• •
段睿阳1( ), 王帅2, 吴乐3, 康丽霞1(
), 王帅2, 吴乐3, 康丽霞1( ), 刘永忠1
), 刘永忠1
收稿日期:2025-09-16
修回日期:2025-11-17
出版日期:2025-11-18
通讯作者:
康丽霞
作者简介:段睿阳(2002—),男,硕士研究生,ryduan@stu.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Ruiyang DUAN1( ), Shuai WANG2, Le WU3, Lixia KANG1(
), Shuai WANG2, Le WU3, Lixia KANG1( ), Yongzhong LIU1
), Yongzhong LIU1
Received:2025-09-16
Revised:2025-11-17
Online:2025-11-18
Contact:
Lixia KANG
摘要:
本文以实际百万吨级煤制尿素工艺为对象,首先结合全流程模拟、技术经济性分析和全生命周期分析技术,系统评估了该工艺的能源利用效率、经济性和环境性。结果表明,煤制尿素工艺热量需求大,通过热量集成可基本实现内部工艺流股的升温需求,全流程热集成回收余热271MW,完全覆盖冷流股升温需求,系统能量利用效率从44.7 %提升至52.9 %,但气化炉仍需1340MW的外部高温供热。经济性分析表明,煤气化投资和公用工程费用分别是煤制尿素工艺投资费用和运营费用的主要来源,占比均超过60 %,煤价和空分装置投资则是影响煤制尿素工艺生产成本的关键因素。生命周期评价(LCA)结果显示,煤制氢、氨和尿素的全球变暖潜值(GWP)分别为21.77 t CO2-eq/t H2、4.725 t CO2-eq/t NH3和2.374 t CO2-eq/t 尿素。其中原料煤相关的碳排占53.2 %,其次为热电相关的间接排放,因此需要通过原料替代和引入绿电绿热以降低碳排。其次,在考虑绿电、绿氢、绿热替代的基础上,探讨了绿氢制尿素工艺相较于传统煤基工艺的经济和环境效益,结果表明绿氢制尿素工艺的投资费用是煤基工艺的1.81倍,其中电解槽费用占72.73 %。使用电网、可再生电力、可再生热电的工艺的生产成本分别为传统工艺的1.61、1.22和1.35倍。最后,分析和对比了电解槽投资成本与绿电价格变化时的生产成本演化规律,以提供新型工艺替代煤基工艺的阈值条件。碳排方面,仅替代电力来源、替代原料煤并使用绿电以及联用绿电绿热三个场景的GWP分别为2.29 t CO2-eq/t 尿素、0.61 t CO2-eq/t 尿素和0.29 t CO2-eq/t 尿素。以上研究不但可为煤制尿素及其他煤基化工行业的低碳转型与可持续发展提供量化分析工具,还可为煤化工企业的降本、节能、减排等策略制定提供精准指导。
中图分类号:
段睿阳, 王帅, 吴乐, 康丽霞, 刘永忠. 考虑绿电-绿氢-绿热替代的煤制尿素工艺的能量-经济-环境分析[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251044.
Ruiyang DUAN, Shuai WANG, Le WU, Lixia KANG, Yongzhong LIU. Energy-economic-environmental analysis of coal-based urea production considering green power-hydrogen-heat substitution[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20251044.
| 单元/设备 | 模型 | 操作参数 |
|---|---|---|
| 煤气化炉 | RYield | 操作温度:700 ℃ |
| 操作压力:30 bar | ||
| RGibbs | 操作温度:1400 ℃ | |
| 操作压力:30 bar | ||
| 水汽变换单元1 | REquil | 操作压力:62 bar |
| 段间冷却器1 | Heater | 操作温度:264.9 ℃ |
| 水汽变换单元2 | REquil | 操作压力:60.5 bar |
| 段间冷却器2 | Heater | 操作温度:240.4 ℃ |
| 水汽变换单元3 | REquil | 操作压力:59.4 bar |
| 水汽变换后除水 | Flash | 操作温度:30 ℃ |
| 操作压力:34.5 bar | ||
| 酸气脱除单元 | Sep | 分离率:0.99 |
| 变压吸附单元 | Sep | 分离率:0.99 |
| 合成氨单元 | RPlug | 依据反应动力学 |
| 汽提塔 | RadFrac | 塔顶压力:135 bar |
| 塔底压力:138 bar | ||
| 高压冷凝塔 | RStoic | 转化率:0.38,以CO2为基 |
| 尿素合成塔 | RadFrac | 依据反应动力学 |
| 蒸馏塔 | Sep | 分离率:0.998 |
| 高压洗涤塔 | RadFrac | 塔顶压力:135bar |
| 塔底压力:138 bar |
表1 模拟关键单元或设备选用的模型与操作参数
Table 1 Models and operating parameters selected for simulating critical units or equipment
| 单元/设备 | 模型 | 操作参数 |
|---|---|---|
| 煤气化炉 | RYield | 操作温度:700 ℃ |
| 操作压力:30 bar | ||
| RGibbs | 操作温度:1400 ℃ | |
| 操作压力:30 bar | ||
| 水汽变换单元1 | REquil | 操作压力:62 bar |
| 段间冷却器1 | Heater | 操作温度:264.9 ℃ |
| 水汽变换单元2 | REquil | 操作压力:60.5 bar |
| 段间冷却器2 | Heater | 操作温度:240.4 ℃ |
| 水汽变换单元3 | REquil | 操作压力:59.4 bar |
| 水汽变换后除水 | Flash | 操作温度:30 ℃ |
| 操作压力:34.5 bar | ||
| 酸气脱除单元 | Sep | 分离率:0.99 |
| 变压吸附单元 | Sep | 分离率:0.99 |
| 合成氨单元 | RPlug | 依据反应动力学 |
| 汽提塔 | RadFrac | 塔顶压力:135 bar |
| 塔底压力:138 bar | ||
| 高压冷凝塔 | RStoic | 转化率:0.38,以CO2为基 |
| 尿素合成塔 | RadFrac | 依据反应动力学 |
| 蒸馏塔 | Sep | 分离率:0.998 |
| 高压洗涤塔 | RadFrac | 塔顶压力:135bar |
| 塔底压力:138 bar |
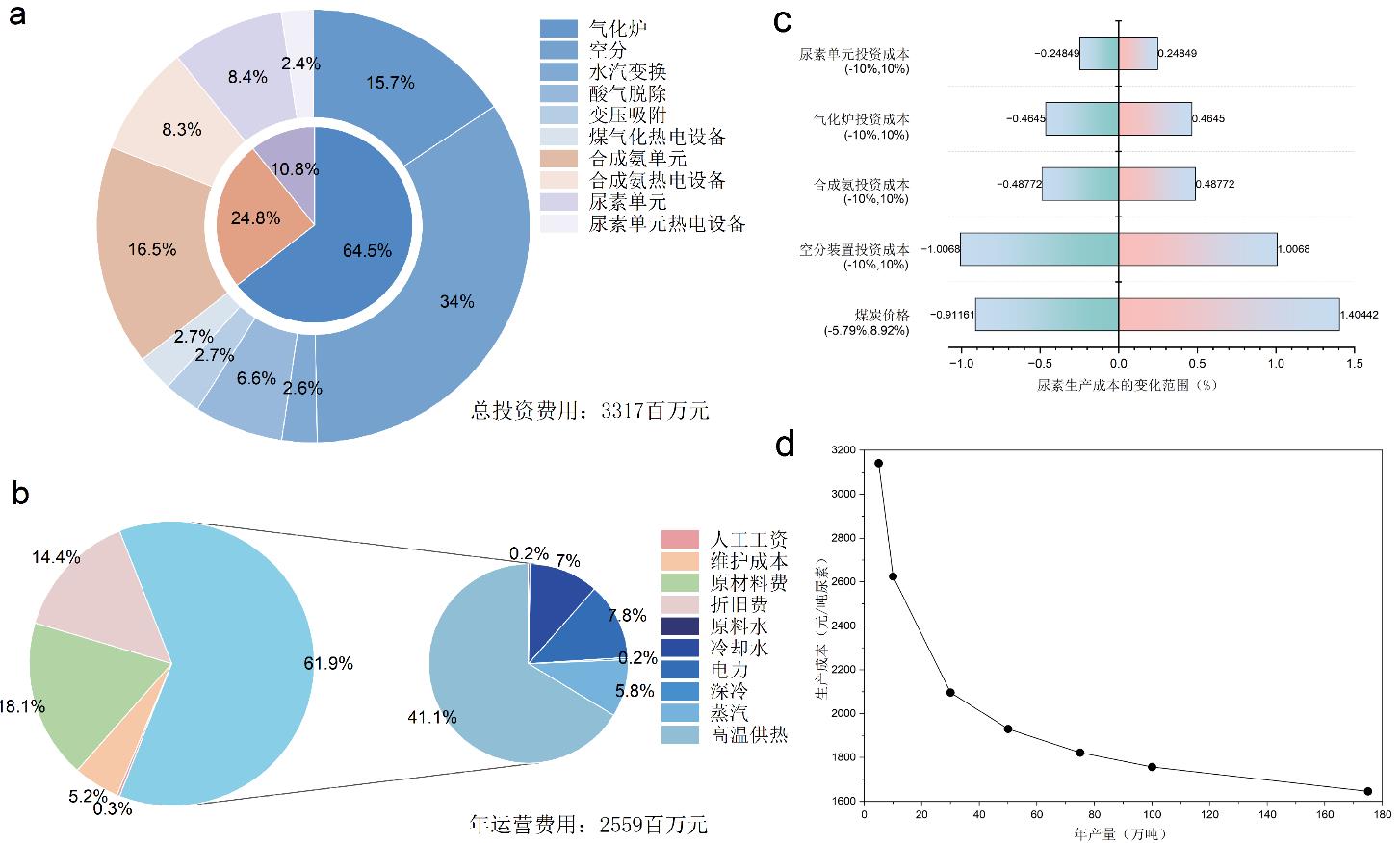
图4 煤制尿素工艺总投资成本(a)、年运营费用(b)、敏感度分析(c)与规模对成本的影响(d)
Fig.4 Calculation of total investment costs(a), annual operating costs(b), sensitivity analysis(c) results of coal-to-urea and the impact of scale on cost(d)
| [1] | Kohse-Höinghaus K. Combustion, chemistry, and carbon neutrality[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2023, 123(8): 5139-5219. |
| [2] | 金涌, 胡永琪, 胡山鹰, 等. 煤炭热力学高效和化学高价值利用新工艺[J]. 化工学报, 2014, 65(2): 381-389. |
| Jin Y, Hu Y Q, Hu S Y, et al. New technology for thermo-chemical comprehensive utilization of coal[J]. CIESC Journal, 2014, 65(2): 381-389. | |
| [3] | 熊敏, 刘冬妹, 王智超, 等. 变负荷条件下绿氨生产操作参数的调控与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2791-2801. |
| Xiong M, Liu D M, Wang Z C, et al. Optimization and adjustment of operating parameters for green ammonia production under variable load conditions[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025, 76(6): 2791-2801. | |
| [4] | Gosens J, Turnbull A B H, Jotzo F. China's decarbonization and energy security plans will reduce seaborne coal imports: Results from an installation-level model[J]. Joule, 2022, 6(4): 782-815. |
| [5] | Jiang P, Wang C H, Li L, et al. Green impacts of transforming green electricity into microwave for ammonia and urea production[J]. AIChE Journal, 2025, 71(5): e18743. |
| [6] | Wu D, Zheng H T, Li Q, et al. Toxic potency-adjusted control of air pollution for solid fuel combustion[J]. Nature Energy, 2022, 7(2): 194-202. |
| [7] | Liu S W, Guo Y, Wagner F, et al. Diversifying heat sources in China's urban district heating systems will reduce risk of carbon lock-in[J]. Nature Energy, 2024, 9(8): 1021-1031. |
| [8] | 市场监管总局. 关于开展产品碳足迹标识认证试点工作的通知[EB/OL]. (2024-08-30) [2025-06-10]. . |
| State Administration for Market Regulation. Notice on launching the pilot project for product carbon footprint labeling and certification[EB/OL]. (2024-08-30) [2025-06-10]. . | |
| [9] | 国家发展改革委. 工业重点领域能效标杆水平和基准水平[EB/OL]. (2023-06-06) [2025-04-30]. . |
| National Development and Reform Commission. Energy efficiency benchmarking and baseline levels in key industrial sectors[EB/OL]. (2023-06-06) [2025-04-30]. . | |
| [10] | 国家发展改革委. 可再生能源消费最低比重目标和可再生能源电力消纳责任权重制度实施办法(征求意见稿)[EB/OL]. (2025-10-13) [2025-10-15]. . |
| National Development and Reform Commission. Implementation measures for the minimum renewable energy consumption proportion targer and renewable energy power consumption responsibility weight system (draft for comments)[EB/OL]. (2025-10-13) [2025-10-15]. . | |
| [11] | Katerina Kermeli E W, Graus Wina, Corsten Mariëlle. Energy efficiency and cost saving opportunities for ammonia and nitrogenous fertilizer production: an ENERGY STAR guide for energy and plant managers[R]. The United States: United States Environmental Protection Agency, 2017. |
| [12] | Stamicarbon. NX Stami Urea Launch Brochure[R]. Nederlands: Stamicarbon, 2025. |
| [13] | Baboo P. Energy saving in urea plant by modification in heat exchangers & process[J]. International Journal of Engineering Research Technology, 2016, 5(6): 382-389. |
| [14] | 中原期货. 供强需弱格局延续,关注出口兑现情况[EB/OL]. (2025-07-22) [2025-08-15]. . |
| Central China Futures. The pattern of strong supply and weak demand persists, with focus on the fulfillment of exports[EB/OL]. (2025-07-22) [2025-08-15]. . | |
| [15] | 小牛行研. 尿素各工艺生产成本测算[EB/OL]. (2025-02-24) [2025-08-15]. . |
| Xiaoniu Industry Research. Calculation of production costs for various urea processes[EB/OL]. (2025-02-24) [2025-08-15]. . | |
| [16] | 东方财富证券. 尿素当前生产成本调研[EB/OL]. (2025-06-18) [2025-08-15]. . |
| Securities Eastmoney. Survey on current production cost of urea[EB/OL]. (2025-06-18) [2025-08-15]. . | |
| [17] | 张科, 肖敦峰, 夏炎华, 等. 湖北荆州地区建设煤制尿素项目的可行性分析[J]. 化肥设计, 2021, 59(1): 1-4. |
| Zhang K, Xiao D F, Xia Y H, et al. Study on the feasibility of constructing coal-to-urea projects in Jingzhou area of Hubei Province[J]. Chemical Fertilizer Design, 2021, 59(1): 1-4. | |
| [18] | 中国产业经济信息网, 中国氮肥工业协会. 推进合成氨/尿素碳足迹量化国标制定[EB/OL]. (2025-06-03) [2025-08-10]. . |
| China Industrial Economy Information Network, China Nitrogen Fertilizer Industry Association. Promote the development of national standards for quantifying the carbon footprint of synthetic ammonia/urea[EB/OL]. (2025-06-03) [2025-08-10]. . | |
| [19] | 中国氮肥工业协会. 温室气体产品碳足迹量化方法与要求[EB/OL]. (2025-09-15) [2025-09-26]. . |
| China Nitrogen Fertilizer Industry Association. Quantification methods and requirements for carbon footprint of greenhouse gas products[EB/OL]. (2025-09-15) [2025-09-26]. . | |
| [20] | 李红泰. "双碳"背景下煤基合成氨/尿素行业减排之路初探[J]. 中氮肥, 2022(4): 31-35. |
| Li H T. Preliminary study on emission reduction of coal-based ammonia/urea industry under the background of "double carbon"[J]. M-Sized Nitrogenous Fertilizer Progress, 2022(4): 31-35. | |
| [21] | Shi L Y, Liu L Y, Yang B, et al. Evaluation of industrial urea energy consumption (EC) based on life cycle assessment (LCA)[J]. Sustainability, 2020, 12(9): 3793. |
| [22] | Zhang Y, Yuan Z W, Margni M, et al. Intensive carbon dioxide emission of coal chemical industry in China[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 236: 540-550. |
| [23] | Meng W L, Wang D L, Zhou H R, et al. Carbon dioxide from oxy-fuel coal-fired power plant integrated green ammonia for urea synthesis: Process modeling, system analysis, and techno-economic evaluation[J]. Energy, 2023, 278: 127537. |
| [24] | Chen Y H, Lyu Y F, Yang X D, et al. Performance comparison of urea production using one set of integrated indicators considering energy use, economic cost and emissions' impacts: a case from China[J]. Energy, 2022, 254: 124489. |
| [25] | 国务院办公厅. 2024-2025年节能降碳行动方案[EB/OL]. (2025-05-23) [2025-09-26]. . |
| General Office of the State Council. Action plan for energy conservation and carbon reduction in 2024-2025[EB/OL]. (2025-05-23) [2025-09-26]. . | |
| [26] | 生态环境部. 全国碳市场发展报告[EB/OL]. (204-07-22) [2025-08-17]. . |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment. National carbon market development report[EB/OL]. (2024-07-22) [2025-08-17]. . | |
| [27] | 国家发展改革委. 关于促进可再生能源绿色电力证书市场高质量发展的意见[EB/OL]. (2025-03-18) [2025-08-17]. . |
| National Development and Reform Commission. Opinions and promoting high-quality development of the renewable energy green power certificate market[EB/OL]. (2025-03-18) [2025-08-17]. . | |
| [28] | Soroodan E, Huang S E, Milani D, et al. Techno-economic assessment of green urea production integrated with direct air capture[J]. Energy Conversion and Management: X, 2025, 26: 101015. |
| [29] | Devkota S, Karmacharya P, Maharjan S, et al. Decarbonizing urea: Techno-economic and environmental analysis of a model hydroelectricity and carbon capture based green urea production[J]. Applied Energy, 2024, 372: 123789. |
| [30] | Alfian M, Purwanto W W. Multi-objective optimization of green urea production[J]. Energy Science & Engineering, 2019, 7(2): 292-304. |
| [31] | Galusnyak S C, Petrescu L, Sandu V C, et al. Environmental impact assessment of green ammonia coupled with urea and ammonium nitrate production[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2023, 343: 118215. |
| [32] | Tang J P, Kang L X, Liu Y Z. Design and optimization of a clean ammonia synthesis system based on biomass gasification coupled with a Ca–Cu chemical loop[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2022, 61(23): 8128-8140. |
| [33] | Zhang Y, Zhang L, Kang L X, et al. Techno-economic analysis of a hybrid system with carbon capture for simultaneous power generation and coal-to-hydrogen conversion[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(18): 7048-7057. |
| [34] | Higman C, Tam S. Advances in coal gasification, hydrogenation, and gas treating for the production of chemicals and fuels[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(3): 1673-1708. |
| [35] | Smith C, Hill A K, Torrente-Murciano L. Current and future role of Haber–Bosch ammonia in a carbon-free energy landscape[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(2): 331-344. |
| [36] | Morud J C, Skogestad S. Analysis of instability in an industrial ammonia reactor[J]. AIChE Journal, 1998, 44(4): 888-895. |
| [37] | Moura I P, Reis A C, Bresciani A E, et al. Carbon dioxide abatement by integration of methane bi-reforming process with ammonia and urea synthesis[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 151: 111619. |
| [38] | Zhou L, Hu S Y, Li Y R, et al. Study on co-feed and co-production system based on coal and natural gas for producing DME and electricity[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2008, 136(1): 31-40. |
| [39] | Demirhan C D, Tso W W, Powell J B, et al. Sustainable ammonia production through process synthesis and global optimization[J]. AIChE Journal, 2019, 65(7): e16498. |
| [40] | Pujol A, Heuckendorff M, Helmer Pedersen T. Techno-economic analysis of two novel direct air capture-to-urea concepts based on process intensification[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2025, 496: 144932. |
| [41] | Palys M J, McCormick A, Cussler E L, et al. Modeling and optimal design of absorbent enhanced ammonia synthesis[J]. Processes, 2018, 6(7): 91. |
| [42] | Martsinchyk K, Martsinchyk A, Łazor M, et al. Feasibility study and techno-economic assessment of power-to-gas (P2G) technology based on solid oxide electrolysis (SOE)[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 354: 120425. |
| [43] | Zhang H F, Wang L G, Van herle J, et al. Techno-economic comparison of 100% renewable urea production processes[J]. Applied Energy, 2021, 284: 116401. |
| [44] | Suh D H. Interfuel substitution and biomass use in the U.S. industrial sector: a differential approach[J]. Energy, 2016, 102: 24-30. |
| [45] | 生态环境部. 中国产品全生命周期温室气体排放系数集[EB/OL]. (2022-01-05) [2025-08-06]. . |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Set of greenhouse gas emission factors for the entire life cycle of Chinese products[EB/OL]. (2022-01-05) [2025-08-06]. . | |
| [46] | 宫海玲. 2024年煤炭市场回顾及2025年展望[EB/OL]. (2024-12-31) [2025-06-30]. . |
| Gong H L. Review of the coal market in 2024 and outlook for 2025[EB/OL]. (2024-12-31) [2025-06-30]. . | |
| [47] | 工业和信息化部. 合成氨行业规范条件[EB/OL]. (2023-10-13) [2025-08-01]. . |
| Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. Regulatory conditions for the synthetic ammonia industry[EB/OL]. (2023-10-13) [2025-08-01]. . | |
| [48] | 新浪财经. 24地:2024年新能源交易电量、电价[EB/OL]. (2025-03-04) [2025-08-10]. . |
| Finance Sina. 24 regions: new energy trading volume and electricity price in 2024[EB/OL]. (2025-03-04) [2025-08-10]. . | |
| [49] | Di Micco S, Romano F, Jannelli E, et al. Techno-economic analysis of a multi-energy system for the co-production of green hydrogen, renewable electricity and heat[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48(81): 31457-31467. |
| [1] | 杨语晴, 李银龙, 晏刚. 采用低GWP制冷剂的级联加热自复叠高温热泵循环热力学分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 43-53. |
| [2] | 王宇涛, 龚建英, 李祥宇, 吴馨, 刘秀芳. 基于压电-声流效应的液滴定向驱动技术研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 181-186. |
| [3] | 石一帆, 柯钢, 陈浩, 黄孝胜, 叶芳, 李成娇, 郭航. 大型高低温环境实验室温度控制仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 268-280. |
| [4] | 吴成云, 孙浩然. 民用飞机空调系统性能仿真与燃油代偿损失研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 351-359. |
| [5] | 周有苗, 刘晔, 余锋, 罗小钰, 王斌辉. 双源压缩-喷射复合热泵系统构建及特性分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 36-42. |
| [6] | 李卫, 陈浩, 柯钢, 黄孝胜, 李成娇, 郭航, 叶芳. 高原环境适应性试验室模拟平台新风系统仿真[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 360-369. |
| [7] | 佟丽丽, 陈英, 艾敏华, 舒玉美, 张香文, 邹吉军, 潘伦. ZnO/WO3异质结光催化环烯烃[2+2]环加成制备高能量密度燃料[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4882-4892. |
| [8] | 周怀荣, 伊嘉伟, 曹阿波, 郭奥雪, 王东亮, 杨勇, 杨思宇. 共电解耦合CO2间接加氢制甲醇工艺集成设计与性能评价[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4586-4600. |
| [9] | 田鹏, 张忠林, 任超, 孟国超, 郝晓刚, 刘叶刚, 侯起旺, ABUDULA Abuliti, 官国清. 基于自热再生的一种低温甲醇洗工艺建模与优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4601-4612. |
| [10] | 周奕彤, 周明熙, 刘若晨, 叶爽, 黄伟光. 光伏与电网协同驱动氢基直接还原铁炼钢的技术经济分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4318-4330. |
| [11] | 杨鹏, 尤万里, 凌忠钱, 曾宪阳, 李允超, 林佳一, 王丽建, 袁定琨. 紧凑式三室RTO系统处理乙酸乙酯废气性能的实验研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3585-3595. |
| [12] | 余嘉桐, 孟祥铠, 赵文静, 刘磊, 张力豪, 彭旭东. 热力耦合作用下涡轮泵用镶装式机械密封端面变形规律研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(6): 2900-2912. |
| [13] | 张冰, 李建惠, 马欣蓉, 陈杨, 李晋平, 李立博. 蒸气相辅助法制备MOF基材料的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(5): 2026-2041. |
| [14] | 产文, 余万, 王岗, 苏华山, 黄芬霞, 胡涛. 改进回热布局的Allam循环热力、经济性能分析和双目标优化[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1680-1692. |
| [15] | 刘亮, 吴佳俊, 卿梦霞, 周光亚, 贺梓航. 落地油泥热解特性及工艺系统能量平衡分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(4): 1779-1787. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号