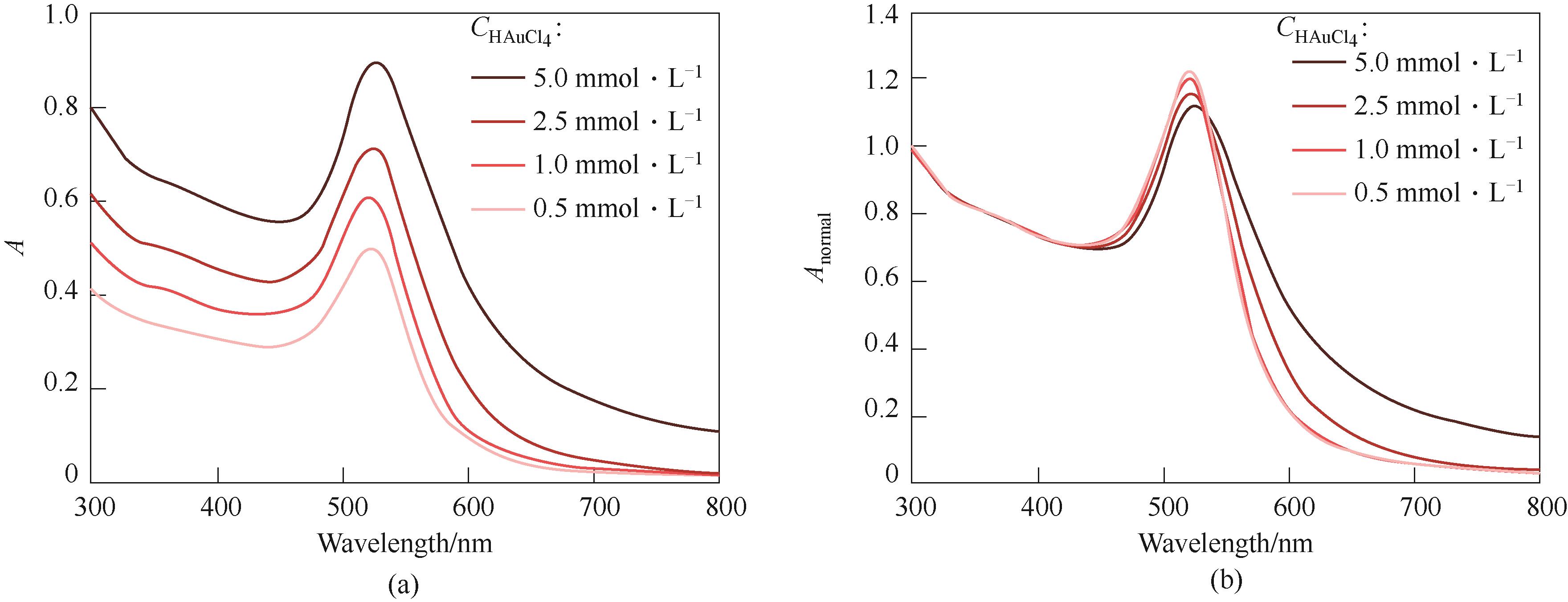
图3 HAuCl4和Na3Ct浓度对金颗粒特征吸收峰的影响(实验条件:QHAuCl4 = QNa3Ct = 200 μl·min-1,τ = 9.8 min,nNa3Ct/nHAuCl4 = 3.5)
Fig.3 Effect of HAuCl4 and Na3Ct concentrations on the characteristic absorption peak of Au particles
| pH (25℃) | Qtotal=400 μl·min-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| d50 / nm | PDI/% | ||
| 0.5 | 6.2 | 23.2 | 7.3 |
| 1.0 | 5.8 | 21.9 | 10.1 |
| 2.5 | 5.5 | 24.7 | 29.0 |
| 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.2 | 34.1 |
表2 不同反应物浓度实验的颗粒粒径分布
Table 2 Particle size distribution in experiments with different reactant concentrations
| pH (25℃) | Qtotal=400 μl·min-1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| d50 / nm | PDI/% | ||
| 0.5 | 6.2 | 23.2 | 7.3 |
| 1.0 | 5.8 | 21.9 | 10.1 |
| 2.5 | 5.5 | 24.7 | 29.0 |
| 5.0 | 5.3 | 26.2 | 34.1 |

图4 单相流体系连续微反应合成实验(实验条件:QHAuCl4 = QNa3Ct = 400 μl·min-1,CHAuCl4 = 0.5 mmol·L-1,nNa3Ct/nHAuCl4 = 3.0,τ = 4.9 min)
Fig.4 Continuous microreaction synthesis experiment in single-phase flow system
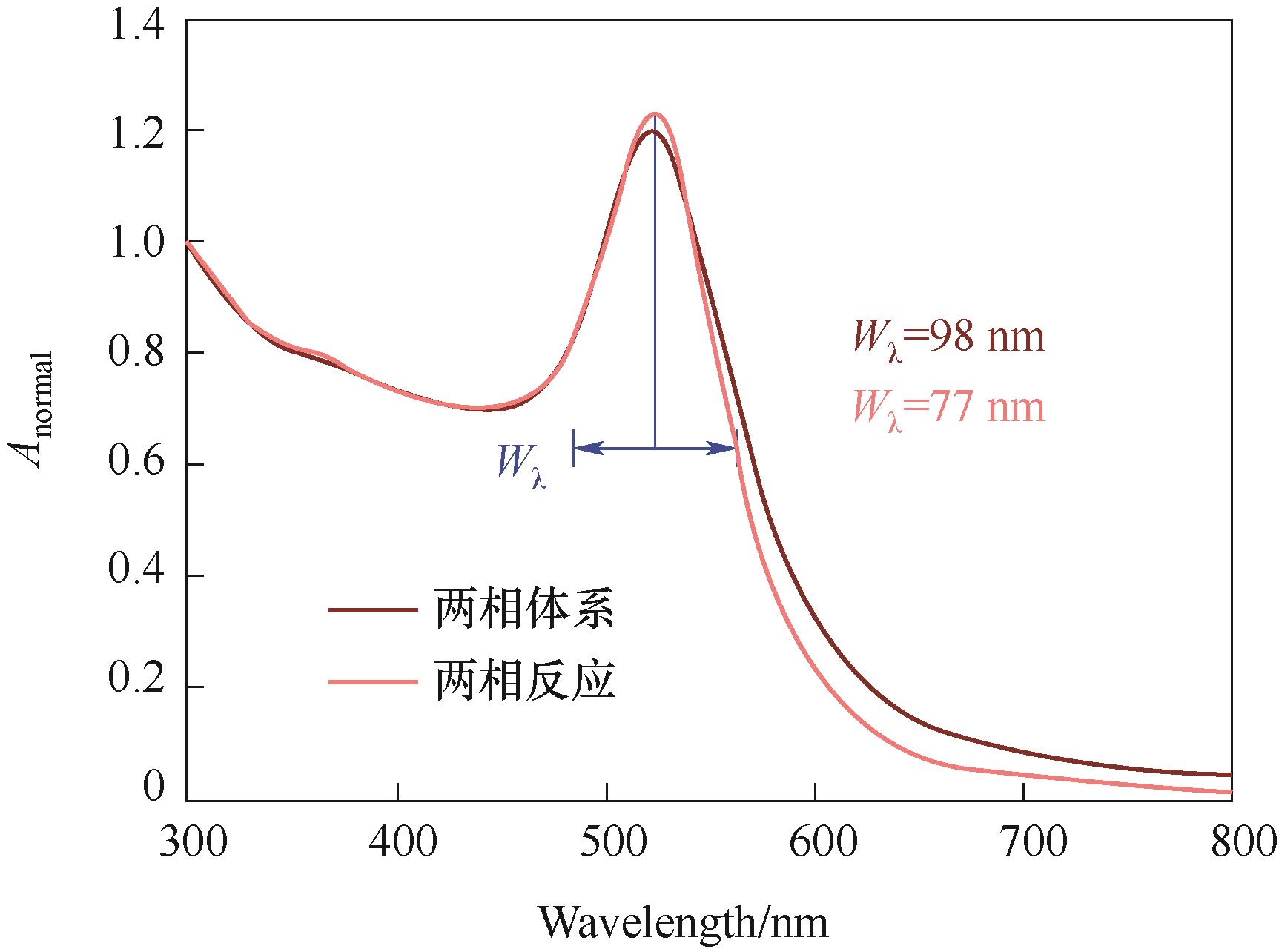
图5 单相与两相反应代表性产物颗粒的吸收光谱对比(实验条件:CHAuCl4 = 0.5 mmol·L-1,nNa3Ct/nHAuCl4 = 3.0,τ = 4.9 min,单相反应QHAuCl4 = QNa3Ct = 400 μl·min-1;两相反应QHAuCl4 = QNa3Ct= 300 μl·min-1,?QC10H22 = 200 μl·min-1)
Fig.5 Comparison of absorption spectra of representative product particles of single-phase and two-phase reactions
| 1 | Daniel M C, Astruc D. Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104(1): 293-346. |
| 2 | Al-Johani H, Abou-Hamad E, Jedidi A, et al. The structure and binding mode of citrate in the stabilization of gold nanoparticles[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2017, 9(9): 890-895. |
| 3 | Lohse S E, Eller J R, Sivapalan S T, et al. A simple millifluidic benchtop reactor system for the high-throughput synthesis and functionalization of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and shapes[J]. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(5): 4135-4150. |
| 4 | Dasog M, Hou W B, Scott R W J. Controlled growth and catalytic activity of gold monolayer protected clusters in presence of borohydride salts[J]. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(30): 8569. |
| 5 | Zhang Y L, McKelvie I D, Cattrall R W, et al. Colorimetric detection based on localised surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles: merits, inherent shortcomings and future prospects[J]. Talanta, 2016, 152: 410-422. |
| 6 | Boleininger J, Kurz A, Reuss V, et al. Microfluidic continuous flow synthesis of rod-shaped gold and silver nanocrystals[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2006, 8(33): 3824-3827. |
| 7 | Du H, Chen R Y, Du J J, et al. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric recognition of creatinine with good selectivity and sensitivity[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(48): 12334-12340. |
| 8 | Wang Y, Zeiri O, Raula M, et al. Host-guest chemistry with water-soluble gold nanoparticle supraspheres[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2017, 12(2): 170-176. |
| 9 | Li X K, Wang J E, Sun L L, et al. Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assay for selective detection of aluminium cation on living cellular surfaces[J]. Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(6): 988-990. |
| 10 | Yuan Z Q, Hu C C, Chang H T, et al. Gold nanoparticles as sensitive optical probes[J]. The Analyst, 2016, 141(5): 1611-1626. |
| 11 | Yue G Z, Su S, Li N, et al. Gold nanoparticles as sensors in the colorimetric and fluorescence detection of chemical warfare agents[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2016, 311: 75-84. |
| 12 | Pacławski K, Streszewski B, Jaworski W, et al. Gold nanoparticles formation via gold(Ⅲ) chloride complex ions reduction with glucose in the batch and in the flow microreactor systems[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2012, 413: 208-215. |
| 13 | Sebastián V, Lee S, Zhou C, et al. One-step continuous synthesis of biocompatible gold nanorods for optical coherence tomography[J]. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(53): 6654-6656. |
| 14 | Huang H, du Toit H, Ben-Jaber S, et al. Rapid synthesis of gold nanoparticles with carbon monoxide in a microfluidic segmented flow system[J]. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 4(5): 884-890. |
| 15 | Azubel M, Kornberg R D. Synthesis of water-soluble, thiolate-protected gold nanoparticles uniform in size[J]. Nano Letters, 2016, 16(5): 3348-3351. |
| 16 | Turkevich J, Stevenson P C, Hillier J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold[J]. Discussions of the Faraday Society, 1951, 11: 55. |
| 17 | Bandulasena M V, Vladisavljević G T, Odunmbaku O G, et al. Continuous synthesis of PVP stabilized biocompatible gold nanoparticles with a controlled size using a 3D glass capillary microfluidic device[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 171: 233-243. |
| 18 | Ji X H, Song X N, Li J, et al. Size control of gold nanocrystals in citrate reduction: the third role of citrate[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(45): 13939-13948. |
| 19 | Jia L F, He T, Li Z P, et al. Monolayer-protected gold nanoparticle surface-bound catalysts: preparation and application[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2010, 31(11/12): 1307-1315. |
| 20 | Li X M, Paraschiv V, Huskens J, et al. Sulfonic acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles: a colloid-bound catalyst for soft lithographic application on self-assembled monolayers[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2003, 125(14): 4279-4284. |
| 21 | Lévy R, Thanh N T K, Doty R C, et al. Rational and combinatorial design of peptide capping ligands for gold nanoparticles[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2004, 126(32): 10076-10084. |
| 22 | Jung Y L, Park J H, Kim M I, et al. Label-free colorimetric detection of biological thiols based on target-triggered inhibition of photoinduced formation of AuNPs[J]. Nanotechnology, 2016, 27(5): 055501. |
| 23 | Llevot A, Astruc D. Applications of vectorized gold nanoparticles to the diagnosis and therapy of cancer[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(1): 242-257. |
| 24 | Pan L J, Tu J W, Ma H T, et al. Controllable synthesis of nanocrystals in droplet reactors[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2018, 18(1): 41-56. |
| 25 | Niu G D, Ruditskiy A, Vara M, et al. Toward continuous and scalable production of colloidal nanocrystals by switching from batch to droplet reactors[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(16): 5806-5820. |
| 26 | Sui J S, Yan J Y, Liu D, et al. Continuous synthesis of nanocrystals via flow chemistry technology[J]. Small, 2020, 16(15): 1902828. |
| 27 | Uson L, Sebastian V, Arruebo M, et al. Continuous microfluidic synthesis and functionalization of gold nanorods[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 285: 286-292. |
| 28 | Sebastian Cabeza V, Kuhn S, Kulkarni A A, et al. Size-controlled flow synthesis of gold nanoparticles using a segmented flow microfluidic platform[J]. Langmuir, 2012, 28(17): 7007-7013. |
| 29 | Du L, Wang Y J, Ren Z Q, et al. Preparation of Au nanocolloids by in situ dispersion and their applications in surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) films[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2016, 55(24): 6783-6791. |
| 30 | Wagner J, Köhler J M. Continuous synthesis of gold nanoparticles in a microreactor[J]. Nano Letters, 2005, 5(4): 685-691. |
| 31 | Ftouni J, Penhoat M, Addad A, et al. Highly controlled synthesis of nanometric gold particles by citrate reduction using the short mixing, heating and quenching times achievable in a microfluidic device[J]. Nanoscale, 2012, 4(15): 4450-4454. |
| 32 | Baber R, Mazzei L, Thanh N T K, et al. An engineering approach to synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles by controlling hydrodynamics and mixing based on a coaxial flow reactor[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(37): 14149-14161. |
| 33 | Huang H, Toit H D, Besenhard M O, et al. Continuous flow synthesis of ultrasmall gold nanoparticles in a microreactor using trisodium citrate and their SERS performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 189: 422-430. |
| 34 | Bayazit M K, Yue J, Cao E H, et al. Controllable synthesis of gold nanoparticles in aqueous solution by microwave assisted flow chemistry[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2016, 4(12): 6435-6442. |
| 35 | du Toit H, MacDonald T J, Huang H, et al. Continuous flow synthesis of citrate capped gold nanoparticles using UV induced nucleation[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(16): 9632-9638. |
| 36 | Wang K, Zhang H M, Shen Y, et al. Thermoformed fluoropolymer tubing for in-line mixing[J]. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 3(5): 707-713. |
| 37 | Adamo A, Heider P L, Weeranoppanant N, et al. Membrane-based, liquid-liquid separator with integrated pressure control[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(31): 10802-10808. |
| 38 | Song J, Zhang S L, Wang K, et al. Synthesis of million molecular weight polyacrylamide with droplet flow microreactors[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2019, 98: 78-84. |
| 39 | Wang K, Luo G S. Microflow extraction: a review of recent development[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 169: 18-33. |
| [1] | 陈爱强, 代艳奇, 刘悦, 刘斌, 吴翰铭. 基板温度对HFE7100液滴蒸发过程的影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 191-197. |
| [2] | 谈莹莹, 刘晓庆, 王林, 黄鲤生, 李修真, 王占伟. R1150/R600a自复叠制冷循环开机动态特性实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 213-222. |
| [3] | 程小松, 殷勇高, 车春文. 不同工质在溶液除湿真空再生系统中的性能对比[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3494-3501. |
| [4] | 汪尔奇, 彭书舟, 杨震, 段远源. 含HFO混合体系气液相平衡的理论模型评价[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3216-3225. |
| [5] | 仪显亨, 周骛, 蔡小舒, 蔡天意. 光纤后向动态光散射测量纳米颗粒的浓度适用范围研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3320-3328. |
| [6] | 黄可欣, 李彤, 李桉琦, 林梅. 加装旋转叶轮T型通道流场的模态分解[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(7): 2848-2857. |
| [7] | 李勇, 高佳琦, 杜超, 赵亚丽, 李伯琼, 申倩倩, 贾虎生, 薛晋波. Ni@C@TiO2核壳双重异质结的构筑及光热催化分解水产氢[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2458-2467. |
| [8] | 张艳梅, 袁涛, 李江, 刘亚洁, 孙占学. 高效SRB混合菌群构建及其在酸胁迫条件下的性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(6): 2599-2610. |
| [9] | 姚晓宇, 沈俊, 李健, 李振兴, 康慧芳, 唐博, 董学强, 公茂琼. 流体气液临界参数测量方法研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1847-1861. |
| [10] | 党玉荣, 莫春兰, 史科锐, 方颖聪, 张子杨, 李作顺. 综合评价模型联合遗传算法的混合工质ORC系统性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(5): 1884-1895. |
| [11] | 杨星宇, 马优, 朱春英, 付涛涛, 马友光. 梳状并行微通道内液液分布规律研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 698-706. |
| [12] | 章承浩, 罗京, 张吉松. 微反应器内基于氮氧自由基催化剂连续氧气/空气氧化反应的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 511-524. |
| [13] | 张梦波, 楼琳瑾, 冯艺荣, 郑雨婷, 张浩淼, 王靖岱, 阳永荣. 烷基铝氧烷合成技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 525-534. |
| [14] | 谢煜, 张民, 胡卫国, 王玉军, 骆广生. 利用膜分散微反应器高效溶解D-7-ACA的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 748-755. |
| [15] | 付家崴, 陈帅帅, 方凯伦, 蒋新. 微反应器共沉淀反应制备铜锰催化剂[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(2): 776-783. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号