• •
陈楠( ), 李雨霜(
), 李雨霜( ), 汪惟一, 温伯尧, 骆政园(
), 汪惟一, 温伯尧, 骆政园( ), 白博峰
), 白博峰
收稿日期:2025-08-20
修回日期:2025-10-27
出版日期:2025-11-25
通讯作者:
骆政园
作者简介:陈楠(2000—),男,博士研究生,chd2018900329@163.com基金资助:
Nan CHEN( ), Yushuang LI(
), Yushuang LI( ), Weiyi WANG, Boyao WEN, Zhengyuan LUO(
), Weiyi WANG, Boyao WEN, Zhengyuan LUO( ), Bofeng BAI
), Bofeng BAI
Received:2025-08-20
Revised:2025-10-27
Online:2025-11-25
Contact:
Zhengyuan LUO
摘要:
多孔介质中液滴的运移与堵塞行为是理解复杂孔隙结构中多相流体动力学的关键问题,对预测物质输运效率与调控流动至关重要。现有文献对具有显著渗透率差异的裂缝-基质双重多孔介质中液滴群动态行为的研究匮乏。本研究创新性设计了不同裂缝结构的裂缝-基质双重多孔介质微观可视化芯片,系统地研究了油水液滴群的流动和堵塞行为。明确了典型工况下双重多孔介质中单分散液滴群的运动特性,发现液滴在裂缝和基质具有截然不同的流动特性,运动速度差异达2倍。分析了多孔介质结构和液滴自身性质对液滴群运移的影响,结果表明裂缝结构参数与渗透率差异共同影响液滴群的输运特性,液滴波及范围和堵塞概率在液滴-孔隙尺寸比极端的情况下较高,且随着毛细数增大而减小,液滴堵塞体积占比最高可达到85%左右。通过分析不同液滴-孔隙尺寸比和裂缝基质渗透率差异下双重多孔介质中液滴波及状态相图,揭示了双重多孔介质中液滴群波及状态的临界控制机制,可为双重多孔介质中的流体流动研究及油田开发提供理论依据。
中图分类号:
陈楠, 李雨霜, 汪惟一, 温伯尧, 骆政园, 白博峰. 裂缝-基质双重多孔介质中油水液滴群流动及堵塞特性[J]. 化工学报, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250938.
Nan CHEN, Yushuang LI, Weiyi WANG, Boyao WEN, Zhengyuan LUO, Bofeng BAI. Flow and clogging characteristics of oil-water droplet clusters in a dual-porous medium with both fractures and matrix[J]. CIESC Journal, DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250938.
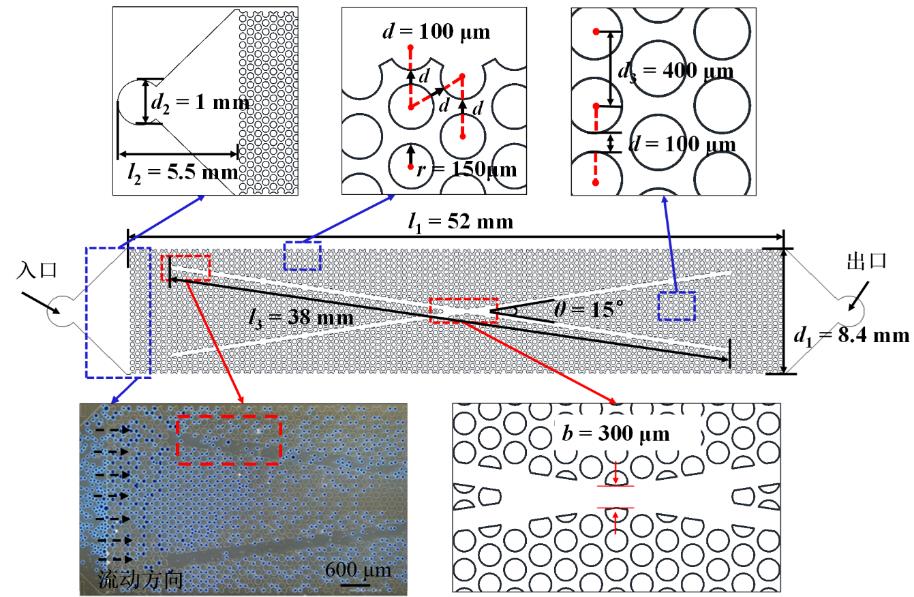
图1 裂缝-基质型双重多孔介质结构示意图(以裂缝宽度为300 μm为例)
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of the fracture-matrix dual-porous medium structure (taking a fracture width of 300 μm as an example)

图2 典型工况下液滴群在双重多孔介质中流动和堵塞特征图。(a) 不同时刻多孔介质中液滴群堵塞和流动图像(图中黑色点为多孔介质中的动态流动的液滴,红色点为多孔介质中堵塞的液滴); (b) 不同时刻裂缝中间和尾部的液滴流动和堵塞图像; (c) 基质和裂缝中的液滴堵塞体积占比随时间的变化; (d) 液滴流动和堵塞局部图像
Fig.2 Typical operating conditions of droplet clusters flowing and blocking in dual porous media. (a) Images of droplet clusters blocking and flowing in the porous medium at different times (the black dots in the figure represent the dynamically flowing droplets in the porous medium, and the red dots represent the blocked droplets in the porous medium); (b) Images of droplet flow and blocking in the middle and tail of the fractures at different times; (c) Changes in the proportion of droplet blocking volume in the matrix and fractures over time; (d) Local images of droplet flow and blocking
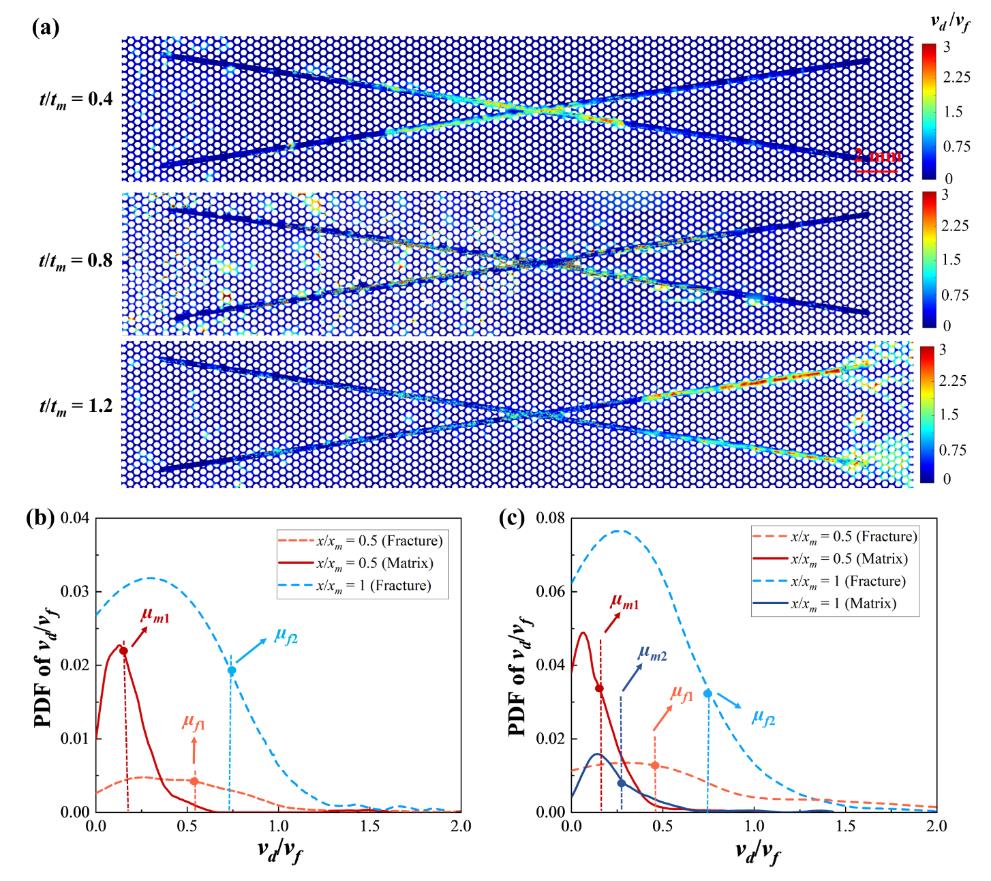
图3 不同时刻双重多孔介质内速度变化特征图。(a) 整个多孔介质内速度变化云图,包括流动初期t/tm = 0.4; 流动中期t/tm = 0.8; 流动后期t/tm= 1.2; 图中vd /vf 相对速度,即液滴速度vd 与流体平均速度vf 之比; (b) t/tm = 0.5时裂缝于基质中速度概率密度函数; (c) t/tm = 1时裂缝于基质中速度概率密度函数
Fig.3 Characteristics of velocity changes in the dual porous medium at different times. (a) Velocity change cloud map of the entire porous medium, including the initial flow stage t/tm = 0.4; the middle flow stage t/tm = 0.8; the later flow stage t/tm = 1.2; the relative velocity vd /vf in the figure, which is the ratio of droplet velocity vd to the average velocity vf of the fluid; (b) Probability density function of velocity of fractures within the matrix at t/tm = 0.5; (c) Probability density function of velocity of fractures within the matrix at t/tm = 1
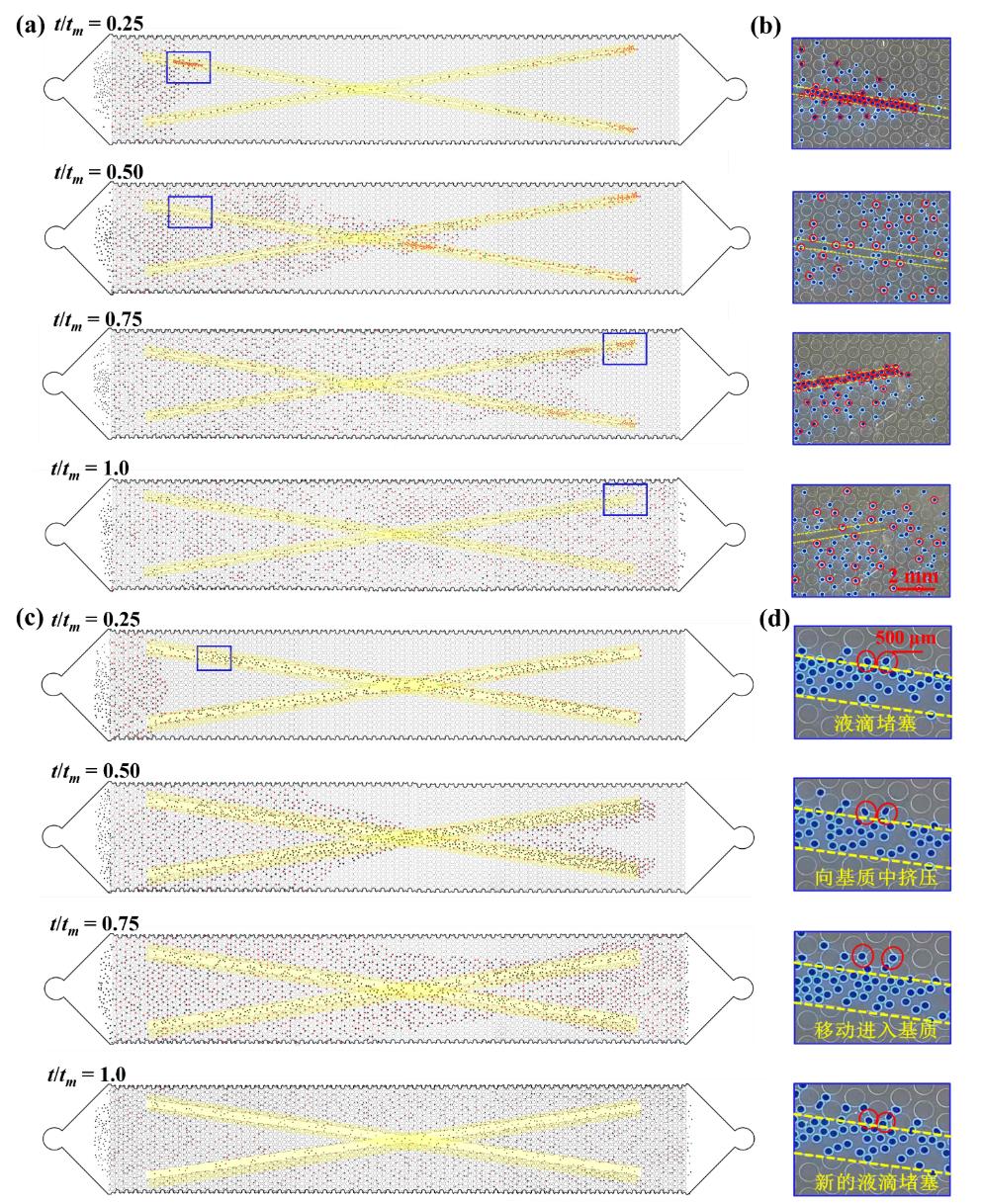
图4 不同裂缝结构下液滴在双重多孔介质中的堵塞和波及特性。(a) 裂缝宽度为200 μm液滴群在多孔介质中的流动和堵塞分布图像; (b) 裂缝宽度为200 μm液滴群在局部孔隙中的流动和堵塞动态演变; (c) 裂缝宽度为600 μm液滴群在多孔介质中的流动和堵塞分布图像; (d) 裂缝宽度为600 μm液滴群在局部孔隙中的流动和堵塞动态演变
Fig.4 The blocking and propagation characteristics of droplets in a dual porous medium under different fracture structures. (a) Flow and blocking distribution images of droplet clusters with a fracture width of 200 μm in the porous medium; (b) Dynamic evolution of flow and blocking of droplet clusters with a fracture width of 200 μm in the local pores; (c) Flow and blocking distribution images of droplet clusters with a fracture width of 600 μm in the porous medium; (d) Dynamic evolution of flow and blocking of droplet clusters with a fracture width of 600 μm in the local pores

图5 不同裂缝结构下液滴在双重多孔介质中的堵塞特性,b表示裂缝宽度。(a) 不同裂缝宽度下液滴在基质中的堵塞体积随时间的变化曲线;(b) 不同裂缝宽度下液滴在裂缝中的堵塞体积随时间的变化曲线
Fig.5 The clogging characteristics of droplets in dual-porosity media under different fracture structures, where b represents the fracture width. (a) The variation curve of the clogging volume of droplets in the matrix with time under different fracture widths; (b) The variation curve of the clogging volume of droplets in the fractures with time under different fracture widths

图6 不同基质孔隙率下液滴在双重多孔介质中的运移和堵特性。(a) ϕm = 36.3%时液滴的流动分布和动态变化图像; (b) ϕm = 24.1%时液滴的流动分布和局部堵塞图像; (c) 液滴在基质中的堵塞体积随时间的变化; (d) 液滴在裂缝中的堵塞体积随时间的变化
Fig.6 Migration and plugging characteristics of droplets in dual-porosity media under different matrix porosities. (a) Flow distribution and dynamic change images of droplets when ϕm = 36.3%; (b) Flow distribution and local plugging images of droplets when ϕm = 24.1%; (c) Changes in the plugging volume of droplets in the matrix over time; (d) Changes in the plugging volume of droplets in fractures over time
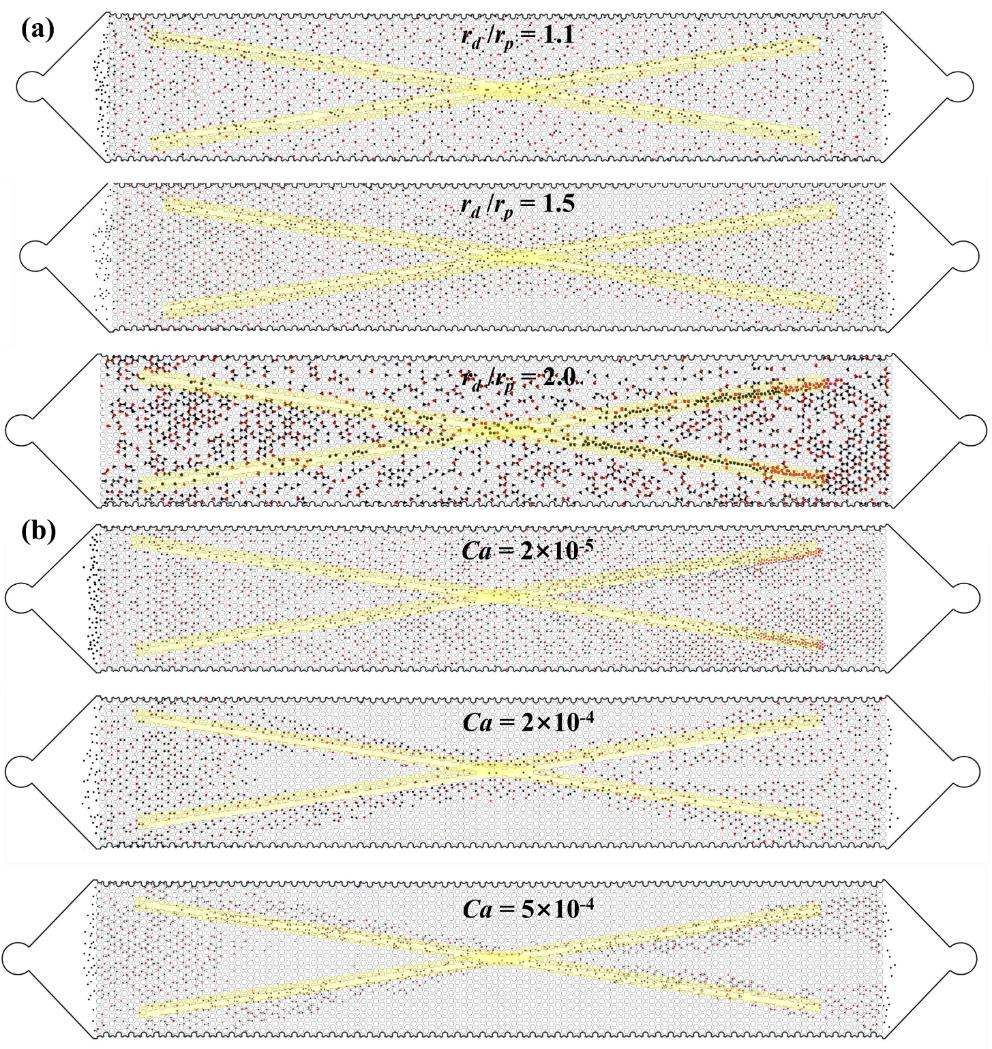
图7 不同rd/rp、Ca条件下液滴在双重多孔介质中的流动和堵塞分布图像。(a) 不同液滴-孔隙尺寸比下液滴群流动与堵塞; (b) 不同毛细数下液滴群流动与堵塞
Fig.7 Images of droplet flow and blockage distribution in a dual porous medium under different rd /rp and Ca conditions. (a) Droplet group flow and blockage under different droplet-pore size ratios; (b) Droplet group flow and blockage under different capillary numbers
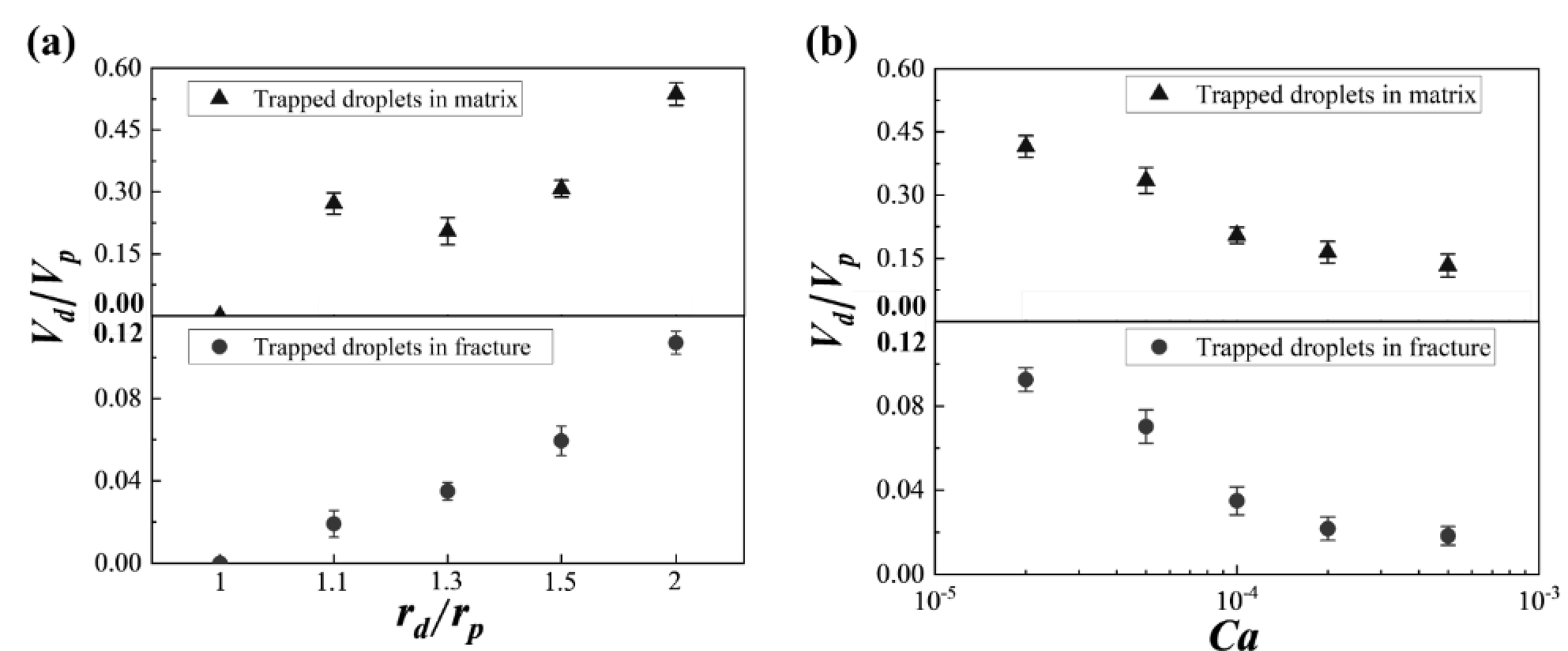
图8 不同液rd /rp 和Ca下液滴在双重多孔介质中的堵塞特性。(a) 不同液滴-孔隙尺寸比下液滴在裂缝和基质堵塞特性; (b) 不同毛细数下液滴在裂缝和基质中的堵塞特性
Fig.8 The blocking characteristics of droplets in dual porous media under different rd /rp . (a) Blocking characteristics of droplets in fractures and matrix under different droplet-pore size ratios; (b) Blocking characteristics of droplets in fractures and matrix under different Ca
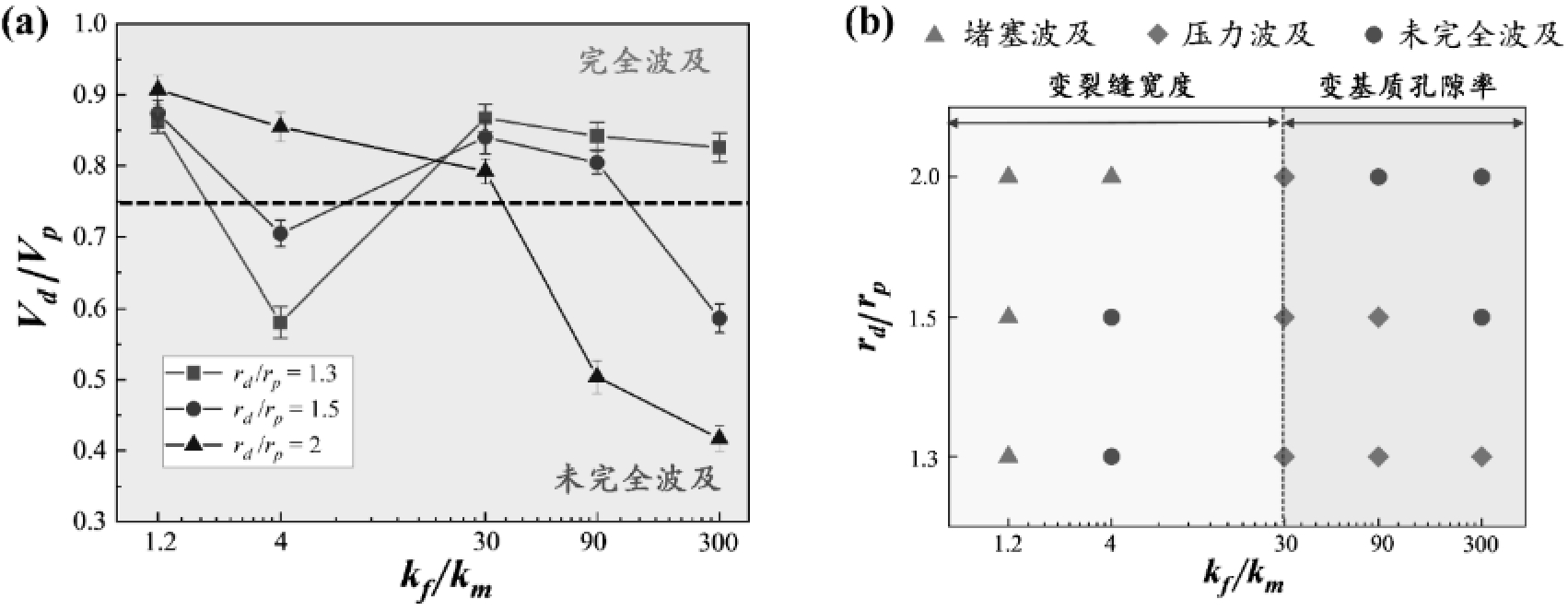
图9 不同条件下双重多孔介质中液滴的波及状态相图。(a) 不同液滴-孔隙尺寸比的液滴群波及面积占比随裂缝与基质渗透率差异的变化规律; (b) 液滴在双重多孔介质中的波及状态相图(变裂缝宽度范围内基质孔隙率为51.1%,变基质孔隙率范围内裂缝宽度为600 µm)
Fig.9 Phase diagram of droplet sweep states in dual porous media under different conditions. (a) Variation of the sweep area ratio of droplet groups with different droplet-pore size ratios as a function of the permeability difference between fractures and matrix; (b) Phase diagram of droplet sweep states in dual porous media (with a matrix porosity of 51.1% within the variable fracture width range, and a fracture width of 600 µm within the variable matrix porosity range)
| [1] | Arain A H, Negash B M, Yekeen N, et al. Synergising nanoparticles and low salinity waterflooding for enhanced oil recovery: a state-of-the-art review[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2024, 400: 124495. |
| [2] | 马良, 周朝辉, 杜猛, 等. 岩心多孔介质中乳状液乳化性能评价和驱油效果研究[J]. 应用化工, 2024, 53(5): 1003-1008+1014. |
| Ma L, Zhou Z H, Du M, et al. Study on emulsification performance evaluation and oil displacement effect of different emulsion composite systems[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2024, 53(5): 1003-1008+1014. | |
| [3] | 姚军, 黄涛, 黄朝琴, 等. 磁场-渗流场耦合作用下的铁磁流体多孔介质流动数值模拟[J]. 科学通报, 2017, 62(8): 836-846. |
| Yao J, Huang T, Huang Z Q, et al. Numerical simulation of ferrofluid flow in porous media under coupled magnetic and seepage fields[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(8): 836-846. | |
| [4] | de Borst R. Fluid flow in fractured and fracturing porous media: a unified view[J]. Mechanics Research Communications, 2017, 80: 47-57. |
| [5] | Réthoré J, de Borst R, Abellan M A. A two-scale approach for fluid flow in fractured porous media[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2007, 71(7): 780-800. |
| [6] | Duguid J O, Lee P C Y. Flow in fractured porous media[J]. Water Resources Research, 1977, 13(3): 558-566. |
| [7] | 王俊英, 金辉. 超临界CO2与石油烃溶解度参数的分子动力学研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025: 1-16. |
| Wang J Y, Jin H. Molecular dynamics investigation on the solubility parameters of supercritical CO2 and petroleum hydrocarbon[J]. CIESC Journal, 2025: 1-16. | |
| [8] | Romero M I, Carvalho M S, Alvarado V. Experiments and network model of flow of oil-water emulsion in porous media[J]. Physical Review. E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2011, 84(4 Pt 2): 046305. |
| [9] | Chen Z, Li R X, Yang S J, et al. A novel algorithm for asphaltene precipitation modeling in shale reservoirs with the consideration of capillary pressure during the CCUS processes[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 248: 123217. |
| [10] | Shi A N, Wu H C, Schwartz D K. Nanomotor-enhanced transport of passive Brownian particles in porous media[J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(48): eadj2208. |
| [11] | Guo C J, Zhang X W, Iqbal S. Does oil price volatility and financial expenditures of the oil industry influence energy generation intensity? Implications for clean energy acquisition[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2024, 434: 139907. |
| [12] | Perazzo A, Tomaiuolo G, Preziosi V, et al. Emulsions in porous media: From single droplet behavior to applications for oil recovery[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2018, 256: 305-325. |
| [13] | McKellar M, Wardlaw N C. A method of viewing "water" and "Oil" distribution in native-state and restored-state reservoir core: geologic NOTE [J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1988, 72: 703C8F1A-1707-11D7-8645000102C1865D. |
| [14] | Perez-Sanchez J F, Diaz-Zavala N P, Gonzalez-Santana S, et al. Water-In-oil emulsions through porous media and the effect of surfactants: theoretical approaches[J]. Processes, 2019, 7(9): 620. |
| [15] | Shapoval A, Alzahrani M, Xue W J, et al. Oil-water interactions in porous media during fluid displacement: Effect of potential determining ions (PDI) on the formation of in situ emulsions and oil recovery[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 210: 110079 |
| [16] | 刘萌, 刘霞, 吴玉国, 等. 水包油型稠油乳状液稳定性影响综述[J]. 辽宁石油化工大学学报, 2019, 39(4): 11-18. |
| Liu M, Liu X, Wu Y G, et al. Review on stability of oil-in-water heavy oil emulsion[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Petroleum & Chemical Technology, 2019, 39(4): 11-18. | |
| [17] | 吴俊, 景文珩, 邢卫红, 等. 一体式陶瓷外膜直接乳化法制备单分散水包油乳液[J]. 化工学报, 2005, 56(7): 1284-1287. |
| Wu J, Jing W H, Xing W H, et al. Preparation of monodispersed oil-in-water emulsions by ceramic external membrane emulsification technique[J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering (China), 2005, 56(7): 1284-1287. | |
| [18] | Gaafar G R, Tewari R D, Zain Z M. Overview of advancement in core analysis and its importance in reservoir characterisation for maximising recovery[C]//SPE Asia Pacific Enhanced Oil Recovery Conference. August 11-13, 2015. LumpurKuala, Malaysia. Richardson: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2015: SPE 174583-MS. |
| [19] | Wei J G, Liang S, Zhang D, et al. Frozen core experimental study on oil-water distribution characteristics at different stages of water flooding in low permeability oil reservoirs[J]. Energy, 2023, 278: 128007. |
| [20] | Yu F W, Jiang H Q, Fan Z, et al. Formation and flow behaviors of in situ emulsions in heavy oil reservoirs[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(7): 5961-5970. |
| [21] | 贾磊磊, 钟立国, 王国栋, 等. 多孔介质中油包水乳状液流动规律及液阻效应[J]. 油田化学, 2024, 41(4): 664-670, 679. |
| Jia L L, Zhong L G, Wang G D, et al. Flow law and liquid resistance effect of water-in-oil emulsion in porous media[J]. Oilfield Chemistry, 2024, 41(4): 664-670, 679. | |
| [22] | Soo H, Radke C J. Flow mechanism of dilute, stable emulsions in porous media[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 1984, 23(3): 342-347. |
| [23] | Ding B X, Dong M Z, Yu L. A model of emulsion plugging ability in sandpacks: Yield pressure drop and consistency parameter[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2020, 211: 115248. |
| [24] | Guo Y H, Liu F, Qiu J J, et al. Microscopic transport and phase behaviors of CO2 injection in heterogeneous formations using microfluidics[J]. Energy, 2022, 256: 124524. |
| [25] | Lei Z D, Liu Y S, Wang R, et al. A microfluidic experiment on CO2 injection for enhanced oil recovery in a shale oil reservoir with high temperature and pressure[J]. Energies, 2022, 15(24): 9461. |
| [26] | Wang H Y, Wei B, Hou J, et al. Investigation of microflow mechanisms and emulsion size distribution in porous media[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2023, 35(10): 102003. |
| [27] | Azizov I, Dudek M, Øye G. Emulsions in porous media from the perspective of produced water re-injection–A review[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 206: 109057. |
| [28] | de Amorim C, de Almeida R V, Ponce R V, et al. Visualization and quantification of mobility reduction in porous media flow associated with pore blocking by emulsion drops[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(51): 22093-22102. |
| [29] | Kozeny J. Ueber kapillare leitung des wassers im boden[M]. Sitzungsberichte der Akademie der Wissenschaften in Wien, 1927: 5-6. |
| [30] | Chatzis I, Kuntamukkula M S, Morrow N R. Effect of capillary number on the microstructure of residual oil in strongly water-wet sandstones[J]. SPE Reservoir Engineering, 1988, 3(3): 902-912. |
| [31] | Wei B, Liu Y S, Hou J, et al. Heavy oil emulsification and emulsions flow through porous media: a microfluidic experimental study[J]. SPE Journal, 2025: 1-14. |
| [32] | Fu C, Zhu T T, Huang B, et al. The efficiency of migration and profile control with emulsion systems in class III reservoirs[J]. Royal Society Open Science, 2019, 6(5): 181634. |
| [33] | Sousa A M, Pereira M J, Matos H A. Oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions formation and demulsification[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 210: 110041. |
| [34] | Sunil L K, Brij B M, Roy W. Flow of Emulsions in Porous Media[J]. Advances in Chemistry, 1992, 231: 219-262. |
| [1] | 郭纪超, 徐肖肖, 孙云龙. 基于植物工厂中的CO2浓度气流模拟及优化研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 237-245. |
| [2] | 吴梓航, 徐震原, 游锦方, 潘权稳, 王如竹. 基于吸附式储冷技术的深井钻探设备冷却系统[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 309-317. |
| [3] | 郭松源, 周晓庆, 缪五兵, 汪彬, 耑锐, 曹庆泰, 陈成成, 杨光, 吴静怡. 火箭上升段含多孔板液氧贮箱增压输运数值研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(S1): 62-74. |
| [4] | 段炼, 周星睿, 袁文君, 陈飞. 连续相速度脉动对微通道内聚合物液滴生成和形貌的影响规律[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4578-4585. |
| [5] | 刘卓龙, 甘云华, 屈可扬, 陈宁光, 潘铭晖. 均匀电场对生物柴油小尺度射流扩散燃烧特性影响研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4800-4808. |
| [6] | 解勤勤, 翁俊旗, 林振利, 叶光华, 周兴贵. 固定床反应器中甲醇制芳烃工业催化剂结构影响的研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(9): 4487-4498. |
| [7] | 周航, 张斯婧, 刘剑, 张小松. 小通道内非共沸工质流动沸腾换热数值分析[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3864-3872. |
| [8] | 刘建海, 王磊, 鲁朝金, 白志山, 张平雨. 耦合电化学与多相流模型的电解槽性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3885-3893. |
| [9] | 常心泉, 张克学, 王军, 夏国栋. 自由分子区内不规则颗粒的热泳力计算[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3944-3953. |
| [10] | 马永丽, 安澍, 杨捷, 刘明言. 气液固流化床直接数值模拟研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 3772-3788. |
| [11] | 佘海龙, 胡光忠, 崔晓钰, 柳忠彬, 彭帝, 李航. 不同节流工质下叠层微通道分布式节流制冷器性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(8): 4017-4029. |
| [12] | 唐羽丰, 陶春珲, 王永正, 李印辉, 段然, 赵泽一, 马和平. 超高比表面积碳基多孔吸附剂制备及其Kr气存储性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3339-3349. |
| [13] | 高照, 吴熙, 夏丹, 张霖宙. 石油加工分子管理平台热力学及分离单元模块开发[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3212-3225. |
| [14] | 王孝宇, 戴贵龙, 邓树坤, 龚凌诸. Laguerre-Voronoi开孔泡沫流动-传热综合性能孔隙尺度模拟[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3259-3273. |
| [15] | 陈曦, 王淑彦, 邵宝力, 丁诺, 谢磊. 基于颗粒动态恢复系数二阶矩模型的液固流化床数值模拟研究[J]. 化工学报, 2025, 76(7): 3246-3258. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
 京公网安备 11010102001995号
京公网安备 11010102001995号