化工学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 75 ›› Issue (2): 695-705.DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20231166
收稿日期:2023-11-13
修回日期:2024-01-05
出版日期:2024-02-25
发布日期:2024-04-10
通讯作者:
李见波
作者简介:王灵洁(1997—),女,硕士研究生,2392360434@qq.com
基金资助:
Lingjie WANG( ), Hailong GAO, Jipeng JIN, Zhihao WANG, Jianbo LI(
), Hailong GAO, Jipeng JIN, Zhihao WANG, Jianbo LI( )
)
Received:2023-11-13
Revised:2024-01-05
Online:2024-02-25
Published:2024-04-10
Contact:
Jianbo LI
摘要:
海水淡化装置排出的浓缩卤水会造成盐差能的浪费,逆电渗析电堆可以有效回收这种盐差能,并直接转换为电能。但是以海水和浓缩卤水为工作溶液的电堆性能易受工作溶液中不溶性物质的影响。为揭示这种影响规律,对逆电渗析电堆进行了定期的污染物附着实验研究。首先定期测试逆电渗析电堆的输出性能,获得了电堆性能衰减的规律;进而采用扫描电镜和能谱分析仪对离子交换膜和隔垫上的污染物种类进行分析,探究各附着物引起电堆性能下降的原因。结果表明:运行初期(0~20 d),电堆的开路电压、最大功率密度、能量转换效率,以及内阻变化速度快;运行后期(20~45 d),浓缩卤水侧的压降增速较快。本研究可为逆电渗析电堆的清洗策略提供一定的理论支持。
中图分类号:
王灵洁, 高海龙, 靳继鹏, 王志浩, 李见波. 海水中的污染物对逆电渗析电堆性能的影响[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 695-705.
Lingjie WANG, Hailong GAO, Jipeng JIN, Zhihao WANG, Jianbo LI. Influence of pollutants in seawater on performance of reverse electrodialysis stacks[J]. CIESC Journal, 2024, 75(2): 695-705.
| 名称 | 型号 | 精度 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 电化学工作站 | CHI-660C | 0.0001 | A/V |
| 电流放大器 | CHI-660E | 0.0001 | A/V |
| 电导率仪 | FE38-Standard | 0.01 | μS·cm-1 |
| 电子天平 | XY-1000-2C | 0.01 | g |
| 恒温水浴箱 | HH-600 | 0.1 | ℃ |
| 压力传感器 | CCY15-P-07B-A117 | 0. 01 | Pa |
| 蠕动泵-1 | LabN6 | 0.001 | ml·min-1 |
| 蠕动泵-2 | V6-3L | 0.001 | ml·min-1 |
| 超纯水机 | UPT-I-10T | 0.054 | μS·cm-1 |
表1 实验仪器及参数
Table 1 Experimental apparatus and parameters
| 名称 | 型号 | 精度 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 电化学工作站 | CHI-660C | 0.0001 | A/V |
| 电流放大器 | CHI-660E | 0.0001 | A/V |
| 电导率仪 | FE38-Standard | 0.01 | μS·cm-1 |
| 电子天平 | XY-1000-2C | 0.01 | g |
| 恒温水浴箱 | HH-600 | 0.1 | ℃ |
| 压力传感器 | CCY15-P-07B-A117 | 0. 01 | Pa |
| 蠕动泵-1 | LabN6 | 0.001 | ml·min-1 |
| 蠕动泵-2 | V6-3L | 0.001 | ml·min-1 |
| 超纯水机 | UPT-I-10T | 0.054 | μS·cm-1 |
| 组件 | 参数 | 数值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 离子交换膜 | 数量 | 20 | — |
| 宽度 | 300 | mm | |
| 长度 | 200 | mm | |
| 电极 | 数量 | 2 | — |
| 宽度 | 118 | mm | |
| 长度 | 65 | mm | |
| 数量 | 10 | — | |
| 隔垫 | 宽度 | 300 | mm |
| 长度 | 200 | mm | |
| 厚度 | 0.3 | mm |
表2 RED 电堆的主要结构参数
Table 2 Main structural parameters of the RED stack
| 组件 | 参数 | 数值 | 单位 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 离子交换膜 | 数量 | 20 | — |
| 宽度 | 300 | mm | |
| 长度 | 200 | mm | |
| 电极 | 数量 | 2 | — |
| 宽度 | 118 | mm | |
| 长度 | 65 | mm | |
| 数量 | 10 | — | |
| 隔垫 | 宽度 | 300 | mm |
| 长度 | 200 | mm | |
| 厚度 | 0.3 | mm |
| 参数 | AEM-type Ⅱ | CEM-type Ⅱ |
|---|---|---|
| 类型 | 均质膜 | 均质膜 |
| 厚度/μm | 160 | 160 |
| 选择渗透性(NaCl)/% | 95 | 96 |
| 膜阻/(Ω·cm2) | 3.5 | 6.1 |
| 水的渗透性/(ml·bar-1·m-2·h-1) | 3 | 3.5 |
| pH稳定性 | 2~10 | 4~12 |
表3 离子交换膜参数
Table 3 Ion exchange membrane parameters
| 参数 | AEM-type Ⅱ | CEM-type Ⅱ |
|---|---|---|
| 类型 | 均质膜 | 均质膜 |
| 厚度/μm | 160 | 160 |
| 选择渗透性(NaCl)/% | 95 | 96 |
| 膜阻/(Ω·cm2) | 3.5 | 6.1 |
| 水的渗透性/(ml·bar-1·m-2·h-1) | 3 | 3.5 |
| pH稳定性 | 2~10 | 4~12 |
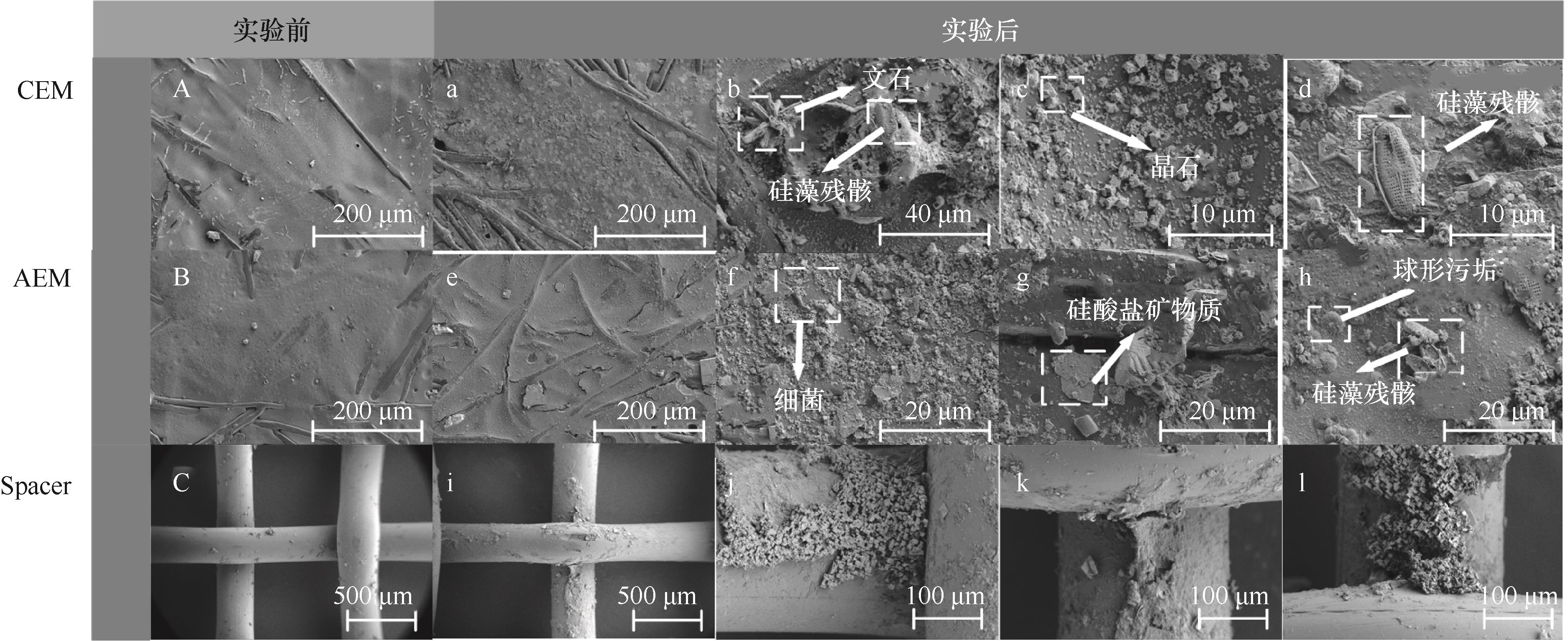
图5 实验前后海水侧IEMs以及隔垫污染电镜图对比
Fig.5 Comparison of seawater-side IEMs and spacer contamination electron micrographs on the seawater side before and after experiments
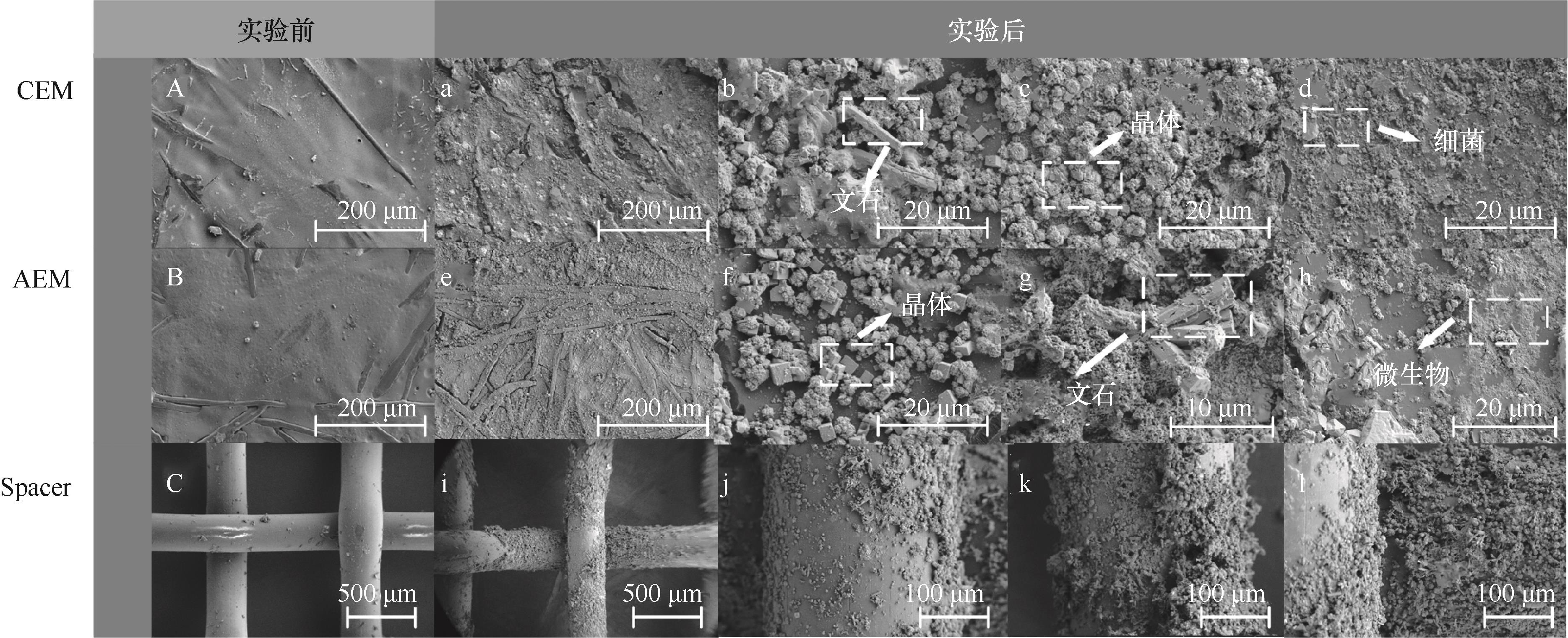

图6 实验前后浓缩卤水侧IEMs以及隔垫污染电镜图对比
Fig.6 Comparison of IEMs and spacer contamination electron micrographs on the concentrated brine side before and after the experiment
| 1 | 王项南, 麻常雷. “双碳”目标下海洋可再生能源资源开发利用[J]. 华电技术, 2021, 43(11): 91-96. |
| Wang X N, Ma C L. Utilization of marine renewable energy resources under the goal of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality[J]. Huadian Technology, 2021, 43(11): 91-96. | |
| 2 | Roldan-Carvajal M, Vallejo-Castaño S, Álvarez-Silva O, et al. Salinity gradient power by reverse electrodialysis: a multidisciplinary assessment in the Colombian context[J]. Desalination, 2021, 503: 114933. |
| 3 | 李秀敏, 陈庆. 反电渗析应用于盐差能提取的研究[J]. 辽宁化工, 2019, 48(7): 625-627. |
| Li X M, Chen Q. Study on application of reverse electrodialysis in the extraction of salinity gradient energy[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(7): 625-627. | |
| 4 | 邓会宁, 何云飞, 胡柏松, 等. 反电渗析法盐差能发电用离子交换膜研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2017, 36(1): 224-231. |
| Deng H N, He Y F, Hu B S, et al. Progress in ion exchange membranes for reverse electrodialysis[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2017, 36(1): 224-231. | |
| 5 | 刘伯羽, 李少红, 王刚. 盐差能发电技术的研究进展[J]. 可再生能源, 2010, 28(2): 141-144. |
| Liu B Y, Li S H, Wang G. Progress in extracting power from salinity gradient[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2010, 28(2): 141-144. | |
| 6 | 王燕, 刘邦凡, 段晓宏. 盐差能的研究技术、产业实践与展望[J]. 中国科技论坛, 2018(5): 49-56. |
| Wang Y, Liu B F, Duan X H. Research technology, industrial practice and prospect of gradient energy in China[J]. Forum on Science and Technology in China, 2018(5): 49-56. | |
| 7 | 刘媛媛, 周帅强, 张伟明. 基于反电渗析法盐差发电[J]. 辽宁化工, 2016, 45(4): 419-420, 429. |
| Liu Y Y, Zhou S Q, Zhang W M. Salinity gradient power generation based on reverse electrodialysis method[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2016, 45(4): 419-420, 429. | |
| 8 | Cambridge M L, Zavala-Perez A, Cawthray G R, et al. Effects of desalination brine and seawater with the same elevated salinity on growth, physiology and seedling development of the seagrass Posidonia australis [J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 140: 462-471. |
| 9 | Ihsanullah I, Atieh M A, Sajid M, et al. Desalination and environment: a critical analysis of impacts, mitigation strategies, and greener desalination technologies[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 780: 146585. |
| 10 | Li J B, Zhang C, Liu K, et al. Experimental study on salinity gradient energy recovery from desalination seawater based on RED[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 244: 114475. |
| 11 | Vermaas D A, Veerman J, Saakes M, et al. Influence of multivalent ions on renewable energy generation in reverse electrodialysis[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(4): 1434-1445. |
| 12 | Hulme A M, Davey C J, Tyrrel S, et al. Transitioning from electrodialysis to reverse electrodialysis stack design for energy generation from high concentration salinity gradients[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2021, 244: 114493. |
| 13 | Veerman J, Saakes M, Metz S J, et al. Reverse electrodialysis: performance of a stack with 50 cells on the mixing of sea and river water[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2009, 327(1/2): 136-144. |
| 14 | Merino-Garcia I, Velizarov S. New insights into the definition of membrane cleaning strategies to diminish the fouling impact in ion exchange membrane separation processes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 277: 119445. |
| 15 | 刘淑永, 王丹, 王庆吉, 等. 膜蒸馏处理炼油化工高含盐废水的膜污染及控制研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2023, 43(10): 79-83. |
| Liu S Y, Wang D, Wang Q J, et al. Research progress on membrane fouling and control in treating with high salinity wastewater from refining chemical industry by membrane distillation[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2023, 43(10): 79-83. | |
| 16 | 郭洪涛, 李大强, 张彦海, 等. 电厂反渗透膜污染及控制策略的研究进展[J]. 能源与环境, 2023(5): 110-113. |
| Guo H T, Li D Q, Zhang Y H, et al. Research progress of reverse osmosis membrane pollution and control strategy in power plant[J]. Energy and Environment, 2023(5): 110-113. | |
| 17 | 高倩, 张崇淼, 魏样, 等. 饮用水超滤处理中的膜污染及减缓技术研究进展[J]. 中国给水排水, 2020, 36(18): 13-18. |
| Gao Q, Zhang C M, Wei Y, et al. Research progress of membrane fouling and mitigation techniques in ultrafiltration treatment of drinking water[J]. China Water & Wastewater, 2020, 36(18): 13-18. | |
| 18 | 郭玉阳, 梁松苗. 反渗透膜污染类型分析及清洗技术的研究进展[J]. 当代化工研究, 2023(17): 123-125. |
| Guo Y Y, Liang S M. Research progress in analysis of fouling types and cleaning techniques for reverse osmosis membranes[J]. Modern Chemical Research, 2023(17): 123-125. | |
| 19 | 班福忱, 于涵同. 水处理中超滤膜污染成因及其控制方法研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2023, 49(2): 1-5, 17. |
| Ban F C, Yu H T. Study on causes and control methods of ultrafiltration membrane fouling in water treatment[J]. Technology of Water Treatment, 2023, 49(2): 1-5, 17. | |
| 20 | Chon K, Jeong N, Rho H, et al. Fouling characteristics of dissolved organic matter in fresh water and seawater compartments of reverse electrodialysis under natural water conditions[J]. Desalination, 2020, 496: 114478. |
| 21 | Vermaas D A, Kunteng D, Saakes M, et al. Fouling in reverse electrodialysis under natural conditions[J]. Water Research, 2013, 47(3): 1289-1298. |
| 22 | Santoro S, Tufa R A, Avci A H, et al. Fouling propensity in reverse electrodialysis operated with hypersaline brine[J]. Energy, 2021, 228: 120563. |
| 23 | Avci A H, Sarkar P, Tufa R A, et al. Effect of Mg2+ ions on energy generation by reverse electrodialysis[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016, 520: 499-506. |
| 24 | Roman M, van Dijk L H, Gutierrez L, et al. Key physicochemical characteristics governing organic micropollutant adsorption and transport in ion-exchange membranes during reverse electrodialysis[J]. Desalination, 2019, 468: 114084. |
| 25 | Mikhaylin S, Bazinet L. Fouling on ion-exchange membranes: classification, characterization and strategies of prevention and control[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 229: 34-56. |
| 26 | Pawlowski S, Galinha C F, Crespo J G, et al. 2D fluorescence spectroscopy for monitoring ion-exchange membrane based technologies—reverse electrodialysis (RED)[J]. Water Research, 2016, 88: 184-198. |
| 27 | Rijnaarts T, Moreno J, Saakes M, et al. Role of anion exchange membrane fouling in reverse electrodialysis using natural feed waters[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 560: 198-204. |
| 28 | Kang S B, Li J B, Wang Z H, et al. Salinity gradient energy capture for power production by reverse electrodialysis experiment in thermal desalination plants[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 519: 230806. |
| 29 | 郑武, 于萍. 吸附预处理减缓微滤膜污染试验研究[J]. 四川大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 55(6): 1265-1269. |
| Zheng W, Yu P. Study of effect of adsorption pretreatment on mitigating fouling of micromembrane[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 55(6): 1265-1269. | |
| 30 | Moreno J, de Hart N, Saakes M, et al. CO2 saturated water as two-phase flow for fouling control in reverse electrodialysis[J]. Water Research, 2017, 125: 23-31. |
| [1] | 刘昌会, 肖桐, 刘庆祎, 耿龙, 赵佳腾. 多孔二氧化钛强化的相变材料储热机理研究[J]. 化工学报, 2024, 75(2): 706-714. |
| [2] | 黄琮琪, 吴一梅, 陈建业, 邵双全. 碱性电解水制氢装置热管理系统仿真研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(S1): 320-328. |
| [3] | 张佳怡, 何佳莉, 谢江鹏, 王健, 赵鹬, 张栋强. 渗透汽化技术用于锂电池生产中N-甲基吡咯烷酮回收的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3203-3215. |
| [4] | 张瑞航, 曹潘, 杨锋, 李昆, 肖朋, 邓春, 刘蓓, 孙长宇, 陈光进. ZIF-8纳米流体天然气乙烷回收工艺的产品纯度关键影响因素分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3386-3393. |
| [5] | 胡亚丽, 胡军勇, 马素霞, 孙禹坤, 谭学诣, 黄佳欣, 杨奉源. 逆电渗析热机新型工质开发及电化学特性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(8): 3513-3521. |
| [6] | 肖忠良, 尹碧露, 宋刘斌, 匡尹杰, 赵亭亭, 刘成, 袁荣耀. 废旧锂离子电池回收工艺研究进展及其安全风险分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(4): 1446-1456. |
| [7] | 陈瑞哲, 程磊磊, 顾菁, 袁浩然, 陈勇. 纤维增强树脂复合材料化学回收技术研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 981-994. |
| [8] | 王思琪, 顾天宇, 陈献富, 王通, 李佳, 柯威, 李小锋, 范益群. 陶瓷膜用于杜仲叶提取液澄清的分离特性与膜污染机制研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(3): 1113-1125. |
| [9] | 许万, 陈振斌, 张慧娟, 牛昉昉, 火婷, 刘兴盛. 线性温敏性聚合物嵌段调控的 |
| [10] | 齐欣欣, 贾辉, 高菲, 王琦, 尹延梅, 王捷. 基于双侧阵列电极的电阻抗成像原位膜污染监测[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(11): 4720-4729. |
| [11] | 周昉, 刘剑, 张小松. 基于多参数评估原则筛选高温热泵用三元非共沸混合工质[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(11): 4487-4500. |
| [12] | 武庭宇, 王超, 秦余涛, 庄钰, 都健. 乙酸乙酯/乙醇/水体系预分离萃取精馏工艺研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(11): 4578-4586. |
| [13] | 刘壮壮, 鞠然, 刘崇涛, 宋建超, 李洋洋, 吴厚凯, 李同, 陶秀萍. 电化学膜生物反应器处理污水性能提升策略及研究现状[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(11): 4433-4444. |
| [14] | 贺巍, 曹永娜, 尚宏儒, 李崯雪, 郭超, 于艳玲. 生物质发酵余热回收系统优化设计与性能分析[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4302-4310. |
| [15] | 童文华, 李义隆, 张永奎, 王雅博. 碱辅助四氧化三锰降解磷酸三丁酯及磷元素回收研究[J]. 化工学报, 2023, 74(10): 4277-4285. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号