化工学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 76 ›› Issue (8): 3772-3788.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250035
收稿日期:2025-01-08
修回日期:2025-02-20
出版日期:2025-08-25
发布日期:2025-09-17
通讯作者:
刘明言
作者简介:马永丽(1989—),女,博士,副教授,mayl@tju.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yongli MA1( ), Shu AN1, Jie YANG1, Mingyan LIU1,2(
), Shu AN1, Jie YANG1, Mingyan LIU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-01-08
Revised:2025-02-20
Online:2025-08-25
Published:2025-09-17
Contact:
Mingyan LIU
摘要:
气液固流化床在化工等过程工业中有着广阔的应用前景。但是,由于流动的复杂性(多尺度、非稳态和非线性等)和测试方法以及机理模型的局限性,还难以对其进行科学设计和放大。基于计算流体力学的数值模拟是量化描述三相流动的有效途径。三相流数值模拟方法分为模型化方法和直接数值模拟方法。其中,直接数值模拟是在没有引入曳力模型等的条件下,从微观尺度解析气泡、颗粒和流体间的相互作用,可以揭示气液固三相间的相互作用机理,是重点关注的方法。综述了常用的多相流动直接数值模拟方法,包括流体体积法、水平集法、界面跟踪法、浸没边界法、虚拟区域法、格子玻尔兹曼法和光滑粒子动力学法等,并分析了各种模拟方法的优势和不足,之后对三相流直接数值模拟的研究进展进行了评述,最后给出了目前三相流数值模拟方法存在的问题以及今后进一步研究的方向。
中图分类号:
马永丽, 安澍, 杨捷, 刘明言. 气液固流化床直接数值模拟研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3772-3788.
Yongli MA, Shu AN, Jie YANG, Mingyan LIU. A review on direct numerical simulation of gas-liquid-solid fluidized bed[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(8): 3772-3788.
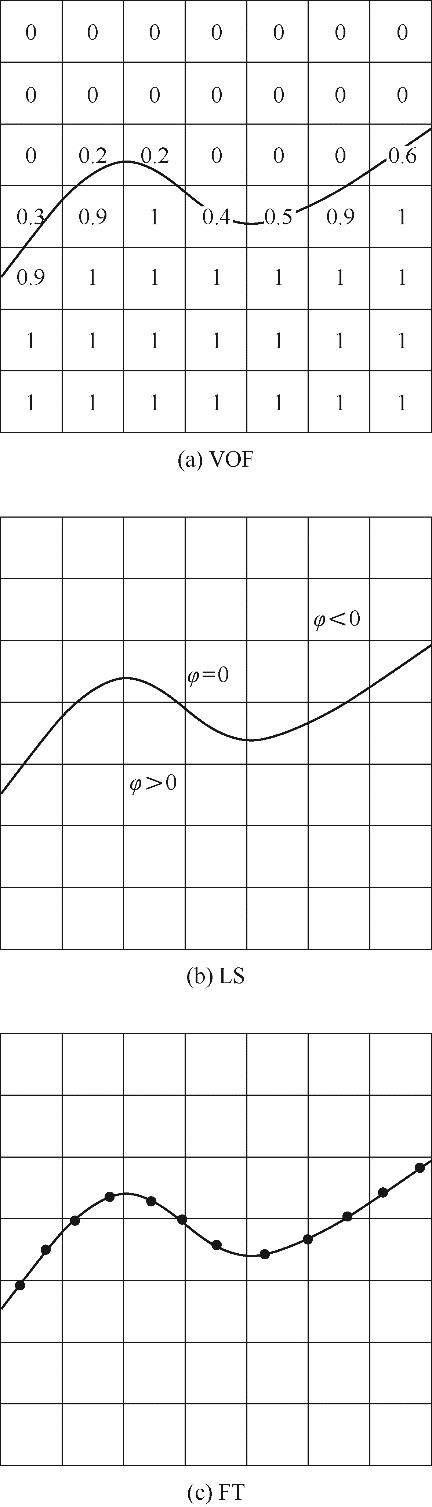
图1 气液相界面相关算法的示意图数字—某一相的体积分数;φ—符号距离函数;实心点—Lagrange追踪点
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of gas-liquid phase interface correlation algorithmnumber—the liquid volume fraction in the local grid; φ—the symbolic distance function; solid dots—Lagrange tracking points
| 方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|
| VOF | 简便;质量守恒性好;自动处理界面的合并、破裂 | 界面重构复杂,特别是三维情况;无法直接获取界面信息;界面不连续 |
| LS | 易于三维并行;自动处理合并、破裂;易获得界面信息,如曲率;界面形状更加光滑 | 质量不守恒;重初始化增加计算成本 |
| FT | 精确的界面追踪;质量守恒 | 计算复杂度高;无法自动处理合并、破裂 |
表1 VOF方法、LS方法和FT方法的对比
Table 1 Comparison of VOF method, LS method and FT method
| 方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|
| VOF | 简便;质量守恒性好;自动处理界面的合并、破裂 | 界面重构复杂,特别是三维情况;无法直接获取界面信息;界面不连续 |
| LS | 易于三维并行;自动处理合并、破裂;易获得界面信息,如曲率;界面形状更加光滑 | 质量不守恒;重初始化增加计算成本 |
| FT | 精确的界面追踪;质量守恒 | 计算复杂度高;无法自动处理合并、破裂 |
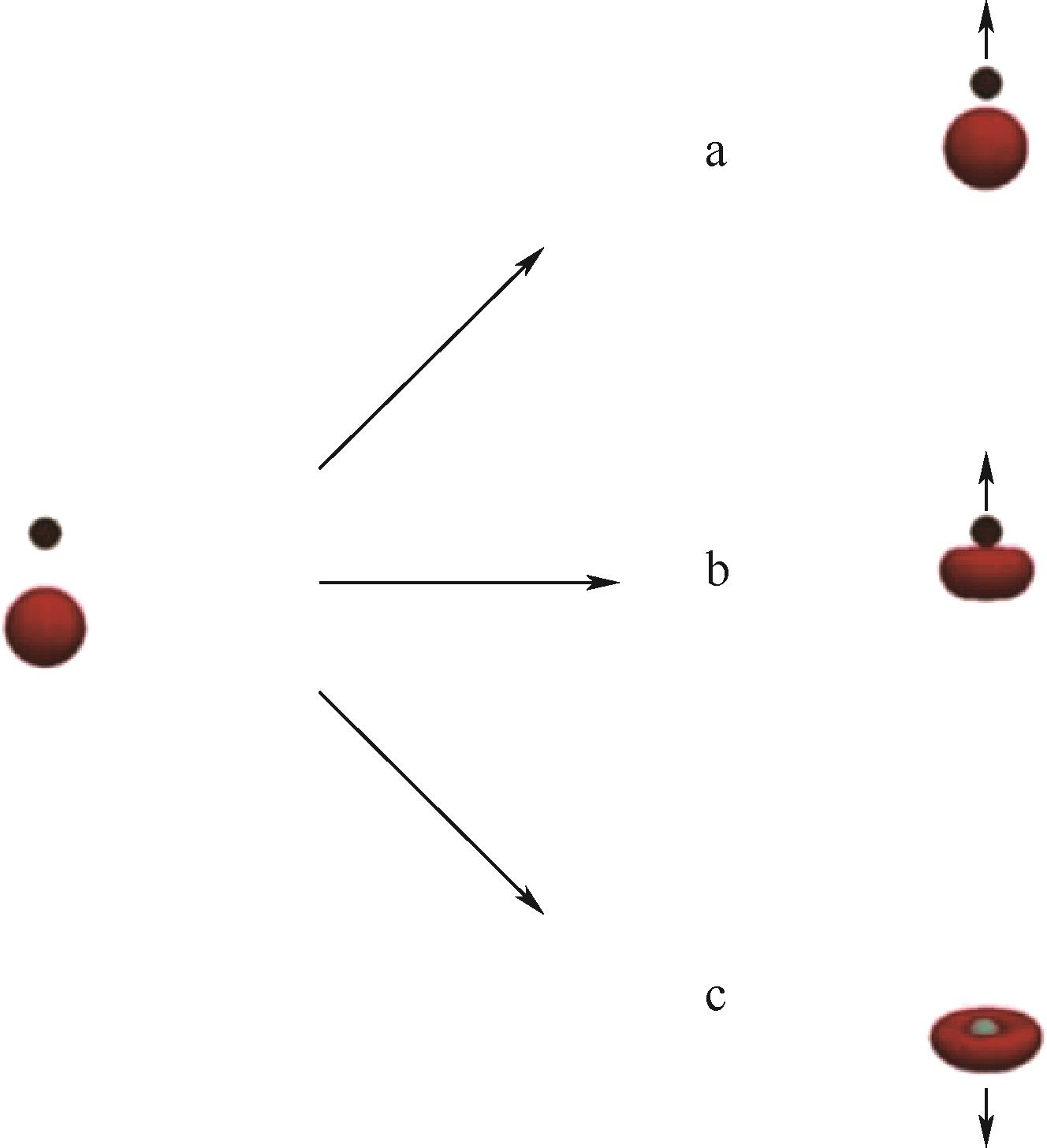
图4 液相中50 μm颗粒与130 μm气泡间碰撞的直接数值模拟[38]a—轻颗粒和球形气泡;b—轻颗粒和变形气泡;c—重颗粒和变形气泡
Fig.4 The collision between 50 μm particles and 130 μm bubbles in liquid phase used by directly numerical simulation[38]a—light particles and spherical bubbles; b—light particles and deformed bubbles; c—heavy particles and deformed bubbles

图5 不同拉伸时刻下的液桥[41]:(a) t = 12.5 ms,(b) t = 125 ms,(c) t = 170 ms,(d) t = 175 ms
Fig.5 Simulated liquid bridge under stretching at different time instants[41]: (a) t = 12.5 ms, (b) t = 125 ms, (c) t = 170 ms, (d) t = 175 ms
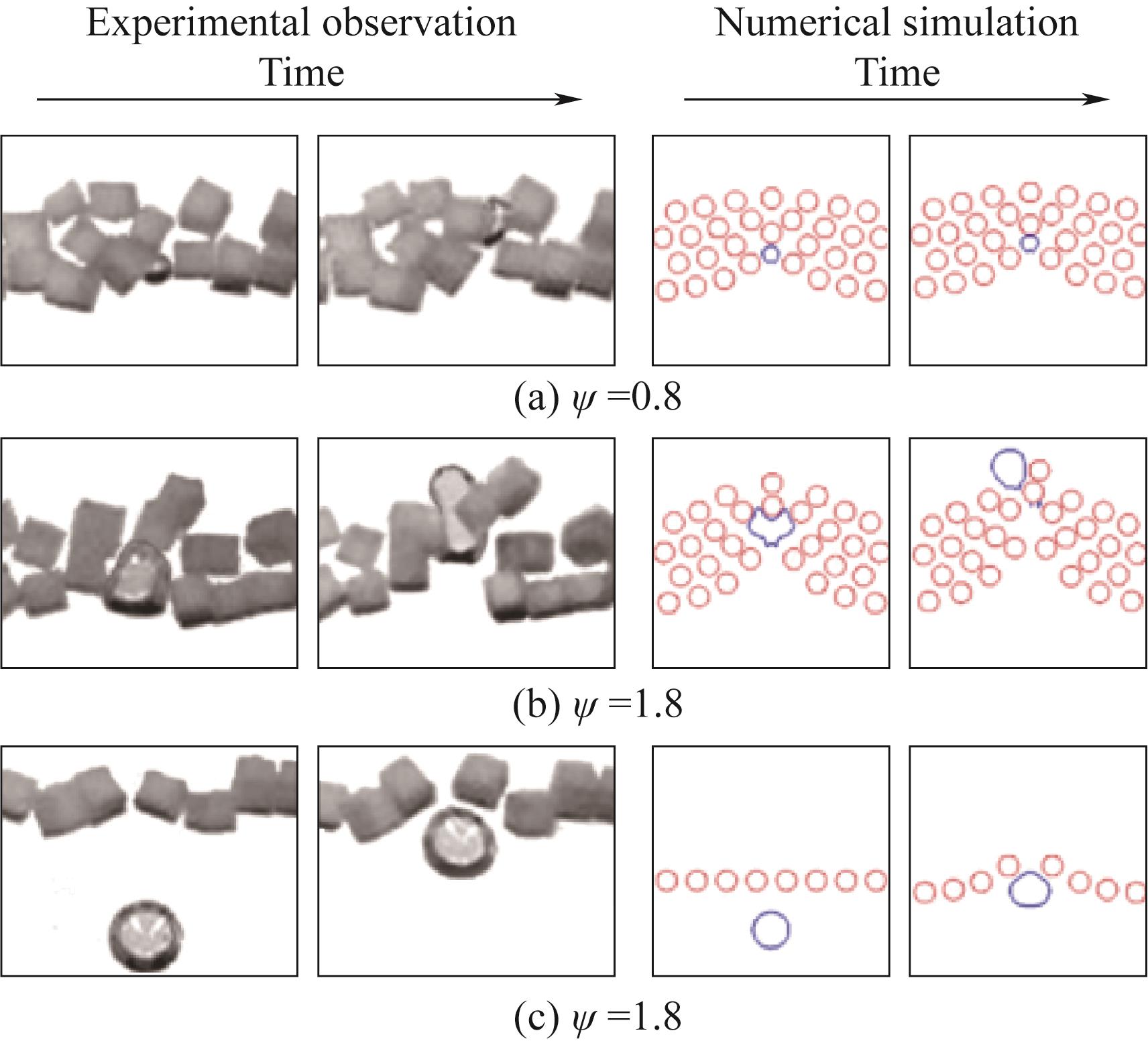
图7 气泡与悬浮刚性粒子之间的相互作用(ψ为气泡尺寸与颗粒尺寸的比值)[43]
Fig.7 Interaction between bubble and suspended rigid particles(ψ represents the ratio of bubble size to particle size)[43]
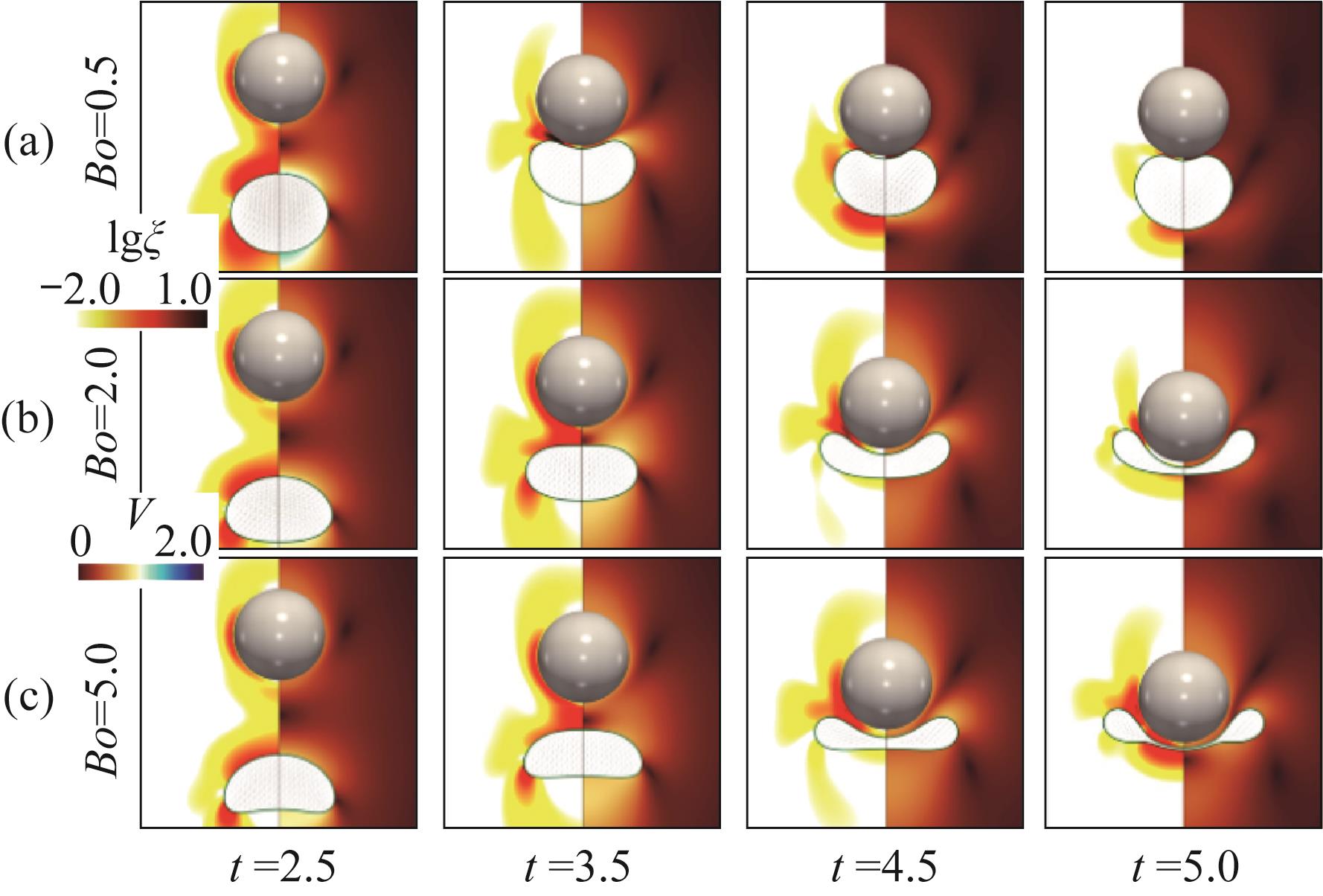
图8 气泡-粒子相互作用动力学的时空演化(左侧白色区域:流体中黏性耗散函数的对数值;右侧红色区域:流体的速度大小)[48]
Fig.8 Spatiotemporal evolution of the bubble-particle interaction dynamics (the contours on the left-hand part of each panel show the logarithm of the viscous dissipation function log10ξ in the fluid, and the contours on the right-hand part show the velocity magnitude in the fluid)[48]
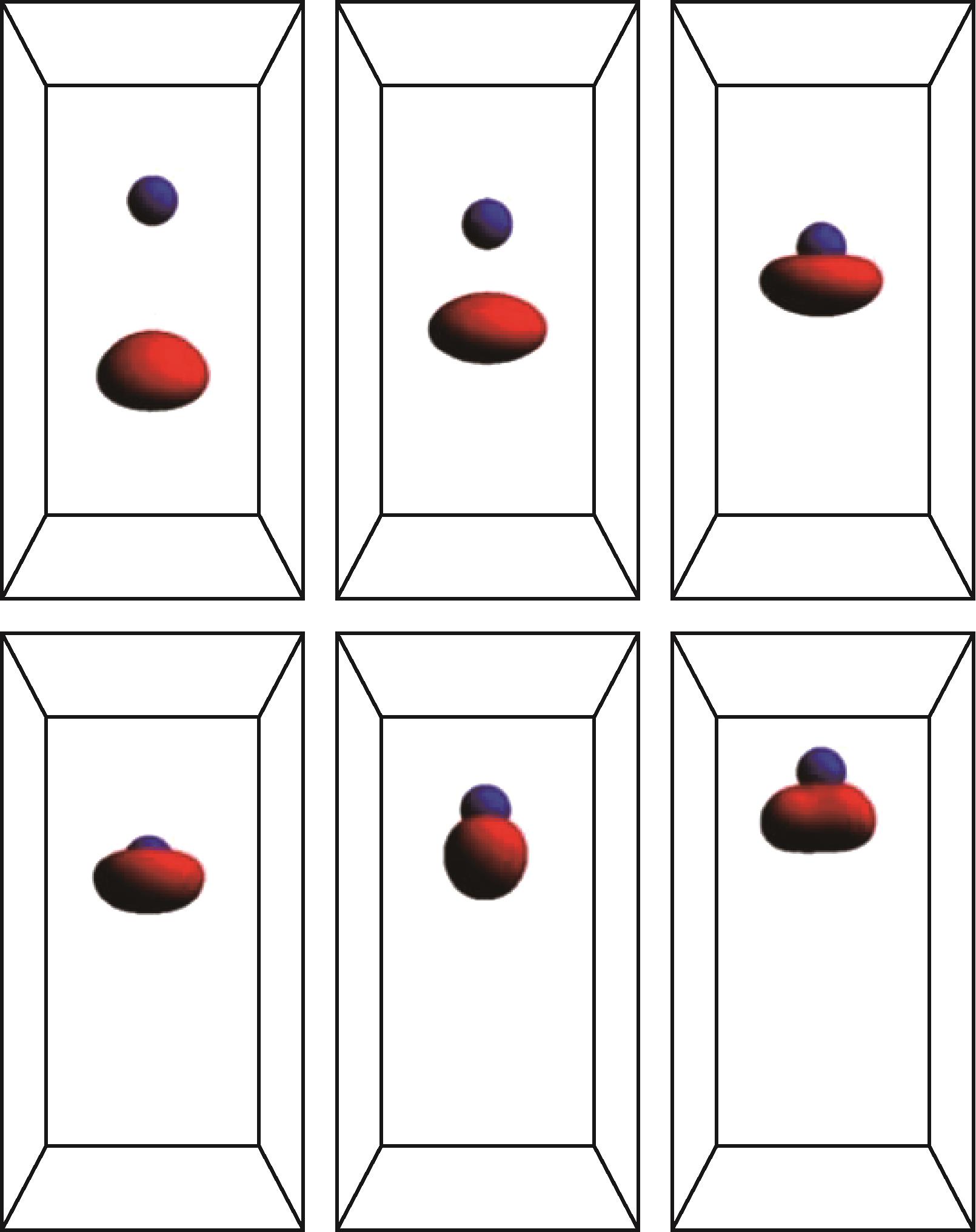
图9 单个球形颗粒(蓝色,直径0.01 m)与单个上升气泡(红色,直径0.02 m)的碰撞过程[49]
Fig.9 Collision process between a single spherical particle (blue) of 0.01 m diameter and a single rising bubble (red) of 0.02 m diameter[49]
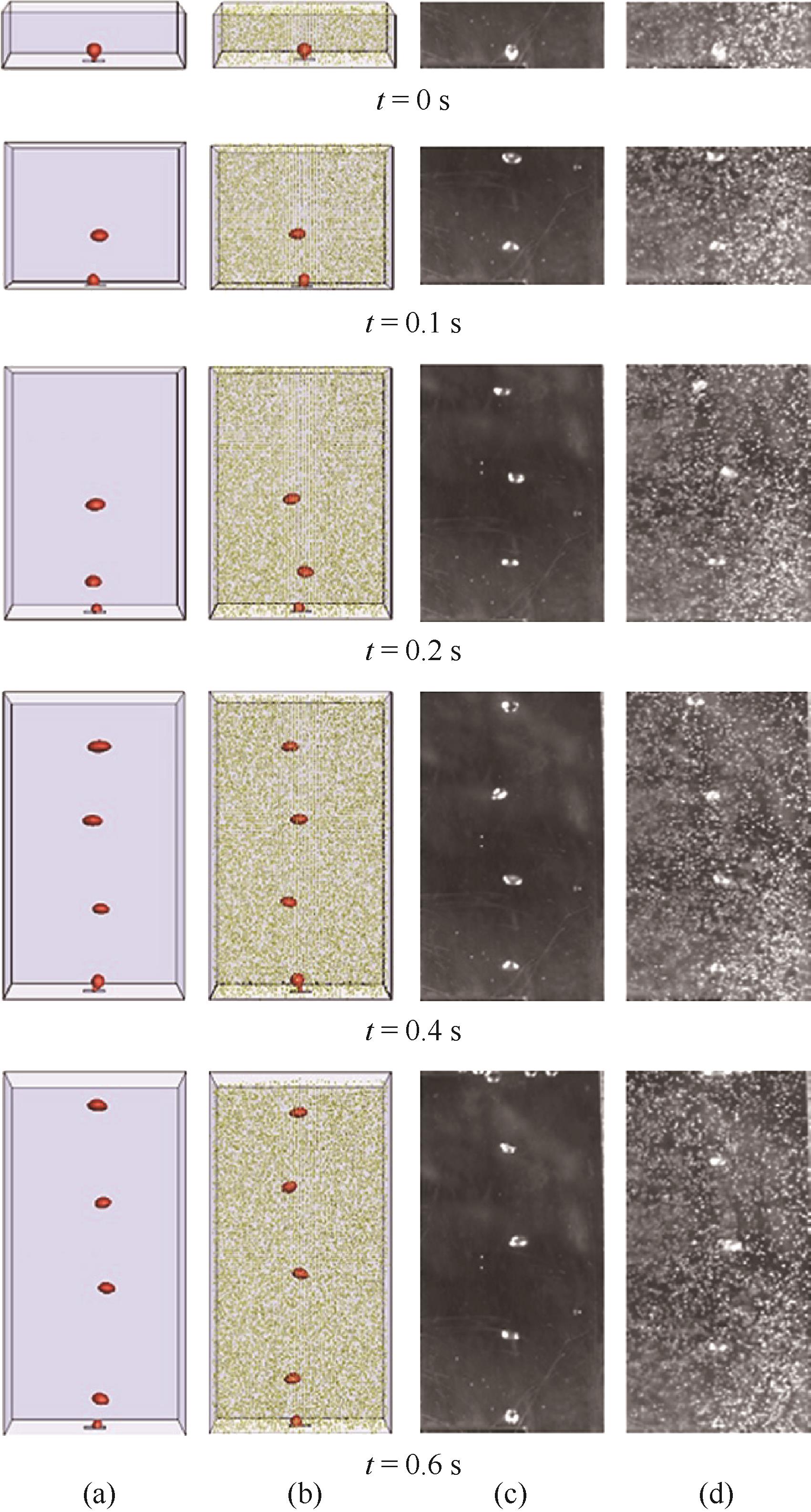
图11 单气泡形成和上升运动的直接数值模拟和实验比较[55](a)气液两相流单气泡VOF模拟;(b)固含率为0.3%时气液固三相流模拟;(c)气液两相流单气泡VOF实验图;(d)固含率为0.3%时气液固三相流实验图
Fig.11 Directly numerical simulation and experimental comparison of single bubble formation and rising movements[55](a) gas-liquid single bubble VOF simulation; (b) gas-liquid-solid flow simulation when the solid holdup is 0.3%; (c) gas-liquid single bubble VOF experimental diagram; (d) gas-liquid-solid flow experimental diagram when the solid holdup is 0.3%
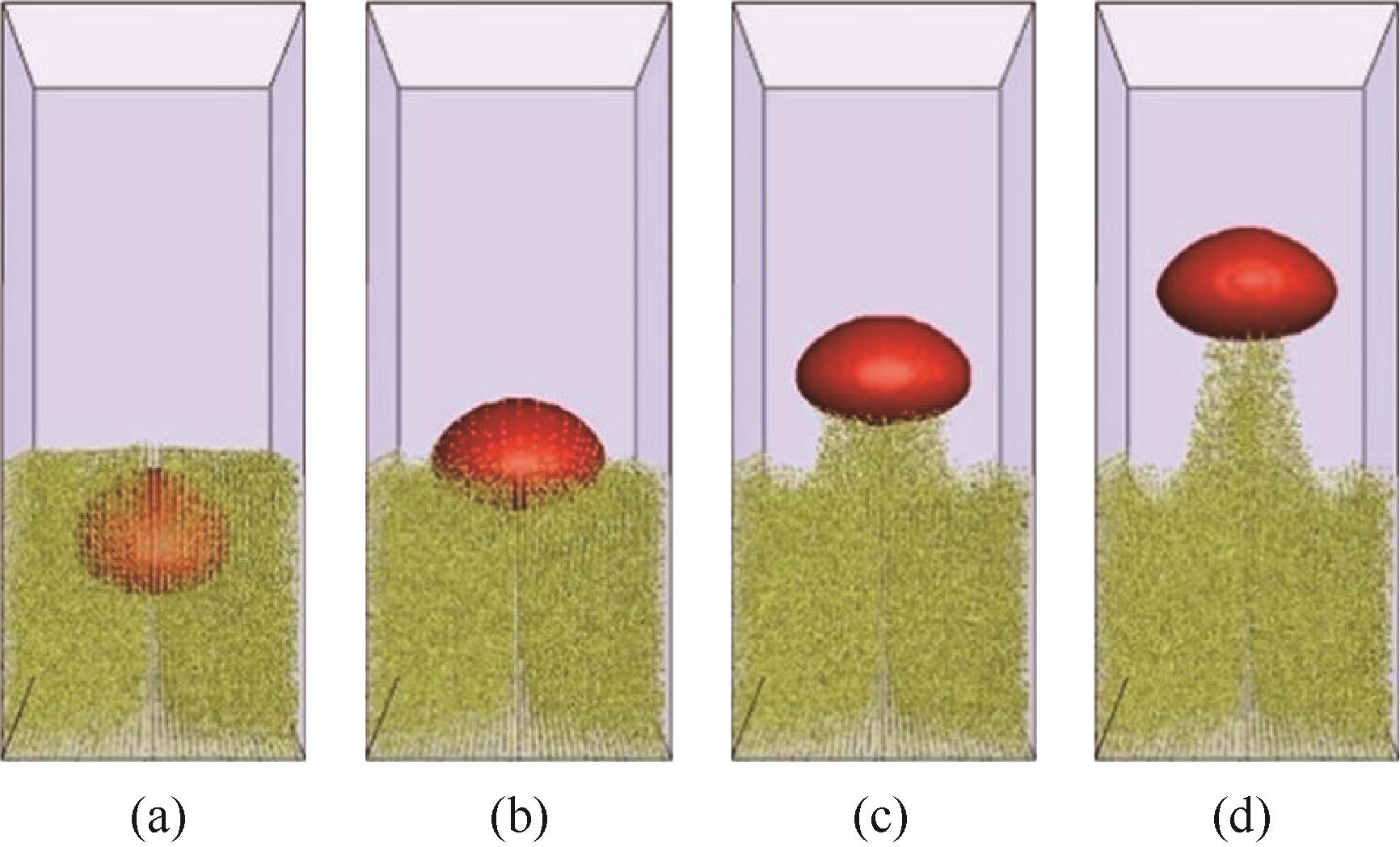
图12 单气泡离开三相流化床进入自由空间区时气泡及其尾涡的运动行为[55]
Fig.12 Motion behavior of single bubble and its trailing vortices when it leaves the three-phase fluidized bed and enters the free space[55]
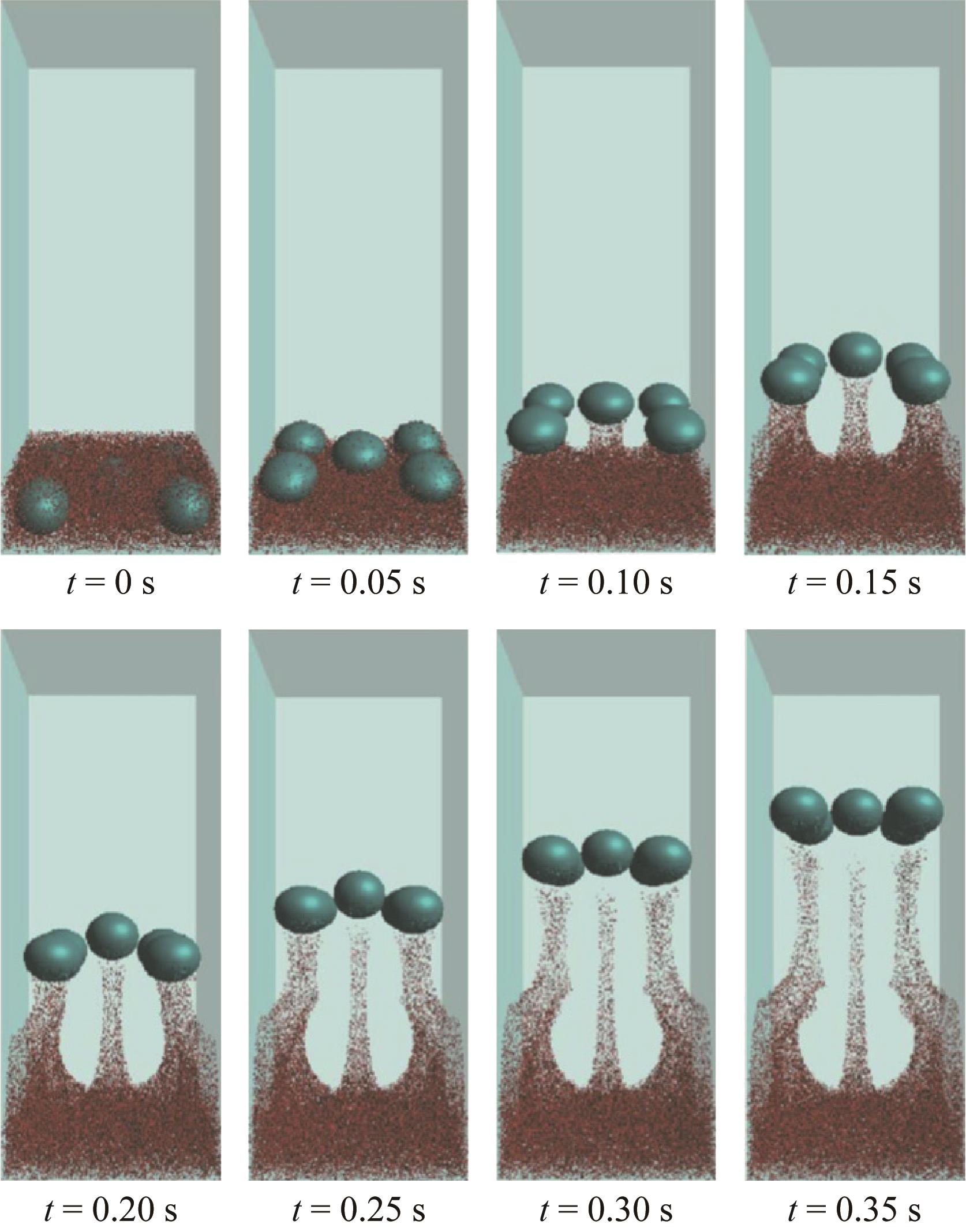
图14 初始直径为0.016 m的5个气泡阵列通过60000个颗粒沉积层的上升过程[57]
Fig.14 Five bubbles with an initial diameter of 0.016 m pass through the ascent process of a sediment layer of 60000 particles[57]
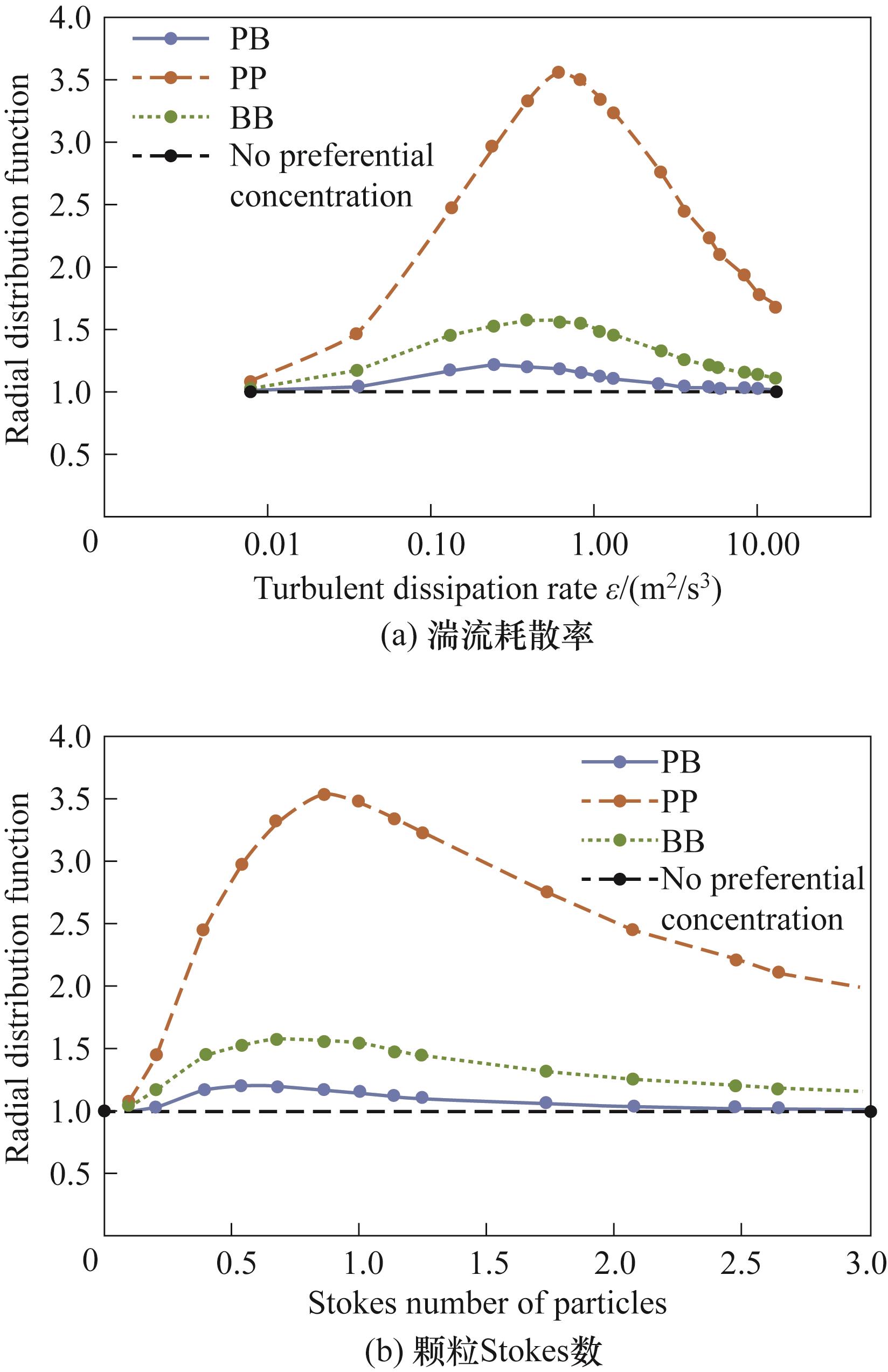
图15 颗粒-颗粒对、气泡-气泡对、颗粒-气泡对的径向分布函数变化[72]
Fig.15 The changes of radial distribution functions (pairs of particle-particle, bubble-bubble and particle-bubble)[72]
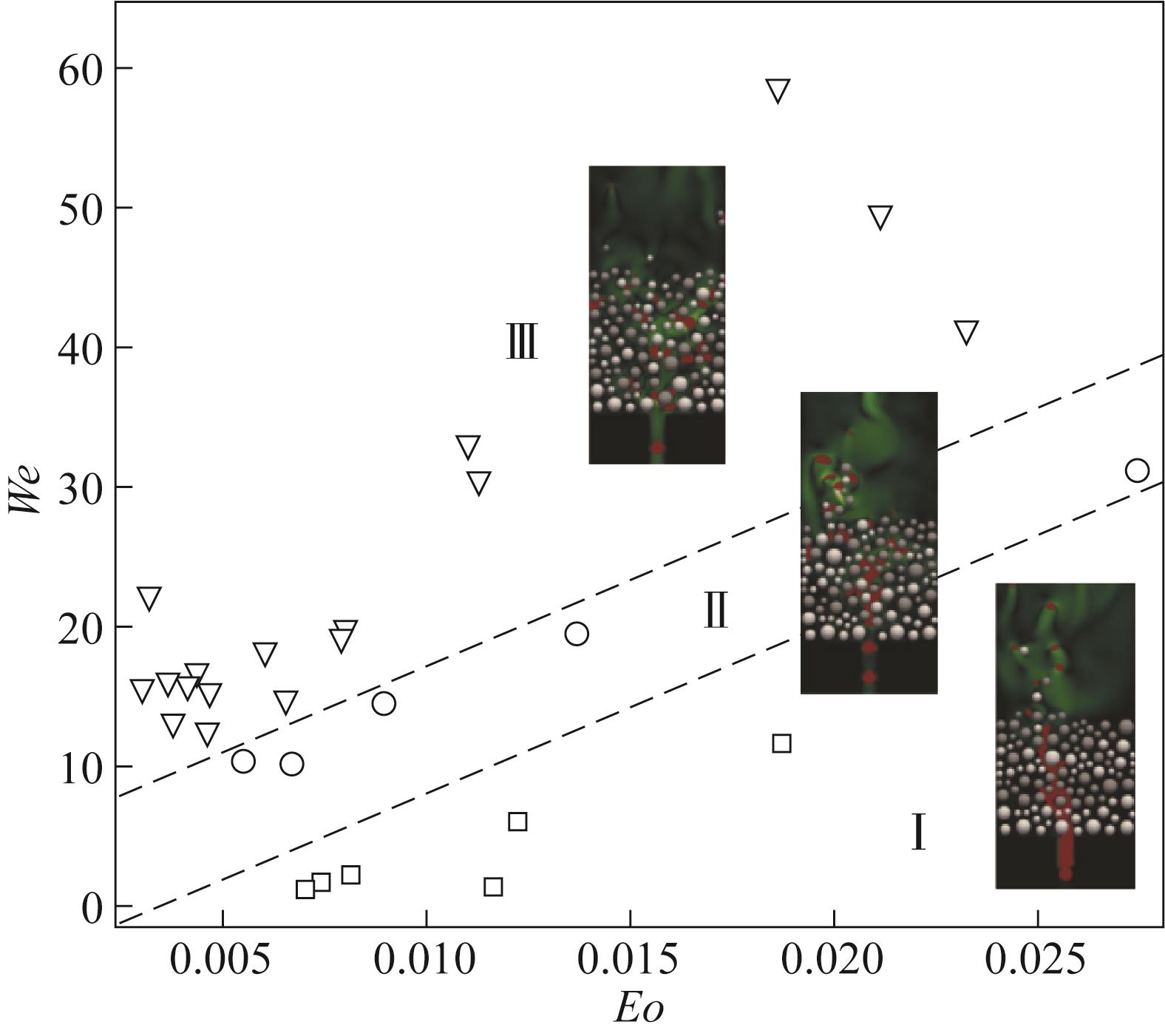
图16 气泡穿过颗粒层过程中的三种不同的流动形式(Ⅰ:连通指流;Ⅱ:过渡流;Ⅲ:分散气泡流)[73]
Fig.16 Three different flow patterns of bubbles passing through the particle layer (Ⅰ: connected finger flow, Ⅱ: transitional flow, Ⅲ: dispersed bubble flow)[73]
| [17] | Jiang M Q. Direct numerical simulations of particles settling over a wide range of density ratios based on boundary-thickening based immersed boundary method[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2021. |
| [18] | Hirt C W, Nichols B D. Volume of fluid (VOF) method for the dynamics of free boundaries[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1981, 39(1): 201-225. |
| [19] | Sussman M. A level set approach for computing solutions to incompressible two-phase flow[D]. Los Angeles: University of California, 1994. |
| [20] | Unverdi S O, Tryggvason G. A front-tracking method for viscous, incompressible, multi-fluid flows[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1992, 100(1): 25-37. |
| [21] | Peskin C S. Numerical analysis of blood flow in the heart[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1977, 25(3): 220-252. |
| [22] | van der Hoef M A, Beetstra R, Kuipers J A M. Lattice-Boltzmann simulations of low-Reynolds-number flow past mono- and bidisperse arrays of spheres: results for the permeability and drag force[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2005, 528: 233-254. |
| [23] | Brackbill J U, Kothe D B, Zemach C. A continuum method for modeling surface tension[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1992, 100(2): 335-354. |
| [24] | Osher S, Fedkiw R P. Level set methods: an overview and some recent results[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2001, 169(2): 463-502. |
| [25] | Yu Z S, Shao X M. Direct numerical simulation of particulate flows with a fictitious domain method[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2010, 36(2): 127-134. |
| [26] | Haeri S, Shrimpton J S. On the application of immersed boundary, fictitious domain and body-conformal mesh methods to many particle multiphase flows[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2012, 40: 38-55. |
| [27] | Hirt C W, Amsden A A, Cook J L. An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian computing method for all flow speeds[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1974, 14(3): 227-253. |
| [28] | Tezduyar T E, Sathe S. Modelling of fluid-structure interactions with the space-time finite elements: solution techniques[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2007, 54(6/7/8): 855-900. |
| [29] | Glowinski R, Pan T W, Hesla T I, et al. A distributed Lagrange multiplier/fictitious domain method for particulate flows[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 1999, 25(5): 755-794. |
| [30] | Glowinski R, Pan T W, Hesla T I, et al. A fictitious domain approach to the direct numerical simulation of incompressible viscous flow past moving rigid bodies: application to particulate flow[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2001, 169(2): 363-426. |
| [31] | Fogelson A L, Peskin C S. A fast numerical method for solving the three-dimensional Stokes' equations in the presence of suspended particles[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1988, 79(1): 50-69. |
| [32] | Lai M C, Peskin C S. An immersed boundary method with formal second-order accuracy and reduced numerical viscosity[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2000, 160(2): 705-719. |
| [33] | Hoomans B P B, Kuipers J A M, Briels W J, et al. Discrete particle simulation of bubble and slug formation in a two-dimensional gas-fluidised bed: a hard-sphere approach[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1996, 51(1): 99-118. |
| [34] | Tsuji Y, Tanaka T, Ishida T. Lagrangian numerical simulation of plug flow of cohesionless particles in a horizontal pipe[J]. Powder Technology, 1992, 71(3): 239-250. |
| [35] | Jain D, Deen N G, Kuipers J A M, et al. Direct numerical simulation of particle impact on thin liquid films using a combined volume of fluid and immersed boundary method[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2012, 69(1): 530-540. |
| [36] | Morton K, Baines M. Numerical Methods in Fluid Dynamics[M]. London: Cambridge University Press, 1982: 273-285. |
| [37] | Fadlun E A, Verzicco R, Orlandi P, et al. Combined immersed-boundary finite-difference methods for three-dimensional complex flow simulations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2000, 161(1): 35-60. |
| [38] | Sasic S, Karimi Sibaki E, Ström H. Direct numerical simulation of a hydrodynamic interaction between settling particles and rising microbubbles[J]. European Journal of Mechanics - B/Fluids, 2014, 43: 65-75. |
| [39] | Extrand C W, Moon S I. Using the flotation of a single sphere to measure and model capillary forces[J]. Langmuir, 2009, 25(11): 6239-6244. |
| [40] | Ulrich S, Aspelmeier T, Zippelius A, et al. Dilute wet granular particles: nonequilibrium dynamics and structure formation[J]. Physical Review E, 2009, 80(3): 031306. |
| [1] | Fan L S. Gas-Liquid-Solid Fluidization Engineering[M]. Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann, 1989. |
| [2] | 金涌. 流态化工程原理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2001. |
| Jin Y. Fluidization Engineering Principles[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2001. | |
| [3] | 郭慕孙, 李洪钟. 流态化手册[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008. |
| Guo M S, Li H Z. Handbook of Fluidization[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008. | |
| [4] | 刘明言, 马永丽, 白丁荣, 等. 多相流态化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2022. |
| Liu M Y, Ma Y L, Bai D R, et al. Multiphase Fluidization[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2022. | |
| [5] | Gidaspow D, Bahary M, Jayaswal U K. Hydrodynamic models for gas-liquid-solid fluidization[C]//Crowe C T. Numerical Methods in Multiphase Flows, FED 185. New York: ASME, 1994: 117-124. |
| [6] | Mitra-Majumdar D, Farouk B, Shah Y T. Hydrodynamic modeling of three-phase flows through a vertical column[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1997, 52(24): 4485-4497. |
| [7] | 罗运柏, 李绍箕, 闻建平, 等. 三相反应器的气含率与液速分布和数值模拟[J]. 武汉水利电力大学学报, 1998, 31(1): 100-103. |
| Luo Y B, Li S J, Wen J P, et al. Measuring and modeling of gas holdup and liquid axial velocity in a countercurrent three phase bubble column[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 1998, 31(1): 100-103. | |
| [8] | Li Y, Zhang J P, Fan L S. Numerical simulation of gas-liquid-solid fluidization systems using a combined CFD-VOF-DPM method: bubble wake behavior[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 1999, 54(21): 5101-5107. |
| [9] | 罗运柏, 胡宗定. 烟气脱硫三相流化床反应器的数学模拟与预测放大[J]. 化工学报, 2002, 53(2): 122-127. |
| [41] | Sun X S, Sakai M. Direct numerical simulation of gas-solid-liquid flows with capillary effects: an application to liquid bridge forces between spherical particles[J]. Physical Review E, 2016, 94(6): 063301. |
| [42] | Ge Y, Fan L S. Three-dimensional direct numerical simulation for film-boiling contact of moving particle and liquid droplet[J]. Physics of fluids, 2006, 18(11): 117104. |
| [43] | Qin Z P, Suckale J. Direct numerical simulations of gas-solid-liquid interactions in dilute fluids[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2017, 96: 34-47. |
| [44] | Chorin A J. On the convergence of discrete approximations to the Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Mathematics of Computation, 1969, 23(106): 341-353. |
| [45] | Briley W R, McDonald H. Solution of the multidimensional compressible Navier-Stokes equations by a generalized implicit method[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1977, 24(4): 372-397. |
| [46] | Kim J, Moin P. Application of a fractional-step method to incompressible Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1985, 59(2): 308-323. |
| [47] | Belien I B, Cashman K V, Rempel A W. Gas accumulation in particle-rich suspensions and implications for bubble populations in crystal-rich magma[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 297(1/2): 133-140. |
| [48] | Abdal A M, Kahouadji L, Shin S, et al. On the interaction between a rising bubble and a settling particle[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2024, 999: A18. |
| [49] | Deen N G, van Sint Annaland M, Kuipers J A M. Direct numerical simulation of complex multi-fluid flows using a combined front tracking and immersed boundary method[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(9): 2186-2201. |
| [50] | Baltussen M W, Seelen L J H, Kuipers J A M, et al. Direct numerical simulations of gas-liquid-solid three phase flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2013, 100: 293-299. |
| [51] | Baltussen M W, Kuipers J A M, Deen N G. Direct numerical simulation of effective drag in dense gas-liquid-solid three-phase flows[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 158: 561-568. |
| [52] | Zhang J P, Li Y, Fan L S. Numerical studies of bubble and particle dynamics in a three-phase fluidized bed at elevated pressures[J]. Powder Technology, 2000, 112(1/2): 46-56. |
| [9] | Luo Y B, Hu Z D. Scale-up and modeling of countercurrent three-phase fluidized reactor for flue gas desulfurization[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2002, 53(2): 122-127. |
| [10] | Zhou X H, Ma Y L, Liu M Y, et al. CFD-PBM simulations on hydrodynamics and gas-liquid mass transfer in a gas-liquid-solid circulating fluidized bed[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 362: 57-74. |
| [11] | Pan H, Chen X Z, Liang X F, et al. CFD simulations of gas-liquid-solid flow in fluidized bed reactors: a review[J]. Powder Technology, 2016, 299: 235-258. |
| [12] | 是勋刚. 湍流[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 1994. |
| Shi X G. Turbulence[M]. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press, 1994. | |
| [13] | 王圣业, 符翔, 杨小亮, 等. 高阶矩湍流模型研究进展及挑战[J]. 力学进展, 2021, 51(1): 29-61. |
| Wang S Y, Fu X, Yang X L, et al. Progresses and challenges of high-order-moment turbulence closure[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2021, 51(1): 29-61. | |
| [14] | 仇轶, 由长福, 祁海鹰, 等. 多相流动的直接数值模拟进展[J]. 力学进展, 2003, 33(4): 507-517. |
| Qiu Y, You C F, Qi H Y, et al. Direct numerical simulations of multiphase flows[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2003, 33(4): 507-517. | |
| [15] | Deen N G, van Sint Annaland M, van der Hoef M A, et al. Review of discrete particle modeling of fluidized beds[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(1/2): 28-44. |
| [16] | Maxey M R, Riley J J. Equation of motion for a small rigid sphere in a nonuniform flow[J]. Physics of Fluids, 1983, 26(4): 883-889. |
| [17] | 江茂强. 基于边界增厚浸入边界法的颗粒群沉降密度比效应直接数值模拟研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2021. |
| [53] | Li Y, Yang G Q, Zhang J P, et al. Numerical studies of bubble formation dynamics in gas-liquid-solid fluidization at high pressures[J]. Powder Technology, 2001, 116(2/3): 246-260. |
| [54] | Zhang J P, Li Y, Fan L S. Discrete phase simulation of gas-liquid-solid fluidization systems: single bubble rising behavior[J]. Powder Technology, 2000, 113(3): 310-326. |
| [55] | Xu Y G, Liu M Y, Tang C. Three-dimensional CFD-VOF-DPM simulations of effects of low-holdup particles on single-nozzle bubbling behavior in gas-liquid-solid systems[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 222: 292-306. |
| [56] | Liu Q, Luo Z H. CFD-VOF-DPM simulations of bubble rising and coalescence in low hold-up particle-liquid suspension systems[J]. Powder Technology, 2018, 339: 459-469. |
| [57] | van Sint Annaland M, Deen N G, Kuipers J A M. Numerical simulation of gas-liquid-solid flows using a combined front tracking and discrete particle method[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2005, 60(22): 6188-6198. |
| [58] | 李彦鹏, 王焕然. 基于Level Set方法的气-液-固三相流动模型与模拟[J]. 应用力学学报, 2008, 25(4): 578-582, 731. |
| Li Y P, Wang H R. Modeling and simulation of gas-liquid-solid three-phase flows based on Level Set method[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2008, 25(4): 578-582, 731. | |
| [59] | Fayed H E, Ragab S A. Direct numerical simulation of particles-bubbles collisions kernel in homogeneous isotropic turbulence[J]. The Journal of Computational Multiphase Flows, 2013, 5(3): 167-188. |
| [60] | Wan D D, Yi X, Wang L P, et al. Study of collisions between particles and unloaded bubbles with point-particle model embedded in the direct numerical simulation of turbulent flows[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2020, 146: 106137. |
| [61] | Shan X, Chen H. Simulation of nonideal gases and liquid-gas phase transitions by the lattice Boltzmann equation[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical Physics, Plasmas, Fluids, and Related Interdisciplinary Topics, 1994, 49(4): 2941-2948. |
| [62] | Shan X, Chen H. Lattice Boltzmann model for simulating flows with multiple phases and components[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical Physics, Plasmas, Fluids, and Related Interdisciplinary Topics, 1993, 47(3): 1815-1819. |
| [63] | Swift M R, Orlandini E, Osborn W R, et al. Lattice Boltzmann simulations of liquid-gas and binary fluid systems[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical Physics, Plasmas, Fluids, and Related Interdisciplinary Topics, 1996, 54(5): 5041-5052. |
| [64] | Fakhari A, Rahimian M H. Phase-field modeling by the method of lattice Boltzmann equations[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2010, 81(3 Pt 2): 036707. |
| [65] | 付宇航, 赵述芳, 王文坦, 等. 多相/多组分LBM模型及其在微流体领域的应用[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(7): 2535-2543. |
| Fu Y H, Zhao S F, Wang W T, et al. Application of lattice Boltzmann method for simulation of multiphase/multicomponent flow in microfluidics[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(7): 2535-2543. | |
| [66] | Seta T, Yamamoto K, Yoshino M, et al. Lattice Boltzmann method for multiphase and multicomponent flows: a review[J]. Multiphase Science and Technology, 2022, 34(3): 47-61. |
| [67] | Sudhakar T, Das A K. Evolution of multiphase lattice Boltzmann method: a review[J]. Journal of the Institution of Engineers (India): Series C, 2020, 101(4): 711-719. |
| [68] | 黄海波, 刘魁. 格子Boltzmann方法: 从入门到精通[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2023. |
| Huang H B, Liu K. Lattice Boltzmann Method[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2023. | |
| [69] | Kano Y, Sato T, Oyama H. Numerical study on the formations of gas channels and subsequent bubbles in unconsolidated sandy seabed sediment using a coupled LBM-DEM method[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 74: 103101. |
| [70] | 冯鑫. 基于伪势LBM的Janus微颗粒气泡驱动机理研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2021. |
| Feng X. Study on mechanism of bubble-driven Janus particle based on pseudo-potential lattice Boltzmann method[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2021. | |
| [71] | Yang B, Chen S. Simulation of interaction between a freely moving solid particle and a freely moving liquid droplet by lattice Boltzmann method[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 127: 474-484. |
| [72] | Chen S Y, Chen X H, Wan D D, et al. A lattice Boltzmann study of the collisions in a particle-bubble system under turbulent flows[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 361: 759-768. |
| [73] | Jiang F, Liu H H, Chen X, et al. A coupled LBM-DEM method for simulating the multiphase fluid-solid interaction problem[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2022, 454: 110963. |
| [74] | 陈海楠, 孙东科, 戴挺, 等. 凝固前沿和气泡相互作用的大密度比格子玻尔兹曼方法模拟[J]. 物理学报, 2013, 62(12): 38-48. |
| Chen H N, Sun D K, Dai T, et al. Modeling of the interaction between solidification interface and bubble using the lattice Boltzmann method with large density ratio[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(12): 38-48. | |
| [75] | Gingold R A, Monaghan J J. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: theory and application to non-spherical stars[J]. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1977, 181(3): 375-389. |
| [76] | Ye T, Pan D Y, Huang C, et al. Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) for complex fluid flows: recent developments in methodology and applications[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2019, 31(1): 011301. |
| [77] | Jo Y B, Park S H, Yoo H S, et al. GPU-based SPH-DEM method to examine the three-phase hydrodynamic interactions between multiphase flow and solid particles[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2022, 153: 104125. |
| [78] | 陈飞国, 葛蔚. 多相流动的光滑粒子流体动力学方法研究综述[J]. 力学学报, 2021, 53(9): 2357-2373. |
| Chen F G, Ge W. A review of smoothed particle hydrodynamics family methods for multiphase flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2021, 53(9): 2357-2373. | |
| [79] | Sun P N, Colagrossi A, Marrone S, et al. Multi-resolution delta-plus-SPH with tensile instability control: towards high Reynolds number flows[J]. Computer Physics Communications, 2018, 224: 63-80. |
| [80] | 马永丽, 刘明言, 胡宗定. 气液固流化床流动介尺度模型研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(6): 2438-2451. |
| Ma Y L, Liu M Y, Hu Z D. Development of flow mesoscale modeling of the gas-liquid-solid fluidized beds[J]. CIESC Journal, 2022, 73(6): 2438-2451. | |
| [81] | 侯亚祺, 张玮, 张鸿, 等. 基于机器学习与粒子群算法的LBM多相流模型优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(3): 1120-1132. |
| Hou Y Q, Zhang W, Zhang H, et al. Optimisation of LBM multiphase flow models based on machine learning and particle swarm algorithm[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(3): 1120-1132. | |
| [82] | Li X N, Liu M Y, Dong T T, et al. VOF-DEM simulation of single bubble behavior in gas-liquid-solid mini-fluidized bed[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2020, 155: 108-122. |
| [1] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [2] | 孙九春, 桑运龙, 王海涛, 贾浩, 朱艳. 泥水盾构仓体内射流对泥浆输送特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 246-257. |
| [3] | 王泽, 胡琼, 陈雅静, 王衍, 耿佳旭, 沈斐然. 液体自冲击密封泄漏特性、密封机理与优化设计[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4194-4204. |
| [4] | 刘建海, 王磊, 鲁朝金, 白志山, 张平雨. 耦合电化学与多相流模型的电解槽性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3885-3893. |
| [5] | 常心泉, 张克学, 王军, 夏国栋. 自由分子区内不规则颗粒的热泳力计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3944-3953. |
| [6] | 苏国庆, 田学梅, 李彦, 张建文, 张志军. 气力输送系统弯管三通的冲蚀分析及改进[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3894-3904. |
| [7] | 周航, 张斯婧, 刘剑, 张小松. 小通道内非共沸工质流动沸腾换热数值分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3864-3872. |
| [8] | 夏天炜, 王谙词, 句子涵, 孙晓霞, 胡定华. 基于三周期极小曲面结构的高密度储热器蓄放热特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3605-3614. |
| [9] | 陈曦, 王淑彦, 邵宝力, 丁诺, 谢磊. 基于颗粒动态恢复系数二阶矩模型的液固流化床数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3246-3258. |
| [10] | 王富玉, 周晅毅. 结合非定常伴随方程和遗传算法的化工区反演[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 3104-3114. |
| [11] | 张亿韵, 陈恒志, 李洋, 慕长安, 王泉海. 湍流对双组分颗粒流化床气体径向扩散的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2559-2568. |
| [12] | 郭江悦, 常守金, 胡海涛. 水平管内甲醇流动冷凝数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2580-2588. |
| [13] | 王令颁, 孙漪霏, 卜禹豪, 许振彬, 孙贤, 邵瀚锋, 孙长宇, 陈光进. 大尺度扇柱形反应釜内甲烷水合物降压开采规律研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2958-2973. |
| [14] | 谷德银, 杨豪, 李昌树, 刘作华. 分形穿流桨搅拌槽内假塑性流体的混合行为[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2569-2579. |
| [15] | 牛宏斌, 邱丽, 杨景轩, 张忠林, 郝晓刚, 赵忠凯, 阿布里提, 官国清. 筒体直径对旋风分离器性能的影响及其流场机制[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2367-2376. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号